The Gal4-Type Transcription Factor Pro1 Integrates Inputs from Two Different MAPK Cascades to Regulate Development in the Fungal Pathogen Fusarium oxysporum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Isolates and Growth Conditions
2.2. Nucleic Acid Manipulation and Quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) Analysis
2.3. Generation of Gene Deletion Mutants and Complemented Strains
2.4. Cellophane Penetration Assay
2.5. Quantification of Vegetative Hyphal Fusion and Hyphal Aggregation
2.6. Quantification of Microconidial Germination and Hyphal Chemotropism
2.7. Colony Growth Assays
2.8. Tomato Plant Infection Assay
2.9. Sequence Retrieval and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
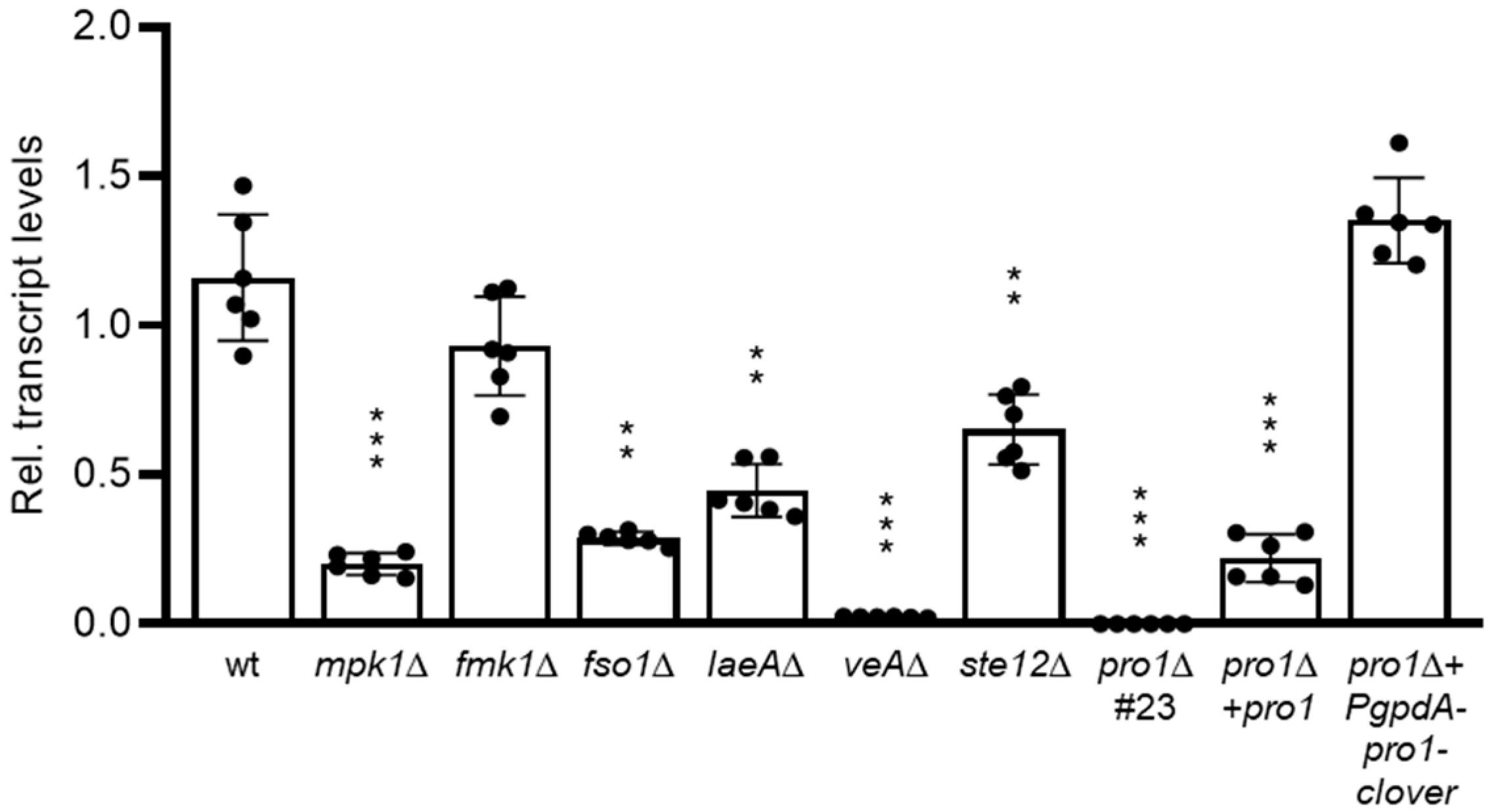
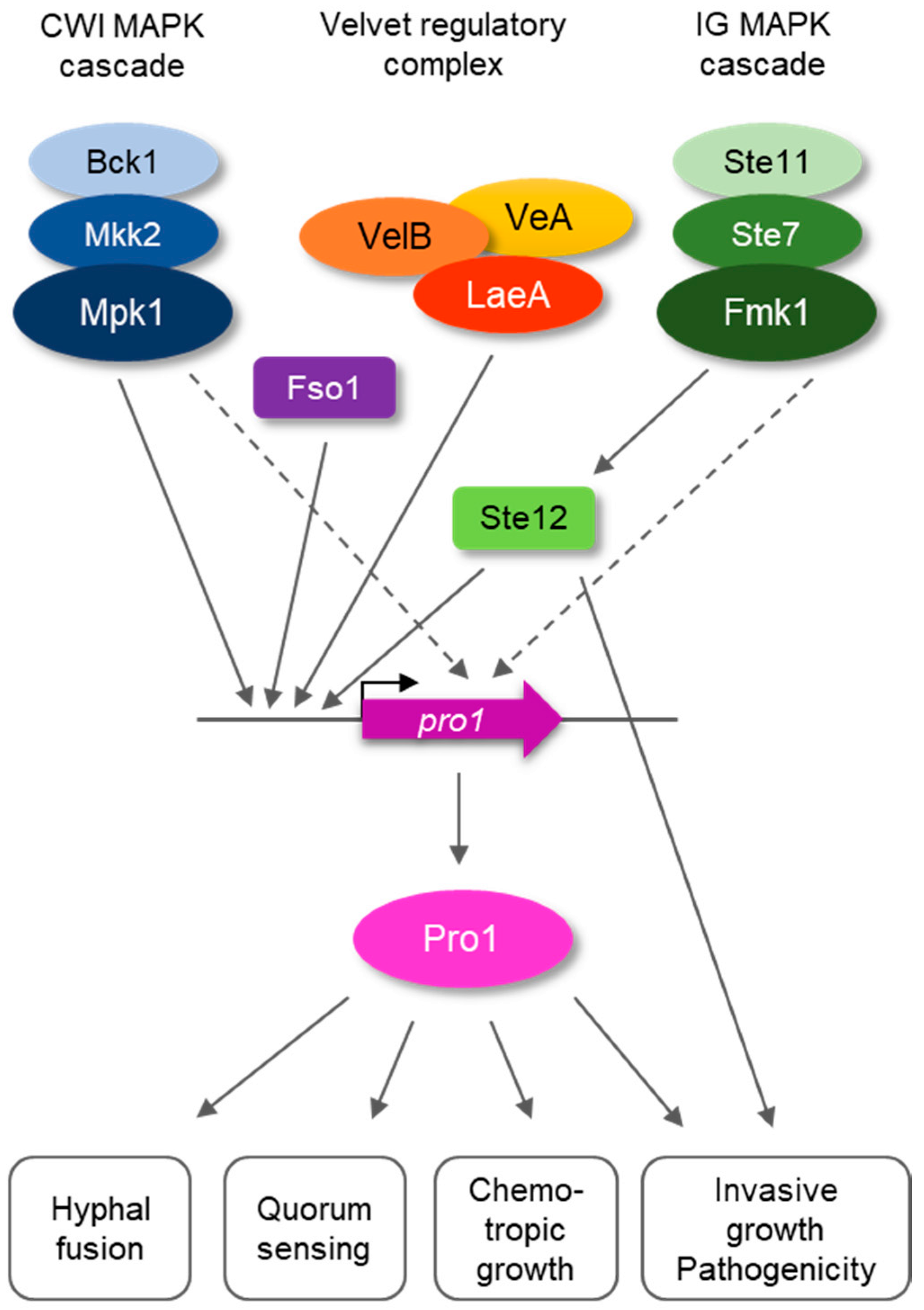
3.1. Pro1 in F. oxysporum Is under Complex Transcriptional Control by the Fmk1 and Mpk1 MAPK Cascades and the Regulators Fso1 and Velvet
3.2. Generation of Pro1 Deletion Mutants
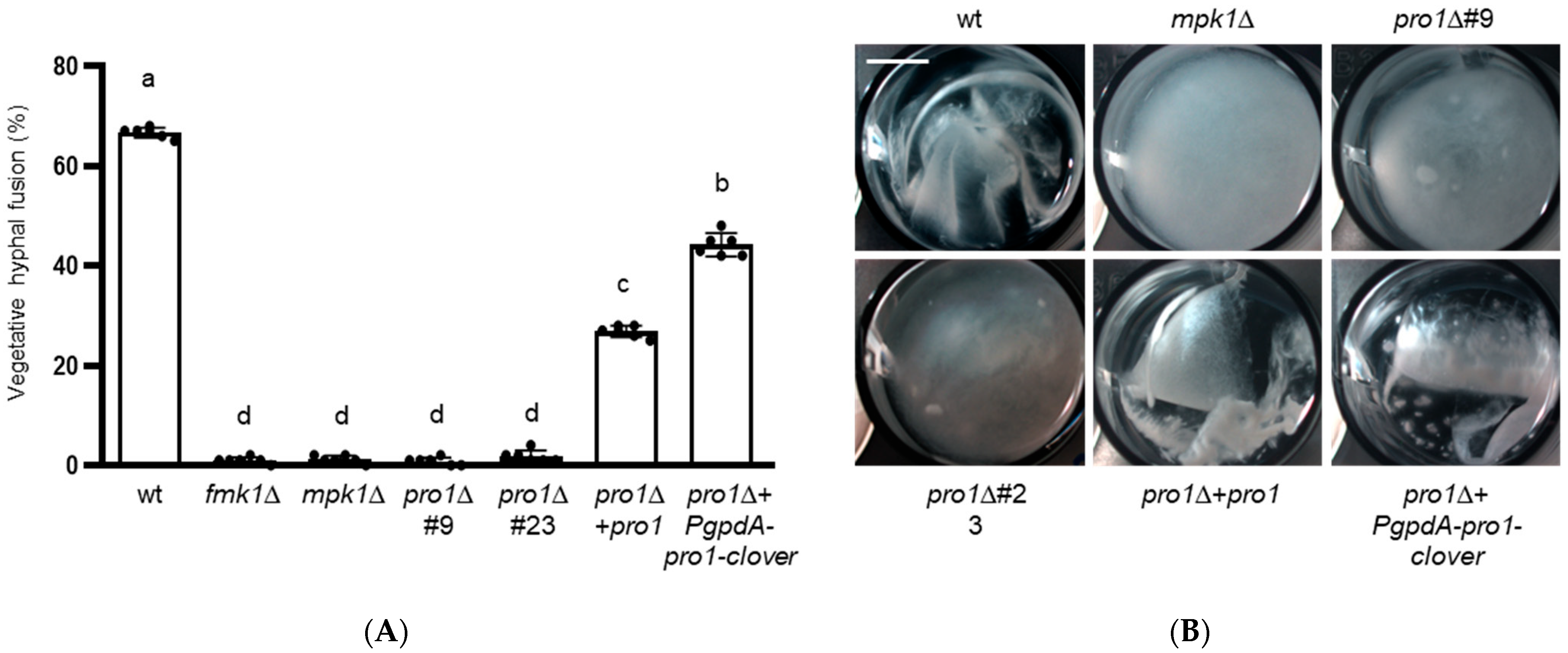
3.3. Pro1 Is Required for Vegetative Hyphal Fusion and Hyphal Aggregation
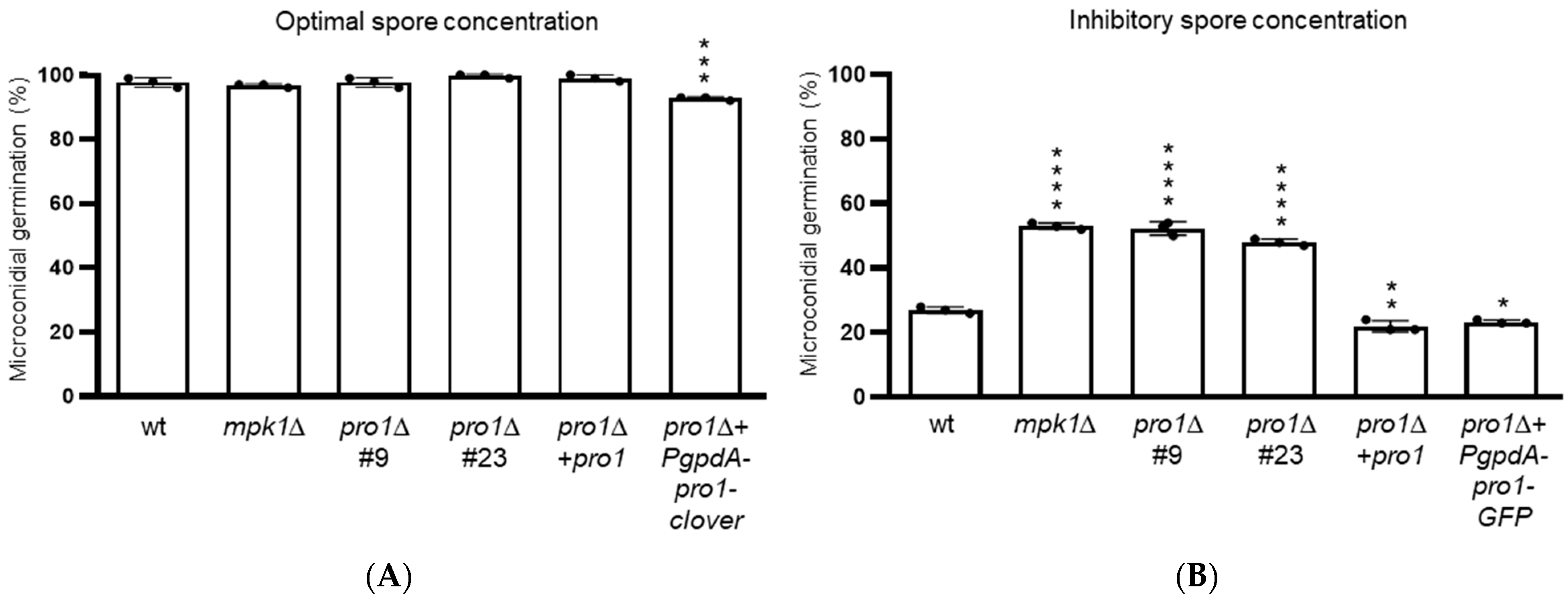
3.4. Pro1 Contributes to Quorum Sensing during Germination of Microconidia
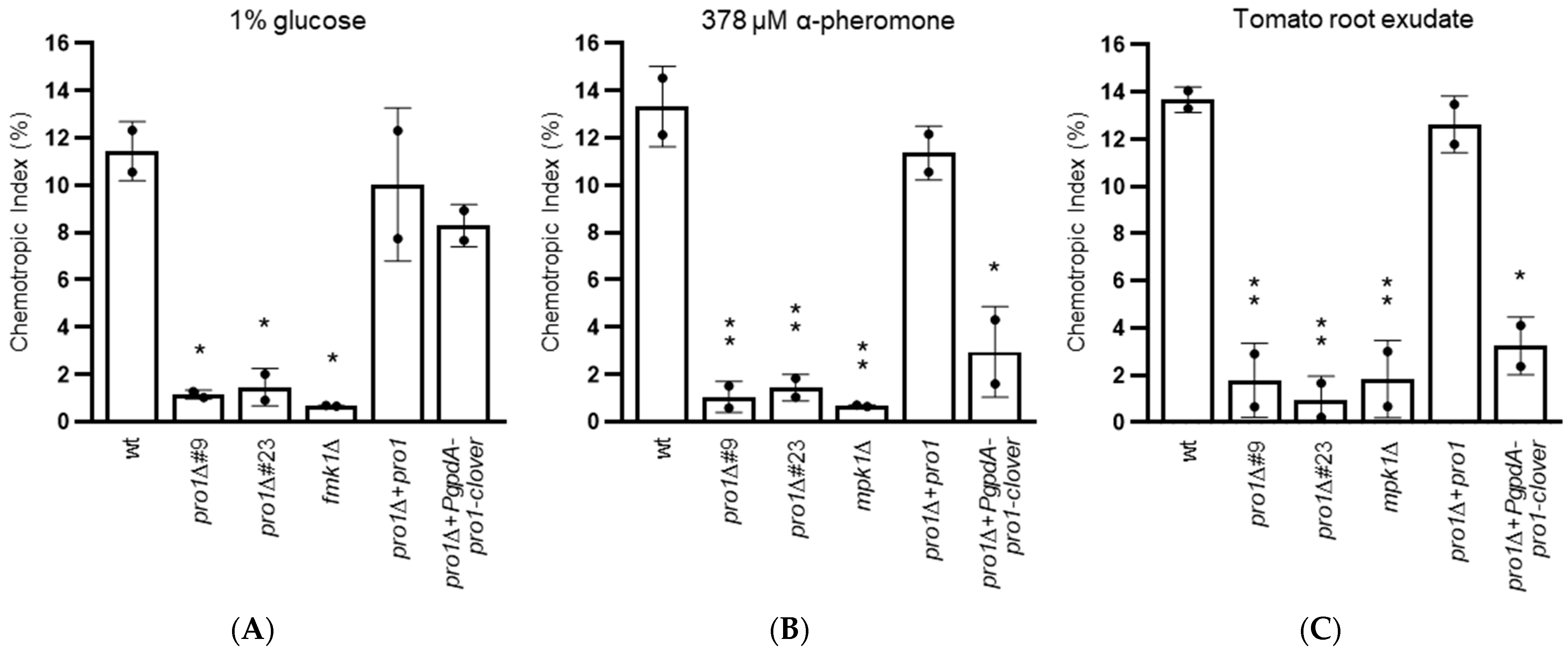
3.5. Pro1 Is Required for Chemotropic Growth towards Nutrients, Plant Chemoattractants and Peptide Pheromone
3.6. Pro1 Does Not Contribute to Cell Wall, Oxidative and Heat Stress Responses
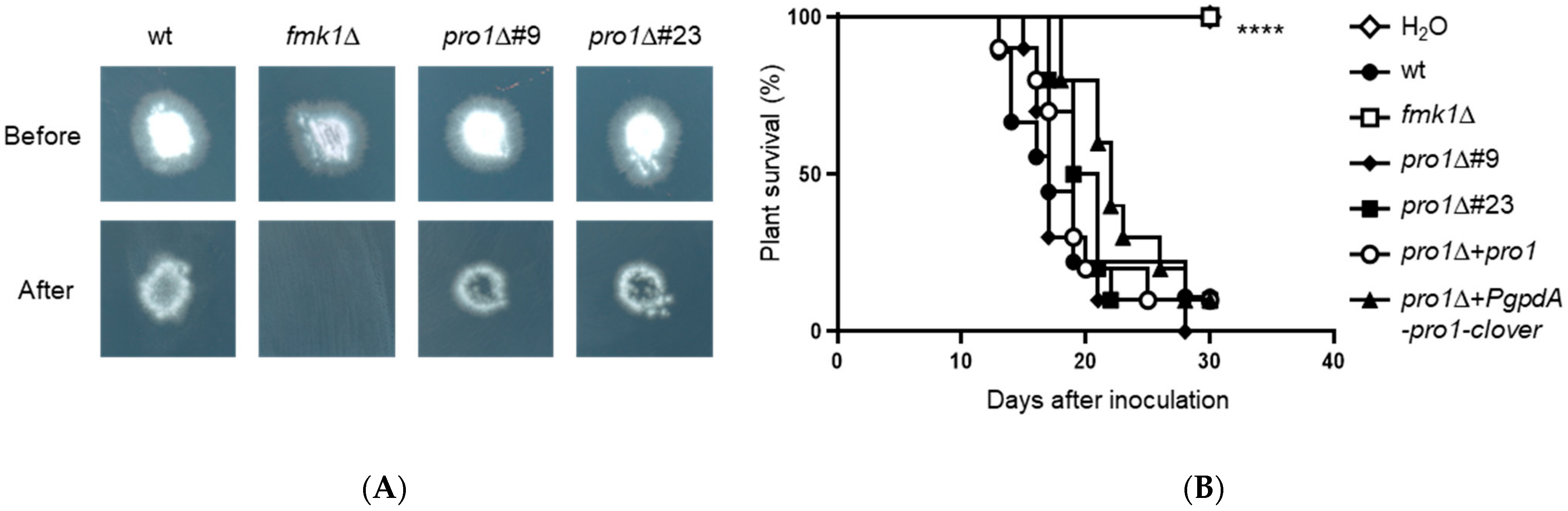
3.7. Pro1 Is Dispensable for Invasive Hyphal Growth and Plant Infection
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, L.; Karin, M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 2001, 410, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmann, C.; Gibson, S.; Jarpe, M.; Johnson, G. Mitogen-activated protein kinase: Conservation of a three-kinase module from yeast to human. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 143–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turrà, D.; Segorbe, D.; Di Pietro, A. Protein Kinases in Plant-Pathogenic Fungi: Conserved Regulators of Infection. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.E.; Thorner, J. Function and regulation in MAPK signaling pathways: Lessons learned from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1311–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, R.; Van Kan, J.A.; Pretorius, Z.A.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Di Pietro, A.; Spanu, P.D.; Rudd, J.J.; Dickman, M.; Kahmann, R.; Ellis, J.; et al. The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2012, 13, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, A.; García-MacEira, F.I.; Méglecz, E.; Roncero, M.I. A MAP kinase of the vascular wilt fungus Fusarium oxysporum is essential for root penetration and pathogenesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rispail, N.; Di Pietro, A. Fusarium oxysporum Ste12 Controls Invasive Growth and Virulence Downstream of the Fmk1 MAPK Cascade. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prados Rosales, R.C.; Di Pietro, A. Vegetative hyphal fusion is not essential for plant infection by Fusarium oxysporum. Eukaryot. Cell 2008, 7, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Berges, M.S.; Rispail, N.; Prados-Rosales, R.C.; Di Pietro, A. A nitrogen response pathway regulates virulence functions in Fusarium oxysporum via the protein kinase TOR and the bZIP protein MeaB. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2459–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrà, D.; El Ghalid, M.; Rossi, F.; Di Pietro, A. Fungal pathogen uses sex pheromone receptor for chemotropic sensing of host plant signals. Nature 2015, 527, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrà, D.; Di Pietro, A. Chemotropic sensing in fungus–plant interactions. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 2015, 26, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segorbe, D.; Di Pietro, A.; Pérez-Nadales, E.; Turrà, D. Three Fusarium oxysporum mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) have distinct and complementary roles in stress adaptation and cross-kingdom pathogenicity. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 18, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.; Di Pietro, A.; Turrà, D. Autocrine pheromone signalling regulates community behaviour in the fungal pathogen Fusarium oxysporum. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Nadales, E.; Di Pietro, A. The membrane mucin Msb2 regulates invasive growth and plant infection in Fusarium oxysporum. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masloff, S.; Pöggeler, S.; Kück, U. The pro1(+) gene from Sordaria macrospora encodes a C6 zinc finger transcription factor required for fruiting body development. Genetics 1999, 152, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schjerling, P.; Holmberg, S. Comparative amino acid sequence analysis of the C6 zinc cluster family of transcriptional regulators. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 4599–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vienken, K.; Scherer, M.; Fischer, R. The Zn(II)2Cys6 putative Aspergillus nidulans transcription factor repressor of sexual development inhibits sexual development under low-carbon conditions and in submersed culture. Genetics 2005, 169, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colot, H.V.; Park, G.; Turner, G.E.; Ringelberg, C.; Crew, C.M.; Litvinkova, L.; Weiss, R.L.; Borkovich, K.A.; Dunlap, J.C. A high-throughput gene knockout procedure for Neurospora reveals functions for multiple transcription factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10352–10357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vienken, K.; Fischer, R. The Zn(II)2Cys6 putative transcription factor NosA controls fruiting body formation in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 61, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Choi, G.H.; Nuss, D.L. Hypovirus-responsive transcription factor gene pro1 of the chestnut blight fungus Cryphonectria parasitica is required for female fertility, asexual spore development, and stable maintenance of hypovirus infection. Eukaryot. Cell 2009, 8, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Ao, J.; Dettmann, A.; Seiler, S.; Free, S.J. Characterization of the Neurospora crassa cell fusion proteins, HAM-6, HAM-7, HAM-8, HAM-9, HAM-10, AMPH-1 and WHI-2. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautier, V.; Tong, L.C.H.; Nguyen, T.S.; Debuchy, R.; Silar, P. PaPro1 and IDC4, two genes controlling stationary phase, sexual development and cell degeneration in Podospora anserina. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, A.; Cartwright, G.M.; Saikia, S.; Kayano, Y.; Takemoto, D.; Kato, M.; Tsuge, T.; Scott, B. ProA, a transcriptional regulator of fungal fruiting body development, regulates leaf hyphal network development in the Epichloe festucae-Lolium perenne symbiosis. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 90, 551–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekhang, R.; Wu, C.; Smith, K.; Lamb, T.; Peterson, M.; Bredeweg, E.L.; Ibarra, O.; Emerson, J.M.; Karunarathna, N.; Lyubetskaya, A.; et al. The Neurospora Transcription Factor ADV-1 Transduces Light Signals and Temporal Information to Control Rhythmic Expression of Genes Involved in Cell Fusion. Genes Genom. Genet. 2017, 7, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Spraker, J.; Bok, J.; Velk, T.; He, Z.; Keller, N.P. A Cellular Fusion Cascade Regulated by LaeA Is Required for Sclerotial Development in Aspergillus flavus. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Kim, K.H.; La Rota, M.; Scott, D.; Santopietro, G.; Callihan, M.; Mitchell, T.K.; Lawrence, C.B. Identification of novel virulence factors associated with signal transduction pathways in Alternaria brassicicola. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 72, 1316–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Wu, V.; Lee, J.; O’Malley, R.; Glass, N.L. Regulation of Cell-to-Cell Communication and Cell Wall Integrity by a Network of MAP Kinase Pathways and Transcription Factors in Neurospora crassa. Genetics 2018, 209, 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhalla, J.E. Compatibility reactions on solid medium and interstrain inhibition in Ustilago maydis. Genetics 1968, 60, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, A.; García-Maceira, F.I.; Huertas-González, M.D.; Ruíz-Roldan, M.C.; Caracuel, Z.; Barbieri, A.S.; Roncero, M.I. Endopolygalacturonase PG1 in different formae speciales of Fusarium oxysporum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 1967–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- López-Berges, M.S.; Capilla, J.; Turrà, D.; Schafferer, L.; Matthijs, S.; Jochl, C.; Cornelis, P.; Guarro, J.; Haas, H.; Di Pietro, A. HapX-mediated iron homeostasis is essential for rhizosphere competence and virulence of the soilborne pathogen Fusarium oxysporum. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 3805–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catlett, N.L.; Lee, B.; Yoder, O.C.; Turgeon, B.G. Split-marker recombination for efficient targeted deletion of fungal genes. Fungal Genet. Rep. 2003, 50, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, A.; Roncero, M.I. Cloning, expression, and role in pathogenicity of pg1 encoding the major extracellular endopolygalacturonase of the vascular wilt pathogen Fusarium oxysporum. Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact. 1998, 11, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuivanen, J.; Korja, V.; Holmström, S.; Richard, P. Development of microtiter plate scale CRISPR/Cas9 transformation method for Aspergillus niger based on in vitro assembled ribonucleoprotein complexes. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2019, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punt, P.; Oliver, R.; Dingemanse, M.; Pouwels, P.; van den Hondel, C. Transformation of Aspergillus based on the hygromycin B resistance marker from Escherichia coli. Gene 1987, 56, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Fernandes, T.A. Intracellular pH as a New Mechanism of Signal Transduction. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cordoba, Cordoba, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Berges, M.; Hera, C.; Sulyok, M.; Schäfer, K.; Capilla, J.; Guarro, J.; Di Pietro, A. The velvet complex governs mycotoxin production and virulence of Fusarium oxysporum on plant and mammalian hosts. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 87, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeder, A.C.; Palma-Guerrero, J.; Glass, N.L. The social network: Deciphering fungal language. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitarra, G.S.; Abee, T.; Rombouts, F.M.; Posthumus, M.A.; Dijksterhuis, J. Germination of Penicillium paneum conidia is regulated by 1-octen-3-ol, a volatile self-inhibitor. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 2823–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Garcia, E.; Garzia, A.; Cordobés, S.; Espeso, E.A.; Ugalde, U. 8-Carbon oxylipins inhibit germination and growth, and stimulate aerial conidiation in Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Biol. 2011, 115, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffens, E.K.; Becker, K.; Krevet, S.; Teichert, I.; Kück, U. Transcription factor PRO1 targets genes encoding conserved components of fungal developmental signaling pathways. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 102, 792–8090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayram, O.; Krappmann, S.; Ni, M.; Bok, J.W.; Helmstaedt, K.; Valerius, O.; Braus-Stromeyer, S.; Kwon, N.J.; Keller, N.P.; Yu, J.H.; et al. VelB/VeA/LaeA complex coordinates light signal with fungal development and secondary metabolism. Science 2008, 320, 1504–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bok, J.W.; Keller, N.P. LaeA, a regulator of secondary metabolism in Aspergillus spp. Eukaryot. Cell 2004, 3, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redkar, A.; Sabale, M.; Schudoma, C.; Zechmann, B.; Gupta, Y.K.; López-Berges, M.S.; Venturini, G.; Gimenez-Ibanez, S.; Turrà, D.; Solano, R.; et al. Conserved secreted effectors contribute to endophytic growth and multihost plant compatibility in a vascular wilt fungus. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 3214–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palos-Fernández, R.; Turrà, D.; Pietro, A.D. The Gal4-Type Transcription Factor Pro1 Integrates Inputs from Two Different MAPK Cascades to Regulate Development in the Fungal Pathogen Fusarium oxysporum. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121242
Palos-Fernández R, Turrà D, Pietro AD. The Gal4-Type Transcription Factor Pro1 Integrates Inputs from Two Different MAPK Cascades to Regulate Development in the Fungal Pathogen Fusarium oxysporum. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(12):1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121242
Chicago/Turabian StylePalos-Fernández, Rafael, David Turrà, and Antonio Di Pietro. 2022. "The Gal4-Type Transcription Factor Pro1 Integrates Inputs from Two Different MAPK Cascades to Regulate Development in the Fungal Pathogen Fusarium oxysporum" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 12: 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121242
APA StylePalos-Fernández, R., Turrà, D., & Pietro, A. D. (2022). The Gal4-Type Transcription Factor Pro1 Integrates Inputs from Two Different MAPK Cascades to Regulate Development in the Fungal Pathogen Fusarium oxysporum. Journal of Fungi, 8(12), 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8121242






