Abstract
Background: Veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (V-V ECMO) represents a progressively adopted life-sustaining intervention worldwide, particularly in the management of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nevertheless, data concerning the prognostic significance of fungal isolation in this setting remain unclear. This study aims (i) to assess the incidence of fungal infection and colonization in a homogeneous cohort of V-V ECMO patients, and (ii) to evaluate the association between fungal infection or colonization and 1-year mortality, with a focus on the impact of specific fungal species. Methods: All consecutive adults admitted to the Intensive Care Units of five Italian university-affiliated hospitals and requiring V-V ECMO were screened. Exclusion criteria were age < 18 years, pregnancy, veno-arterial or mixed ECMO-configuration, incomplete records and survival < 24 h after V-V ECMO placement. A standard protocol of microbiological surveillance was applied and the distinction between different fungal species were made through in vivo and vitro tests. Cox-proportional hazards models, Kaplan–Meier curves and linear logistic regressions were applied for investigating mortality. Results: Two-hundred and seventy-nine V-V ECMO patients (72% male) were enrolled. The overall fungal isolation was 41% (n. 114): 23% infections and 18% colonizations. The overall 1-year mortality, among fungal isolations, was 40%, with no different risk in case of fungal infection (26 out of 63, 41%) (aHR 0.85, 95% CI [0.53–1.37], p-value 0.505) and colonization (20 out of 51, 39%) (aHR 0.86, 95%CI [0.51–1.43], p-value 0.556), as compared to patients never detecting fungi (68 out of 165, 41%, reference). According to the isolated mycotic species, as compared to Candida sp. group (reference), the risk of death was greater when different fungal species (e.g., Aspergillus sp. and Candida sp.) were concomitantly isolated in the same patient (OR 1.17, 95%CI [1.12–11.07], p-value 0.031. Conclusions: In the overall population, 23% V-V ECMO patients recorded ‘late’ fungal infections and 18% fungal colonizations, with a similar risk of death as compared to patients never experiencing fungi during the V-V ECMO course. The detection of concomitant different fungal species was an independent risk factor for 1-year mortality.
1. Background
Veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (V-V ECMO) is increasingly adopted worldwide as a life-sustaining therapy, particularly in patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) unresponsive to conventional mechanical ventilation [1,2,3,4]. By providing extracorporeal gas exchange, V-V ECMO can fully substitute the lungs’ function in oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide removal [1,5,6,7]. According to the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO) registry, more than 56,000 adult respiratory ECMO cases have been reported, emphasizing its growing significance in critical care [1]. Despite its life-saving potential in cases of respiratory failure, V-V ECMO is associated with a heightened risk of infections, including invasive fungal infections (IFIs). This increased susceptibility is multifactorial, involving prolonged ICU stays, extensive use of broad-spectrum antimicrobials and immune dysregulation due to critical illness [1,2,3,4,5]. While the overall burden of IFIs in ICU populations is well recognized, data specifically focused on IFIs among V-V ECMO recipients remain limited.
Since the initial definitions proposed by the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group (EORTC) in 2002 [8], considerable efforts have been dedicated to understanding the clinical implications of fungal infections (FIs). The latest guidelines from the European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID), published in 2017, emphasize a multifaceted diagnostic approach involving clinical evaluation, radiological imaging, and both serological and microbiological testing [9]. Nonetheless, the incidence and outcomes of FIs in patients undergoing V-V ECMO support remain poorly characterized.
IFIs are well established as major contributors to morbidity and mortality, especially among immunocompromised individuals. However, IFIs also affect non-neutropenic critically ill patients, usually admitted to the ICU, even in the absence of traditional risk factors for fungal infections [10,11,12,13,14]. The recently published CHARTER-IFI study, which assessed over 700 ICU patients, reported an incidence of 4.0 fungal infections per 1.000 ICU admissions. However, it did not analyze outcomes specifically in patients receiving extracorporeal support [15]. Similarly, the Italian AURORA study identified 105 IFI episodes among 5.561 ICU patients over an 18-month period, with infections predominantly caused by yeasts rather than filamentous fungi—corresponding to overall incidences of 16.5 and 2.3 cases per 1.000 admissions, respectively. The crude mortality rate was alarmingly high (42.8%), particularly in cases of mold infections (61.5%) [16]. Yet, neither of these studies addressed the incidence or prognostic impact of IFIs in the context of V-V ECMO.
Building on these gaps, we designed the present multicenter retrospective study with the primary aim of investigating, in a large cohort of V-V ECMO patients, (i) the prevalence of fungal infections and colonization, and (ii) the associated 1-year mortality risk, compared to patients who did not experience fungal isolation during their V-V ECMO course, with an additional analysis based on fungal species.
2. Methods
This multicenter observational study was conducted between 1 January 2017 and 31 December 2022 in 5 ICU of Italian university-affiliated hospitals, overall accounting for a total of 70-ICU beds (i.e., Mater Domini Hospital (Catanzaro); Padua University Hospital; Verona University Hospital; Policlinico University Hospital (Bari) and Fondazione IRCSS Gerardo Hospital dei Tintori Hospital (Monza)). We included adult patients, over 18 years of age, who received V-V ECMO for respiratory support during the study period. The exclusion criteria were age < 18 years old, pregnancy, veno-arterial (V-A) or mixed ECMO-configuration (e.g., V-VA), incomplete records for the main outcomes (absence of 1-year mortality and/or microbiological surveillance) and survival <24 h after cannulation. The study was conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki and the approval for the investigation was granted by the local Ethics Committee “Comitato Etico Territoriale Regione Calabria” (approval n. 22 on 27 September 2023), which waived the need for informed consent due to the retrospective observational nature of the study. All patient data was anonymized and de-identified before analysis. This study followed the ‘Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement guidelines for observational cohort studies’ (Supplementary Table S1) [17].
The decision to start V-V ECMO treatment was made by senior intensivists (PN, FL, EB, GF, LG, SG), according to the ELSO guidelines/recommendations [1]. All V-V ECMOs were placed exclusively in the ICU, and a femoro-jugular configuration was preferred. All centers kept the ECMO circuit isolated as much as possible (e.g., withdrawals or infused medications were not recommended). Antimicrobial prophylaxis, at the time of cannulation, was uniformly not administered [18]. Routine microbiological surveillance was uniformly conducted in all centers, starting from ICU admission, as previously published [18]. All positive bacterial and fungal cultures were independently evaluated, considering the available clinical, laboratory and radiographic data, by specialized intensivists and infectious diseases specialists. In case of fungal cultures, strict communication between ICUs, microbiology laboratories and infectious disease specialist consultants were mandatory before starting a targeted antifungal therapy. The microbiological follow-up for this study arbitrarily ended 72 h after V-V ECMO decannulation.
According to the FUNDICU consensus definition, published in 2024, V-V ECMO patients were distinguished in 3 groups: the ‘fungal infection’ group (i), including patients with the presence of fungal cultures, collected from bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), soft tissue, blood stream, urine etc., and in the presence of symptoms, radiological and endobronchial changes, or the presence of histological changes consistent with fungal invasion of tissue [19,20,21]; the ‘fungal colonization’ group (ii), when mycological evidence was not supported by clinical symptoms, radiological or endobronchial changes; and the ‘absence of fungi’ group (iii), including the population without evidence of FIs or colonizations. Moreover, we also recorded some fungal biomarkers (i.e., galactomannan (GM) antigen and β-D-glucan), quantified concomitantly to microbiological cultures. Specifically, they were requested at least once in each patient with fungal infections, while the percentage was lower (around 60%) in the case of the colonization solely.
3. Data Collection
The electronic health records were retrospectively examined, and the following variables were collected: demographic and baseline characteristics, Charlson’s Comorbidity index, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score at ICU admission and at V-V ECMO cannulation, initiation of invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV), indications for V-V ECMO support, year of V-V ECMO connection, overall V-V ECMO duration, concomitant isolation of viral or bacterial isolations (Table 1), outcomes of interest (1-year mortality, 28-day ventilator-free days, Intensive Care Unit (ICU) length of stay (LOS) [22], microbiological results obtained during V-V ECMO support, type of fungal isolation, site of isolation and fungal biomarkers [18] (Table 2).
4. Statistical Analysis
Continuous variables are presented as medians and interquartile ranges (IQR) or as mean and standard deviation (SD), while categorical variables are presented as numbers (percentages). Baseline patients’ characteristics and outcome variables were compared between two or three pre-defined subpopulations, as follows: (1) ‘fungal infections’, (2) ‘fungal colonitazions’, and (3) ‘absence of fungi’. The sample size could not be calculated due to the explorative design of our investigation and the scarcity of data on this topic. The t-test, Mann–Whitney test, ANOVA or Kruskal–Wallis test was properly used to compare continuous variables and adjusted by Benjamini–Hochberg method. Chi-square and Fisher’s exact tests were used for comparing categorical variables.
Regarding 1-year mortality, the Kaplan–Meier curves were provided only as graphical support (Figures S1 and S2). For investigating the risk of mortality, the adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) and 95% confidence intervals [CI] were calculated using Cox-proportional hazards models (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Cox-proportional hazards models assume that the hazard ratio is constant over time; therefore, the test for proportional hazard assumption was verified for each covariate included in the univariable model. The time-dependent variable started from ICU admission. All variables described in Table 1, with a significance p-value < 0.10, were included in an univariable Cox-proportional hazards model investigating 1-year mortality (*). Then, as shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, the multivariable adjustment was provided according to significant confounders (p-value < 0.05) identified through the univariable Cox-proportional hazards model, as mentioned above (*). Given the low incidence of pre-existing fungal infections (~4%), a statistical analysis solely dedicated to this subgroup was not feasible. For investigating the impact of fungal isolation (in terms of species and site) on the risk of 1-year mortality, a linear logistic regression was applied (Table 3). The unadjusted odds ratio (OR) and 95% CI were calculated, all tests were two-sided and p-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. The analyses were performed using R (version 4.0.3, R foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
5. Results
From January 2017 to December 2022, 482 ICU patients treated with ECMOs for severe respiratory failure were screened. After excluding 199 subjects needing V-A or mixed ECMO-configuration, 2 patients because of incomplete records and 2 due to a survival shorter than 24 h after V-V ECMO initiation, 279 patients (median age 54 years; 72% male) were included in the final analysis (see Figure S3). Patients’ demographic characteristics, SOFA scores, indications for V-V ECMO support, corticosteroids use and other baseline information are summarized in Table 1.
5.1. Baseline Characteristics and Primary Outcome
In our cohort, the prevalence of mycotic isolation among V-V ECMO patients was 42% (n. 114): among 279 patients, 63 (23%) were defined “infected” and 51 (18%) as “colonized”, while 165 (59%) subjects had no occurrence of fungi during extracorporeal treatment. Of those patients with fungal isolations, only 4 (4%) subjects had pre-detected fungal infections at the start of V-V ECMO, mostly Aspergillus sp. (time of the first fungal isolation: 2 [0–4] days after ICU admission). As described in Table 1, patients’ baseline characteristics were not different among the three subgroups, except for SOFA at the V-V ECMO connection that was significantly higher in case of fungal colonizations (9 [5–12]) as compared to other subgroups (p-value 0.008) (Table 1). As compared to patients never experiencing fungi, V-V ECMO duration was longer in the case of fungal isolation (infection: 16 [10–27] days, colonization: 16 [11–26] days) (p-value < 0.001); also, the length of ICU was remarkably more prolonged both in the case of fungal infection (35 [23–53] days) and colonization (35 [23–54]) days) (p-value < 0.001). Moreover, 49 out of 63 (78%) patients with fungal infection and 38 out of 51 (18%) patients with fungal colonization had a greater rate of concomitant GN bacteria isolation, usually detected before fungal isolation (p-value 0.007) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Patients’ characteristics and outcomes.
Table 1.
Patients’ characteristics and outcomes.
| Overall Population (N = 279, 100%) | Fungal Infections 1 (N = 63, 23%) | Fungal Colonizations 2 (N = 51, 18%) | Others 3 (N = 165, 59%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline characteristics | |||||
| Age, years | 54 [44–61] | 54 [45–59] | 51 [38–63] | 55 [45–61] | 0.636 |
| Gender (male), n (%) | 200 (72) | 44 (70) | 36 (71) | 120 (72) | 0.146 |
| TBW, Kg | 66 [60–71] | 67 [58–71] | 67 [61–72] | 65 [57–70] | 0.583 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index (w/o age) | 1 [0–2] | 1 [0–2] | 1 [0–1] | 1 [0–2] | 0.610 |
Sepsis Organ Failure Assessment
| 8 [6–11] | 8 [6–9] | 8 [4–10] | 10 [7–12] | 0.065 * |
| 9 [7–12] | 8 [7–9] | 9 [5–12] | 9 [7–12] | 0.008 a |
| Mechanical ventilation before V-V ECMO connection, days | 2 [1–5] | 3 [1–5] | 2 [1–6] | 2 [1–5] | 0.113 |
| Corticosteroids > 7 days | 271 (97) | 60 (95) | 51 (100) | 160 (97) | 0.999 |
| Indications for V-V ECMO support | |||||
| 233 (84) | 61 (97) | 37 (73) | 135 (82) | 0.767 |
| 46 (16) | 15 (24) | 11 (22) | 30 (18) | 0.767 |
| Year of V-V ECMO connection, n (%) | |||||
| 101 (36) | 18 (29) | 22 (43) | 61 (40) | 0.266 |
| 178 (64) | 45 (71) | 29 (57) | 104 (63) | 0.266 |
| V-V ECMO duration, days | 12 [8–22] | 16 [10–27] | 16 [11–26] | 11 [7–17] | <0.001 b* |
| Concomitant isolation of | |||||
| 157 (56) | 28 (44) | 31 (61) | 98 (59) | 0.103 |
| 183 (66) | 49 (78) | 38 (75) | 96 (58) | 0.007 e |
| 139 (50) | 34 (54) d | 27 (53) d | 78 (47) | 0.200 |
| 44 (16) | 15 (24) | 11 (22) | 18 (11) | 0.200 |
| 57 (20) | 12 (19) | 14 (27) | 31 (19) | 0.393 |
| Outcomes | |||||
| Mortality at 1-year, n (%) | 116 (42) | 26 (41) | 20 (39) | 68 (41) | 0.970 |
| 28-day ventilator-free days | 0 [0–8] | 0 [0–5] | 0 [0–6] | 0 [0–9] | 0.478 |
| ICU LOS, days | 27 [18–43] | 35 [23–53] | 35 [23–54] | 23 [16–34] | <0.001 f |
Data are presented as absolute frequency (% of the included patients) or as median and interquartile range or as mean ± SD. Three groups are compared and named ‘1’, ‘2’ and ‘3’. a: (1) vs. (2) p-value 0.039; b: (1) vs. (3) p-value < 0.001, (2) vs. (3) p-value < 0.001; c: in the case of multiple bacterial isolations, only the worst resistance pattern was counted. d: 17 MDR/ESBL Gram-negative bacteria were detected before fungal infections, while 6 were detected before fungal colonizations (p-value 0.028); e: (1) vs. (3) p-value 0.006, (2) vs. (3) p-value 0.047; f: (1) vs. (3) p-value < 0.001, (2) vs. (3) p-value < 0.001. *: covariates available for univariable analysis. Abbreviations: ICU: intensive Care Unit; IBW: ideal body weight; ECMO: extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; N or n: number; SD: standard deviation; V-V: veno-venous; CLAD: chronic lung allograft dysfunction; ESBL: extended spectrum beta-lactamases; MDR: multidrug resistant.
5.2. Secondary Outcomes
As shown in Table 2, Aspergillus sp. (40%) was more frequently detected in case of infection, as compared to colonization (33%), while Candida sp. was prevalent in case of mycotic colonization (63% versus 38%) (overall p-value 0.004).

Table 2.
Microbiological characteristics.
Table 2.
Microbiological characteristics.
| Fungal Infections (N = 63, 100%) | Fungal Colonizations (N = 51, 100%) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microbiological pattern |  | 0.004 | ||
| 24 (38) | 32 (63) | ||
| 25 (40) | 17 (33) | ||
| 14 (22) | 2 (4) | ||
| Site of fungal isolation | ||||
| 24 (38) | 45 (88) |  | <0.001 |
| 11 (17) | 0 (0) | ||
| 9 (14) | 0 (0) | ||
| 15 (24) | 1 (2) | ||
| 4 (6) | 5 (10) | ||
| Fungal biomarkers | ||||
| 18 (29) | 2 (4) | <0.001 | |
| 8 (13) | 3 (6) | 0.340 | |
Data are presented as absolute frequency (% of the included patients). For more details about survival, see Figure 1 and Figure 2. a: time of isolation 8 [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14] days after ICU admission; b: time of isolation 11 [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16] days after ICU admission, except in pre-detected patients; c: Different fungal isolations were included in this group. Abbreviations: N or n: number; sp.: species; BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; ICU, Intensive Care Unit.
With regards to infections, many fungi were isolated from airways (38%) (i.e., mostly Aspergillus sp.) or from urinary tract (24%) (i.e., mainly Candida sp.); while, considering fungal colonizations, mycotic isolations from airways were prevalent (88%) (overall p-value < 0.001). BAL galactomannan antigen was usually greater than 1 in case of infection, as compared to colonization (overall p-value < 0.001), while no differences were found considering β-D-glucan (reference > 80 pg/mL) (p-value 0.340).
As shown in Table 1, the 1-year mortality was not different in patients experiencing fungal infection (26 out of 63, 41%) (aHR 0.85, 95% CI [0.53–1.37], p-value 0.505) or fungal colonization (20 out of 51, 39%) (aHR 0.86, 95% CI [0.51–1.43], p-value 0.556), as compared to those patients without mycotic isolation (68 out of 165, 41%, reference) (Figure 1).
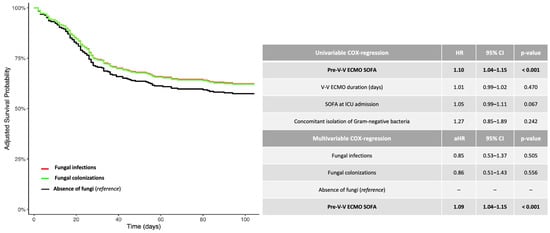
Figure 1.
Adjusted 1-year survival curves (Cox regression model: fungal infection versus fungal colonization versus absence of fungi). The adjusted (covariate: SOFA score at V-V ECMO connection) HRs were calculated according to the univariable and multivariable Cox-proportional hazards models described in the table. Data are presented as HR, aHR and 95% CI. For unadjusted Kaplan–Meier survival curves, see Figure S2. Abbreviations: ECMO: extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; HR: hazard ratio; aHR: adjusted hazard ratio; CI: confidential interval; V-V: veno-venous.
Additional summary data on patients with documented fungal isolation are reported in Figure 2.
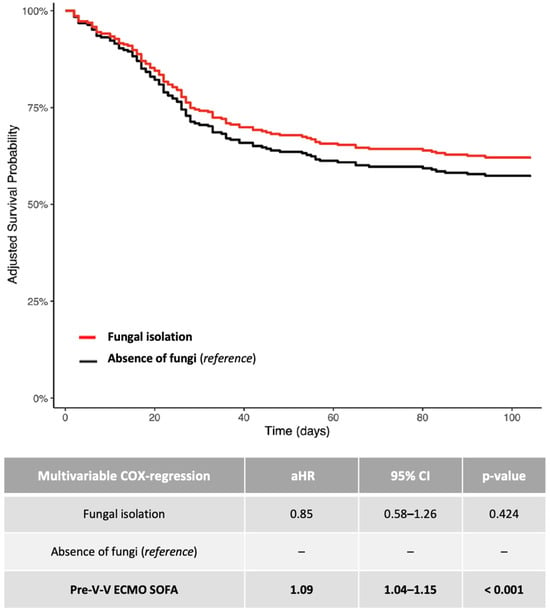
Figure 2.
Adjusted 1-year survival curves (Cox regression model: fungal isolation versus absence of fungi). The adjusted (covariate: SOFA score at V-V ECMO connection) HRs were calculated according to the univariable and multivariable Cox-proportional hazards models described in the table. Data are presented as HR, aHR and 95% CI. For unadjusted Kaplan–Meier survival curves, see Figure S2. Abbreviations: ECMO: extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; HR: hazard ratio; aHR: adjusted hazard ratio; CI: confidential interval; V-V: veno-venous.
According to the type of isolated mycotic species, as compared to those patients culturing Candida sp. solely (reference), the risk of death was significantly greater in patients detecting simultaneously different fungal species (OR 1.17, 95% CI [1.12–11.07], p-value 0.031), while not in the case of Aspergillus sp. solely (OR 1.04, 95% CI [0.31–3.50], p-value 0.952), (Table 3). Finally, the site of isolation was not correlated to death (Table 3).

Table 3.
Unadjusted odds of 1-year mortality according to isolated fungal species and site of detection.
Table 3.
Unadjusted odds of 1-year mortality according to isolated fungal species and site of detection.
| Linear Logistic Regression | aOR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aspergillus sp. | 1.04 | 0.31–3.50 | 0.952 |
| Concomitant different fungal sp. | 1.17 | 1.12–11.07 | 0.031 |
| Candida sp. (reference) | - | - | - |
| Isolation from airways and/or blood stream (reference: other sites) | 1.17 | 0.27–5.06 | 0.831 |
Abbreviations: OR: odds ratio; CI: confidential interval; sp., species.
6. Discussion
In this multicenter retrospective study, we found that among 279 consecutive adult patients supported by V-V ECMO for acute respiratory failure, the prevalence of fungal colonization was 18%, while the prevalence of mycotic infection was 23% during V-V ECMO course. The 1-year mortality was not different in patients experiencing fungal infections (41%) or fungal colonizations (39%), as compared to those patients without mycotic isolation (41%), while the risk of death was greater in patients where different species of fungi were concomitantly isolated, as compared to one species.
In the past decade, IFIs have emerged as a growing concern in the ICU setting and recognized as a cause of morbidity and mortality not only in immunocompromised patients but also in the general critically ill population [22]. Recent studies have highlighted a rising incidence of IFIs among ICU patients, with estimates indicating that up to 20% may develop fungal infections during hospitalization [16,23].
The COVID-19 pandemic further altered the epidemiological landscape of fungal infections in critically ill patients [15]. As the pandemic progressed, clinicians increasingly focused on identifying and managing co-infections, particularly invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA) [24]. This heightened awareness contributed to improved recognition and reporting of fungal infections in ICU settings [21,25]. For instance, mortality rates in COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis have been reported to range from 30% to over 50%, especially when antifungal treatment is delayed—highlighting the need for heightened clinical vigilance, standardized diagnostic criteria, and early therapeutic interventions [26,27,28].
Corroborating this alarming trend, our study found fungal isolation in nearly half of the patients. This rate appears notably higher than those previously reported in studies of mixed ECMO populations [29], as well as in both V-A [30] and V-V ECMO cohorts [31]. This discrepancy may be explained by the fact that these earlier studies were more focused on proven infections rather than on fungal isolations. Moreover, both abovementioned investigations did not include COVID-19 patients, as we did.
A systematic review confirmed that critically ill patients on ECMO are more likely to develop candidemia and other fungal infections compared to those not receiving ECMO support [32]. Several risk factors contribute to this elevated vulnerability. Many ECMO patients have pre-existing comorbidities such as diabetes, cancer, or chronic lung disease, which predispose them to IFIs [30,33]. Additionally, the acute illness often leads to malnutrition or altered nutritional status, further weakening immune defenses [33].
With regards to the fact that in our cohort, the isolation of fungi was not necessarily related to a poorer outcome, we can speculate that fungal infections acquired during V-V ECMO support tend to occur relatively late. These infections are likely not severe enough to impact late mortality among patients who survive longer. This observation may also explain why, in the group without fungal isolations—which experienced a higher rate of early mortality, moslty due to bacterial or viral infections—fewer patients survived long enough to be at risk of acquiring a fungal infection. Therefore, the acquisition of such infections does not appear to be a clinically relevant factor influencing prognosis. Indeed, the p-values comparing the black and red curves (Figure 1 and Figure 2) were not statistically significant.
This interpretation is consistent with the previous literature reporting that fungal infections during ECMO typically develop later in the course of treatment and are more often associated with prolonged support or underlying risk factors, rather than being direct contributors to early mortality [34,35].
Moreover, broad-spectrum antibiotics, frequently administered to these V-V ECMO patients to combat pre-detected bacterial infections, can disrupt the microbiome and promote fungal overgrowth [18,36]. We attempted to explore this potential association indirectly by including the variable ‘concomitant isolation of GN bacteria’ in the multivariable Cox regression analysis, as shown in Figure 1. Unfortunately, this variable did not reach statistical significance in our cohort. However, our findings should be confirmed by larger prospective studies. Additionally, immunosuppressive therapies—including corticosteroids—further exacerbate the risk of Fis [36,37].
Moreover, the extensive use of invasive devices, such as central venous catheters, endotracheal tubes, and arterial lines, which are common in ECMO-supported patients, increases the risk of fungal colonization and subsequent infection [33,36]. Prolonged ICU stays, often necessary for ECMO, further increase exposure to these risks [33,36].
With regards to mortality, in our cohort, the overall survival rate aligns with data from the ELSO registry, which reports a 48% survival to hospital discharge in patients undergoing either V-A or V-V ECMO [29]. However, the current literature lacks specific data on the prognostic impact of fungal isolation—including both colonization and invasive infection—in patients receiving V-V ECMO. Nonetheless, the clinical relevance of IFIs as drivers of morbidity and mortality in ICU patients, particularly among immunocompromised individuals, is well documented [21]. For example, the Italian AURORA study reported 105 IFI episodes among 5.561 ICU patients over 18 months, with a crude mortality exceeding 40%, and reaching over 60% in cases of mold infections [16]. In particular, invasive aspergillosis is associated with significantly higher mortality than candidemia in critically ill or immunocompromised patients, with rates often exceeding 50% compared to 20–40% for invasive candidiasis [28,38,39,40]. However, in our V-V ECMO cohort, only the concomitant isolation of different mycotic species, usually including Aspergillus sp. and Candida sp., was linked to a higher risk of 1-year mortality.
Indeed, in the high-risk setting of V-V ECMO, where fungal isolation is strikingly common, early recognition and prompt intervention are paramount—not only to curb the progression from colonization to invasive infection, but potentially to alter the trajectory of patient survival.
This study had several limitations. First, it is a retrospective observational study which bears the limits of this design. Second, despite a wide population consisting exclusively of V-V ECMO adult patients, the categorization of the cohort according to the fungal isolation status inevitably resulted in three small-size subgroups. We believe that a broader cohort in the future would better delineate outcomes and validate our findings. Third, we did not investigate whether the cannulation site may influence the infectious risk, despite the internal jugular and femoral vein being the most common sites of catheterization (>80% in our cohort) [41]. Fourth, according to our previous findings, describing an inverse relationship between MDR GN bacteria occurrence and local institutional experience, we cannot exclude also a higher rate of fungal infection occurring in those centers with a lower annual hospital V-V ECMO volume [18].
7. Conclusions
In the overall population, 23% V-V ECMO patients recorded fungal infections and 18% recorded mycotic colonizations (of those, 40% died within 1 year), with a similar risk of death as compared to patients never experiencing fungi during V-V ECMO course. The detection of concomitant different fungal species was an independent risk factor for 1-year mortality.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jof11050377/s1; Table S1. STROBE Statement—Checklist; Figure S1. 1 year-mortality (Kaplan Meier: fungal isolation versus absence of fungi); Figure S2. 1 year-mortality; Figure S3. Flowchart; (Kaplan Meier: fungal infection versus fungal colonization versus absence of fungi)
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B. (Annalisa Boscolo), A.P., E.B., F.L., P.N., M.G., E.G., N.S., T.P., A.B. (Andrea Bruni) and G.F.; data curation, M.G., E.G., N.S., T.P., A.B. (Andrea Bruni), A.P., M.B., M.P. (Matteo Palcani), M.P. (Matteo Pozzi), E.F., F.M., L.G., F.L. and G.F.; formal analysis, F.M. and S.G.; investigation, M.B., M.P. (Matteo Palcani), M.P. (Matteo Pozzi) and E.F.; methodology, M.G., E.G., N.S., T.P., A.B. (Andrea Bruni), A.B. (Annalisa Boscolo), A.P., M.B., M.P. (Matteo Palcani), E.R., M.P. (Matteo Pozzi), E.F., E.B., F.M., L.G., S.G., P.N. and G.F.; supervision, A.B. (Annalisa Boscolo), A.P., M.B., E.B., L.G., F.L., S.G. and P.N.; validation, M.P. (Matteo Palcani), E.F., M.G., E.G., N.S., T.P., A.B. (Andrea Bruni) and P.N.; writing—original draft, A.B. (Annalisa Boscolo), E.R., M.P. (Matteo Pozzi), E.F., E.B., F.L. and S.G.; writing—review and editing, A.B. (Annalisa Boscolo), E.R., F.M., L.G. and G.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The approval for the investigation was granted by the “Comitato Etico Territoriale Regione Calabria” (approval n. 22 on 27 September 2023), which waived the need for informed consent due to the retrospective observational nature of the study.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to all infectious disease colleagues (Annamaria Cattelan (Padua), Guglielmo Marco Migliorino (Monza), Alessandro Russo (Catanzaro), Evelina Tacconelli (Verona), Annalisa Saracino and Nicolò De Gennaro (Bari)) for their priceless help in revising microbiological records. We thank all ICU colleagues (Ida Caregnato, Silvia Crociani, Arméla Anne-Sabine Tagne, Giuseppe Neri, Alessandra Pasqua, Lucia Lentini and Antonio Civita) who made this work possible. In addition, the authors thank Kirstin Elisabeth Rose for proofreading the article and editing English language.
Conflicts of Interest
None related to the present work. PN research lab received grants/research equipment from Draeger, Mindray, Intersurgical SPA, and Gilead. PN receives royalties from Intersurgical SPA for the Helmet Next invention. He also received speaking fees from Getinge, Intersurgical SPA, Gilead, MSD, Draeger. NS received speaking fees from Getinge. MG received congress travel and accommodation support from Getinge. SG received grants/research equipment from Estor (Italy) and speaking fees from Getinge.
List of Abbreviations
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| BAL | Bronchoalveolar lavage |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| ELSO | Extracorporeal Life Support Organization |
| ESCMID | European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases |
| EORTC | European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer |
| FIs | Fungal infections |
| GN | Gram-negative |
| GM | Galactomannan |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| IFI(s) | Invasive fungal infection(s) |
| IMV | Invasive mechanical ventilation |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| LOS | Length of stay |
| MDR | Multi-drug resistant |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SOFA | Sequential Organ Failure Assessment |
| STROBE | Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology |
| V-A ECMO | Veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| V-V ECMO | Veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| V-VA ECMO | Veno-veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
References
- Tonna, J.E.; Abrams, D.; Brodie, D.; Greenwood, J.C.; Rubio Mateo-Sidron, J.A.; Usman, A.; Fan, E. Management of Adult Patients Supported with Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (VV ECMO): Guideline from the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO). ASAIO J. 2021, 67, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.G.; Pham, T.; Fan, E.; Brochard, L.; Esteban, A.; Gattinoni, L.; van Haren, F.; Larsson, A.; McAuley, D.F.; et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA 2016, 315, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasselli, G.; Calfee, C.S.; Camporota, L.; Poole, D.; Amato, M.B.P.; Antonelli, M.; Arabi, Y.M.; Baroncelli, F.; Beitler, J.R.; Bellani, G.; et al. ESICM guidelines on acute respiratory distress syndrome: Definition, phenotyping and respiratory support strategies. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 49, 727–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ARDS Definition Task Force; Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar]
- Peek, G.J.; Mugford, M.; Tiruvoipati, R.; Wilson, A.; Allen, E.; Thalanany, M.M.; Hibbert, C.L.; Truesdale, A.; Clemens, F.; Cooper, N.; et al. Efficacy and economic assessment of conventional ventilatory support versus extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe adult respiratory failure (CESAR): A multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009, 374, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sella, N.; Pettenuzzo, T.; Zarantonello, F.; Andreatta, G.; De Cassai, A.; Schiavolin, C.; Simoni, C.; Pasin, L.; Boscolo, A.; Navalesi, P. Electrical impedance tomography: A compass for the safe route to optimal PEEP. Respir. Med. 2021, 187, 106555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, D.; Bacchetta, M. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for ARDS in adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascioglu, S.; Rex, J.H.; de Pauw, B.; Bennett, J.E.; Bille, J.; Crokaert, F.; Denning, D.W.; Donnelly, J.P.; Edwards, J.E.; Erjavec, Z.; et al. Defining opportunistic invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients with cancer and hematopoietic stem cell transplants: An international consensus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, A.J.; Aguado, J.M.; Arikan-Akdagli, S.; Denning, D.W.; Groll, A.H.; Lagrou, K.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Lewis, R.E.; Munoz, P.; Verweij, P.E.; et al. Diagnosis and management of Aspergillus diseases: Executive summary of the 2017 ESCMID-ECMM-ERS guideline. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24 (Suppl. S1), e1–e38. [Google Scholar]
- Bassetti, M.; Bouza, E. Invasive mould infections in the ICU setting: Complexities and solutions. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72 (Suppl. S1), i39–i47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, M.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Vena, A.; Trucchi, C.; Ansaldi, F.; Antonelli, M.; Adamkova, V.; Alicino, C.; Almyroudi, M.P.; Atchade, E.; et al. Incidence and outcome of invasive candidiasis in intensive care units (ICUs) in Europe: Results of the EUCANDICU project. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaloye, J.; Calandra, T. Invasive candidiasis as a cause of sepsis in the critically ill patient. Virulence 2014, 5, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Al-Obaidi, M. Invasive Fungal Infections in the Intensive Care Unit. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 31, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taccone, F.S.; Van den Abeele, A.M.; Bulpa, P.; Misset, B.; Meersseman, W.; Cardoso, T.; Paiva, J.A.; Blasco-Navalpotro, M.; De Laere, E.; Dimopoulos, G.; et al. Epidemiology of invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients: Clinical presentation, underlying conditions, and outcomes. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viale, P.L.; Mirandola, S.; Natalini, C.; Esposti, L.D.; Dovizio, M.; Veronesi, C.; Forcina, G.; Navalesi, P.; Boscolo, A. A retrospective Italian analysis on the characteristics of invasive fungal infections in the intensive care unit setting: CHARTER-IFI study. Mycoses 2024, 67, e13779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, M.T.; Caggiano, G.; Lovero, G.; De Giglio, O.; Coretti, C.; Cuna, T.; Iatta, R.; Giglio, M.; Dalfino, L.; Bruno, F.; et al. Epidemiology of invasive fungal infections in the intensive care unit: Results of a multicenter Italian survey (AURORA Project). Infection 2013, 41, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscolo, A.; Bruni, A.; Giani, M.; Garofalo, E.; Sella, N.; Pettenuzzo, T.; Bombino, M.; Palcani, M.; Rezoagli, E.; Pozzi, M.; et al. Retrospective ANalysis of multi-drug resistant Gram-nEgative bacteRia on veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. The multicenter RANGER STUDY. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, J.P.; Chen, S.C.; Kauffman, C.A.; Steinbach, W.J.; Baddley, J.W.; Verweij, P.E.; Clancy, C.J.; Wingard, J.R.; Lockhart, S.R.; Groll, A.H.; et al. Revision and Update of the Consensus Definitions of Invasive Fungal Disease From the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer and the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, A.P.C.; Husain, S. Infection prophylaxis and management of fungal infections in lung transplant. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, M.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Agvald-Ohman, C.; Akova, M.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Arikan-Akdagli, S.; Azoulay, E.; Blot, S.; Cornely, O.A.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; et al. Invasive Fungal Diseases in Adult Patients in Intensive Care Unit (FUNDICU): 2024 consensus definitions from ESGCIP, EFISG, ESICM, ECMM, MSGERC, ISAC, and ISHAM. Intensive Care Med. 2024, 50, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renard Triché, L.; Futier, E.; De Carvalho, M.; Piñol-Domenech, N.; Bodet-Contentin, L.; Jabaudon, M.; Pereira, B. Sample size estimation in clinical trials using ventilator-free days as the primary outcome: A systematic review. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortorano, A.M.; Dho, G.; Prigitano, A.; Breda, G.; Grancini, A.; Emmi, V.; Cavanna, C.; Marino, G.; Morero, S.; Ossi, C.; et al. Invasive fungal infections in the intensive care unit: A multicentre, prospective, observational study in Italy (2006–2008). Mycoses 2012, 55, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortarezza, F.; Boscolo, A.; Pezzuto, F.; Lunardi, F.; Jesús Acosta, M.; Giraudo, C.; Del Vecchio, C.; Sella, N.; Tiberio, I.; Godi, I.; et al. Proven COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with severe respiratory failure. Mycoses 2021, 64, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poth, J.M.; Schewe, J.C.; Lehmann, F.; Weller, J.; Schmandt, M.W.; Kreyer, S.; Muenster, S.; Putensen, C.; Ehrentraut, S.F. COVID-19 Is an Independent Risk Factor for Detrimental Invasive Fungal Disease in Patients on Veno-Venous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Retrospective Study. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehler, P.; Bassetti, M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Chen, S.C.A.; Colombo, A.L.; Hoenigl, M.; Klimko, N.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Oladele, R.O.; Vinh, D.C.; et al. Defining and managing COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: The 2020 ECMM/ISHAM consensus criteria for research and clinical guidance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, e149–e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.L.; Dhillon, R.; Cordey, A.; Hughes, H.; Faggian, F.; Soni, S.; Pandey, M.; Whitaker, H.; May, A.; Morgan, M.; et al. A National Strategy to Diagnose Coronavirus Disease 2019-Associated Invasive Fungal Disease in the Intensive Care Unit. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e1634–e1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoletti, M.; Pascale, R.; Cricca, M.; Rinaldi, M.; Maccaro, A.; Bussini, L.; Fornaro, G.; Tonetti, T.; Pizzilli, G.; Francalanci, E.; et al. Epidemiology of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Among Intubated Patients With COVID-19: A Prospective Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e3606–e3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavayas, Y.A.; Yusuff, H.; Porter, R. Fungal infections in adult patients on extracorporeal life support. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Shu, H.; Xia, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Fang, M.; et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poth, J.M.; Schewe, J.C.; Putensen, C.; Ehrentraut, S.F. Impact of Invasive Fungal Diseases on Survival under Veno-Venous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for ARDS. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srisurapanont, K.; Lerttiendamrong, B.; Meejun, T.; Thanakitcharu, J.; Manothummetha, K.; Thongkam, A.; Chuleerarux, N.; Sanguankeo, A.; Li, L.X.; Leksuwankun, S.; et al. Candidemia Following Severe COVID-19 in Hospitalised and Critical Ill Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mycoses 2024, 67, e13798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulenti, D.; Papathanakos, G.; Blot, S. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in the ICU: Tale of a broadening risk profile. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2023, 29, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzarro, M.J.; Conrad, S.A.; Kaufman, D.A.; Rycus, P. Infections acquired during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in neonates, children, and adults. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 12, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Bréchot, N.; Hariri, S.; Guiguet, M.; Luyt, C.E.; Makri, R.; Leprince, P.; Trouillet, J.L.; Pavie, A.; Chastre, J.; et al. Nosocomial infections in adult cardiogenic shock patients supported by venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Shan, Q.; Xia, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Qiu, L.; Xie, Y.; Lin, N.; Wang, L. Incidence, risk factors and mortality of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with influenza: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mycoses 2022, 65, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscolo, A.; Cattelan, A.; Marinello, S.; Medici, F.; Pettenon, G.; Congedi, S.; Sella, N.; Presa, N.; Pistollato, E.; Silvestrin, S.; et al. Fungal Infections and Colonization after Bilateral Lung Transplant: A Six-Year Single-Center Experience. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedi-Shahandashti, R.; Lass-Flörl, C. Novel Antifungal Agents and Their Activity against Aspergillus Species. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, T.; Maertens, J. Clinical considerations in the early treatment of invasive mould infections and disease. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72 (Suppl. S1), i29–i38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, P.G.; Kauffman, C.A.; Andes, D.R.; Clancy, C.J.; Marr, K.A.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Reboli, A.C.; Schuster, M.G.; Vazquez, J.A.; Walsh, T.J.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Candidiasis: 2016 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, e1–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivellari, M.; Pappalardo, F. Femoro-jugular cannulation in veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation PRO/CON. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10 (Suppl. S5), S613–S615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).