Abstract
The galactomannan (GM) that is produced by the human fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus is an emblematic biomarker in medical mycology. The GM is composed of two monosaccharides: mannose and galactofuranose. The furanic configuration of galactose residues, absent in mammals, is responsible for the antigenicity of the GM and has favoured the development of ELISA tests to diagnose aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients. The GM that is produced by A. fumigatus is a unique fungal polysaccharide containing a tetramannoside repeat unit and having three different forms: (i) membrane bound through a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchor, (ii) covalently linked to β-1,3-glucans in the cell wall, or (iii) released in the culture medium as a free polymer. Recent studies have revealed the crucial role of the GM during vegetative and polarized fungal growth. This review highlights these recent data on its biosynthetic pathway and its biological functions during the saprophytic and pathogenic life of this opportunistic human fungal pathogen.
1. Introduction
The galactomannan (GM) that is produced by the human fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus is an emblematic biomarker in medical mycology. A. fumigatus is the Aspergillus species most frequently involved in human disease in developed countries. Global multinational prevalence of aspergillosis reaches an estimated 3,000,000 cases per year of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis and 250,000 cases per year of invasive aspergillosis [1]. In the 1970s, the galactomannan polymer was identified as a circulating molecule in the biological fluids of immunocompromised patients that were infected with Aspergillus [2,3]. The identification of rat monoclonal antibodies against the GM has led to the development of a sensitive diagnositic enzyme immunoassay [4]. The GM is composed of two monosaccharides: mannose and galactofuranose. The furanic configuration of galactose residues, absent in mammmals, is responsible for the antigenicity of the GM. Despite the presence of false positive and negative detection and despite other available biomarkers, such as β-1,3-glucans or the development of a PCR method, the GM remains the unavoidable biomarker for the IA diagnosis [5,6] and has led to the recent development of new monoclonal antibodies and the lateral flow assay (LFA)-GM technology [7,8].
Although the GM polymer was described more than 50 years ago, the biological functions and biochemical pathway that are responsible for its biosynthesis remain insufficiently understood. This review highlights the last data on the GM produced by A. fumigatus and shows that the GM play an essential role for fungal apical growth and host-pathogen interactions.
2. GM: A Unique Fungal Specific Polysaccharide
In 1994, Latgé and his colleagues have described the chemical structure of a soluble 20 kDa GM produced by A. fumigatus, which was isolated from the culture supernatant. Carbohydrate analyses of this extracellular polymer showed that the GM was composed of a linear mannan core with an α-1,2-linked mannotetraose repeating unit attached via α-1,6-linkage. Side chains that are composed of an average of 4 to 5 β-1,5-galactofuranose units are linked to C-6 and C-3 positions of α-1,2-linked mannose units of the mannan (Figure 1). The complete chemical structure of the GM, which was initially elucidated by Latgé et al. [9], was completed over the years. NMR development for biomolecules and chemical carbohydrate synthesis allowed for updating the GM structure. The mannan chain structure containing a repeat unit has been confirmed, but galactofuran side chains appeared more variable and complex. The presence of β-1,6-glycosidic intrachain linkage has been now confirmed [10,11]. The size of galactofuranose side chain is highly dependent on the growth conditions and it could be up to 10 residues [9,10]. The apparent molecular weight of GM varies from 15 up to 50 kDa according to the variation of the galactofuranose content [10].
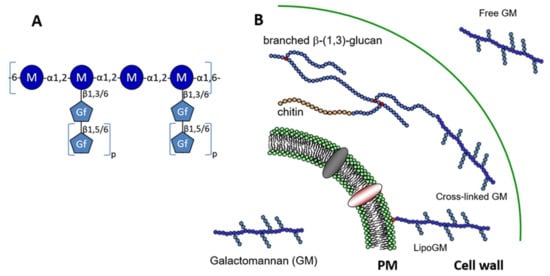
Figure 1.
Structure and localisation of the galactomannan. (A) Structure of the repeat unit of the galactomannan (GM). The main mannan chain is composed of a tetra-α-1,2-mannoside connected through a α-1,6 linkage. Side chains are composed of galactofuranose residues linked to mannose through a β-1,3 or β-1,6 linkage. Depending on the growth condition, variations of galactofuranose content and glycosidic linkage were observed (0.2 to 2.6 galactose residues per mannose residue were observed [9,10]. The size of side-chain is variable from 1 up to 10 galactofuranose residues (0 < p < 10), where galactofuranoses were linked in β-1,5. The presence of β-1,6 were also described in some growth condition where it represents up to 10% of total β-galactofuranose [10,11]. (B) The galactomannan exists under three forms: plasma membrane bound through a inositolphosphoceramide anchor [18], cell wall where the GM is cross linked to β-1,3-glucan [17] and secreted as a free polymer [9].
The presence of such mannan structure was described in secreted fungal polymers isolated from other Aspergillus species and other ascomycetous species such as Penicillium or Trichophyton [12,13,14,15]. This specific mannan sequence is totally unrelated to the mannan polymers that were found in yeast. Saccharomyces cerevisiae mannans result from the elongation of N-glycan and are composed of an α-1,6-mannan linear chain with side chains of α-1,2-mannoside of one to five residues with or without a α-1,3-mannoside end capping [16]. The use of strong chemical degradation, i.e., hydrazinolysis and nitrous deamination to purify the A. fumigatus GM from the culture medium did not allow for demonstrating its linkage to putative protein carrier. Other studies from Latgé’s group have shown that (1) GM is part of the fungal cell wall where it is covalently linked to β-1,3-glucan [17] and (2) GM is bound to cellular membrane through a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchor (called lipo-GM)[18]. The specific degradation by acetolysis of these three species of GM bound to the plasma membrane or the cell wall or secreted has confirmed the presence of the same tetramannoside repeat unit in all these molecules. These two later forms of GM were described in A. fumigatus in both conidia and mycelium. The GPI-lipid anchor is an inositol-phosphoceramide (IPC), where the ceramide is composed of a C18-phytosphingosine with an N-linked 2-hydroxyfatty acid. In fungi, the GPI glycan moiety is mainly composed of a tetra-α-mannoside, being identical to the repeat unit of the GM, which is linked to a glucosamine residue. The glycan moiety may be capped by an α-1,3-linked mannose residue [19,20]. The GM chain is linked to the IPC anchor via mannan chain to the glycan core of GPI.
GM from the culture supernatant has been suggested to be the N-glycan moiety of glycoproteins in A. fumigatus [10]. However, in this later investigation, the demonstration of covalent linkage between protein and GM through PNGase or protease digestions were missing. Other studies have described glycoprotein extracellular antigens with molecular weights of between 20 to >200 kDa, which were positively labeled by an anti-GM MAb [21,22,23,24]. Glycan moities containing galactofuranose residues could be N- or O-linked to proteins [10,22,23,24,25], complicating the studies in the identification of the nature of the real circulating antigen. In addition, different investigations of N-glycans from purified glycoproteins [23] or crude glycoprotein fractions have shown that A. fumigatus mycelium produces relative short N-glycan containing five up to 11 hexose residues [26,27]. No larger N-mannan with a 20 kDa size has been identified to be linked to protein in these studies, showing that the presence of mannotetraose repeating unit in glycan structure linked to a carrier protein remains to be demonstrated. In addition, because the presence of a membrane-bound GPI anchored GM was identified, the presence of a lipid anchor on the GM released the culture surpernatant has been also investigated by chromatographic purification on octyl-sepharose. In contrast to the lipo-GM isolated from membrane preparation, the GM that is released in the culture medium does not possess a lipid-anchor [28].
Taking together all the data on the GM structure, GM that is produced by A. fumigatus is a unique fungal polysaccharide having three different forms: membrane bound through a GPI-anchor, cell wall localized GM where it is covalently linked to β-1,3-glucans and released in the culture medium as a free polymer (Figure 1).
3. Biosynthesis of the GM in A. fumigatus
The structural cell wall polysaccharides (chitin and β-1,3-glucan) are synthesized at the plasma membrane level by protein complexes [29]. In contrast, the GM is intracellularly synthesized, where Golgi transporters of GDP-Man and UDP-Galf are required for the GM polymerisation.
3.1. What Are the Initial Steps Leading to Lipo-GM Biosynthesis?
The similarity of the carbohydrate and lipid moieties of the lipo-GM with thoses of GPI-anchored proteins (GPI-APs) suggested that the GM might follow the GPI biosynthetic pathway. The GPI synthesis pathway occurs at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. Nine biochemical steps are required for the complete synthesis of the intermediate prior to being transferred to the targeted protein: transfer of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) onto a phosphatidylinositol (PI), GlcNAc deacetylation, inositol acylation, and the addition of four mannose and three phosphoethanolamine residues. This pathway is conserved in filamentous fungi, including in A. fumigatus [30,31]. After the transfer to the protein bearing the C-terminal signal sequence for GPI attachment and before the exit of ER, a GPI remodeling occurs to modify the lipid moiety and remove the first two phosphoethanolamine groups. In fungi, a specific lipid remodeling leads to the substitution of the diacylglycerol by a ceramide [32] and occurs in three steps where the de-O-acetylation by the phospholipase A2 activity of Per1p is a key step [33]. A comparative structure analysis by the mass spectrometry of lipid anchor of GPI-anchored proteins (GPI-APs) and lipo-GM was performed with the Δper1 mutant in A. fumigatus [34]. The ∆per1 mutant was still producing the Lipo-GM and its lipid anchor contains an inositol-phospho-ceramide (IPC) identical to the one of the parental strain; whereas, the GPI-APs of Δper1 mutant only contained inositol-phosphodiacylglycerol as lipid anchor. The defect on GPI lipid remodelling has no effect on the lipid anchoring of GM, showing that the biosynthesis of the Lipo-GM is independent of the biosynthetic pathway of the GPI-anchor.
Another possibility was that the synthesis of the Lipo-GM could follow a similar pathway to the synthesis of glycosyl-inositolphosphoceramides (GIPC) where monosaccharides are sequentially added to the IPC anchor. Two types of GIPC are produced in A. fumigatus, acidic and zwitterionic GIPC [35,36] and their synthesis, are independent of PER1. The biosynthesis of GIPCs starts with the addition of glucosamine or mannose residue onto the inositol ring of the IPC [37,38]. However, the inactivation of mannosyltransferase (MitA) and N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (GntA) required for the GIPC synthesis has no effect on the Lipo-GM synthesis [37,38]. This result indicated that the Lipo-GM synthesis is also independent of GIPC synthesis and it required specific glycosyltransferase activities unidentified to date.
3.2. Synthesis of the Mannan Chain
The polymerisation of the mannan chain of the GM requires α-mannosyltransferases, and most of them use the GDP-Man as sugar donor. The first study describing a defect in GM synthesis in A. fumigatus resulted from the deletion of the GDP-Man transporter, Gmt1 [39]. GMT1 is the heterologous gene of VRG4 in yeasts [40,41]. Vrg4 allows for the transport of GDP-Man from the cytosol into the lumen of the Golgi where numerous glycosyltransferases are located. It is essential for the full N- and O-mannolysation of glycoproteins and the GIPC synthesis. In A. fumigatus, the deletion of GMT1 leads to the absence of Lipo-GM in cellular membrane and cell wall-GM, showing that the biosynthesis of the GM starts in the Golgi apparatus [39].
In silico analysis of the genome of A. fumigatus has allowed for the identification of 23 putatives Golgi α-mannosyltransferases. Most of them have orthologs in yeasts. Among investigations of the function of mannosyltrasferases in A. fumigatus, an undecuple multiple mutant has been constructed, where α-1,2 or α-1,6-mannosyltransferase members of CAzy GT32 (Och orthologs), GT34 (α-1,6-mannosyltransferases), GT62 (Mnn9, Anp1, and Van1 orthologs), and GT71 (α-1,2-mannosyltransferases) were deleted [42]. No difference in growth and GM content have been observed in this multiple mutant, showing that no-one of these gene are essential for GM synthesis. Recently, two independent research teams have shown that two α-mannosyltransferase members (CmsA/Ktr4 and CmsB/Ktr7) of the GT15 family (Mnt1/Kre2 family) are essential to the GM synthesis in A. fumigatus [43,44]. Both single and the double mutants produce a low amount of GM released in the culture medium. NMR data showed that core-mannan signals were absent or substantially truncated, indicating that core-mannan structures are altered and/or lost in the absence of CmsA/Ktr4 or CmsB/Ktr7 [43]. At the cell wall level, the deletion of both genes led to the absence of GM cross-linked to β-1,3-glucan [44].
In vitro enzymatic analysis of recombinant CmsA/Ktr4p has shown that it carries an α-1,2-mannosyltransferase activity, which suggested that the two other members of GT15 family in A. fumigatus possess the same activity [43,44]. Ktr1p is not required for the GM synthesis and did not compensate the deletion of the two others, showing differences between homologous enzymes in the same CAZyme family [44,45]. The CMSA/KTR4 and the CMSB/KTR7 genes are both essential to the GM synthesis, but are not redundant. Our current hypothesis is that CmsA/Ktr4p and CmsB/Ktr7p are α-1,2-mannosyltransferases acting sequentially during the synthesis of the tetra-α-1,2-mannoside unit. The product of the first transferase activity would then be the acceptor of the second one and the recognition of the acceptor by the transferase activity represents a critical point for driving the sequential addition of α-1,2-mannoside residue [44]. This hypothesis also suggests the requirement of a transglycosidase/transferase able to polymerase tetramannoside oligomers through an α-1,6 linkage. Such a type of enzyme activity remains to be identified.
Surprisingly, a lipo-GM fraction was still produced by ΔcmsA/ktr4 and ΔcmsB/ktr7 mutants. However, the analysis of the lipo-GM structure clearly showed that this lipo-GM possesses a totally altered mannan structure that was characterised by the absence of the classical tetramannoside repeat unit found in the native GM (Figure 2A). GIPC analysis showed that the deletion led also to an increase in the size of the carbohydrate moiety of the GIPC (Figure 2B). These data clearly showed that the deletion of KTR4 and KTR7 led to the absence of synthesis of the cell wall GM and induce the synthesis of new mannosylated structures, probably due to the compensation by other unknown mannosyltransferase activities.
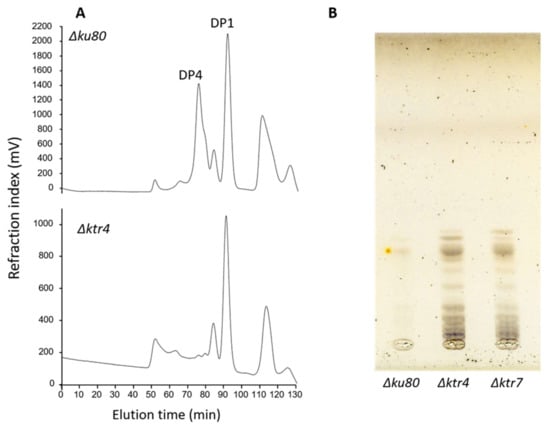
Figure 2.
The structures of lipid anchored galactomannans are totally altered in Δktr mutants. (A) Analysis by acetolysis of the Lipo-galactomannan like produced by Δktr4 mutant. Lipo-GM fraction was purified from total membrane of mycelium and purified as previously described [18,34]. Mannan structure was analysed by acetolysis degradation and gel filtration chromatography on TSK-40S column. The degradation of Lipo-GM from the parental strain (Δku80) leads to the release to two main products: DP1, corresponding to the galactofuranose that is sensitive to acetolysis and a DP4 corresponding to the tetramannoside repeat unit. Acetolysis cleaves preferentially α-1,6-mannosyl linkage. The degradation of the Lipo-GM produced by the Δktr4 mutant did not release specifically a tetramannoside showing the absence of α-1,2-mannose linked residues. (DP: degree of polymerization). (B) TLC analysis of Glycosyl-Inositolphosphoceramide (GIPC) fraction produced by Δktr mutants. GIPC fractions was purified from from total membrane of mycelium and analysed by TLC (Thin layer chromatography), as previously described [36]. In comparaison to parental Δku80 strain, both GM deficient mutants (Δktr4 and Δktr7) produce larger GIPCs in higher amount.
The number of mannosyltransferase are functional in A. fumigatus [37,42,45,46,47]. In S. cerevisiae, Ktr orthologs belong to the GT15 family in the CAZy database and have been characterised as α-1,2-mannosyltransferases playing a role in N- and O-mannosylation of glycoproteins [48,49,50,51]. Although A. fumigatus AfKtr4p and AfKtr7p share high sequence homologies with the yeast Ktrp orthologs and display α-1,2-mannosyltransferase activity, the deletion of A. fumigatus KTR4 and KTR7 genes did not alter protein mannosylation, but led to the loss of the galactomannan polysaccharide. These data provide another clear example of the finding that orthologous genes code for proteins that may have very different biological functions in yeasts and filamentous fungi, even though they have very related enzymatic activities, at least in vitro.
3.3. Addition of Galactofuran Side Chains
Galactofuran side chains are dependent of several activities that are involved in the synthesis of UDP-galactofuranose (UDP-Galf), the transport of the nucleotide sugar and then the elongation of the galactofuran chains. UDP-galactopyranose mutase is a key enzyme in UDP-Galf biosynthesis in microorganisms. Such enzyme activity that was able to convert the pyranic configuration into furanic one was described for long time in procaryotes and described in eucaryotes (Aspergillus and Leishmania) for the first time in 2005 [52]. Only one UGM1/GLFA gene is present in A. fumigatus genome and its deletion led to the total absence of galactofuranose containing molecules, such as galactose moieties of glycoproteins, GIPCs, and the GM polymers [53,54]. Interestingly, the absence of UDP-Galf did not prevent the synthesis of the mannan chain of the GM, neither its integration into the cell wall showing that the polymerisation of the repeat mannan unit is not dependent on the presence of galactofuranose side chain.
The first identification of a nucleotide-sugar transporter specific for UDP-Galf has been identified in A. fumigatus [26]. The protein was called GlfB because of its implication in galactofuranose metabolism and it was selected from its homology to other members of the nucleotide-sugar transporter (NST) family, its location on chromosome 3 directly downstream of the UGM1/GLFA gene. It is a 400-amino acid protein with 11 predicted transmembrane helices. It is a very distinct member of the NST family, because NSTs classically exhibit 8–10 predicted hydrophobic domains with both the N and C terminus situated on the cytoplasmic side of the Golgi. The homolgous gene of AfUGM1/GLFA are present in other fungal species [55,56]. Deletion of the GLFB in A. fumigatus or homologs in other Aspergillus species leads to a similar phenotype as the UGM1/GLFA deletion. No more galactofuranose residues are found in any carbohydrate structures [26], showing that only one NTP-sugar is sufficient to specifically transport UDP-Galf into the Golgi where galactofuranosyltransferases are localized.
The first fungal β-galactofuranosyltransferase GfsA that has been identified in A. nidulans and A. fumigatus is a Golgi type II transmembrane protein [57]. This member of the CAzy GT31 family is involved in the addition of galactofuranose residues to mannan structure. In vitro, it was shown that the recombinant AfGfsA acts as a UDP-α-d-galactofuranose: β-d-galactofuranoside β-1,5-galactofuranosyltransferase involved in the biosynthesis of galactomannans [58]. A. niger, as well as A. nidulans and A. fumigatus, contain three β-galactofuranosyltransferases encoding genes in their genomes [58,59]. The deletion of AfGFSA1 leads to the absence of detection of secreted glycoproteins by an anti-Galf MAb and a reduction of 84% of β-1,5-galactofuranoside residues in the GM [58], showing that the UDP-Gal mutase, transporter specific for UDP-Galactofuranose, and β-galactofuranosyltransferase are equally essential for obtaining a correct β-galactofuranosylation.
3.4. Cross-linking to Cell Wall β-1,3-Glucan
The cell wall GM is cross-linked to β-1,3-glucans and its amount is dependent on the growth conditions and morphotypes analysed (conidia versus mycelium) [60,61]. Recently, we have shown that DFG members of the CAZy GH76 family are essential for the covalent anchoring of the GM to the cell wall [28]. AfDfgp are homologs of yeast Dfg5 and Dcw1 proteins. The increased release of GPI-anchored proteins in the dfg5 mutant or the dcw1 mutant in yeast suggested that these proteins were involved in the cross-linking of GPI-CWPs to the cell wall glucans [62,63]. In A. fumigatus, seven members of Dfg proteins were identified. Single gene deletion suggested that Dfg3 was the most important member of the Dfg family. However, all members of the family were involved in the cross-linking process. Since the total loss of GM bound to β-1,3-glucans requires the successive sequential deletion of all members of the family. However, the Δdfg mutants still produced membrane-bound GM with the same chemical structure as the one of the parental strain, which showed that Dfg proteins are not involved in GM biosynthesis, but that these Dfg proteins only play a key role in the cross-linking of GM to β-1,3-glucans [28].
Two bacterial members of GH76 family have an α-1,6mannosidase activity [64,65]. In fungi, no mannan hydrolytic activity was identified while using recombinant Dfg protein. However, the Yeast DFG5 deletion mutant could be complemented by the AfDFG3 showing that yeast and filamentous homologs have similar function, even though the structures transferred would be different since there is no GM in yeast and the yeast cell wall mannan are not cross-linked to β-glucans but are the N-glycan moiety of cell wall glycoproteins [16]. Since the lipid-anchor of fungal GPI-APs and Lipo-GM are similar, it was also tempting to speculate that such Dfg proteins were involved in the cross-linking of membrane GPI-anchored molecules onto cell wall glucan. However, in both yeast and filamentous Δdfg mutants, GPI-anchored and non-GPI cell wall mannoproteins were both released, as has been frequently seen in many other cell wall mutants [28,62,66,67]. Because all attempts to show a transglycosidase activity in vitro with recombinant proteins have failed to date, the biochemical function of Dfg orthologs remains unknown.
3.5. Conclusion on the GM Biosynthetic Pathways
Figure 3 summarizes the biosynthetic pathway of the GM in A. fumigatus, which remains unique in the fungal kingdom. This pathway required (1) the synthesis of nucleotide-sugar that occurs in the cytosol and their specific transport into the lumen of the Golgi, (2) the polymerisation of the mannan chain on a lipid acceptor, probably an IPC, and the addition of galactofuranose side chain, (3) the trafficking of the lipo-GM to the external face of the plasma membrane, and (4) the translocation onto the cell wall β-1,3-glucans where Dfgp play a key role.
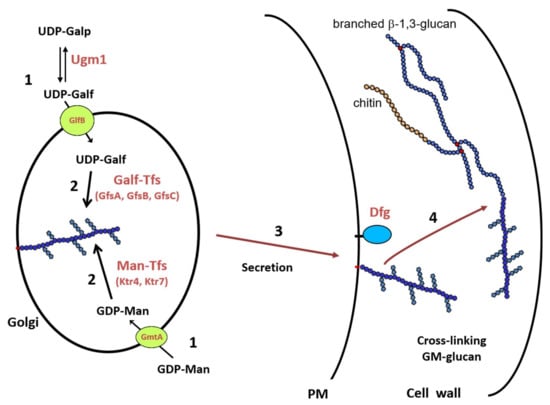
Figure 3.
Biosynthetic scheme of the cell wall GM biosynthesis in A. fumigatus. (1) Synthesis of nucleotide-sugars in the cytosol and their transport into the lumen of the Golgi; (2) Polymerization of the GM by glycosyltransferases; (3) Intracellular trafficking of the lipo-GM to the plasma membrane; (4) Cross-linking of the GM onto cell wall β-1,3-glucan. Abbreviations: UDP-Galp: UDP-galactoyranose; UDP-Galf: UDP-galactofuranose; GDP-Man: GDP-mannose; Ugm1: UDP-galactose mutase; GmtA: GDP-Man transporter; GlfB: UDP-Galf transporter; GfsA,B,C: β-galactofuranosyltransferases; Ktr4,7: α-1,2-Mannosyltransferases.
All of the glycosyltransferases that are involved in the lipo-GM synthesis are not yet identified. The N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase and the consecutive N-deacetylase required for the formation of GlcN-IPC lipid-anchor are unknown. Based on its structure with a repeat unit, our current hypothesis that the biosynthesis of the mannan chain should be processed in two steps: the synthesis of the tetra-α-1,2-mannoside repeat unit, where CmsA/Ktr4p and CmsB/Ktr7p are essential, and the polymerisation of the repeat unit. Such a process described in procaryotes required specific enzymes and acceptor [68,69] that are not yet identified in A. fumigatus. The release into the culture medium is independent of Dfg proteins [28], but other enzyme activity, such as phospholipase or glycohydrolase, is required to remove the lipid anchor.
4. Functions of the GM
The functions of the GM during the fungal life and infections remain insufficiently understood. Recent discoveries on the mannan biosynthesis and the construction of GM deficient mutant have highlighted the importance of this unique fungal polysaccharide.
4.1. A Cell Wall Without Galf Has an Altered Structure
Phenotype analysis of the galactofuranose deficient Aspergillus mutants brought some clues of the biological functions of galactofuranose containing molecules in the fungal life. In Aspergillus species, phenotypes were first described in UDP-Gal mutase deficient strains. In A. niger and A. nidulans, the absence of galactofuranose induces a slight growth reduction with an increase sensitivity to temperature as well as cell wall disturbing compounds, such as calcofluor white. Respective mycelium are hyperbranched, which suggests a role of galactofuranose residues in the cell wall organisation and permeability [55,70]. In A. fumigatus, similar phenotypes were observed but were less pronounced [53,54]. However, the weak phenotype seen for these mutants may result from compensatory reactions due to other cell wall associated enzymes. The deletion of UGM1 led to a cell surface alteration inducing an increase of adherence to abiotic and biotic surface and an increase of hydrophobicity. Particularly, the presence of galactofuranose was initially thought to be responsible for the reduction of the adherence properties of mannan chain to plastic and glass solid surface [53]. This change in adhesion properties was in fact due to the unmasking of the cell wall mannan, but also to a complete modification of the surface structure resulting from the overproduction of galactosaminogalactan [53,71]. In A. niger, the absence of galactofuranose synthesis is compensated by an overexpression of α-1,3-glucan synthesis [56,72], which makes it difficult to conclude on exact functions of galactofuranose residues in Aspergillus species. The phenotype of mutant deficient in UDP-Galf transporter or in β-galactofuranosyltransferase share similar phenotypes (reduced growth, aberrant branching morphology, reduced conidiation, increased sensitivity to CFW, and increased expression of AGSA) [59].
4.2. Mannan Controls Polarized Growth in Aspergillus
The absence of GDP-Man transporter (Gmt1) led to a strong defect in growth of AfS35 wild type A. fumigatus [39]. While using the heterokaryon rescue methodology, we showed that GMT1 is an essential gene in the A. fumigatus akuB CEA17 genetic background (Lambou and Latgé, personnal communication), showing that the importance of mannosylation in Aspergillus depends of the fungal strain genetic background.
The phenotype of the α-mannosyltransferase mutants depends strongly of the gene deleted and suggested that these enzymes have a different function probably linked to their respective substrate acceptors. The deletion of Golgi mannosyltransferases involved in N-mannan elongation of glycoproteins or in GIPC synthesis have no or weak effect on filamentous growth [37,42,45,46,47]. In A. fumigatus, N-mannan elongation play a major role at the conidia level, where multiple deletion of α-mannosyltransferase genes led to conidial cell wall alteration and permeability, showing the presence of different mannan polymers, depending on the morphotype [42]. In agreement with the essentiality of GDP-Man transport into the Golgi, the deletion of the CMSA/KTR4 or CMSB/KTR7 led to a severe phenotype. Δktr4 and Δktr7 mutants both have strong defects in vegetative growth, conidiophore formation and conidiation [43,44]. Mycelium of these mutants were hyperbranched with formation of swollen filaments (balloon morphology) after 48 h of growth showing altered cell wall organisation. At the conidia level, the absence of GM synthesis led to enlarged and fragile conidia and to a mis-regulation of the germination process where the polarization of germ tube formation was altered [44].
GM is part of the structural cell wall skeleton, where it is covalently linked to the chitin-β-1,3-glucan complex. A defect in the cross-linking of GM into the cell wall of A. fumigatus that resulted in the deletion of DFG family members led to a strong defect in conidiation and hyperbranched reduced mycelial growth [28]. Although the GM is still present at the plasma membrane level in DFG mutants as in WT, its absence of covalent linkage in the cell wall was not compensated by the higher production of chitin (a compensatory reaction often seen in cell wall mutants), showing that the formation of the linkage of GM to the core chitin-β-1,3-glucan plays an essential role in the vegetative growth. In contrast, the absence of synthesis of other cell wall polymers (α-glucan, β-1,3/1,4-glucan, galactosaminogalactan (GAG)) did not alter the filamentous polarized growth [71,73,74].
4.3. GM Induces a Host Immune Response
The fact that GM is secreted in the infected patient suggested that this polysaccharide may induce a specific response of the host [75,76]. Indeed, in a vaccination mouse model of aspergillosis, the intranasal administration of purified GM or Lipo-GM failed to induce protection, which was concomitant to a (IL-4/Gata3), and Th17 (IL-17A and F/Rorc) activation, which was independent to the presence of the lipid anchor of the GM [77]. However, very few studies analysed the role of GM during the pathobiology of aspergillosis in the immunocompromised and immunocompetent host [29,78]. The recognition of GM by PRR remains particularly poorly understood.
The first step in the induction of the immune response is the recognition of the GM by host cells. How is GM recognised by host cells? Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and C type lectins are major players in the recognition of mannosylated structures by the host [79,80]. The role of TLR 2 and 4 in the recognition of A. fumigatus cells has been shown [81,82,83,84]. GM immunomodulates the proinflammatory responses, mainly through the TLR4 signalling [85]. However, the mechanisms by which TLR4 and TLR2 recognise mannose-containing glycoconjugates and other fungal polysaccharides are still unknown [86]. The finding that Th2-type cytokines increase the susceptibility to invasive aspergillosis has prompted studies on the role of dentritic cells (DC) during Aspergillus infections [87,88]. DCs and macrophages bind and internalize A. fumigatus conidia via the DC-SIGN receptor, and this binding can be inhibited by GM isolated from A. fumigatus [89,90]. The use of sugar-conjugated nanoparticle showed that the β-galactofuranose residues are recognised by DC-SIGN [91]. In vitro, fungal-like particles decorated with galactomannan isolated from A. fumigatus are recognised by macrophage and induced TNF-α production through Dectin-2 [92]. The presence of α-1,2-mannoside sequence in the GM structure is in agreement with its interaction with the Dectin-2 [80]. In vivo, the investigation of Dectin-2 and MMR expression both at transcriptional and translational levels in human lung revealed that Dectin-2 and MMR proteins which are expressed relatively low level in normal lung samples exhibited marked overexpression in A. fumigatus–invaded lung tissues in both ABPA and invasive aspergillosis patients [93]. It is still unknown whether GM plays a major role in this immune response. The interaction between human plasmacystoid dentritic cells (pDCs) and A. fumigatus hyphae is mediated through Dectin-2 [94]. This interaction that triggers antifungal activity and cytokine release was partially inhibited by anti-Dectin-2 antibodies and yeast α-mannans [94]. Although it has been shown that MMR interacts with A. fumigatus [95], the biochemical recognition of GM by MMR remains to be investigated.
Other PPRs may interact with fungal mannans. Mannose binding lectin (MBL) and other collectins (SP-D and SP-A) play plausible role in pulmonary defence against A. fumigatus [21,96,97,98]. The pulmonary surfactant protein D (SP-D) recognises GM in a calcium dependent manner, whereas MBL and SP-A show, respectively, a weak or the absence of binding to GM [99]. In addition, A. fumigatus produces a number of glycoproteins and glycosphingolipids containing α-mannoside residues and an unique cell wall mannan in Aspergillus conidia [42]. All of these carbohydrate structures may interact with the same PRRs as GM, making difficult to understand the true in vivo function of GM during infection.
The tools available to analyse the host immune response only start to be developed. In the past, some authors used erroneously commercially available GMs, which are isolated from plants. These plant GMs are structurally unrelated to the one that was produced by A. fumigatus and make conclusions associated to the role of GM totally wrong and inappropriate. Using GM mutants to assess the role of GM during the infection is also difficult, because the cell wall of these mutants may be modified to compensate for the absence of GM and these modifications may be more important for the fungal virulence than the lack of the GM itself. As example, GM deficient mutants, which are less virulent, have a slow growth and produce a high amount of cell wall chitin [44] and galactofuranose deficient mutant overproduces GAG, which is a virulence factor [71]. In addition, the virulence of ΔUgm1/GlfA mutant in a mouse infection model of invasive aspergillosis seems to also depend on the genetic background of the A. fumigatus parental strain [53,54]. Chemically synthesized oligosaccharides are essential tools that allow for precisely deciphering the specificity of the immune response. Using this system, it was shown that the antibodies recognised the terminal disaccharide Galf-β-1,5-Galf [100]. The same Galf-β1,5-Galf dissacharide is the minimal size that is required to induce the production of the specific cytokines, interleukin 1 beta (IL-1), IL-1Ra, IL-6, produced by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). In contrast, the mannan moiety of the GM does not induce antibody or cytokine response [100].
5. Perspectives
The GM that is produced by A. fumigatus is a unique fungal polysaccharide. Although it has been described 50 years ago, recent discoveries on its biosynthesis highlight its importance for the vegetative growth and for the fungal cell wall organisation. The overall functions of this polysaccharide are summarized in Figure 4. Based on this prevalence of aspergillosis infections, future investigations will be operated under three axes:
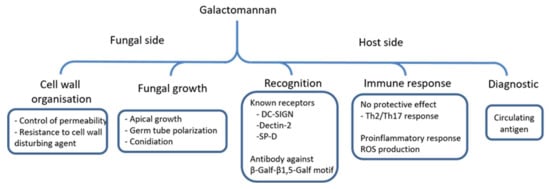
Figure 4.
Functions of the GM produced by A. fumigatus. The scheme summarizes biological functions of the GM and its host interaction during infection.
- (1)
- Improvement of diagnostic test. Earliers detection of aspergillosis is required to improve antifungal treatment and eliminate fungal burden. The GM diagnostic test is based on the detection by ELISA of galactofuranose side chain. According to the carbohydrate structure of the GM, a double detection that is based on the development of antibodies on the specific mannan chain and side chain of galactofuranose may improve the specificity of detection. Galactofuran chains are part of the GM as well as of glycoproteins and GIPC. Carbohydrate structures that are produced by A. fumigatus during infection have never been investigated. Such studies of the GM and other cell wall polymers released during infection may identify new aspergillus biomarkers.
- (2)
- GM biosynthesis may be a new drug target. The strong defect of vegetative growth in mannan deficient mutant in A. fumigatus shows the essential role of the GM inside the cell wall, particularly in the organisation of the structural core. The cross-linking of the GM to the β-glucan-chitin complex is also an essential event for the polarized fungal growth. The biosynthetic pathway of the GM includes two crucial steps for the vegetative growth, GDP-mannose transport into the lumen of the Golgi, and the mannan polymerisation. Because Gmt1p transporter and α-1,2-mannosyltransferase members of the GT15 family are absent in human, the development of specific inhibitors of both activities that are essential to GM polymerisation are new approaches to design new anti-Aspergillus drugs. The main question is to understand how this GM, which is present at relatively low concentration in the cell wall, is so crucial. The GM is originally a soluble polymer and its organisation and interaction with the other polysaccharides of the structural core are unknown. The cell wall GM is present under two forms: bound to the outer layer of the plasma membrane and covalently linked inside the cell wall. One of our hypotheses is that the GM may be required for the interaction between the plasma membrane and cell wall, essential to polarized fungal growth
- (3)
- What is the role of a circulating polysaccharide in the systemic immune response of the host? It is essential to define the immune receptors interacting with Aspergillus GM and driving the host reponses during infections. Although the fungal mannans usually play a critical role in innate host response, the mannan of the GM is not recognised by the human antibody. This lack of recognition has not been investigated to date. Deep investigations using GM mutants as well as purified GM in combination or not with other cell wall components are required to better understand the role of GM during Aspergillus infection and host immune response.
Funding
This research was funded by the Aviesan project Aspergillus, the French Government’s Investissement d’Avenir program, Laboratoire d’Excellence “Integrative Biology of Emerging Infectious Diseases” (grant ANR-10-LABX-62-IBEID), la Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (DEQ20150331722 LATGE Equipe FRM 2015) and ANR-DFG AfuINF.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Bongomin, F.; Gago, S.; Oladele, R.O.; Denning, D.W. Global and Multi-National Prevalence of Fungal Diseases—Estimate Precision. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, P.F.; Reiss, E. Invasive aspergillosis: Antiserum for circulating antigen produced after immunization with serum from infected rabbits. Infect. Immun. 1978, 20, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, E.; Lehmann, P.F. Galactomannan antigenemia in invasive aspergillosis. Infect. Immun. 1979, 25, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stynen, D.; Goris, A.; Sarfati, J.; Latgé, J.P. A new sensitive sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect galactofuran in patients with invasive aspergillosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamoth, F. Galactomannan and 1,3-β-d-Glucan Testing for the Diagnosis of Invasive Aspergillosis. J. Fungi 2016, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boch, T.; Reinwald, M.; Spiess, B.; Liebregts, T.; Schellongowski, P.; Meybohm, P.; Rath, P.-M.; Steinmann, J.; Trinkmann, F.; Britsch, S.; et al. Detection of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients by combined use of conventional culture, galactomannan, 1-3-beta-D-glucan and Aspergillus specific nested polymerase chain reaction in a prospective pilot study. J. Crit. Care 2018, 47, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matveev, A.L.; Krylov, V.B.; Emelyanova, L.A.; Solovev, A.S.; Khlusevich, Y.A.; Baykov, I.K.; Fontaine, T.; Latgé, J.-P.; Tikunova, N.V.; Nifantiev, N.E. Novel mouse monoclonal antibodies specifically recognize Aspergillus fumigatus galactomannan. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, P.L.; Price, J.S.; Posso, R.; Cutlan-Vaughan, M.; Vale, L.; Backx, M. Evaluation of the Performance of the IMMY sona Aspergillus Galactomannan Lateral Flow Assay When Testing Serum To Aid in Diagnosis of Invasive Aspergillosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00053-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latgé, J.P.; Kobayashi, H.; Debeaupuis, J.P.; Diaquin, M.; Sarfati, J.; Wieruszeski, J.M.; Parra, E.; Bouchara, J.P.; Fournet, B. Chemical and immunological characterization of the extracellular galactomannan of Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 5424–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudoh, A.; Okawa, Y.; Shibata, N. Significant structural change in both O- and N-linked carbohydrate moieties of the antigenic galactomannan from Aspergillus fumigatus grown under different culture conditions. Glycobiology 2015, 25, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylov, V.B.; Argunov, D.A.; Solovev, A.S.; Petruk, M.I.; Gerbst, A.G.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Shashkov, A.S.; Latgé, J.-P.; Nifantiev, N.E. Synthesis of oligosaccharides related to galactomannans from Aspergillus fumigatus and their NMR spectral data. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unkefer, C.J.; Gander, J.E. The 5-O-beta-D-galactofuranosyl-containing peptidophosphogalactomannan of Penicillium charlesii. Characterization of the mannan by 13C NMR spectroscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bardalaye, P.C.; Nordin, J.H. Chemical structure of the galactomannan from the cell wall of Aspergillus niger. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 2584–2591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gander, J.E.; Jentoft, N.H.; Drewes, L.R.; Rick, P.D. The 5-O-beta-D-galactofuranosyl-containing exocellular glycopeptide of Penicillium charlesii. Characterization of the phosphogalactomannan. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 2063–2072. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ikuta, K.; Shibata, N.; Blake, J.S.; Dahl, M.V.; Nelson, R.D.; Hisamichi, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Suzuki, S.; Okawa, Y. NMR study of the galactomannans of Trichophyton mentagrophytes and Trichophyton rubrum. Biochem. J. 1997, 323, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlean, P. Architecture and biosynthesis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall. Genetics 2012, 192, 775–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, T.; Simenel, C.; Dubreucq, G.; Adam, O.; Delepierre, M.; Lemoine, J.; Vorgias, C.E.; Diaquin, M.; Latgé, J.-P. Molecular Organization of the Alkali-insoluble Fraction ofAspergillus fumigatus Cell Wall. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 27594–27607. [Google Scholar]
- Costachel, C.; Coddeville, B.; Latgé, J.-P.; Fontaine, T. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored Fungal Polysaccharide in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 39835–39842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, T.; Magnin, T.; Melhert, A.; Lamont, D.; Latgé, J.; Ferguson, M.A.J. Structures of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchors from Aspergillus fumigatus membrane proteins. Glycobiology 2003, 13, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fankhauser, C.; Homans, S.W.; Thomas-Oates, J.E.; McConville, M.J.; Desponds, C.; Conzelmann, A.; Ferguson, M.A. Structures of glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchors from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 26365–26374. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, G.; Rolle, A.-M.; Maurer, A.; Spycher, P.R.; Schillinger, C.; Solouk-Saran, D.; Hasenberg, M.; Weski, J.; Fonslet, J.; Dubois, A.; et al. Towards Translational ImmunoPET/MR Imaging of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis: The Humanised Monoclonal Antibody JF5 Detects Aspergillus Lung Infections In Vivo. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3398–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastebois, A.; Mouyna, I.; Simenel, C.; Clavaud, C.; Coddeville, B.; Delepierre, M.; Latgé, J.-P.; Fontaine, T. Characterization of a New β(1–3)-Glucan Branching Activity of Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 2386–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelle, W.; Bernard, M.; Debeaupuis, J.-P.; Buitrago, M.; Tabouret, M.; Latgé, J.-P. Galactomannoproteins of Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 2005, 4, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitao, E.A.; Bittencourt, V.C.B.; Haido, R.M.T.; Valente, A.P.; Peter-Katalinic, J.; Letzel, M.; de Souza, L.M.; Barreto-Bergter, E. Beta-galactofuranose-containing O-linked oligosaccharides present in the cell wall peptidogalactomannan of Aspergillus fumigatus contain immunodominant epitopes. Glycobiology 2003, 13, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, M. Protein O-glycosylation in fungi: Diverse structures and multiple functions. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J.; Schmalhorst, P.S.; Dörk-Bousset, T.; Ferrières, V.; Routier, F.H. A Single UDP-galactofuranose Transporter Is Required for Galactofuranosylation in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 33859–33868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotz, A.; Wagener, J.; Engel, J.; Routier, F.H.; Echtenacher, B.; Jacobsen, I.; Heesemann, J.; Ebel, F. Approaching the secrets of N-glycosylation in Aspergillus fumigatus: Characterization of the AfOch1 protein. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muszkieta, L.; Fontaine, T.; Beau, R.; Mouyna, I.; Vogt, M.S.; Trow, J.; Cormack, B.P.; Essen, L.-O.; Jouvion, G.; Latgé, J.-P. The Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-Anchored DFG Family Is Essential for the Insertion of Galactomannan into the β-(1,3)-Glucan–Chitin Core of the Cell Wall of Aspergillus fumigatus. mSphere 2019, 4, e00397-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latgé, J.-P.; Beauvais, A.; Chamilos, G. The Cell Wall of the Human Fungal Pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus: Biosynthesis, Organization, Immune Response, and Virulence. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittet, M.; Conzelmann, A. Biosynthesis and function of GPI proteins in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bba-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2007, 1771, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, T.; Smith, T.K.; Crossman, A.; Brimacombe, J.S.; Latgé, J.-P.; Ferguson, M.A.J. In Vitro Biosynthesis of Glycosylphosphatidylinositol in Aspergillus fumigatus†. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 15267–15275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Jigami, Y. Lipid remodeling of GPI-anchored proteins and its function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bba-Gen. Subj. 2008, 1780, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Umemura, M.; Yoko-o, T.; Jigami, Y. PER1 Is Required for GPI-Phospholipase A2 Activity and Involved in Lipid Remodeling of GPI-anchored Proteins. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 5253–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mouyna, I.; Henry, C.; Moyrand, F.; Malosse, C.; Chamot-Rooke, J.; Janbon, G.; Latgé, J.-P.; Fontaine, T. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol Anchors from Galactomannan and GPI-Anchored Protein Are Synthesized by Distinct Pathways in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, M.S.; Levery, S.B.; Bennion, B.; Guimaraes, L.L.; Castle, S.A.; Lindsey, R.; Momany, M.; Park, C.; Straus, A.H.; Takahashi, H.K. Analysis of glycosylinositol phosphorylceramides expressed by the opportunistic mycopathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 1801–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simenel, C.; Coddeville, B.; Delepierre, M.; Latgé, J.-P.; Fontaine, T. Glycosylinositolphosphoceramides in Aspergillus Fumigatus. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotz, A.; Wagener, J.; Engel, J.; Routier, F.; Echtenacher, B.; Pich, A.; Rohde, M.; Hoffmann, P.; Heesemann, J.; Ebel, F. The mitA gene of Aspergillus fumigatus is required for mannosylation of inositol-phosphorylceramide, but is dispensable for pathogenicity. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2010, 47, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J.; Schmalhorst, P.S.; Krüger, A.T.; Müller, C.T.; Buettner, F.F.R.; Routier, F.H. Characterization of an N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase involved in Aspergillus fumigatus zwitterionic glycoinositolphosphoceramide biosynthesis. Glycobiology 2015, 25, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J.; Schmalhorst, P.S.; Routier, F.H. Biosynthesis of the Fungal Cell Wall Polysaccharide Galactomannan Requires Intraluminal GDP-mannose. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 44418–44424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, N.; Zhang, Y.B.; Poster, J.B. The VRG4 gene is required for GDP-mannose transport into the lumen of the Golgi in the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 31908–31914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, A.; Poster, J.B.; Jigami, Y.; Dean, N. Molecular and Phenotypic Analysis of CaVRG4, Encoding an Essential Golgi Apparatus GDP-Mannose Transporter. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, C.; Fontaine, T.; Heddergott, C.; Robinet, P.; Aimanianda, V.; Beau, R.; Beauvais, A.; Mouyna, I.; Prevost, M.-C.; Fekkar, A.; et al. Biosynthesis of cell wall mannan in the conidium and the mycelium of Aspergillusfumigatus. Cell. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1881–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoue, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Hagiwara, D.; Ekino, K.; Watanabe, A.; Ohta, K.; Kamei, K.; Shibata, N.; Goto, M.; Oka, T. Identification of Two Mannosyltransferases Contributing to Biosynthesis of the Fungal-type Galactomannan α-Core-Mannan Structure in Aspergillus fumigatus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, C.; Li, J.; Danion, F.; Alcazar-Fuoli, L.; Mellado, E.; Beau, R.; Jouvion, G.; Latgé, J.-P.; Fontaine, T. Two KTR Mannosyltransferases Are Responsible for the Biosynthesis of Cell Wall Mannans and Control Polarized Growth in Aspergillus fumigatus. mBio 2019, 10, e02647-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagener, J.; Echtenacher, B.; Rohde, M.; Kotz, A.; Krappmann, S.; Heesemann, J.; Ebel, F. The Putative α-1,2-Mannosyltransferase AfMnt1 of the Opportunistic Fungal Pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus Is Required for Cell Wall Stability and Full Virulence. Eukaryot. Cell 2008, 7, 1661–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambou, K.; Perkhofer, S.; Fontaine, T.; Latge, J.-P. Comparative functional analysis of the OCH1 mannosyltransferase families in Aspergillus fumigatus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 2010, 27, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, A.T.; Engel, J.; Buettner, F.F.R.; Routier, F.H. Aspergillus fumigatus Cap59-like protein A is involved in α1,3-mannosylation of GPI-anchors. Glycobiology 2016, 26, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lussier, M.; Sdicu, A.-M.; Bussereau, F.; Jacquet, M.; Bussey, H. The Ktr1p, Ktr3p, and Kre2p/Mnt1p Mannosyltransferases Participate in the Elaboration of Yeast O- andN-linked Carbohydrate Chains. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 15527–15531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lussier, M.; Sdicu, A.-M.; Bussey, H. The KTR and MNN1 mannosyltransferase families of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bba-Gen. Subj. 1999, 1426, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, K.; Boone, C.; Goebl, M.; Puccia, R.; Sdicu, A.M.; Bussey, H. Yeast Kre2 Defines a New Gene Family Encoding Probable Secretory Proteins, and Is Required for the Correct N-Glycosylation of Proteins. Genetics 1992, 130, 273–283. [Google Scholar]
- Reason, A.J.; Dell, A.; Romero, P.A.; Herscovics, A. Specificity of the mannosyltransferase which initiates outer chain formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Glycobiology 1991, 1, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, H.; Kleczka, B.; Gerardy-Schahn, R.; Routier, F.H. Identification and partial characterization of two eukaryotic UDP-galactopyranose mutases. Biol. Chem. 2005, 386, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarre, C.; Beau, R.; Balloy, V.; Fontaine, T.; Hoi, J.W.S.; Guadagnini, S.; Berkova, N.; Chignard, M.; Beauvais, A.; Latgé, J.-P. Galactofuranose attenuates cellular adhesion of Aspergillus fumigatus. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1612–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalhorst, P.S.; Krappmann, S.; Vervecken, W.; Rohde, M.; Müller, M.; Braus, G.H.; Contreras, R.; Braun, A.; Bakker, H.; Routier, F.H. Contribution of Galactofuranose to the Virulence of the Opportunistic Pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 2008, 7, 1268–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ganiny, A.M.; Sanders, D.A.R.; Kaminskyj, S.G.W. Aspergillus nidulans UDP-galactopyranose mutase, encoded by ugmA plays key roles in colony growth, hyphal morphogenesis, and conidiation. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2008, 45, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damveld, R.A.; Franken, A.; Arentshorst, M.; Punt, P.J.; Klis, F.M.; van den Hondel, C.A.M.J.J.; Ram, A.F.J. A Novel Screening Method for Cell Wall Mutants in Aspergillus niger Identifies UDP-Galactopyranose Mutase as an Important Protein in Fungal Cell Wall Biosynthesis. Genetics 2008, 178, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komachi, Y.; Hatakeyama, S.; Motomatsu, H.; Futagami, T.; Kizjakina, K.; Sobrado, P.; Ekino, K.; Takegawa, K.; Goto, M.; Nomura, Y.; et al. gfsA encodes a novel galactofuranosyltransferase involved in biosynthesis of galactofuranose antigen of O-glycan in Aspergillus nidulans and A. fumigatus. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 90, 1054–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katafuchi, Y.; Li, Q.; Tanaka, Y.; Shinozuka, S.; Kawamitsu, Y.; Izumi, M.; Ekino, K.; Mizuki, K.; Takegawa, K.; Shibata, N.; et al. GfsA is a β1,5-galactofuranosyltransferase involved in the biosynthesis of the galactofuran side chain of fungal-type galactomannan in Aspergillus fumigatus. Glycobiology 2017, 27, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arentshorst, M.; de Lange, D.; Park, J.; Lagendijk, E.L.; Alazi, E.; van den Hondel, C.A.M.J.J.; Ram, A.F.J. Functional analysis of three putative galactofuranosyltransferases with redundant functions in galactofuranosylation in Aspergillus niger. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauvais, A.; Fontaine, T.; Aimanianda, V.; Latgé, J.-P. Aspergillus cell wall and biofilm. Mycopathologia 2014, 178, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouyna, I.; Fontaine, T. Cell Wall of Aspergillus fumigatus: A Dynamic Structure. Aspergillus Fumigatus Aspergillosis 2009, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.; Goddard, N.; Hicks, C.; Ovalle, R.; Rauceo, J.M.; Jue, C.K.; Lipke, P.N. A screen for deficiencies in GPI-anchorage of wall glycoproteins in yeast. Yeast Chichester Engl. 2010, 27, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagaki, H.; Wu, H.; Shimoi, H.; Ito, K. Two homologous genes, DCW1 (YKL046c) and DFG5, are essential for cell growth and encode glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored membrane proteins required for cell wall biogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 46, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Maitra, S.K.; Ballou, C.E. An endo-alpha1 leads to 6-D-mannanase from a soil bacterium. Purification, properties, and mode of action. J. Biol. Chem. 1976, 251, 174–181. [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, Y.; Nakajima, T. The aman6 Gene Encoding a Yeast Mannan Backbone Degrading 1,6-α-D-Mannanase in Bacillus circulans: Cloning, Sequence Analysis, and Expression. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 2018–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, J.; Chinnici, J.L.; Maddi, A.; Free, S.J. The N-Linked Outer Chain Mannans and the Dfg5p and Dcw1p Endo-α-1,6-Mannanases Are Needed for Incorporation of Candida albicans Glycoproteins into the Cell Wall. Eukaryot. Cell 2015, 14, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddi, A.; Fu, C.; Free, S.J. The Neurospora crassa dfg5 and dcw1 Genes Encode α-1,6-Mannanases That Function in the Incorporation of Glycoproteins into the Cell Wall. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, C. Biosynthesis and assembly of capsular polysaccharides in Escherichia coli. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006, 75, 39–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, L.P.P.; Rathinavelan, T. Targeting the Sugary Armor of Klebsiella Species. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heesemann, L.; Kotz, A.; Echtenacher, B.; Broniszewska, M.; Routier, F.; Hoffmann, P.; Ebel, F. Studies on galactofuranose-containing glycostructures of the pathogenic mold Aspergillus fumigatus. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 301, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravelat, F.N.; Beauvais, A.; Liu, H.; Lee, M.J.; Snarr, B.D.; Chen, D.; Xu, W.; Kravtsov, I.; Hoareau, C.M.Q.; Vanier, G.; et al. Aspergillus Galactosaminogalactan Mediates Adherence to Host Constituents and Conceals Hyphal β-Glucan from the Immune System. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Tefsen, B.; Heemskerk, M.J.; Lagendijk, E.L.; van den Hondel, C.A.M.J.J.; van Die, I.; Ram, A.F.J. Identification and functional analysis of two Golgi-localized UDP-galactofuranose transporters with overlapping functions in Aspergillus niger. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C.; Latgé, J.-P.; Beauvais, A. α1,3 Glucans Are Dispensable in Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 2012, 11, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samar, D.; Kieler, J.B.; Klutts, J.S. Identification and deletion of Tft1, a predicted glycosyltransferase necessary for cell wall β-1,3;1,4-glucan synthesis in Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauvais, A.; Latgé, J.-P. Aspergillus Biofilm In Vitro and In Vivo. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loussert, C.; Schmitt, C.; Prevost, M.-C.; Balloy, V.; Fadel, E.; Philippe, B.; Kauffmann-Lacroix, C.; Latgé, J.P.; Beauvais, A. In vivo biofilm composition of Aspergillus fumigatus. Cell. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozza, S.; Clavaud, C.; Giovannini, G.; Fontaine, T.; Beauvais, A.; Sarfati, J.; D’Angelo, C.; Perruccio, K.; Bonifazi, P.; Zagarella, S.; et al. Immune Sensing of Aspergillus fumigatus Proteins, Glycolipids, and Polysaccharides and the Impact on Th Immunity and Vaccination. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2407–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latgé, J.-P.; Chamilos, G. Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillosis in 2019. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 33, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhithasri, V.; Nisha, N.; Biswas, L.; Anil Kumar, V.; Biswas, R. Innate immune recognition of microbial cell wall components and microbial strategies to evade such recognitions. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geijtenbeek, T.B.H.; Gringhuis, S.I. C-type lectin receptors in the control of T helper cell differentiation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.E.; Warris, A.; Ellingsen, E.A.; Jørgensen, P.F.; Flo, T.H.; Espevik, T.; Solberg, R.; Verweij, P.E.; Aasen, A.O. Involvement of CD14 and Toll-Like Receptors in Activation of Human Monocytes by Aspergillus fumigatus Hyphae. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 2402–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellocchio, S.; Montagnoli, C.; Bozza, S.; Gaziano, R.; Rossi, G.; Mambula, S.S.; Vecchi, A.; Mantovani, A.; Levitz, S.M.; Romani, L. The Contribution of the Toll-Like/IL-1 Receptor Superfamily to Innate and Adaptive Immunity to Fungal Pathogens In Vivo. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 3059–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balloy, V.; Si-Tahar, M.; Takeuchi, O.; Philippe, B.; Nahori, M.-A.; Tanguy, M.; Huerre, M.; Akira, S.; Latgé, J.-P.; Chignard, M. Involvement of toll-like receptor 2 in experimental invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 5420–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mambula, S.S.; Sau, K.; Henneke, P.; Golenbock, D.T.; Levitz, S.M. Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling in response to Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 39320–39326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.Y.A.; Vonk, A.G.; Kullberg, B.J.; Verweij, P.E.; Verschueren, I.; van der Meer, J.W.M.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Latgé, J.-P.; Netea, M.G. Aspergillus fumigatus cell wall components differentially modulate host TLR2 and TLR4 responses. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto-Bergter, E.; Figueiredo, R.T. Fungal glycans and the innate immune recognition. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenci, E.; Perito, S.; Enssle, K.H.; Mosci, P.; Latgé, J.P.; Romani, L.; Bistoni, F. Th1 and Th2 cytokines in mice with invasive aspergillosis. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvia Bozza, R.G. Dendritic Cells Transport Conidia and Hyphae of Aspergillus fumigatus from the Airways to the Draining Lymph Nodes and Initiate Disparate Th Responses to the Fungus. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 1362–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Gómez, D.; Domínguez-Soto, A.; Ancochea, J.; Jimenez-Heffernan, J.A.; Leal, J.A.; Corbí, A.L. Dendritic Cell-Specific Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 3-Grabbing Nonintegrin Mediates Binding and Internalization of Aspergillus fumigatus Conidia by Dendritic Cells and Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 5635–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Gómez, D.; Leal, J.A.; Corbí, A.L. DC-SIGN mediates the binding of Aspergillus fumigatus and keratinophylic fungi by human dendritic cells. Immunobiology 2005, 210, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodo, F.; Marradi, M.; Park, J.; Ram, A.F.J.; Penadés, S.; van Die, I.; Tefsen, B. Galactofuranose-Coated Gold Nanoparticles Elicit a Pro-inflammatory Response in Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells and Are Recognized by DC-SIGN. Acs Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reedy, J.L.; Wuethrich, M.; Latgé, J.; Vyas, J.M. Dectin-2 is a Receptor for Galactomannan. In Proceedings of the Advances Against Aspergillosis, Manchester, UK, 3–5 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Xu, X.-Y.; Shao, H.-T.; Su, X.; Wu, X.-D.; Wang, Q.; Shi, Y. Dectin-2 is predominately macrophage restricted and exhibits conspicuous expression during Aspergillus fumigatus invasion in human lung. Cell. Immunol. 2013, 284, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loures, F.V.; Röhm, M.; Lee, C.K.; Santos, E.; Wang, J.P.; Specht, C.A.; Calich, V.L.G.; Urban, C.F.; Levitz, S.M. Recognition of Aspergillus fumigatus Hyphae by Human Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Is Mediated by Dectin-2 and Results in Formation of Extracellular Traps. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazi, U.; Rosas, M.; Singh, S.; Heinsbroek, S.; Haq, I.; Johnson, S.; Brown, G.D.; Williams, D.L.; Taylor, P.R.; Martinez-Pomares, L. Fungal Recognition Enhances Mannose Receptor Shedding through Dectin-1 Engagement. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 7822–7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, T. Potential of lung surfactant proteins, SP-A and SP-D, and mannan binding lectin for therapy and genetic predisposition to allergic and invasive aspergillosis. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2007, 1, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, K.; Tokue, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Takahashi, H.; Watanabe, A.; Fujita, T.; Nukiwa, T. Mannose-binding lectin gene polymorphism is a modulating factor in repeated respiratory infections. Chest 2004, 126, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Crosdale, D.J.; Poulton, K.V.; Ollier, W.E.; Thomson, W.; Denning, D.W. Mannose-binding lectin gene polymorphisms as a susceptibility factor for chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 184, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.S.W.; Rani, M.; Dodagatta-Marri, E.; Ibrahim-Granet, O.; Kishore, U.; Bayry, J.; Latgé, J.-P.; Sahu, A.; Madan, T.; Aimanianda, V. Fungal melanin stimulates surfactant protein D-mediated opsonization of and host immune response to Aspergillus fumigatus spores. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 4901–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.S.W.; Krylov, V.B.; Argunov, D.A.; Karelin, A.A.; Bouchara, J.-P.; Fontaine, T.; Latgé, J.-P.; Nifantiev, N.E. Potential of Chemically Synthesized Oligosaccharides To Define the Carbohydrate Moieties of the Fungal Cell Wall Responsible for the Human Immune Response, Using Aspergillus fumigatus Galactomannan as a Model. mSphere 2020, 5, e00688-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).