Identification of the chaA and fwA Spore Color Genes of Aspergillus nidulans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Media
2.2. Strains
2.3. Molecular Genetic Methods
2.4. Transformation Procedure
3. Results
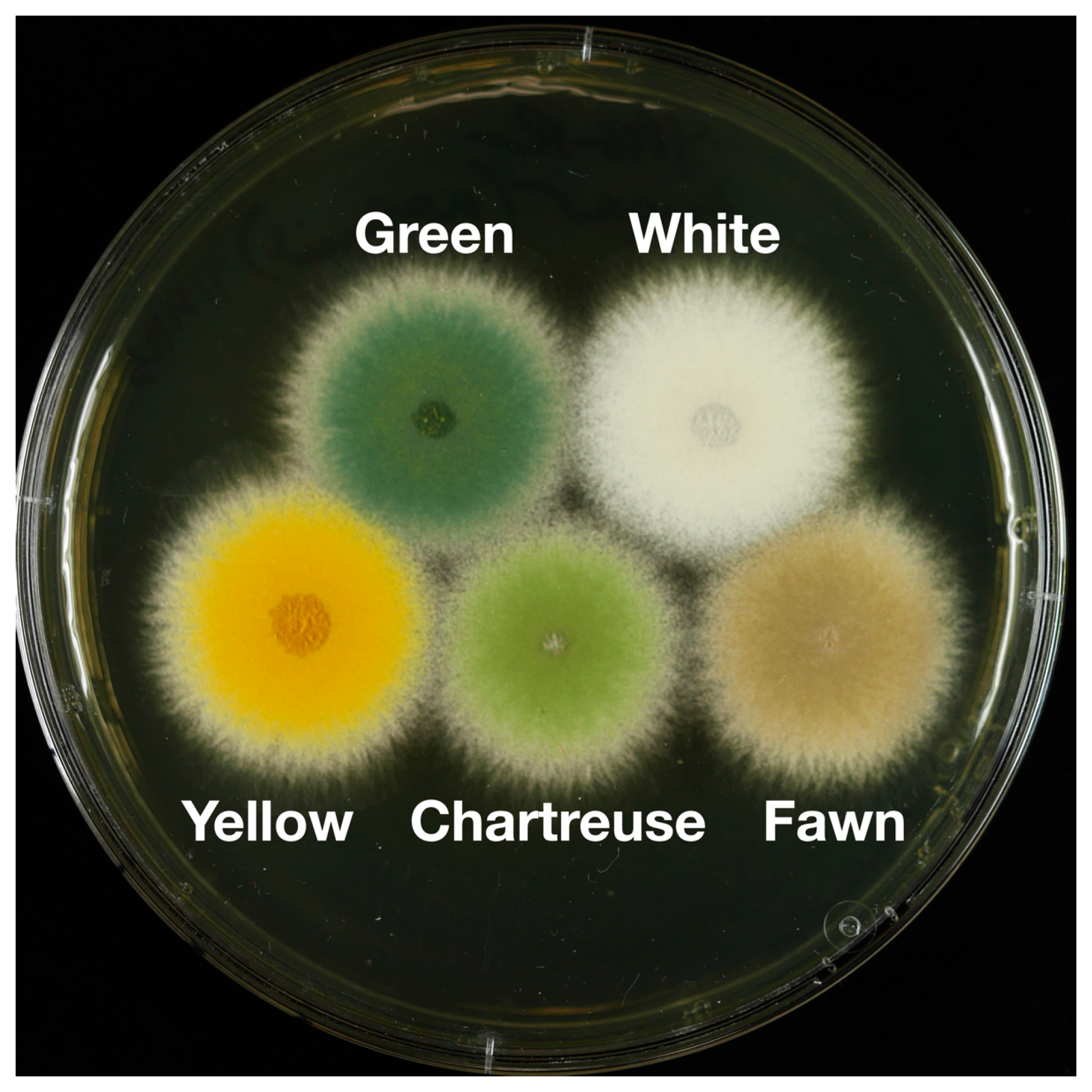
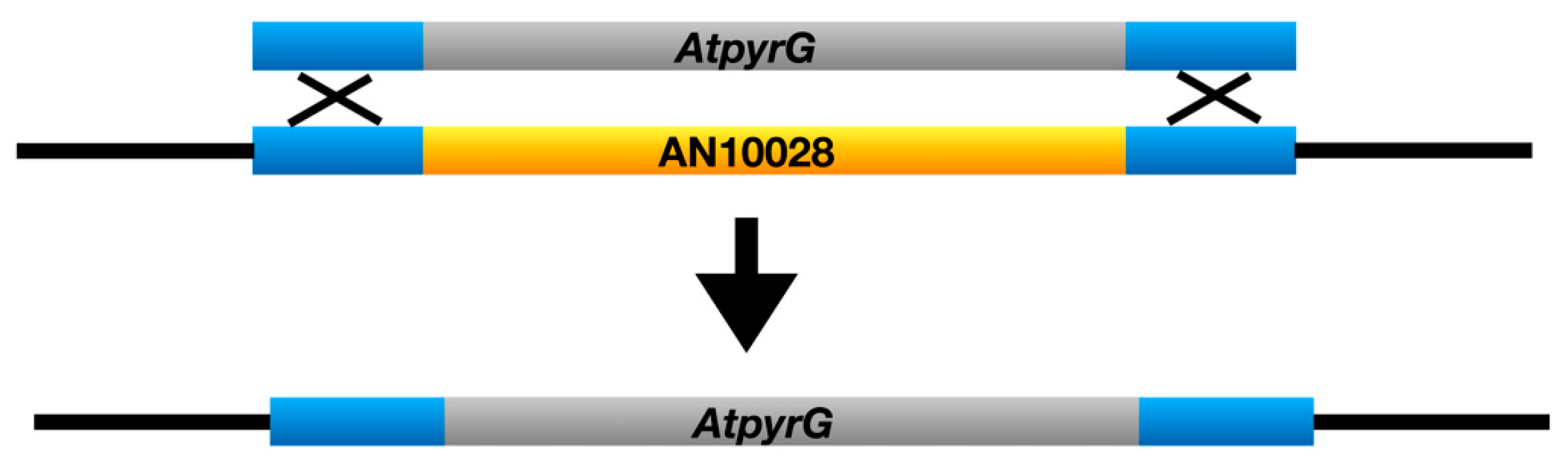
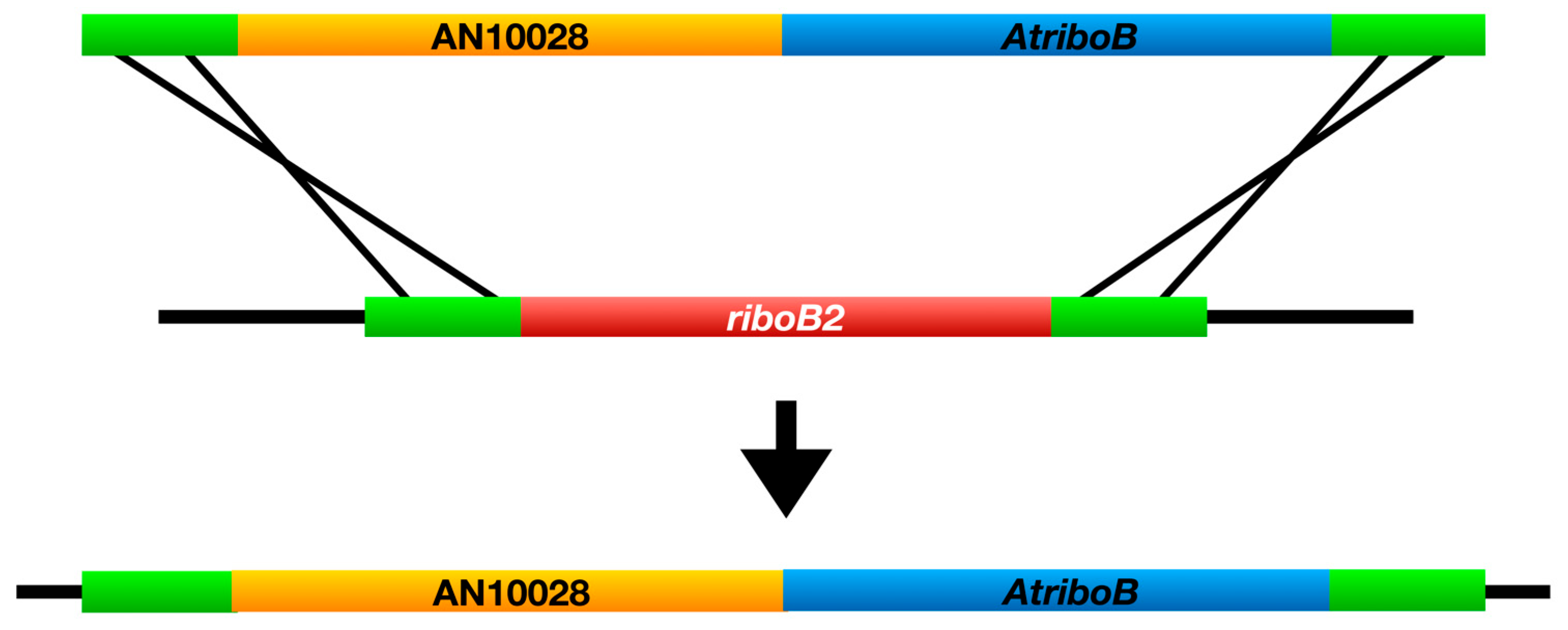
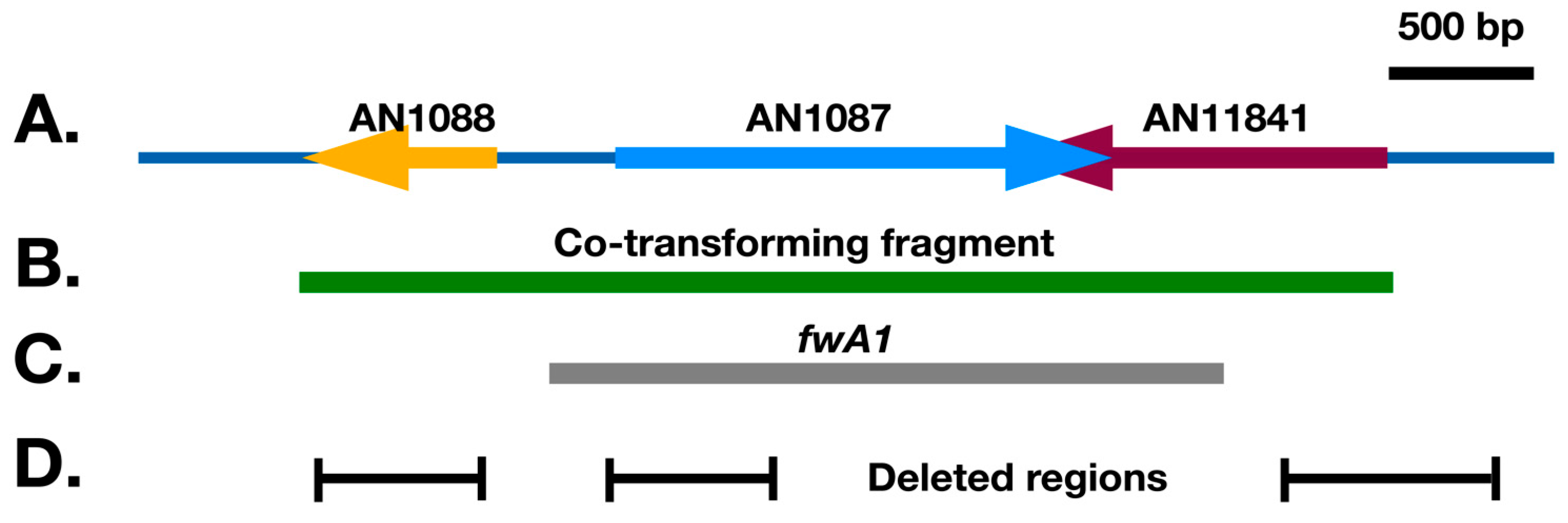
3.1. Identification of the chaA Gene
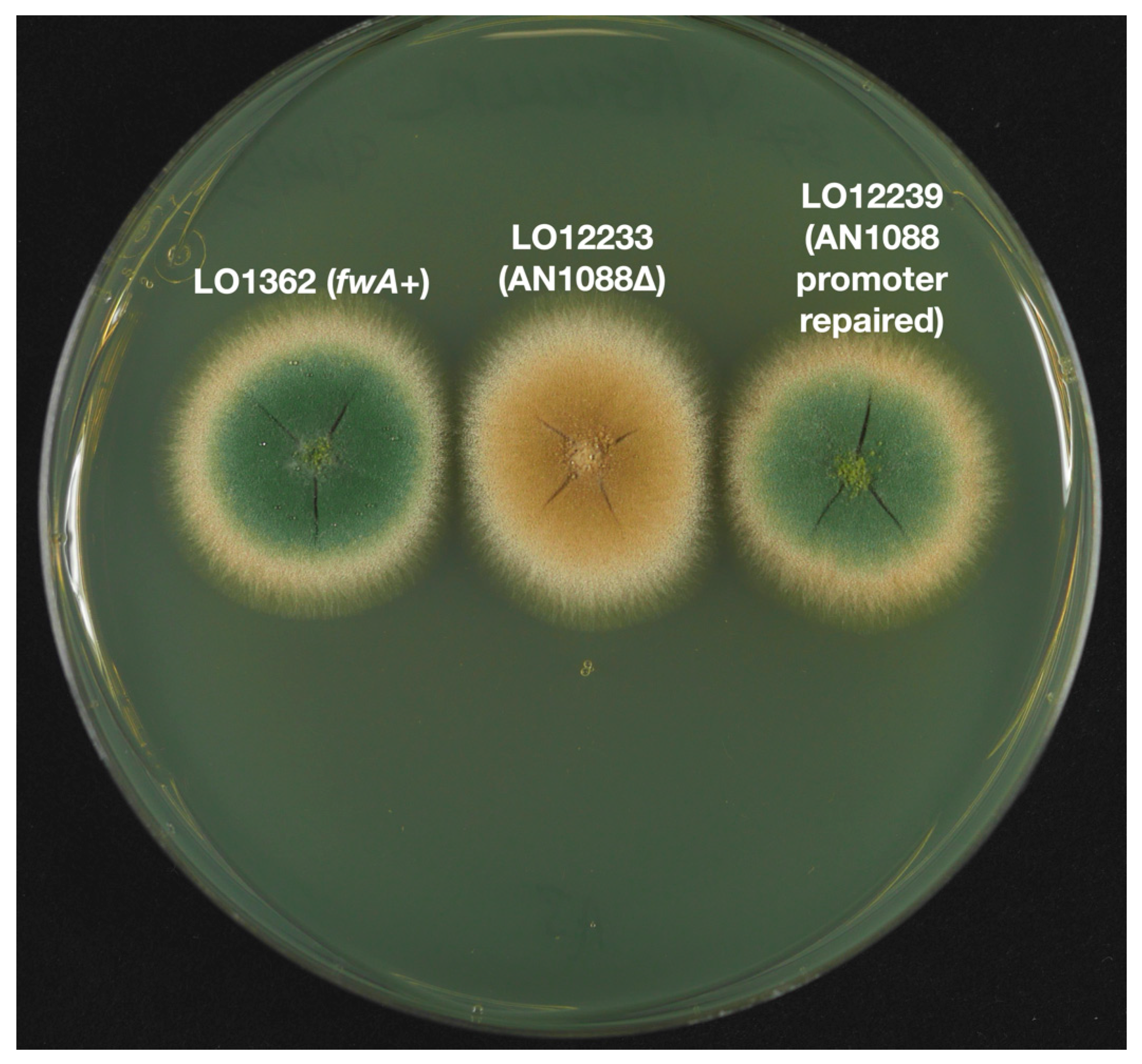
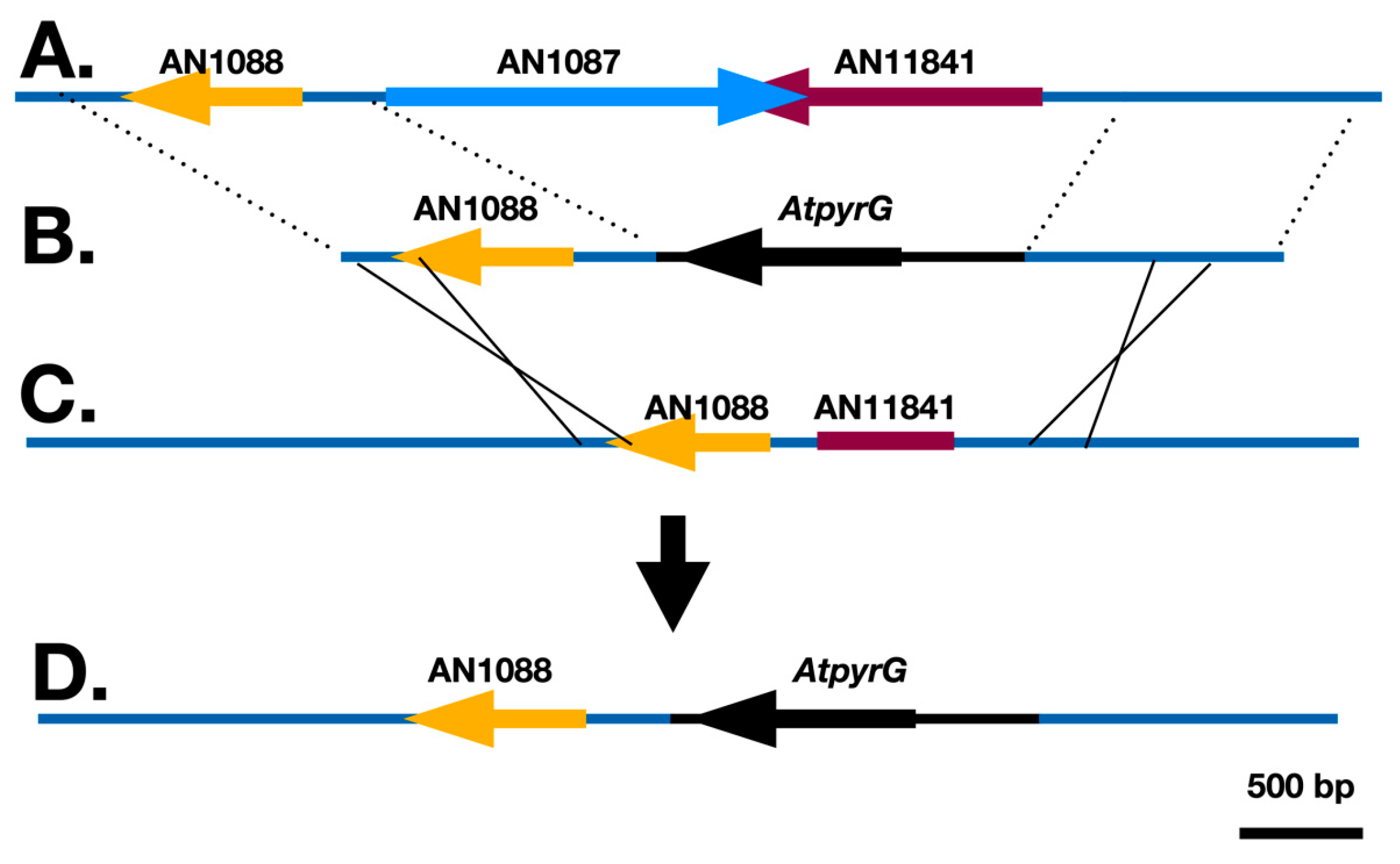
3.2. Identification of the fwA Gene
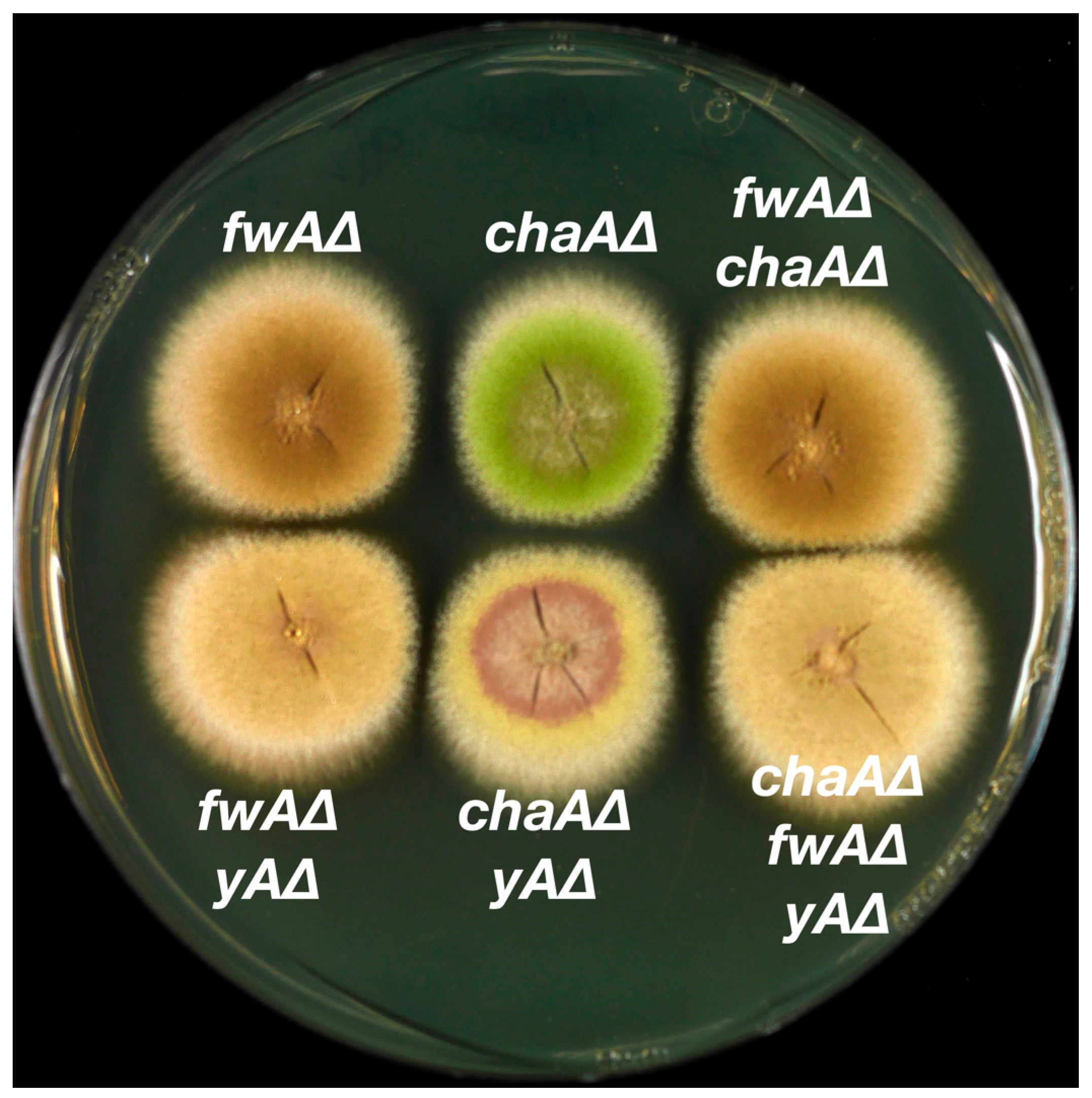
3.3. Epistasis Relationships among Conidial Color Markers
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, P.K.; Cary, J.W.; Lebar, M.D. Biosynthesis of conidial and sclerotial pigments in Aspergillus species. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.J.; Pateman, J.A. Ultraviolet-light sensitive mutants of Aspergillus nidulans. Mutat. Res. 1970, 9, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga, M.E.; Timberlake, W.E. Isolation and molecular characterization of the Aspergillus nidulans wA gene. Genetics 1990, 126, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga, M.E.; Timberlake, W.E. The developmentally regulated Aspergillus nidulans wA gene encodes a polypeptide homologous to polyketide and fatty acid synthases. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1992, 235, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, A.; Fujii, I.; Sankawa, U.; Mayorga, M.E.; Timberlake, W.E.; Ebizuka, Y. Re-identification of Aspergillus nidulans wA gene to code for a polyketide synthase of naphthopyrone. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, M.B.; Champe, S.P. Purification and characterization of the conidial laccase of Aspergillus nidulans. J. Bacteriol. 1982, 151, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clutterbuck, A.J. Absence of laccase from yellow-spored mutants of Aspergillus nidulans. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1972, 70, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, E.B.; Timberlake, W.E. Molecular characterization of the Aspergillus nidulans yA locus. Genetics 1989, 121, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontecorvo, G.; Roper, J.A.; Hemmons, L.M.; MacDonald, K.D.; Bufton, A.W. The genetics of Aspergillus nidulans. Adv. Genet. 1953, 5, 141–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.M.; Oakley, C.E.; Ahuja, M.; Entwistle, R.; Schultz, A.; Chang, S.L.; Sung, C.T.; Wang, C.C.C.; Oakley, B.R. An efficient system for heterologous expression of secondary metabolite genes in Aspergillus nidulans. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7720–7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käfer, E. The processes of spontaneous recombination in vegetative nuclei of Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics 1961, 46, 1581–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clutterbuck, A.J. A fawn conidia mutant in Aspergillus nidulans. Aspergillus Newslett. 1965, 6, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Szewczyk, E.; Nayak, T.; Oakley, C.E.; Edgerton, H.; Xiong, Y.; Taheri-Talesh, N.; Osmani, S.A.; Oakley, B.R. Fusion PCR and gene targeting in Aspergillus nidulans. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 3111–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, C.E.; Edgerton-Morgan, H.; Oakley, B.R. Tools for manipulation of secondary metabolism pathways: Rapid promoter replacements and gene deletions in Aspergillus nidulans. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 944, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgerton-Morgan, H.; Oakley, B.R. γ-Tubulin plays a key role in inactivating APC/CCdh1 at the G1-S boundary. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 198, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, T.; Szewczyk, E.; Oakley, C.E.; Osmani, A.; Ukil, L.; Murray, S.L.; Hynes, M.J.; Osmani, S.A.; Oakley, B.R. A versatile and efficient gene-targeting system for Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics 2006, 172, 1557–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, C.E.; Oakley, B.R. Identification of γ-tubulin, a new member of the tubulin superfamily encoded by mipA gene of Aspergillus nidulans. Nature 1989, 338, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballance, D.J.; Buxton, F.P.; Turner, G. Transformation of Aspergillus nidulans by the orotidine-5’-phosphate decarboxylase gene of Neurospora crassa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1983, 112, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, B.R.; Rinehart, J.E.; Mitchell, B.L.; Oakley, C.E.; Carmona, C.; Gray, G.L.; May, G.S. Cloning, mapping and molecular analysis of the pyrG (orotidine-5’-phosphate decarboxylase) gene of Aspergillus nidulans. Gene 1987, 61, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvaux, S.; Chevalier, F.; Le Dantec, C.; Fayolle, F.; Miras, I.; Kunst, F.; Beguin, P. Cloning of a genetically unstable cytochrome P-450 gene cluster involved in degradation of the pollutant ethyl tert-butyl ether by Rhodococcus ruber. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 6551–6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Xia, Y.; Xiao, G.; Xiong, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Genome sequence of the insect pathogenic fungus Cordyceps militaris, a valued traditional Chinese medicine. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, J.F.; Entwistle, R.; Hung, J.H.; Yaegashi, J.; Jain, S.; Chiang, Y.-M.; Wang, C.C.C.; Oakley, B.R. Genome-based deletion analysis reveals the prenyl xanthone biosynthesis pathway in Aspergillus nidulans. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 4010–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Tong, Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, B. Metarhizium robertsii MrAbaA affects conidial pigmentation via regulating MrPks1 and MrMlac1 expression. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2023, 197, 107892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, S.; Mesarich, C.H.; Saccomanno, B.; Vaisberg, A.; De Wit, P.J.; Cox, R.; Collemare, J. Elucidation of cladofulvin biosynthesis reveals a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase required for anthraquinone dimerization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6851–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clutterbuck, A.J. The validity of the Aspergillus nidulans linkage map. Fungal Genet Biol. 1997, 21, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Strain | Genotype | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| G191 | pyrG89, pabaA1, fwA1, uaY9 | From G. Turner via C. F. Roberts |
| LO1 | A. nidulans wt, no nutritional requirements | |
| LO1362 | pyrG89, pyroA4, riboB2, nkuA::argB | =TN02A7 and FGSC A1145 |
| LO2460 | mad2::AfpyrG, pyroA4, pabaA1, fwA1, nkuA::argB (may carry pyrG89) | |
| LO2647 | pyrG89, fwA1, nkuA::argB | |
| LO12192 | chaA::AtpyrG, pyrG89, pyroA4, riboB2, nkuA::argB | |
| LO12193 | chaA::AtpyrG, pyrG89, pyroA4, riboB2, nkuA::argB | |
| LO12195 | riboB2::chaA-AtriboB, chaA::AtpyrG pyrG89, pyroA4, riboB2, nkuA::argB | |
| LO12233 | fwA::AtpyrG, pyrG89, pyroA4, riboB2, nkuA::argB | |
| LO12236 | fwA::AtriboB, chaA::AtpyrG pyrG89, pyroA4, riboB2, nkuA::argB | |
| LO12239 | fwA(p)-AfpyroA, mad2::pyrG, pyroA4, pabaA1, fwA1, nkuA::argB | Promoter of fwA repaired |
| LO12245 | yA::AtriboB, chaA::AtpyrG pyrG89, pyroA4, riboB2, nkuA::argB | |
| LO12248 | yA::AtriboB, fwA::AtpyrG, pyrG89, pyroA4, riboB2, nkuA::argB | |
| LO12251 | yA::AfpyroA, fwA::AtriboB, chaA::AtpyrG pyrG89, pyroA4, riboB2, nkuA::argB | |
| R21 | pabaA1, yA2 | From C. F. Roberts |
| R153 | pyroA4, wA3 | From C. F. Roberts |
| Gene | AN1059 | AN1063 | AN1087 | AN10167 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fawn | Green | Fawn | Green | Fawn | Green | Fawn | Green | |
| 37 | 0 | 53 | 0 | 27 | 12 | 61 | 0 | |
| Gene Deleted | AN1087 | AN1088 | AN11841 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain | LO1362 | LO12192 | LO1362 | LO12192 | LO1362 | LO12192 | ||||||
| fw | gr | fw | cha | fw | gr | fw | cha | fw | gr | fw | cha | |
| 1 | 141 | 0 | 109 | 216 | 0 | 280 | 2 | 0 | 197 | 0 | 221 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oakley, C.E.; Barton, T.S., Jr.; Oakley, B.R. Identification of the chaA and fwA Spore Color Genes of Aspergillus nidulans. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10020104
Oakley CE, Barton TS Jr., Oakley BR. Identification of the chaA and fwA Spore Color Genes of Aspergillus nidulans. Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(2):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10020104
Chicago/Turabian StyleOakley, C. Elizabeth, Thomas S. Barton, Jr., and Berl R. Oakley. 2024. "Identification of the chaA and fwA Spore Color Genes of Aspergillus nidulans" Journal of Fungi 10, no. 2: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10020104
APA StyleOakley, C. E., Barton, T. S., Jr., & Oakley, B. R. (2024). Identification of the chaA and fwA Spore Color Genes of Aspergillus nidulans. Journal of Fungi, 10(2), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10020104






