The Use of Host Biomarkers for the Management of Invasive Fungal Disease
Abstract
1. Background
2. An Overview of Invasive Fungal Disease
3. Invasive Aspergillosis
4. Invasive Candidiasis
5. IFD—General Considerations
6. Current Fungal Diagnosis and Therapeutics
7. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Host Biomarkers
8. Gene Expression Host Biomarkers
9. Cytokines and Chemokines as Host Biomarkers
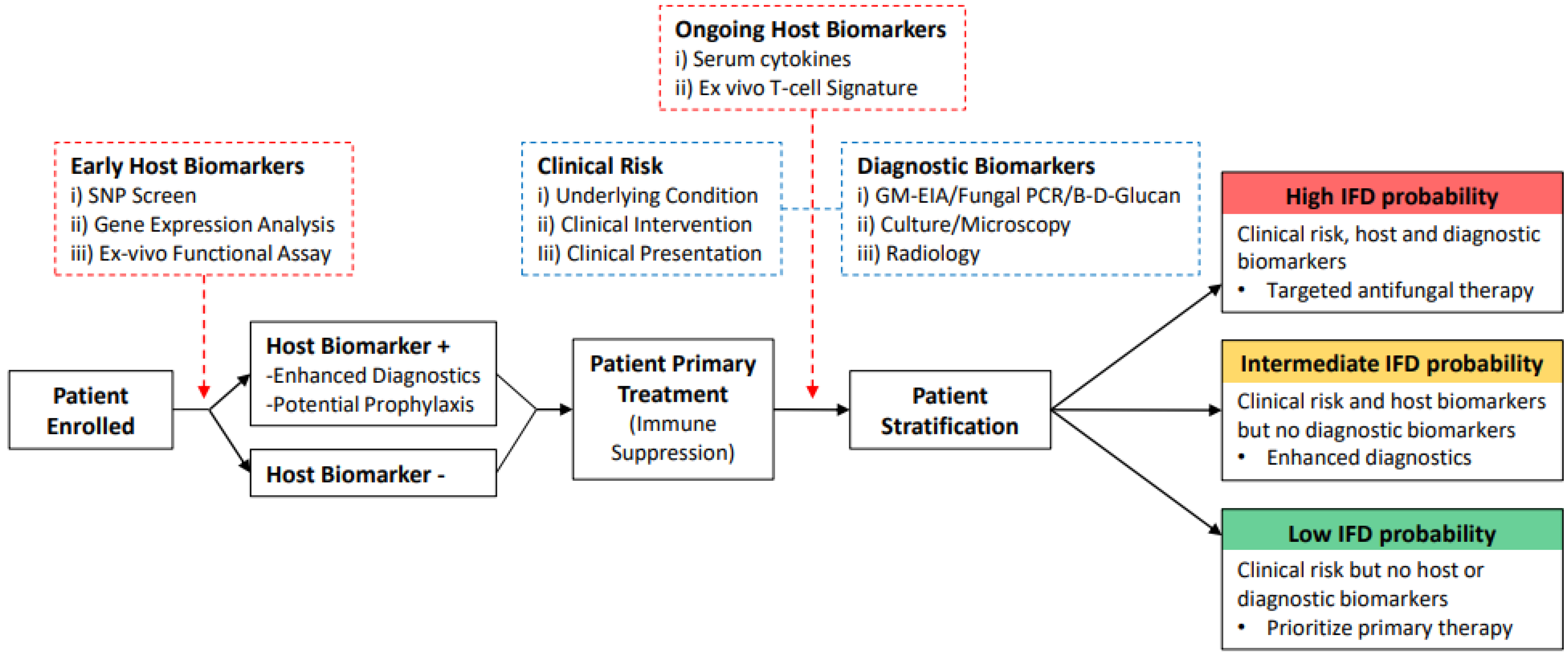
10. Host Biomarkers in IFD Predictive Modelling
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bongomin, F.; Gago, S.; Oladele, R.O.; Denning, D.W. Global and Multi-National Prevalence of Fungal Diseases-Estimate Precision. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNeil, A.; Glaziou, P.; Sismanidis, C.; Date, A.; Maloney, S.; Floyd, K. Global Epidemiology of Tuberculosis and Progress Toward Meeting Global Targets-Worldwide, 2018. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, T.D.; Carter, A.; Jahagirdar, D.; Biehl, M.H.; Douwes-Schultz, D.; Larson, S.L.; Arora, M.; Dwyer-Lindgren, L.; Steuben, K.M.; Abbastabar, H.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and mortality of HIV, 1980–2017, and forecasts to 2030, for 195 countries and territories: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2017. Lancet HIV 2019, 6, e831–e859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, D.J.; Lucas, T.C.D.; Nguyen, M.; Nandi, A.K.; Bisanzio, D.; Battle, K.E.; Cameron, E.; Twohig, K.A.; Pfeffer, D.A.; Rozier, J.A.; et al. Mapping the global prevalence, incidence, and mortality of Plasmodium falciparum, 2000–2017: A spatial and temporal modelling study. Lancet 2019, 394, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puerta-Alcalde, P.; Garcia-Vidal, C. Changing Epidemiology of Invasive Fungal Disease in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Marr, K.A.; Park, B.J.; Alexander, B.D.; Anaissie, E.J.; Walsh, T.J.; Ito, J.; Andes, D.R.; Baddley, J.W.; Brown, J.M.; et al. Prospective surveillance for invasive fungal infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients, 2001–2006: Overview of the Transplant-Associated Infection Surveillance Network (TRANSNET) Database. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolle, M.C.; Bénet, T.; Thiebaut, A.; Bienvenu, A.L.; Voirin, N.; Duclos, A.; Sobh, M.; Cannas, G.; Thomas, X.; Nicolini, F.E.; et al. Invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies: Incidence and description of 127 cases enrolled in a single institution prospective survey from 2004 to 2009. Haematologica 2011, 96, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neofytos, D.; Treadway, S.; Ostrander, D.; Alonso, C.D.; Dierberg, K.L.; Nussenblatt, V.; Durand, C.M.; Thompson, C.B.; Marr, K.A. Epidemiology, outcomes, and mortality predictors of invasive mold infections among transplant recipients: A 10-year, single-center experience. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2013, 15, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugui, J.A.; Kwon-Chung, K.J.; Juvvadi, P.R.; Latgé, J.P.; Steinbach, W.J. Aspergillus fumigatus and related species. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 5, a019786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latge, J.P. Aspergillus fumigatus and aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 310–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousha, M.; Tadi, R.; Soubani, A.O. Pulmonary aspergillosis: A clinical review. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2011, 20, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.; Thiel, E. Cerebral aspergillosis: Tissue penetration is the key. Med. Mycol. 2009, 47 (Suppl. S1), S387–S393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-J.; Schranz, J.; Teutsch, S.M. Aspergillosis Case-Fatality Rate: Systematic Review of the Literature. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, N.; Mitterbauer, M.; Tobudic, S.; Kalhs, P.; Rabitsch, W.; Greinix, H.; Burgmann, H.; Willinger, B.; Presterl, E.; Forstner, C. Incidence and characteristics of invasive fungal diseases in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, K.A.; Carter, R.A.; Crippa, F.; Wald, A.; Corey, L. Epidemiology and outcome of mould infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, L.; Caira, M.; Candoni, A.; Offidani, M.; Fianchi, L.; Martino, B.; Pastore, D.; Picardi, M.; Bonini, A.; Chierichini, A.; et al. The epidemiology of fungal infections in patients with hematologic malignancies: The SEIFEM-2004 study. Haematologica 2006, 91, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Bassetti, M.; Azoulay, E.; Kullberg, B.J.; Ruhnke, M.; Shoham, S.; Vazquez, J.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Calandra, T. EORTC/MSGERC Definitions of Invasive Fungal Diseases: Summary of Activities of the Intensive Care Unit Working Group. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72 (Suppl. S2), S121–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, C.O.; White, P.L.; Barnes, R.A.; Klingspor, L.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Lagrou, K.; Bretagne, S.; Melchers, W.; Mengoli, C.; Caliendo, A.M.; et al. Determining the analytical specificity of PCR-based assays for the diagnosis of IA: What is Aspergillus? Med. Mycol. 2017, 55, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, P.E.; Rijnders, B.J.A.; Brüggemann, R.J.M.; Azoulay, E.; Bassetti, M.; Blot, S.; Calandra, T.; Clancy, C.J.; Cornely, O.A.; Chiller, T.; et al. Review of influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis in ICU patients and proposal for a case definition: An expert opinion. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1524–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, P.; Bassetti, M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Chen, S.C.A.; Colombo, A.L.; Hoenigl, M.; Klimko, N.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Oladele, R.O.; Vinh, D.C.; et al. Defining and managing COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: The 2020 ECMM/ISHAM consensus criteria for research and clinical guidance. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, e149–e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyes, D.L.; Wilson, D.; Richardson, J.P.; Mogavero, S.; Tang, S.X.; Wernecke, J.; Hofs, S.; Gratacap, R.L.; Robbins, J.; Runglall, M.; et al. Candidalysin is a fungal peptide toxin critical for mucosal infection. Nature 2016, 532, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, J.P.; Brown, R.; Kichik, N.; Lee, S.; Priest, E.; Mogavero, S.; Maufrais, C.; Wickramasinghe, D.N.; Tsavou, A.; Kotowicz, N.K.; et al. Candidalysins Are a New Family of Cytolytic Fungal Peptide Toxins. mBio 2022, 13, e0351021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Du, Z.; Kang, Y.; Zang, B.; Cui, W.; Qin, B.; Fang, Q.; Qiu, H.; Li, J. Catheter-related Candidabloodstream infection in intensive care unit patients: A subgroup analysis of the China-SCAN study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pappas, P.G.; Rex, J.H.; Lee, J.; Hamill, R.J.; Larsen, R.A.; Powderly, W.; Kauffman, C.A.; Hyslop, N.; Mangino, J.E.; Chapman, S.; et al. A prospective observational study of candidemia: Epidemiology, therapy, and influences on mortality in hospitalized adult and pediatric patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 37, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullberg, B.J.; Arendrup, M.C. Invasive Candidiasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, P.G.; Lionakis, M.S.; Arendrup, M.C.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Kullberg, B.J. Invasive candidiasis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.D.; Denning, D.W.; Gow, N.A.; Levitz, S.M.; Netea, M.G.; White, T.C. Hidden killers: Human fungal infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 165rv113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.D.; Denning, D.W.; Levitz, S.M. Tackling human fungal infections. Science 2012, 336, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulware, D.R.; Rolfes, M.A.; Rajasingham, R.; von Hohenberg, M.; Qin, Z.; Taseera, K.; Schutz, C.; Kwizera, R.; Butler, E.K.; Meintjes, G.; et al. Multisite validation of cryptococcal antigen lateral flow assay and quantification by laser thermal contrast. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botterel, F.; Cabaret, O.; Foulet, F.; Cordonnier, C.; Costa, J.M.; Bretagne, S. Clinical significance of quantifying Pneumocystis jirovecii DNA by using real-time PCR in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from immunocompromised patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiada, A.; Pavleas, I.; Drogari-Apiranthitou, M. Epidemiology and Diagnosis of Mucormycosis: An Update. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M.W.; Katragkou, A.; Iosifidis, E.; Roilides, E.; Walsh, T.J. Recent Advances in the Treatment of Scedosporiosis and Fusariosis. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, M.; Coleman, J.J.; Carneiro, H.A.; Mylonakis, E. The challenge of managing fusariosis. Virulence 2011, 2, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, J.P.; Chen, S.C.; Kauffman, C.A.; Steinbach, W.J.; Baddley, J.W.; Verweij, P.E.; Clancy, C.J.; Wingard, J.R.; Lockhart, S.R.; Groll, A.H.; et al. Revision and Update of the Consensus Definitions of Invasive Fungal Disease From the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer and the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.A. Early diagnosis of fungal infection in immunocompromised patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61 (Suppl. S1), i3–i6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avni, T.; Leibovici, L.; Paul, M. PCR diagnosis of invasive candidiasis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.L.; Chen, X.; Zhu, C.G.; Li, Z.W.; Xia, Y.; Guo, X.G. Pooled analysis of T2 Candida for rapid diagnosis of candidiasis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengoli, C.; Cruciani, M.; Barnes, R.A.; Loeffler, J.; Donnelly, J.P. Use of PCR for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitis, M.; Ziakas, P.D.; Zacharioudakis, I.M.; Zervou, F.N.; Caliendo, A.M.; Mylonakis, E. PCR in diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis: A meta-analysis of diagnostic performance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3731–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruciani, M.; Mengoli, C.; Barnes, R.; Donnelly, J.P.; Loeffler, J.; Jones, B.L.; Klingspor, L.; Maertens, J.; Morton, C.O.; White, L.P. Polymerase chain reaction blood tests for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised people. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 9, Cd009551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuon, F.F. A systematic literature review on the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) from bronchoalveolar lavage clinical samples. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2007, 24, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Wang, K.; Gao, W.; Su, X.; Qian, Q.; Lu, X.; Song, Y.; Guo, Y.; Shi, Y. Evaluation of PCR on bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis: A bivariate metaanalysis and systematic review. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avni, T.; Levy, I.; Sprecher, H.; Yahav, D.; Leibovici, L.; Paul, M. Diagnostic accuracy of PCR alone compared to galactomannan in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: A systematic review. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3652–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summah, H.; Zhu, Y.G.; Falagas, M.E.; Vouloumanou, E.K.; Qu, J.M. Use of real-time polymerase chain reaction for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia in immunocompromised patients: A meta-analysis. Chin. Med. J. Engl. 2013, 126, 1965–1973. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.C.; Lu, H.W.; Cheng, K.B.; Li, H.P.; Xu, J.F. Evaluation of PCR in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia: A bivariate meta-analysis and systematic review. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ling, G.; Qiang, C.; Ming, Q.; Wu, C.; Wang, K.; Ying, Z. PCR diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia: A bivariate meta-analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 4361–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeflang, M.M.; Debets-Ossenkopp, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Visser, C.E.; Scholten, R.J.; Hooft, L.; Bijlmer, H.A.; Reitsma, J.B.; Zhang, M.; Bossuyt, P.M.; et al. Galactomannan detection for invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, Cd007394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, C.D.; Fine, J.P.; Safdar, N. Diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis using a galactomannan assay: A meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Tang, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, P.; Huang, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Fan, X. Systematic review and meta-analysis of detecting galactomannan in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for diagnosing invasive aspergillosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.L.; Chen, Y.Q.; Wang, K.; Qin, S.M.; Wu, C.; Kong, J.L. Accuracy of BAL galactomannan in diagnosing invasive aspergillosis: A bivariate metaanalysis and systematic review. Chest 2010, 138, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, S.C.; Morrissey, O.; Chen, S.C.; Thursky, K.; Manser, R.L.; Nation, R.L.; Kong, D.C.; Slavin, M. Utility of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid galactomannan alone or in combination with PCR for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in adult hematology patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 41, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgopoulos, D.E.; Vouloumanou, E.K.; Ntziora, F.; Michalopoulos, A.; Rafailidis, P.I.; Falagas, M.E. β-D-glucan assay for the diagnosis of invasive fungal infections: A meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 750–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Hang, J.P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, D.C.; Gong, F.H. A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy of serum 1,3-β-D-glucan for invasive fungal infection: Focus on cutoff levels. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2015, 48, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Y.; Liu, Y.; Gu, X.M.; Hao, S.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Yan, D.; Jiang, S.J. Diagnostic value of (1 → 3)-β-D-glucan in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for invasive fungal disease: A meta-analysis. Respir. Med. 2016, 117, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Fu, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, J. Diagnostic accuracy of a novel lateral-flow device in invasive aspergillosis: A meta-analysis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temfack, E.; Rim, J.J.B.; Spijker, R.; Loyse, A.; Chiller, T.; Pappas, P.G.; Perfect, J.; Sorell, T.C.; Harrison, T.S.; Cohen, J.F.; et al. Cryptococcal Antigen in Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid for Detecting Cryptococcal Meningitis in Adults Living With Human Immunodeficiency Virus: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 1268–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.A.; Stocking, K.; Bowden, S.; Poynton, M.H.; White, P.L. Prevention and diagnosis of invasive fungal disease in high-risk patients within an integrative care pathway. J. Infect. 2013, 67, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maertens, J.; Lodewyck, T.; Peter Donnelly, J.; Chantepie, S.; Robin, C.; Blijlevens, N.; Turlure, P.; Selleslag, D.; Baron, F.; Aoun, M.; et al. Empiric versus pre-emptive antifungal strategy in high-risk neutropenic patients on fluconazole prophylaxis: A randomized trial of the European organization for Research and Treatment of cancer (EORTC 65091). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcazar-Fuoli, L.; Mellado, E. Current status of antifungal resistance and its impact on clinical practice. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 166, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, N.; Caplan, T.; Cowen, L.E. Molecular Evolution of Antifungal Drug Resistance. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 753–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.C.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Berman, J.; Bicanic, T.; Bignell, E.M.; Bowyer, P.; Bromley, M.; Brüggemann, R.; Garber, G.; Cornely, O.A.; et al. Tackling the emerging threat of antifungal resistance to human health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, C.J.; Nguyen, M.H. Emergence of Candida auris: An International Call to Arms. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, J.; Abdolrasouli, A.; Farrer, R.A.; Cuomo, C.A.; Aanensen, D.M.; Armstrong-James, D.; Fisher, M.C.; Schelenz, S. Genomic epidemiology of the UK outbreak of the emerging human fungal pathogen Candida auris. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roemer, T.; Krysan, D.J. Antifungal drug development: Challenges, unmet clinical needs, and new approaches. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a019703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, P.L.; Parr, C.; Barnes, R.A. Predicting Invasive Aspergillosis in Hematology Patients by Combining Clinical and Genetic Risk Factors with Early Diagnostic Biomarkers. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01122-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.L.; Dhillon, R.; Cordey, A.; Hughes, H.; Faggian, F.; Soni, S.; Pandey, M.; Whitaker, H.; May, A.; Morgan, M.; et al. A National Strategy to Diagnose Coronavirus Disease 2019-Associated Invasive Fungal Disease in the Intensive Care Unit. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e1634–e1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glocker, E.O.; Hennigs, A.; Nabavi, M.; Schaffer, A.A.; Woellner, C.; Salzer, U.; Pfeifer, D.; Veelken, H.; Warnatz, K.; Tahami, F.; et al. A homozygous CARD9 mutation in a family with susceptibility to fungal infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvilain, E.; Casanova, J.L.; Puel, A. Inherited CARD9 Deficiency: Invasive Disease Caused by Ascomycete Fungi in Previously Healthy Children and Adults. J. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 38, 656–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, J.L.; Metz, A.E.; Horn, D.; Schoeb, T.R.; Hewitt, M.M.; Schwiebert, L.M.; Faro-Trindade, I.; Brown, G.D.; Steele, C. Requisite Role for the Dectin-1 β-Glucan Receptor in Pulmonary Defense against Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 4938–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.; Griffiths, J.S.; Walker, L.; da Fonseca, D.M.; Lee, K.K.; Taylor, P.R.; Gow, N.A.R.; Orr, S.J. Dependence on Dectin-1 Varies With Multiple Candida Species. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.; Rapaka, R.R.; Metz, A.; Pop, S.M.; Williams, D.L.; Gordon, S.; Kolls, J.K.; Brown, G.D. The beta-glucan receptor dectin-1 recognizes specific morphologies of Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS Pathog. 2005, 1, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, J.S.; Thompson, A.; Stott, M.; Benny, A.; Lewis, N.A.; Taylor, P.R.; Forton, J.; Herrick, S.; Orr, S.J.; McGreal, E.P. Differential susceptibility of Dectin-1 isoforms to functional inactivation by neutrophil and fungal proteases. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 3385–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferwerda, B.; Ferwerda, G.; Plantinga, T.S.; Willment, J.A.; van Spriel, A.B.; Venselaar, H.; Elbers, C.C.; Johnson, M.D.; Cambi, A.; Huysamen, C.; et al. Human dectin-1 deficiency and mucocutaneous fungal infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, C.; Di Ianni, M.; Bozza, S.; Giovannini, G.; Zagarella, S.; Zelante, T.; D’Angelo, C.; Pierini, A.; Pitzurra, L.; Falzetti, F.; et al. Dectin-1 Y238X polymorphism associates with susceptibility to invasive aspergillosis in hematopoietic transplantation through impairment of both recipient- and donor-dependent mechanisms of antifungal immunity. Blood 2010, 116, 5394–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.Y.A.; de Boer, M.G.J.; van der Velden, W.J.F.M.; Plantinga, T.S.; van Spriel, A.B.; Jacobs, C.; Halkes, C.J.M.; Vonk, A.G.; Blijlevens, N.M.; van Dissel, J.T.; et al. The Y238X Stop Codon Polymorphism in the Human β-Glucan Receptor Dectin-1 and Susceptibility to Invasive Aspergillosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz, J.; Lupiáñez, C.B.; Segura-Catena, J.; Vazquez, L.; Ríos, R.; Oyonarte, S.; Hemminki, K.; Försti, A.; Jurado, M. Dectin-1 and DC-SIGN Polymorphisms Associated with Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.L.; Price, J.S. Incorporating the Detection of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Associated With Invasive Aspergillosis Into the Clinic. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 860779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, J.S.; White, P.L.; Czubala, M.A.; Simonazzi, E.; Bruno, M.; Thompson, A.; Rizkallah, P.J.; Gurney, M.; da Fonseca, D.M.; Naglik, J.R.; et al. A Human Dectin-2 Deficiency Associated With Invasive Aspergillosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, C.; Aversa, F.; Lacerda, J.F.; Busca, A.; Kurzai, O.; Grube, M.; Löffler, J.; Maertens, J.A.; Bell, A.S.; Inforzato, A.; et al. Genetic PTX3 deficiency and aspergillosis in stem-cell transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, C.; Carvalho, A. Genetic defects in fungal recognition and susceptibility to invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Med. Mycol. 2019, 57 (Suppl. S2), S211–S218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, C.; Monteiro, A.A.; Oliveira-Coelho, A.; Kühne, J.; Rodrigues, F.; Sasaki, S.D.; Schio, S.M.; Camargo, J.J.; Mantovani, A.; Carvalho, A.; et al. PTX3-Based Genetic Testing for Risk of Aspergillosis After Lung Transplant. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 1893–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wójtowicz, A.; Lecompte, T.D.; Bibert, S.; Manuel, O.; Rüeger, S.; Berger, C.; Boggian, K.; Cusini, A.; Garzoni, C.; Hirsch, H.; et al. PTX3 Polymorphisms and Invasive Mold Infections After Solid Organ Transplant. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Li, H.; Rui, Y.; Liu, L.; He, B.; Shi, Y.; Su, X. Pentraxin 3 Gene Polymorphisms and Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, C.E.; Hohl, T.M.; Fan, W.; Storer, B.E.; Levine, D.M.; Zhao, L.P.; Martin, P.J.; Warren, E.H.; Boeckh, M.; Hansen, J.A. Validation of single nucleotide polymorphisms in invasive aspergillosis following hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood 2017, 129, 2693–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupiañez, C.B.; Canet, L.M.; Carvalho, A.; Alcazar-Fuoli, L.; Springer, J.; Lackner, M.; Segura-Catena, J.; Comino, A.; Olmedo, C.; Ríos, R.; et al. Polymorphisms in Host Immunity-Modulating Genes and Risk of Invasive Aspergillosis: Results from the AspBIOmics Consortium. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, L. Immunity to fungal infections. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.; Cunha, C.; Carotti, A.; Aloisi, T.; Guarrera, O.; Di Ianni, M.; Falzetti, F.; Bistoni, F.; Aversa, F.; Pitzurra, L.; et al. Polymorphisms in Toll-like receptor genes and susceptibility to infections in allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Exp. Hematol. 2009, 37, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.; Pasqualotto, A.C.; Pitzurra, L.; Romani, L.; Denning, D.W.; Rodrigues, F. Polymorphisms in Toll-Like Receptor Genes and Susceptibility to Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koldehoff, M.; Beelen, D.W.; Elmaagacli, A.H. Increased susceptibility for aspergillosis and post-transplant immune deficiency in patients with gene variants of TLR4 after stem cell transplantation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2013, 15, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, J.S.; White, P.L.; Thompson, A.; da Fonseca, D.M.; Pickering, R.J.; Ingram, W.; Wilson, K.; Barnes, R.; Taylor, P.R.; Orr, S.J. A Novel Strategy to Identify Haematology Patients at High Risk of Developing Aspergillosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 780160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolnai, E.; Fidler, G.; Szász, R.; Rejtő, L.; Nwozor, K.O.; Biró, S.; Paholcsek, M. Free circulating mircoRNAs support the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies and neutropenia. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Gupta, M.; Fliesser, M.; Springer, J.; Breitschopf, T.; Schlossnagel, H.; Schmitt, A.L.; Kurzai, O.; Hünniger, K.; Einsele, H.; Löffler, J. Aspergillus fumigatus induces microRNA-132 in human monocytes and dendritic cells. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Pilar Jiménez, A.M.; Viriyakosol, S.; Walls, L.; Datta, S.K.; Kirkland, T.; Heinsbroek, S.E.; Brown, G.; Fierer, J. Susceptibility to Coccidioides species in C57BL/6 mice is associated with expression of a truncated splice variant of Dectin-1 (Clec7a). Genes Immun. 2008, 9, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.M.; Brown, G.D. The Dectin-2 family of C-type lectins in immunity and homeostasis. Cytokine 2009, 48, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoran, T.; Weber, M.; Springer, J.; White, P.L.; Bauer, J.; Schober, A.; Löffler, C.; Seelbinder, B.; Hünniger, K.; Kurzai, O.; et al. Treatment with etanercept and low monocyte concentration contribute to the risk of invasive aspergillosis in patients post allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezger, M.; Steffens, M.; Beyer, M.; Manger, C.; Eberle, J.; Toliat, M.R.; Wienker, T.F.; Ljungman, P.; Hebart, H.; Dornbusch, H.J.; et al. Polymorphisms in the chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 10 are associated with invasive aspergillosis after allogeneic stem-cell transplantation and influence CXCL10 expression in monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Blood 2008, 111, 534–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoran, T.; Seelbinder, B.; White, P.L.; Price, J.S.; Kraus, S.; Kurzai, O.; Linde, J.; Häder, A.; Loeffler, C.; Grigoleit, G.U.; et al. Molecular Profiling Reveals Characteristic and Decisive Signatures in Patients after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Suffering from Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauruschkat, C.D.; Page, L.; White, P.L.; Etter, S.; Davies, H.E.; Duckers, J.; Ebel, F.; Schnack, E.; Backx, M.; Dragan, M.; et al. Development of a Simple and Robust Whole Blood Assay with Dual Co-Stimulation to Quantify the Release of T-Cellular Signature Cytokines in Response to Aspergillus fumigatus Antigens. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, V.; Tebruegge, M.; Zufferey, C.; Germano, S.; Forbes, B.; Cosentino, L.; Matchett, E.; McBryde, E.; Eisen, D.; Robins-Browne, R.; et al. Cytokine biomarkers for the diagnosis of tuberculosis infection and disease in adults in a low prevalence setting. Tuberculosis 2019, 114, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo-Velasco, Á.; Peñarrubia-Ponce, M.J.; Álvarez, F.J.; Gonzalo-Benito, H.; de la Fuente, I.; Martín-Fernández, M.; Eiros, J.M.; Martínez-Paz, P.; Miramontes-González, J.P.; Fiz-López, A.; et al. Evaluation of Cytokines as Robust Diagnostic Biomarkers for COVID-19 Detection. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frimpong, A.; Owusu, E.D.A.; Amponsah, J.A.; Obeng-Aboagye, E.; van der Puije, W.; Frempong, A.F.; Kusi, K.A.; Ofori, M.F. Cytokines as Potential Biomarkers for Differential Diagnosis of Sepsis and Other Non-Septic Disease Conditions. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 901433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Assay | Sample Type | Performance Parameter | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | LR + Tive | LR − Tive | DOR | |||
| Candida PCR | Blood | 95.0 | 92.0 | 11.88 | 0.05 | 218.50 | [36] |
| T2 Candida | Blood | 91.0 | 94.0 | 15.17 | 0.09 | 158.41 | [37] |
| Aspergillus PCR | Blood | 88.0 | 75.0 | 3.52 | 0.16 | 22.00 | [38] |
| 84.0 | 76.0 | 3.50 | 0.21 | 16.60 | [39] | ||
| 79.2 | 79.6 | 3.88 | 0.26 | 14.86 | [40] | ||
| BAL fluid | 78.4 | 93.7 | 12.44 | 0.23 | 53.98 | [41] | |
| 79.6 | 94.1 | 13.49 | 0.22 | 62.23 | [42] | ||
| 76.8 | 94.5 | 13.96 | 0.25 | 56.88 | [43] | ||
| PCP PCR | Respiratory | 97.0 | 94.0 | 16.17 | 0.03 | 506.56 | [44] |
| 98.0 | 91.0 | 10.89 | 0.02 | 495.44 | [45] | ||
| 99.0 | 90.0 | 9.90 | 0.01 | 891.00 | [46] | ||
| GM EIA | Blood | 79.3 | 80.5 | 4.07 | 0.26 | 15.81 | [47] |
| 79.3 | 86.3 | 5.79 | 0.24 | 24.13 | [48] | ||
| BAL fluid | 83.6 | 89.4 | 7.88 | 0.18 | 42.99 | [49] | |
| 85.7 | 89.0 | 7.79 | 0.16 | 48.49 | [50] | ||
| 92.0 | 98.0 | 46.0 | 0.08 | 563.5 | [51] | ||
| Β-D-Glucan | Blood | 76.8 | 85.3 | 5.22 | 0.27 | 19.21 | [52] |
| 78.0 | 81.0 | 4.11 | 0.27 | 15.11 | [53] | ||
| BAL fluid | 52.0 | 58.0 | 1.24 | 0.83 | 1.50 | [54] | |
| Aspergillus LFA | Blood | 68.0 | 87.0 | 5.23 | 0.37 | 14.22 | [55] |
| BAL fluid | 86.0 | 93.0 | 12.29 | 0.15 | 81.6 | ||
| Cryptoccocal LFA | Blood | 97.9 | 89.5 | 9.32 | 0.02 | 397.37 | [56] |
| CSF | 99.5 | 99.5 | 199 | 0.01 | 39601 | ||
| Biomarker Category | Host Biomarker | Reference | IFD Susceptibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| SNPs | CARD9 | [67,68] | ↑ |
| DC-SIGN (CD209) | [76,77] | ↑ | |
| CLEC7A (Dectin-1) | [73,75] | ↑ | |
| CLEC6A (Dectin-2) | [78] | ↑ | |
| PTX3 (PENTRAXIN-3) | [79,80,81,82,83,84] | ↑ | |
| IL-4R | [85] | ↑ | |
| CXCL8 (IL-8) | [85] | ↑ | |
| IL-12B | [85] | ↓ | |
| IFNγ | [85] | ↓ | |
| CXCL10 | [96] | ↑ | |
| Gene Expression | Reduced CLEC7A (Dectin-1) | [90] | ↑ |
| Reduced CLEC6A (Dectin-2) | [90] | ↑ | |
| Increased CLEC4D (Mcl) | [90] | ↓ | |
| Increased miR-142-3p | [91] | ↑ | |
| Increased miR-142-5p | [91] | ↑ | |
| Increased miR-26b-5p | [91] | ↑ | |
| Reduced MMP1 | [97] | ↑ | |
| Increased LGALS2 | [97] | ↑ | |
| Gene Splicing | Truncated CLEC7A (Dectin-1) | [72,93] | ↑ |
| Cytokines/Chemokines | Etanercept treatment (TNF blockade) | [95] | ↑ |
| Increased serum IL-8 | [97] | ↑ | |
| Increased serum Caspase-3 | [97] | ↑ | |
| ex vivo PBMC fungal stimulation low/absent TNF response | [90] | ↑ | |
| ex vivo PBMC fungal stimulation low/absent IL-6 response | [90] | ↑ | |
| ex vivo whole blood T-cell assay increased IL-4 | [98] | ↑ | |
| ex vivo whole blood T-cell assay increased IL-5 | [98] | ↑ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Griffiths, J.S.; Orr, S.J.; Morton, C.O.; Loeffler, J.; White, P.L. The Use of Host Biomarkers for the Management of Invasive Fungal Disease. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121307
Griffiths JS, Orr SJ, Morton CO, Loeffler J, White PL. The Use of Host Biomarkers for the Management of Invasive Fungal Disease. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(12):1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121307
Chicago/Turabian StyleGriffiths, James S., Selinda J. Orr, Charles Oliver Morton, Juergen Loeffler, and P. Lewis White. 2022. "The Use of Host Biomarkers for the Management of Invasive Fungal Disease" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 12: 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121307
APA StyleGriffiths, J. S., Orr, S. J., Morton, C. O., Loeffler, J., & White, P. L. (2022). The Use of Host Biomarkers for the Management of Invasive Fungal Disease. Journal of Fungi, 8(12), 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121307








