Role of the osaA Gene in Aspergillus fumigatus Development, Secondary Metabolism and Virulence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Analysis
2.2. Strains and Culture Conditions
2.3. Generation of the osaA Deletion Strain
2.4. Generation of the osaA Complementation Strain
2.5. Construction of the osaA Overexpression Strain
2.6. Morphological Analysis
2.7. Environmental Stress Tests
2.8. Cell Wall Tests
2.9. Adhesion Assay
2.10. Metabolomics Analysis
2.11. Gene Expression Analysis
2.12. Virulence Assay
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of OsaA in A. fumigatus
3.2. Growth, Conidiation, and Germination Rate Are Regulated by osaA in A. fumigatus
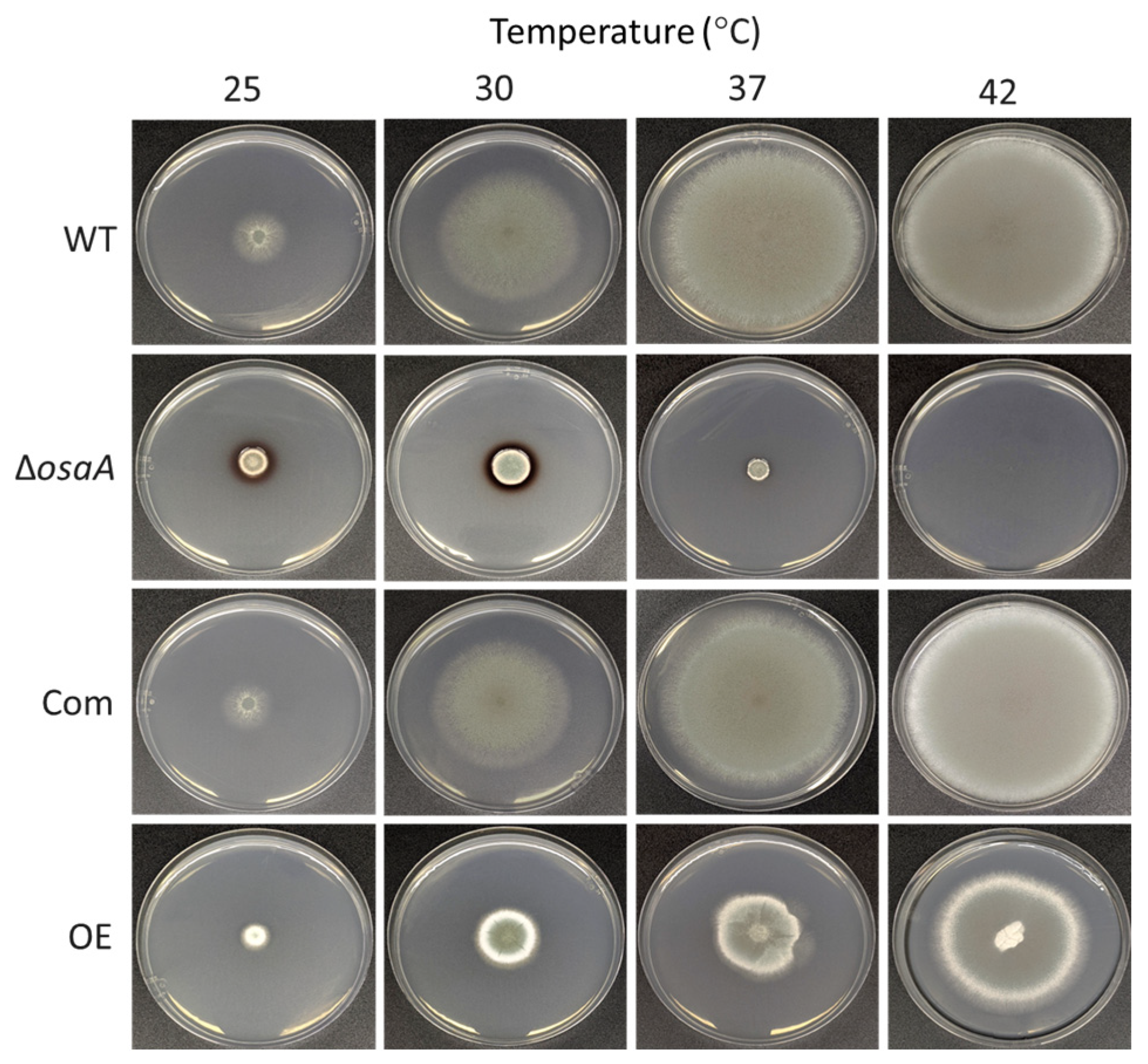
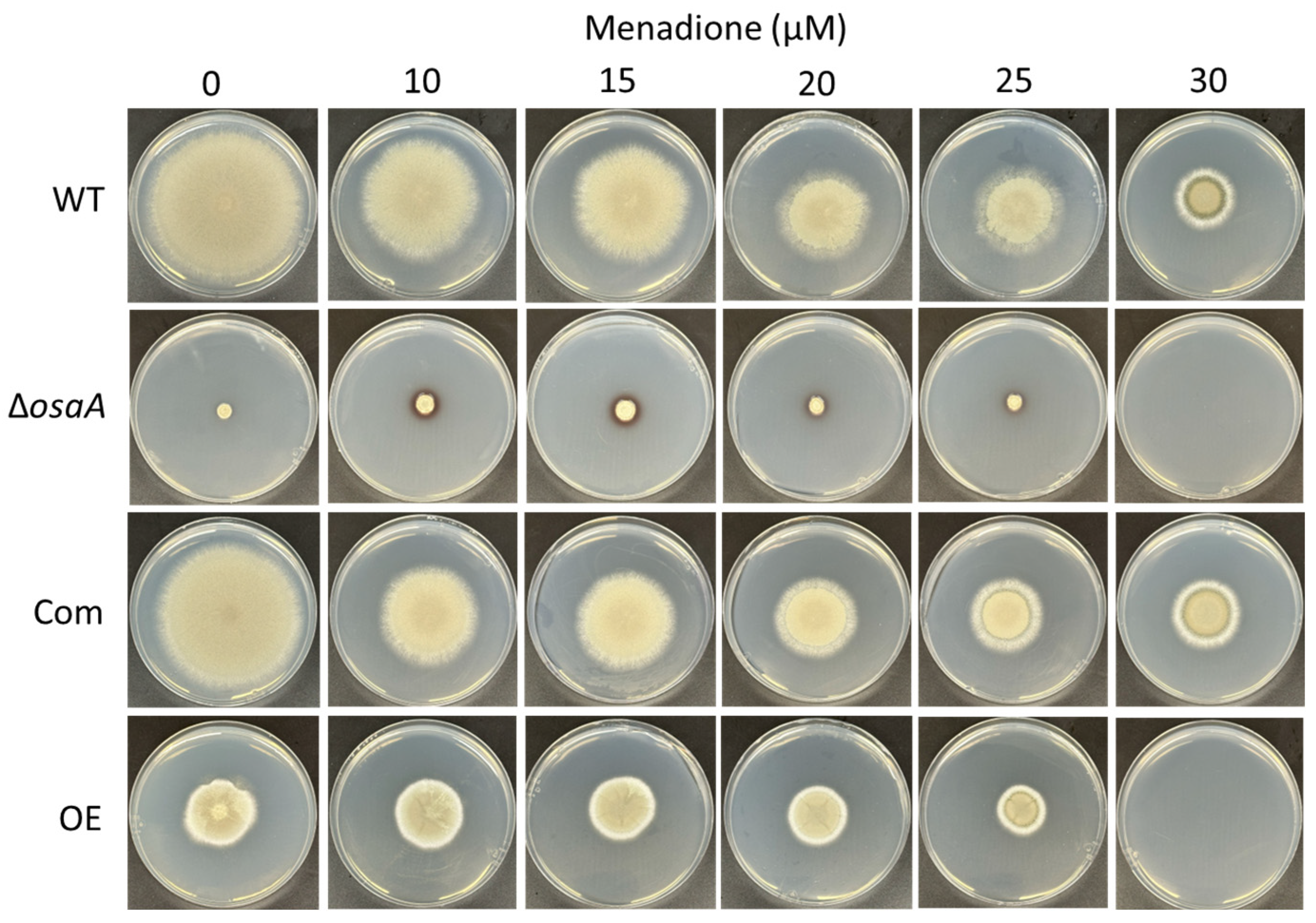
3.3. osaA Influences A. fumigatus Temperature and Oxidative Stress Resistance
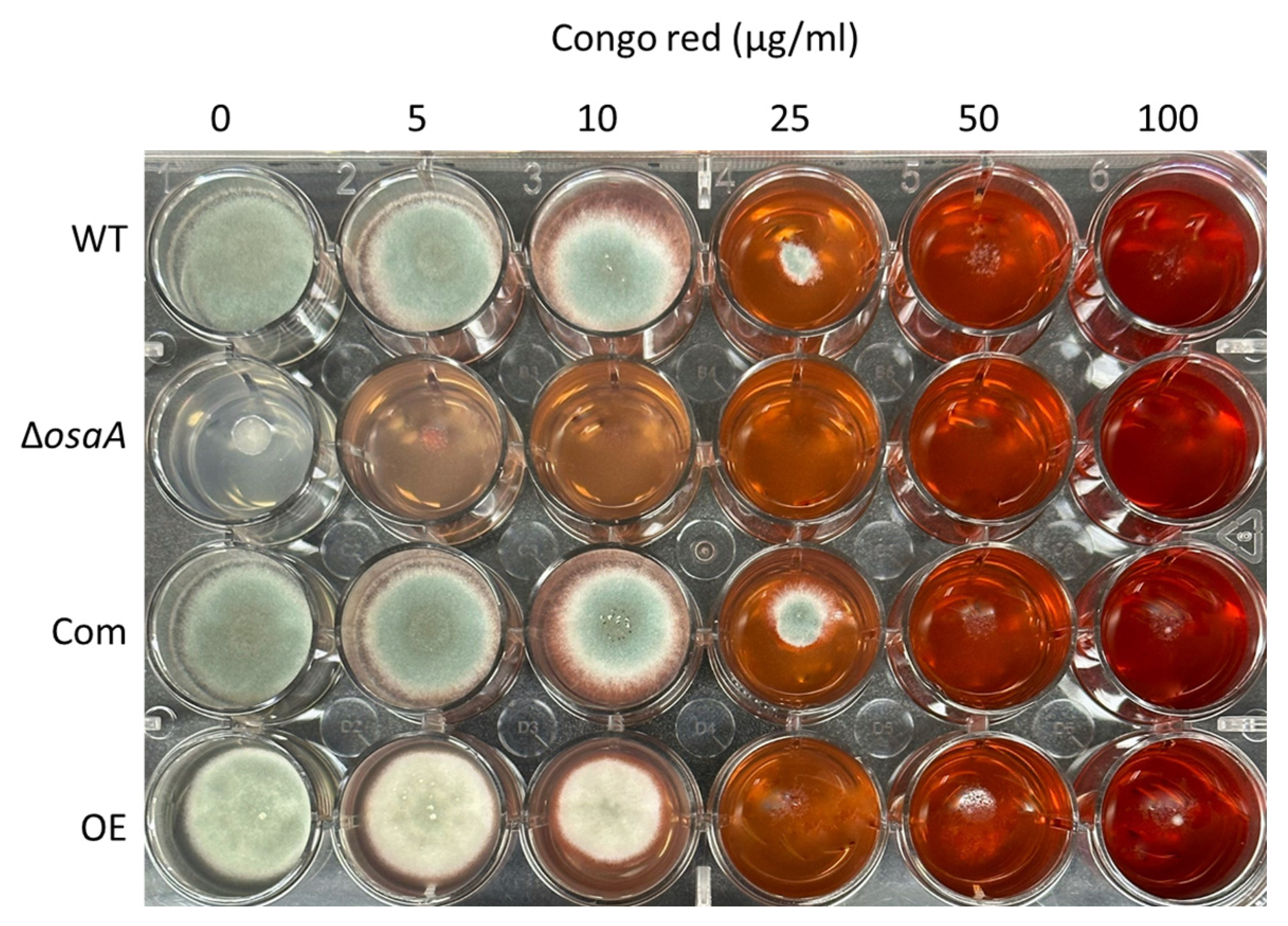
3.4. The Effect of osaA on A. fumigatus Cell Wall and Adhesion Capacity
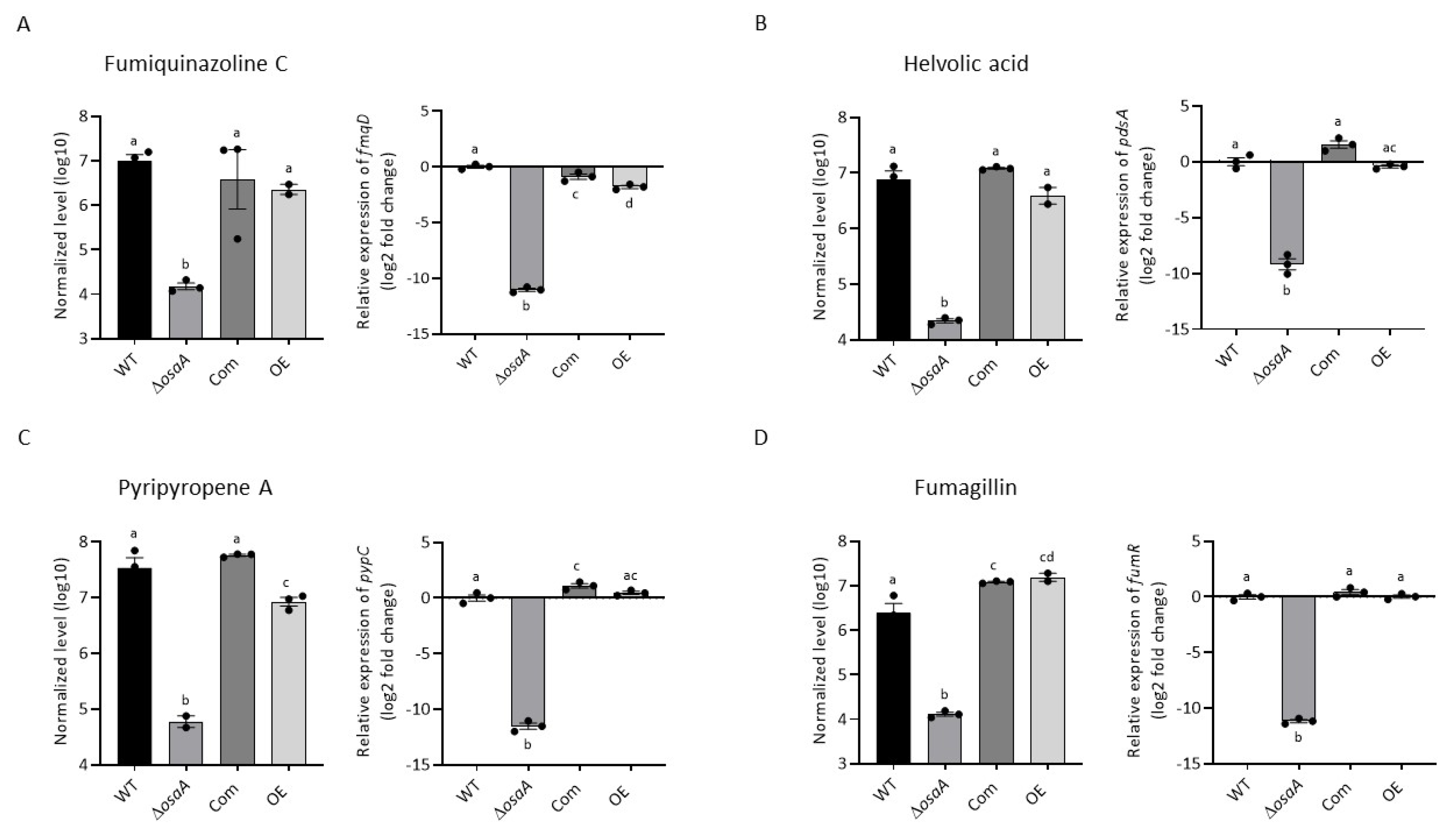
3.5. osaA Regulates Secondary Metabolism in A. fumigatus
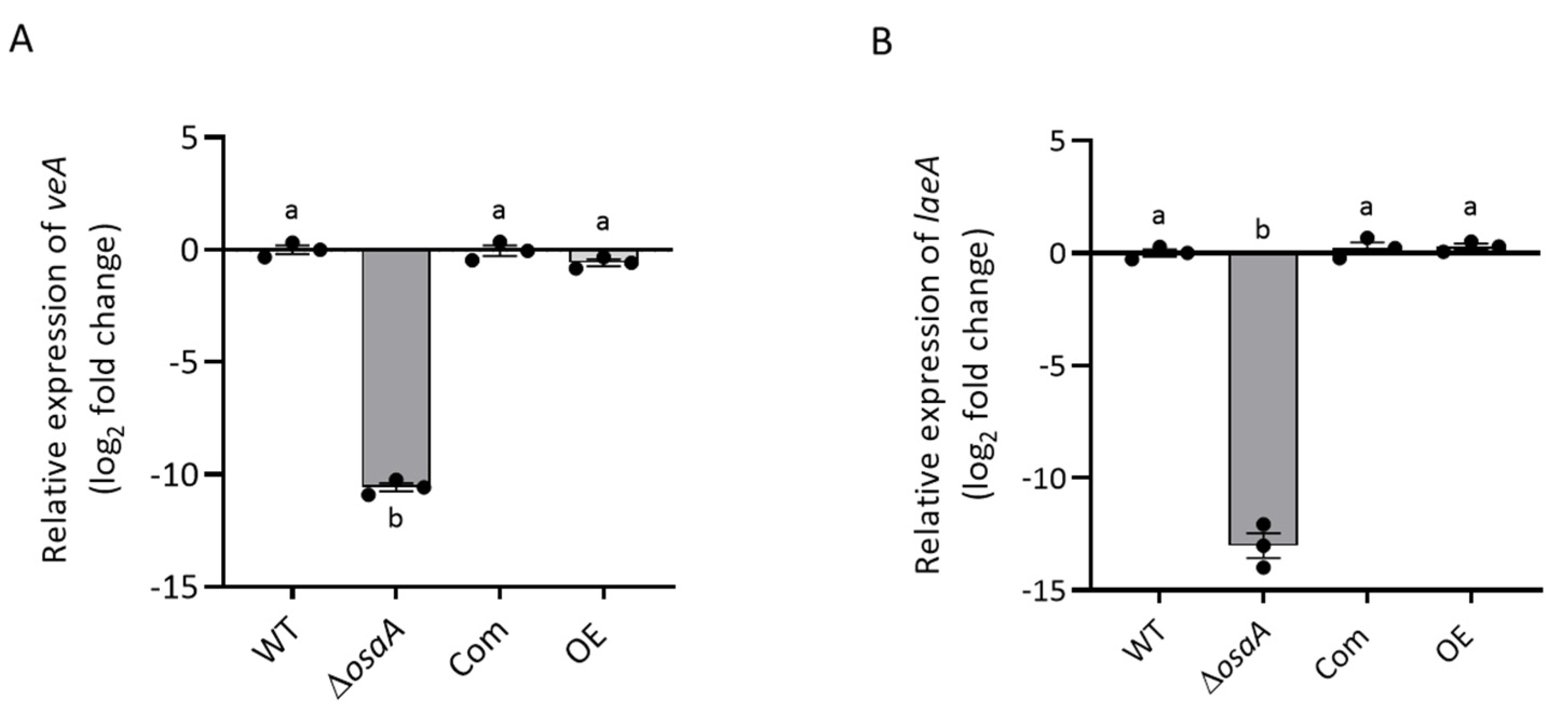
3.6. Gene Expression Analysis of Secondary Metabolite Genes
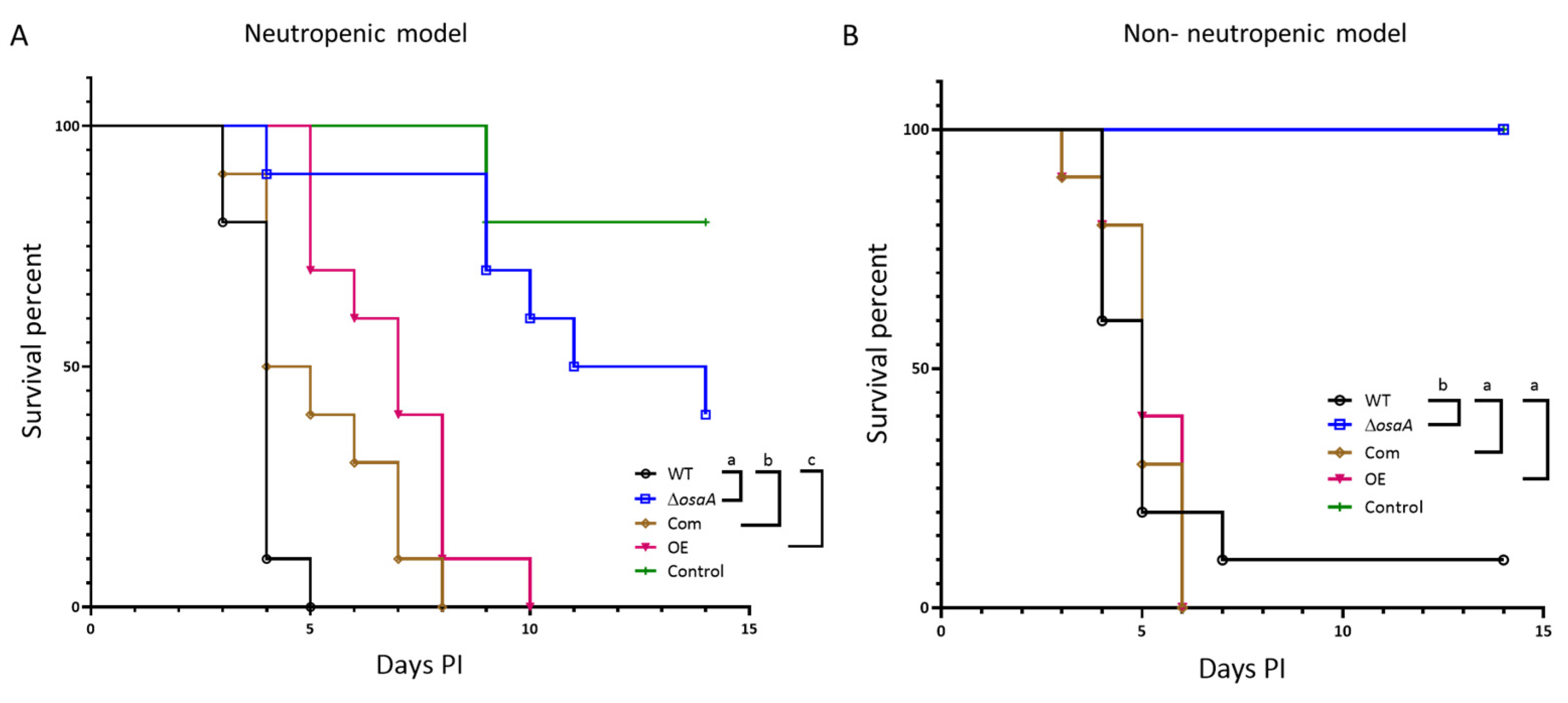
3.7. osaA Is Indispensable for Normal A. fumigatus Virulence in Both Neutropenic and Corticosteroid-Immunodepressed Murine Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Winters, B.; Custer, J.; Galvagno, S.M.; Colantuoni, E.; Kapoor, S.G.; Lee, H.; Goode, V.; Robinson, K.; Nakhasi, A.; Pronovost, P.; et al. Diagnostic Errors in the Intensive Care Unit: A Systematic Review of Autopsy Studies. BMJ Qual. Saf. 2012, 21, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denning, D.W. Invasive Aspergillosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 26, 781–803; quiz 804–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kliasova, G.A.; Petrova, N.A.; Parovichnikova, E.N.; Gotman, L.N.; Isaev, V.G.; Mikhaĭlova, E.A.; Ustinova, E.N.; Khoroshko, N.D.; Vishnevskaia, E.S.; Kremenetskaia, A.M.; et al. Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillesis. Ter. Arkh. 2005, 77, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Pagano, L.; Girmenia, C.; Mele, L.; Ricci, P.; Tosti, M.E.; Nosari, A.; Buelli, M.; Picardi, M.; Allione, B.; Corvatta, L.; et al. Infections Caused by Filamentous Fungi in Patients with Hematologic Malignancies. A Report of 391 Cases by GIMEMA Infection Program. Haematologica 2001, 86, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marr, K.A.; Carter, R.A.; Boeckh, M.; Martin, P.; Corey, L. Invasive Aspergillosis in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients: Changes in Epidemiology and Risk Factors. Blood 2002, 100, 4358–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederhold, N.P.; Lewis, R.E.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Invasive Aspergillosis in Patients with Hematologic Malignancies. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2003, 23, 1592–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, M.J.; Lass-Floerl, C.; Gastl, G.; Nachbaur, D. Invasive Fungal Infections in Allogeneic and Autologous Stem Cell Transplant Recipients: A Single-Center Study of 166 Transplanted Patients. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2007, 9, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latgé, J.P. Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 310–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, R.; Segal, B.H. Pulmonary Aspergillosis: Clinical Presentation, Diagnostic Tests, Management and Complications. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2010, 16, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohl, T.M.; Feldmesser, M. Aspergillus fumigatus: Principles of Pathogenesis and Host Defense. Eukaryot. Cell 2007, 6, 1953–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, G.; Almyroudi, M.-P.; Myrianthefs, P.; Rello, J. COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CAPA). J. Intensive Med. 2021, 1, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergün, M.; Brüggemann, R.J.M.; Alanio, A.; Dellière, S.; van Arkel, A.; Bentvelsen, R.G.; Rijpstra, T.; van der Sar-van der Brugge, S.; Lagrou, K.; Janssen, N.A.F.; et al. Aspergillus Test Profiles and Mortality in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0122921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoletti, M.; Pascale, R.; Cricca, M.; Rinaldi, M.; Maccaro, A.; Bussini, L.; Fornaro, G.; Tonetti, T.; Pizzilli, G.; Francalanci, E.; et al. Epidemiology of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Among Intubated Patients with COVID-19: A Prospective Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e3606–e3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.; Valerio, M.; Álvarez-Uría, A.; Olmedo, M.; Veintimilla, C.; Padilla, B.; De la Villa, S.; Guinea, J.; Escribano, P.; Ruiz-Serrano, M.J.; et al. Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in the COVID-19 Era: An Expected New Entity. Mycoses 2021, 64, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-J.; Schranz, J.; Teutsch, S.M. Aspergillosis Case-Fatality Rate: Systematic Review of the Literature. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagenais, T.R.T.; Keller, N.P. Pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus in Invasive Aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parums, D.V. Editorial: The World Health Organization (WHO) Fungal Priority Pathogens List in Response to Emerging Fungal Pathogens During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Med. Sci. Monit. 2022, 28, e939088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. Available online: www.cdc.gov/DrugResistance/Biggest-Threats.html (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Ellis, M. Therapy of Aspergillus fumigatus-Related Diseases. Contrib. Microbiol. 1999, 2, 105–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, I.; Goldstein, N. Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2002, 8, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Bodey, G.P. Invasive Aspergillosis in 2002: An Update. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2002, 21, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, H.J.; Blevins, A.; Sobeck, K.; Armstrong, D. Aspergillus Species from Hospital Air and from Patients. Mycoses 1990, 33, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüchel, R.; Reichard, U. Pathogenesis and Clinical Presentation of Aspergillosis. Contrib. Microbiol. 1999, 2, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, R.A. The Genus Aspergillus with Special Regard to the Aspergillus fumigatus Group. Contrib. Microbiol. 1999, 2, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenguer, J.; Allende, M.C.; Lee, J.W.; Garrett, K.; Lyman, C.; Ali, N.M.; Bacher, J.; Pizzo, P.A.; Walsh, T.J. Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Aspergillosis. Granulocytopenia versus Cyclosporine and Methylprednisolone-Induced Immunosuppression. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, D.W. Aspergillosis: Diagnosis and Treatment. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 1996, 6, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balloy, V.; Huerre, M.; Latgé, J.-P.; Chignard, M. Differences in Patterns of Infection and Inflammation for Corticosteroid Treatment and Chemotherapy in Experimental Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stergiopoulou, T.; Meletiadis, J.; Roilides, E.; Kleiner, D.E.; Schaufele, R.; Roden, M.; Harrington, S.; Dad, L.; Segal, B.; Walsh, T.J. Host-Dependent Patterns of Tissue Injury in Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 127, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, L.Y.; Sheppard, D.C.; Gravelat, F.N.; Patterson, T.F.; Filler, S.G. Aspergillus fumigatus Stimulates Leukocyte Adhesion Molecules and Cytokine Production by Endothelial Cells in Vitro and during Invasive Pulmonary Disease. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 3429–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionakis, M.S.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Glucocorticoids and Invasive Fungal Infections. Lancet 2003, 362, 1828–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummer, E.; Maqbool, A.; Stevens, D.A. In Vivo GM-CSF Prevents Dexamethasone Suppression of Killing of Aspergillus fumigatus Conidia by Bronchoalveolar Macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001, 70, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamberi, M.; Brummer, E.; Stevens, D.A. Regulation of Bronchoalveolar Macrophage Proinflammatory Cytokine Production by Dexamethasone and Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor after Stimulation by Aspergillus Conidia or Lipopolysaccharide. Cytokine 2002, 19, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Osusky, I.; Schoedon, G.; Bläuer, F.; Schneemann, M.; Schaffner, A. Comparison of the Antimicrobial Activity of Deactivated Human Macrophages Challenged with Aspergillus fumigatus and Listeria monocytogenes. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 174, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roilides, E.; Uhlig, K.; Venzon, D.; Pizzo, P.A.; Walsh, T.J. Prevention of Corticosteroid-Induced Suppression of Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte-Induced Damage of Aspergillus fumigatus Hyphae by Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor and Gamma Interferon. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 4870–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roilides, E.; Holmes, A.; Blake, C.; Pizzo, P.A.; Walsh, T.J. Impairment of Neutrophil Antifungal Activity against Hyphae of Aspergillus fumigatus in Children Infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 167, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.; Fei, M.; Yarlagadda, M.; Qi, Z.; Akira, S.; Saijo, S.; Iwakura, Y.; van Rooijen, N.; Gibson, G.A.; St., Croix, C.M.; et al. Rapid Host Defense against Aspergillus fumigatus Involves Alveolar Macrophages with a Predominance of Alternatively Activated Phenotype. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakhage, A.A.; Langfelder, K.; Wanner, G.; Schmidt, A.; Jahn, B. Pigment Biosynthesis and Virulence. Contrib. Microbiol. 1999, 2, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.F.; Wheeler, M.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Kwon-Chung, K.J. A Developmentally Regulated Gene Cluster Involved in Conidial Pigment Biosynthesis in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 6469–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahn, B.; Boukhallouk, F.; Lotz, J.; Langfelder, K.; Wanner, G.; Brakhage, A.A. Interaction of Human Phagocytes with Pigmentless Aspergillus Conidia. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 3736–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, K.; Jahn, B.; Gehringer, H.; Schmidt, A.; Wanner, G.; Brakhage, A.A. Identification of a Polyketide Synthase Gene (PksP) of Aspergillus fumigatus Involved in Conidial Pigment Biosynthesis and Virulence. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 1998, 187, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Enfert, C.; Diaquin, M.; Delit, A.; Wuscher, N.; Debeaupuis, J.P.; Huerre, M.; Latge, J.P. Attenuated Virulence of Uridine-Uracil Auxotrophs of Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 4401–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, D.K.; Sandhu, R.S.; Khan, Z.U.; Damodaran, V.N. Conditional Virulence of a P-Aminobenzoic Acid-Requiring Mutant of Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect. Immun. 1976, 13, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.S.; Aufauvre-Brown, A.; Brown, J.; Jennings, J.M.; Arst, H.; Holden, D.W. Signature-Tagged and Directed Mutagenesis Identify PABA Synthetase as Essential for Aspergillus fumigatus Pathogenicity. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 36, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krappmann, S.; Bignell, E.M.; Reichard, U.; Rogers, T.; Haynes, K.; Braus, G.H. The Aspergillus fumigatus Transcriptional Activator CpcA Contributes Significantly to the Virulence of This Fungal Pathogen. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 52, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, A.M.; Wilson, R.A.; Bok, J.W.; Keller, N.P. Relationship between Secondary Metabolism and Fungal Development. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, C.-C.; Tang, J.Y.M.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y. Taxonomy and Evolution of Aspergillus, Penicillium and Talaromyces in the Omics Era—Past, Present and Future. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoufache, K.; Puel, O.; Loiseau, N.; Delaforge, M.; Rivollet, D.; Coste, A.; Cordonnier, C.; Escudier, E.; Botterel, F.; Bretagne, S. Verruculogen Associated with Aspergillus fumigatus Hyphae and Conidia Modifies the Electrophysiological Properties of Human Nasal Epithelial Cells. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhingra, S.; Andes, D.; Calvo, A.M. VeA Regulates Conidiation, Gliotoxin Production, and Protease Activity in the Opportunistic Human Pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 2012, 11, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, T.; Wang, X.; Sifuentes Dos Santos, J.; Fysikopoulos, A.; Tadrist, S.; Canlet, C.; Artigot, M.P.; Loiseau, N.; Oswald, I.P.; Puel, O. Trypacidin, a spore-borne toxin from Aspergillus fumigatus, is cytotoxic to lung cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, C.A. Fungal Infections. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2006, 3, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, L.E.; Sanglard, D.; Howard, S.J.; Rogers, P.D.; Perlin, D.S. Mechanisms of Antifungal Drug Resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 5, a019752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, D.; Watanabe, A.; Kamei, K.; Goldman, G.H. Epidemiological and Genomic Landscape of Azole Resistance Mechanisms in Aspergillus Fungi. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanvoine, A.; Rocchi, S.; Bellanger, A.P.; Reboux, G.; Millon, L. Azole-Resistant Aspergillus fumigatus: A Global Phenomenon Originating in the Environment? Med. Mal. Infect. 2020, 50, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelièvre, L.; Groh, M.; Angebault, C.; Maherault, A.-C.; Didier, E.; Bougnoux, M.-E. Azole Resistant Aspergillus fumigatus: An Emerging Problem. Med. Mal. Infect. 2013, 43, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crystal Structure of the WOPR-DNA Complex and Implications for Wor1 Function in White-Opaque Switching of Candida albicans—PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4152732/ (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Kunitomo, H.; Sugimoto, A.; Wilkinson, C.R.; Yamamoto, M. Schizosaccharomyces pombe Pac2+ Controls the Onset of Sexual Development via a Pathway Independent of the CAMP Cascade. Curr. Genet. 1995, 28, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.Q.; Sil, A. Temperature-Induced Switch to the Pathogenic Yeast Form of Histoplasma capsulatum Requires Ryp1, a Conserved Transcriptional Regulator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4880–4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zordan, R.E.; Galgoczy, D.J.; Johnson, A.D. Epigenetic Properties of White-Opaque Switching in Candida albicans Are Based on a Self-Sustaining Transcriptional Feedback Loop. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12807–12812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonkers, W.; Dong, Y.; Broz, K.; Kistler, H.C. The Wor1-like Protein Fgp1 Regulates Pathogenicity, Toxin Synthesis and Reproduction in the Phytopathogenic Fungus Fusarium graminearum. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michielse, C.B.; van Wijk, R.; Reijnen, L.; Manders, E.M.M.; Boas, S.; Olivain, C.; Alabouvette, C.; Rep, M. The Nuclear Protein Sge1 of Fusarium oxysporum Is Required for Parasitic Growth. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahyyat, F.; Ni, M.; Kim, S.C.; Yu, J.-H. The WOPR Domain Protein OsaA Orchestrates Development in Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käfer, E. Meiotic and Mitotic Recombination in Aspergillus and Its Chromosomal Aberrations. In Advances in Genetics; Caspari, E.W., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1977; Volume 19, pp. 33–131. [Google Scholar]
- Szewczyk, E.; Nayak, T.; Oakley, C.E.; Edgerton, H.; Xiong, Y.; Taheri-Talesh, N.; Osmani, S.A.; Oakley, B.R. Fusion PCR and Gene Targeting in Aspergillus nidulans. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 3111–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thammahong, A.; Caffrey-Card, A.K.; Dhingra, S.; Obar, J.J.; Cramer, R.A. Aspergillus fumigatus Trehalose-Regulatory Subunit Homolog Moonlights to Mediate Cell Wall Homeostasis through Modulation of Chitin Synthase Activity. mBio 2017, 8, e00056-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, R.R.; Smith, T.D.; Elsawa, S.F.; Puel, O.; Tadrist, S.; Calvo, A.M. RtfA Controls Development, Secondary Metabolism, and Virulence in Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterlee, T.; Nepal, B.; Lorber, S.; Puel, O.; Calvo, A.M. The Transcriptional Regulator HbxA Governs Development, Secondary Metabolism, and Virulence in Aspergillus fumigatus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01779-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, S.S.; Zheng, J.; Yin, Y.; Lorber, S.; Puel, O.; Dhingra, S.; Espeso, E.A.; Calvo, A.M. Homeobox transcription factor HbxA Influences Expression of Over One Thousand Genes in the Model Fungus Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhingra, S.; Buckey, J.C.; Cramer, R.A. Hyperbaric Oxygen Reduces Aspergillus fumigatus Proliferation In Vitro and Influences In Vivo Disease Outcomes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01953-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.-H. Regulation of Development in Aspergillus nidulans and Aspergillus fumigatus. Mycobiology 2010, 38, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultman, K.M.; Kowalski, C.H.; Cramer, R.A. Aspergillus fumigatus Virulence through the Lens of Transcription Factors. Med. Mycol. 2017, 55, myw120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lim, F.Y.; Ames, B.; Walsh, C.T.; Keller, N.P. Co-Ordination between BrlA Regulation and Secretion of the Oxidoreductase FmqD Directs Selective Accumulation of Fumiquinazoline C to Conidial Tissues in Aspergillus fumigatus. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1267–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodeiro, S.; Xiong, Q.; Wilson, W.K.; Ivanova, Y.; Smith, M.L.; May, G.S.; Matsuda, S.P.T. Protostadienol Biosynthesis and Metabolism in the Pathogenic Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 1241–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, A.L.; Lim, F.Y.; Soukup, A.A.; Keller, N.P.; Rokas, A. An LaeA- and BrlA-Dependent Cellular Network Governs Tissue-Specific Secondary Metabolism in the Human Pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. mSphere 2018, 3, e00050-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-C.; Chooi, Y.-H.; Dhingra, S.; Xu, W.; Calvo, A.M.; Tang, Y. The Fumagillin Biosynthetic Gene Cluster in Aspergillus fumigatus Encodes a Cryptic Terpene Cyclase Involved in the Formation of β-Trans-Bergamotene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4616–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiya, S.; Grundmann, A.; Li, X.; Li, S.-M.; Turner, G. Identification of a Hybrid PKS/NRPS Required for Pseurotin A Biosynthesis in the Human Pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Chembiochem 2007, 8, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bok, J.W.; Chung, D.; Balajee, S.A.; Marr, K.A.; Andes, D.; Nielsen, K.F.; Frisvad, J.C.; Kirby, K.A.; Keller, N.P. GliZ, a Transcriptional Regulator of Gliotoxin Biosynthesis, Contributes to Aspergillus fumigatus Virulence. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 6761–6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupfahl, C.; Heinekamp, T.; Geginat, G.; Ruppert, T.; Härtl, A.; Hof, H.; Brakhage, A.A. Deletion of the GliP Gene of Aspergillus fumigatus Results in Loss of Gliotoxin Production but Has No Effect on Virulence of the Fungus in a Low-Dose Mouse Infection Model. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, M.B.; Rosenberg, O.S.; Cox, J.S.; Stroud, R.M.; Finer-Moore, J.S.; Johnson, A.D. Structure of a New DNA-Binding Domain Which Regulates Pathogenesis in a Wide Variety of Fungi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10404–10410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, M.B.; Zordan, R.E.; Cain, C.W.; Johnson, A.D. Distinct Class of DNA-Binding Domains Is Exemplified by a Master Regulator of Phenotypic Switching in Candida albicans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14105–14110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, M.A.; Beyhan, S.; Voorhies, M.; Shubitz, L.F.; Galgiani, J.N.; Orbach, M.J.; Sil, A. The WOPR Family Protein Ryp1 Is a Key Regulator of Gene Expression, Development, and Virulence in the Thermally Dimorphic Fungal Pathogen Coccidioides posadasii. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1009832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maresca, B.; Carratù, L.; Kobayashi, G.S. Morphological Transition in the Human Fungal Pathogen Histoplasma capsulatum. Trends Microbiol. 1994, 2, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon-Chung, K.J.; Sugui, J.A. Aspergillus fumigatus—What Makes the Species a Ubiquitous Human Fungal Pathogen? PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, C.A.; Culibrk, L.; Moore, M.M.; Tebbutt, S.J. Interactions of Aspergillus fumigatus Conidia with Airway Epithelial Cells: A Critical Review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhabhra, R.; Askew, D.S. Thermotolerance and Virulence of Aspergillus fumigatus: Role of the Fungal Nucleolus. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43, S87–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabri, J.H.T.M.; Rocha, M.C.; Fernandes, C.M.; Persinoti, G.F.; Ries, L.N.A.; da Cunha, A.F.; Goldman, G.H.; Del Poeta, M.; Malavazi, I. The Heat Shock Transcription Factor HsfA Is Essential for Thermotolerance and Regulates Cell Wall Integrity in Aspergillus fumigatus. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 656548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, D.C. Molecular Mechanism of Aspergillus fumigatus Adherence to Host Constituents. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, L.; Sen, P.; Bhattacharya, A.K.; Vijayaraghavan, P. Isoeugenol Affects Expression Pattern of Conidial Hydrophobin Gene RodA and Transcriptional Regulators MedA and SomA Responsible for Adherence and Biofilm Formation in Aspergillus fumigatus. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loor, G.; Kondapalli, J.; Schriewer, J.M.; Chandel, N.S.; Vanden Hoek, T.L.; Schumacker, P.T. Menadione Triggers Cell Death through ROS-Dependent Mechanisms Involving PARP Activation without Requiring Apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zuo, X.; Cheng, P.; Ren, X.; Sun, S.; Xu, J.; Holmgren, A.; Lu, J. The Production of Reactive Oxygen Species Enhanced with the Reduction of Menadione by Active Thioredoxin Reductase. Metallomics 2019, 11, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.B.; Kakeya, H.; Osada, H. Novel Mammalian Cell Cycle Inhibitors, Tryprostatins A, B and Other Diketopiperazines Produced by Aspergillus fumigatus. II. Physico-Chemical Properties and Structures. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, N.P. Fungal Secondary Metabolism: Regulation, Function and Drug Discovery. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, N.; Keller, N.P. A Call to Arms: Mustering Secondary Metabolites for Success and Survival of an Opportunistic Pathogen. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Kang, S.; Lee, D.; Yun, C.-W. Regulation of Pseurotin A Biosynthesis by GliZ and Zinc in Aspergillus fumigatus. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallon, J.P.; Reeves, E.P.; Kavanagh, K. Inhibition of Neutrophil Function Following Exposure to the Aspergillus fumigatus Toxin Fumagillin. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Qiu, P.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, L.; He, J.; Wang, C.; Guo, Q.; Kenny, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, J.; et al. Pseurotin A Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis and Prevents Ovariectomized-Induced Bone Loss by Suppressing Reactive Oxygen Species. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1634–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-B.; Du, S.-Y.; Ji, B.; Ji, C.-J.; Xiao, Y.-W.; Yan, R.-M.; Zhu, D. New Helvolic Acid Derivatives with Antibacterial Activities from Sarocladium oryzae DX-THL3, an Endophytic Fungus from Dongxiang Wild Rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Molecules 2021, 26, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, C.M.; Kenaley, S.C.; Rittenour, W.R.; Panaccione, D.G. Association of Ergot Alkaloids with Conidiation in Aspergillus fumigatus. Mycologia 2007, 99, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-X.; Himaya, S.W.A.; Dewapriya, P.; Zhang, C.; Kim, S.-K. Fumigaclavine C from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus Induces Apoptosis in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 5063–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guruceaga, X.; Perez-Cuesta, U.; Abad-Diaz de Cerio, A.; Gonzalez, O.; Alonso, R.M.; Hernando, F.L.; Ramirez-Garcia, A.; Rementeria, A. Fumagillin, a Mycotoxin of Aspergillus fumigatus: Biosynthesis, Biological Activities, Detection, and Applications. Toxins 2019, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiya, S.; Grundmann, A.; Li, S.-M.; Turner, G. The Fumitremorgin Gene Cluster of Aspergillus fumigatus: Identification of a Gene Encoding Brevianamide F Synthetase. Chembiochem 2006, 7, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon-Chung, K.J.; Sugui, J.A. What Do We Know about the Role of Gliotoxin in the Pathobiology of Aspergillus fumigatus? Med. Mycol. 2009, 47, S97–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boysen, J.M.; Saeed, N.; Hillmann, F. Natural Products in the Predatory Defence of the Filamentous Fungal Pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1814–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bok, J.W.; Balajee, S.A.; Marr, K.A.; Andes, D.; Nielsen, K.F.; Frisvad, J.C.; Keller, N.P. LaeA, a Regulator of Morphogenetic Fungal Virulence Factors. Eukaryot. Cell 2005, 4, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, A.M.; Lohmar, J.M.; Ibarra, B.; Satterlee, T. 18 Velvet Regulation of Fungal Development. In Growth, Differentiation and Sexuality; Wendland, J., Ed.; The Mycota; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 475–497. ISBN 978-3-319-25844-7. [Google Scholar]
- Lind, A.L.; Smith, T.D.; Satterlee, T.; Calvo, A.M.; Rokas, A. Regulation of Secondary Metabolism by the Velvet Complex Is Temperature-Responsive in Aspergillus. G3 2016, 6, 4023–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bok, J.W.; Keller, N.P. LaeA, a Regulator of Secondary Metabolism in Aspergillus spp. Eukaryot. Cell 2004, 3, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.; Lee, M.-K.; Bok, I.; Bok, J.W.; Keller, N.P.; Yu, J.-H. Unraveling the Gene Regulatory Networks of the Global Regulators VeA and LaeA in Aspergillus nidulans. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0016623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, R.M.; Fedorova, N.D.; Bok, J.W.; Cramer, R.A.; Wortman, J.R.; Kim, H.S.; Nierman, W.C.; Keller, N.P. Transcriptional regulation of chemical diversity in Aspergillus fumigatus by LaeA. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
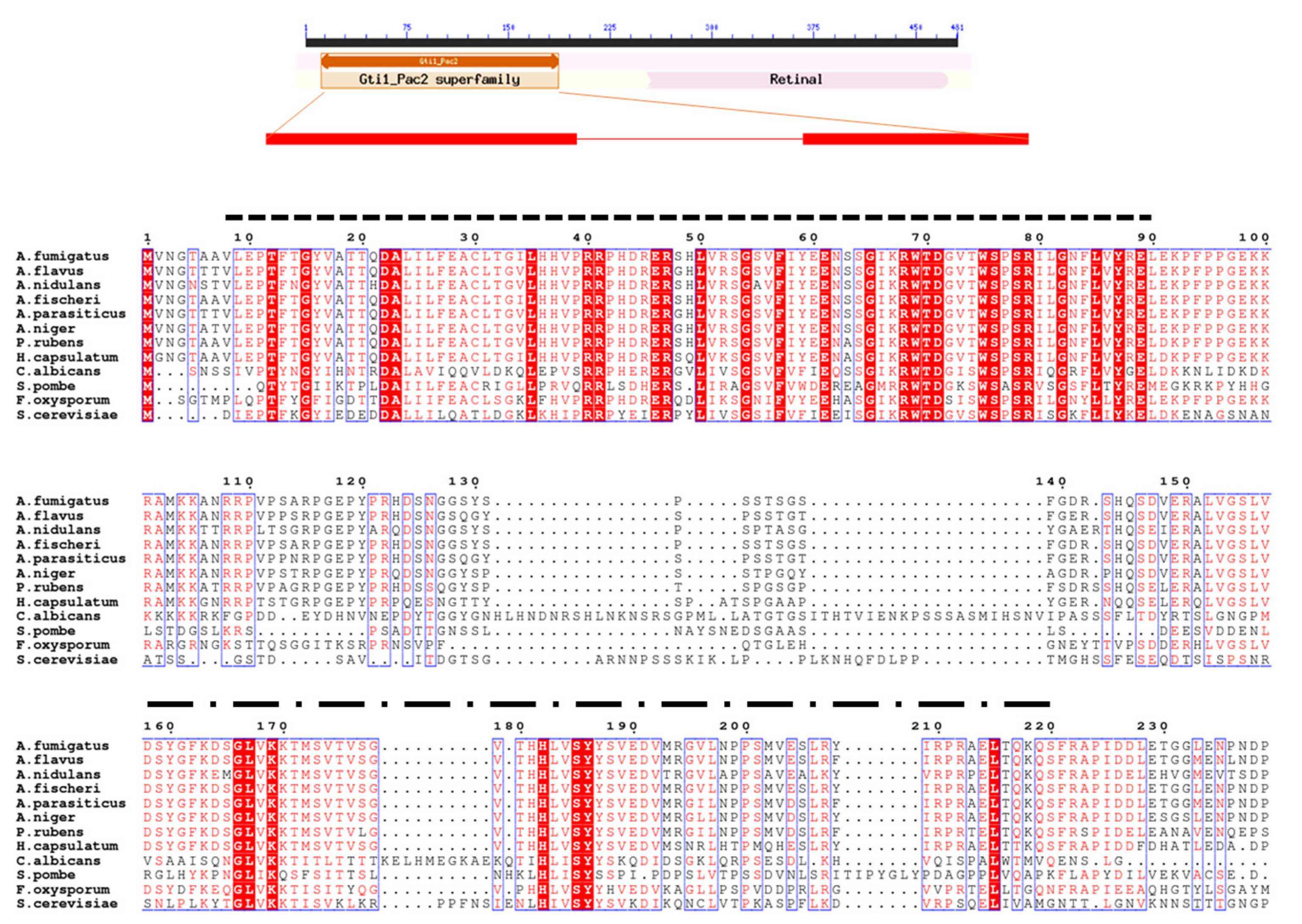
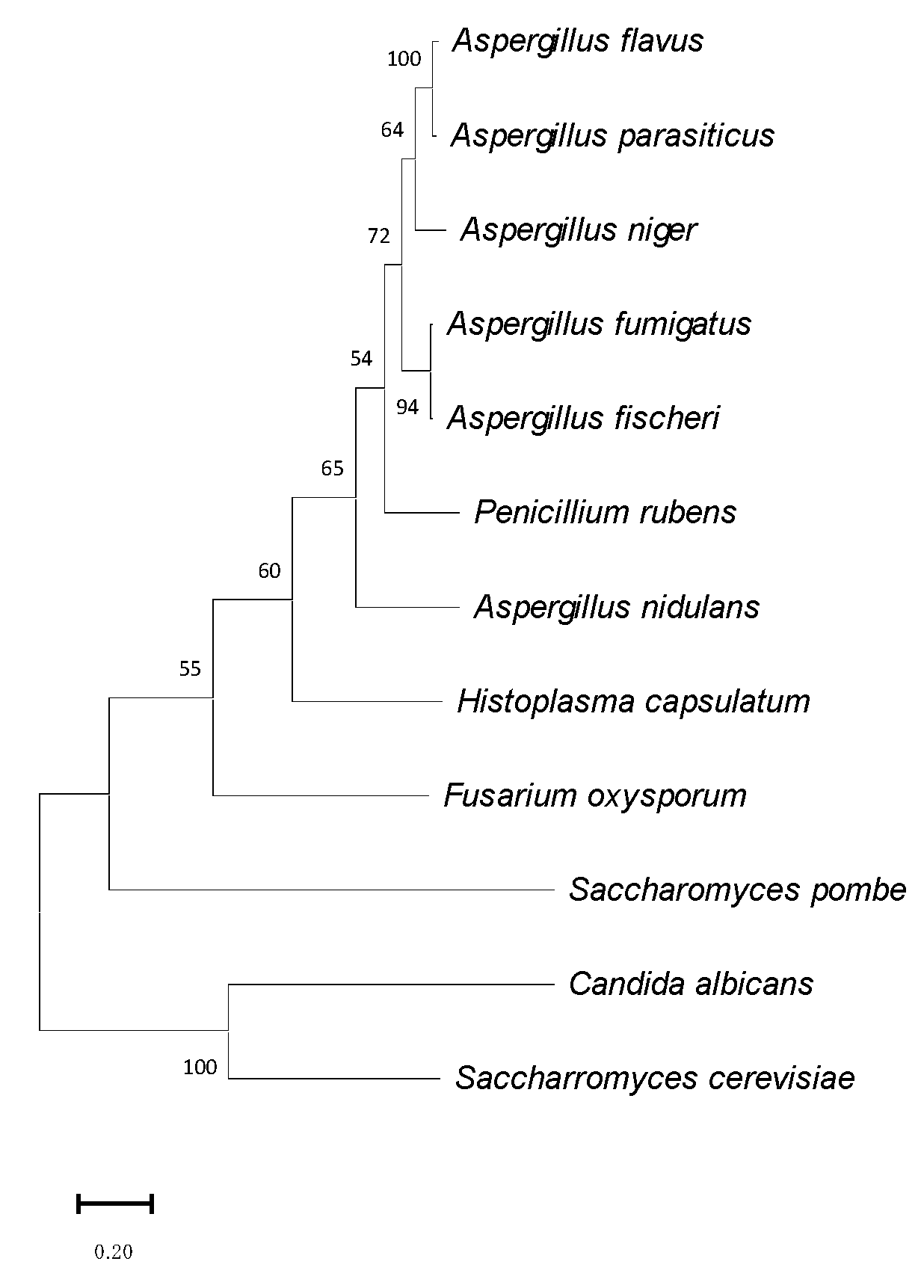
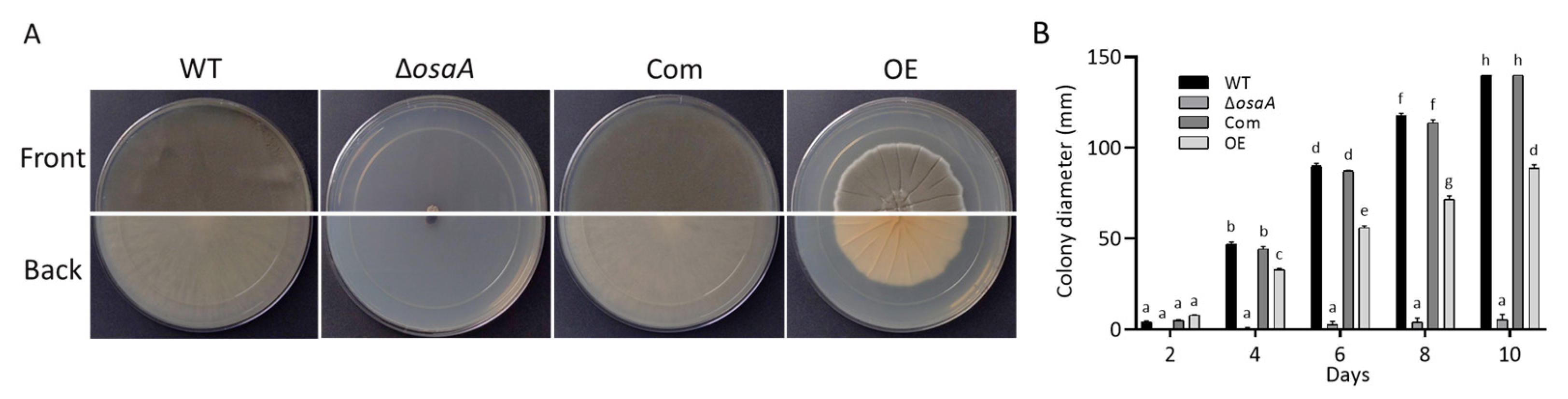
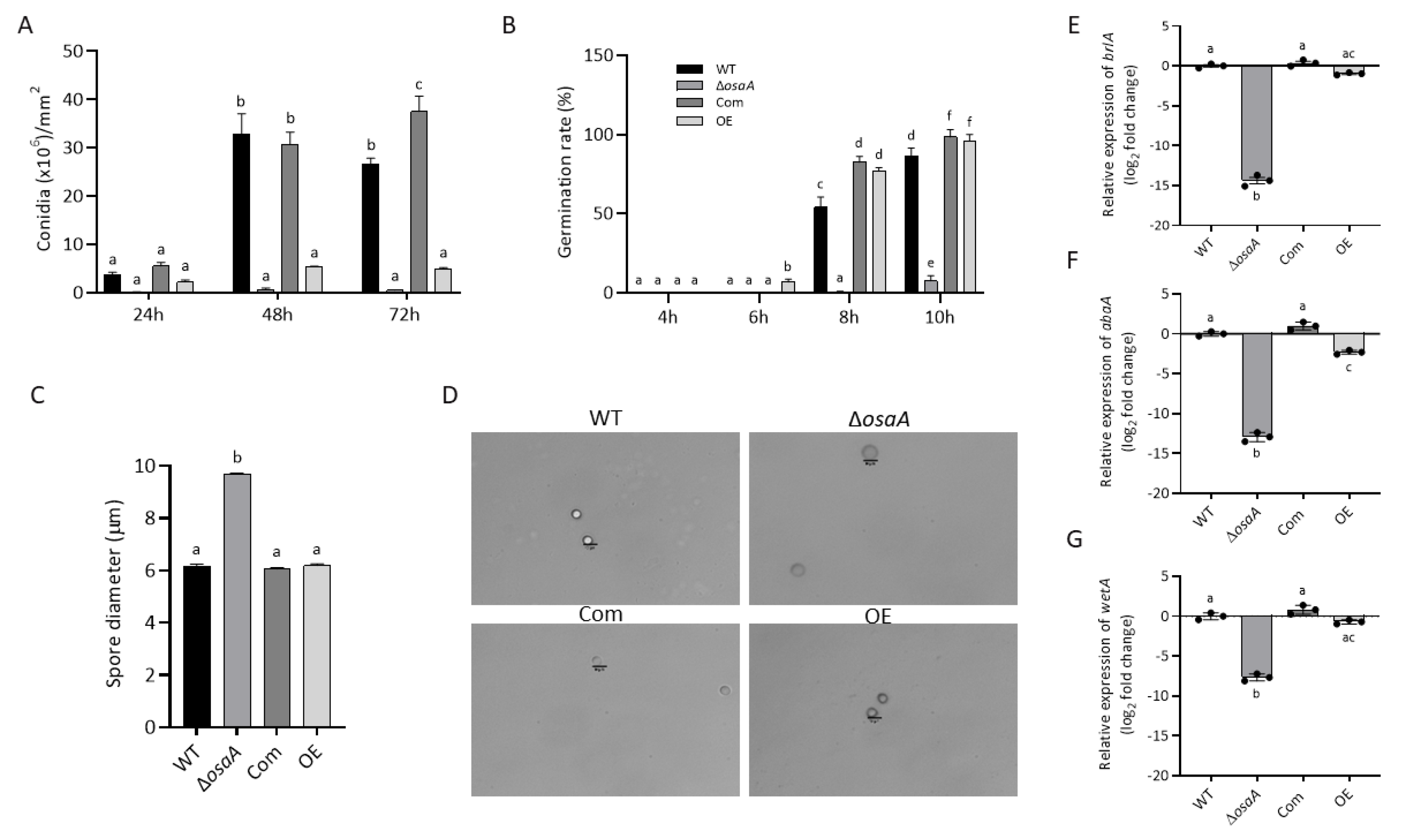
| Strain Name | Genotype | Source |
|---|---|---|
| CEA10 | Wild-type | Gift from Robert Cramer |
| CEA17 | pyrG1 | Gift from Robert Cramer |
| TAD1.1 | pyrG1ΔosaA::pyrGAparasiticus | This study |
| TAD2.1 | pyrG1 ΔosaA::pyrG osaA::hyg | This study |
| TSSP41.1 | gpdA::osaA::trpC::pyrG | This study |
| Accession Number | Organism Name | % Identity | % Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAQ53329.1 | Aspergillus flavus | 82.32 | 89.5 |
| AN6578.2 | Aspergillus nidulans | 64.24 | 73.1 |
| XP_001257654.1 | Aspergillus fischeri | 98.96 | 99.4 |
| KAB8200295.1 | Aspergillus parasiticus | 82.32 | 89.7 |
| XM_001396613.1 | Aspergillus niger | 82.42 | 88.4 |
| XM_002563660.1 | Penicillium rubens | 72.57 | 80.4 |
| ABX74945.1 | Histoplasma capsulatum | 58.13 | 64.9 |
| Q5AP80 | Candida albicans | 30.02 | 24.1 |
| BAC54908.1 | Saccharomyces pombe | 35.45 | 25.5 |
| XM_018389881 | Fusarium oxysporum | 44.16 | 38.9 |
| NC_001137 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 30.00 | 33.5 |
| Compound | WT | ΔosaA | Com | OE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fumiquinazoline C | 2.58 × 107 ± 2.80 × 106 | 1.43 × 104 ± 1.06 × 103 | 2.99 × 107 ± 2.99 × 106 | 2.92 × 106 ± 1.38 × 106 |
| Pyripyropene A | 1.20 × 108 ± 1.86 × 107 | 1.02 × 106 ± 5.52 × 105 | 1.15 × 108 ± 3.14 × 107 | 1.88 × 107 ± 1.16 × 107 |
| Helvolic acid | 9.55 × 106 ± 2.70 × 106 | Not detected | 1.50 × 107 ± 1.34 × 106 | 2.96 × 106 ± 1.50 × 106 |
| Helvolinic acid | 3.59 × 106 ± 3.96 × 105 | Not detected | 5.03 × 106 ± 6.99 × 105 | 8.91 × 105 ± 4.01 × 105 |
| 1,2-dihydrohelvolic acid | 1.88 × 106 ± 4.36 × 105 | Not detected | 3.11 × 106 ± 5.14 × 105 | 5.34 × 105 ± 2.14 × 105 |
| Fumagillin | 2.27 × 107 ± 1.74 × 106 | Not detected | 2.76 × 107 ± 4.85 × 106 | 8.59 × 106 ± 2.83 × 106 |
| Gliotoxin | 7.50 × 104 ± 1.55 × 104 | Not detected | 7.01 × 104 ± 1.47 × 104 | Not detected |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dabholkar, A.; Pandit, S.; Devkota, R.; Dhingra, S.; Lorber, S.; Puel, O.; Calvo, A.M. Role of the osaA Gene in Aspergillus fumigatus Development, Secondary Metabolism and Virulence. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10020103
Dabholkar A, Pandit S, Devkota R, Dhingra S, Lorber S, Puel O, Calvo AM. Role of the osaA Gene in Aspergillus fumigatus Development, Secondary Metabolism and Virulence. Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(2):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10020103
Chicago/Turabian StyleDabholkar, Apoorva, Sandesh Pandit, Ritu Devkota, Sourabh Dhingra, Sophie Lorber, Olivier Puel, and Ana M. Calvo. 2024. "Role of the osaA Gene in Aspergillus fumigatus Development, Secondary Metabolism and Virulence" Journal of Fungi 10, no. 2: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10020103
APA StyleDabholkar, A., Pandit, S., Devkota, R., Dhingra, S., Lorber, S., Puel, O., & Calvo, A. M. (2024). Role of the osaA Gene in Aspergillus fumigatus Development, Secondary Metabolism and Virulence. Journal of Fungi, 10(2), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10020103






