Detection of Pestalotiopsis abbreviata sp. nov., the Causal Agent of Pestalotiopsis Leaf Blight on Camellia japonica Based on Metagenomic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Description and Sample Collection
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction and PCR Amplifications, Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatic Processing
2.4. Data Preparation and Metagenomic Statistical Analysis
2.5. Microscopy
2.6. Multi-Gene Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
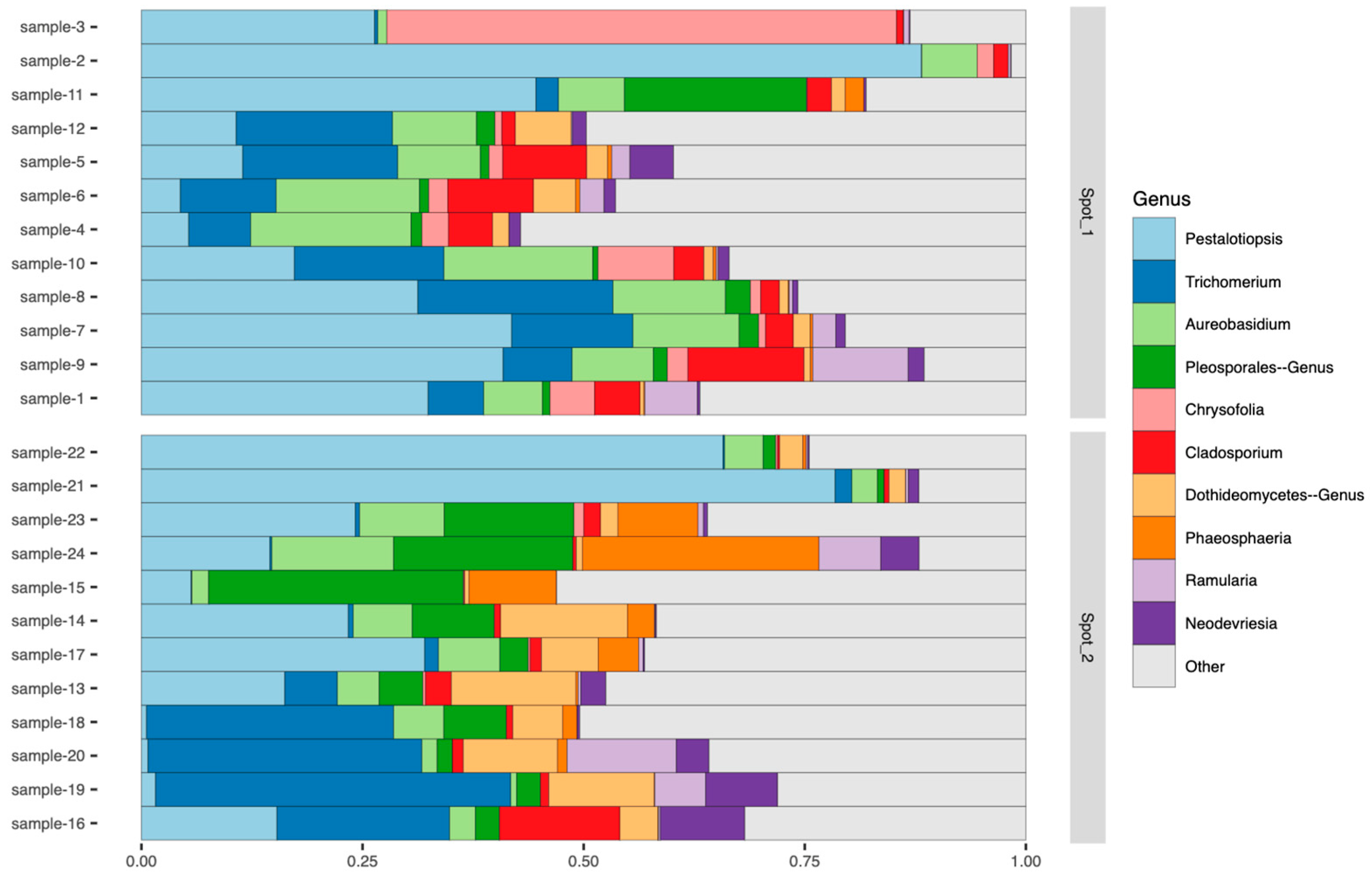
3.1. Metagenomic Assessment of Fungal Diversity on Camellia japonica
3.2. Detection of a Putative Fungal Pathogen Associated with Leaf Blight on Camellia japonica Based on Metagenomic Analysis
3.3. Identification of a Putative Fungal Pathogen Associated with Leaf Blight on Camellia japonica
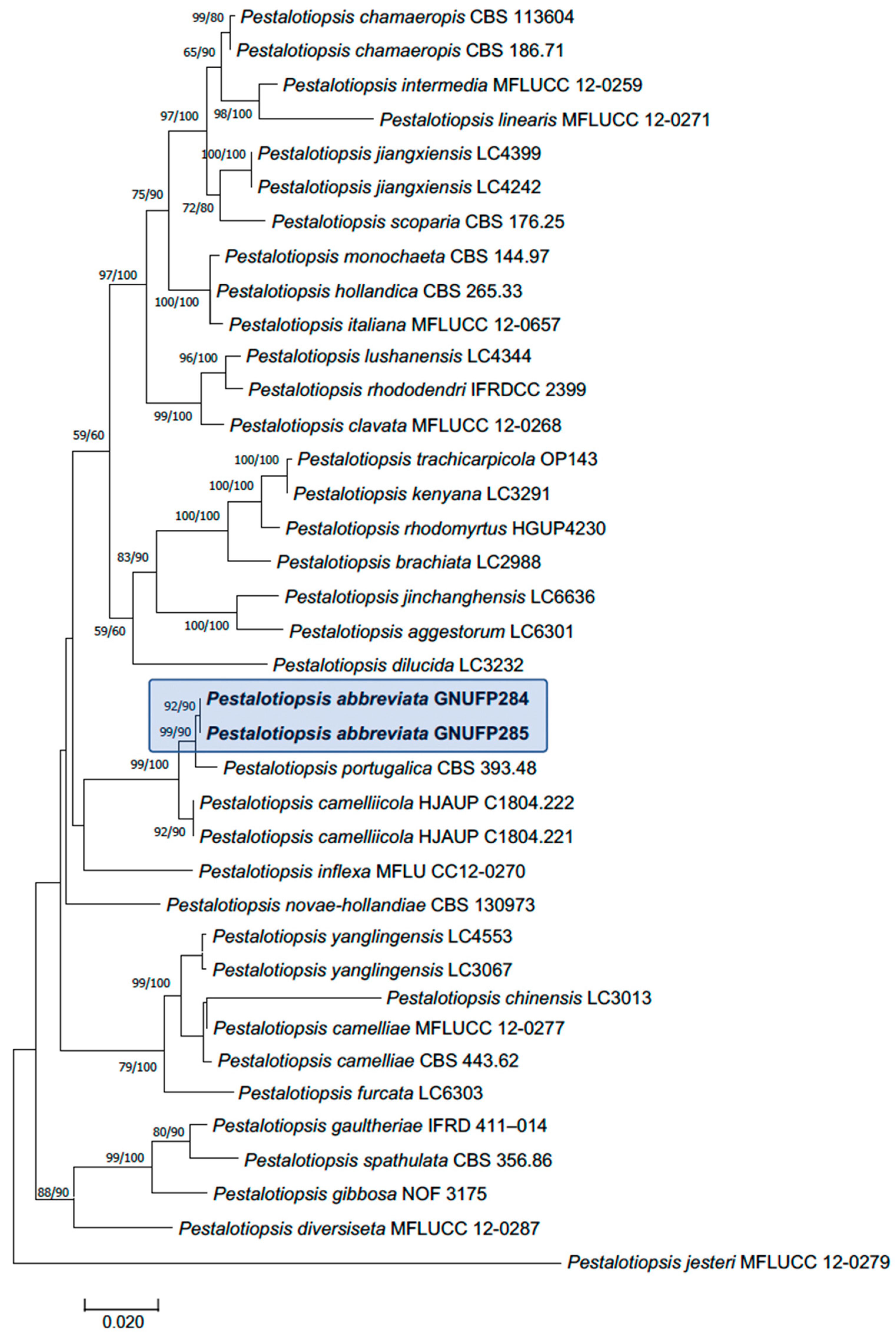
3.3.1. Multi-Gene Phylogenetic Analyses
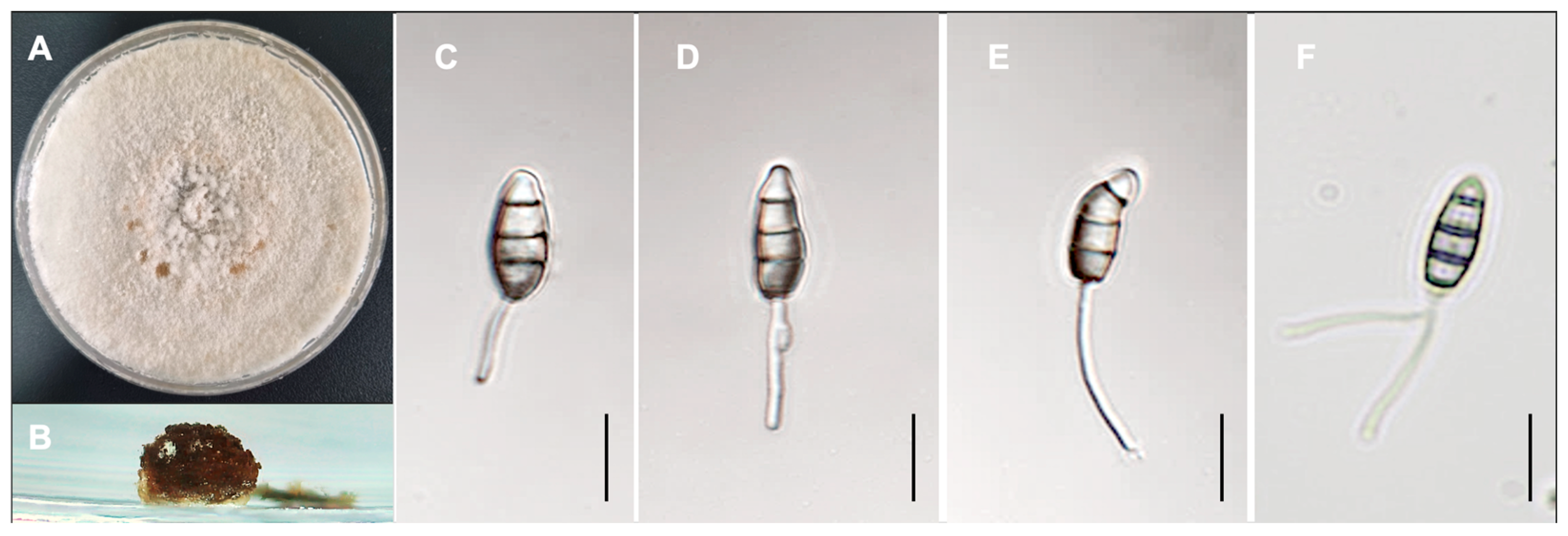
3.3.2. Taxonomy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steyaert, R.L. Contributions à l’étude monographique de Pestalotia de Not. et Monochaetia Sacc. (Truncatella gen. nov. et Pestalotiopsis gen. nov.). Bull. Jard. Bot. Brux. 1949, 19, 285–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bate-Smith, E.C.; Metcalfe, C.R. Leucanthocyanins.3. The nature and systematic distribution of tannin in dicotyledonous plants. J. Linn. Soc. 1957, 55, 669–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.; Guo, L.D.; Chukeatirote, E.; Bahkali, A.H.; Hyde, K.D. Pestalotiopsis—Morphology, phylogeny, biochemistry and diversity. Fungal Divers. 2011, 50, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.; Hyde, K.D.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Xu, J.; Crous, P.W. Pestalotiopsis revisited. Stud. Mycol. 2014, 79, 121–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crous, P.W.; Summerell, B.A.; Swart, L.; Denman, S.; Taylor, J.E.; Bezuidenhout, C.M.; Palm, M.E.; Marincowitz, S.; Groenewald, J.Z. Fungal pathogens of Proteaceae. Pers. Mol. Phylogeny Evol. Fungi 2011, 27, 20–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.; Guo, L.D.; Cai, L.; Chukeatirote, E.; Wu, W.P.; Sun, X.; Crous, P.W.; Bhat, D.J.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Bahkali, A.H.; et al. A multi-locus backbone tree for Pestalotiopsis, with a polyphasic characterization of 14 new species. Fungal Divers. 2012, 56, 95–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.; Chukeatirote, E.; Guo, L.D.; Crous, P.W.; Mckenzie, E.H.; Hyde, K.D. Pestalotiopsis species associated with Camellia sinensis (tea). Mycotaxon 2013, 123, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.; Wei, J.G.; McKenzie, E.; Hyde, K.D. Pestalotiopsis camelliae, a new species associated with grey blight of Camellia japonica in China. Sydowia 2012, 64, 335–344. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, K.; Motohashi, K.; Ono, Y. Description of Pestalotiopsis pallidotheae: A new species from Japan. Mycoscience 2010, 51, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbab, A.; Aly, A.H.; Proksch, P. Mangrove derived fungal endophytes–a chemical and biological perception. Fungal Divers. 2013, 61, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeewon, R.; Liew, E.C.; Simpson, J.A.; Hodgkiss, I.J.; Hyde, K.D. Phylogenetic significance of morphological characters in the taxonomy of Pestalotiopsis species. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 27, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Jeewon, R.; Zhou, D.; Zhou, T.; Hyde, K.D. Phylogenetic diversity of endophytic Pestalotiopsis species in Pinus armandii and Ribes spp.: Evidence from rDNA and β-tubulin gene phylogenies. Fungal Divers. 2007, 24, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gökdemir, F.Ş.; İşeri, Ö.D.; Sharma, A.; Achar, P.N.; Eyidoğan, F. Metagenomics next generation sequencing (mNGS): An exciting tool for early and accurate diagnostic of fungal pathogens in plants. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongman, M.; Carmichael, P.C.; Bill, M. Technological advances in phytopathogen detection and metagenome profiling techniques. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.P.; Prabha, R.; Rai, A.; Arora, D.K. Bioinformatics-assisted microbiological research: Tasks, developments and upcoming challenges. Am. J. Bioinform. 2012, 1, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongman, M.; Chidamba, L.; Korsten, L. Bacterial biomes and potential human pathogens in irrigation water and leafy greens from different production systems described using pyrosequencing. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.W.; Hodkinson, T.R.; Parnell, J.A. Phylogenetics of global Camellia (Theaceae) based on three nuclear regions and its implications for systematics and evolutionary history. J. Syst. Evol. 2023, 61, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.G.; Garcia-Perez, P.; Cassani, L.; Chamorro, F.; Cao, H.; Barba, F.J.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Prieto, M.A. Camellia japonica: A phytochemical perspective and current applications facing its industrial exploitation. Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J.W. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal rna genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, K.J.; Rygiewicz, P.T. Fungal-specific PCR primers developed for analysis of the ITS region of environmental DNA extracts. BMC Microbiol. 2005, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzicalupo, A.L.; Balint, M.; Schmitt, I. Comparison of ITS1 and ITS2 rDNA in 454 sequencing of hyperdiverse fungal communities. Fungal Ecol. 2013, 6, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, R.H.; Larsson, K.H.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Jeppesen, T.S.; Schigel, D.; Kennedy, P.; Picard, K.; Glöckner, F.O.; Tedersoo, L.; et al. The UNITE database for molecular identification of fungi: Handling dark taxa and parallel taxonomic classifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D259–D264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’Hara, B.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Oksanen, M.J.; Suggests, M.A.S.S. The vegan package. Commun. Ecol. Pack. 2007, 10, 631–637. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, D.J.; Arts, I.C.; Penders, J. microViz: An R package for microbiome data visualization and statistics. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, N.L.; Donaldson, G.C. Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, K.; Cigelnik, E. Two divergent intragenomic rDNA ITS2 types within a monophyletic lineage of the fungus Fusarium are nonorthologous. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1997, 7, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K.; Kistler, H.C.; Cigelnik, E.; Ploetz, R.C. Multiple evolutionary origins of the fungus causing Panama disease of banana: Concordant evidence from nuclear and mitochondrial gene genealogies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2044–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, I.; Kohn, L.M. A method for designing primer sets for speciation studies in filamentous ascomycetes. Mycologia 1999, 91, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Crous, P.W. Phylogenetic reassessment of the coelomycete genus Harknessia and its teleomorph Wuestneia (Diaporthales), and the introduction of Apoharknessia gen. nov. Stud. Mycol. 2004, 50, 235–252. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML-VI-HPC: Maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2688–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A.; Hoover, P.; Rougemont, J. A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML Web servers. Syst. Biol. 2008, 57, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.X.; Liao, M.G.; Zhang, K.; Castañeda-Ruíz, R.F.; Ma, J.; Xu, Z.H. Morphological and phylogenetic analyses reveal eight novel species of Pestalotiopsis (Sporocadaceae, Amphisphaeriales) from southern China. MycoKeys 2024, 109, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, A.M.; Gafencu, A.M.; Lipșa, F.D.; Gabur, I.; Ulea, E. Occurrence of Pestalotiopsis sp. on ornamental plants Camellia japonica L. in Romanian public gardens. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, C.L.; Seifert, K.A.; Huhndorf, S.; Robert, V.; Spouge, J.L.; Levesque, C.A.; Chen, W.; Bolchacova, E.; Voigt, K.; Crous, P.W.; et al. Nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region as a universal DNA barcode marker for Fungi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6241–6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korean Society of Plant Pathology. Korea’s List of Plant Diseases, 6th ed.; Korean Society of Plant Pathology: Suwon, Republic of Korea, 2023; pp. 123–124. [Google Scholar]



| Species | Isolates | ITS | TUB | TEF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. abbreviata | GNUFP284 | OR478187 | OR480768 | OR480770 |
| P. abbreviata | GNUFP285 | OR478188 | OR480769 | OR480771 |
| P. aggestorum | LC6301 | KX895015 | KX895348 | KX895234 |
| P. brachiata | LC2988 | KX894933 | KX895265 | KX895150 |
| P. camelliae | CBS 433.62 | KM199336 | KM199424 | KM199512 |
| P. camelliae | MFLUCC 12-0277 | JX399010 | JX399041 | JX399074 |
| P. camelliicola | HJAUP C1804.221 | PP962357 | PP952229 | PP952236 |
| P. camelliicola | HJAUP C1804.222 | PP962358 | PP952230 | PP952235 |
| P. chamaeropis | CBS 113604 | KM199323 | KM199389 | KM199471 |
| P. chamaeropis | CBS 186.71 | KM199326 | KM199391 | KM199473 |
| P. chinensis | LC3013 | KX894939 | KX895271 | KX895156 |
| P. clavata | MFLUCC 12-0268 | JX398990 | JX399025 | JX399056 |
| P. dilucida | LC3232 | KX894961 | KX895293 | KX895178 |
| P. diversiseta | MFLUCC 12-0287 | NR 120187 | JX399040 | JX399073 |
| P. furcata | LC6303 | KX895016 | KX895349 | KX895235 |
| P. gaultheriae | IFRD 411–014 | KC537805 | KC537819 | KC537812 |
| P. gibbosa | NOF 3175 | LC311589 | LC311590 | LC311591 |
| P. hollandica | CBS 265.33 | KM199328 | KM199388 | KM199481 |
| P. inflexa | MFLUCC 12-0270 | JX399008 | JX399039 | JX399072 |
| P. intermedia | MFLUCC 12-0259 | JX398993 | JX399028 | JX399059 |
| P. italiana | MFLUCC 12-0657 | KP781878 | KP781882 | KP781881 |
| P. jesteri | MFLUCC 12-0279 | JX399012 | JX399043 | JX399076 |
| P. jiangxiensis | LC4242 | KX895035 | KX895327 | KX895213 |
| P. jiangxiensis | LC4399 | KX895009 | KX895341 | KX895227 |
| P. jinchanghensis | LC6636 | KX895028 | KX895361 | KX895247 |
| P. kenyana | LC3291 | KX894962 | KX895294 | KX895179 |
| P. linearis | MFLUCC 12-0271 | JX398992 | JX399027 | JX399058 |
| P. lushanensis | LC4344 | KX895005 | KX895337 | KX895223 |
| P. monochaeta | CBS 144.97 | KM199327 | KM199386 | KM199479 |
| P. novae-hollandiae | CBS 130973 | NR_147557 | KM199425 | KM199511 |
| P. portugalica | CBS 393.48 | KM199335 | KM199422 | KM199510 |
| P. rhododendri | IFRDCC 2399 | KC537804 | KC537818 | KC537811 |
| P. rhodomyrtus | HGUP4230 | KF412648 | KF412642 | KF412645 |
| P. scoparia | CBS 176.25 | KM199330 | KM199393 | KM199478 |
| P. spathulata | CBS 356.86 | NR 147558 | KM199423 | KM199513 |
| P. trachicarpicola | OP143 | KC537809 | KC537823 | KC537816 |
| P. yanglingensis | LC3067 | KX894949 | KX895281 | KX895166 |
| P. yanglingensis | LC4553 | KX895012 | KX895345 | KX895231 |
| Class | Order | Family | Genus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classified ASV | 876 | 798 | 692 | 626 |
| Identified taxa | 11 | 47 | 119 | 180 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, S.-E.; Park, K.H.; Shin, K.; Lee, D.-H. Detection of Pestalotiopsis abbreviata sp. nov., the Causal Agent of Pestalotiopsis Leaf Blight on Camellia japonica Based on Metagenomic Analysis. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080553
Cho S-E, Park KH, Shin K, Lee D-H. Detection of Pestalotiopsis abbreviata sp. nov., the Causal Agent of Pestalotiopsis Leaf Blight on Camellia japonica Based on Metagenomic Analysis. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(8):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080553
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Sung-Eun, Ki Hyeong Park, Keumchul Shin, and Dong-Hyeon Lee. 2025. "Detection of Pestalotiopsis abbreviata sp. nov., the Causal Agent of Pestalotiopsis Leaf Blight on Camellia japonica Based on Metagenomic Analysis" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 8: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080553
APA StyleCho, S.-E., Park, K. H., Shin, K., & Lee, D.-H. (2025). Detection of Pestalotiopsis abbreviata sp. nov., the Causal Agent of Pestalotiopsis Leaf Blight on Camellia japonica Based on Metagenomic Analysis. Journal of Fungi, 11(8), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11080553







