Larvicidal and Immunomodulatory Effects of Conidia and Blastospores of Beauveria bassiana and Beauveria brongniartii in Aedes aegypti
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mosquito Rearing
2.2. Fungal Cultures and Fungal Species
2.3. Larvicidal Infection Bioassays
2.4. RNA Extraction and Gene Expression Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Conidial Propagules from B. bassiana MBC076 and B. brongniartii MBC397 Are More Effective than Blastospores at Reducing Larval Survival of Ae. aegypti Mosquitoes
3.2. Conidial Propagules Primarily Kill at the Larval Stage, but Infection with B. brongniartii MBC397 Blastospores Exacts Significantly Greater Mortality at the Pupal Stage
3.3. Increased Fungal Loads in Larvae Exposed to Fungal Propagules and Induction of Fungal Infection Markers
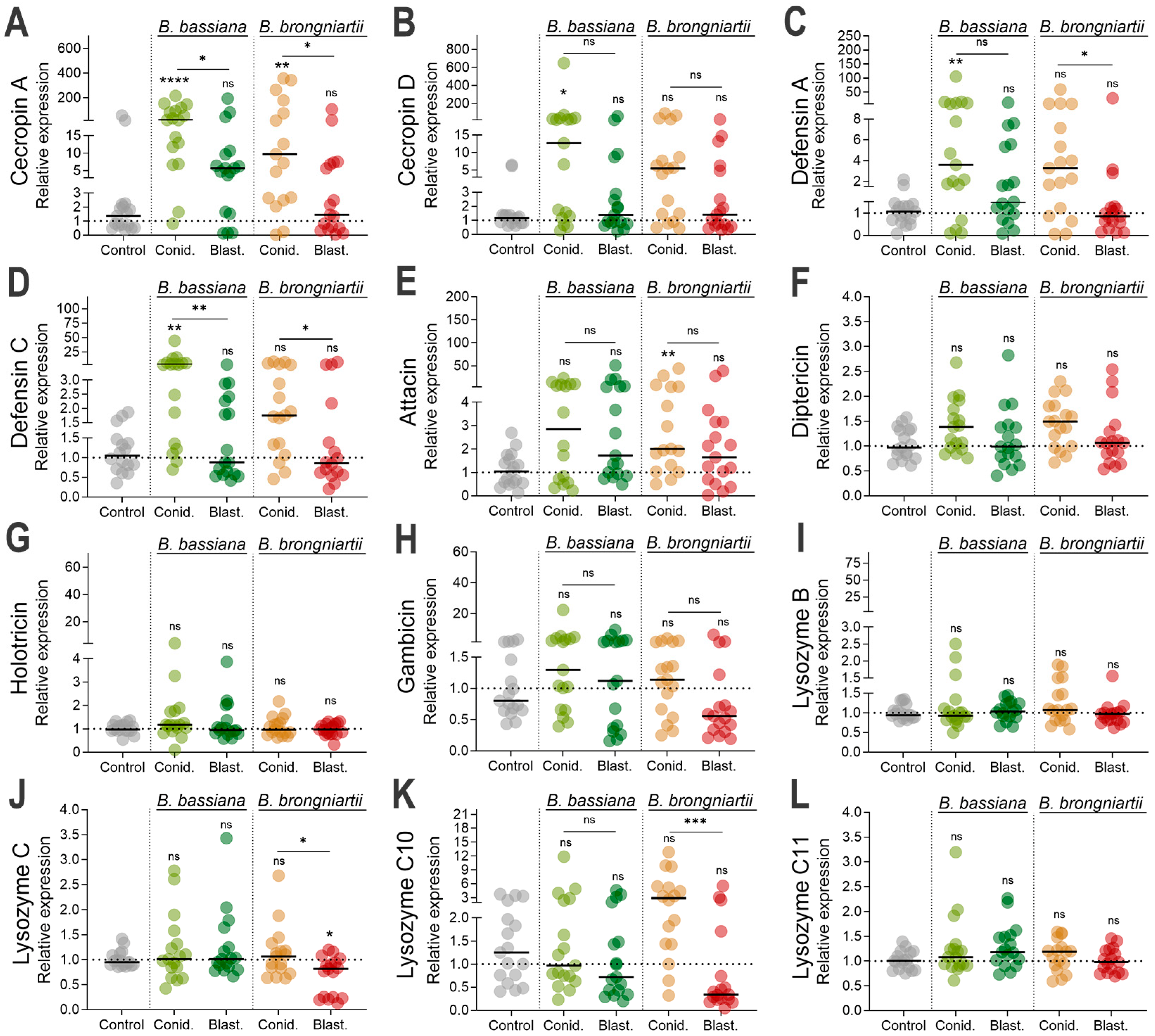
3.4. Cecropin, Defensin, and Attacin Were the Most Significantly Induced Antimicrobial Effectors as Part of the Larval Resistance to Entomopathogenic Fungi
3.5. Significant Reduction in Prophenoloxidase Expression During Infections with B. brongniartii MBC397 Blastospore Propagules
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, M.B.; Read, A.F. Can fungal biopesticides control malaria? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhaibari, A.M.; Carolino, A.T.; Bull, J.C.; Samuels, R.I.; Butt, T.M. Differential Pathogenicity of Metarhizium Blastospores and Conidia Against Larvae of Three Mosquito Species. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanford, S.; Shi, W.; Christian, R.; Marden, J.H.; Koekemoer, L.L.; Brooke, B.D.; Coetzee, M.; Read, A.F.; Thomas, M.B. Lethal and pre-lethal effects of a fungal biopesticide contribute to substantial and rapid control of malaria vectors. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achonduh, O.A.; Tondje, P.R. First report of pathogenicity of Beauveria bassiana RBL 1034 to the malaria vector, Anopheles gambiae s.l. (Diptera; Culicidae) in Cameroon. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 931–935. [Google Scholar]
- Blanford, S.; Jenkins, N.E.; Read, A.F.; Thomas, M.B. Evaluating the lethal and pre-lethal effects of a range of fungi against adult Anopheles stephensi mosquitoes. Malar. J. 2012, 11, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, D. Chapter 5—Basic and Applied Research on Entomopathogenic Fungi A2. In Microbial Control of Insect and Mite Pests; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 69–89. [Google Scholar]
- Butt, T.M.; Coates, C.J.; Dubovskiy, I.M.; Ratcliffe, N.A. Chapter Nine—Entomopathogenic Fungi: New Insights into Host–Pathogen Interactions. In Advances in Genetics; Lovett, B., Leger, R.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 94, pp. 307–364. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhaibari, A.M.; Carolino, A.T.; Yavasoglu, S.I.; Maffeis, T.; Mattoso, T.C.; Bull, J.C.; Samuels, R.I.; Butt, T.M. Metarhizium brunneum Blastospore Pathogenesis in Aedes aegypti Larvae: Attack on Several Fronts Accelerates Mortality. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Barbosa Bitencourt, R.; Corrêa, T.A.; Santos-Mallet, J.; Santos, H.A.; Lowenberger, C.; Moreira, H.V.S.; Gôlo, P.S.; Bittencourt, V.R.E.P.; da Costa Angelo, I. Beauveria bassiana interacts with gut and hemocytes to manipulate Aedes aegypti immunity. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.L.; Syazwan, S.A.; Hamdan, R.H.; Najwa, N.S.; Ramli, M.F.; Harshiny, N.; Ishak, I.H. Virulence and proteomic responses of Metarhizium anisopliae against Aedes albopictus larvae. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 203, 105982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charnley, A.K. Fungal pathogens of insects: Cuticle degrading enzymes and toxins. Adv. Bot. Res. 2003, 40, 241–321. [Google Scholar]
- Jaronski, S.T.; Mascarin, G.M. Chapter 9—Mass Production of Fungal Entomopathogens A2. In Microbial Control of Insect and Mite Pests; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 141–155. [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado-Blanco, M.G.; Lizzette, G.-S.J.; Gabriela, F.-P.; Francisco, S.-C.C.; Elías-Santos, M. Effect of culture medium on the production and virulence of submerged spores of Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana against larvae and adults of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, B.P.; Peace, A.; Evans, H.; Dudley, E.; Ansari, M.A.; Butt, T.M. Identification of Metarhizium strains highly efficacious against Aedes, Anopheles and Culex larvae. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2015, 25, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riba, G.; Keita, A.; Soares, G.G., Jr.; Ferron, P. Comparative studies of Metarhizium anisopliae and Tolypocladium cylindrosporum as pathogens of mosquito larvae. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1986, 2, 469–473. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhaibari, A.M.; Lord, A.M.; Maffeis, T.; Bull, J.C.; Olivares, F.L.; Samuels, R.I.; Butt, T.M. Highly specific host-pathogen interactions influence Metarhizium brunneum blastospore virulence against Culex quinquefasciatus larvae. Virulence 2018, 9, 1449–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitencourt, R.D.O.B.; Santos-Mallet, J.R.D.; Lowenberger, C.; Ventura, A.; Gôlo, P.S.; Bittencourt, V.R.E.P.; Angelo, I.D.C. A Novel Model of Pathogenesis of Metarhizium anisopliae Propagules Through the Midguts of Aedes aegypti Larvae. Insects 2023, 14, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.L.; Dunlap, C.A.; Muturi, E.J.; Barletta, A.B.F.; Rooney, A.P. Entomopathogenic fungal infection leads to temporospatial modulation of the mosquito immune system. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.L.; Muturi, E.J.; Flor-Weiler, L.B.; Vermillion, K.; Rooney, A.P. Peptidoglycan Recognition Proteins (PGRPs) Modulates Mosquito Resistance to Fungal Entomopathogens in a Fungal-Strain Specific Manner. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 9, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawidian, P.; Rhodes, V.L.; Michel, K. Mosquito-fungus interactions and antifungal immunity. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 111, 103182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.W.; Kokoza, V.; Bian, G.; Cheon, H.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Raikhel, A.S. REL1, a homologue of Drosophila dorsal, regulates toll antifungal immune pathway in the female mosquito Aedes aegypti. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 16499–16507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.L.; Leger, R.J. Insect Immunity to Entomopathogenic Fungi. Adv. Genet. 2016, 94, 251–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, J.L.; Muturi, E.J.; Barletta, A.B.F.; Rooney, A.P. The Aedes aegypti IMD pathway is a critical component of the mosquito antifungal immune response. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 95, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Morton, J.C., Jr.; Ramirez, J.L.; Souza-Neto, J.A.; Dimopoulos, G. The entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana activate toll and JAK-STAT pathway-controlled effector genes and anti-dengue activity in Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.L.; Hampton, K.J.; Rosales, A.M.; Muturi, E.J. Multiple mosquito AMPs are needed to potentiate their antifungal effect against entomopathogenic fungi. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1062383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Wang, S. Interaction of entomopathogenic fungi with the host immune system. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 83, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassine, H.; Kamareddine, L.; Osta, M.A. The mosquito melanization response is implicated in defense against the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1003029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, Y.; An, C.; Chu, Y.; Raikhel, A.S.; Zou, Z. Activation of Aedes aegypti prophenoloxidase-3 and its role in the immune response against entomopathogenic fungi. Insect Mol. Biol. 2017, 26, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, J.L.; Muturi, E.J.; Dunlap, C.; Rooney, A.P. Strain-specific pathogenicity and subversion of phenoloxidase activity in the mosquito Aedes aegypti by members of the fungal entomopathogenic genus Isaria. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Hu, Y.; Xing, L.S.; Jiang, H.; Hu, S.N.; Raikhel, A.S.; Zou, Z. A Critical Role for CLSP2 in the Modulation of Antifungal Immune Response in Mosquitoes. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, D.A.; Walker, T.; Carrington, L.B.; De Bruyne, J.T.; Kien, D.H.T.; Hoang, N.L.T.; Chau, N.V.V.; Iturbe-Ormaetxe, I.; Simmons, C.P.; O’Neill, S.L. Establishment of a Wolbachia Superinfection in Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes as a Potential Approach for Future Resistance Management. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzaki, N.; Ramli, K.N.; Azlan, A.; Ishak, I.H.; Azzam, G. Evaluation of reference genes at different developmental stages for quantitative real-time PCR in Aedes aegypti. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.S.; Blanford, S.; Jenkins, N.; Thomas, M.B.; Read, A.F. Real-time quantitative PCR for analysis of candidate fungal biopesticides against malaria: Technique validation and first applications. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2009, 100, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.A.; Carolino, A.T.; Teodoro, T.B.P.; Silva, G.A.; Bitencourt, R.d.O.B.; Silva, C.P.; Alkhaibari, A.M.; Butt, T.M.; Samuels, R.I. The Potential of Metarhizium anisopliae Blastospores to Control Aedes aegypti Larvae in the Field. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranpuri, G.S.; Khachatourians, G.G. Infection sites of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana in the larvae of the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1991, 59, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero-Jiménez, C.A.; Faino, L.; Spring in’t Veld, D.; Smit, S.; Zwaan, B.J.; van Kan, J.A.L. Comparative genomics of Beauveria bassiana: Uncovering signatures of virulence against mosquitoes. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascarin, G.M.; Iwanicki, N.S.A.; Ramirez, J.L.; Delalibera, Í.; Dunlap, C.A. Transcriptional Responses of Beauveria bassiana Blastospores Cultured Under Varying Glucose Concentrations. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 644372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, T.M.; Greenfield, B.P.; Greig, C.; Maffeis, T.G.; Taylor, J.W.; Piasecka, J.; Dudley, E.; Abdulla, A.; Dubovskiy, I.M.; Garrido-Jurado, I.; et al. Metarhizium anisopliae pathogenesis of mosquito larvae: A verdict of accidental death. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lu, A.; Li, X.; Shao, Q.; Beerntsen, B.T.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Ling, E. A systematic study on hemocyte identification and plasma prophenoloxidase from Culex pipiens quinquefasciatus at different developmental stages. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 127, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Yuan, C.; Lu, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, C.-Y.; Zhang, P.; Dobens, L.; Zou, Z.; Wang, C.; et al. Prophenoloxidase-Mediated Ex Vivo Immunity to Delay Fungal Infection after Insect Ecdysis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Dong, S.; Chen, X.; Stanley, D.; Beerntsen, B.; Feng, Q.; Song, Q. Relish2 mediates bursicon homodimer-induced prophylactic immunity in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramirez, J.L.; Schumacher, M.K.; Ower, G.; Palmquist, D.E.; Juliano, S.A. Impacts of fungal entomopathogens on survival and immune responses of Aedes albopictus and Culex pipiens mosquitoes in the context of native Wolbachia infections. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursic Bedoya, R.J.; Mitzey, A.M.; Obraztsova, M.; Lowenberger, C. Molecular cloning and transcriptional activation of lysozyme-encoding cDNAs in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Insect Mol. Biol. 2005, 14, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- League, G.P.; Estévez-Lao, T.Y.; Yan, Y.; Garcia-Lopez, V.A.; Hillyer, J.F. Anopheles gambiae larvae mount stronger immune responses against bacterial infection than adults: Evidence of adaptive decoupling in mosquitoes. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bali, G.K.; Kaur, S.; Kour, B.G. Phenoloxidase activity in haemolymph of Spodoptera litura (Fabricius) mediating immune responses challenge with entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) Vuillmin. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2013, 1, 1180123. [Google Scholar]
- Matskevich, A.A.; Quintin, J.; Ferrandon, D. The Drosophila PRR GNBP3 assembles effector complexes involved in antifungal defenses independently of its Toll-pathway activation function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Shang, Y.; Cen, K.; Wang, C. Fungal biosynthesis of the bibenzoquinone oosporein to evade insect immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11365–11370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafaluk-Mohr, C.; Wagner, S.; Joop, G. Cryptic changes in immune response and fitness in Tribolium castaneum as a consequence of coevolution with Beauveria bassiana. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 152, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, M.C.; Huarte-Bonnet, C.; Davyt-Colo, B.; Pedrini, N. Is the Insect Cuticle the only Entry Gate for Fungal Infection? Insights into Alternative Modes of Action of Entomopathogenic Fungi. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhou, G.; Wu, J.; Bian, G.; Lu, P.; Raikhel, A.S.; Xi, Z. Wolbachia induces reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent activation of the Toll pathway to control dengue virus in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E23–E31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, A.B.; Silva, M.C.; Sorgine, M.H. Validation of Aedes aegypti Aag-2 cells as a model for insect immune studies. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Pang, X.; Wang, P.; Cheng, G. Complement-related proteins control the flavivirus infection of Aedes aegypti by inducing antimicrobial peptides. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, J.L.; Souza-Neto, J.; Torres Cosme, R.; Rovira, J.; Ortiz, A.; Pascale, J.M.; Dimopoulos, G. Reciprocal tripartite interactions between the Aedes aegypti midgut microbiota, innate immune system and dengue virus influences vector competence. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
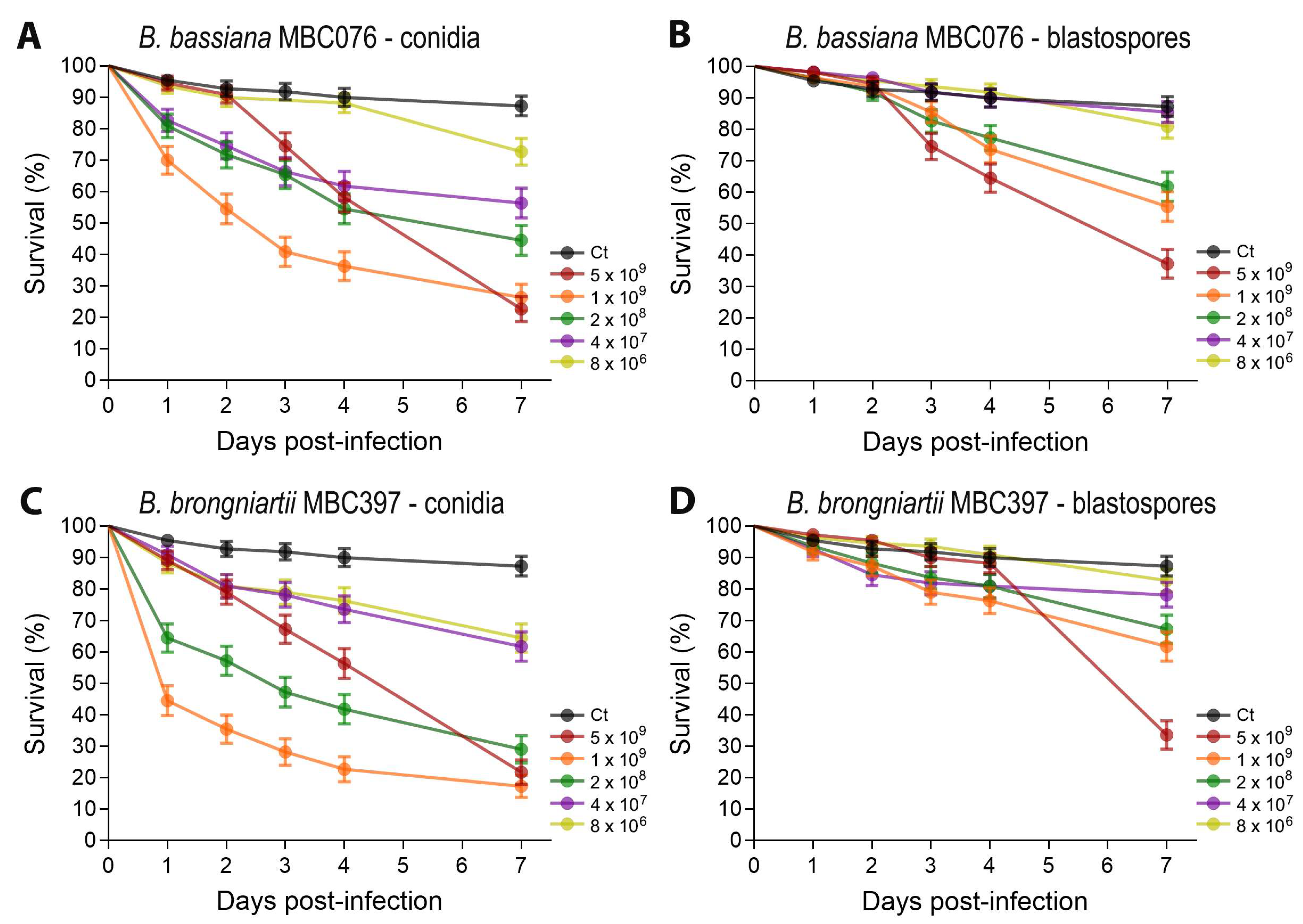
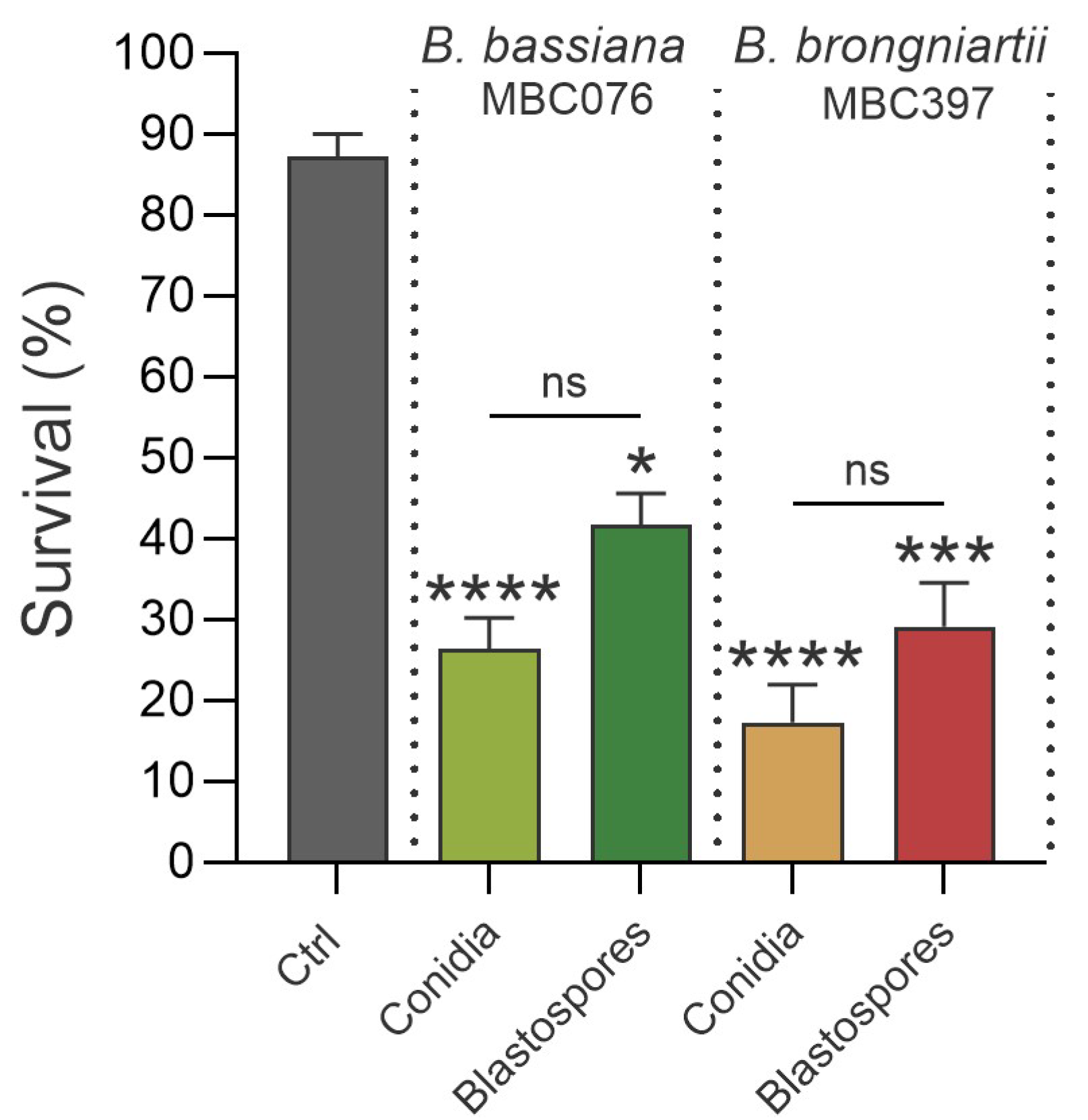
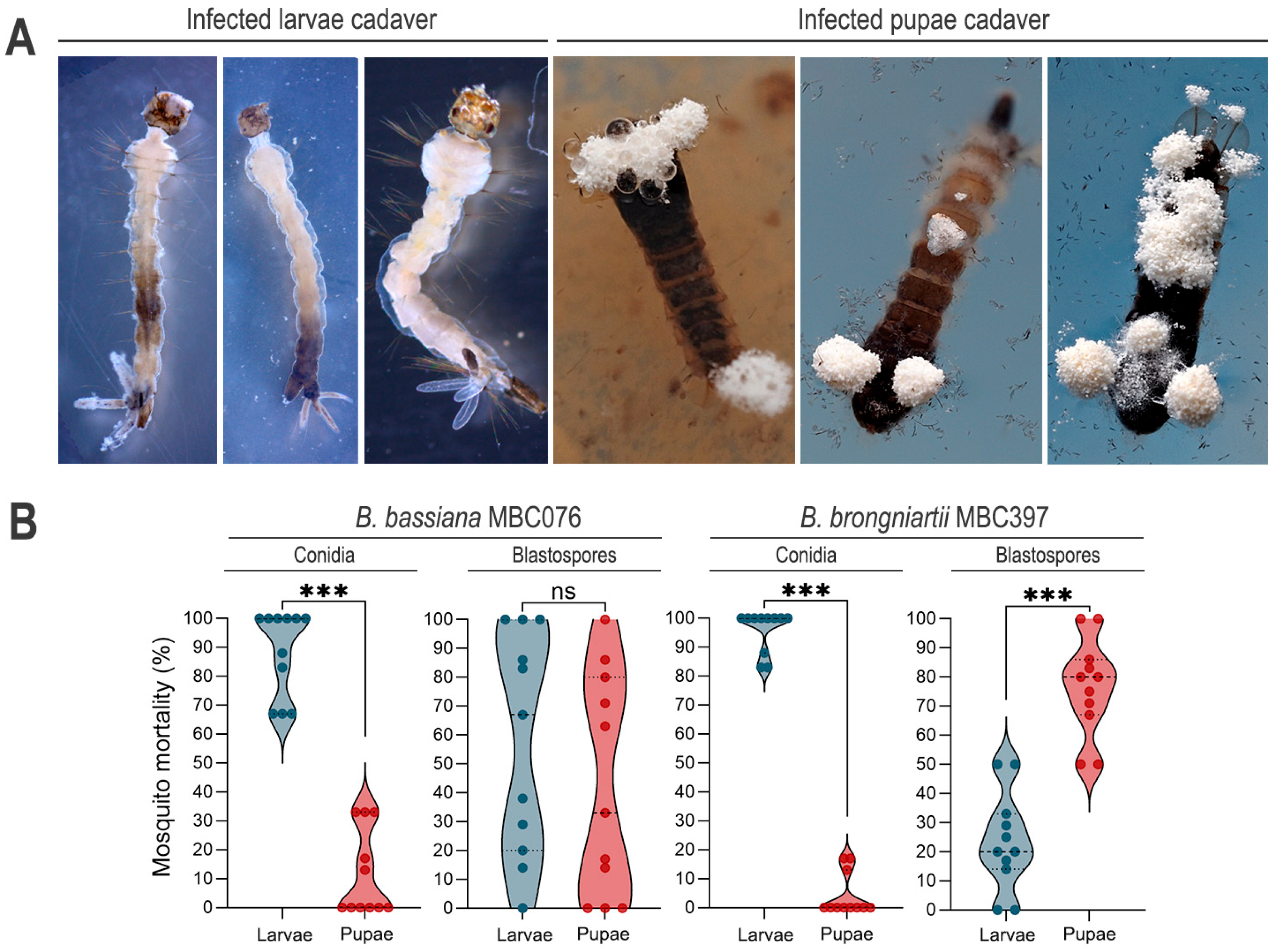
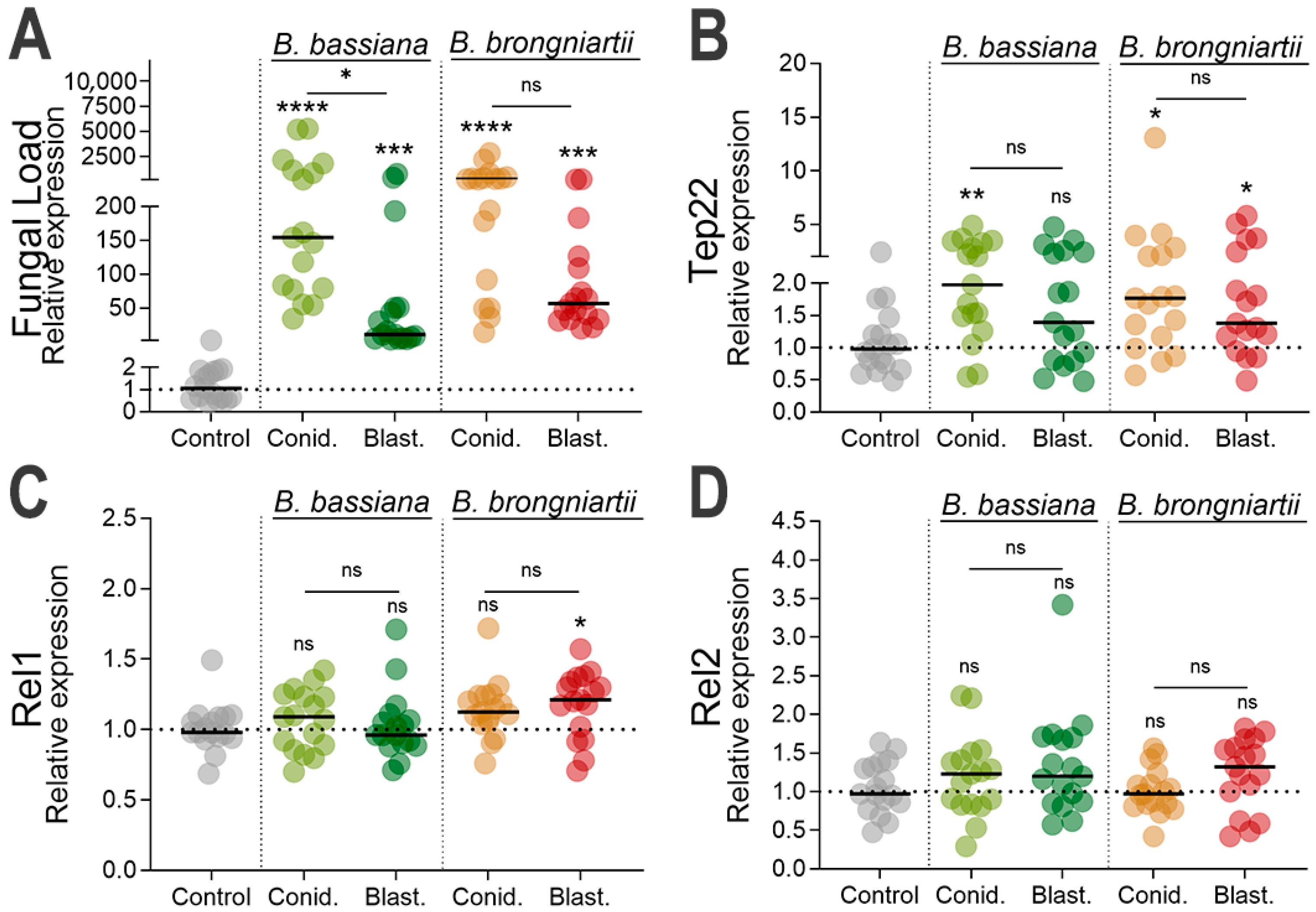

| Fungal Isolate | Propagule Type | LC50 (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| B. bassiana (MBC-076) | conidia | 4.2 × 107 (1.0 × 107–1.8 × 108) |
| B. bassiana (MBC-076) | blastospores | 2.0 × 108 (2.0 × 107–2.1 × 109) |
| B. brongniartii (MBC-397) | conidia | 1.7 × 107 (5.3 × 106–5.4 × 107) |
| B. brongniartii (MBC-397) | blastospores | 8.5 × 108 (6.0 × 107–1.3 × 1010) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramirez, J.L.; Gore, H.M.; Payne, A.; Pinto, S.M.N.; Flor-Weiler, L.B.; Fernandes, E.K.K.; Muturi, E.J. Larvicidal and Immunomodulatory Effects of Conidia and Blastospores of Beauveria bassiana and Beauveria brongniartii in Aedes aegypti. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080608
Ramirez JL, Gore HM, Payne A, Pinto SMN, Flor-Weiler LB, Fernandes EKK, Muturi EJ. Larvicidal and Immunomodulatory Effects of Conidia and Blastospores of Beauveria bassiana and Beauveria brongniartii in Aedes aegypti. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(8):608. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080608
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamirez, José L., Haley M. Gore, Angela Payne, Salorrane Miranda Nascimento Pinto, Lina B. Flor-Weiler, Everton K. K. Fernandes, and Ephantus J. Muturi. 2025. "Larvicidal and Immunomodulatory Effects of Conidia and Blastospores of Beauveria bassiana and Beauveria brongniartii in Aedes aegypti" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 8: 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080608
APA StyleRamirez, J. L., Gore, H. M., Payne, A., Pinto, S. M. N., Flor-Weiler, L. B., Fernandes, E. K. K., & Muturi, E. J. (2025). Larvicidal and Immunomodulatory Effects of Conidia and Blastospores of Beauveria bassiana and Beauveria brongniartii in Aedes aegypti. Journal of Fungi, 11(8), 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080608








