Role of Hydrophobins in Aspergillus fumigatus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Sequence Analysis
2.3. Gene Expression Quantification
2.4. Mutant Constructions
2.5. Localization of Hydrophobins
2.5.1. RodC-Flag Construction
2.5.2. Recombinant RodA, RodB, and RodF
2.5.3. Production of Polyclonal Antisera against RodA, RodB, and RodF
2.6. Conidia Permeabilization
2.7. FITC Labeling, Immunofluorescence, and Immunoblotting
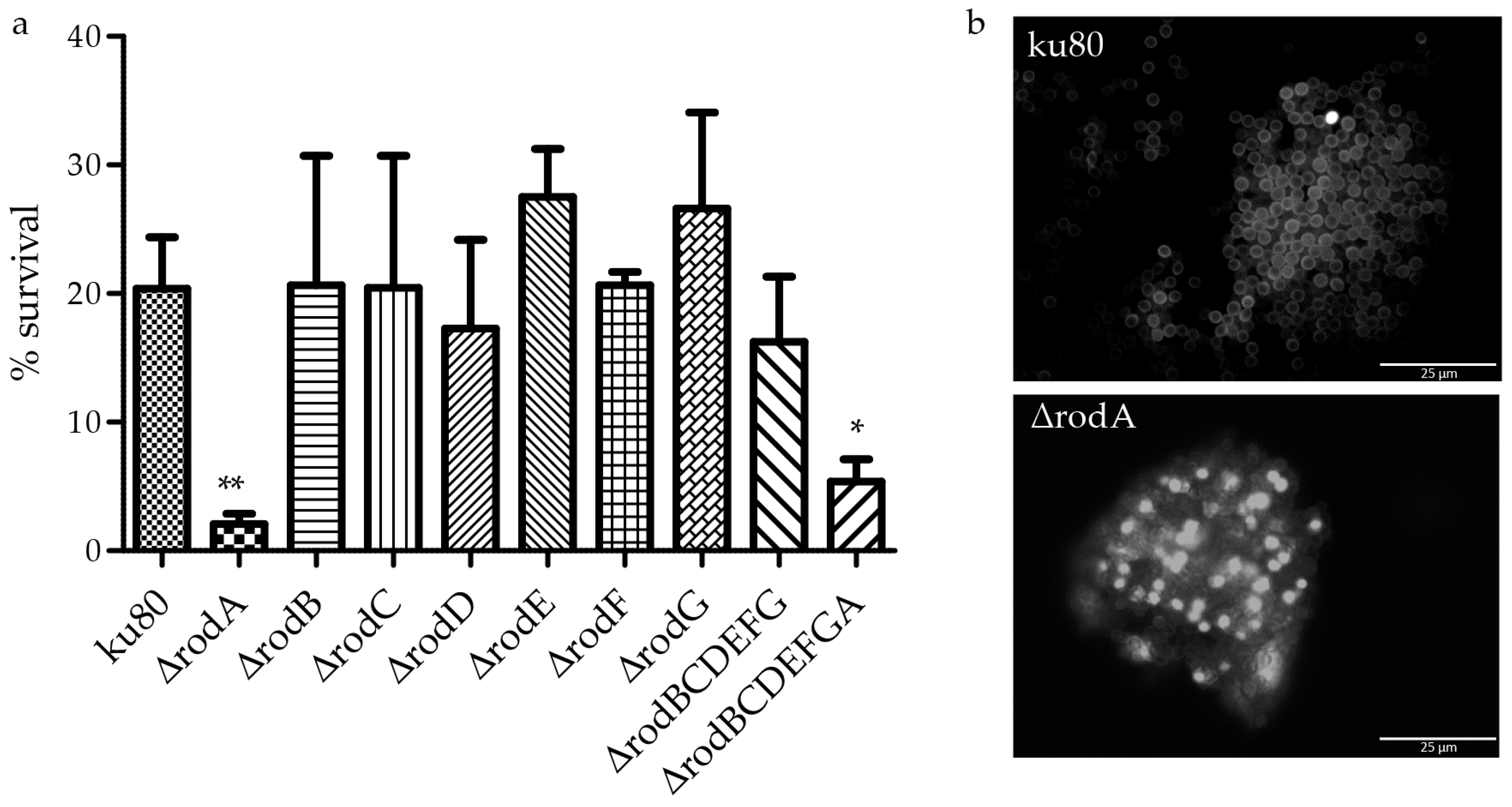
2.8. Conidiation Measurement and Survival
2.9. Hydrophobicity Measurements
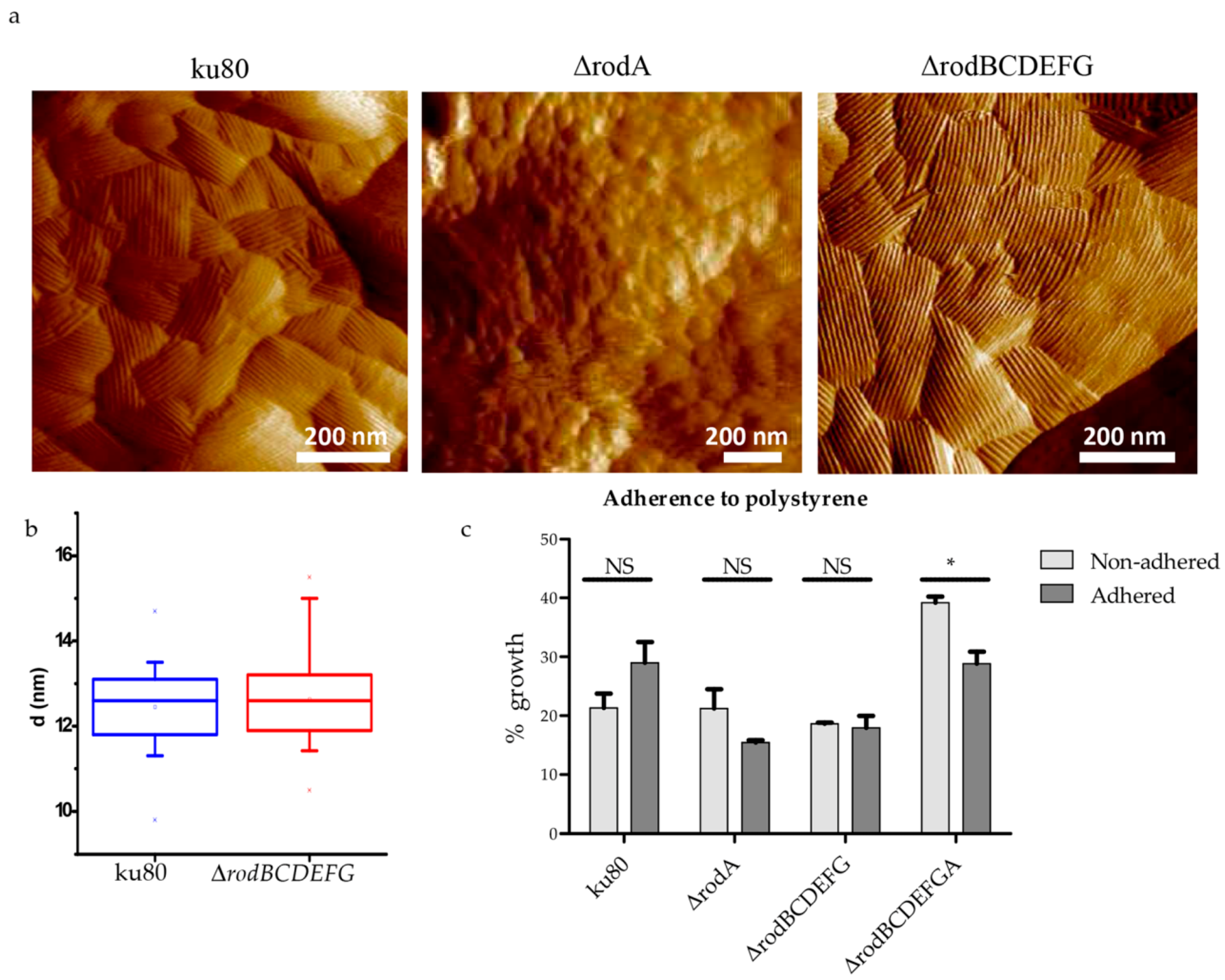
2.10. Analysis of the Conidial Surface by Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.11. Adherence Assays
2.12. Resistance of Conidia to Glass Beads Disruption
2.13. Drug Susceptibility Testing
2.14. Aerial Static Biofilm and Shaken Submerged Conditions
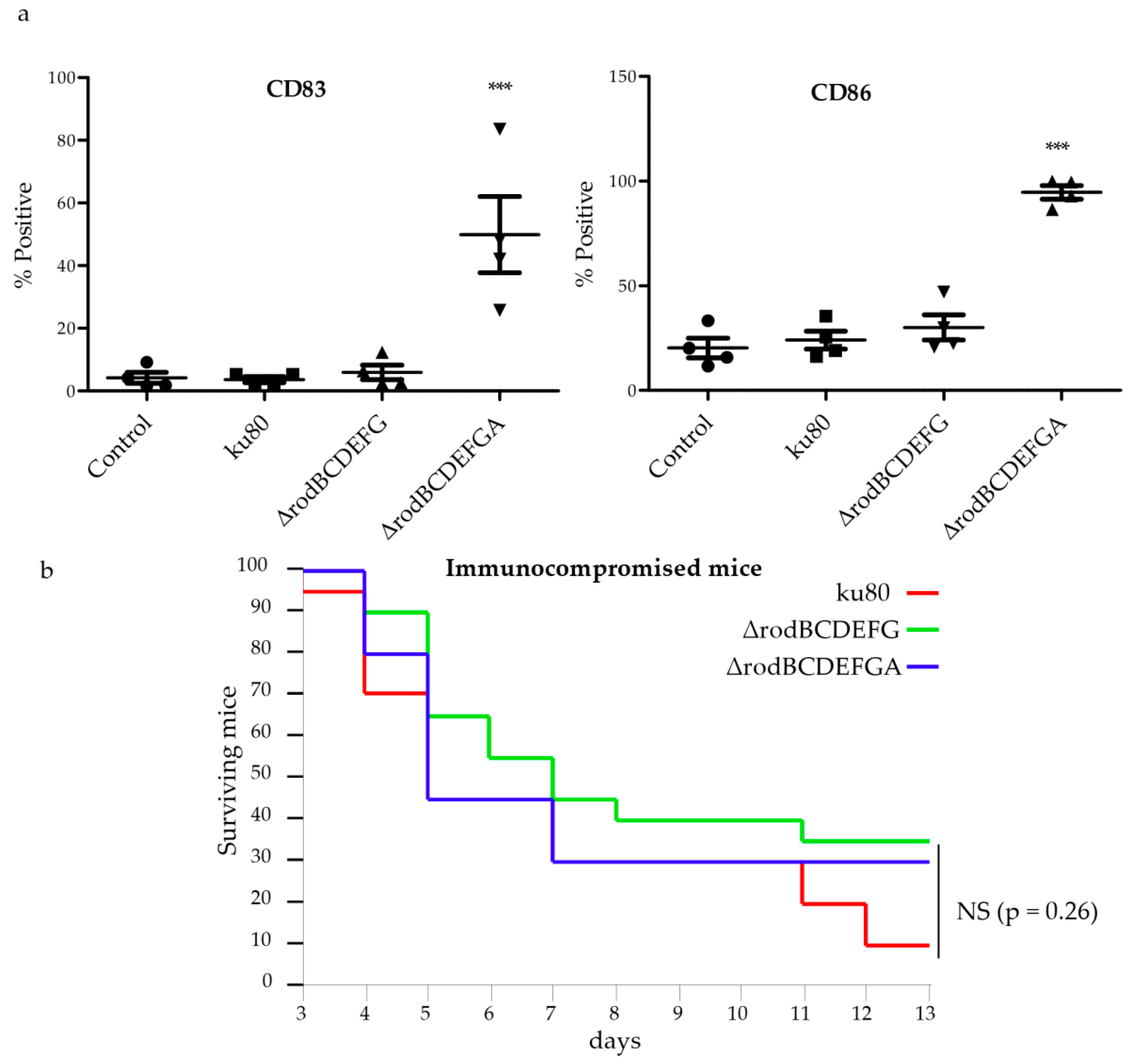
2.15. Generation and Culture of Human Dendritic Cells
2.16. Virulence Assays in Mice
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Analysis
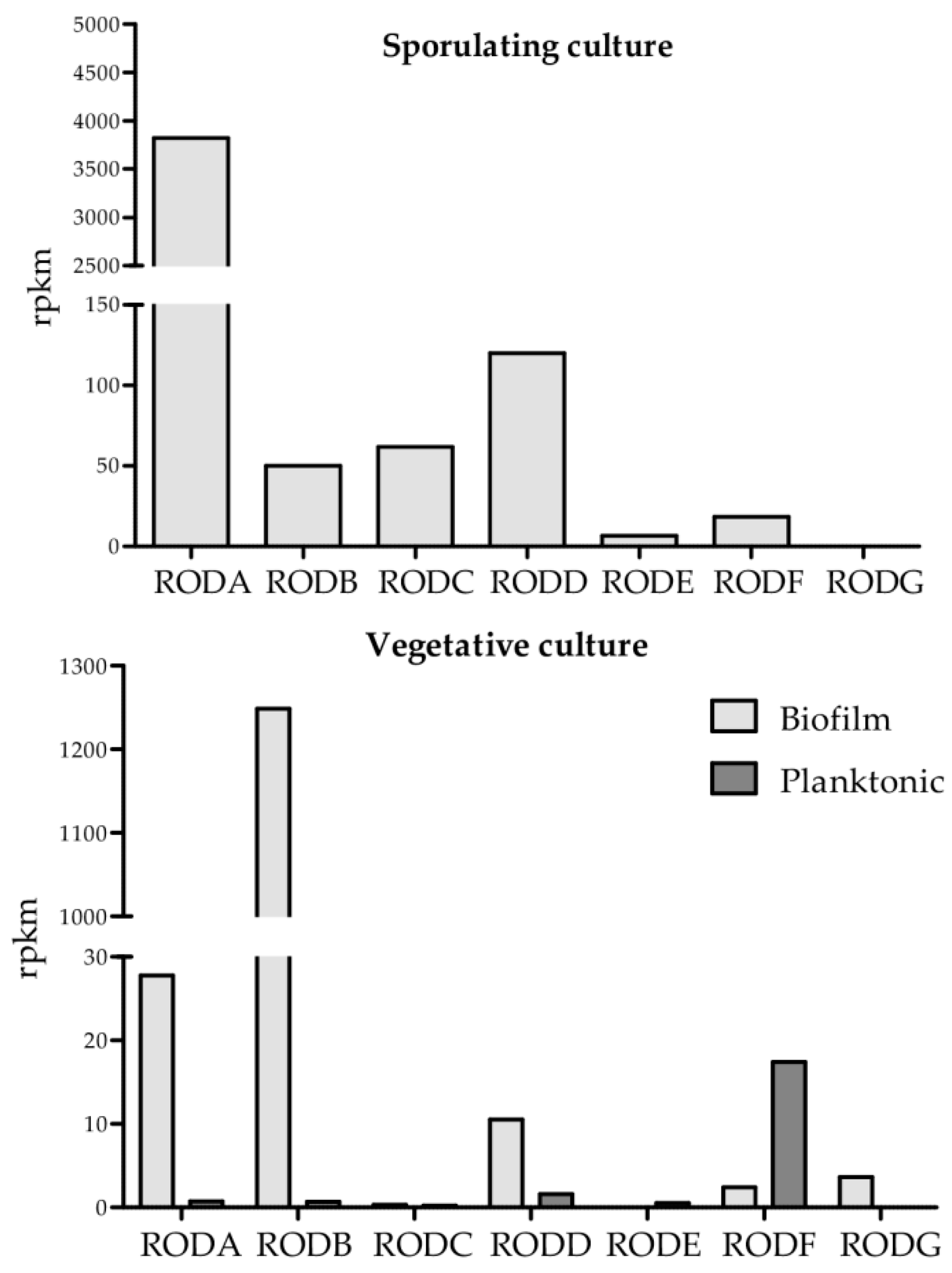
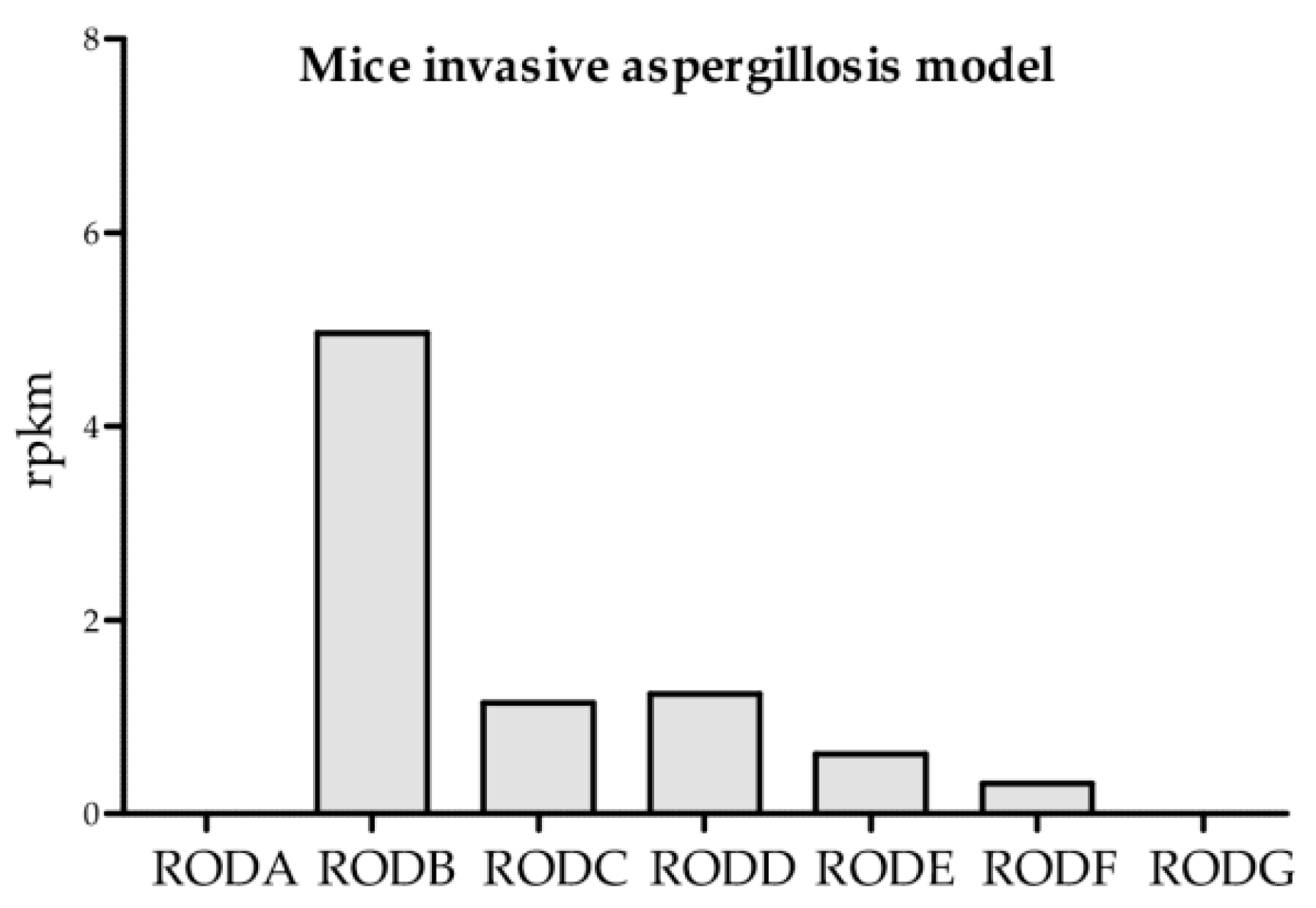
3.2. Expression Analysis
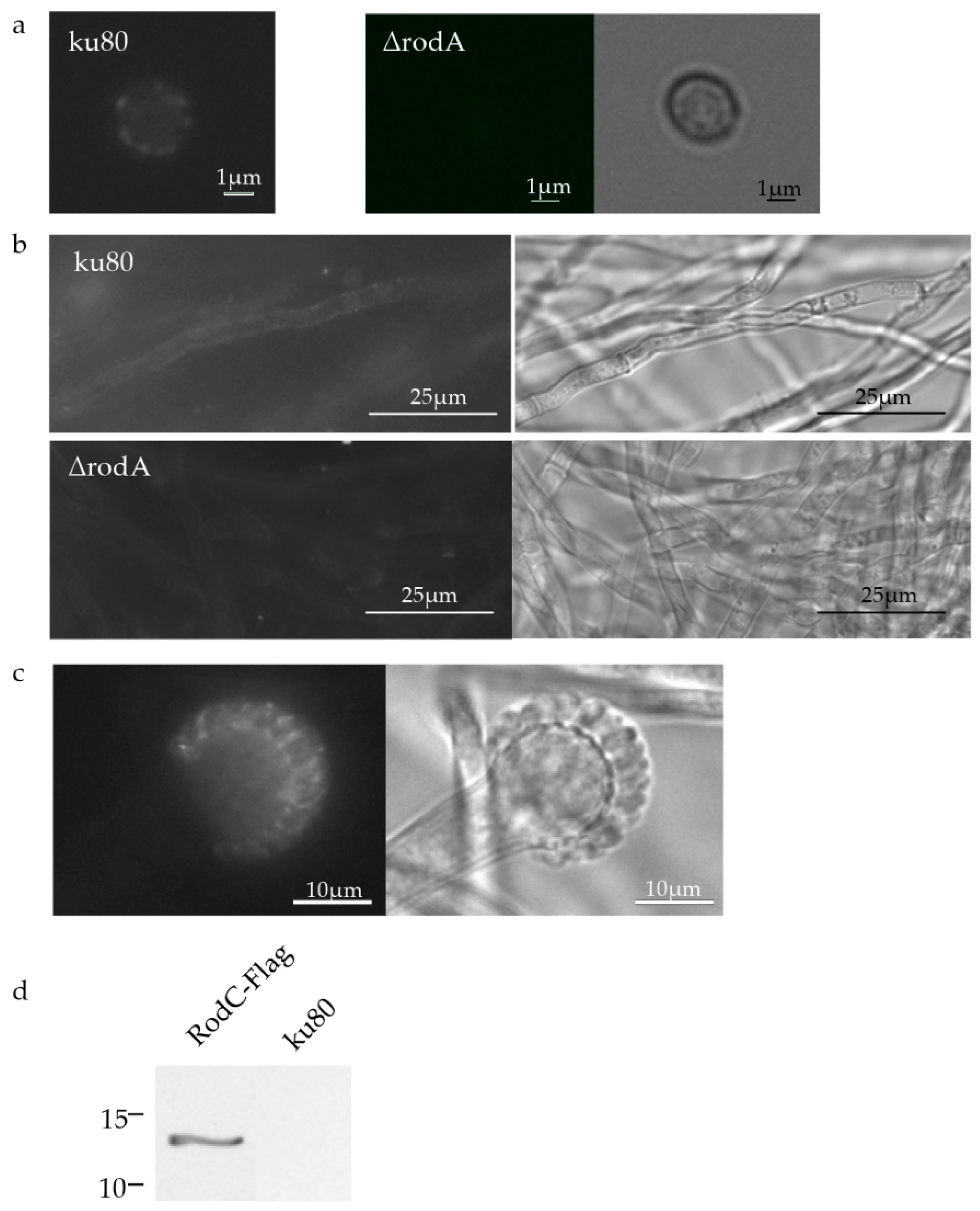
3.3. Localization of Hydrophobins
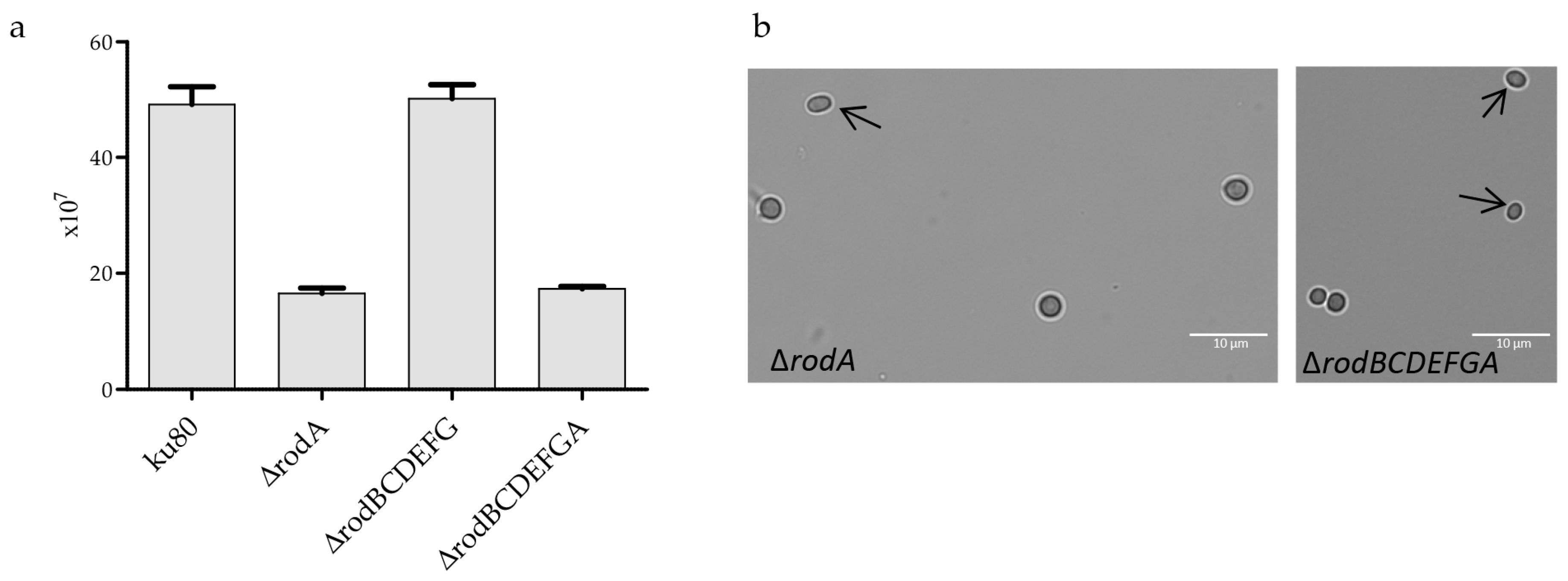
3.4. Hydrophobin Mutant Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sunde, M.; Kwan, A.H.Y.; Templeton, M.D.; Beever, R.E.; Mackay, J.P. Structural analysis of hydrophobins. Micron 2008, 39, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, B.G.; Andersen, M.R.; Pedersen, M.H.; Frisvad, J.C.; Søndergaard, I. Hydrophobins from Aspergillus species cannot be clearly divided into two classes. BMC Res. Notes 2010, 3, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wessels, J.G. Hydrophobins: Proteins that change the nature of the fungal surface. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 1997, 38, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Littlejohn, K.A.; Hooley, P.; Cox, P.W. Bioinformatics predicts diverse Aspergillus hydrophobins with novel properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latgé, J.P. Aspergillus fumigatus and aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 310–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paris, S.; Debeaupuis, J.-P.; Crameri, R.; Carey, M.; Charlès, F.; Prévost, M.C.; Schmitt, C.; Philippe, B.; Latgé, J.P. Conidial hydrophobins of Aspergillus fumigatus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimanianda, V.; Bayry, J.; Bozza, S.; Kniemeyer, O.; Perruccio, K.; Elluru, S.R.; Clavaud, C.; Paris, S.; Brakhage, A.A.; Kaveri, S.V.; et al. Surface hydrophobin prevents immune recognition of airborne fungal spores. Nature 2009, 460, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerqueira, G.C.; Arnaud, M.B.; Inglis, D.O.; Skrzypek, M.S.; Binkley, G.; Simison, M.; Miyasato, S.R.; Binkley, J.; Orvis, J.; Shah, P.; et al. The Aspergillus Genome Database: Multispecies curation and incorporation of RNA-Seq data to improve structural gene annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D705–D710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, R.; Ansari, F.A.; Raghunandanan, M.V.; Ramachandran, S. FungalRV: Adhesin prediction and immunoinformatics portal for human fungal pathogens. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thau, N.; Monod, M.; Crestani, B.; Rolland, C.; Tronchin, G.; Latgé, J.P.; Paris, S. Rodletless mutants of Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 4380–4388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dague, E.; Alsteens, D.; Latgé, J.-P.; Dufrêne, Y.F. High-resolution cell surface dynamics of germinating Aspergillus fumigatus conidia. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Ferreira, M.E.; Kress, M.R.V.Z.; Savoldi, M.; Goldman, M.H.S.; Härtl, A.; Heinekamp, T.; Brakhage, A.A.; Goldman, G.H. The akuBKU80 mutant deficient for nonhomologous end joining is a powerful tool for analyzing pathogenicity in Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 2006, 5, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briard, B.; Bomme, P.; Lechner, B.E.; Mislin, G.L.A.; Lair, V.; Prévost, M.-C.; Latgé, J.-P.; Haas, H.; Beauvais, A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa manipulates redox and iron homeostasis of its microbiota partner Aspergillus fumigatus via phenazines. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauvais, A.; Schmidt, C.; Guadagnini, S.; Roux, P.; Perret, E.; Henry, C.; Paris, S.; Mallet, A.; Prévost, M.-C.; Latgé, J.P. An extracellular matrix glues together the aerial-grown hyphae of Aspergillus fumigatus. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1588–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayry, J.; Beaussart, A.; Dufrêne, Y.F.; Sharma, M.; Bansal, K.; Kniemeyer, O.; Aimanianda, V.; Brakhage, A.A.; Kaveri, S.V.; Kwon-Chung, K.J.; et al. Surface structure characterization of Aspergillus fumigatus conidia mutated in the melanin synthesis pathway and their human cellular immune response. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 3141–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentzer, M.; Riedel, K.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Heydorn, A.; Andersen, J.B.; Parsek, M.R.; Rice, S.A.; Eberl, L.; Molin, S.; Høiby, N.; et al. Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm bacteria by a halogenated furanone compound. Microbiology 2002, 148, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briard, B.; Rasoldier, V.; Bomme, P.; ElAouad, N.; Guerreiro, C.; Chassagne, P.; Muszkieta, L.; Latgé, J.-P.; Mulard, L.; Beauvais, A. Dirhamnolipids secreted from Pseudomonas aeruginosa modify antifungal susceptibility of Aspergillus fumigatus by inhibiting β1,3 glucan synthase activity. ISME J. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Higgins, D.G. Multiple sequence alignment using ClustalW and ClustalX. Curr. Protoc. Bioinforma. 2002, Chapter 2, Unit 2.3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.A.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2--a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsolis, A.C.; Papandreou, N.C.; Iconomidou, V.A.; Hamodrakas, S.J. A consensus method for the prediction of “aggregation-prone” peptides in globular proteins. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, J.G.; Beauvais, A.; Beau, R.; McGary, K.L.; Latgé, J.-P.; Rokas, A. Global transcriptome changes underlying colony growth in the opportunistic human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 2012, 11, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valsecchi, I.; Sarikaya-Bayram, Ö.; Wong Sak Hoi, J.; Muszkieta, L.; Gibbons, J.; Prevost, M.-C.; Mallet, A.; Krijnse-Locker, J.; Ibrahim-Granet, O.; Mouyna, I.; et al. MybA, a transcription factor involved in conidiation and conidial viability of the human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 105, 880–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. Trim Galore!: A wrapper tool around Cutadapt and FastQC to consistently apply quality and adaptor trimming ro fastQfiles, with some extra functionnality for MspI-digested RRBS-type (Reduced Representation Bisulfite-seq) libraries. Available online: http://www. bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/trim_galore 2012.
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, J.; Meyer, C.A.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.S.; Shirley Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. GFOLD: A generalized fold change for ranking differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2782–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, T.; Dümig, M.; Jaber, B.M.; Szewczyk, E.; Olbermann, P.; Morschhäuser, J.; Krappmann, S. Validation of a self-excising marker in the human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus by employing the β-rec/six site-specific recombination system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 6313–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoumianaki, T.; Kyrmizi, I.; Valsecchi, I.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Samonis, G.; Drakos, E.; Boumpas, D.; Muszkieta, L.; Prevost, M.-C.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; et al. Aspergillus Cell Wall Melanin Blocks LC3-Associated Phagocytosis to Promote Pathogenicity. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambou, K.; Lamarre, C.; Beau, R.; Dufour, N.; Latge, J.-P. Functional analysis of the superoxide dismutase family in Aspergillus fumigatus. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 75, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pille, A.; Kwan, A.H.; Cheung, I.; Hampsey, M.; Aimanianda, V.; Delepierre, M.; Latge, J.-P.; Sunde, M.; Guijarro, J.I. 1H, 13C and 15N resonance assignments of the RodA hydrophobin from the opportunistic pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Biomol. NMR Assign. 2015, 9, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopp, T.P.; Prickett, K.S.; Price, V.L.; Libby, R.T.; March, C.J.; Pat Cerretti, D.; Urdal, D.L.; Conlon, P.J. A Short Polypeptide Marker Sequence Useful for Recombinant Protein Identification and Purification. Bio. Technology 1988, 6, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanzariti, A.-M.; Soboleva, T.A.; Jans, D.A.; Board, P.G.; Baker, R.T. An efficient system for high-level expression and easy purification of authentic recombinant proteins. Protein Sci. Publ. Protein Soc. 2004, 13, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latgé, J.P.; Moutaouakil, M.; Debeaupuis, J.P.; Bouchara, J.P.; Haynes, K.; Prévost, M.C. The 18-kilodalton antigen secreted by Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 2586–2594. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harris, S.D.; Morrell, J.L.; Hamer, J.E. Identification and characterization of Aspergillus nidulans mutants defective in cytokinesis. Genetics 1994, 136, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beauvais, A.; Bozza, S.; Kniemeyer, O.; Formosa, C.; Formosa, C.; Balloy, V.; Henry, C.; Roberson, R.W.; Dague, E.; Chignard, M.; et al. Deletion of the α-(1,3)-glucan synthase genes induces a restructuring of the conidial cell wall responsible for the avirulence of Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C.; Fontaine, T.; Heddergott, C.; Robinet, P.; Aimanianda, V.; Beau, R.; Beauvais, A.; Mouyna, I.; Prevost, M.-C.; Fekkar, A.; et al. Biosynthesis of cell wall mannan in the conidium and the mycelium of Aspergillus fumigatus. Cell. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1881–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavaud, C.; Beauvais, A.; Barbin, L.; Munier-Lehmann, H.; Latgé, J.-P. The composition of the culture medium influences the β-1,3-glucan metabolism of Aspergillus fumigatus and the antifungal activity of inhibitors of β-1,3-glucan synthesis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 3428–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grünbacher, A.; Throm, T.; Seidel, C.; Gutt, B.; Röhrig, J.; Strunk, T.; Vincze, P.; Walheim, S.; Schimmel, T.; Wenzel, W.; Fischer, R. Six hydrophobins are involved in hydrophobin rodlet formation in Aspergillus nidulans and contribute to hydrophobicity of the spore surface. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, A.H.Y.; Winefield, R.D.; Sunde, M.; Matthews, J.M.; Haverkamp, R.G.; Templeton, M.D.; Mackay, J.P. Structural basis for rodlet assembly in fungal hydrophobins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3621–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakanpää, J.; Paananen, A.; Askolin, S.; Nakari-Setälä, T.; Parkkinen, T.; Penttilä, M.; Linder, M.B.; Rouvinen, J. Atomic resolution structure of the HFBII hydrophobin, a self-assembling amphiphile. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Kwan, A.H.; Sunde, M. Solution structure and interface-driven self-assembly of NC2, a new member of the Class II hydrophobin proteins. Proteins 2014, 82, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, C.L.L.; Rey, A.; Lo, V.; Soulès, M.; Ren, Q.; Meisl, G.; Knowles, T.P.J.; Kwan, A.H.; Sunde, M. Self-assembly of MPG1, a hydrophobin protein from the rice blast fungus that forms functional amyloid coatings, occurs by a surface-driven mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder, M.B.; Szilvay, G.R.; Nakari-Setälä, T.; Penttilä, M.E. Hydrophobins: The protein-amphiphiles of filamentous fungi. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 877–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xia, Y.X.; Kim, B.; Keyhani, N.O. Two hydrophobins are involved in fungal spore coat rodlet layer assembly and each play distinct roles in surface interactions, development and pathogenesis in the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 80, 811–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, R.D.; Kelkar, H.S.; Dean, R.A. An eight-cysteine-containing CFEM domain unique to a group of fungal membrane proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, A.; Ramage, G.; Blanes, R.; Murgui, A.; Casanova, M.; Martínez, J.P. Some biological features of Candida albicans mutants for genes coding fungal proteins containing the CFEM domain. FEMS Yeast Res. 2011, 11, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; He, J.; Sun, Y.; Reynolds, M.; Zhang, L.; Han, S.; Liang, S.; Sui, H.; Lin, Y. Display of fungal hydrophobin on the Pichia pastoris cell surface and its influence on Candida antarctica lipase B. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 5883–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Wetter, M.A.; Wösten, H.A.; Sietsma, J.H.; Wessels, J.G. Hydrophobin gene expression affects hyphal wall composition in Schizophyllum commune. Fungal Genet. Biol. FG B 2000, 31, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastebois, A.; Fontaine, T.; Latgé, J.-P.; Mouyna, I. β(1-3)Glucanosyltransferase Gel4p is essential for Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 2010, 9, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Li, C.; Liang, J.; Sun, S. The Aspergillus fumigatus β-1,3-glucanosyltransferase Gel7 plays a compensatory role in maintaining cell wall integrity under stress conditions. Glycobiology 2014, 24, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muszkieta, L.; Aimanianda, V.; Mellado, E.; Gribaldo, S.; Alcàzar-Fuoli, L.; Szewczyk, E.; Prevost, M.-C.; Latgé, J.-P. Deciphering the role of the chitin synthase families 1 and 2 in the in vivo and in vitro growth of Aspergillus fumigatus by multiple gene targeting deletion. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1784–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochstenbach, F.; Klis, F.M.; van den Ende, H.; van Donselaar, E.; Peters, P.J.; Klausner, R.D. Identification of a putative α-glucan synthase essential for cell wall construction and morphogenesis in fission yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9161–9166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauvais, A.; Maubon, D.; Park, S.; Morelle, W.; Tanguy, M.; Huerre, M.; Perlin, D.S.; Latgé, J.P. Two α(1-3) glucan synthases with different functions in Aspergillus fumigatus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Sato, H.; Ichinose, S.; Tanaka, M.; Miyazawa, K.; Yoshimi, A.; Abe, K.; Shintani, T.; Gomi, K. Cell wall α-1,3-glucan prevents α-amylase adsorption onto fungal cell in submerged culture of Aspergillus oryzae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 124, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuya, K.; Takaoka, M.; Uchida, K.; Wakayama, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Takahashi, K.; Paris, S.; Latge, J.P.; Naoe, S. Histopathology of experimental invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in rats: Pathological comparison of pulmonary lesions induced by specific virulent factor deficient mutants. Microb. Pathog. 1999, 27, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Strains | ku80 | ΔrodA | ΔrodBCDEFG | ΔrodBCDEFGA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC CR (µg/mL) | 100 | >300 | 100 | >300 |
| MIC CFW (µg/mL) | 80 | 150 | 80 | 150 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valsecchi, I.; Dupres, V.; Stephen-Victor, E.; Guijarro, J.I.; Gibbons, J.; Beau, R.; Bayry, J.; Coppee, J.-Y.; Lafont, F.; Latgé, J.-P.; et al. Role of Hydrophobins in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4010002
Valsecchi I, Dupres V, Stephen-Victor E, Guijarro JI, Gibbons J, Beau R, Bayry J, Coppee J-Y, Lafont F, Latgé J-P, et al. Role of Hydrophobins in Aspergillus fumigatus. Journal of Fungi. 2018; 4(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleValsecchi, Isabel, Vincent Dupres, Emmanuel Stephen-Victor, J. Iñaki Guijarro, John Gibbons, Rémi Beau, Jagadeesh Bayry, Jean-Yves Coppee, Frank Lafont, Jean-Paul Latgé, and et al. 2018. "Role of Hydrophobins in Aspergillus fumigatus" Journal of Fungi 4, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4010002
APA StyleValsecchi, I., Dupres, V., Stephen-Victor, E., Guijarro, J. I., Gibbons, J., Beau, R., Bayry, J., Coppee, J.-Y., Lafont, F., Latgé, J.-P., & Beauvais, A. (2018). Role of Hydrophobins in Aspergillus fumigatus. Journal of Fungi, 4(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4010002







