Characterization of Key Metabolic Markers in Hongqujiu Across Different Aging Years Using Metabolomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples for Testing
2.2. GC-MS Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) in Hongqujiu
2.3. LC-MS Analysis of Non-Volatile Compounds (NVCs) in Hongqujiu
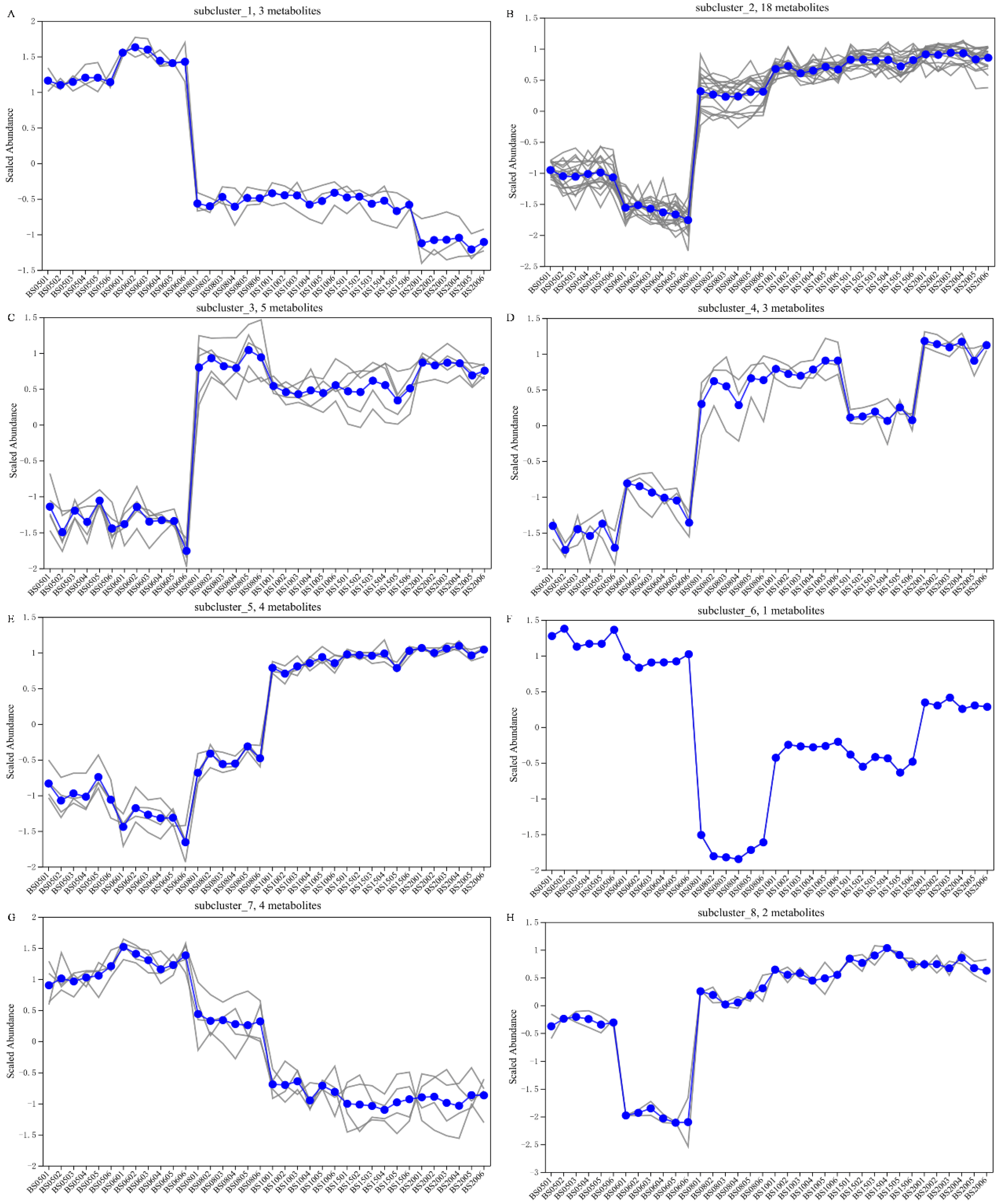
2.4. Data Preprocessing and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
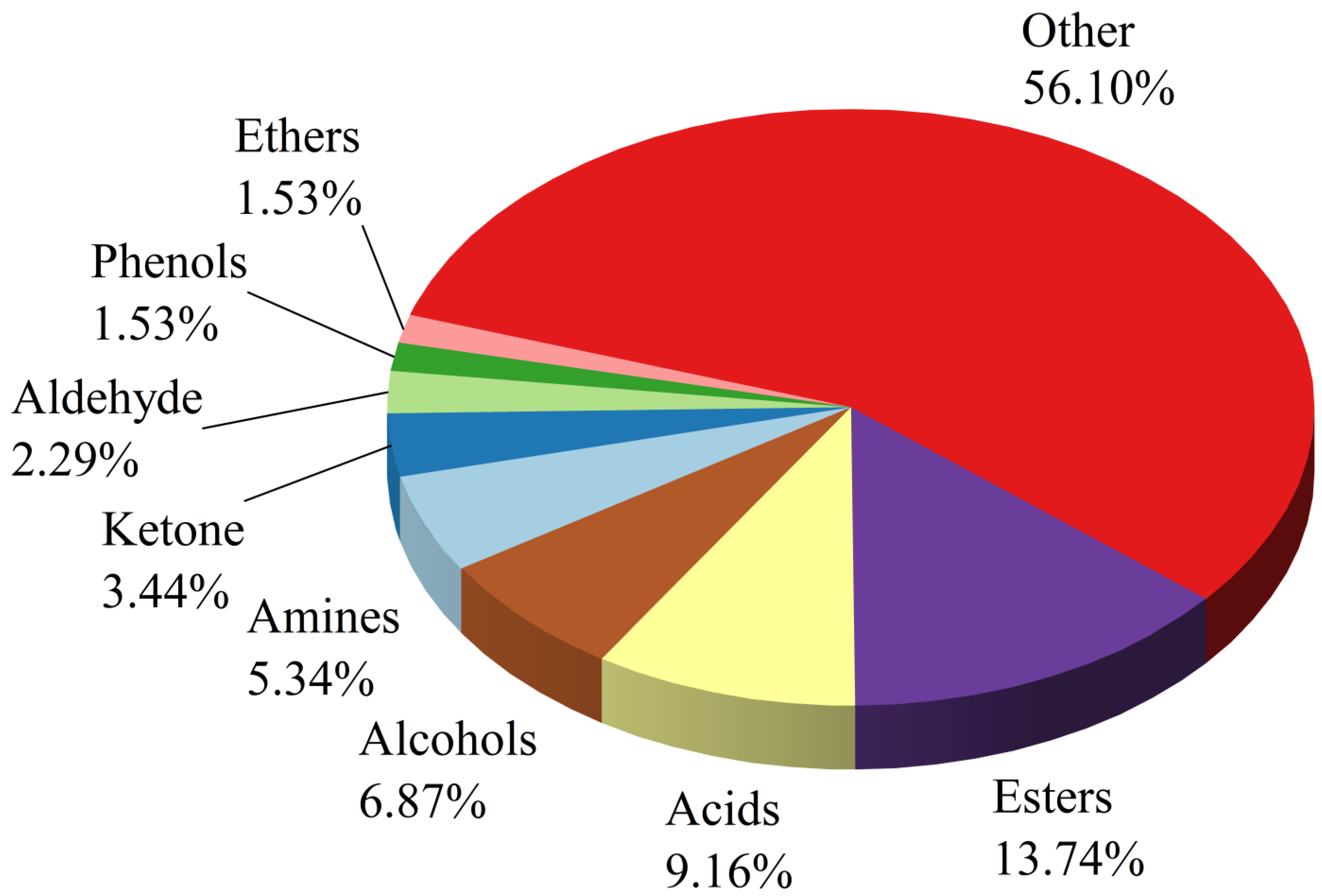
3.1. Results of Volatile Compound Analysis for Six Aging Years of BSHQJ
3.1.1. Detection Results of Volatile Compounds
3.1.2. Cluster Analysis of BSHQJ Samples Based on GC-MS
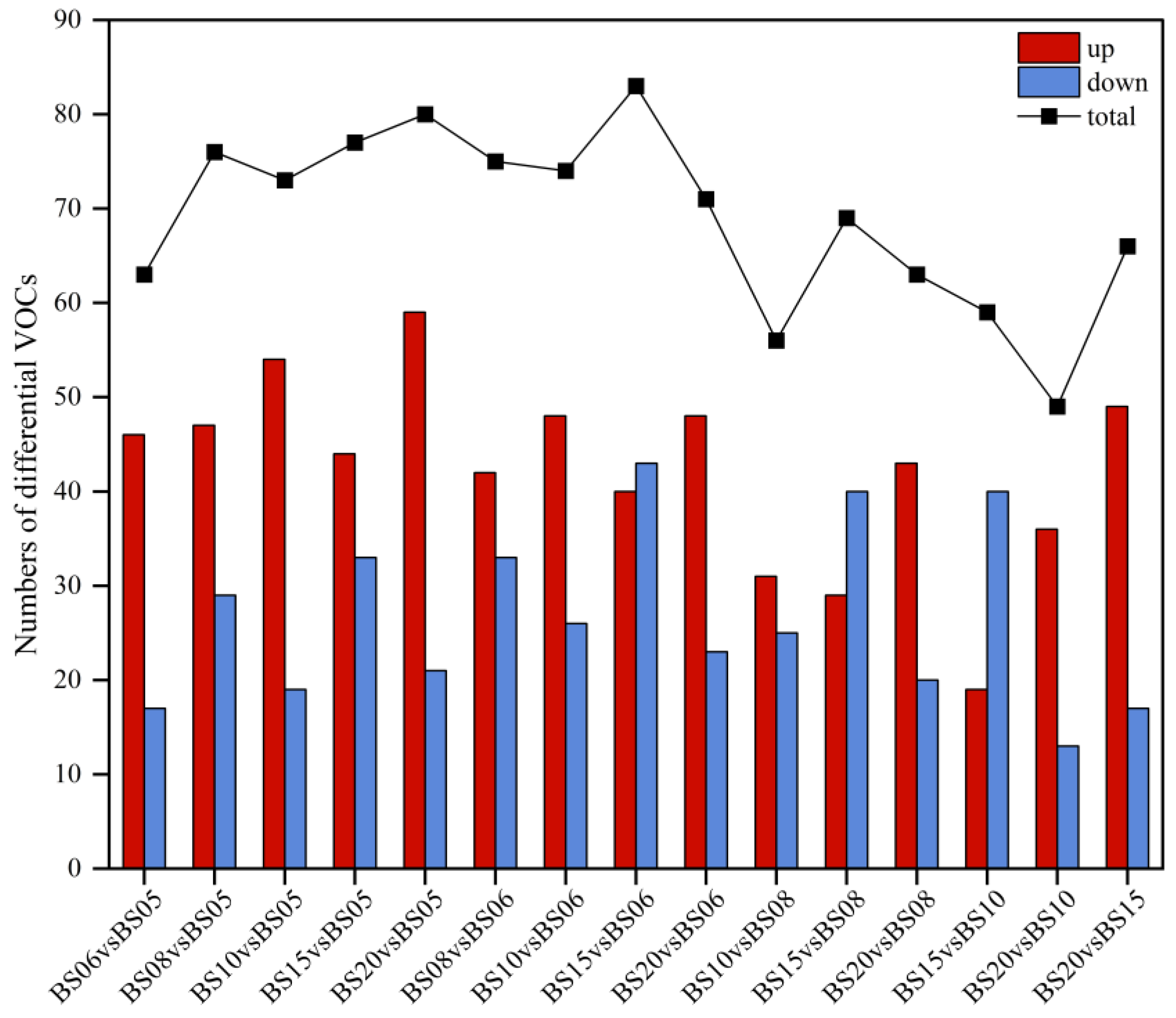
3.1.3. Identification and Analysis of Differential VOCs in BSHQJ
Comparative Pairwise Analysis of Six Different Aging Years of BSHQJ Based on OPLS-DA
Comparative Analysis of BSHQJ Between the Low-Year Group and the High-Year Group Based on OPLS-DA
3.1.4. Cluster Analysis of Differential VOCs of BSHQJ in the Low-Year Group and the High-Year Group
3.2. Results of Non-Volatile Compound Analysis for Six Aging Years of BSHQJ
3.2.1. Detection Results of Non-Volatile Compounds
3.2.2. Cluster Analysis of BSHQJ Samples Based on GC-MS
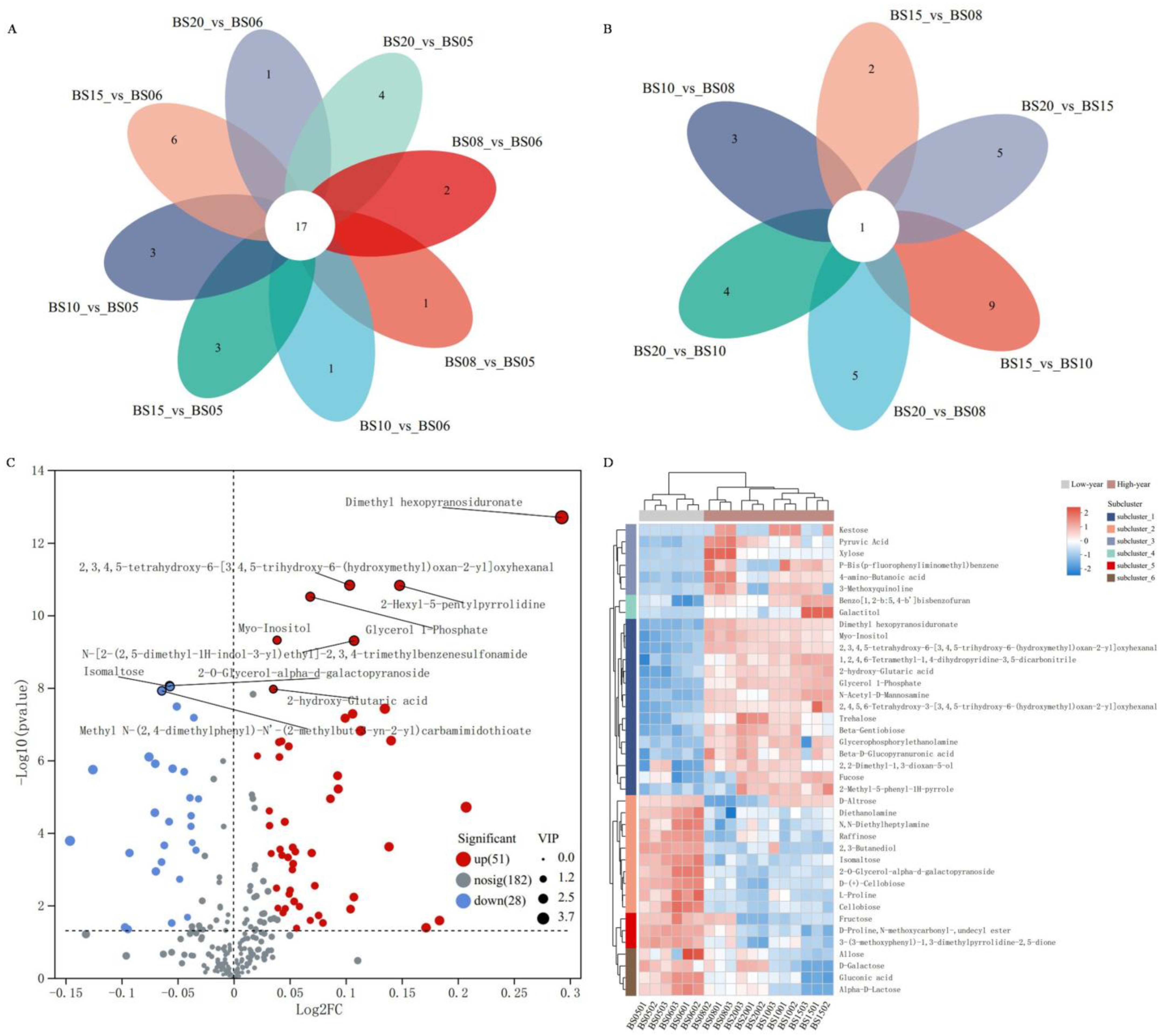
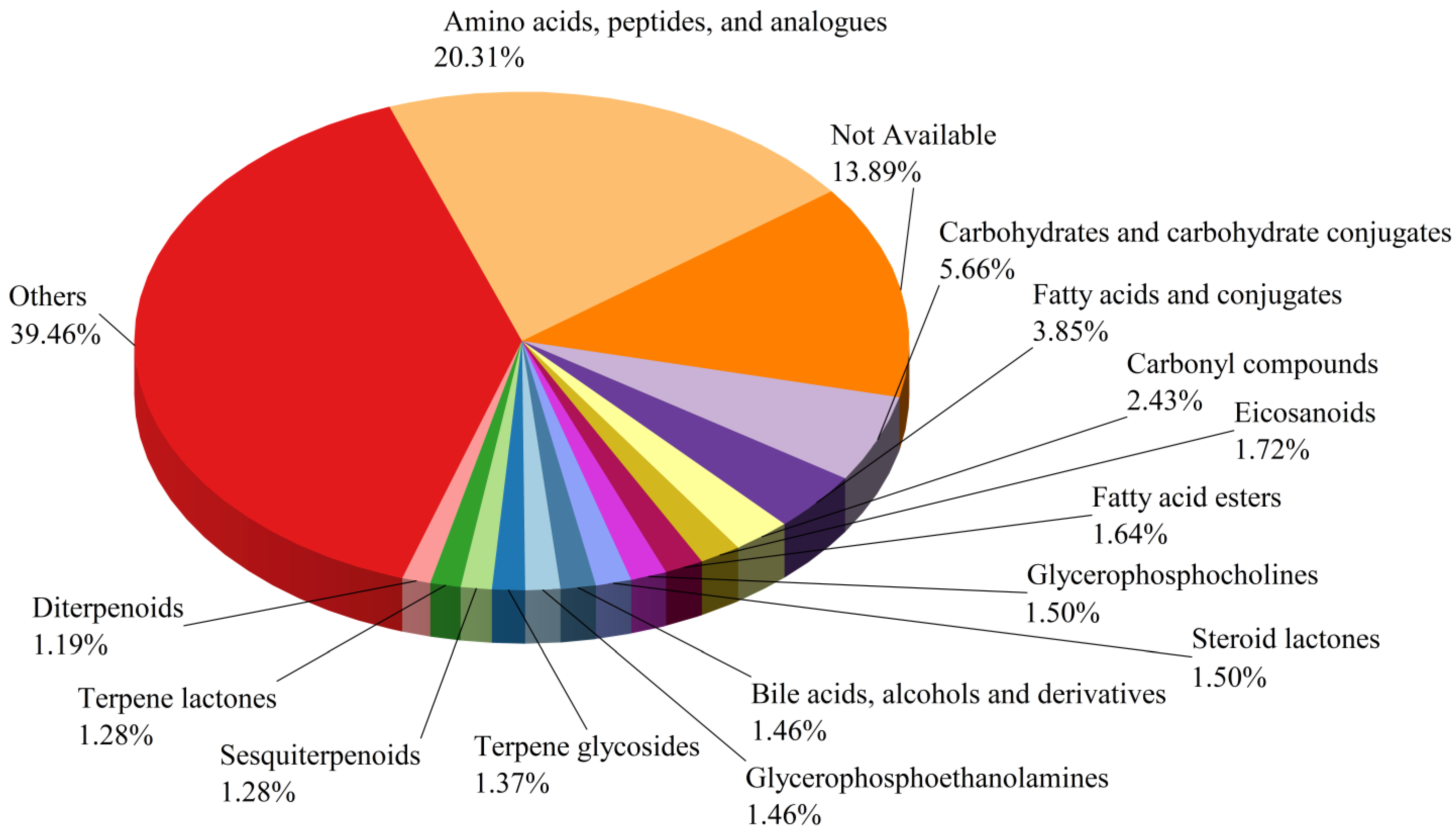
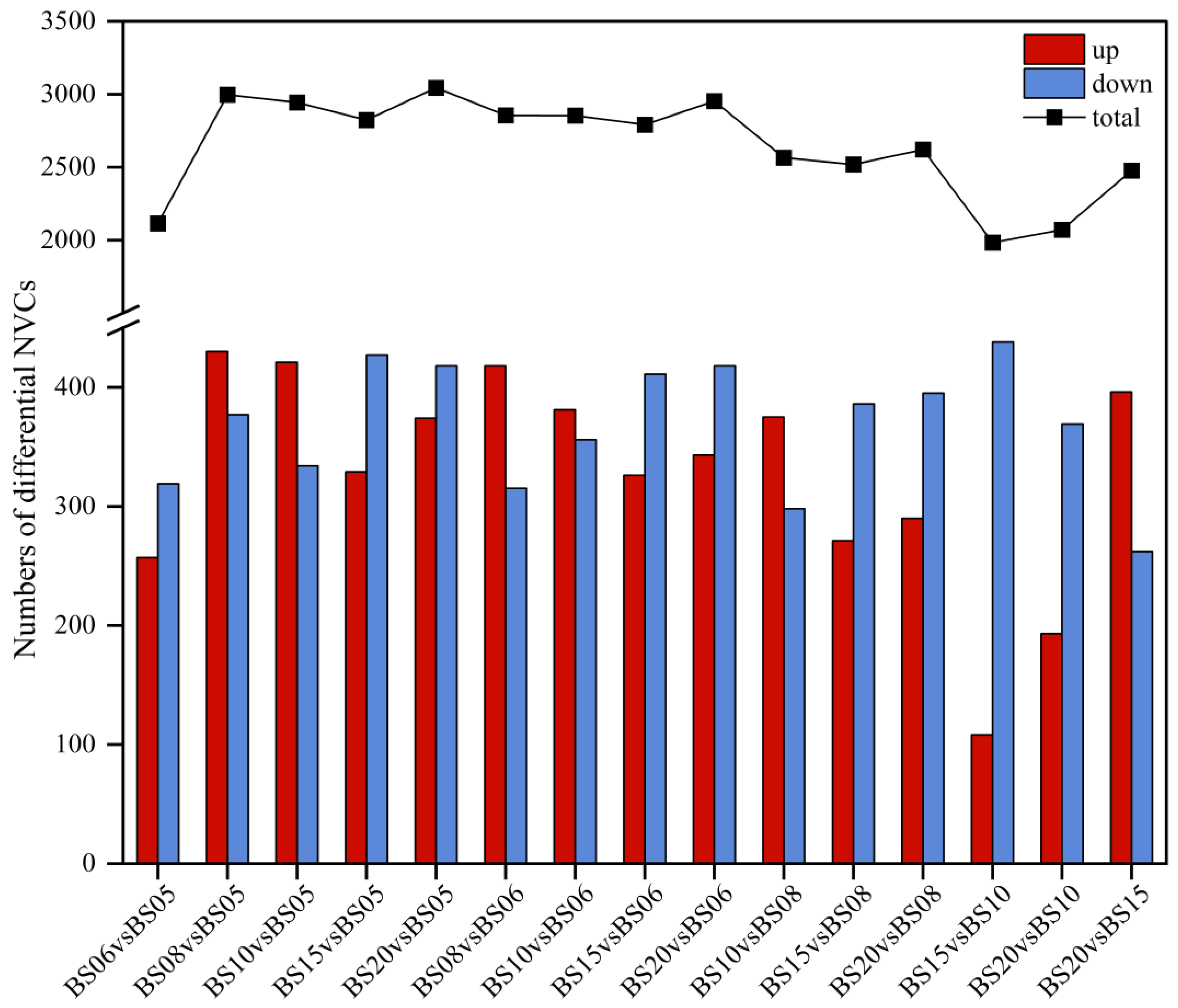
3.2.3. Identification and Analysis of Differential NVCs in BSHQJ
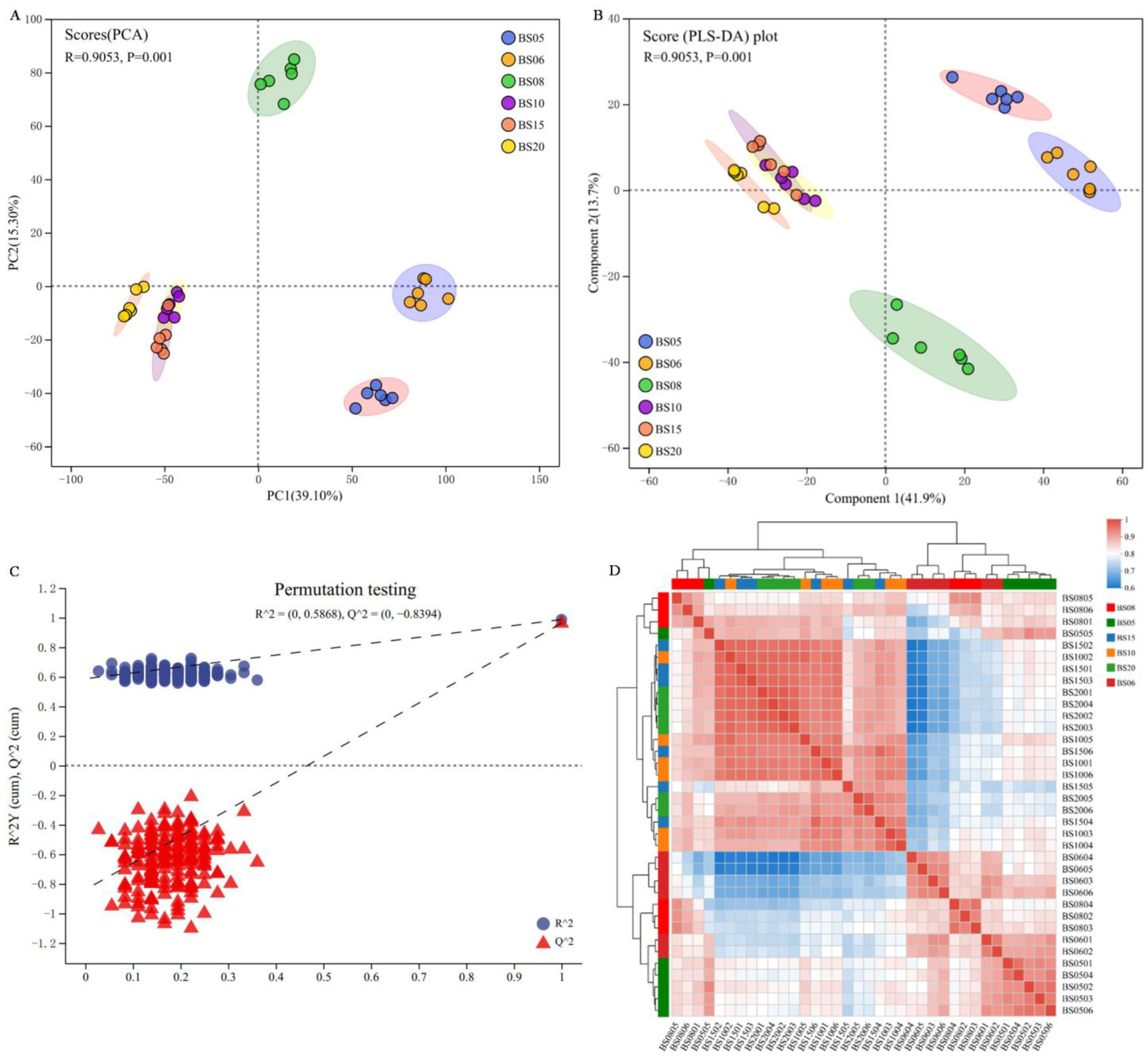
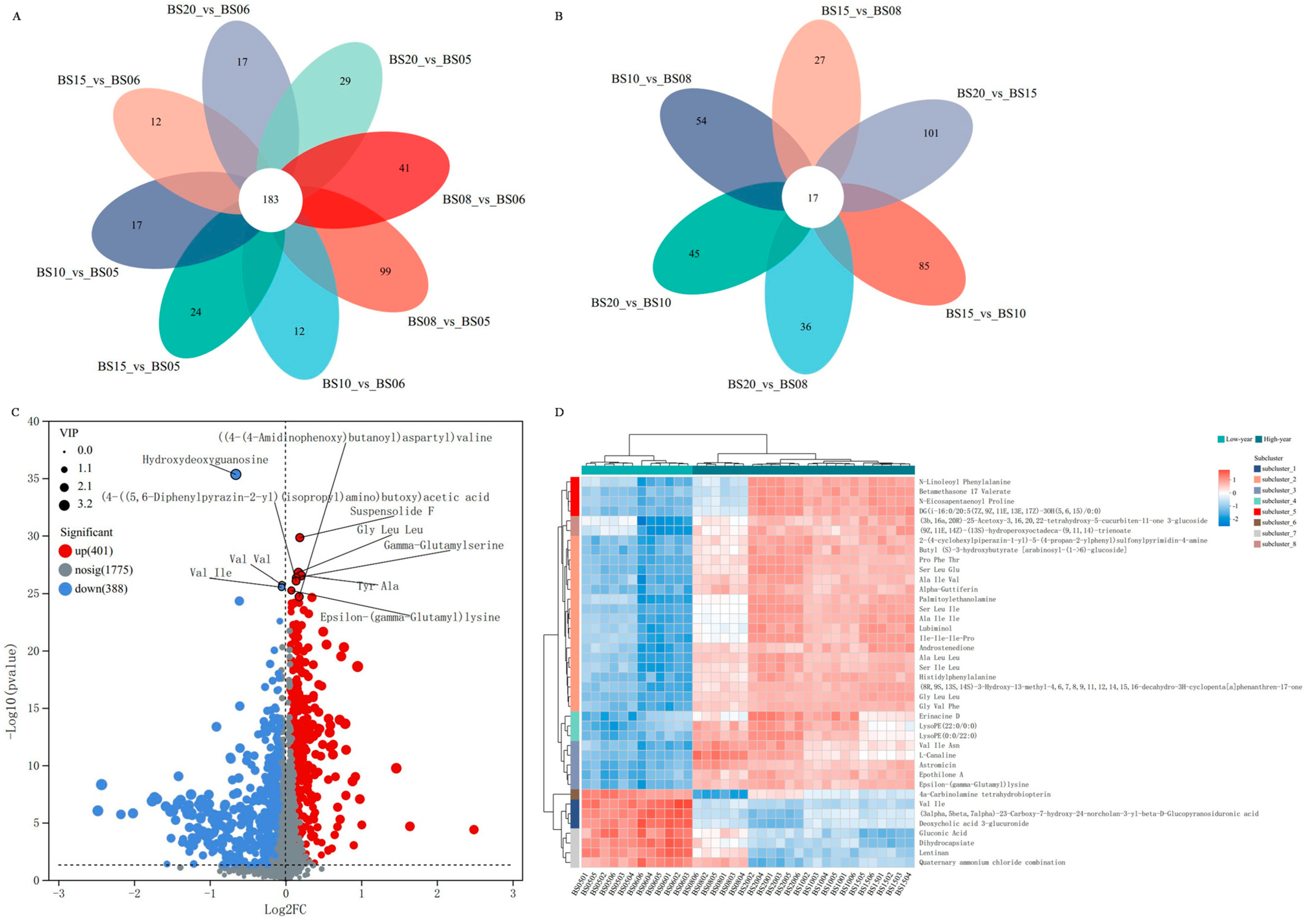
Comparative Pairwise Analysis of Six Different Aging Years of BSHQJ Based on OPLS-DA
Comparative Analysis of BSHQJ Between the Low-Year Group and the High-Year Group Based on OPLS-DA
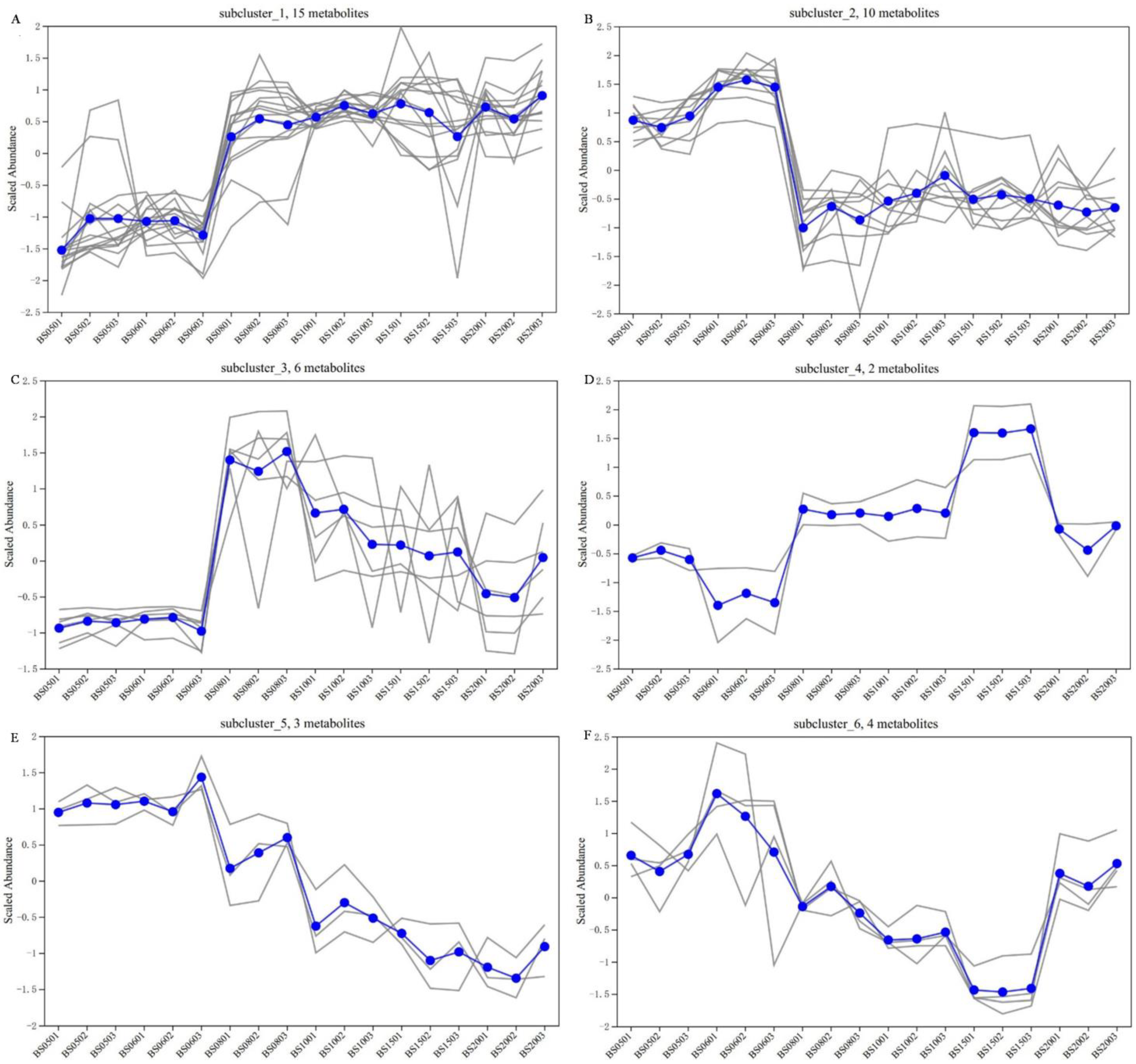
3.2.4. Cluster Analysis of Differential NVCs of BSHQJ in the Low-Year Group and the High-Year Group
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Lin, M.; Yang, B.; Dai, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, B. East meets west in alcoholic beverages: Flavor comparison, microbial metabolism and health effects. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zeng, W.; Fang, F.; Zhou, J.; Du, G. The microbiome of Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu). Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhu, X.; Chen, L.; Ni, L. Comparison study of the volatile profiles and microbial communities of Wuyi Qu and Gutian Qu, two major types of traditional fermentation starters of Hong Qu glutinous rice wine. Food Microbiol. 2018, 69, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukami, H.; Higa, Y.; Hisano, T.; Asano, K.; Hirata, T.; Nishibe, S. A review of red yeast rice, a traditional fermented food in Japan and East Asia: Its characteristic ingredients and application in the maintenance and improvement of health in lipid metabolism and the circulatory system. Molecules 2021, 26, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Huang, Z.; Wu, L.; Wu, Q.; Guo, W.; Zhao, W.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Rao, P.; Lv, X.; et al. Microbial diversity and flavor of Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu): An overview of current research and future prospects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 12, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Cai, Q.; Ke, X.; Chen, F.; Rao, P.; Ni, L. Characterization of fungal community and dynamics during the traditional brewing of Wuyi Hong Qu glutinous rice wine by means of multiple culture-independent methods. Food Control 2015, 54, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Hong, J.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Guo, W.; Pan, Y.; Chen, S.; Bai, W.; Rao, P.; Ni, L.; et al. Exploring core functional microbiota responsible for the production of volatile flavour during the traditional brewing of Wuyi Hong Qu glutinous rice wine. Food Microbiol. 2018, 76, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Qian, M.; Dong, H.; Liu, X.; Bai, W.; Liu, G.; Lv, X. Effect of Hong Qu on the flavor and quality of Hakka yellow rice wine (Huangjiu) produced in Southern China. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 160, 113264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, W.; Xia, Y.; Mu, Z.; Tao, L.; Song, X.; Zhang, H.; Ni, B.; Ai, L. Flavor formation in Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu): Impacts of the flavor-active microorganisms, raw materials, and fermentation technology. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 580247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Zhan, P.; Wang, P.; He, W.; Tian, H. A quality comparison for Xiecun Huangjiu with different aging stages based on chemical profile, aroma composition and microbial succession. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Z. Characterization of volatile organic compounds as potential aging markers in Chinese rice wine using multivariable statistics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 6444–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Z. Age-dependent characterization of volatile organic compounds and age discrimination in Chinese rice wine using an untargeted GC/MS-based metabolomic approach. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zheng, D.; Xie, T.; Xie, J.; Tian, H.; Ai, L.; Chen, C. Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography mass spectrometry-based untargeted metabolomics to clarify the dynamic variations in the volatile composition of Huangjiu of different ages. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krastanov, A. Announcement—Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2014, 28, 1. [Google Scholar]
- García-Pérez, P.; Becchi, P.P.; Zhang, L.; Rocchetti, G.; Lucini, L. Metabolomics and chemometrics: The next-generation analytical toolkit for the evaluation of food quality and authenticity. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2024, 147, 104481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, L.; Fu, L.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, X. GC/MS-based untargeted metabolomics reveals the differential metabolites for discriminating vintage of Chenxiang-type baijiu. Food Res. Int. 2024, 186, 114319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Huang, M.; Sun, B.; Ren, F.; Wu, J.; Meng, N.; Zhang, J. Identification of nonvolatile chemical constituents in Chinese Huangjiu using widely targeted metabolomics. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Lin, X.; He, Z.; Ren, X.; Li, W.; Molnár, I. Fungal community diversity and fermentation characteristics in regional varieties of traditional fermentation starters for Hong Qu glutinous rice wine. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Guo, W.; Zhou, W.; Li, L.; Xu, J.; Hong, J.; Liu, H.; Zeng, F.; Bai, W.; Liu, B.; et al. Microbial communities and volatile metabolites in different traditional fermentation starters used for Hong Qu glutinous rice wine. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, P.J.; Loret, M.O.; Goma, G. Production of citrinin by various species of Monascus. Biotechnol. Lett. 1995, 17, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Masumoto, N.; Makino, T.; Matsushima, Y.; Morikawa, T.; Ito, M. Novel compounds isolated from health food products containing beni-koji (red yeast rice) with adverse event reports. J. Nat. Med. 2024, 78, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Huang, J.; Xie, T.; Huang, L.; Zhuang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, B. Oenological characteristics, amino acids and volatile profiles of Hongqu rice wines during pottery storage: Effects of high hydrostatic pressure processing. Food Chem. 2016, 203, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.; Liang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Cai, Q.; Weng, Q.; Guo, W.; Ni, L.; Lv, X. Metagenomics reveals the differences in flavor quality of rice wines with Hongqu and Maiqu as the fermentation starters. Food Microbiol. 2025, 125, 104647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Rao, P.; Ni, L. Identification and characterization of filamentous fungi isolated from fermentation starters for Hong Qu glutinous rice wine brewing. J. Gen. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 58, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Sun, S.; Zhao, W.; Qian, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, W. Determination of ethyl carbamate (EC) by GC-MS and characterization of aroma compounds by HS-SPME-GC-MS during wine frying status in Hakka yellow rice wine. Food Anal. Method 2016, 10, 2068–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qian, M.; Dong, H.; Bai, W.; Zhao, W.; Li, X.; Liu, G. Effect of ageing process on carcinogen ethyl carbamate (EC), its main precursors and aroma compound variation in Hakka Huangjiu produced in southern China. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 55, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xie, T.; Xie, J.; Ai, L.; Tian, H. Characterization of key aroma compounds in Chinese rice wine using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and gas chromatography-olfactometry. Food Chem. 2019, 293, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ai, L.; Mu, Z.; Liu, H.; Yan, X.; Ni, L.; Zhang, H.; Xia, Y. Flavor compounds with high odor activity values (OAV > 1) dominate the aroma of aged Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu) by molecular association. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perestrelo, R.; Barros, A.S.; Camara, J.S.; Rocha, S.M. In-depth search focused on furans, lactones, volatile phenols, and acetals as potential age markers of Madeira wines by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with time-of-flight mass spectrometry combined with solid phase microextraction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3186–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, F.; Yin, S.; Hu, F. The formation, influencing factors, efficacy, and analytical techniques of flavor substances in Huangjiu. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 135, 106585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Dai, X.; Zhu, J.; Yu, H.; Department, O.F.S.A.; Shanghai, I.O.T. Classification of Chinese rice wine according to geographic origin and wine age based on chemometric methods and SBSE-TD-GC-MS analysis of volatile compounds. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2015, 21, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, F.; Tian, H.; Ma, X. Characterization of Chinese rice wine taste attributes using liquid chromatographic analysis, sensory evaluation, and an electronic tongue. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 997, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, C.; Huang, Y.; Mao, J. Component and microbial community structure change of Huangjiu undergoing rancidification during pottery jar storage. CyTA J. Food 2023, 21, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, C.; Gao, X.; Kang, Y.; Huang, M.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of key aroma compounds in Huangjiu from northern China by sensory-directed flavor analysis. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ji, Z.; Liu, S.; Han, X.; Zheng, F.; Mao, J. Characterization of the volatile compounds of huangjiu using com-prehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled to time of flight mass spectrometry (GC x GC-TOFMS). J. Food Process. Pres. 2019, 43, e14159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Lee, R.; Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Henning, S.M.; Hong, X.; Heber, D.; Li, Z. Quantification of bioactive constituents and antioxidant activity of Chinese yellow wine. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 44, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, C.; Qian, M.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in aged Chinese rice wine by comparative aroma extract dilution analysis, quantitative measurements, aroma recombination, and omission studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4876–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, E.; Ryan, P.M.; Wiley, N.; Carafa, I.; Sherwin, E.; Moloney, G.; Franciosi, E.; Mandal, R.; Wishart, D.S.; Tuohy, K.; et al. Gamma-aminobutyric acid-producing Lactobacilli positively affect metabolism and depressive-like behaviour in a mouse model of metabolic syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.C.; Lin, X.Z.; He, Z.G.; Su, H.; Li, W.X.; Guo, Q.Q. Comparison of microbial communities and amino acid metabolites in different traditional fermentation starters used during the fermentation of Hong Qu glutinous rice wine. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Ni, L. The dynamics of volatile compounds and their correlation with the microbial succession during the traditional solid-state fermentation of Gutian Hong Qu glutinous rice wine. Food Microbiol. 2020, 86, 103347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Huang, J.; Xiao, G.; You, Y.; Yuan, H.; Chen, F.; Liu, S.; Mao, J.; Li, B. Determination of γ-aminobutyric acid in Chinese rice wines and its evolution during fermentation. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 123, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Mao, X.; Liu, P.; Lin, H.; Du, Z.; Lv, N.; Han, J.; Qiu, C. Research into the functional components and antioxidant activities of North China rice wine (Ji Mo Lao Jiu). Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 1, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Xu, E.; Long, J.; Pan, X.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z.; Jiao, A. Comparison between ATR-IR, Raman, concatenated ATR-IR and Raman spectroscopy for the determination of total antioxidant capacity and total phenolic content of Chinese rice wine. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Niu, X.; Yang, D.; Ying, Y.; Li, B.; Zhu, G.; Wu, J. Determination of amino acids in Chinese rice wine by fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9809–9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhai, X.; Zuo, M.; Liu, S.; Yang, Z. Effects of protein components on the chemical composition and sensory properties of Millet Huangjiu (Chinese Millet Wine). Foods 2023, 12, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Mao, J.; Meng, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, H. Changes in flavour characteristics and bacterial diversity during the traditional fermentation of Chinese rice wines from Shaoxing region. Food Control 2014, 44, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zou, M.; Tang, C.; Ao, H.; He, L.; Qiu, S.; Li, C. The insights into sour flavor and organic acids in alcoholic beverages. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guo, W.L.; Zhou, W.B.; Lin, Y.C.; Hong, J.L.; Liu, H.P.; Liu, B.; Ni, L.; Rao, P.F.; Lu, X.C. The effects of Hongqu and Baiqu on the formation of aroma components in Hongqu Rice Wine. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 20, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Jairajpuri, D.S.; Jairajpuri, Z.S. Isoferulic acid action against glycation-induced changes in structural and functional attributes of human high-density lipoprotein. Biochemistry 2016, 81, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ispirli, H.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Sahin, E.; Sagdic, O.; Dertli, E. Preparation of gentiobiose-derived oligosaccharides by glucansucrase E81 and determination of prebiotic and immune-modulatory functions. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 486, 107837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.S.; Taguchi, T.; Sakai, K.; Kikuchi, K.; Wang, M.W.; Miwa, I. Antioxidant activities of chitobiose and chitotriose. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Huang, J.; Yun, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zabed, H.M.; Ravikumar, Y.; Qi, X. D-Arabitol ameliorates obesity and metabolic disorders via the gut microbiota-SCFAs-WAT browning axis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, B.; Zhu, G.; Li, W.; Tian, Y.; Wang, L.; Zong, S.; Sheng, P.; Li, M.; Chen, S.; et al. Selenium-lentinan inhibits tumor progression by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2018, 360, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, D.M.; Nakamichi, Y.; Morita, T.; Inoue, H.; Mizukami, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Suzuki, T. Xylobiose treatment strengthens intestinal barrier function by regulating claudin 2 and heat shock protein 27 expression in human Caco-2 cells. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 2518–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, G.; Marcinek, P.; Sulzinger, N.; Schieberle, P.; Krautwurst, D. Food sources and biomolecular targets of tyramine. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.M.; Li, W.L.; Tong, S.G.; Qiu, Y.T.; Han, J.Z.; Lv, X.C.; Ai, L.Z.; Sun, J.Y.; Sun, B.G.; Ni, L. Effects of the microbial community on the formation of volatile compounds and biogenic amines during the traditional brewing of Hongqu rice wine. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesselink, J.M.K.; Kopsky, D.J.; Witkamp, R.F. Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA)—‘Promiscuous’ anti-inflammatory and analgesic molecule at the interface between nutrition and pharma. PharmaNutrition 2014, 2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagishi, H.; Simada, A.; Shizuki, K.; Mori, H.; Okamoto, K.; Sakamoto, H.; Furukaw, S. Erinacine D, a Stimulator of NGF-synthesis, from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceum. Heterocycl. Commun. 1996, 2, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Y.; Yan, S.; Huang, S.; Yang, B.; Mo, W.; Xiao, L.; Li, X.; Huang, Z. Characterization of Key Metabolic Markers in Hongqujiu Across Different Aging Years Using Metabolomics. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11050353
Cai Y, Yan S, Huang S, Yang B, Mo W, Xiao L, Li X, Huang Z. Characterization of Key Metabolic Markers in Hongqujiu Across Different Aging Years Using Metabolomics. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(5):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11050353
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Yiyang, Sunan Yan, Simei Huang, Bin Yang, Wenlan Mo, Lishi Xiao, Xiangyou Li, and Zhiwei Huang. 2025. "Characterization of Key Metabolic Markers in Hongqujiu Across Different Aging Years Using Metabolomics" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 5: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11050353
APA StyleCai, Y., Yan, S., Huang, S., Yang, B., Mo, W., Xiao, L., Li, X., & Huang, Z. (2025). Characterization of Key Metabolic Markers in Hongqujiu Across Different Aging Years Using Metabolomics. Journal of Fungi, 11(5), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11050353





