Characterization of the Largest Secretory Protein Family, Ricin B Lectin-like Protein, in Nosema bombycis: Insights into Microsporidian Adaptation to Host
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Prediction and Identification of NbRBLs
2.2. Sequence Features of NbRBLs
2.3. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis of NbRBLs
2.4. Expressions of Nbrbls during N. bombycis Infection
2.5. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA)
2.6. Transfection and RNA-seq
3. Results
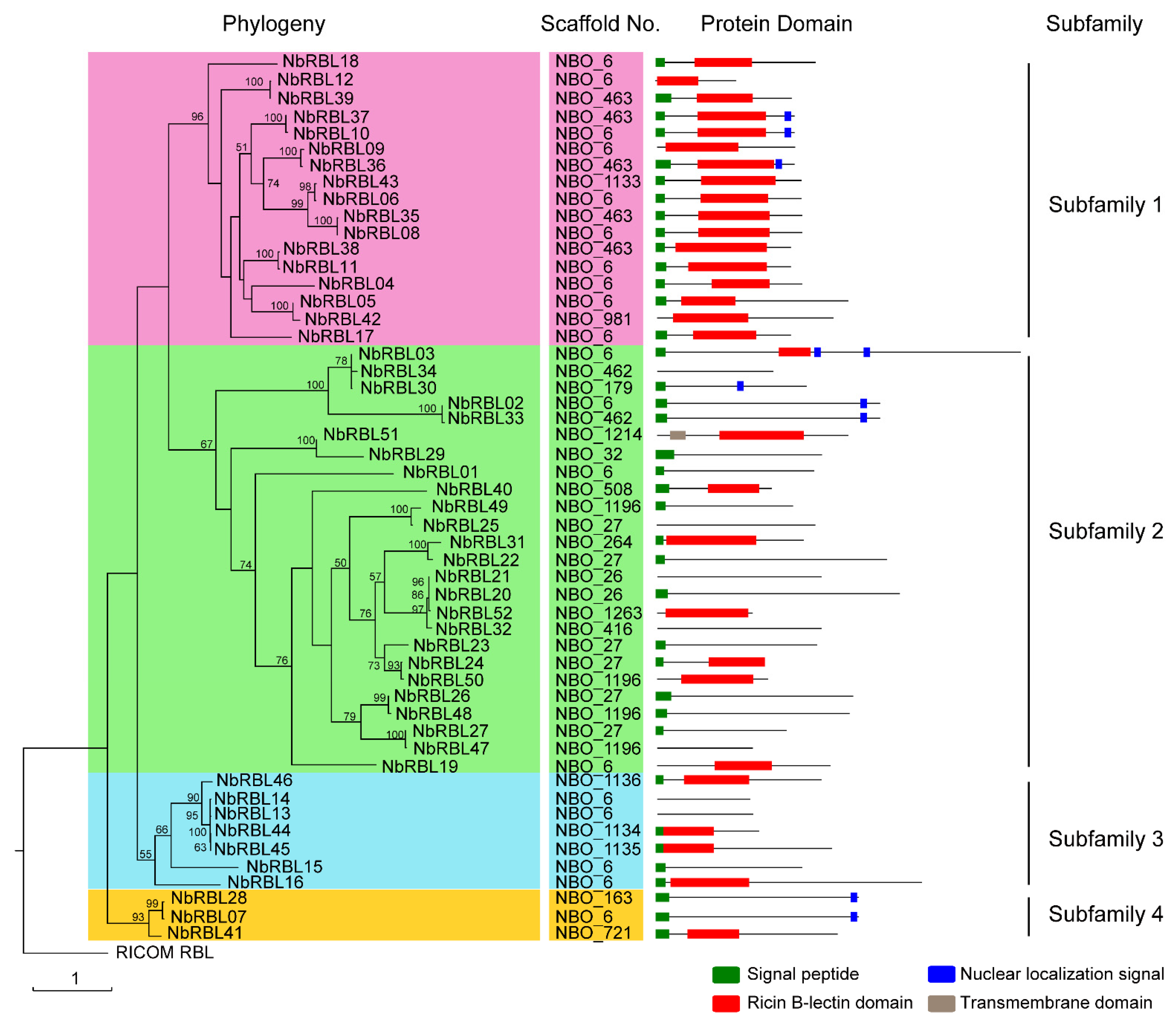
3.1. The Nbrbls Identified in N. bombycis Genome
3.2. The NbRBLs Are High Divergent
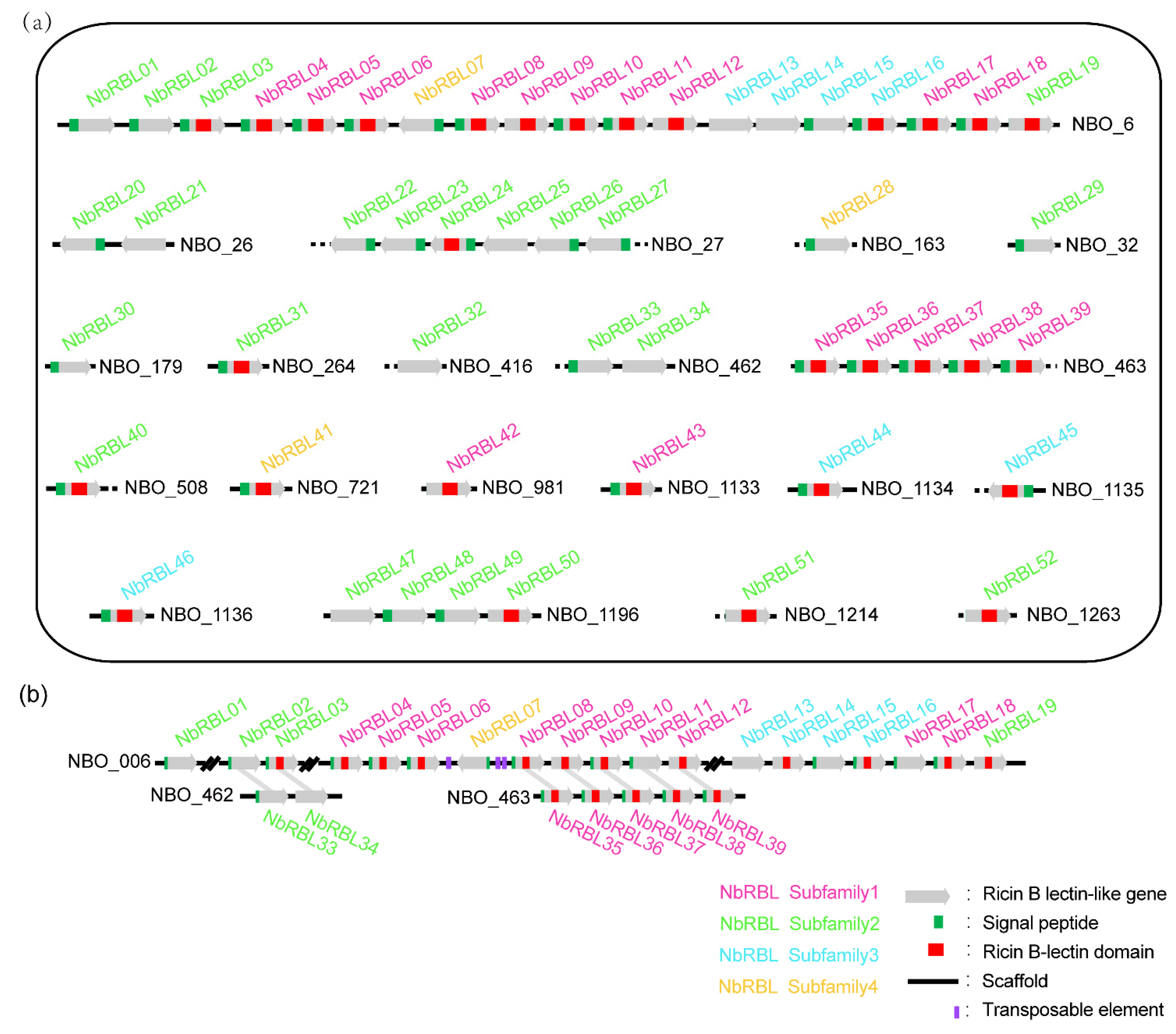
3.3. Expansive Mechanisms of the NbRBL Family
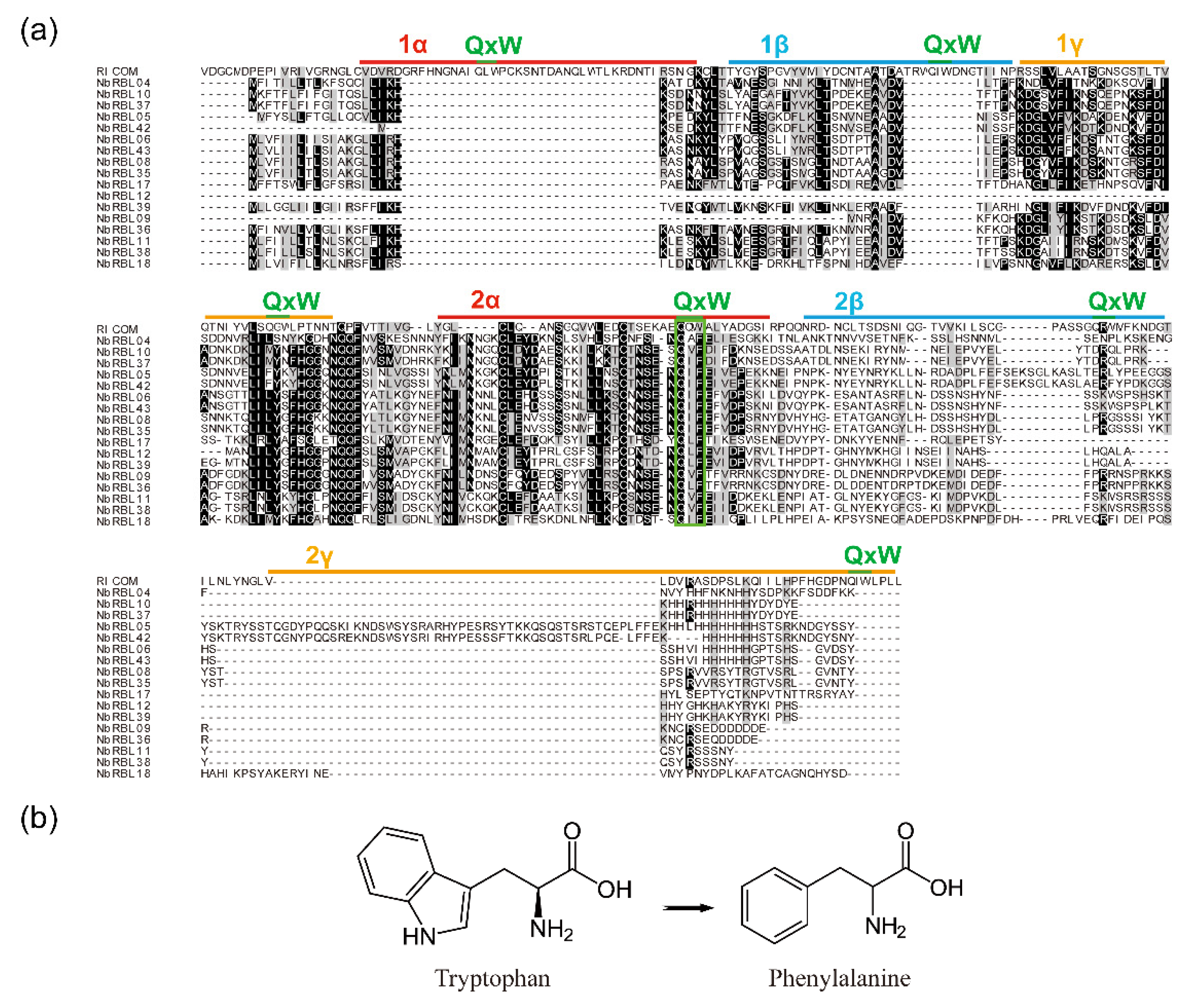
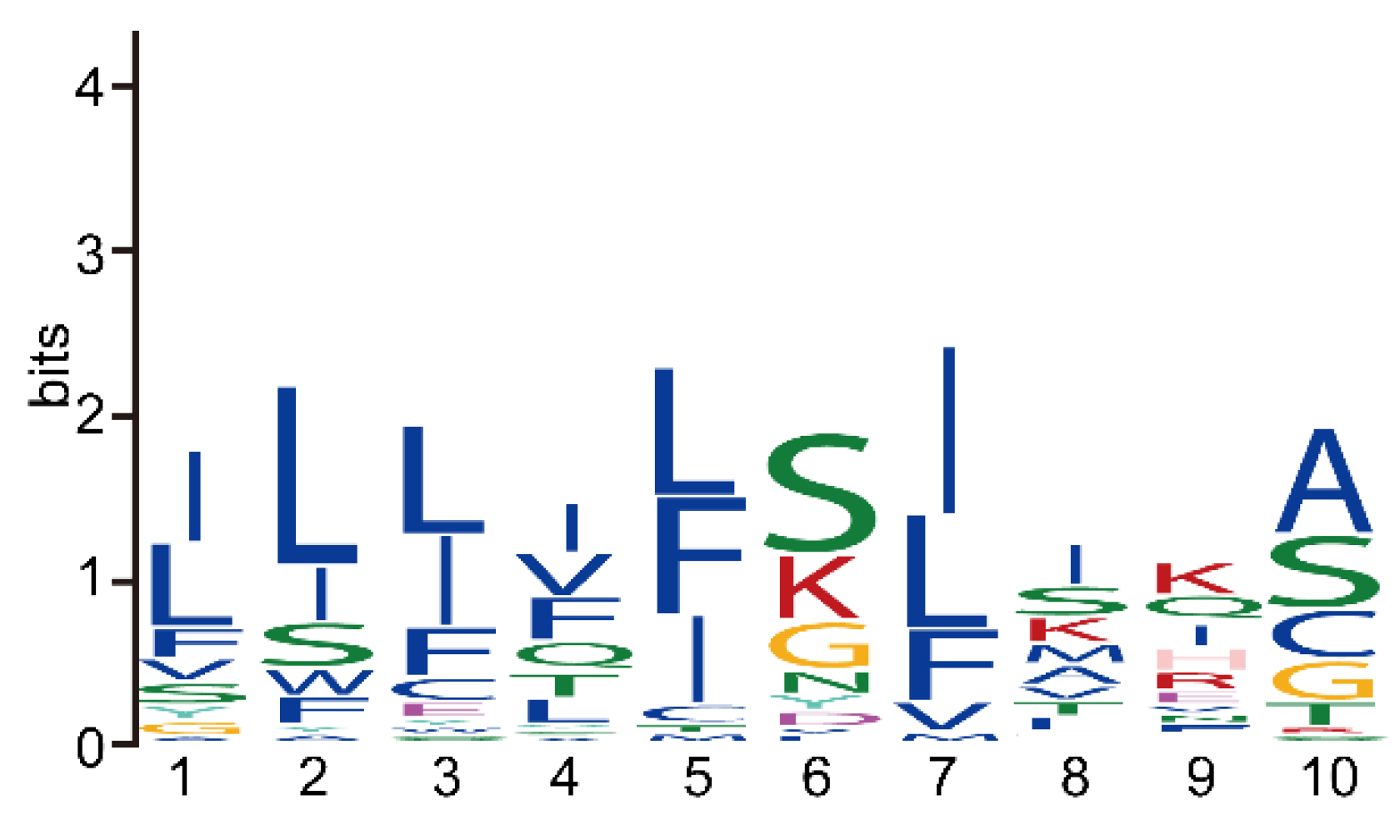
3.4. The Reduction of Key Motifs in NbRBL
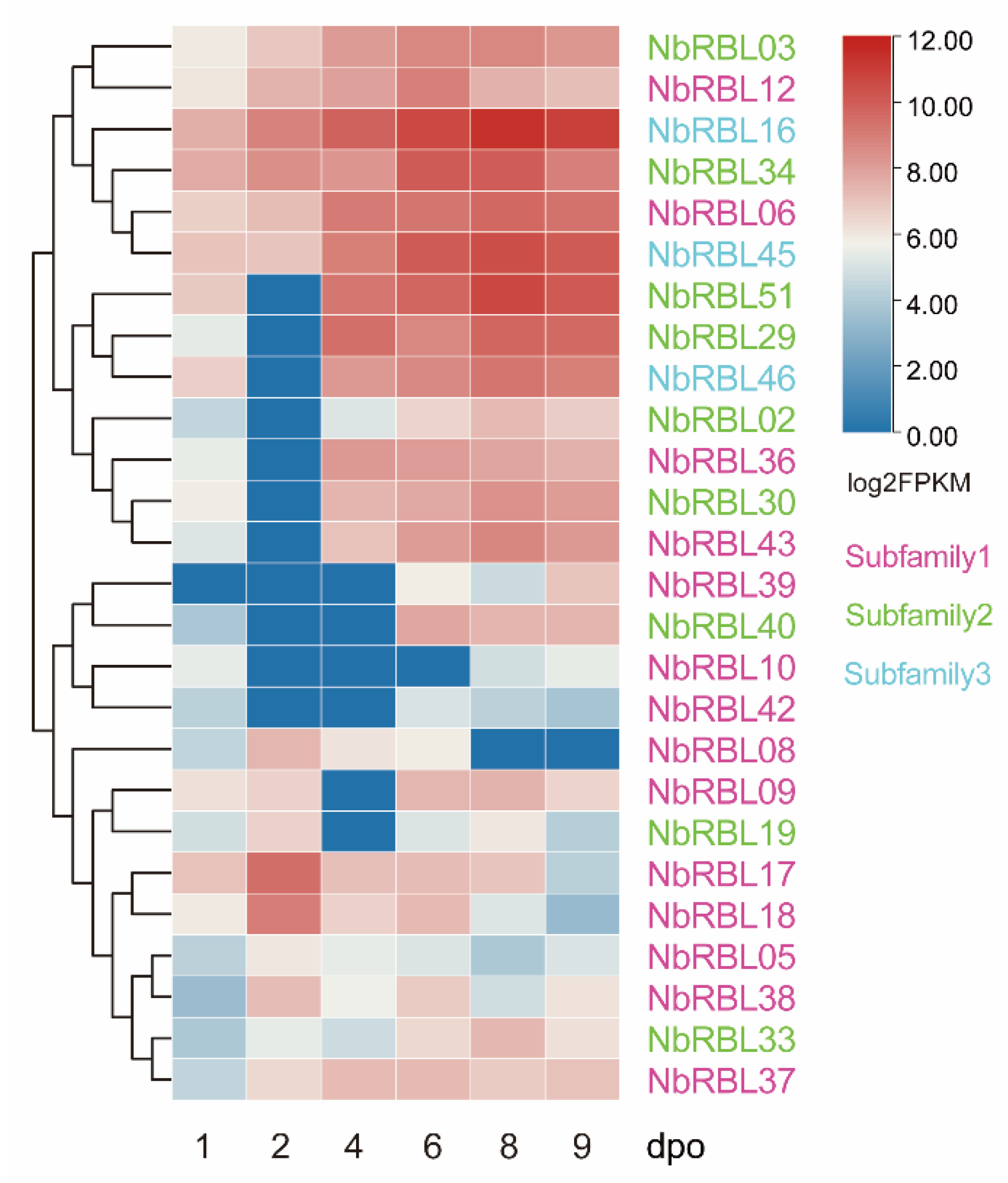
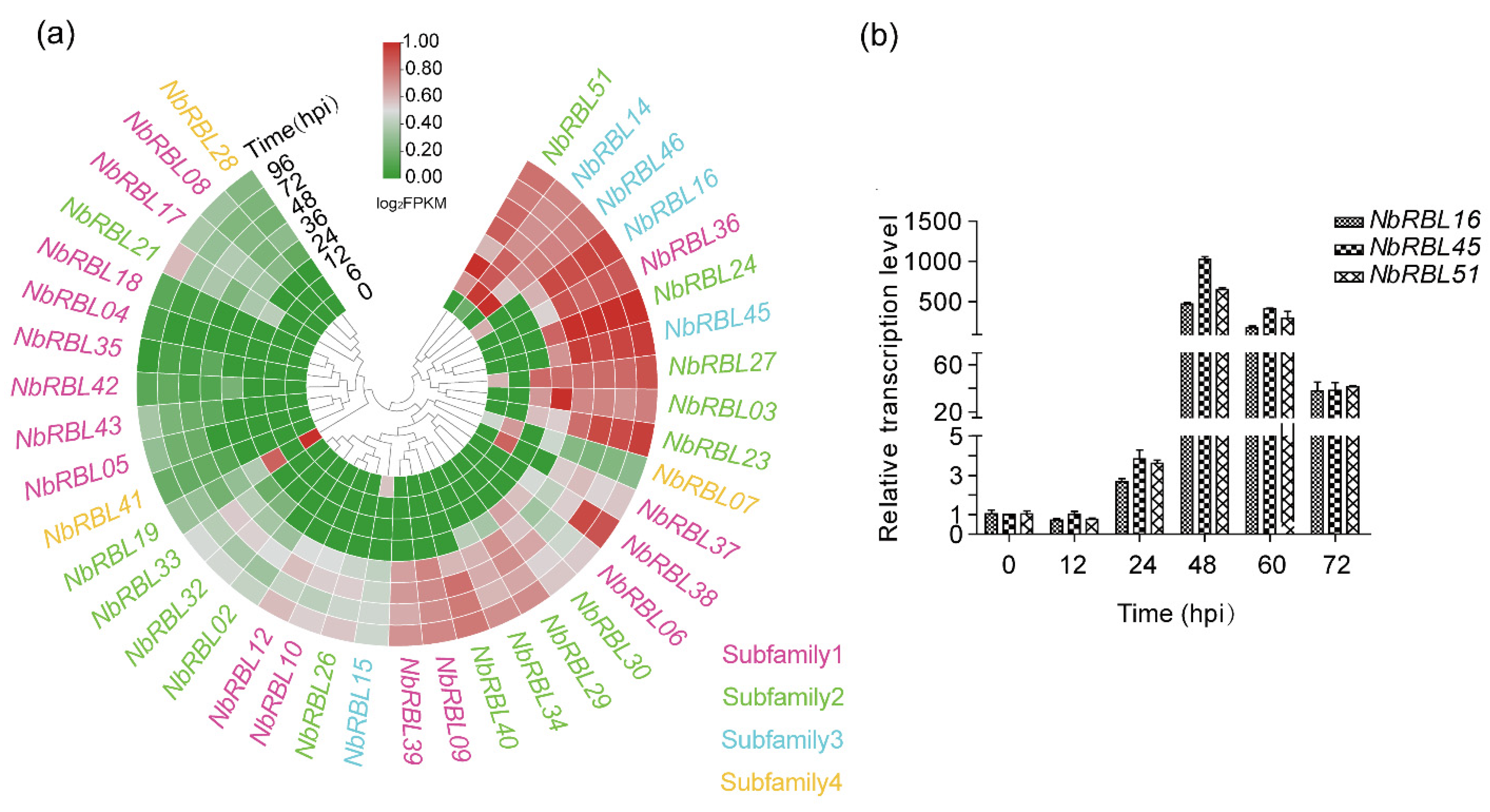
3.5. Expressions of Nbrbls during Infection
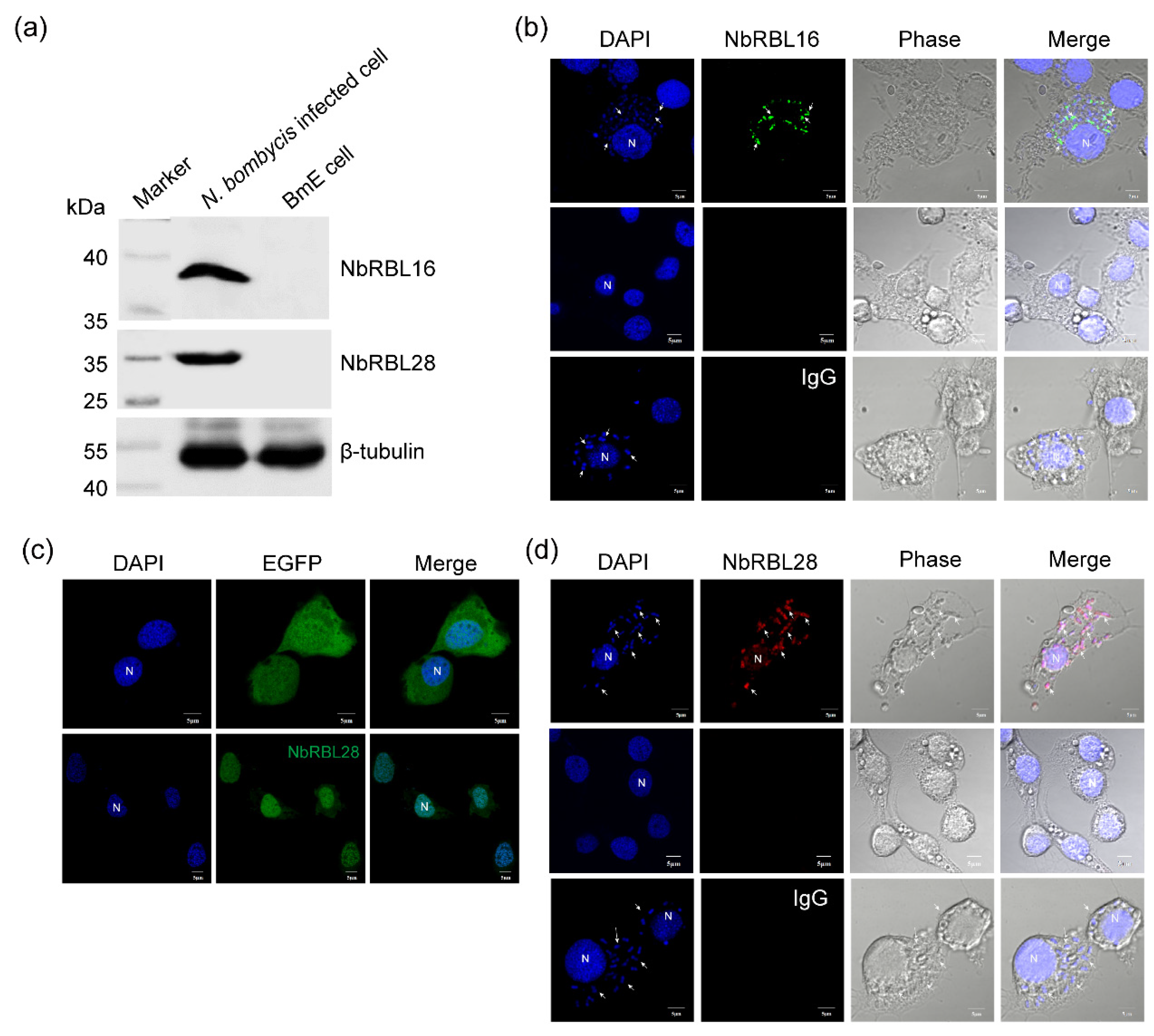
3.6. Subcellular Localization of NbRBL16 and NbRBL28
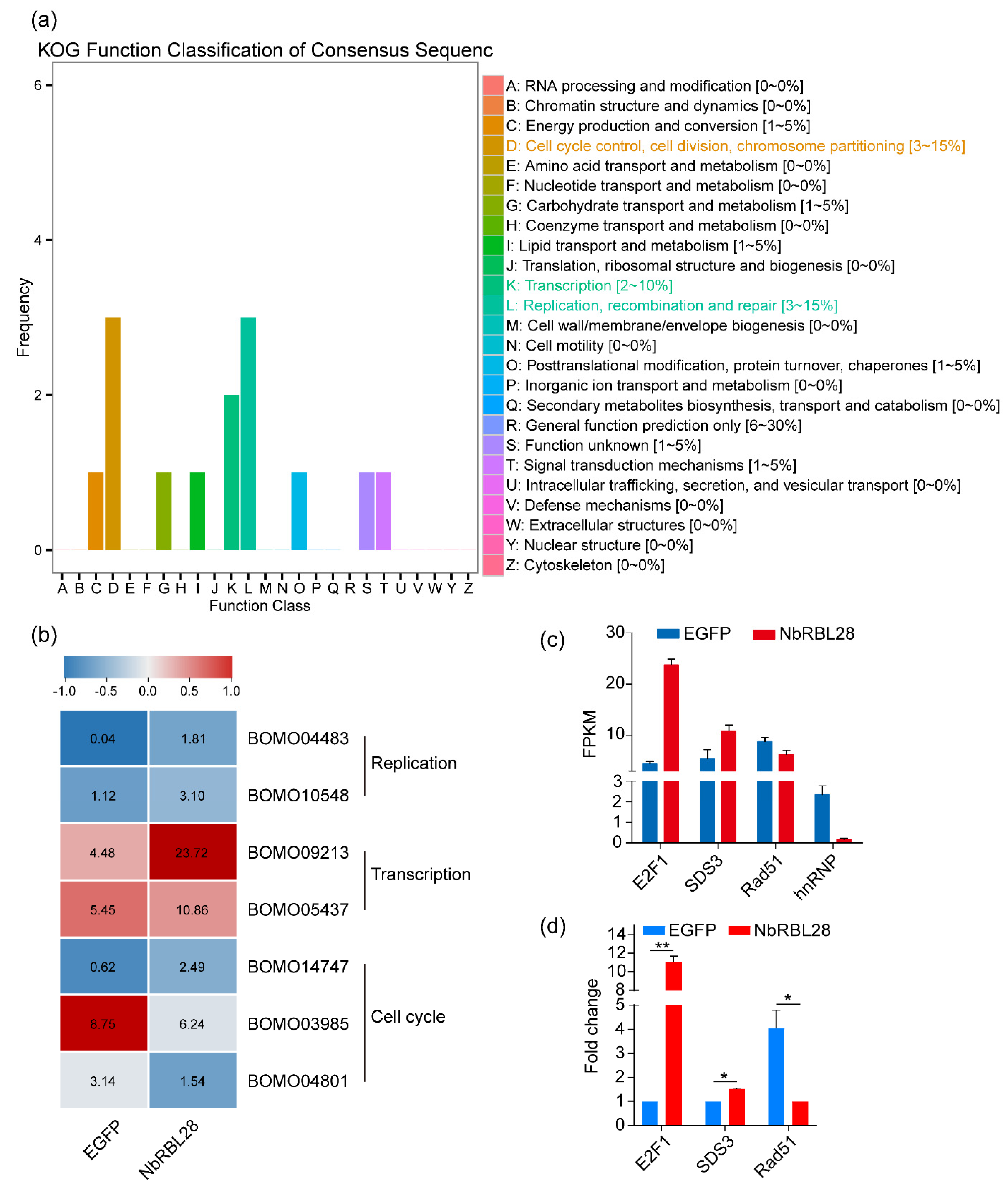
3.7. NbRBL28 Regulates Gene Expressions Involved in Host Cell Cycle
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hiller, N.L.; Bhattacharjee, S.; van Ooij, C.; Liolios, K.; Harrison, T.; Lopez-Estraño, C.; Haldar, K. A host-targeting signal in virulence proteins reveals a secretome in malarial infection. Science 2004, 306, 1934–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didier, E.S.; Didier, P.J.; Snowden, K.F.; Shadduck, J.A. Microsporidiosis in mammals. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzen, C. Microsporidia: A review of 150 years of research. Open Parasitol. J. 2008, 2, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.; Xu, X.; He, Q.; Li, L.; Guo, J.; Bao, J.; Pan, G.; Li, T.; Zhou, Z. The largest meta-analysis on the global prevalence of microsporidia in mammals, avian and water provides insights into the epidemic features of these ubiquitous pathogens. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, L.; Güleğen, E.; Girişgin, O.; Kurtaraner, L. Occurrence of Nosema bombycis (Naegeli, 1857) in silkworms in Turkey. Turk. J. Parasitol. 2007, 31, 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Cuomo, C.A.; Desjardins, C.A.; Bakowski, M.A.; Goldberg, J.; Ma, A.T.; Becnel, J.J.; Didier, E.S.; Fan, L.; Heiman, D.I.; Levin, J.Z.; et al. Microsporidian genome analysis reveals evolutionary strategies for obligate intracellular growth. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 2478–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; He, Q.; Ma, Z.; Li, T.; Zhang, X.; Debrunner-Vossbrinck, B.A.; Zhou, Z.; Vossbrinck, C.R. The Genome of Nosema sp. Isolate YNPr: A Comparative Analysis of Genome Evolution within the Nosema/Vairimorpha Clade. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audi, J.; Belson, M.; Patel, M.; Schier, J.; Osterloh, J. Ricin poisoning: A comprehensive review. JAMA 2005, 294, 2342–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutenber, E.; Ready, M.; Robertus, J.D. Structure and evolution of ricin B chain. Nature 1987, 326, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutenber, E.; Robertus, J.D. Structure of ricin B-chain at 2.5 A resolution. Proteins 1991, 10, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munishkin, A.; Wool, I.G. Systematic deletion analysis of ricin A-chain function. Single amino acid deletions. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 30581–30587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, N.W.; Estes, M.K.; Langridge, W.H. Ricin toxin B subunit enhancement of rotavirus NSP4 immunogenicity in mice. Viral Immunol. 2006, 19, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, M.; Chandra, N. Lectins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1999, 9, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.E.; Williams, T.A.; Yousuf, A.; Soanes, D.M.; Paszkiewicz, K.H.; Williams, B.A. The genome of Spraguea lophii and the basis of host-microsporidian interactions. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Li, M.; Cai, S.; He, X.; Shao, Y.; Lu, X. Ricin-B-lectin enhances microsporidia Nosema bombycis infection in BmN cells from silkworm Bombyx mori. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2016, 48, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prybylski, N.; Fayet, M.; Dubuffet, A.; Delbac, F.; Kocer, A.; Gardarin, C.; Michaud, P.; El Alaoui, H.; Dubessay, P. Ricin B lectin-like proteins of the microsporidian Encephalitozoon cuniculi and Anncaliia algerae are involved in host-cell invasion. Parasitol. Int. 2022, 87, 102518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Pan, G.Q.; Vossbrinck, C.R.; Xu, J.S.; Li, C.F.; Chen, J.; Long, M.X.; Yang, M.; Xu, X.F.; Xu, C.; et al. SilkPathDB: A comprehensive resource for the study of silkworm pathogens. Database (Oxford) 2017, 1, bax001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.E.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.; Park, K.J.; Obayashi, T.; Fujita, N.; Harada, H.; Adams-Collier, C.J.; Nakai, K. WoLF PSORT: Protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W585–W587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sønderby, C.K.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML-VI-HPC: Maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2688–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v4: Recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W256–W259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Pan, G.; Tan, X.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xiang, Z. Proteomic analysis of spore wall proteins and identification of two spore wall proteins from Nosema bombycis (Microsporidia). Proteomics 2008, 8, 2447–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Luo, J.; Xu, J.Z.; Meng, X.Z.; Pan, G.Q.; Li, T.; Zhou, Z.Y. Characterization of Hsp70 gene family provides insight into its functions related to microsporidian proliferation. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2020, 174, 107394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Vossbrinck, C.R.; Yang, Q.; Meng, X.Z.; Luo, J.; Pan, G.Q.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Li, T. Evolutionary and functional studies on microsporidian ATP-binding cassettes: Insights into the adaptation of microsporidia to obligated intracellular parasitism. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, T.; He, Z.; Wu, Y.; He, Q.; Li, T.; Li, C.; Long, M.; et al. Proliferation characteristics of the intracellular microsporidian pathogen Nosema bombycis in congenitally infected embryos. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2020, 169, 107310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, M.; Good, R.T.; Rug, M.; Knuepfer, E.; Cowman, A.F. Targeting malaria virulence and remodeling proteins to the host erythrocyte. Science 2004, 306, 1930–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeGregori, J.; Johnson, D.G. Distinct and Overlapping Roles for E2F Family Members in Transcription, Proliferation and Apoptosis. Curr. Mol. Med. 2006, 6, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vélez-Cruz, R.; Manickavinayaham, S.; Biswas, A.K.; Clary, R.W.; Premkumar, T.; Cole, F.; Johnson, D.G. RB localizes to DNA double-strand breaks and promotes DNA end resection and homologous recombination through the recruitment of BRG1. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 2500–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; McCorvie, T.J.; Yates, L.A.; Zhang, X. Structural basis of homologous recombination. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krejci, L.; Altmannova, V.; Spirek, M.; Zhao, X. Homologous recombination and its regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 5795–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candy, L.; Peumans, W.J.; Menu-Bouaouiche, L.; Astoul, C.H.; Van Damme, J.; Van Damme, E.J.; Erard, M.; Rouge, P. The Gal/GalNAc-specific lectin from the plant pathogenic basidiomycete Rhizoctonia solani is a member of the ricin-B family. BioChem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 282, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurrecoechea, C.; Barreto, A.; Brestelli, J.; Brunk, B.P.; Caler, E.V.; Fischer, S.; Gajria, B.; Gao, X.; Gingle, A.; Grant, G.; et al. AmoebaDB and MicrosporidiaDB: Functional genomic resources for Amoebozoa and Microsporidia species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D612–D619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katinka, M.D.; Duprat, S.; Cornillot, E.; Méténier, G.; Thomarat, F.; Prensier, G.; Barbe, V.; Peyretaillade, E.; Brottier, P.; Wincker, P.; et al. Genome sequence and gene compaction of the eukaryote parasite Encephalitozoon cuniculi. Nature 2001, 414, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, G.; Xu, J.; Li, T.; Xia, Q.; Liu, S.L.; Zhang, G.; Li, S.; Li, C.; Liu, H.; Yang, L.; et al. Comparative genomics of parasitic silkworm microsporidia reveal an association between genome expansion and host adaptation. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radoshevich, L.; Cossart, P. Listeria monocytogenes: Towards a complete picture of its physiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. MicroBiol. 2018, 16, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villares, M.; Berthelet, J.; Weitzman, J.B. The clever strategies used by intracellular parasites to hijack host gene expression. Semin. Immunopathol. 2020, 42, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougdour, A.; Durandau, E.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.P.; Ortet, P.; Barakat, M.; Kieffer, S.; Curt-Varesano, A.; Curt-Bertini, R.L.; Bastien, O.; Coute, Y.; et al. Host cell subversion by Toxoplasma GRA16, an exported dense granule protein that targets the host cell nucleus and alters gene expression. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, L.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.P.; Hammoudi, P.M.; Cannella, D.; Kieffer-Jaquinod, S.; Vollaire, J.; Josserand, V.; Touquet, B.; Coute, Y.; Tardieux, I.; et al. The Toxoplasma effector TEEGR promotes parasite persistence by modulating NF-kappaB signalling via EZH2. Nat. MicroBiol. 2019, 4, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, M.; Panas, M.W.; Marino, N.D.; Lee, M.C.; Buchholz, K.R.; Kelly, F.D.; Bednarski, J.J.; Sleckman, B.P.; Pourmand, N.; Boothroyd, J.C. A Novel Secreted Protein, MYR1, Is Central to Toxoplasma’s Manipulation of Host Cells. mBio 2016, 7, e02231-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gay, G.; Braun, L.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.P.; Vollaire, J.; Josserand, V.; Bertini, R.L.; Varesano, A.; Touquet, B.; De Bock, P.J.; Coute, Y.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii TgIST co-opts host chromatin repressors dampening STAT1-dependent gene regulation and IFN-gamma-mediated host defenses. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 1779–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, L.A.; Ravindran, S.; Turetzky, J.M.; Boothroyd, J.C.; Bradley, P.J. Toxoplasma gondii targets a protein phosphatase 2C to the nuclei of infected host cells. Eukaryot. Cell 2007, 6, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olias, P.; Etheridge, R.D.; Zhang, Y.; Holtzman, M.J.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma Effector Recruits the Mi-2/NuRD Complex to Repress STAT1 Transcription and Block IFN-gamma-Dependent Gene Expression. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabou, M.; Doderer-Lang, C.; Leyer, C.; Konjic, A.; Kubina, S.; Lennon, S.; Rohr, O.; Viville, S.; Cianferani, S.; Candolfi, E.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii ROP16 kinase silences the cyclin B1 gene promoter by hijacking host cell UHRF1-dependent epigenetic pathways. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 2141–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loukas, A.; Maizels, R.M. Helminth C-type lectins and host-parasite interactions. Parasitol. Today 2000, 16, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Name | Forward Primers (5′ to 3′) | Reverse Primers (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Nbrbl16 | GTTCTGTCAATCCAAGTGTTCC | ACTGTGCTTAGAAAGACGATCA |
| Nbrbl45 | TCCTGTTGATCAAAACGTTGTC | TGAGTGTGGTGTATATCGTCAG |
| Nbrbl51 | TGTGTCTACGTGTGTCGATAAA | TCAAGAGAACCAGCAGTAAGAC |
| Nbtubulin | CTGGGGATAGTATGATCGCAAGA | CACAGCATCCATTGGAAACG |
| E2FI | GAAATCTTCACAGAACGGAGTG | AGAACGTTCGTGATGTCGTATA |
| SDS3 | AAACATCTCAACTCTGGCAGTA | CCTTATTCGTTCCACATTCGTC |
| Rad51 | ACAGTCGTCCCACAGCAA | CGATGAGGCAGTGTAGGT |
| SW22934 | TTCGTACTGGCTCTTCTCGT | CAAAGTTGATAGCAATTCCCT |
| NbRBLs | Locus ID | GenBank Accession No. | Amino Acid Residues (Aa) | Molecular Weight (Da) | pI | Signal Peptide | Subcellular Localization | Domain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NbRBL01 | NBO_6:56729..57397:+ | ON211418 | 222 | 25,337.44 | 7.56 | 1-13 | cytosol | NA |
| NbRBL02 | NBO_6g0014 | ON211419 | 315 | 36,999.70 | 7.96 | 1-17 | nucleus | NA |
| NbRBL03 | NBO_6g0015 | ON211420 | 514 | 57,702.24 | 6.00 | 1-15 | nucleus | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL04 | NBO_6g0041 | ON211421 | 205 | 23,554.40 | 9.09 | 1-14 | nucleus | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL05 | NBO_6g0043 | ON211422 | 270 | 31,416.47 | 7.74 | 1-16 | nucleus | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL06 | NBO_6g0045 | ON211423 | 204 | 22,808.19 | 7.26 | 1-14 | mitochondria | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL07 | NBO_6g0046 | ON211424 | 285 | 32,927.32 | 9.00 | 1-20 | nucleus | NA |
| NbRBL08 | NBO_6g0047 | ON211425 | 205 | 22,803.26 | 8.99 | 1-14 | extracellular | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL09 | NBO_6g0048 | ON211426 | 153 | 17,934.29 | 4.70 | No | nucleus | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL10 | NBO_6g0049 | ON211427 | 194 | 22,864.24 | 6.25 | 1-14 | nucleus | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL11 | NBO_6:123114..123683:− | ON211428 | 189 | 21,566.63 | 8.76 | 1-16 | extracellular | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL12 | NBO_6g0050 | ON211429 | 115 | 13,064.90 | 8.63 | No | cytoskeleton | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL13 | NBO_6:131790..132149:− | ON211430 | 119 | 13,888.14 | 6.32 | No | nucleus | NA |
| NbRBL14 | NBO_6g0058 | ON211431 | 123 | 14,260.48 | 6.39 | No | nucleus | NA |
| NbRBL15 | NBO_6g0060 | ON211432 | 205 | 23,463.03 | 8.99 | 1-15 | nucleus | NA |
| NbRBL16 | NBO_6gi003 | ON211433 | 374 | 42,355.07 | 6.35 | 1-15 | nucleus | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL17 | NBO_6g0061 | ON211434 | 189 | 22,357.92 | 5.74 | 1-17 | nucleus | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL18 | NBO_6g0062 | ON211435 | 224 | 25,993.40 | 6.83 | 1-14 | Golgi complex | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL19 | NBO_6g0108 | ON211436 | 245 | 26,625.59 | 8.65 | No | nucleus | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL20 | NBO_26:48175..49206:+ | ON211437 | 343 | 37,408.14 | 8.46 | 1-18 | extracellular | NA |
| NbRBL21 | NBO_26g0023 | ON211438 | 230 | 24,843.75 | 6.49 | No | nucleus | NA |
| NbRBL22 | NBO_27:44489..45466:+ | ON211439 | 325 | 35,631.08 | 5.67 | 1-14 | extracellular | NA |
| NbRBL23 | NBO_27g0016 | ON211440 | 342 | 37,076.99 | 6.18 | 1-15 | extracellular | NA |
| NbRBL24 | NBO_27g0018 | ON211441 | 259 | 28,920.21 | 8.68 | 1-12 | extracellular | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL25 | NBO_27:50577..51263:+ | ON211442 | 228 | 26,353.80 | 5.90 | No | mitochondria | NA |
| NbRBL26 | NBO_27g0019 | ON211443 | 278 | 30,457.43 | 9.04 | 1-23 | extracellular | NA |
| NbRBL27 | NBO_27g0020 | ON211444 | 322 | 35,330.53 | 8.64 | 1-12 | extracellular | NA |
| NbRBL28 | NBO_163g0001 | ON211445 | 285 | 32,984.50 | 9.13 | 1-20 | nucleus | NA |
| NbRBL29 | NBO_32g0011 | ON211446 | 233 | 26,695.26 | 8.92 | 1-27 | nucleus | NA |
| NbRBL30 | NBO_179g0001 | ON211447 | 211 | 24,218.89 | 5.12 | 1-15 | nucleus | NA |
| NbRBL31 | NBO_264:2462..3085:− | ON211448 | 207 | 23,435.10 | 8.81 | 1-12 | nucleus | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL32 | NBO_416g0002 | ON211449 | 232 | 25,229.27 | 7.74 | No | nucleus | NA |
| NbRBL33 | NBO_462g0008 | ON211450 | 315 | 36,938.62 | 7.96 | 1-17 | nucleus | NA |
| NbRBL34 | NBO_462g0009 | ON211451 | 173 | 18,373.24 | 7.84 | No | nucleus | NA |
| NbRBL35 | NBO_463g0001 | ON211452 | 205 | 22,747.16 | 8.99 | 1-14 | extracellular | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL36 | NBO_463g0002 | ON211453 | 194 | 22,561.94 | 5.71 | 1-22 | endoplasmic reticulum | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL37 | NBO_463g0004 | ON211454 | 194 | 22,912.32 | 6.30 | 1-14 | nucleus | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL38 | NBO_463g0005 | ON211455 | 189 | 21,464.43 | 8.76 | 1-14 | extracellular | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL39 | NBO_463g0006 | ON211456 | 190 | 21,675.99 | 9.06 | 1-23 | extracellular | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL40 | NBO_508g0001 | ON211457 | 162 | 18,502.31 | 9.07 | 1-20 | extracellular | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL41 | NBO_721g0001 | ON211458 | 255 | 29,309.34 | 9.10 | 1-20 | nucleus | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL42 | NBO_981g0001 | ON211459 | 249 | 28,931.56 | 8.28 | No | nucleus | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL43 | NBO_1133g0001 | ON211460 | 204 | 22,731.15 | 7.23 | 1-14 | extracellular | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL44 | NBO_1134:2994..3426:+ | ON211461 | 144 | 16,418.60 | 6.81 | 1-24 | extracellular | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL45 | NBO_1135g0001 | ON211462 | 247 | 28,315.53 | 6.74 | 1-24 | extracellular | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL46 | NBO_1136g0001 | ON211463 | 232 | 26,654.78 | 8.78 | 1-12 | mitochondria | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL47 | NBO_1196:1..366:− | ON211464 | 122 | 12,946.28 | 4.55 | No | nucleus | NA |
| NbRBL48 | NBO_1196:1677..2495:− | ON211465 | 272 | 29,582.35 | 8.93 | 1-17 | mitochondria | NA |
| NbRBL49 | NBO_1196:2983..3561:− | ON211466 | 192 | 22,211.52 | 7.63 | 1-15 | mitochondria | NA |
| NbRBL50 | NBO_1196:4918..5391:− | ON211467 | 157 | 17,024.65 | 5.00 | No | cytosol | Ricin B-lectin |
| NbRBL51 | NBO_1214g0002 | ON211468 | 270 | 31,043.06 | 8.89 | No | endoplasmic reticulum | Ricin B-lectin Transmembrane |
| NbRBL52 | NBO_1263:1090..1494:+ | ON211469 | 135 | 14,919.37 | 5.24 | No | cytosol | Ricin B-lectin |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Luo, J.; Chen, J.; Vossbrinck, C.R.; Li, T.; Zhou, Z. Characterization of the Largest Secretory Protein Family, Ricin B Lectin-like Protein, in Nosema bombycis: Insights into Microsporidian Adaptation to Host. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8060551
Xu J, Luo J, Chen J, Vossbrinck CR, Li T, Zhou Z. Characterization of the Largest Secretory Protein Family, Ricin B Lectin-like Protein, in Nosema bombycis: Insights into Microsporidian Adaptation to Host. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(6):551. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8060551
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jinzhi, Jian Luo, Jiajing Chen, Charles R. Vossbrinck, Tian Li, and Zeyang Zhou. 2022. "Characterization of the Largest Secretory Protein Family, Ricin B Lectin-like Protein, in Nosema bombycis: Insights into Microsporidian Adaptation to Host" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 6: 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8060551
APA StyleXu, J., Luo, J., Chen, J., Vossbrinck, C. R., Li, T., & Zhou, Z. (2022). Characterization of the Largest Secretory Protein Family, Ricin B Lectin-like Protein, in Nosema bombycis: Insights into Microsporidian Adaptation to Host. Journal of Fungi, 8(6), 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8060551







