Serum Type 2 Cytokine Levels Are Elevated in a Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis Subgroup with High Serum Total Immunoglobulin E Level
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
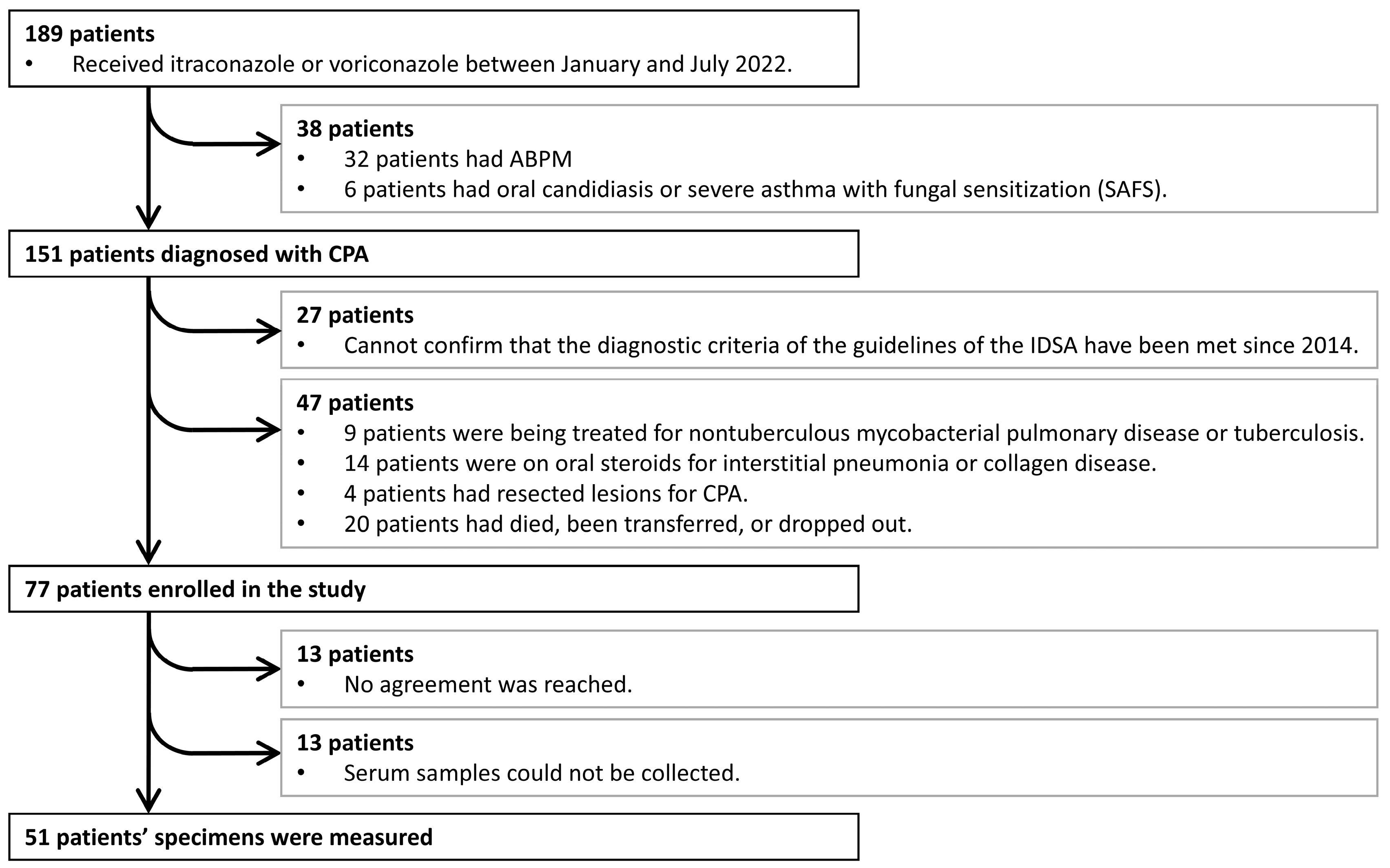
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Data and Sample Collection
2.3. Serum Cytokine Levels
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics (HCs vs. Patients with CPA)
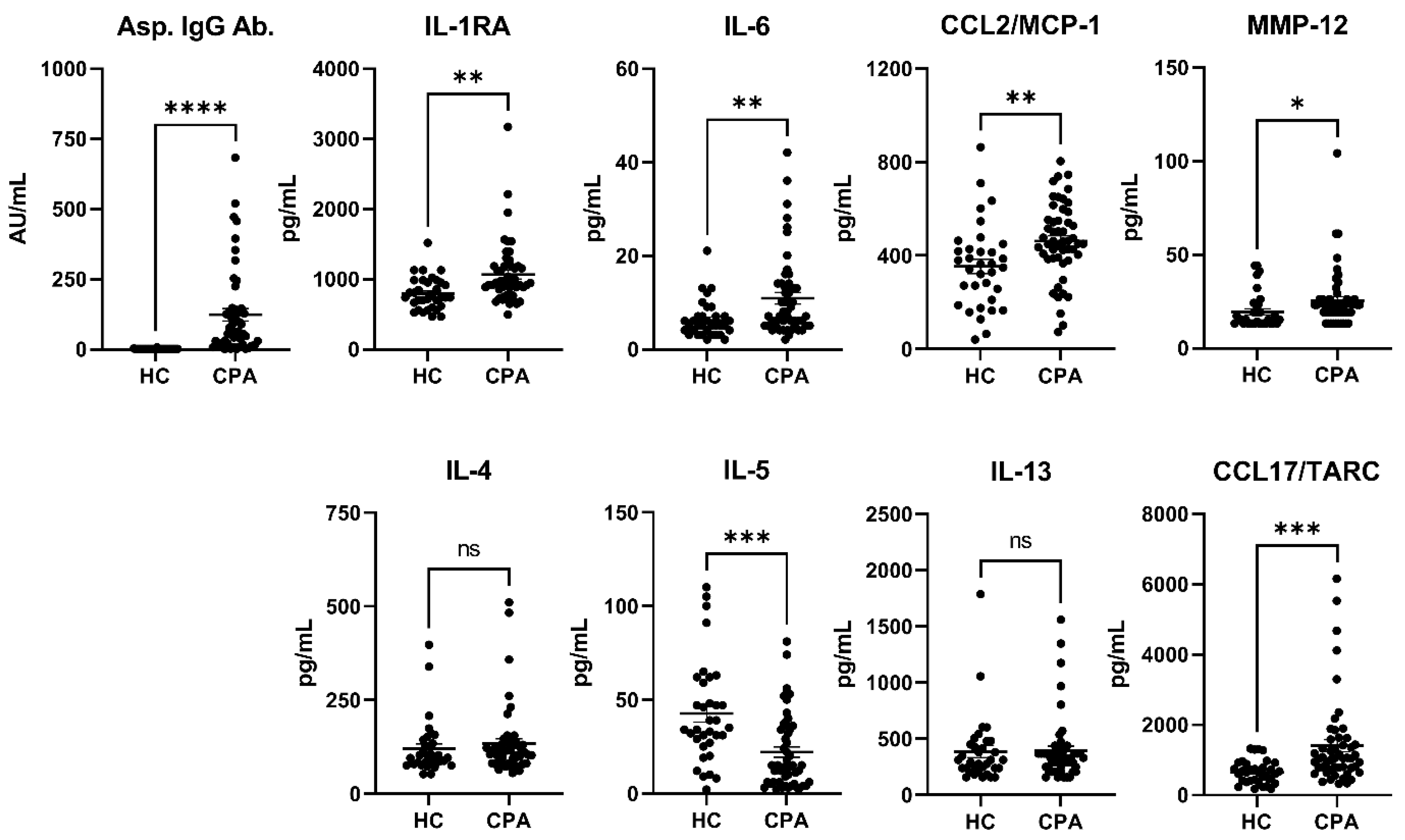
3.2. Cytokines (HCs vs. CPA)
3.3. Patient Characteristics (IgE Levels < or ≥500 IU/mL in Patients with CPA)
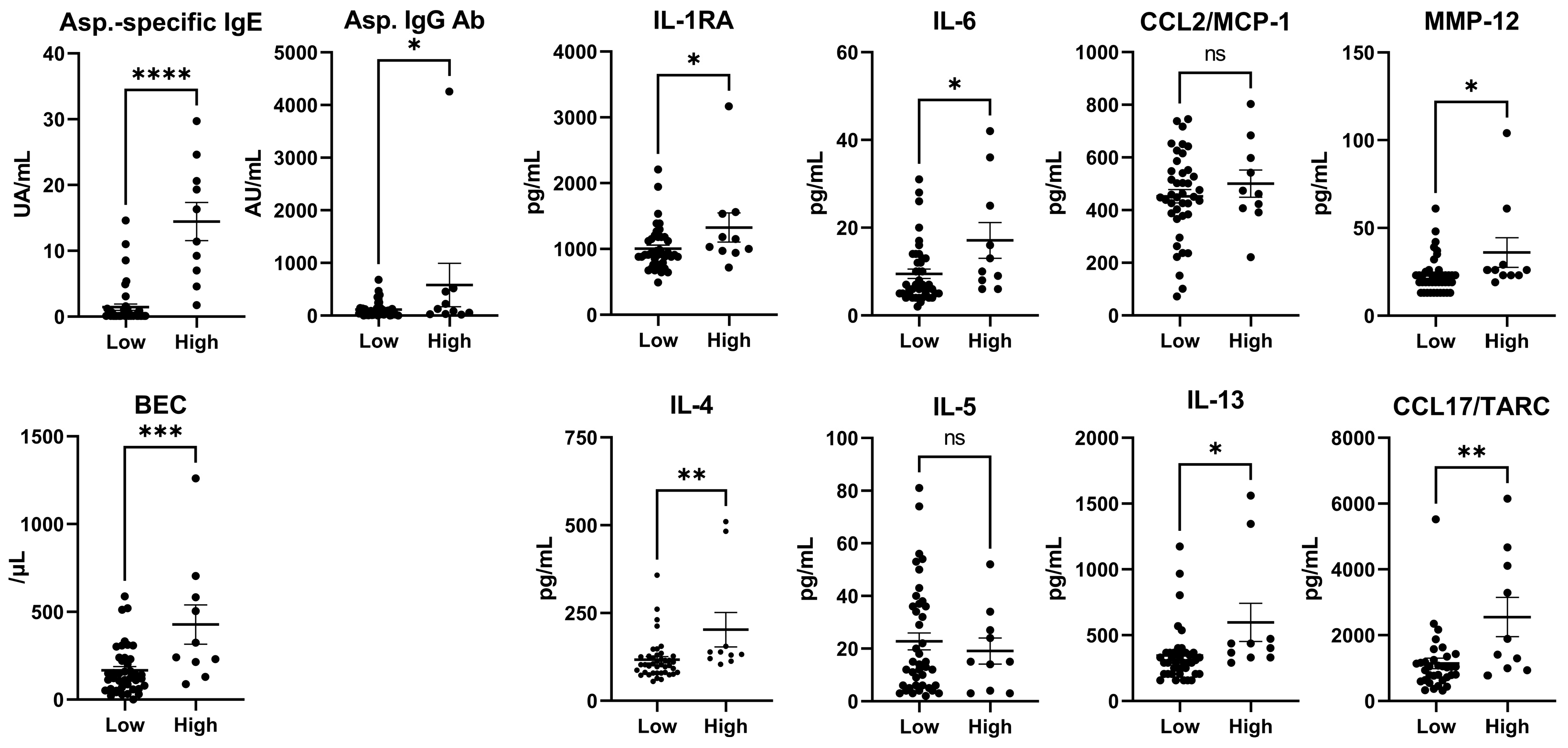
3.4. Cytokines (Total IgE Levels < or ≥500 IU/mL in Patients with CPA)
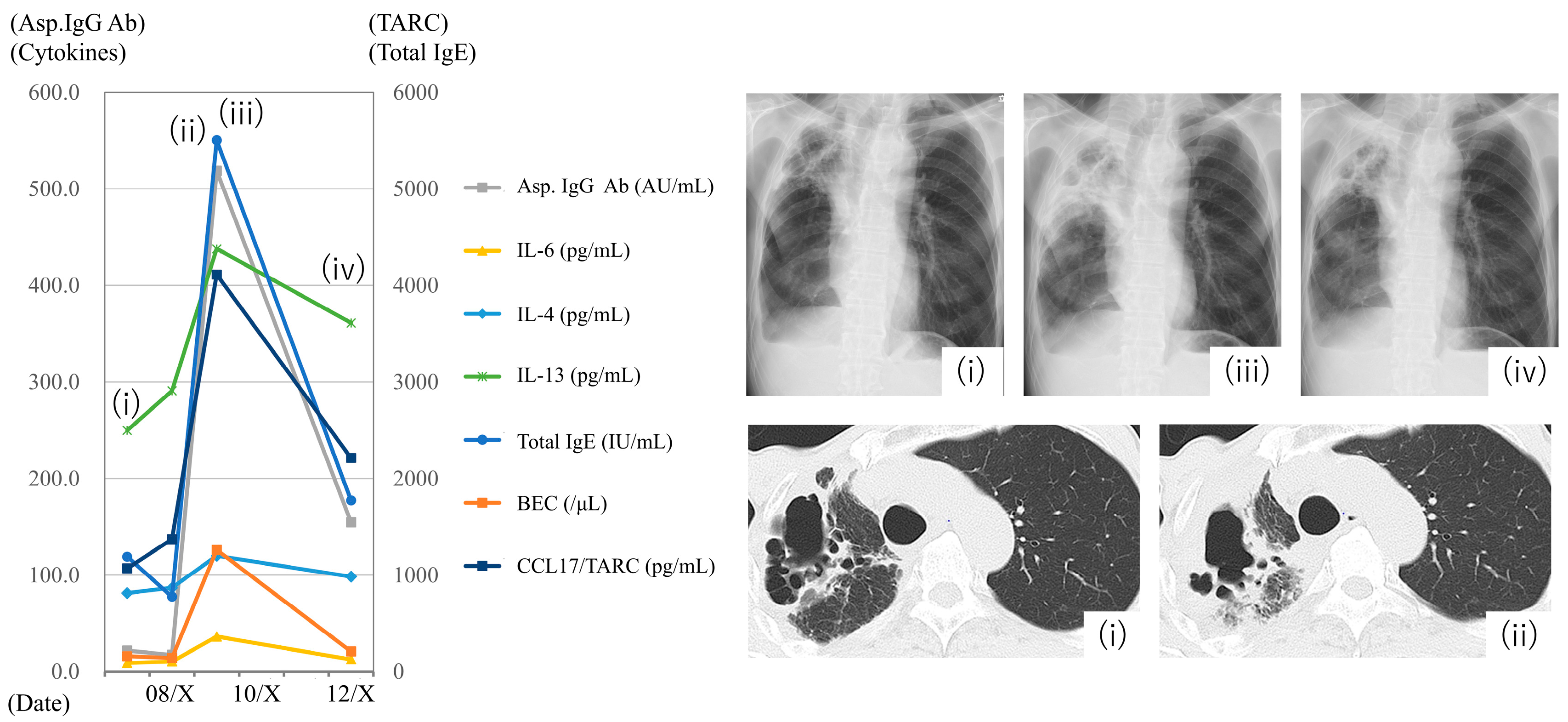
3.5. Case Presentation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABPA | allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis |
| BECs | blood eosinophil counts |
| CCL | chemokine C-C motif ligand |
| CHI3-L1 | chitinase-3-like protein 1 |
| COPD | chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CPA | chronic pulmonary aspergillosis |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| HCs | healthy controls |
| IDSA | Infectious Diseases Society of America |
| IFN | interferon |
| IgE | immunoglobulin E |
| IgG | immunoglobulin G |
| IL | interleukin |
| MCP | monocyte chemoattractant protein |
| MIP | macrophage inflammatory protein |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| NTM | nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease |
| PDGF-BB | platelet-derived growth factor-BB |
| RANTES | regulated on activation normal T cell expressed and secreted |
| TARC | thymus and activation-regulated chemokine |
| TGF | transforming growth factor |
| Th2 | type 2 helper T |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
References
- Jaggi, T.K.; Agarwal, R.; Tiew, P.Y.; Shah, A.; Lydon, E.C.; Hage, C.A.; Waterer, G.W.; Langelier, C.R.; Delhaes, L.; Chotirmall, S.H. Fungal lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 64, 2400803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowes, D.; Al-Shair, K.; Newton, P.J.; Morris, J.; Harris, C.; Rautemaa-Richardson, R.; Denning, D.W. Predictors of mortality in chronic pulmonary aspergillosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, A.; Ray, A.; Upadhyay, A.D.; Izumikawa, K.; Tashiro, M.; Kimura, Y.; Bongomin, F.; Su, X.; Maitre, T.; Cadranel, J.; et al. Mortality in chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: A systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, I.S.; Choudhary, H.; Dhooria, S.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Garg, M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Agarwal, R. Is There an Overlap in Immune Response Between Allergic Bronchopulmonary and Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, I.S.; Dhooria, S.; Muthu, V.; Rudramurthy, S.M.; Prasad, K.T.; Chakrabarti, A.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Agarwal, R. Identification of distinct immunophenotypes in chronic pulmonary aspergillosis using cluster analysis. Mycoses 2022, 66, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Suzuki, J.; Suzukawa, M.; Takeda, K.; Imoto, S.; Kitani, M.; Fukami, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Hebisawa, A.; Matsui, H. Serum total IgE may be a biomarker among chronic pulmonary aspergillosis patients with elevated serum total IgE levels: A cohort study with pathological evaluations. Med. Mycol. 2022, 60, myac006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, N.A.; Maekawa, A.; Rahman, O.M.; Austen, K.F.; Kanaoka, Y. Dectin-2 recognition of house dust mite triggers cysteinyl leukotriene generation by dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saluja, R.; Metz, M.; Maurer, M. Role and relevance of mast cells in fungal infections. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, H.F. Immunopathogenesis of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis and airway remodeling. Front. Biosci. 2003, 8, e190–e196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Takazono, T.; Obase, Y.; Fukahori, S.; Ashizawa, N.; Hirayama, T.; Tashiro, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Imamura, Y.; Hosogaya, N.; et al. Serum Cytokines Usefulness for Understanding the Pathology in Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis and Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.F.; Huang, C.C.; Chou, K.T.; Chan, Y.J.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, F.D. Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis: Disease Severity Using Image Analysis and Correlation with Systemic Proinflammation and Predictors of Clinical Outcome. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, T.F.; Thompson, G.R., 3rd; Denning, D.W.; Fishman, J.A.; Hadley, S.; Herbrecht, R.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Marr, K.A.; Morrison, V.A.; Nguyen, M.H.; et al. Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Aspergillosis: 2016 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, e1–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Sehgal, I.S.; Muthu, V.; Denning, D.W.; Chakrabarti, A.; Soundappan, K.; Garg, M.; Rudramurthy, S.M.; Dhooria, S.; Armstrong-James, D.; et al. Revised ISHAM-ABPA working group clinical practice guidelines for diagnosing, classifying and treating allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis/mycoses. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 63, 2400061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, K.; Hebisawa, A.; Ishiguro, T.; Takayanagi, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Suzuki, J.; Okada, N.; Tanaka, J.; Fukutomi, Y.; Ueki, S.; et al. New clinical diagnostic criteria for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis/mycosis and its validation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1261–1268.e1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, K.; Nakanishi, K.; Tsutsui, H. Interleukin-18 in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Su, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; You, Q. Chitinase-3 like-protein-1 function and its role in diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, L.G.N.; Thode, H.; Eslambolchi, Y.; Chopra, S.; Young, D.; Gill, S.; Devel, L.; Dufour, A. Matrix Metalloproteinases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2022, 74, 712–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, S.A.P.; Hashad, R.; Denning, D.W.; Kumararatne, D.S.; Ceron-Gutierrez, L.; Barcenas-Morales, G.; MacDonald, A.S.; Harris, C.; Doffinger, R.; Kosmidis, C. Defective Interferon-Gamma Production Is Common in Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 1822–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, E.J.M.; Harris, C.; Döffinger, R.; Hayes, G.; Denning, D.W.; Kosmidis, C. Interferon gamma replacement as salvage therapy in chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: Effects on frequency of acute exacerbation and all-cause hospital admission. Thorax 2020, 75, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardamone, C.; Parente, R.; Feo, G.D.; Triggiani, M. Mast cells as effector cells of innate immunity and regulators of adaptive immunity. Immunol. Lett. 2016, 178, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.; Nakajima, H.; Suzuki, K.; Kagami, S.; Hirose, K.; Suto, A.; Saito, Y.; Iwamoto, I. Mast cells produce interleukin-25 upon Fc epsilon RI-mediated activation. Blood 2003, 101, 3594–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupancu, T.J.; Eivazitork, M.; Hamilton, J.A.; Achuthan, A.A.; Lee, K.M. CCL17/TARC in autoimmunity and inflammation-not just a T-cell chemokine. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2023, 101, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juremalm, M.; Olsson, N.; Nilsson, G. CCL17 and CCL22 attenuate CCL5-induced mast cell migration. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2005, 35, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Fan, L.C.; Li, M.H.; Cao, W.J.; Xu, J.F. Beneficial effects of Omalizumab therapy in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: A synthesis review of published literature. Respir. Med. 2017, 122, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Suzukawa, M.; Tashimo, H.; Ohshima, N.; Asari, I.; Imoto, S.; Kobayashi, N.; Tohma, S.; Nagase, T.; Ohta, K. High serum cytokine levels may predict the responsiveness of patients with severe asthma to benralizumab. J. Asthma 2022, 59, 1604–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, M.L.; Villanueva, J.M.; Buckmeier, B.K.; Yamada, Y.; Filipovich, A.H.; Assa’ad, A.H.; Rothenberg, M.E. Anti-IL-5 (mepolizumab) therapy reduces eosinophil activation ex vivo and increases IL-5 and IL-5 receptor levels. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 1473–1483.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Damera, G.; Newbold, P.; Ranade, K. Reductions in eosinophil biomarkers by benralizumab in patients with asthma. Respir. Med. 2016, 111, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinfuku, K.; Suzuki, J.; Takeda, K.; Kawashima, M.; Morio, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Nagai, H.; Watanabe, A.; Matsui, H.; Kamei, K. Validity of Platelia Aspergillus IgG and Aspergillus Precipitin Test To Distinguish Pulmonary Aspergillosis from Colonization. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0343522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| HCs | Patients with CPA | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 34 | n = 51 | |||||
| Age (years) | 42.5 | (35.0–53.0) | 69.0 | (55.0–77.0) | <0.0001 | **** |
| Men | 11 | 32.4% | 39 | 76.5% | <0.0001 | **** |
| Smoking | 8 | 23.5% | 27 | 52.9% | 0.008 | ** |
| Bronchial asthma | 6 | 17.6% | 6 | 11.8% | 0.53 | ns |
| Atopic dermatitis | 3 | 8.8% | 1 | 2.0% | 0.29 | ns |
| Allergic rhinitis | 5 | 14.7% | 1 | 2.0% | 0.035 | * |
| Diabetes mellitus | - | 7 | 13.7% | - | ||
| Old tuberculosis | - | 24 | 47.1% | - | ||
| NTM | - | 9 | 17.6% | - | ||
| COPD | - | 13 | 25.5% | - | ||
| Number of exacerbations per year | - | 0.35 | ±0.63 | - | ||
| Number of cavities | - | 1.45 | ±1.02 | - | ||
| Wall thickness < 3 mm | - | 14 | 27.5% | - | ||
| BAE | - | 12 | 23.5% | - | ||
| HCs | Patients with CPA | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total IgE (IU/mL) | - | 345.7 ± 827.6 | - | |
| Asp.-specific IgE (UA/mL) | - | 4.0 ± 7.1 | - | |
| CRP (mg/dL) | - | 0.9 ± 1.8 | - | |
| BEC (/μL) | - | 218.1 ± 221.5 | - | |
| Albumin (g/dL) | - | 3.9 ± 0.5 | - | |
| HbA1c (%) | - | 6.2 ± 1.0 | - | |
| Asp. IgG Ab. (AU/mL) | 0.4 ± 1.1 | 205.3 ± 598.5 | <0.0001 | **** |
| IFN-γ | 79.6 ± 155 | 69.4 ± 156.9 | 0.77 | |
| IL-1RA | 794 ± 230.3 | 1067 ± 443.7 | 0.0014 | ** |
| IL-2 | 17.5 ± 14.1 | 16.7 ± 11.4 | 0.78 | |
| IL-4 | 120.4 ± 72.4 | 133.7 ± 90.7 | 0.48 | |
| IL-5 | 42.7 ± 27.4 | 22 ± 19.7 | 0.0001 | *** |
| IL-6 | 6.2 ± 3.9 | 11 ± 8.8 | 0.0041 | ** |
| IL-7 | 35.8 ± 18.2 | 38.6 ± 15.6 | 0.46 | |
| IL-12p70 | 161.2 ± 164.1 | 185.2 ± 188.7 | 0.55 | |
| IL-13 | 384.9 ± 306.7 | 395.2 ± 287.1 | 0.88 | |
| IL-18 | 173.8 ± 63.3 | 288.1 ± 283.5 | 0.024 | * |
| IL-25 | 272.3 ± 232.8 | 269 ± 168.3 | 0.94 | |
| IL-33 | 31.8 ± 45.9 | 33.4 ± 75.1 | 0.91 | |
| CCL2/MCP-1 | 353 ± 180.3 | 461.9 ± 162.9 | 0.0049 | ** |
| CCL3/MIP-1α | 315.4 ± 77.2 | 341.7 ± 73.9 | 0.12 | |
| CCL4/MIP-1β | 583.4 ± 167.3 | 627.3 ± 190.8 | 0.28 | |
| CCL5/RANTES | 30,349 ± 14,838 | 30,039 ± 15,215 | 0.93 | |
| CCL11/eotaxin | 215.7 ± 135.2 | 271 ± 262.5 | 0.26 | |
| CCL17/TARC | 651.1 ± 330.2 | 1410 ± 1247 | 0.0009 | *** |
| CXCL8/IL-8 | 18.1 ± 10.2 | 21.7 ± 10.6 | 0.12 | |
| CXCL10/IP-10 | 12.9 ± 3.8 | 15 ± 9.3 | 0.21 | |
| CHI3-L1 | 41,817 ± 53,524 | 202,221 ± 242,726 | 0.0003 | *** |
| Leptin | 17,925 ± 18,791 | 10,720 ± 13,404 | 0.042 | * |
| MMP-1 | 3399 ± 2412 | 4146 ± 2122 | 0.14 | |
| MMP-3 | 18,597 ± 8392 | 24,988 ± 18,494 | 0.062 | |
| MMP-8 | 821.6 ± 430.2 | 1536 ± 1609 | 0.013 | * |
| MMP-12 | 19.5 ± 9.5 | 25.5 ± 15.5 | 0.049 | * |
| PDGF-BB | 7617 ± 2903 | 8443 ± 2837 | 0.20 | |
| Periostin | 250,336 ± 86,290 | 241,604 ± 94,467 | 0.67 | |
| ST2/IL-33R | 22,872 ± 6835 | 29,079 ± 8477 | 0.0006 | *** |
| TGF-β1 | 25,185 ± 9017 | 17,296 ± 6234 | <0.0001 | **** |
| TIMP-1 | 130,314 ± 32,424 | 134,878 ± 25,525 | 0.47 | |
| TNF-α | 10.8 ± 7.8 | 10.6 ± 6.2 | 0.89 | |
| Total IgE < 500 IU/mL | Total IgE ≥ 500 IU/mL | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 41 | n = 10 | |||||
| Age (years) | 69 | (57.5–77.0) | 55.5 | (49.0–72.0) | 0.11 | ns |
| Men | 31 | 75.6% | 8 | 80.0% | >0.99 | ns |
| Smoking | 20 | 48.8% | 7 | 70.0% | 0.30 | ns |
| Bronchial asthma | 3 | 7.3% | 3 | 30.0% | 0.08 | ns |
| Atopic dermatitis | 0 | 0% | 1 | 10.0% | 0.20 | ns |
| Allergic rhinitis | 1 | 2.4% | 0 | 0.0% | 0.20 | ns |
| Diabetes mellitus | 4 | 9.8% | 3 | 30.0% | 0.12 | ns |
| Old tuberculosis | 20 | 48.8% | 4 | 40.0% | 0.73 | ns |
| NTM | 7 | 17.1% | 2 | 20.0% | >0.99 | ns |
| COPD | 11 | 26.8% | 2 | 20.0% | >0.99 | ns |
| Period of morbidity | 5.0 | (1.0–10.5) | 3.5 | (1.8–10.3) | 0.90 | ns |
| Number of exacerbations per year | 0.29 | ±0.61 | 0.60 | ±0.70 | 0.17 | ns |
| Number of cavities | 1.3 | ±0.9 | 2.0 | ±1.33 | 0.058 | ns |
| Wall thickness < 3 mm | 12 | 29.2% | 3 | 30.0% | >0.99 | ns |
| BAE | 8 | 19.5% | 4 | 40.0% | 0.22 | ns |
| Total IgE < 500 IU/mL | Total IgE ≥ 500 IU/mL | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total IgE (IU/mL) | 95.8 ± 103.8 | 1370.0 ± 1519.0 | <0.0001 | **** |
| Asp.-specific IgE (UA/mL) | 1.4 ± 3.1 | 14.5 ± 9.1 | <0.0001 | **** |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 0.8 ± 1.6 | 1.5 ± 2.2 | 0.24 | |
| BEC (/μL) | 166.9 ± 139.0 | 427.6 ± 355.0 | 0.0005 | *** |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.9 ± 0.5 | 3.7 ± 0.6 | 0.24 | |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.0 ± 0.6 | 6.7 ± 1.6 | 0.084 | |
| Asp. IgG Ab. (AU/mL) | 113.9 ± 145.9 | 580.1 ± 1304.0 | 0.026 | * |
| IFN-γ | 55.3 ± 124.9 | 127.1 ± 250.6 | 0.2 | |
| IL-1RA | 1004.0 ± 340.3 | 1326.0 ± 697.4 | 0.038 | * |
| IL-2 | 14.8 ± 7.0 | 24.5 ± 20.4 | 0.014 | * |
| IL-4 | 116.9 ± 57.9 | 202.5 ± 155.7 | 0.0062 | ** |
| IL-5 | 22.8 ± 20.7 | 19.1 ± 15.6 | 0.6 | |
| IL-6 | 9.5 ± 6.9 | 17.1 ± 12.9 | 0.013 | * |
| IL-7 | 35.6 ± 11.9 | 50.9 ± 22.7 | 0.0044 | ** |
| IL-12p70 | 151.8 ± 116.3 | 322.1 ± 334.4 | 0.0091 | ** |
| IL-13 | 345.8 ± 207.9 | 597.5 ± 457.2 | 0.011 | * |
| IL-18 | 302.9 ± 307.9 | 227.3 ± 141.8 | 0.46 | |
| IL-25 | 237.7 ± 123.6 | 397.1 ± 258.3 | 0.006 | ** |
| IL-33 | 28.4 ± 67.1 | 53.5 ± 103.9 | 0.35 | |
| CCL2/MCP-1 | 452.5 ± 163.1 | 500.4 ± 164.5 | 0.41 | |
| CCL3/MIP-1α | 325.6 ± 59.7 | 407.6 ± 92.2 | 0.0011 | ** |
| CCL4/MIP-1β | 596.8 ± 162.9 | 752.6 ± 250.1 | 0.019 | * |
| CCL5/RANTES | 28,019 ± 12,809 | 38,319 ± 21,499 | 0.054 | |
| CCL11/eotaxin | 233.5 ± 127.1 | 424.4 ± 527.7 | 0.057 | |
| CCL17/TARC | 1131.0 ± 859.4 | 2553.0 ± 1883.0 | 0.0021 | ** |
| CXCL8/IL-8 | 21.5 ± 10.9 | 22.6 ± 9.5 | 0.77 | |
| CXCL10/IP-10 | 15.0 ± 10.2 | 15.4 ± 4.9 | 0.89 | |
| CHI3-L1 | 206,442 ± 223,098 | 184,915 ± 325,093 | 0.80 | |
| Leptin | 11,732 ± 14,368 | 6572 ± 7546 | 0.28 | |
| MMP-1 | 3844 ± 2088 | 5385 ± 1877 | 0.038 | * |
| MMP-3 | 24,600 ± 18,768 | 26,580 ± 18,194 | 0.76 | |
| MMP-8 | 1445 ± 1634 | 1909 ± 1523 | 0.42 | |
| MMP-12 | 22.9 ± 10.4 | 36.0 ± 26.7 | 0.012 | * |
| PDGF-BB | 7807 ± 1698 | 11,051 ± 4744 | 0.0007 | *** |
| Periostin | 243,088 ± 87,985 | 235,522 ± 122,964 | 0.82 | |
| ST2/IL-33R | 28,433 ± 8605 | 31,729 ± 7774 | 0.27 | |
| TGF-β1 | 16,432 ± 5450 | 20,840 ± 8158 | 0.044 | * |
| TIMP-1 | 131,387 ± 24,488 | 149,191 ± 25,908 | 0.0047 | * |
| TNF-α | 9.4 ± 4.3 | 15.3 ± 10.0 | 0.0055 | ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watanabe, S.; Suzuki, J.; Suzukawa, M.; Nishimura, T.; Watanabe, M.; Enomoto, Y.; Takeda, K.; Kusaka, K.; Kawashima, M.; Morio, Y.; et al. Serum Type 2 Cytokine Levels Are Elevated in a Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis Subgroup with High Serum Total Immunoglobulin E Level. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040303
Watanabe S, Suzuki J, Suzukawa M, Nishimura T, Watanabe M, Enomoto Y, Takeda K, Kusaka K, Kawashima M, Morio Y, et al. Serum Type 2 Cytokine Levels Are Elevated in a Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis Subgroup with High Serum Total Immunoglobulin E Level. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(4):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040303
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatanabe, Shizuka, Junko Suzuki, Maho Suzukawa, Taku Nishimura, Masato Watanabe, Yu Enomoto, Keita Takeda, Kei Kusaka, Masahiro Kawashima, Yoshiteru Morio, and et al. 2025. "Serum Type 2 Cytokine Levels Are Elevated in a Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis Subgroup with High Serum Total Immunoglobulin E Level" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 4: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040303
APA StyleWatanabe, S., Suzuki, J., Suzukawa, M., Nishimura, T., Watanabe, M., Enomoto, Y., Takeda, K., Kusaka, K., Kawashima, M., Morio, Y., Tamura, A., Nagai, H., Sasaki, Y., & Matsui, H. (2025). Serum Type 2 Cytokine Levels Are Elevated in a Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis Subgroup with High Serum Total Immunoglobulin E Level. Journal of Fungi, 11(4), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040303






