Proteomic Analysis of Pathogenic Fungi Reveals Highly Expressed Conserved Cell Wall Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Strains
2.2. Culture Conditions
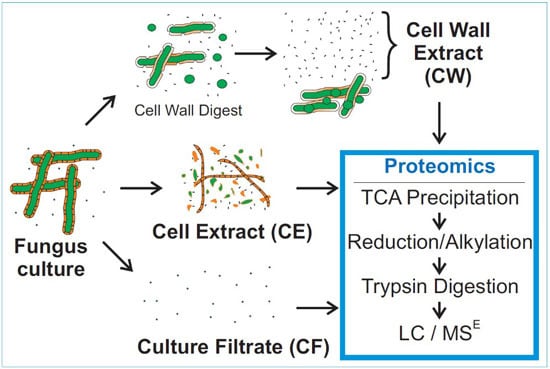
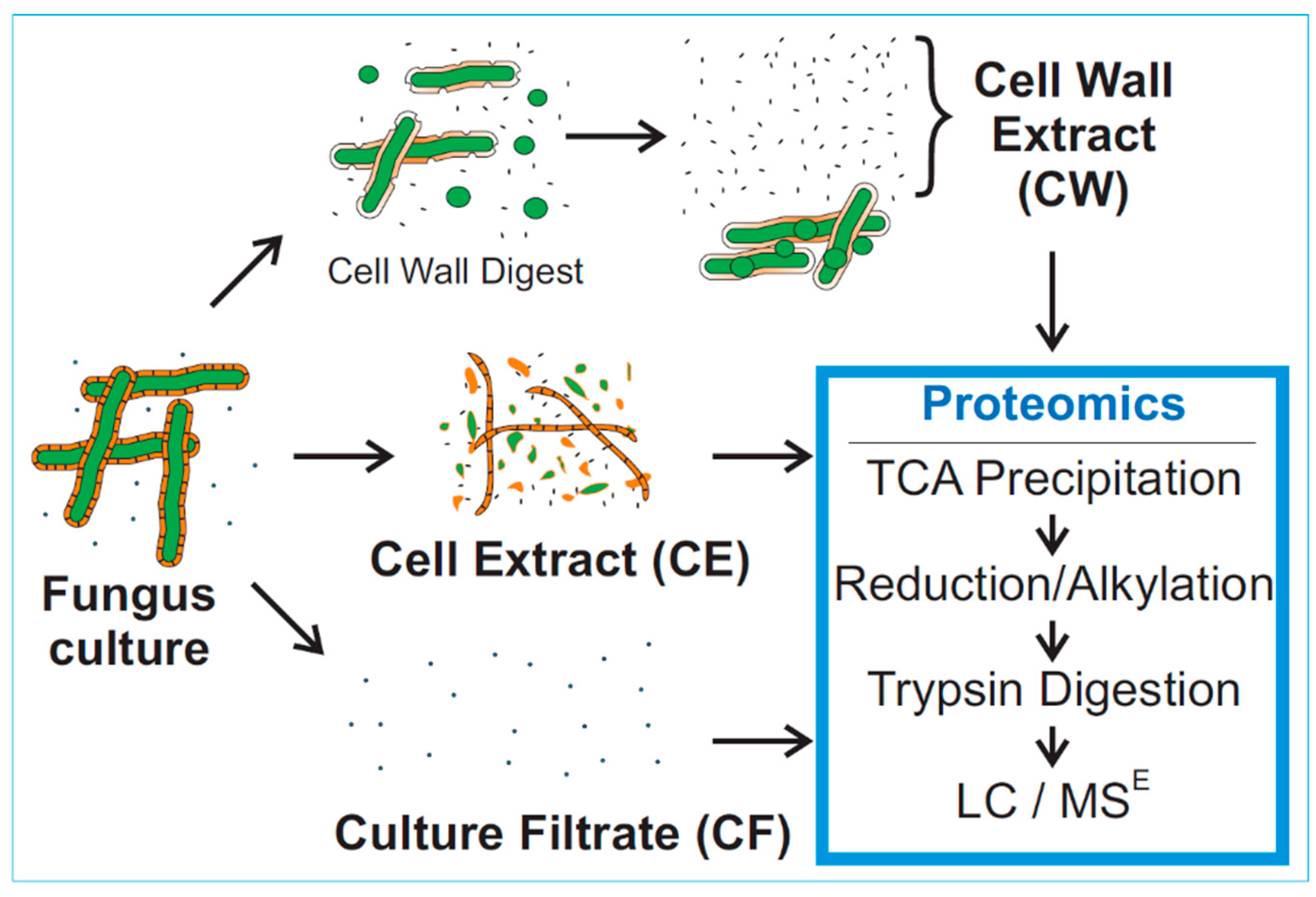
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Firefly Luciferase Quantification Standard for MSE
2.5. Mass Spectrometry
2.6. Protein Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MSE Label-Free Protein Quantification
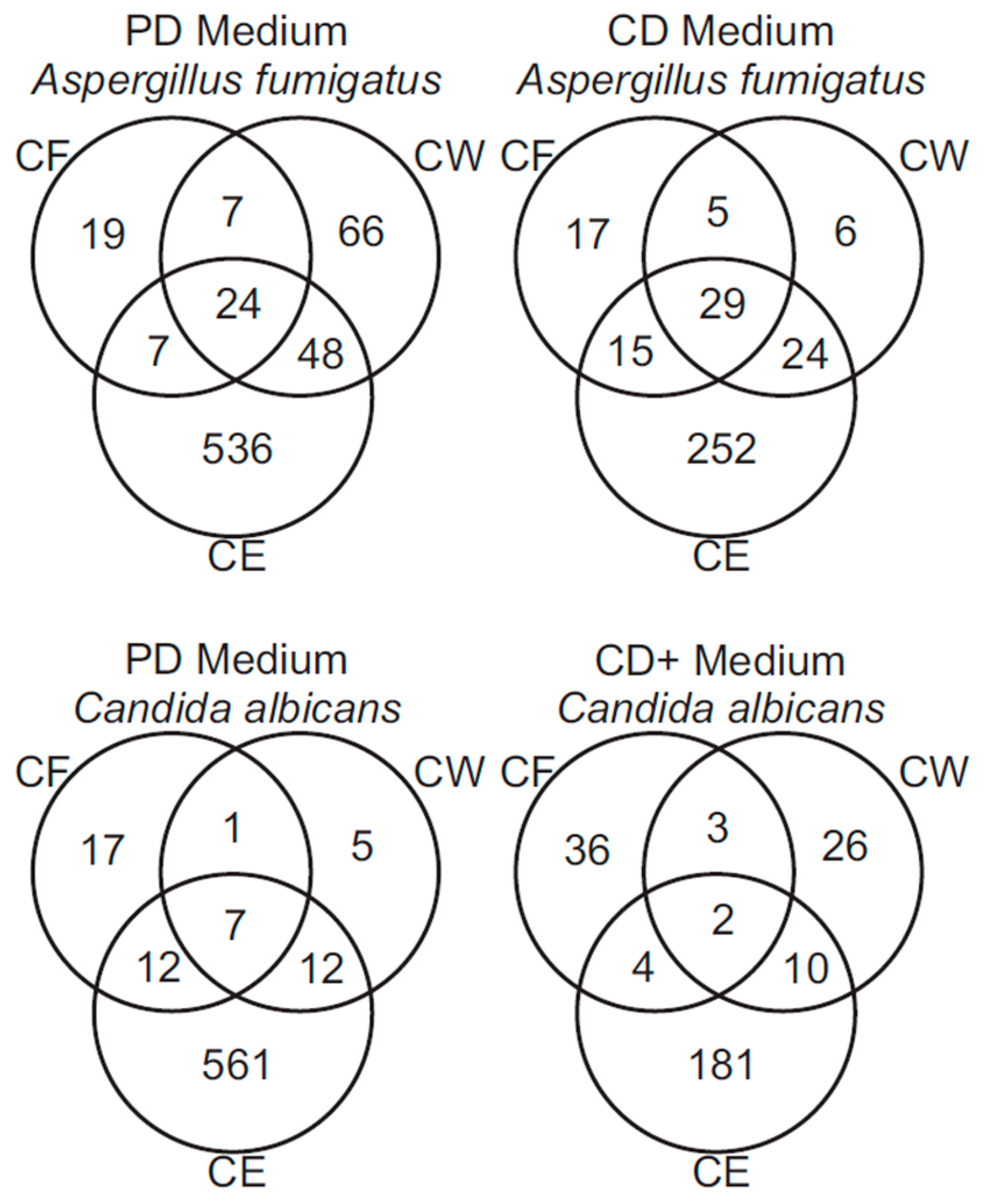
3.2. Mass Spectrometry of Fungal Fractions
| Species | Growth Medium | CE | CF | %SSL | CW | %SSL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspergillus flavus | PD | 508 | 25 | 80% | 86 | 38% |
| Aspergillus flavus | CD | 132 | 41 | 76% | 36 | 72% |
| Aspergillus fumigatus | PD | 615 | 57 | 70% | 145 | 38% |
| Aspergillus fumigatus 685 | PD | 510 | 62 | 95% | 194 | 33% |
| Aspergillus fumigatus | CD | 320 | 66 | 77% | 64 | 70% |
| Aspergillus nidulans | PD | 450 | 68 | 43% | 46 | 61% |
| Aspergillus niger | PD | 511 | 35 | 97% | 17 | 88% |
| Aspergillus terreus | PD | 580 | 25 | 96% | 84 | 50% |
| Aspergillus terreus | CD | 204 | 27 | 56% | 45 | 64% |
| Candida albicans | PD | 592 | 38 | 61% | 25 | 60% |
| Candida albicans | CD+ | 197 | 45 | 42% | 41 | 37% |
| Candida glabrata | PD | 363 | 33 | 91% | 57 | 33% |
| Candida parapsilosis | PD | 664 | 48 | 40% | 78 | 27% |
| Candida tropicalis | PD | 375 | 24 | 63% | 51 | 41% |
| Coccidioides posadasii | PD | 403 | 131 | 34% | 53 | 28% |
| Cryptococcus neoformans | PD | 609 | 15 | 80% | 30 | 40% |
| Mucor circinelloides | PD | 419 | 25 | 88% | 40 | 53% |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | PD | 481 | 16 | 94% | 46 | 28% |
3.3. Analysis of A. fumigatus and C. albicans Proteins
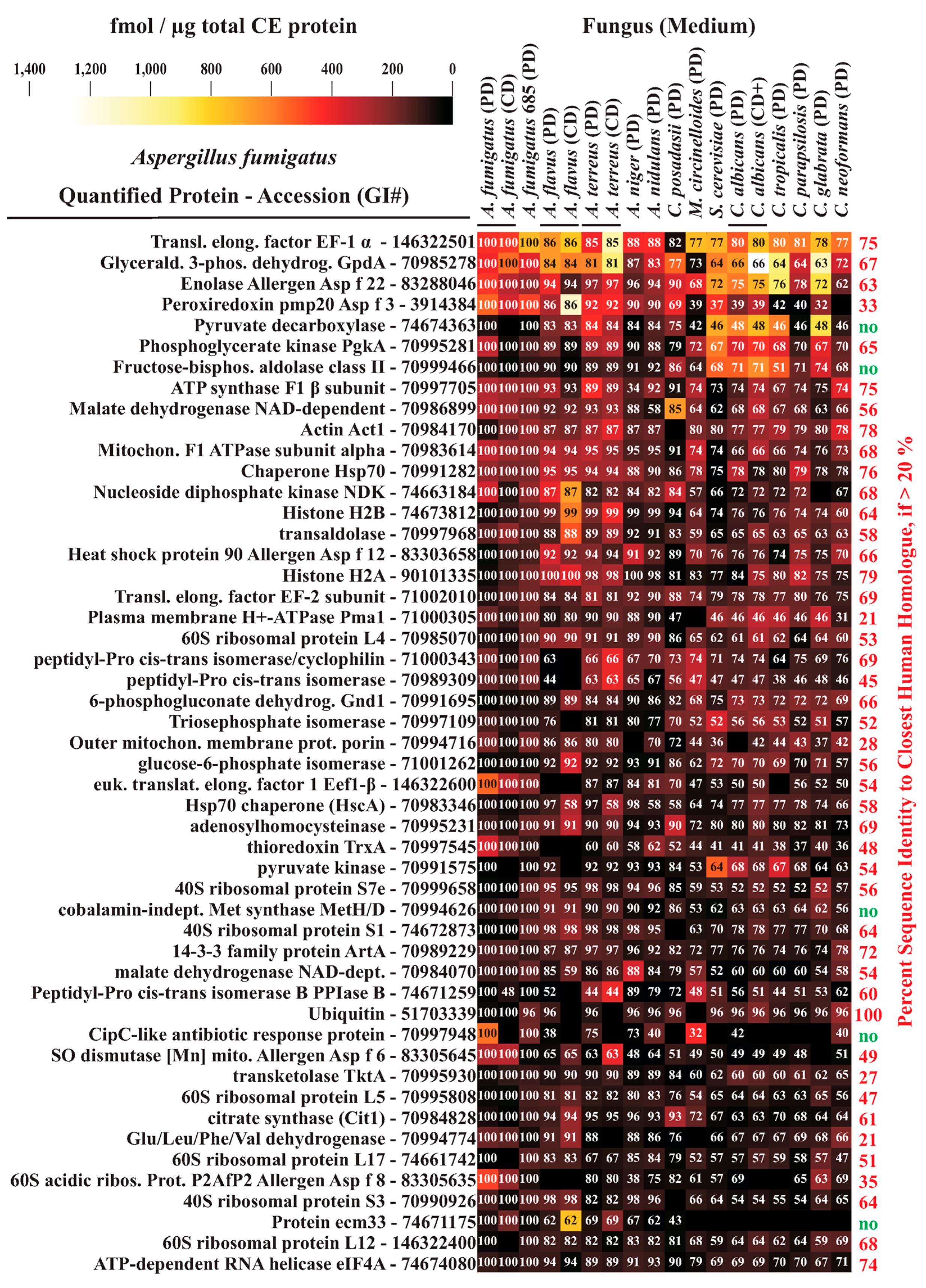
3.4. Interspecies Protein Comparisons
| Fraction | A. flavus | A. flavus CD | A. terreus | A. terreus CD | A. niger | A. nidulans | C. posadasii | M. circinelloides | S. cerevisiae | C. albicans | C. albicans CD+ | C. tropicalis | C. parapsilosi | C. glabrata | C. neoformans |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # Proteins, CE | 47 | 40 | 50 | 47 | 49 | 50 | 46 | 46 | 48 | 48 | 47 | 46 | 48 | 46 | 48 |
| Average % Identity | 85 ± 14 | 87 ± 10 | 85 ± 12 | 84 ± 12 | 85 ± 15 | 84 ± 13 | 79 ± 13 | 62 ± 12 | 64 ± 12 | 66 ± 12 | 65 ± 12 | 64 ± 13 | 66 ± 13 | 65 ± 13 | 63 ± 12 |
| # Proteins, CF | 13 | 17 | 25 | 12 | 25 | 11 | 17 | 3 | 7 | 9 | 1 | 9 | 7 | 10 | 1 |
| Average % Identity | 56 ± 19 | 53 ± 17 | 60 ± 15 | 60 ± 17 | 56 ± 14 | 57 ± 12 | 49 ± 11 | 33 ± 3 | 42 ± 5 | 42 ± 5 | 39 ± 0 | 40 ± 6 | 37 ± 7 | 42 ± 6 | 31 ± 0 |
| # Proteins, CW | 25 | 23 | 34 | 25 | 17 | 30 | 13 | 3 | 9 | 7 | 4 | 12 | 9 | 12 | 1 |
| Average % Identity | 59 ± 17 | 62 ± 16 | 61 ± 16 | 64 ± 15 | 53 ± 16 | 59 ± 14 | 50 ± 12 | 33 ± 3 | 42 ± 6 | 41 ± 6 | 41 ± 7 | 39 ± 8 | 39 ± 7 | 41 ± 5 | 31 ± 0 |
| Fraction | A. fumigatus | A. fumigatus CD | A. fumigatus 685 | A. flavus | A. flavus CD | A. terreus | A. terreus CD | A. niger | A. nidulans | C. posadasii | M. circinelloides | S. cerevisiae | C. tropicalis | C. parapsilosi | C. glabrata | C. neoformans |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # Proteins, CE | 88 | 74 | 95 | 93 | 75 | 97 | 91 | 91 | 95 | 83 | 93 | 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 | 96 |
| Average % Identity | 66 ± 11 | 65 ± 13 | 66 ± 12 | 66 ± 13 | 66 ± 14 | 65 ± 13 | 64 ± 14 | 67 ± 11 | 65 ± 13 | 65 ± 13 | 63 ± 13 | 74 ± 12 | 90 ± 10 | 87 ± 10 | 74 ± 12 | 63 ± 12 |
| # Proteins, CF | 5 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 1 | 7 | 15 | 14 | 18 | 0 |
| Average % Identity | 41 ± 5 | 41 ± 5 | 41 ± 5 | 40 ± 4 | 40 ± 5 | 41 ± 6 | 42 ± 2 | 39 ± 5 | 37 ± 6 | 41 ± 9 | 32 ± 0 | 50 ± 7 | 56 ± 16 | 54 ± 16 | 47 ± 10 | 0 ± 0 |
| # Proteins, CW | 10 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 11 | 15 | 16 | 13 | 0 |
| Average % Identity | 38 ± 5 | 40 ± 5 | 39 ± 5 | 40 ± 5 | 40 ± 6 | 39 ± 5 | 37 ± 4 | 39 ± 5 | 41 ± 6 | 43 ± 9 | 32 ± 0 | 46 ± 8 | 60 ± 17 | 55 ± 16 | 44 ± 10 | 0 ± 0 |
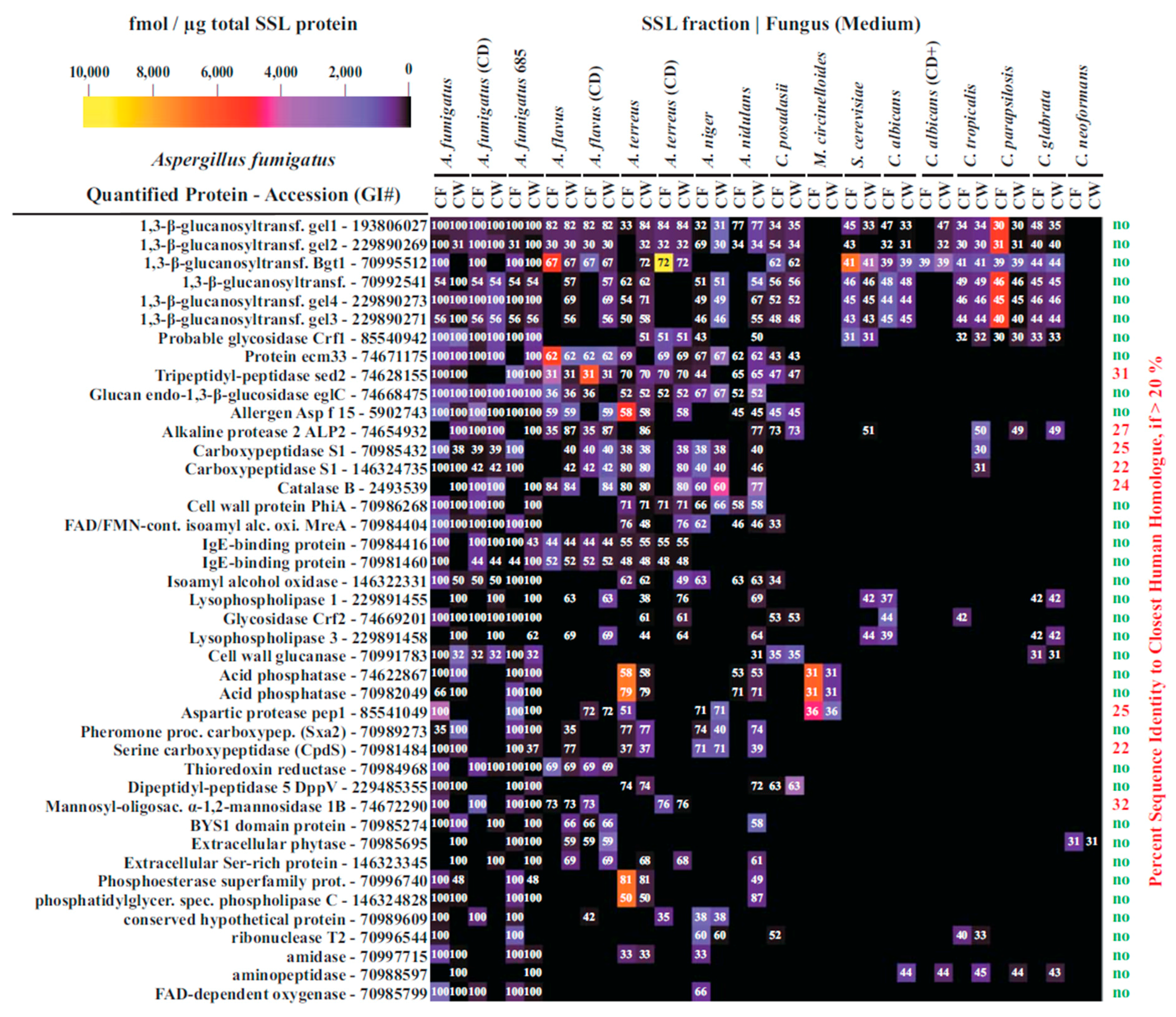
3.5. Functional Annotation of A. fumigatus and C. albicans Proteins
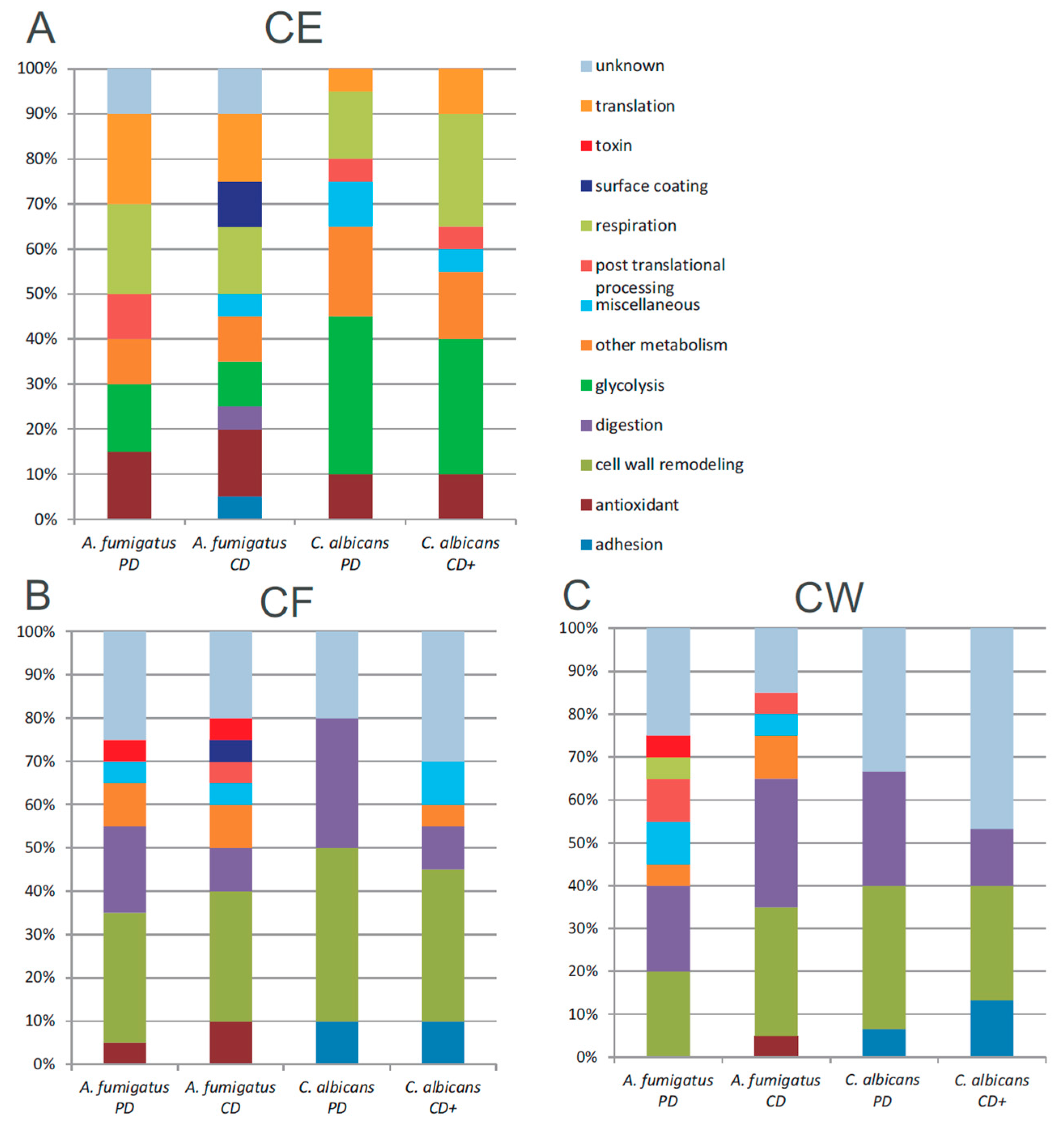
4. Discussion
| Species | CE | CF | CW |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aspergillus flavus | [75,76] | [69,70] | - |
| Aspergillus fumigatus | [58,59,60,61,74] | [61,65,66] | [57,61] |
| Aspergillus nidulans | [77] | - | - |
| Aspergillus niger | - | [68] | - |
| Aspergillus terreus | - | [67] | - |
| Candida albicans | [78,79,80] | [71,72] | [62,63] |
| Candida glabrata | [81] | - | [64] |
| Candida parapsilosis | [87] | - | - |
| Candida tropicalis | - | - | - |
| Coccidioides posadasii | [23,61] | - | - |
| Cryptococcus neoformans | [53,82] | - | - |
| Mucor circinelloides | - | - | - |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | [83,84,85,86] | - | [73] |
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, N.; Paterson, D.L. Aspergillus infections in transplant recipients. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 44–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caston-Osorio, J.J.; Rivero, A.; Torre-Cisneros, J. Epidemiology of invasive fungal infection. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 32, S103–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Marr, K.A.; Park, B.J.; Alexander, B.D.; Anaissie, E.J.; Walsh, T.J.; Ito, J.; Andes, D.R.; Baddley, J.W.; Brown, J.M.; et al. Prospective surveillance for invasive fungal infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients, 2001–2006: Overview of the Transplant-Associated Infection Surveillance Network (TRANSNET) Database. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoham, S.; Marr, K.A. Invasive fungal infections in solid organ transplant recipients. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, L.; Caira, M.; Candoni, A.; Offidani, M.; Fianchi, L.; Martino, B.; Pastore, D.; Picardi, M.; Bonini, A.; Chierichini, A.; et al. The epidemiology of fungal infections in patients with hematologic malignancies: The SEIFEM-2004 study. Haematologica 2006, 91, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dotis, J.; Iosifidis, E.; Roilides, E. Central nervous system aspergillosis in children: A systematic review of reported cases. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 11, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaal, J.V.; Leclerc, T.; Soler, C.; Donat, N.; Cirrode, A.; Jault, P.; Bargues, L. Epidemiology of filamentous fungal infections in burned patients: A French retrospective study. Burns 2015, 41, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denning, D.W.; Follansbee, S.E.; Scolaro, M.; Norris, S.; Edelstein, H.; Stevens, D.A. Pulmonary aspergillosis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, D.A.; Melikian, G.L. Aspergillosis in the “nonimmunocompromised” host. Immunol. Investig. 2011, 40, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hector, R.F.; Laniado-Laborin, R. Coccidioidomycosis—A fungal disease of the Americas. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagenais, T.R.; Keller, N.P. Pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus in invasive aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, P.E.; Howard, S.J.; Melchers, W.J.; Denning, D.W. Azole-resistance in Aspergillus: Proposed nomenclature and breakpoints. Drug Resist. Updat. 2009, 12, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.C.; Playford, E.G.; Sorrell, T.C. Antifungal therapy in invasive fungal infections. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Joseph, L.; Hagen, F.; Meis, J.F.; Khan, Z. Concomitant occurrence of itraconazole-resistant and -susceptible strains of Aspergillus fumigatus in routine cultures. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmann, J.; Hamprecht, A.; Vehreschild, M.J.; Cornely, O.A.; Buchheidt, D.; Spiess, B.; Koldehoff, M.; Buer, J.; Meis, J.F.; Rath, P.M. Emergence of azole-resistant invasive aspergillosis in HSCT recipients in Germany. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 1522–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, J.I.; Lyons, J.M.; Diaz-Arevalo, D.; Hong, T.B.; Kalkum, M. Vaccine progress. Med. Mycol. 2009, 47, S394–S400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Arevalo, D.; Bagramyan, K.; Hong, T.B.; Ito, J.I.; Kalkum, M. CD4+ T Cells mediate the protective effect of the recombinant Asp f3-based anti-aspergillosis vaccine. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 2257–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Arevalo, D.; Ito, J.I.; Kalkum, M. Protective effector cells of the recombinant Asp f3 anti-aspergillosis vaccine. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, J.I.; Lyons, J.M.; Hong, T.B.; Tamae, D.; Liu, Y.K.; Wilczynski, S.P.; Kalkum, M. Vaccinations with recombinant variants of Aspergillus fumigatus Asp f 3 protect against invasive aspergillosis. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 5075–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozza, S.; Gaziano, R.; Lipford, G.B.; Montagnoli, C.; Bacci, A.; di Francesco, P.; Kurup, V.P.; Wagner, H.; Romani, L. Vaccination of mice against invasive aspergillosis with recombinant Aspergillus proteins and CpG oligodeoxynucleotides as adjuvants. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozza, S.; Clavaud, C.; Giovannini, G.; Fontaine, T.; Beauvais, A.; Sarfati, J.; D’Angelo, C.; Perruccio, K.; Bonifazi, P.; Zagarella, S.; et al. Immune sensing of Aspergillus fumigatus proteins, glycolipids, and polysaccharides and the impact on Th immunity and vaccination. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2407–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuehler, C.; Khanna, N.; Bozza, S.; Zelante, T.; Moretti, S.; Kruhm, M.; Lurati, S.; Conrad, B.; Worschech, E.; Stevanovic, S.; et al. Cross-protective TH1 immunity against Aspergillus fumigatus and Candida albicans. Blood 2011, 117, 5881–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsborn, K.I.; Shubitz, L.F.; Peng, T.; Kellner, E.M.; Orbach, M.J.; Haynes, P.A.; Galgiani, J.N. Protein expression profiling of Coccidioides posadasii by two-dimensional differential in-gel electrophoresis and evaluation of a newly recognized peroxisomal matrix protein as a recombinant vaccine candidate. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarcha, E.J.; Basrur, V.; Hung, C.Y.; Gardner, M.J.; Cole, G.T. A recombinant aspartyl protease of Coccidioides posadasii induces protection against pulmonary coccidioidomycosis in mice. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, N.; Xue, J.; Yu, J.J.; Hung, C.Y.; Cole, G.T. A recombinant β-1,3-glucanosyltransferase homolog of Coccidioides posadasii protects mice against coccidioidomycosis. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 3010–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibasaki, S.; Aoki, W.; Nomura, T.; Karasaki, M.; Sewaki, T.; Ueda, M. Evaluation of Mdh1 protein as an antigenic candidate for a vaccine against candidiasis. Biocontrol. Sci. 2014, 19, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilanova, M.; Teixeira, L.; Caramalho, I.; Torrado, E.; Marques, A.; Madureira, P.; Ribeiro, A.; Ferreira, P.; Gama, M.; Demengeot, J. Protection against systemic candidiasis in mice immunized with secreted aspartic proteinase 2. Immunology 2004, 111, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spellberg, B.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Yeaman, M.R.; Lin, L.; Fu, Y.; Avanesian, V.; Bayer, A.S.; Filler, S.G.; Lipke, P.; Otoo, H.; et al. The antifungal vaccine derived from the recombinant N terminus of Als3p protects mice against the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 4574–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spellberg, B.J.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Avanesian, V.; Fu, Y.; Myers, C.; Phan, Q.T.; Filler, S.G.; Yeaman, M.R.; Edwards, J.E., Jr. Efficacy of the anti-Candida rAls3p-N or rAls1p-N vaccines against disseminated and mucosal candidiasis. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.S.; Luo, G.; Gebremariam, T.; Lee, H.; Schmidt, C.S.; Hennessey, J.P., Jr.; French, S.W.; Yeaman, M.R.; Filler, S.G.; Edwards, J.E., Jr. NDV-3 protects mice from vulvovaginal candidiasis through T- and B-cell immune response. Vaccine 2013, 31, 5549–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, C.S.; White, C.J.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Filler, S.G.; Fu, Y.; Yeaman, M.R.; Edwards, J.E., Jr.; Hennessey, J.P., Jr. NDV-3, a recombinant alum-adjuvanted vaccine for Candida and Staphylococcus aureus, is safe and immunogenic in healthy adults. Vaccine 2012, 30, 7594–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassone, A. Development of vaccines for Candida albicans: Fighting a skilled transformer. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, D.A.; Clemons, K.V.; Liu, M. Developing a vaccine against aspergillosis. Med. Mycol. 2011, 49, S170–S176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassone, A.; Rappuoli, R. Universal vaccines: Shifting to one for many. MBio 2010, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.Y.; Blackburn, K.; Lin, Y.M.; Goshe, M.B.; Williamson, J.D. Absolute protein quantification by LC/MSE for global analysis of salicylic acid-induced plant protein secretion responses. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostanci, N.; Heywood, W.; Mills, K.; Parkar, M.; Nibali, L.; Donos, N. Application of label-free absolute quantitative proteomics in human gingival crevicular fluid by LC/MSE (gingival exudatome). J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.Z.; Vissers, J.P.; Silva, J.C.; Golick, D.; Gorenstein, M.V.; Geromanos, S.J. Database searching and accounting of multiplexed precursor and product ion spectra from the data independent analysis of simple and complex peptide mixtures. Proteomics 2009, 9, 1696–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geromanos, S.J.; Vissers, J.P.; Silva, J.C.; Dorschel, C.A.; Li, G.Z.; Gorenstein, M.V.; Bateman, R.H.; Langridge, J.I. The detection, correlation, and comparison of peptide precursor and product ions from data independent LC-MS with data dependant LC-MS/MS. Proteomics 2009, 9, 1683–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vissers, J.P.; Pons, S.; Hulin, A.; Tissier, R.; Berdeaux, A.; Connolly, J.B.; Langridge, J.I.; Geromanos, S.J.; Ghaleh, B. The use of proteome similarity for the qualitative and quantitative profiling of reperfused myocardium. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, J.I.; Lyons, J.M. Vaccination of corticosteroid immunosuppressed mice against invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, H.B.; Stevens, D.A.; Cobb, J.M.; Gebhardt, A.E. Miconazole in coccidioidomycosis. I. Assays of activity in mice and in vitro. J. Infect. Dis. 1975, 132, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capilla, J.; Clemons, K.V.; Liu, M.; Levine, H.B.; Stevens, D.A. Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a vaccine against coccidioidomycosis. Vaccine 2009, 27, 3662–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Capilla, J.; Johansen, M.E.; Alvarado, D.; Martinez, M.; Chen, V.; Clemons, K.V.; Stevens, D.A. Saccharomyces as a vaccine against systemic aspergillosis: “The friend of man” a friend again? J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Gebremariam, T.; Clemons, K.V.; Stevens, D.A.; Ibrahim, A.S. Heat-killed yeast protects diabetic ketoacidotic-steroid treated mice from pulmonary mucormycosis. Vaccine 2014, 32, 3573–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enache-Angoulvant, A.; Hennequin, C. Invasive Saccharomyces infection: A comprehensive review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, T.B.; Kalkum, M. Using A Ball Mill for Cryogenic Disruption of Yeast Cells. Available online: http://www.biosciencetechnology.com/articles/2004/01/using-ball-mill-cryogenic-disruption-yeast-cells (accessed on 6 January 2016).
- Singer, M.A.; Lindquist, S. Multiple effects of trehalose on protein folding in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.; Park, K.J.; Obayashi, T.; Fujita, N.; Harada, H.; Adams-Collier, C.J.; Nakai, K. Wolf Psort: Protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W585–W587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, M.C.; Nakayasu, E.S.; Matsuo, A.L.; Sobreira, T.J.; Longo, L.V.; Ganiko, L.; Almeida, I.C.; Puccia, R. Vesicle and vesicle-free extracellular proteome of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis: Comparative analysis with other pathogenic fungi. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 1676–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, D.L.; Nakayasu, E.S.; Joffe, L.S.; Guimaraes, A.J.; Sobreira, T.J.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Cordero, R.J.; Frases, S.; Casadevall, A.; Almeida, I.C.; et al. Characterization of yeast extracellular vesicles: Evidence for the participation of different pathways of cellular traffic in vesicle biogenesis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peres da Silva, R.; Puccia, R.; Rodrigues, M.L.; Oliveira, D.L.; Joffe, L.S.; Cesar, G.V.; Nimrichter, L.; Goldenberg, S.; Alves, L.R. Extracellular vesicle-mediated export of fungal RNA. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, A.K.; Weintraub, S.T.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L.; Wormley, F.L., Jr. Identification and characterization of Cryptococcus neoformans protein fractions that induce protective immune responses. Proteomics 2013, 13, 3429–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breakspear, A.; Momany, M. The first fifty microarray studies in filamentous fungi. Microbiology 2007, 153, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, A.; Fernandez-Molina, J.V.; Bikandi, J.; Ramirez, A.; Margareto, J.; Sendino, J.; Hernando, F.L.; Ponton, J.; Garaizar, J.; Rementeria, A. What makes Aspergillus fumigatus a successful pathogen? Genes and molecules involved in invasive aspergillosis. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2010, 27, 155–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karkowska-Kuleta, J.; Kozik, A. Cell wall proteome of pathogenic fungi. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2015, 62, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, A.R.; Oellerich, M.; Amstrong, V.W.; Riemenschneider, B.; Monod, M.; Reichard, U. Proteome of conidial surface associated proteins of Aspergillus fumigatus reflecting potential vaccine candidates and allergens. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagas, S.E.; Jain, M.R.; Li, H.; Perlin, D.S. The proteomic signature of Aspergillus fumigatus during early development. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teutschbein, J.; Albrecht, D.; Potsch, M.; Guthke, R.; Aimanianda, V.; Clavaud, C.; Latge, J.P.; Brakhage, A.A.; Kniemeyer, O. Proteome profiling and functional classification of intracellular proteins from conidia of the human-pathogenic mold Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3427–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, M.J.; Fedorova, N.D.; Cagas, S.E.; Hastings, S.; Fleischmann, R.D.; Peterson, S.N.; Perlin, D.S.; Nierman, W.C.; Pieper, R.; Momany, M. Development stage-specific proteomic profiling uncovers small, lineage specific proteins most abundant in the Aspergillus fumigatus conidial proteome. Proteome Sci. 2012, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champer, J.; Diaz-Arevalo, D.; Champer, M.; Hong, T.B.; Wong, M.; Shannahoff, M.; Ito, J.I.; Clemons, K.V.; Stevens, D.A.; Kalkum, M. Protein targets for broad-spectrum mycosis vaccines: Quantitative proteomic analysis of Aspergillus and Coccidioides and comparisons with other fungal pathogens. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1273, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilmann, C.J.; Sorgo, A.G.; Mohammadi, S.; Sosinska, G.J.; de Koster, C.G.; Brul, S.; de Koning, L.J.; Klis, F.M. Surface stress induces a conserved cell wall stress response in the pathogenic fungus Candida albicans. Eukaryot. Cell 2013, 12, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilmann, C.J.; Sorgo, A.G.; Siliakus, A.R.; Dekker, H.L.; Brul, S.; de Koster, C.G.; de Koning, L.J.; Klis, F.M. Hyphal induction in the human fungal pathogen Candida albicans reveals a characteristic wall protein profile. Microbiology 2011, 157, 2297–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Molero, E.; de Boer, A.D.; Dekker, H.L.; Moreno-Martinez, A.; Kraneveld, E.A.; Chauhan, I.N.; Weig, M.; de Soet, J.J.; de Koster, C.G.; et al. Proteomic analysis of hyperadhesive Candida glabrata clinical isolates reveals a core wall proteome and differential incorporation of adhesins. FEMS Yeast Res. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Oellerich, M.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, M.; Bhadoria, D.P.; Reichard, U.; Gupta, V.K.; Sharma, G.L.; Asif, A.R. Immuno-reactive molecules identified from the secreted proteome of Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 5517–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Ahmed, R.; Singh, P.K.; Shukla, P.K. Identification of virulence factors and diagnostic markers using immunosecretome of Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.J.; Kim, N.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Chang, H.N. Extracellular proteome of Aspergillus terreus grown on different carbon sources. Curr. Genet. 2010, 56, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krijgsheld, P.; Altelaar, A.F.; Post, H.; Ringrose, J.H.; Muller, W.H.; Heck, A.J.; Wosten, H.A. Spatially resolving the secretome within the mycelium of the cell factory Aspergillus niger. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 2807–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, M.L.; Haynes, P.A.; Breci, L.; Francisco, W.A. Analysis of secreted proteins from Aspergillus flavus. Proteomics 2005, 5, 3153–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvam, R.M.; Nithya, R.; Devi, P.N.; Shree, R.S.; Nila, M.V.; Demonte, N.L.; Thangavel, C.; Maheshwari, J.J.; Lalitha, P.; Prajna, N.V.; et al. Exoproteome of Aspergillus flavus corneal isolates and saprophytes: Identification of proteoforms of an oversecreted alkaline protease. J. Proteom. 2015, 115, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Bona, A.; Monteoliva, L.; Gil, C. Global proteomic profiling of the secretome of Candida albicans Ecm33 cell wall mutant reveals the involvement of Ecm33 in Sap2 secretion. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 4270–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klis, F.M.; Brul, S. Adaptations of the secretome of Candida albicans in response to host-related environmental conditions. Eukaryot. Cell 2015, 14, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardina, B.J.; Stanley, B.A.; Chiang, H.L. Glucose induces rapid changes in the secretome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proteome Sci. 2014, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vodisch, M.; Albrecht, D.; Lessing, F.; Schmidt, A.D.; Winkler, R.; Guthke, R.; Brakhage, A.A.; Kniemeyer, O. Two-dimensional proteome reference maps for the human pathogenic filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Proteomics 2009, 9, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pechanova, O.; Pechan, T.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Williams, W.P.; Brown, A.E. A two-dimensional proteome map of the aflatoxigenic fungus Aspergillus flavus. Proteomics 2013, 13, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhong, H.; Han, X.; Guo, Z.; Yang, W.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, S. Proteomic profile of Aspergillus flavus in response to water activity. Fungal Biol. 2015, 119, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wartenberg, D.; Vodisch, M.; Kniemeyer, O.; Albrecht-Eckardt, D.; Scherlach, K.; Winkler, R.; Weide, M.; Brakhage, A.A. Proteome analysis of the farnesol-induced stress response in Aspergillus nidulans—The role of a putative dehydrin. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 4038–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, W.; Ueda, T.; Tatsukami, Y.; Kitahara, N.; Morisaka, H.; Kuroda, K.; Ueda, M. Time-course proteomic profile of Candida albicans during adaptation to a fetal serum. Pathog. Dis. 2013, 67, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vialas, V.; Sun, Z.; Loureiro, Y.P.C.V.; Carrascal, M.; Abian, J.; Monteoliva, L.; Deutsch, E.W.; Aebersold, R.; Moritz, R.L.; Gil, C. A Candida albicans PeptideAtlas. J. Proteom. 2014, 97, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vialas, V.; Sun, Z.; Reales-Calderon, J.A.; Hernaez, M.L.; Casas, V.; Carrascal, M.; Abian, J.; Monteoliva, L.; Deutsch, E.W.; Moritz, R.L.; et al. A comprehensive Candida albicans PeptideAtlas build enables deep proteome coverage. J. Proteom. 2016, 131, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, T.S.; Harsha, H.C.; Keerthikumar, S.; Sekhar, N.R.; Selvan, L.D.; Kumar, P.; Pinto, S.M.; Muthusamy, B.; Subbannayya, Y.; Renuse, S.; et al. Proteogenomic analysis of Candida glabrata using high resolution mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santi, L.; Beys-da-Silva, W.O.; Berger, M.; Calzolari, D.; Guimaraes, J.A.; Moresco, J.J.; Yates, J.R., III. Proteomic profile of Cryptococcus neoformans biofilm reveals changes in metabolic processes. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 1545–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraj, N.; Kulak, N.A.; Cox, J.; Neuhauser, N.; Mayr, K.; Hoerning, O.; Vorm, O.; Mann, M. System-wide perturbation analysis with nearly complete coverage of the yeast proteome by single-shot ultra HPLC runs on a bench top Orbitrap. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, A.L.; Hebert, A.S.; Ulbrich, A.; Bailey, D.J.; Coughlin, E.E.; Westphall, M.S.; Coon, J.J. One-hour proteome analysis in yeast. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selevsek, N.; Chang, C.Y.; Gillet, L.C.; Navarro, P.; Bernhardt, O.M.; Reiter, L.; Cheng, L.Y.; Vitek, O.; Aebersold, R. Reproducible and consistent quantification of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteome by SWATH-mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2015, 14, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonk, R.J.; Gargano, A.F.; Davydova, E.; Dekker, H.L.; Eeltink, S.; de Koning, L.J.; Schoenmakers, P.J. Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography with Stationary-Phase-Assisted Modulation Coupled to High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Applied to Proteome Analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5387–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.Y.; Gam, L.H.; Yong, V.C.; Rosli, R.; Ng, K.P.; Chong, P.P. Identification of immunogenic proteins of Candida parapsilosis by serological proteome analysis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, P.S.; Im, H.; Clemons, K.V.; Snyder, M.P.; Stevens, D.A. Evaluating common humoral responses against fungal infections with yeast protein microarrays. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 3924–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Clemons, K.V.; Johansen, M.E.; Martinez, M.; Chen, V.; Stevens, D.A. Saccharomyces as a vaccine against systemic candidiasis. Immunol. Investig. 2012, 41, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, T.; Liu, M.; Chen, V.; Martinez, M.; Alvarado, D.; Clemons, K.V.; Stevens, D.A. Killed Saccharomyces cerevisiae protects against lethal challenge of Cryptococcus grubii. Mycopathologia 2014, 178, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarcha, E.J.; Basrur, V.; Hung, C.Y.; Gardner, M.J.; Cole, G.T. Multivalent recombinant protein vaccine against coccidioidomycosis. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 5802–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Champer, J.; Ito, J.I.; Clemons, K.V.; Stevens, D.A.; Kalkum, M. Proteomic Analysis of Pathogenic Fungi Reveals Highly Expressed Conserved Cell Wall Proteins. J. Fungi 2016, 2, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof2010006
Champer J, Ito JI, Clemons KV, Stevens DA, Kalkum M. Proteomic Analysis of Pathogenic Fungi Reveals Highly Expressed Conserved Cell Wall Proteins. Journal of Fungi. 2016; 2(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof2010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleChamper, Jackson, James I. Ito, Karl V. Clemons, David A. Stevens, and Markus Kalkum. 2016. "Proteomic Analysis of Pathogenic Fungi Reveals Highly Expressed Conserved Cell Wall Proteins" Journal of Fungi 2, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof2010006
APA StyleChamper, J., Ito, J. I., Clemons, K. V., Stevens, D. A., & Kalkum, M. (2016). Proteomic Analysis of Pathogenic Fungi Reveals Highly Expressed Conserved Cell Wall Proteins. Journal of Fungi, 2(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof2010006