Modeling Approaches Reveal New Regulatory Networks in Aspergillus fumigatus Metabolism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cantone, I.; Marucci, L.; Iorio, F.; Ricci, M.A.; Belcastro, V.; Bansal, M.; Santini, S.; di Bernardo, M.; di Bernardo, D.; Cosma, M.P. A yeast synthetic network for in vivo assessment of reverse-engineering and modeling approaches. Cell 2009, 137, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choera, T.; Zelante, T.; Romani, L.; Keller, N.P. A Multifaceted Role of Tryptophan Metabolism and Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Activity in Aspergillus fumigatus-Host Interactions. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, N.P. Fungal secondary metabolism: Regulation, function and drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.M.; Choera, T.; Wiemann, P.; Pisithkul, T.; Amador-Noguez, D.; Keller, N.P. TrpE feedback mutants reveal roadblocks and conduits toward increasing secondary metabolism in Aspergillus fumigatus. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2016, 89, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenas-Huertero, F.; Zaragoza-Ojeda, M.; Sanchez-Alarcon, J.; Milic, M.; Segvic Klaric, M.; Montiel-Gonzalez, J.M.; Valencia-Quintana, R. Involvement of Ahr Pathway in Toxicity of Aflatoxins and Other Mycotoxins. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed-Boussema, I.; Pascussi, J.M.; Zaied, C.; Maurel, P.; Bacha, H.; Hassen, W. Ochratoxin A induces CYP3A4, 2B6, 3A5, 2C9, 1A1, and CYP1A2 gene expression in primary cultured human hepatocytes: A possible activation of nuclear receptors. Drug. Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 35, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neavin, D.R.; Liu, D.; Ray, B.; Weinshilboum, R.M. The Role of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AHR) in Immune and Inflammatory Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuasa, H.J.; Ball, H.J. The evolution of three types of indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenases in fungi with distinct molecular and biochemical characteristics. Gene 2012, 504, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffa, N.; Keller, N.P. A call to arms: Mustering secondary metabolites for success and survival of an opportunistic pathogen. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbach, D.; Costello, J.C.; Kuffner, R.; Vega, N.M.; Prill, R.J.; Camacho, D.M.; Allison, K.R.; Consortium, D.; Kellis, M.; Collins, J.J.; et al. Wisdom of crowds for robust gene network inference. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feist, A.M.; Herrgard, M.J.; Thiele, I.; Reed, J.L.; Palsson, B.O. Reconstruction of biochemical networks in microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, N.; Linial, M.; Nachman, I.; Pe’er, D. Using Bayesian networks to analyze expression data. J. Comput. Biol. 2000, 7, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wiener, M.C.; Zhang, C.; Fridman, A.; Minch, E.; Lum, P.Y.; Sachs, J.R.; Schadt, E.E. Increasing the power to detect causal associations by combining genotypic and expression data in segregating populations. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2007, 3, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, K.; Perez, O.; Pe’er, D.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Nolan, G.P. Causal protein-signaling networks derived from multiparameter single-cell data. Science 2005, 308, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, O.; Yoshida, R.; Imoto, S.; Yamaguchi, R.; Higuchi, T.; Charnock-Jones, D.S.; Print, C.; Miyano, S. Statistical inference of transcriptional module-based gene networks from time course gene expression profiles by using state space models. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmulevich, I.; Dougherty, E.R.; Kim, S.; Zhang, W. Probabilistic Boolean Networks: A rule-based uncertainty model for gene regulatory networks. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, C.; Perkins, E.J.; Gong, P.; Deng, Y. Comparison of probabilistic Boolean network and dynamic Bayesian network approaches for inferring gene regulatory networks. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8 (Suppl. 7), S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acerbi, E.; Zelante, T.; Narang, V.; Stella, F. Gene network inference using continuous time Bayesian networks: A comparative study and application to Th17 cell differentiation. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, J. An introduction to causal inference. Int. J. Biostat. 2010, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, F.M.; Gomez-Vela, F. Computational methods for Gene Regulatory Networks reconstruction and analysis: A review. Artif. Intell. Med. 2019, 95, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acerbi, E.; Vigano, E.; Poidinger, M.; Mortellaro, A.; Zelante, T.; Stella, F. Continuous time Bayesian networks identify Prdm1 as a negative regulator of TH17 cell differentiation in humans. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, K.; Keller, N.P. Genetic involvement of a cAMP-dependent protein kinase in a G protein signaling pathway regulating morphological and chemical transitions in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics 2001, 157, 591–600. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva Ferreira, M.E.; Kress, M.R.; Savoldi, M.; Goldman, M.H.; Hartl, A.; Heinekamp, T.; Brakhage, A.A.; Goldman, G.H. The akuB(KU80) mutant deficient for nonhomologous end joining is a powerful tool for analyzing pathogenicity in Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 2006, 5, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Szewczyk, E.; Nayak, T.; Oakley, C.E.; Edgerton, H.; Xiong, Y.; Taheri-Talesh, N.; Osmani, S.A.; Oakley, B.R. Fusion PCR and gene targeting in Aspergillus nidulans. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 3111–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, F.Y.; Sanchez, J.F.; Wang, C.C.; Keller, N.P. Toward awakening cryptic secondary metabolite gene clusters in filamentous fungi. Methods Enzymol. 2012, 517, 303–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.K.; Park, H.J.; Macleod, M.; Chandler, P.; Munn, D.H.; Mellor, A.L. Tryptophan deprivation sensitizes activated T cells to apoptosis prior to cell division. Immunology 2002, 107, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessede, A.; Gargaro, M.; Pallotta, M.T.; Matino, D.; Servillo, G.; Brunacci, C.; Bicciato, S.; Mazza, E.M.; Macchiarulo, A.; Vacca, C.; et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor control of a disease tolerance defence pathway. Nature 2014, 511, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A. Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism: Regulatory and Functional Aspects. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2017, 10, 1178646917691938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, H.J.; Jusof, F.F.; Bakmiwewa, S.M.; Hunt, N.H.; Yuasa, H.J. Tryptophan-catabolizing enzymes—Party of three. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindo, M.; Costanzi, E.; Pieroni, M.; Costantini, C.; Annunziato, G.; Bruno, A.; Keller, N.P.; Romani, L.; Zelante, T.; Cellini, B. Biochemical Characterization of Aspergillus fumigatus AroH, a Putative Aromatic Amino Acid Aminotransferase. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, D.S.; Leveau, J.H.; Meyer, K.M. Modeling microbial growth and dynamics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8831–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bower, D.S.; Mengersen, K.; Alford, R.A.; Schwarzkopf, L. Using a Bayesian network to clarify areas requiring research in a host-pathogen system. Conserv. Biol. 2017, 31, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
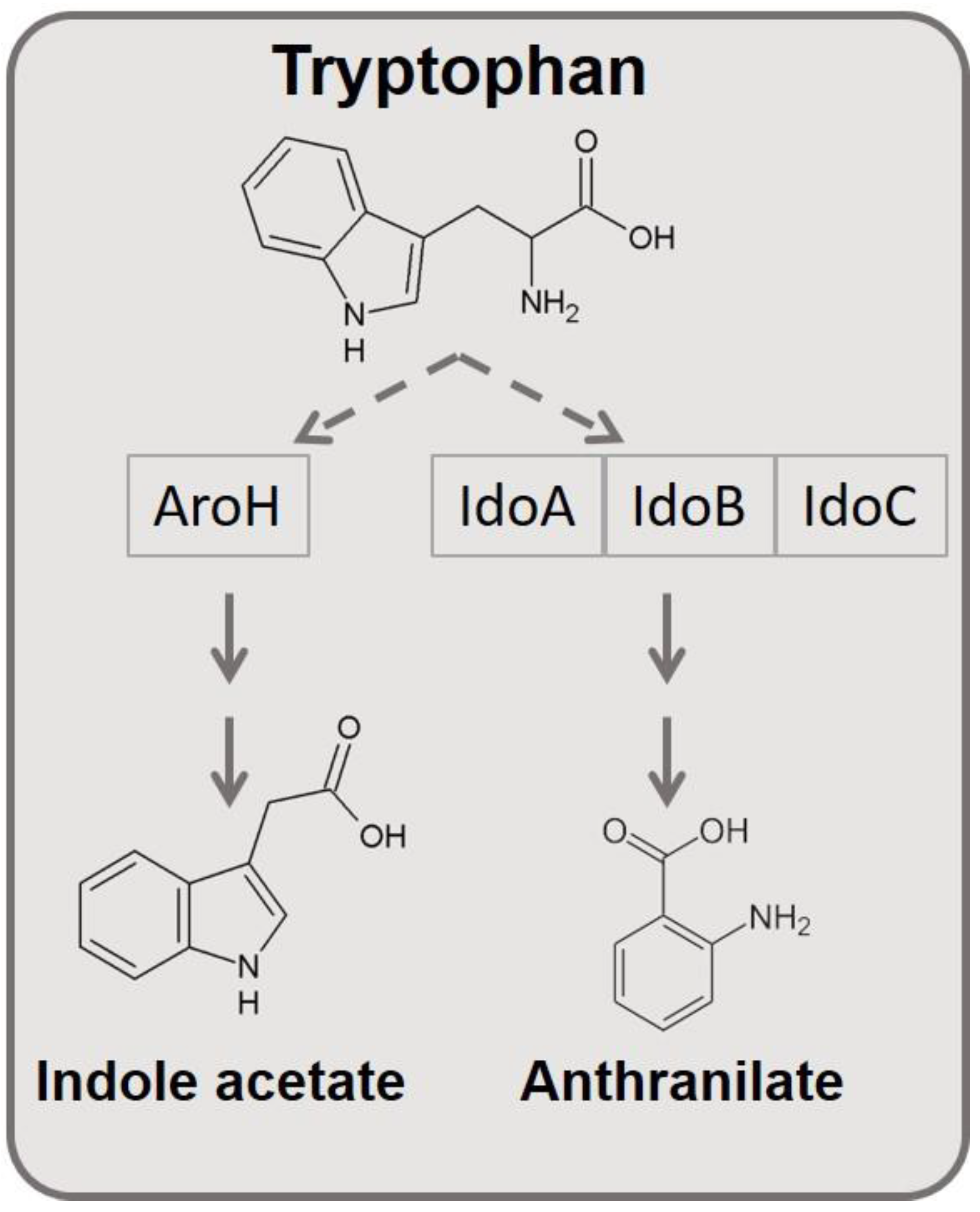
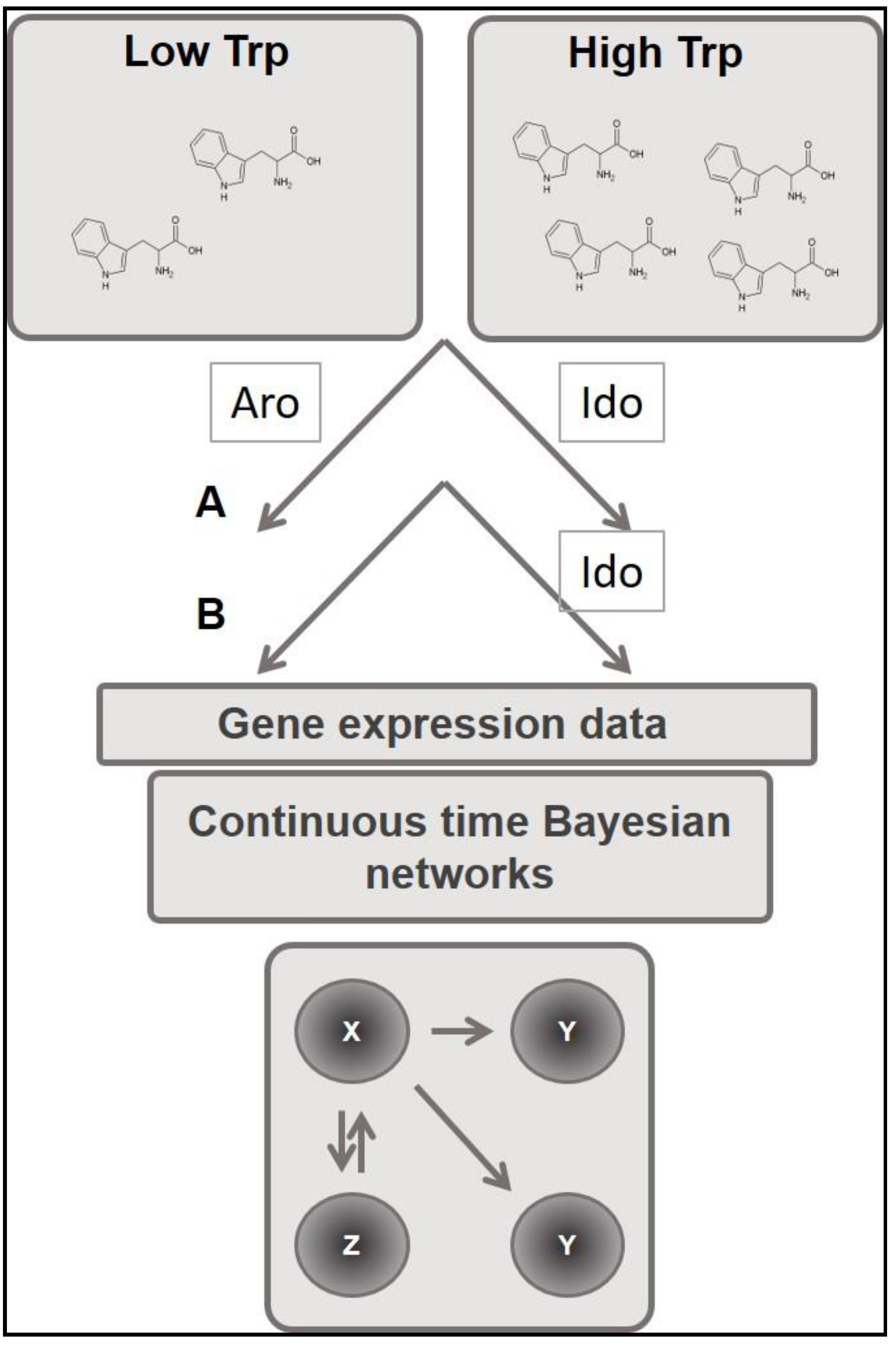
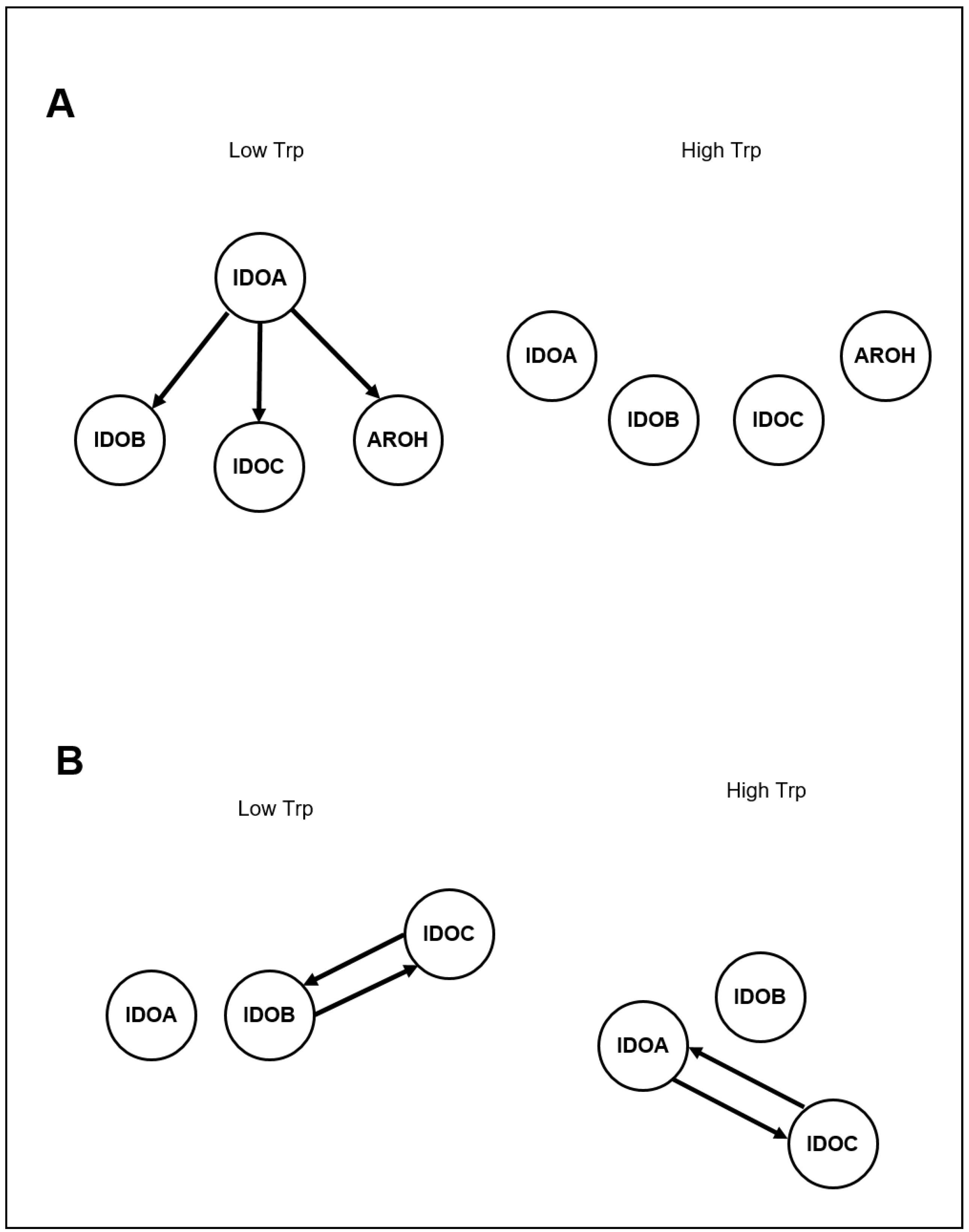
| ID | Strain | Genotype | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CEA17 | CEA17 pyrG- KU80 | pyrG1, ∆akuB::pyrG, pyrG1 | [23] |
| TTC 22.7 | ∆aroH | pyrG1, ∆akuB::pyrG, pyrG1, ∆AFUB_029280:pyrG | This study |
| Gene | Primers Sequence (5′-3′) | Annealing Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| 18S | Sense→GAGCCGATAGTCCCCCTAAG αSense→ATGGCCGTTCTTAGTTGGTG | 58 |
| aroH | Sense→AAAGTCCCGACAGCAATCTACA αSense→TGGGACTTTCACGCTAATCTCT | 60 |
| idoA | Sense→ATGCCTGTCTCGCTATGC αSense→CTCGGGTGTACGGTTTCG | 55 |
| idoB | Sense→AGGAAGTTGTCGCTGATTTACC αSense→ATGCTCGCCGCCATTCTG | 54 |
| idoC | Sense→TCAGCCAGGATGGCAGTC αSense→TCGTCAGTCAGGTCAGGAAG | 55 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acerbi, E.; Hortova-Kohoutkova, M.; Choera, T.; Keller, N.; Fric, J.; Stella, F.; Romani, L.; Zelante, T. Modeling Approaches Reveal New Regulatory Networks in Aspergillus fumigatus Metabolism. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6030108
Acerbi E, Hortova-Kohoutkova M, Choera T, Keller N, Fric J, Stella F, Romani L, Zelante T. Modeling Approaches Reveal New Regulatory Networks in Aspergillus fumigatus Metabolism. Journal of Fungi. 2020; 6(3):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6030108
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcerbi, Enzo, Marcela Hortova-Kohoutkova, Tsokyi Choera, Nancy Keller, Jan Fric, Fabio Stella, Luigina Romani, and Teresa Zelante. 2020. "Modeling Approaches Reveal New Regulatory Networks in Aspergillus fumigatus Metabolism" Journal of Fungi 6, no. 3: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6030108
APA StyleAcerbi, E., Hortova-Kohoutkova, M., Choera, T., Keller, N., Fric, J., Stella, F., Romani, L., & Zelante, T. (2020). Modeling Approaches Reveal New Regulatory Networks in Aspergillus fumigatus Metabolism. Journal of Fungi, 6(3), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6030108








