Aspergillus fumigatus Protease Alkaline Protease 1 (Alp1): A New Therapeutic Target for Fungal Asthma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Role of Fungal Proteases in Initiation of Allergic Airway Inflammation
2.1. A Fungal Protease Allergen Infiltrates the Bronchial Submucosa in Asthma
2.2. Mechanisms Underlying Allergen Protease Sensing and Tissue Deposition
2.3. Alp1 as a Potential Biomarker of Fungal Asthma
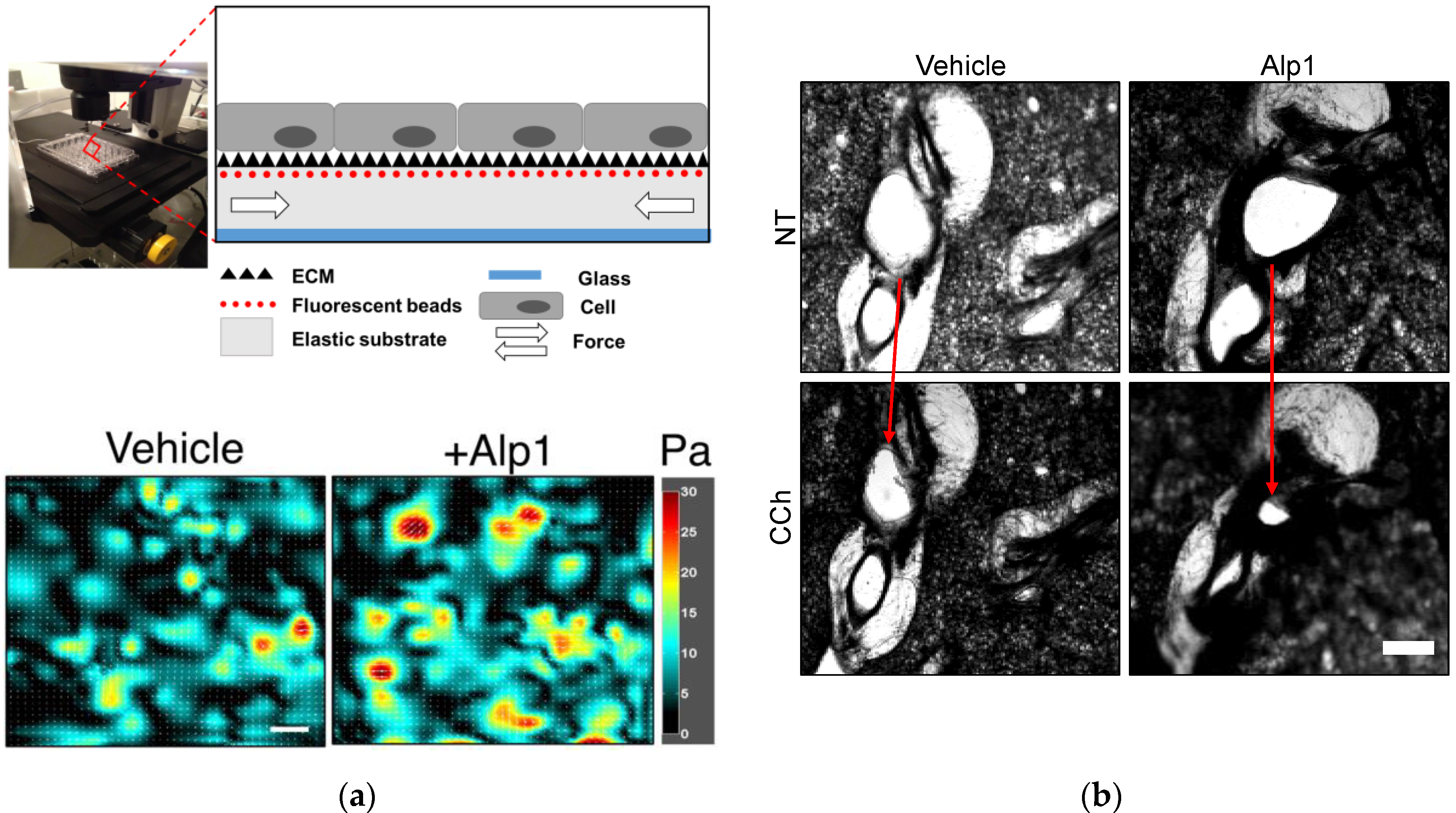
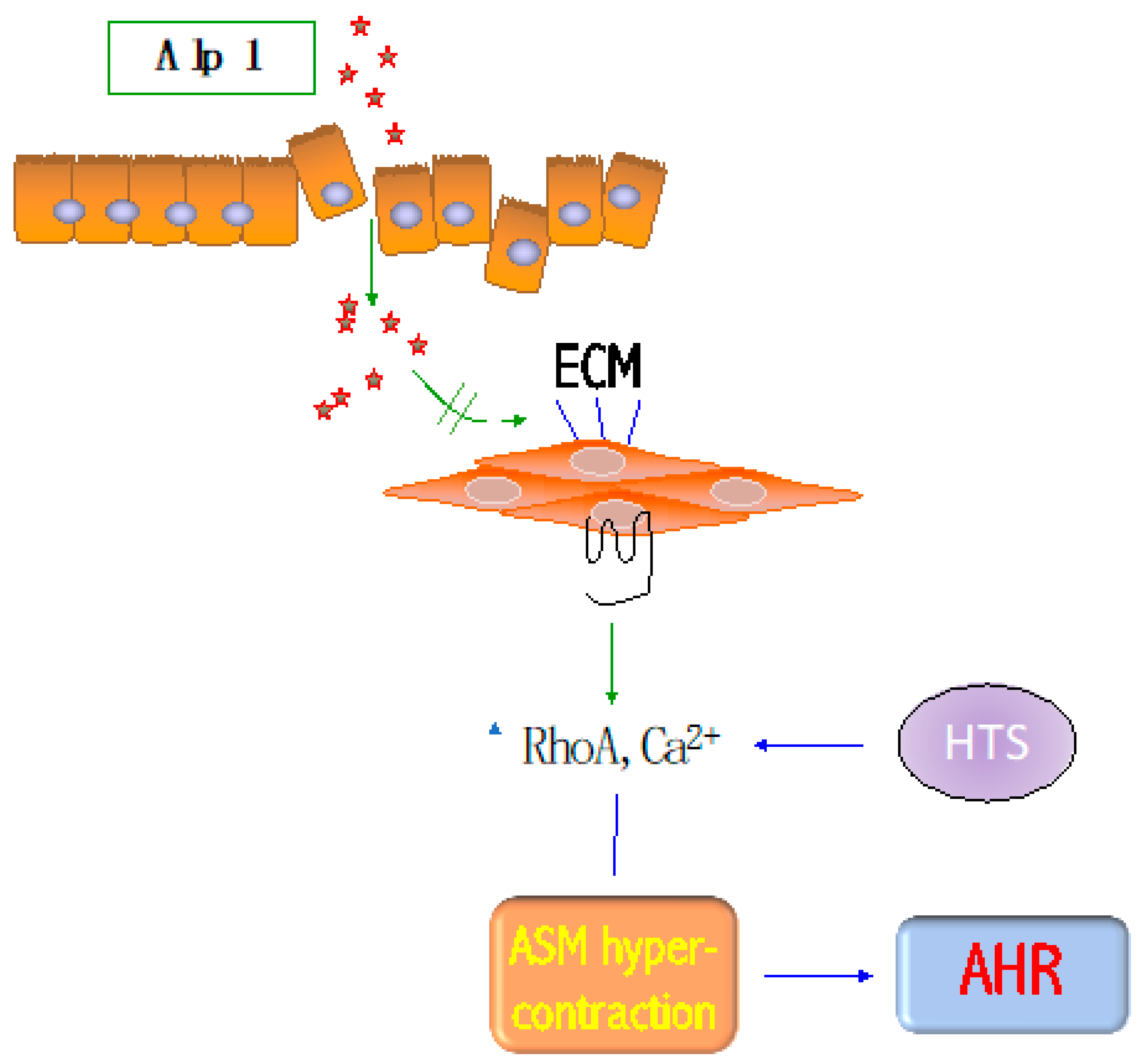
3. Alp1 Induces Airway Smooth Muscle Contraction
4. Alp1 Induces Inflammation and AHR In Vivo
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- To, T.; Stanojevic, S.; Moores, G.; Gershon, A.S.; Bateman, E.D.; Cruz, A.A.; Boulet, L.P. Global asthma prevalence in adults: Findings from the cross-sectional world health survey. Bmc Public Health 2012, 12, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Oriss, T.B.; Wenzel, S.E. Emerging molecular phenotypes of asthma. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2015, 308, L130–L140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Denning, D.W.; Pashley, C.; Hartl, D.; Wardlaw, A.; Godet, C.; Del Giacco, S.; Delhaes, L.; Sergejeva, S. Fungal allergy in asthma-state of the art and research needs. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2014, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Hoselton, S.A.; Schuh, J.M. Allergic Inflammation in Aspergillus fumigatus-Induced Fungal Asthma. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolnough, K.F.; Richardson, M.; Newby, C.; Craner, M.; Bourne, M.; Monteiro, W.; Siddiqui, S.; Bradding, P.; Pashley, C.H.; Wardlaw, A.J. The relationship between biomarkers of fungal allergy and lung damage in asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 47, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrant, J.; Brice, H.; Fowler, S.; Niven, R. Fungal sensitisation in severe asthma is associated with the identification of Aspergillus fumigatus in sputum. J. Asthma Off. J. Assoc. Care Asthma 2016, 53, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wechsler, M.E. Current and Emerging Biologic Therapies for Asthma and COPD. Respir. Care 2018, 63, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, R.B. Treatment options in severe fungal asthma and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 1487–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parulekar, A.D.; Diamant, Z.; Hanania, N.A. Antifungals in severe asthma. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2015, 21, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georas, S.N.; Rezaee, F. Epithelial barrier function: At the front line of asthma immunology and allergic airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, Y.S. Airway smooth muscle in airway reactivity and remodeling: What have we learned? Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2013, 305, L912–L933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosens, R.; Grainge, C. Bronchoconstriction and airway biology: Potential impact and therapeutic opportunities. Chest 2015, 147, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomee, J.F.; Wierenga, A.T.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Kauffman, H.K. Proteases from Aspergillus fumigatus induce release of proinflammatory cytokines and cell detachment in airway epithelial cell lines. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 176, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, T.V.; Jadoun, J.; Mittelman, L.; Hirschberg, K.; Osherov, N. Involvement of secreted Aspergillus fumigatus proteases in disruption of the actin fiber cytoskeleton and loss of focal adhesion sites in infected A549 lung pneumocytes. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 1965–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, H.Y.; Tam, M.F.; Chou, H.; Peng, H.J.; Su, S.N.; Perng, D.W.; Shen, H.D. Pen ch 13 allergen induces secretion of mediators and degradation of occludin protein of human lung epithelial cells. Allergy 2006, 61, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kale, S.L.; Agrawal, K.; Gaur, S.N.; Arora, N. Cockroach protease allergen induces allergic airway inflammation via epithelial cell activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, T.; Seyedmousavi, S.; Sugui, J.A.; Balenga, N.; Zhao, M.; Kwon Chung, K.J.; Biardel, S.; Laviolette, M.; Druey, K.M. Aspergillus fumigatus alkaline protease 1 (Alp1/Asp f13) in the airways correlates with asthma severity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 423–425 e427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balenga, N.A.; Klichinsky, M.; Xie, Z.; Chan, E.C.; Zhao, M.; Jude, J.; Laviolette, M.; Panettieri, R.A., Jr.; Druey, K.M. A fungal protease allergen provokes airway hyper-responsiveness in asthma. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siezen, R.J.; de Vos, W.M.; Leunissen, J.A.; Dijkstra, B.W. Homology modelling and protein engineering strategy of subtilases, the family of subtilisin-like serine proteinases. Protein Eng. 1991, 4, 719–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesner, D.L.; Merkhofer, R.M.; Ober, C.; Kujoth, G.C.; Niu, M.; Keller, N.P.; Gern, J.E.; Brockman-Schneider, R.A.; Evans, M.D.; Jackson, D.J.; et al. Club Cell TRPV4 Serves as a Damage Sensor Driving Lung Allergic Inflammation. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 614–628 e616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedstrom, L. Serine protease mechanism and specificity. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4501–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florsheim, E.; Yu, S.; Bragatto, I.; Faustino, L.; Gomes, E.; Ramos, R.N.; Barbuto, J.A.; Medzhitov, R.; Russo, M. Integrated innate mechanisms involved in airway allergic inflammation to the serine protease subtilisin. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 4621–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Stacey, M.A.; Schmidt, M.; Mori, L.; Mattoli, S. Interaction of mite allergens Der p3 and Der p9 with protease-activated receptor-2 expressed by lung epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, L.L.; Perng, D.W.; Yu, C.H.; Su, S.N.; Chow, L.P. Mold allergen, pen C 13, induces IL-8 expression in human airway epithelial cells by activating protease-activated receptor 1 and 2. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5237–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, H.F.; Tamm, M.; Timmerman, J.A.; Borger, P. House dust mite major allergens Der p 1 and Der p 5 activate human airway-derived epithelial cells by protease-dependent and protease-independent mechanisms. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2006, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, M.C.; Nichols, H.L.; Polley, D.; Saifeddine, M.; Pal, K.; Lee, K.; Wilson, E.H.; Daines, M.O.; Hollenberg, M.D.; Boitano, S.; et al. Protease-activated receptor-2 signaling through beta-arrestin-2 mediates Alternaria alkaline serine protease-induced airway inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2018, 315, L1042–L1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.S.; Redes, J.L.; Balenga, N.; McCullough, M.; Fuentes, N.; Gokhale, A.; Koziol-White, C.; Jude, J.A.; Madigan, L.A.; Chan, E.C.; et al. RGS4 promotes allergen- and aspirin-associated airway hyper-responsiveness by inhibiting PGE2 biosynthesis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.; Hamidi, F.; Leborgne, R.; Beau, R.; Castier, Y.; Mordant, P.; Boukkerou, A.; Latge, J.P.; Pretolani, M. Penetration of the Human Pulmonary Epithelium by Aspergillus fumigatus Hyphae. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sestier, M.; Pineau, L.; Cartier, A.; Martin, R.R.; Malo, J.L. Bronchial responsiveness to methacholine and effects of respiratory maneuvers. J. Appl. Physiol. Respir. Env. Exerc. Physiol. 1984, 56, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbetile, J.; Fairs, A.; Desai, D.; Hargadon, B.; Bourne, M.; Mutalithas, K.; Edwards, R.; Morley, J.P.; Monteiro, W.R.; Kulkarni, N.S.; et al. Isolation of filamentous fungi from sputum in asthma is associated with reduced post-bronchodilator FEV1. Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 42, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redes, J.L.; Basu, T.; Ram-Mohan, S.; Ghosh, C.C.; Chan, E.C.; Sek, A.C.; Zhao, M.; Krishnan, R.; Rosenberg, H.F.; Druey, K.M. Aspergillus fumigatus-Secreted Alkaline Protease 1 Mediates Airways Hyperresponsiveness in Severe Asthma. Immunohorizons 2019, 3, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, Y.; Gunst, S.J. The Small GTPase RhoA Regulates the Contraction of Smooth Muscle Tissues by Catalyzing the Assembly of Cytoskeletal Signaling Complexes at Membrane Adhesion Sites. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 33996–34008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Bhetwal, B.P.; Gunst, S.J. Rho kinase collaborates with p21-activated kinase to regulate actin polymerization and contraction in airway smooth muscle. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 3617–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.Y.; Zhou, E.H.; Tambe, D.; Chen, B.; Lavoie, T.; Dowell, M.; Simeonov, A.; Maloney, D.J.; Marinkovic, A.; Tschumperlin, D.J.; et al. High-throughput screening for modulators of cellular contractile force. Integr. Biol. Quant. Biosci. Nano Macro 2015, 7, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshie, H.; Koushki, N.; Kaviani, R.; Tabatabaei, M.; Rajendran, K.; Dang, Q.; Husain, A.; Yao, S.; Li, C.; Sullivan, J.K.; et al. Traction Force Screening Enabled by Compliant PDMS Elastomers. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 2194–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RamMohan, S.; Bai, Y.; Schaible, N.; Ehrlicher, A.J.; Cook, D.P.; Suki, B.; Stoltz, D.A.; Solway, J.; Ai, X.; Krishnan, R. Tissue traction microscopy to quantify muscle contraction within precision-cut lung slices. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Hoymann, H.G. Invasive and noninvasive lung function measurements in rodents. J. Pharm. Toxicol. Methods 2007, 55, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, G.; Riccio, A.M. Immune induction of airway remodeling. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 46, 101346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.C.; Chuang, J.G.; Su, Y.Y.; Chiang, B.L.; Lin, Y.S.; Chow, L.P. The protease allergen Pen c 13 induces allergic airway inflammation and changes in epithelial barrier integrity and function in a murine model. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 26667–26679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukreja, N.; Sridhara, S.; Singh, B.P.; Arora, N. Effect of proteolytic activity of Epicoccum purpurascens major allergen, Epi p 1 in allergic inflammation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 154, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraishi, Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yoshizaki, T.; Nambu, A.; Shimura, E.; Takamori, A.; Narushima, S.; Nakanishi, W.; Asada, Y.; Numata, T.; et al. IL-33, IL-25 and TSLP contribute to development of fungal-associated protease-induced innate-type airway inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 18052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millien, V.O.; Lu, W.; Shaw, J.; Yuan, X.; Mak, G.; Roberts, L.; Song, L.Z.; Knight, J.M.; Creighton, C.J.; Luong, A.; et al. Cleavage of fibrinogen by proteinases elicits allergic responses through Toll-like receptor 4. Science 2013, 341, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.S.; Bai, T.R.; Bates, J.H.; Black, J.L.; Brown, R.H.; Brusasco, V.; Chitano, P.; Deng, L.; Dowell, M.; Eidelman, D.H.; et al. Airway smooth muscle dynamics: A common pathway of airway obstruction in asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 834–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crameri, R.; Garbani, M.; Rhyner, C.; Huitema, C. Fungi: The neglected allergenic sources. Allergy 2014, 69, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, A.; Schneider, P.; Wally, V.; Breitenbach, M.; Simon-Nobbe, B. Sensitization to fungi: Epidemiology, comparative skin tests, and IgE reactivity of fungal extracts. Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 33, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| FEV1 > 80% | FEV1 < 80% | |
|---|---|---|
| No. | 17 | 18 |
| Age ((mean, range,yr.) ±.) * | 32.7 (18−56) | 46 (23−68) |
| Sex (M/F) | 8/9 | 7/11 |
| Af sensitivity ** | 9/17 | 7/18 |
| Inhaled CCS #& | 958.3 | 1656 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Druey, K.M.; McCullough, M.; Krishnan, R. Aspergillus fumigatus Protease Alkaline Protease 1 (Alp1): A New Therapeutic Target for Fungal Asthma. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6020088
Druey KM, McCullough M, Krishnan R. Aspergillus fumigatus Protease Alkaline Protease 1 (Alp1): A New Therapeutic Target for Fungal Asthma. Journal of Fungi. 2020; 6(2):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6020088
Chicago/Turabian StyleDruey, Kirk M., Morgan McCullough, and Ramaswamy Krishnan. 2020. "Aspergillus fumigatus Protease Alkaline Protease 1 (Alp1): A New Therapeutic Target for Fungal Asthma" Journal of Fungi 6, no. 2: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6020088
APA StyleDruey, K. M., McCullough, M., & Krishnan, R. (2020). Aspergillus fumigatus Protease Alkaline Protease 1 (Alp1): A New Therapeutic Target for Fungal Asthma. Journal of Fungi, 6(2), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6020088




