Abstract
Triangularia mangenotti was analyzed for the production of secondary metabolites, resulting in the isolation of known zopfinol (1) and its new derivatives zopfinol B–C (2–4), the 10-membered lactones 7-O-acetylmultiplolide A (5) and 8-O-acetylmultiplolide A (6), together with sordarin (7), sordarin B (8), and hypoxysordarin (9). The absolute configuration of 1 was elucidated by the synthesis of MPTA-esters. Compound 1 showed antimicrobial activity against the Gram-positive bacteria Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus and the fungus Mucor hiemalis. While 4 was weakly antibacterial, 3 showed stronger antibiotic activity against the Gram-positive bacteria and weak antifungal activity against M. hiemalis and Rhodotorula glutinis. We furthermore observed the cytotoxicity of 1, 3 and 4 against the mammalian cell lines KB3.1 and L929. Moreover, the new genus Pseudorhypophila is introduced herein to accommodate Triangularia mangenotii together with several species of Zopfiella—Z. marina, Z. pilifera, and Z. submersa. These taxa formed a well-supported monophyletic clade in the recently introduced family Navicularisporaceae, located far from the type species of the respective original genera, in a phylogram based on the combined dataset sequences of the internal transcribed spacer region (ITS), the nuclear rDNA large subunit (LSU), and fragments of the ribosomal polymerase II subunit 2 (rpb2) and β-tubulin (tub2) genes. Zopfiella submersa is synonymized with P. marina due to the phylogenetic and morphological similarity. The isolation of zopfinols 1–4 and sordarins 7–9 confirms the potential of this fungal order as producers of bioactive compounds and suggests these compounds as potential chemotaxonomic markers.
1. Introduction
The genus Triangularia was recently found to be polyphyletic, and its species were scattered along the phylogenetic tree of the order Sordariales [1,2]. Two years ago, Wang et al. [3] delimited the genus to the type species, together with other species previously placed in the genera Apiosordaria, Podospora, and Zopfiella. Recently, Triangularia karachiensis was transferred to the new genus Lundqvistomyces, since it was not located in the monophyletic clade comprising Triangularia [4]. On the other hand, the genus Zopfiella could so far not be correctly delimited due to the lack of type material of the type species Z. tabulata [4]. One reference strain of this species was placed with other ones producing ascospores with septate upper cell in the family Lasiosphaeriaceae, suggesting that this is the right monophyletic lineage representing the genus [3,4]. Therefore, other species of Zopfiella not located in this lineage have been transferred to other genera, e.g., Z. longicaudata and Z. tetraspora to Triangularia [3,4], and Z. tanzaniensis to Lundqvistomyces [4]. However, a large number of species that are still placed in Triangularia and Zopfiella need a relocation in different genera to achieve a more natural classification.
Numerous members of the Sordariales are being tested for the production of novel biologically active compounds during the course of an ongoing project, since this group of fungi has been demonstrated to contain prolific producers [5,6]. A prominent example is the production of the antimycotic sordarins by several taxa belonging to this order, e.g., Rhypophila pleiospora [7] and Zopfiella marina [8]. Moreover, several strains of Jugulospora already tested by us demonstrated to be profuse producers of secondary metabolites, as exemplified by the recent report of seven bioactive xanthoquinodin derivatives [9].
Investigations on the secondary metabolism of the type strain of T. mangenotii led to the isolation of a plethora of bioactive metabolites, including three different sordarins—sordarin, sordarin B, and hypoxysordarin—zopfinol, and three new derivatives of this. The structures of these three new compounds and the absolute configuration of zopfinol, which was uncertain until now, were elucidated by one-dimensional and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance (1D- and 2D-NMR) spectroscopy. Details of the isolation, structure elucidation, antimicrobial activity, and cytotoxicity of all the isolated compounds are presented herein. Moreover, the new genus Pseudorhypophila is introduced to accommodate T. mangenotii, which was located far from the monophyletic clade Triangularia, together with other three species of Zopfiella clustering in the same well-supported clade in the family Naviculisporaceae.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phylogenetic Study
A phylogenetic analysis based on the combination of sequences of the internal transcribed spacer region (ITS), the nuclear rDNA large subunit (LSU), and fragments of ribosomal polymerase II subunit 2 (rpb2) and β-tubulin (tub2) genes, and was carried out including sequences of the type strain of Triangularia mangenotii and selected members of the Sordariales, with Camarops amorpha SMH 1450 as an outgroup (Table 1). Each locus was aligned separately using MAFFT v7 [10] and manually adjusted in MEGA v6.06 [11]. Prior to the concatenation of the four loci, the individual locus phylogenies were checked for conflicts [12,13] and the best evolutionary model for each sequence dataset was calculated using MrModeltest v2.3 [14]. The maximum-likelihood (ML) and Bayesian inference (BI) methods were used in a phylogenetic analysis based on the combined aligned data. The ML analyses employed RAxML on the CIPRES portal (www.phylo.org, accessed on 12 November 2020) using RAxML-HPC BlackBox v8.2.12 with default parameters [15]. The BI was carried out in MrBayes v3.2.1 [16], employing the Markov chain Monte Carlo sampling (MCMC) analysis of four parallel runs of 10 M generations, starting from a random tree topology, and stopping automatically when the average standard deviation of split frequencies fell below 0.01. The sampling frequency was set every 1000 generations and the ‘burn-in’ at 25 %, after which the likelihood values were stationary, and the remaining trees were used to calculate posterior probabilities. Bootstrap support (bs) > 70 and posterior probability values (pp) > 0.95 were considered significant [17].

Table 1.
Strains of the order Sordariales included in the phylogenetic study. Taxonomic novelties are indicated in bold italic.
2.2. Fermentation and Extraction
The fungus was grown in yeast malt agar (YM agar; malt extract 10 g/L, yeast extract 4 g/L, d-glucose 4 g/L, agar 20 g/L, pH 6.3 before autoclaving [28]) at 23 °C. Once the fungus was grown, the cultures were cut into small pieces using a cork borer (1 × 1 cm) and five of these pieces were placed into a 200 mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 100 mL of yeast-malt extract broth (YM broth; malt extract 10 g/L, yeast extract 4 g/L, d-glucose 4 g/L, pH 6.3 before autoclaving) under shake conditions at 140 rpm at 23 °C. After 20 days, 10 flasks of 500 mL containing BRFT medium [brown rice 28 g as well as 0.1 L of base liquid (yeast extract 1 g/L, sodium tartrate 0.5 g/L, KH2PO4 0.5 g/L [29])] were inoculated with 6 mL of the seed culture, and incubated for 15 days at 23 °C.
For the compound extraction, the solid cultures in BRFT were covered with acetone, and sonicated in an ultrasonic bath for 30 min at 40 °C. Paper filters were used to separate the acetone from the mycelium, and the latter was again subjected to the same sonication and separation procedure. Both acetone extracts were combined and dried in vacuo at 40 °C. The remaining aqueous residue was diluted with the same amount of ethyl acetate (EtOAc) and extracted twice. The crude extract obtained after drying in vacuo at 40 °C was solved in methanol (MeOH) and extracted twice against one-part methanol-water (distilled water, methanol 1:1) and one-part heptane. Finally, the aqueous phase was again diluted with the same amount of EtOAc and extracted twice. The extracts were combined, dried in vacuo at 40 °C and weighed. Crude extract yield was 2230 mg.
2.3. Isolation of Compounds 1–9
For isolation of 1–9, the crude extract from BFRT medium in MeOH was portioned to 5 × 450 mg and separated using a PLC 2250 preparative HPLC system (Gilson, Middleton, WI, USA) with a Gemini® 10u C18 110Å column (250 × 21.20 mm, 10 µm; Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA) as the stationary phase and in the following conditions: solvent A: H2O + 0.1% formic acid, solvent B: ACN + 0.1% formic acid; flow: 45 mL/min, fractionation: 15 mL, gradient: increase from 5% B to 23% B for 10 min, followed by an increase to 27% B in 25 min, then increase to 45% B in 5 min, followed by an increase to 47% in 25 min, then increase to 100% in 7 min, and a final isocratic step of 100% B for 5 min. This yielded the pure fractions of compound 5 (65 mg, tR = 34–35 min), compound 6 (613 mg, tR = 39–41 min), compound 2 (23 mg, tR = 61.5–62.5 min), compound 8 (18.5 mg, tR = 66.5–67.5 min), compound 7 (140.5 mg, tR = 73.5–74.5 min), as well as the yet impure fractions 7, 9, 10, and 11.
Compound 1 (6.9 mg, tR = 23.5–25 min) was obtained from purification of fraction 9, and 9 (1.92 mg, tR = 36–37 min) from purification of fraction 11 in the same HPLC system with the same solvents, using XBridge® Prep C18 5 μm OBDTM (250 × 19 mm, 5 µm; Waters, Milford, MA, USA) as the stationary phase with a flow rate of 15 mL/min and a fractionation of 5 mL. The HPLC gradient for the purification of fraction 9 is as follows: increase from 33% B to 43% B for 15 min, followed by an increase to 50% B in 30 min, then increase to 100% B in 10 min, and a final isocratic elution of 100% B for 5 min. The HPLC gradient for the purification of fraction 11 consists of an increase from 45% B to 50% B for 10 min, followed by an increase to 55% B in 30 min, then an increase to 100% B in 7 min, and a final isocratic elution of 100% B for 5 min.
Fraction 7 and 10 were further separated using an Agilent 1200 Infinity Series HPLC-UV system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) with a Nucleodur 100-10 C18ec (250 × 10 mm, 10 µm; Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany) as the stationary phase and the following conditions: solvent A: H2O + 0.1% formic acid, solvent B: ACN + 0.1% formic acid; flow: 5 mL/min, fractionation: 2.5 mL. Compound 3 (1.75 mg, tR = 19.5–20.5 min) was obtained from fraction 10 with the following gradient: an increase from 30% B to 40% B for 7 min, then an increase to 60 % B in 30 min, an increase to 100% B in 7 min, and a final isocratic step of 100% B for 7 min. Compound 4 (0.8 mg, tR = 22–23 min) was obtained from fraction 7 with the following gradient: an increase from 25% B to 38% B for 7 min, followed by an increase to 43% B in 20 min, then an increase to 100% B in 7 min, and a final isocratic step of 100% B for 5 min.
2.4. Chromatography and Spectral Methods
Electrospray ionization mass spectra (ESI-MS) were recorded on an UltiMate® 3000 Series UHPLC system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltman, MA, USA) connected to an ion trap mass spectrometer (ESI-Ion Trap-MS, amazon speed, Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA), utilizing a C18 Acquity® UPLC BEH column (2.1 × 50 mm, 1.7 m; Waters, Milford, MA, USA), solvent A: H2O + 0.1% formic acid, solvent B: ACN + 0.1% formic acid, gradient 5% B for 0.5 min, increasing to 100% B in 19.5 min, maintaining 100% B for a further 5 min, flow rate 0.6 mL/min, UV/Vis detection 190–600 nm.
High-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectra (HR-ESI-MS) were acquired with an Agilent 1200 Infinity Series HPLC-UV system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) connected to a time-of-flight mass spectrometer (ESI-TOF-MS, Maxis, Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) (scan range 100–2500 m/z, rate 2 Hz, capillary voltage 4500 V, dry temperature 200 °C), using the same HPLC conditions described in ESI-MS measurements.
The 1D and 2D nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra were recorded with an Avance III 700 spectrometer with a 5 mm TXI cryoprobe (Bruker, 1H NMR: 700 MHz, 13C: 175 MHz, Billerica, MA, USA) and an Avance III 500 (Bruker, 1H NMR: 500 MHz, 13C: 125 MHz, Billerica, MA, USA) spectrometer. The chemical shifts δ were referenced to the solvents DMSO-d6 (1H, δ = 2.50 ppm; 13C, δ = 39.51 ppm), and pyridine-d5 (1H, δ = 7.22 ppm; 13C, δ = 123.87 ppm.
Optical rotations were taken with an MCP 150 circular polarimeter at 20 °C (Anton Paar, Graz, Austria) and UV/Vis spectra with a UV-2450 spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan), both in methanol solution MeOH.
2.5. Spectral Data
2.5.1. Zopfinol (1)
Yellow oil; [α]20D + 19° (c 0.001, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 296.5 (3.5), 256.5 (4.0), 217.5 (4.3); 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR see Table 1; ESI-MS: m/z 339.16 (M − H)− and 363.17 (M + Na) +; high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HRESIMS) m/z 363.1333 (M + Na)+ (calculated for C18H25ClNaO4, 363.1339).
2.5.2. Zopfinol B (2)
Yellow oil; [α]20D + 22° (c 0.001, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 296.0 (3.6), 252.5 (4.1), 218.0 (4.5); 1H- NMR and 13C-NMR see Table 1; ESI-MS: m/z 305.07 (M—H)− and 271.08 (M—2H2O)+; high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HRESIMS) m/z 307.1276 (M + H)+ (calculated for C18H27O4, 307.1909).
2.5.3. Zopfinol C (3)
Colourless-to-white crystals; [α]20D + 13° (c 0.001, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 297.0 (3.6), 256.0 (4.1), 217.5 (4.4); 1H- NMR and 13C-NMR see Table 1; ESI-MS: m/z 341.18 (M − H)− and 307.15 (M—2H2O)+; high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HRESIMS) m/z 365.1491 (M + Na)+ (calculated for C18H27NaClO4, 365.1496).
2.5.4. Zopfinol D (4)
Yellow oil; [α]20D + 22° (c 0.0005, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 295.0 (3.5), 252.5 (3.9), 217.5 (4.3); 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR see Table 1; ESI-MS: m/z 307.15 (M − H)− and 273.11 (M—2H2O)+; high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HRESIMS) m/z 331.1878 (M + Na)+ (calculated for C18H28NaO4, 331.1885).
2.5.5. 7-O-Acetylmultiplolide A (5)
Colourless oil; [α]20D + 46° (c 0.0005, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 202.0 (3.7); 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR were in good agreement with the literature [30]; ESI-MS: m/z 278.99 (M + Na)+; high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HRESIMS) m/z 279.0837 (M + Na)+ (calculated for C12H16NaO6, 279.0845).
2.5.6. 8-O-Acetylmultiplolide A (6)
Colourless oil; [α]20D + 42° (c 0.001, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 202.0 (3.7); 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR were in good agreement with the literature [30]; ESI-MS: m/z 278.98 (M + Na)+; high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HRESIMS) m/z 279.08418 (M + Na)+ (calculated for C12H16NaO6, 279.0845).
2.5.7. Sordarin (7)
White powder; [α]20D − 35° (c 0.001, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 203.0 (3.7); 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR were in good agreement with the literature [31]; ESI-MS: m/z 491.21 (M − H)− and 493.19 (M + H)+; high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HRESIMS) m/z 493.2787 (M + H)+ (calculated for C27H41O8, 493.2801).
2.5.8. Sordarin B (8)
White powder; [α]20D − 61° (c 0.001, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 202.5 (3.7); 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR were in good agreement with the literature [7]; ESI-MS: m/z 491.27 (M − H)− and 493.24 (M + H)+; high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HRESIMS) m/z 493.2786 (M + H)+ (calculated for C27H41O8, 493.2801).
2.5.9. Hypoxysordarin (9)
White powder; [α]20D + 15° (c 0.001, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 210.5 (4.0); 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR were in good agreement with the literature [32]; ESI-MS: m/z 657.35 (M − H)− and 659.33 (M + H)+; high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HRESIMS) m/z 659.3419 (M + H)+ (calculated for C36H51O11, 659.3431).
2.6. Derivatization with MTPA
For the preparation of the (S)-MTPA ester derivative of 1, a portion of compound 1 (1.0 mg) was dissolved in pyridine-d5 (0.6 mL), transferred into a NMR tube and then (R)-(-)-α-methoxy-α-(trifluoromethyl) phenylacetyl chloride (10 μL) was added. The reaction was monitored by 1H NMR followed by the measurement of COSY, TOCSY, HSQC and HMBC NMR spectra. 1H NMR (700 MHz, pyridine-d5): similar to 1, but δH 7.43 (8-H), 6.53 (9-H), 6.36 (10-H), 6.14 (11-H), 6.02 (13-H), 5.55 (12-H), 5.44 (1-H), 1.96 (14-H2), 1.25 (15-H2), 1.20 (17-H2), 1.16 (16-H2), 0.82 (18-H3).
The (R)-MTPA ester was prepared in the same manner by the addition of 10 µL of (S)-MTPA chloride: 1H NMR (700 MHz, pyridine-d5): similar to 1, but δH 7.32 (8-H), 6.26 (9-H), 6.26 (10-H), 6.21 (11-H), 6.17 (13-H), 5.81 (12-H), 5.44 (1-H), 2.02 (14-H2), 1.29 (15-H2), 1.18 (17-H2), 1.15 (16-H2), 0.79 (18-H3).
2.7. Biological Testing
Isolated compounds were tested for their antimicrobial activity against five fungi (Candida albicans, Mucor hiemalis, Rhodotorula glutinis, Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Wickerhamomyces anomalus), four Gram-positive bacteria (Bacillus subtilis, Micrococcus luteus, Mycobacterium smegmatis and Staphylococcus aureus) and three Gram-negative bacteria (Chromobacterium violaceum, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa), using nystatin as a positive control against all the tested fungi and oxytetracycline against all the bacteria, except for My. smegmatis and Ps. aeruginosa, against which kanamycin and gentamycin were used, respectively. Moreover, the cytotoxicity of the compounds against two different mammalian cell lines—human endocervical adenocarcinoma KB 3.1 and mouse fibroblasts L929—were determined by the MTT method using epothilone B as the positive control. Both biological assays were performed following the protocols described by Becker et al. [33].
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis
The lengths of the individual alignments used in the combined dataset were 634 bp (ITS), 891 bp (LSU), 972 bp (rpb2) and 618 bp (tub2), and the final total alignment was 3115 bp. The phylogentic tree obtained from the RAxML analysis of the combined dataset, including bootstrap support and Bayesian posterior probability at the nodes, is shown in Figure 1. The RAxML tree obtained agreed with the topology of the tree generated by the Bayesian analysis. The ex-type strain of Triangularia mangenotii was located in the Naviculisporaceae clade, forming a well-supported clade (100% bs/1 pp) independent from the other lineages of the family, together with the type strains of Zopfiella marina, Z. pilifera and Z. submersa. However, the monophyletic lineage representing the genus Triangularia was placed in the Podosporaceae clade, while the type species of Zopfiella, Z. tabulata was located in the Lasiosphaeriaceae clade. Therefore, the new genus Pseudorhypophila is introduced herein to accommodate these four taxa. Additionally, the close phylogenetic distance between Z. marina and Z. submersa suggested that these could indeed represent the same taxa. The nucleotide similarity of the rpb2 sequences of both taxa was 99.88%, while that of the ITS sequences was 99.78% (the only difference was due to the presence of an indeterminable base-pair in one of the sequences). The same occurred in the LSU sequence comparison, in which the similarity was only 97.43% but the differences were due to indeterminate nucleotide positions in the sequences of Z. marina. The nucleotide similarity of tub2 sequences (a fragment different from the one used in the present phylogenetic study; GenBank acc. numbers MK926951 and MK926953) was also 100%. Therefore, and in accordance with phenotype-derived data, the synonymy of both species is proposed.
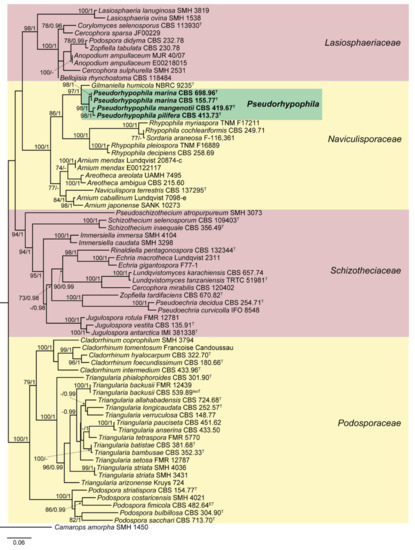
Figure 1.
Randomized axelerated maximum likelihood (RAxML) phylogram obtained from the combined sequences of the internal transcribed spacer region (ITS), the nuclear rDNA large subunit (LSU), and fragments of ribosomal polymerase II subunit 2 (rpb2) and β-tubulin (tub2) genes of selected strains belonging to the families Lasiosphaeriaceae, Naviculisporaceae, Podosporaceae, and Schizotheciaceae, using Camarops amorpha SMH 1450 as outgroup. Bootstrap support values ≥ 70 / Bayesian posterior probability scores ≥ 0.95 are indicated along branches. Branch lengths are proportional to distance. Novel taxa proposed in the present study are in bold. Ex-epitype, ex-isotype, and ex-type strains of the different species are indicated with ET, IsoT, and T, respectively. Different background colors have been used to highlight the major clades.
3.2. Taxonomy
Pseudorhypophila Y. Marín and Stchigel, gen. nov. MycoBank MB838466.
Type species: Pseudorhypophila mangenotii (Arx & Hennebert) Y. Marín & Stchigel.
Etymology: Based on the phylogenetic relation to Rhypophila.
Ascomata non-ostiolate or ostiolate, superficial or immersed, black, globose to subglobose, or ovate to pyriform, almost glabrous or covered by short or long, flexuous hairs; neck short, cylindrical to conical, covered with small black papillae. Asci clavate to cylindrical, stipitate, 4–8-spored, with a small apical ring sometimes indistinct. Periphyses present or absent. Paraphyses present or absent, septate, hyaline. Ascospores biseriate, two-celled; upper cell narrowly conical, acuminate towards apex and rounded at base, or ovoid to limoniform with somewhat truncate base, olivaceous brown to dark brown, with an apical or subapical germ pore, sometimes with a distinct apical appendage; lower cell remaining hyaline, or sometimes becoming pale olivaceous brown or pale brown, occasionally dark brown, cylindrical and straight or curved, or hemisphaerical, or at first broadly obconical and then becoming flattened at apex; gelatinous sheats sometimes present, hyaline, thin. Conidia holoblastic, sessile, borne singly along the vegetative hyphae, hyaline, spherical to subspherical, or ovate to elongate, smooth-walled.
Notes: Pseudorhypophila is related to Gilmaniella and Rhypophila. The former genus produces the humicola-like asexual morph characterized by the production of dark brown, spherical conidia with marked apical germ pores and borne singly or in clusters of up to four [34], while the new genus Pseudorhypophila produces a chrysosporium-like asexual morph, and the asexual morph is absent in Rhypophila [4]. Rhypophila differs from Pseudorhypophila by the production of ascomata with elongate, tuberculate projections in the neck, while these are mostly non-ostiolate ascomata in the new genus. Moreover, Rhypophila is characterized by having mostly more than eight-spored asci and ascospores with lower cell as long as, or longer, than the upper cell.
Zopfiella submersa was introduced by Guarro et al. [35] in 1997. These authors discussed the similarity of this taxon with Zopfiella marina, which was introduced before by Furuya and Udagawa [36]. The main differences between both species according to reference [36] were the presence of a sexual morph and ascospore with an apical pore in the upper cell in Z. marina, whereas the asexual morph is absent and the upper cell of the ascospores have a subapical pore in Z. submersa. Both taxa were isolated only from aquatic environments in Asia (China and Iraq). Whereas Z. marina was found in marine mud (in depth of 120 m), Z. submersa was reported from dead culms of Arundo donax submerged in a river. Due to the scarce molecular and morphological differences between both taxa, we proposed here their synonymy under the new combination P. marina. The other two species of the genus—P. mangenotii and P. pilifera—are also closely related to each other, but these showed only a 98.04 % nucleotide similarity of the rpb2 sequences. Both species are characterized by ascospores with conical upper cells [37], but these can be easily distinguished by the ascomata, being ostiolate in P. mangenotii [38] and non-ostiolate in P. pilifera, and by the presence of an asexual morph in the latter [39].
Key to species of Pseudorhypophila.
1. Ostiolate ascomata................................................................................P. mangenotii
1. Non-ostiolate ascomata............................................................................................2
2. Ascospores with upper and lower cell conical........................................P. pilifera
2. Ascospores with upper cell ovoid to limoniform, and lower cell cylindrical....
..........................................................................................................................P. marina
Pseudorhypophila mangenotii (Arx and Hennebert) Y. Marín and Stchigel, comb. nov. MycoBank MB838467.
Basionym: Triangularia mangenotii Arx and Hennebert, Bull. Trimestriel Soc. Mycol. France 84: 423. 1969.
Pseudorhypophila marina (Furuya and Udagawa) Y. Marín and Stchigel, comb. nov. MycoBank MB838468.
Basionym: Zopfiella marina Furuya and Udagawa, J. Jap. Bot. 50: 249. 1975.
Synonym: Zopfiella submersa Guarro, Al-Saadoon, Gené and Abdullah, Mycologia 89: 958. 1997.
Pseudorhypophila pilifera (Udagawa and Furuya) Y. Marín and Stchigel, comb. nov. MycoBank MB838469.
Basionym: Zopfiella pilifera Udagawa and Furuya, Trans. Mycol. Soc. Japan 13: 255. 1972.
3.3. Structure Elucidation of Compounds 1–4
Zopfinol (1) [40], three novel derivatives of zopfinol (2–4), 7-O-acetylmultiplolide A (5) [30], 8-O-acetylmultiplolide A (6) [30,41], sordarin (7) [42], sordarin B (8) [7], and hypoxysordarin (9) [32] were isolated from the 2230 mg of crude extract obtained from the fermentation in rice of the ex-type strain of Pseudorhypophila mangenotii (Figure 2 and Figure 3) by preparative HPLC. Their structures were elucidated by 1D- and 2D-NMR spectroscopy (Supplementary Figures S1–S26).
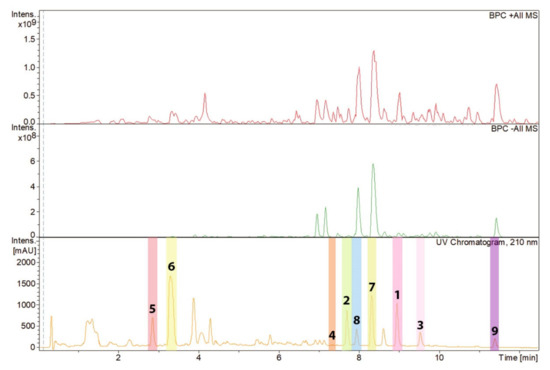
Figure 2.
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) chromatogram (210 nm) of the ethyl acetate (EtOAc) extract from Pseudorhypophila mangenotii with peaks of the compounds isolated referring to the molecules depicted in Figure 3. The peaks representing compounds 1–9 have been highlighted with different colors.
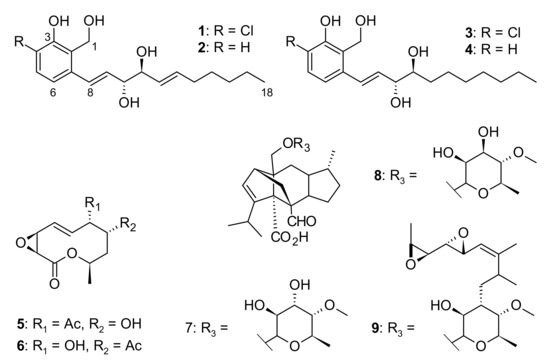
Figure 3.
Chemical structures of compounds 1–9 isolated from Pseudorhypophila mangenotii CBS 419.67.
Compound 1 was obtained as a yellow oil and its molecular formula was established as C18H25ClO4 (six degrees of unsaturation) according to the quasimolecular ion peak cluster at m/z 363.1333 (M + Na)+ in the HRESIMS spectrum. 1H and HSQC spectra (Table 2) of 1 revealed the presence of one methyl, two oxymethines, six olefinic/aromatic methines as well as five methylenes, one of which being an oxymethylene. The carbon spectrum revealed the further presence of four aromatic carbon atom-devoid bound protons. Using COSY and TOCSY data, the long side chain CH–8 to C–18 was assembled. A literature search within the dictionary of natural products with this information identified 1 as the known compound zopfinol [40]. Since no stereochemistry has been assigned for 1 to date, we addressed this issue. However, no 2JC10H11 and 2JC11H10 coupling constants were observed in the HSQC-Hecade and J-HMBC experiments, so the J-based configurational method gave equivocal results. Nevertheless, the synthesis of multi-MTPA esters of 1 yielded a diagnostic ΔδSR sign distribution pattern. The positive values for 8–H/9–H/10–H in addition to the negative ones for 11–H/12–H/13–H/14–H2/15–H2 is characteristic for 1,2-diols with R,S absolute stereochemistry [43] (Figure 4). Consequently, we assigned a 10R,11S absolute configuration for 1.

Table 2.
NMR data of metabolites 1–4 in DMSO-d6 (1H 500 MHz, 13C 125 MHz).
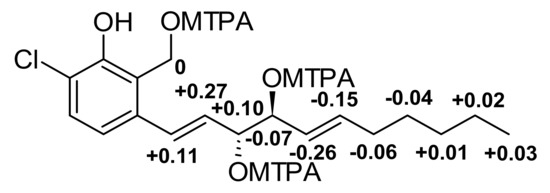
Figure 4.
ΔδSR values for MPTA esters of 1 diagnostic for 10R,11S.
Compound 2 was obtained as a yellow oil. The molecular ion cluster at m/z 307.1276 [M + H]+ in the HRESIMS spectrum indicated that the molecular formula of 2 was C18H26O4, indicating the substitution of the chlorine by a hydrogen atom. This observation was confirmed by the additional aromatic olefin signal for 4–H in the 1H and HSQC spectra of 2. Since other NMR data including coupling constants are virtually identical to 1, a common 10R,11S was assigned for 2, too. Consequently, 2 was elucidated as dechlorozopfinol and named zopfinol B.
Compound 3 was obtained as colorless-to-white crystals. The molecular ion cluster at m/z 365.1491 [M + Na]+ in the HRESIMS spectrum indicated that the molecular formula is C18H27ClO4. The NMR data of 3 were highly similar to those of 2, with the key difference being the exchange of the olefinic methines 12–H/13–H by two methylenes. Therefore, we assigned 3 as 12,13-dihydrozopfinol, the name given to it being zopfinol C.
Compound 4 was obtained as a yellow oil and its molecular formula was established as C18H28O4 according to the mass ion peak at m/z 331.1878 [M + Na]+ in the HRESIMS spectrum, indicating the formal addition of two hydrogens. The key difference in the NMR spectra of 4 compared to 1 was the exchange of the olefinic methines 12–H/13–H by two methylenes. Therefore, we elucidated 4 as dechloro-12,13-dihydrozopfinol, and named it zopfinol D.
3.4. Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activities of Compounds 1–9
From the nine isolated compounds, only 1, 3, 4, 7 and 9 showed antimicrobial activity (Table 3).

Table 3.
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC, µg/mL) of 1–9 against fungi and bacteria.
Zopfinol (1) and two of its derivatives (3 and 4) were active against the Gram-positive bacteria Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus, and compound 3 was also active against Rhodotorula glutinis. Compound 1 and 3 showed weak antifungal activity against Mucor hiemalis.
On the other hand, compound 7 and 9 showed antifungal activity against Candida albicans, even though the activity of 9 was weak. Compound 9 showed a much stronger antifungal activity against Mucor hiemalis.
Compound 1, 3 and 4 showed weak cytotoxic activity against the two different mammalian cell lines tested (Table 4).

Table 4.
Cytotoxicity of 1–9 against mammalian cell lines [half maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50): µM].
4. Discussion
Lasiosphaeriaceous genera have been considered polyphyletic since their taxa were scattered in different clades along the Sordariales [1,3,18,22,26]. This was a consequence of the traditional delimitation of the genera based on the ascospore morphology, which resulted in an extremely homoplastic character not useful in predicting the phylogenetic relationships [1,22]. Recent phylogenetic studies based on the ITS, LSU, rpb2 and tub2 sequences were focused on the right delimitation of both the polyphyletic family and genera, resulting in the introduction of the monophyletic families Podosporaceae [3], Diplogelasinosporaceae, Naviculisporaceae and Schizotheciaceae [4]. Moreover, some of the genera were properly delimited, such as Podospora and Triangularia [3]. However, large genera such as Cercophora and Zopfiella still remain polyphyletic, and other species of the already delimited genera are awaiting a correct taxonomic placement. In that context, the type strain of T. mangenotii, which was located in the family Naviculisporaceae and far from the monophyletic clade of Triangularia in the Podosporaceae, is currently relocated in the new genus Pseudorhypophila, together with other species of Zopfiella far from the type species of the genus, Z. tabulata, which is located in the Lasiosphaeriaceae. This new genus is characterized by mostly non-ostiolate ascomata and a chrysosporium-like asexual morph. On the other hand, the most phylogenetically related genus, Gilmaniella, is characterized by the production of a solely humicola-like asexual morph [34].
Zopfinol (1) is a chloratinated phenol with an aliphatic side chain and was isolated before from the marine fungus Zopfiella marina [40], which we transferred in the present study to the new genus Pseudorhypophila. In addition, the strain we studied produced three new derivatives of zopfinol (2–4). Compound 1 showed weak antimicrobial activity against Mucor hiemalis and Staphylococcus aureus, and moderate antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis. On the other hand, the new derivative 4 showed only a weak activity against the Gram-positive bacteria, B. subtilis and S. aureus. Compound 3 was moderately active against the same two Gram-positive bacteria, and exhibited weak antifungal activity against M. hiemalis and Rhodotorula glutinis.
7-O-acetylmultiplolide A (5) and 8-O-acetylmultiplolide A (6) are 10-membered lactones, first reported from a Diaporthe sp. [30,41], which pertains to the class Sordariomycetes. Both compounds were devoid of antimicrobial activity against the microorganisms tested in the present study. However, compound 6 had shown antifungal activity against Aspergillus niger, Bipolaris maydis, Botrytis cinerea, Fusarium moniliforme, Ophiostoma minus and Talaromyces islandicus, as previously reported by Wu et al. [30]. Surprisingly, compound 5 only showed weak activity against A. niger, even though both compounds 5 and 6 differ only in the position of the acetoxy group [30]. Compound 6 was reported to have significant inhibitory activity towards acetylcholinesterase [41], and antihyperlipidemic activity equivalent to that observed in lovastatin, which was used as a positive control [44]. Other ten-membered lactones have been found in Diaporthe [30,41,44], as well as in other Sordariomycetes, i.e., Xylaria multiplex [45] and Gilmaniella humicola [46], the latter of which is also now located in the Naviculisporaceae like P. mangenotii. Some of these 10-membered lactones also showed antifungal activity, i.e., multiplolides A and B were active against Candida albicans [45]. Moreover, humilactone from Gilmaniella humicola showed strong cytotoxic activity [46], which was not observed in the other related compounds mentioned.
The last group of compounds isolated from P. mangenotii were the sordarins (7–9). Those are a class of natural antifungal agents that act at the protein synthesis level, inhibiting it through their interaction with the elongation factor 2 in eukaryotes (eEF2) [47,48]. This essential enzyme catalyzes the translocation of transfer RNA and messenger RNA after peptide bond formation in the translation process, leading to an inhibition of this step and promoting cell death [49,50]. What makes these compounds have a solely antimycotic activity is the high affinity for fungal eEF2 when it is compared against that of plants or mammals [50]. These compounds are mainly produced by Xylariales, but also by members of Eurotiales, Microascales and Sordariales [8]. In this last order, the taxa reported to produce these kinds of compounds are Podospora araneosa [42], Rhypophila pleiospora [7] and Z. marina [51], which is here transferred to the genus Pseudorhypophila (as P. marina), all of which are members of the family Naviculisporaceae. Therefore, the production of sordarin and related compounds could be restricted to this family. Podospora araneosa clustered in the monophyletic clade of Rhypophila, suggesting that it could belong to this genus. However, further studies including the type material of this species need to be carried out to corroborate this hypothesis. Compound 7 was found in cultures of Podospora araneosa [42] and 8 in Rhypophila pleiospora [7], while 9 was only reported before from Hypoxylon croceum [32], which is located in the Xylariales. Podospora araneosa also produced hydroxysordarin and neosordarin, which is closely related to 9, with only small differences in the aliphatic side chain acylating the hydroxyl in the 3′-position of the sordarose moiety [51]. Pseudorhypophila marina produces the sordarin derivative known as zofimarin [51], which was demonstrated to have antifungal activity against Candida albicans, C. pseudotropicalis and Crytococcus neoformans [52]. In our antimicrobial study, 8 was not active against any of the microorganisms tested. However, Weber et al. [7] observed antifungal activity against Nematospora coryli, Sporobolomyces roseus and Thelebolus nanus. In the present study, 7 was only active against C. albicans, while 9 showed weak activity against C. albicans but moderate activity against M. hiemalis. The higher antifungal activity of 9 with respect to the other sordarin or sordarin-related compounds was already observed by Davoli et al. [53]. In that work, 9 showed antifungal activity against Paecilomyces variotii, Penicillium notatum, Nematospora coryli and M. miehei, while 7 only had activity against the last two fungi. The comparison between the activities of different sordarin derivatives demonstrated that the nature of the side chain plays an important role in the antifungal activity, increasing when there is a 3′-O-acyl group and decreasing in the presence of a hydroxymethyl group in the sugar moiety [52,53].
Pseudorhypophila marina also produced salicylaldehyde and dihydroisobenzofuran derivatives [54], apart from zopfinols [40] and zopfimarin [51], mentioned before. The structures of these compounds are related to zopfinol, but most of them were not active, except for one of the salicylaldehyde derivatives, which showed weak activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Bacillus cereus [54]. Other compounds with structures related to zopfinol and its derivatives are the salicylaldehyde sordarial produced by Neurospora crassa, which also belongs to the order Sordariales [55], and the pyriculols, which are phytotoxic polyketides produced by the sordariomycete phytopathogenic fungus Pyricularia oryzae [56]. Since the phytotoxic pyriculol [57] differs from 2 only in the length of its aliphatic side chain, it would be highly interesting to test the phytotoxicity of zopfinols.
The production of secondary metabolites by the new genus Pseudorhypophila could be useful as chemotaxonomic markers, since the zopfinol is produced by different species of Pseudorhypophila, but it was not reported in any other taxon. Sordarins seem to be present in different taxa belonging to the family Naviculisporaceae, also being a potential chemotaxonomic marker for this family. Chemotaxonomy could help us in the achievement of a more natural classification of the sordariaceous fungi.
Our work, together with those focused on the screening for bioactive metabolites produced by members of the Sordariales [5,6,9], confirms the potential of this fungal order as a producer of bioactive compounds. In particular, the new genus Pseudorhypophila includes species able to produce a plethora of bioactive compounds, including the widely studied antifungal sordarins.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2309-608X/7/3/181/s1, Figure S1: 1H NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol (1), Figure S2: 13C NMR spectrum (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol (1), Figure S3: COSY NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol (1), Figure S4: ROESY NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol (1), Figure S5: HSQC NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol (1), Figure S6: HMBC NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol (1), Figure S7: 1H NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol B (2), Figure S8: 13C NMR spectrum (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol B (2), Figure S9: COSY NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol B (2), Figure S10: NOESY NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol B (2), Figure S11: HSQC NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol B (2), Figure S12: HMBC NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol B (2), Figure S13: 1H NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol C (3), Figure S14: 13C NMR spectrum (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol C (3), Figure S15: COSY NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol C (3), Figure S16: ROESY NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol C (3), Figure S17: HSQC NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol C (3), Figure S18: HMBC NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol C (3), Figure S19: 1H NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol D (4), Figure S20: 13C NMR spectrum (125 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol D (4), Figure S21: COSY NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol D (4), Figure S22: ROESY NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol D (4), Figure S23: HSQC NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol D (4), Figure S24: HMBC NMR spectrum (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) of zopfinol D (4), Figure S25: HSQC NMR spectrum (700 MHz, pyridin-d5) of zopfinol A-S-MTPA ester, Figure S26: HSQC NMR spectrum (700 MHz, pyridin-d5) of zopfinol A-R-MTPA ester.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.S. and Y.M.-F.; methodology, A.M., F.S., K.H. and Y.M.-F.; software, M.S.; validation, A.M., F.S., K.H. and Y.M.-F.; formal analysis, A.M., F.S., K.H. and Y.M.-F.; investigation, A.M., F.S., K.H. and Y.M.-F.; visualization, F.S. and Y.M.-F.; resources, A.M.S. and M.S.; data curation, A.M.S., F.S. and Y.M.-F.; writing—original draft preparation, F.S. and Y.M.-F.; writing—review and editing, A.M.S., A.M., K.H. and M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Yasmina Marin-Felix was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from Alexander-von-Humboldt Foundation, Germany.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The DNA sequences are deposited in GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/) and all other relevant data are included in the Supplementary Information.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Christel Kakoschke and Kirsten Harmrolfs for recording the NMR spectra, Wera Collisi for conducting the bioassays and Mathias Morwinski for helping in the prescreening of members of Sordariales, including the one included in the present study. We also like to thank Takayuki Aoki (National Agriculture and Food Research Organization, Tsukuba, Japan) for providing literature used in the present study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Miller, A.N.; Huhndorf, S.M. Multi-gene phylogenies indicate ascomal wall morphology is a better predictor of phylogenetic relationships than ascospore morphology in the Sordariales (Ascomycota, Fungi). Molec. Phylogen. Evol. 2005, 35, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruys, Å.; Huhndorf, S.M.; Miller, A.N. Coprophilous contributions to the phylogeny of Lasiosphaeriaceae and allied taxa within Sordariales (Ascomycota, Fungi). Fungal Divers. 2015, 70, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Bai, F.Y.; Bensch, K.; Meijer, M.; Sun, B.D.; Han, Y.F.; Crous, P.W.; Samson, R.A.; Yang, F.Y.; Houbraken, J. Phylogenetic re-evaluation of Thielavia with the introduction of a new family Podosporaceae. Stud. Mycol. 2019, 93, 155–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Felix, Y.; Miller, A.N.; Cano-Lira, J.F.; Guarro, J.; García, D.; Stadler, M.; Huhndorf, S.M.; Stchigel, A.M. Re-evaluation of the order Sordariales: Delimitation of Lasiosphaeriaceae s. str., and introduction of the new families Diplogelasinosporaceae, Naviculisporaceae and Schizotheciaceae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.F.; Yin, Z.H.; Zhang, J.J.; Kang, W.Y.; Wang, X.W.; Ding, G.; Chen, L. Chaetomadrasins A and B, two new cytotoxic cytochalasans from desert soil-derived fungus Chaetomium madrasense 375. Molecules 2019, 24, 3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noumeur, S.R.; Teponno, R.B.; Helaly, S.E.; Wang, X.-W.; Harzallah, D.; Houbraken, J.; Crous, P.W.; Stadler, M. Diketopiperazines from Batnamyces globulariicola, gen. & sp. nov. (Chaetomiaceae), a fungus associated with roots of the medicinal plant Globularia alypum in Algeria. Mycol. Progr. 2020, 19, 589–603. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, R.W.S.; Meffert, A.; Anke, H.; Sterner, O. Production of sordarin and related metabolites by the coprophilous fungus Podospora pleiospora in submerged culture and in its natural substrate. Mycol. Res. 2005, 109, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente, F.; Basilio, A.; Platas, G.; Collado, J.; Bills, G.F.; González del Val, A.; Martín, J.; Tormo, J.R.; Harris, G.H.; Zink, D.L.; et al. Distribution of the antifungal agents sordarins across filamentous fungi. Mycol. Res. 2009, 113, 754–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; Marin-Felix, Y.; Surup, F.; Stchigel, A.M.; Stadler, M. Seven new cytotoxic and antimicrobial xanthoquinodins from Jugulospora vestita. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software v. 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Molec. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Molec. Biol. Evol. 2013, 12, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason-Gamer, R.; Kellogg, E. Testing for phylogenetic conflict among molecular data sets in the tribe Triticeae (Gramineae). Syst. Biol. 1996, 45, 524–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiens, J.J. Testing phylogenetic methods with tree congruence: Phylogenetic analysis of polymorphic morphological characters in phrynosomatid lizards. Syst. Biol. 1998, 47, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, J.A.A. MrModeltest v2.2. Uppsala: Distributed by the Author; Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University: Uppsala, Sweden, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaro, M.E.; Zoller, S.; Lutzoni, F. Bayes or bootstrap. A simulation study comparing the performance of Bayesian Markov chainMonte Carlo sampling and bootstrapping in assessing phylogenetic confidence. Molec. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Jeewon, R.; Hyde, K.D. Phylogenetic evaluation and taxonomic revision of Schizothecium based on ribosomal DNA and protein coding genes. Fungal Divers. 2005, 19, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A.N.; Huhndorf, S.M. Using phylogenetic species recognition to delimit species boundaries within Lasiosphaeria. Mycologia 2004, 96, 1106–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réblová, M. Bellojisia, a new sordariaceous genus for Jobellisia rhynchostoma and a description of Jobellisiaceae fam. nov. Mycologia 2008, 100, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stchigel, A.M.; Cano, J.; Miller, A.N.; Calduch, M.; Guarro, J. Corylomyces: A new genus of Sordariales from plant debris in France. Mycol. Res. 2006, 110, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.N.; Huhndorf, S.M. A natural classification of Lasiosphaeria based on nuclear LSU rDNA sequences. Mycol. Res. 2004, 108, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, F.A.; Lutzoni, F.M.; Huhndorf, S.M. Teleomorph-anamorph connections: The new pyrenomycetous genus Carpoligna and its Pleurothecium anamorph. Mycologia 1999, 91, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, F.A.; Miller, A.N.; Huhndorf, S.M.; Lutzoni, F.M.; Zoller, S. Systematics of the genus Chaetosphaeria and its allied genera: Morphological and phylogenetic diversity in north temperate and neotropical taxa. Mycologia 2006, 98, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.; Groenewald, M.; de Vries, M.; Gehrmann, T.; Stielow, B.; Eberhardt, U.; Al-Hatmi, A.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Cardinali, G.; Houbraken, J.; et al. Large-scale generation and analysis of filamentous fungal DNA barcodes boosts coverage for kingdom Fungi and reveals thresholds for fungal species and higher taxon delimitation. Stud. Mycol. 2019, 92, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.H.; Kao, H.W.; Wang, Y.Z. Molecular phylogeny of Cercophora, Podospora, and Schizothecium (Lasiosphaeriaceae, Pyrenomycetes). Taiwana 2010, 55, 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Jeewon, R.; Hyde, K.D. Molecular systematics of Zopfiella and allied genera: Evidence from multi-gene sequence analyses. Mycol. Res. 2006, 110, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupcic, Z.; Rascher, M.; Kanaki, S.; Köster, R.W.; Stadler, M.; Wittstein, K. Two new cyathane diterpenoids from mycelial cultures of the medicinal mushroom Hericium erinaceus and the rare species, Hericium flagellum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Wongkanoun, S.; Wessel, A.-C.; Bills, G.F.; Stadler, M.; Luangsa-ard, J.J. Phylogenetic and chemotaxonomic studies confirm the affinities of Stromatoneurospora phoenix to the coprophilous Xylariaceae. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Chen, Y.W.; Shao, S.C.; Wang, L.D.; Li, Z.Y.; Yang, L.Y.; Li, S.L.; Huang, R. Ten-Membered lactones from Phomopsis sp., an endophytic fungus of Azadirachta indica. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, S.; Kitamura, M.; Narasaka, K. Synthesis of (−)-sordarin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 6931–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daferner, M.; Mensch, S.; Anke, T.; Sterner, O. Hypoxysordarin, a new sordarin derivative from Hypoxylon croceum. Z. Naturforsch. C. J. Biosci. 1999, 54, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Pfütze, S.; Kuhnert, E.; Cox, R.J.; Stadler, M.; Surup, F. Hybridorubrins A–D: Azaphilone heterodimers from stromata of Hypoxylon fragiforme and insights into the biosynthetic machinery for azaphilone diversification. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 1438–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barron, G.L. A new genus of the Hyphomycetes from soil. Mycologia 1964, 56, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarro, J.; Al-Saadoon, A.H.; Gene, J.; Abdullah, S.K. Two new cleistothecial Ascomycetes from Iraq. Mycologia 1997, 89, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, K.; Udagawa, S. Two new species of cleistothecial ascomycetes. J. Jap. Bot. 1975, 50, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Guarro, J.; Gene, J.; Stchigel, A.M.; Figueras, M.J. Atlas of Soil Ascomycetes; CBS Biodiversity Series, no. 10; CBS-KNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Von Arx, J.A.; Hennebert, G.L. Triangularia mangenotii nov.sp. Bull. Soc. Mycol. France 1968, 84, 423–426. [Google Scholar]
- Udagawa, S.I.; Furuya, K. Zopfiella pilifera, a new cleistoascomycete from Japanese soil. Trans. Mycol. Soc. Japan 1972, 13, 255–259. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, M.; Takayama, T.; Furuya, K.; Okudaira, M.; Hayashi, T.; Kinoshita, M. A nuclear magnetic resonance study of zopfinol isolated from Zopfiella marina. Annu. Rep. Sankyo Res. Lab. 1987, 39, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Q.; Yan, X.; Lin, X.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Song, S.; Lu, C.; Shen, Y. Chemical constituents of the endophytic fungal strain Phomopsis sp. NXZ-05 of Camptotheca acuminata. Helv. Chim. Acta 2007, 90, 1811–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, D.; Sigg, H.P. Isolierung und Abbau von Sordarin [Isolation and decomposition of sordarin]. Helv. Chim. Acta 1971, 54, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seco, J.M.; Quinoa, E.; Riguera, R. Assignment of the absolute configuration of polyfunctional compounds by NMR using chiral derivatizing agents. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4603–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Yang, X.Q.; Wan, C.P.; Wang, B.Y.; Yin, H.Y.; Shi, L.J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.B.; Zhoua, H.; Ding, Z.T. Potential antihyperlipidemic polyketones from endophytic Diaporthe sp. JC-J7 in Dendrobium nobile. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 41810–41817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonphong, S.; Kittakoop, P.; Isaka, M.; Pittayakhajonwut, D.; Tanticharoen, M.; Thebtaranonth, Y. Multiplolides A and B, new antifungal 10-membered lactones from Xylaria multiplex. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 965–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, B.; Anke, H.; Sterner, O. Humicolactone, a new bioactive 10-membered lactone from the fungus Gilmaniella humicola. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1995, 7, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, J.M.; Martin, J.J. Identification of elongation factor 2 as the essential protein targeted by sordarins in Candida albicans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 2279–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, M.; Hsu, M.J.; Tse, B.; Ku, T.; Balkovec, J.; Schmatz, D.; Nielsen, J. Elongation factor 2 as a novel target for selective inhibition of fungal protein synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 3148–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, F.; Matsuura, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Fukushima, M.; Eguchi, T. Genome mining of the sordarin biosynthetic gene cluster from Sordaria araneosa Cain ATCC 36386: Characterization of cycloaraneosene synthase and GDP-6-deoxyaltrose transferase. J. Antibiot. 2016, 69, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaichanan, J.; Wiyakrutta, S.; Pongtharangkul, T.; Isarangkul, D.; Meevootisom, V. Optimization of zofimarin production by an endophytic fungus, Xylaria sp. Acra L38. Brazil J. Microbiol. 2014, 45, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogita, J.; Hayashi, A.; Sato, S.; Furutani, W. Antibiotic Zopfimarin. Japan Patent 62-40292, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, T.C.; Webb, G.; Cannell, R.J.P.; Kinsman, O.S.; Middleton, R.F.; Sidebottom, P.J.; Taylor, N.L.; Dawson, M.J.; Buss, A.D. Novel inhibitors of fungal protein synthesis produced by a strain of Graphium putredinis. J. Antibiot. 1998, 51, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Davoli, P.; Engel, G.; Werle, A.; Sterner, O.; Anke, T. Neosordarin and hydroxysordarin, two new antifungal agents from Sordaria araneosa. J. Antibiot. 2002, 55, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chokpaiboon, S.; Unagul, P.; Nithithanasilp, S.; Komwijit, S.; Somyong, W.; Ratiarpakul, T.; Isaka, M.; Bunyapaiboonsri, T. Salicylaldehyde and dihydroisobenzofuran derivatives from the marine fungus Zopfiella marina. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Ying, Y.; Hung, Y.S.; Tang, Y. Genome mining reveals Neurospora crassa can produce the salicylaldehyde sordarial. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motoyama, T. Secondary metabolites of the rice blast fungus Pyricularia oryzae: Biosynthesis and biological function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, S.; Muro, H.; Sasaki, K.; Nozoe, S.; Okuda, S.; Sato, Z. Isolations of phytotoxic substances produced by Pyricularia oryzae Cavara. Tetrahedron Lett. 1973, 14, 3537–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
