Diversity Patterns and Drivers of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities in a Muddy Coastal Wetland of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
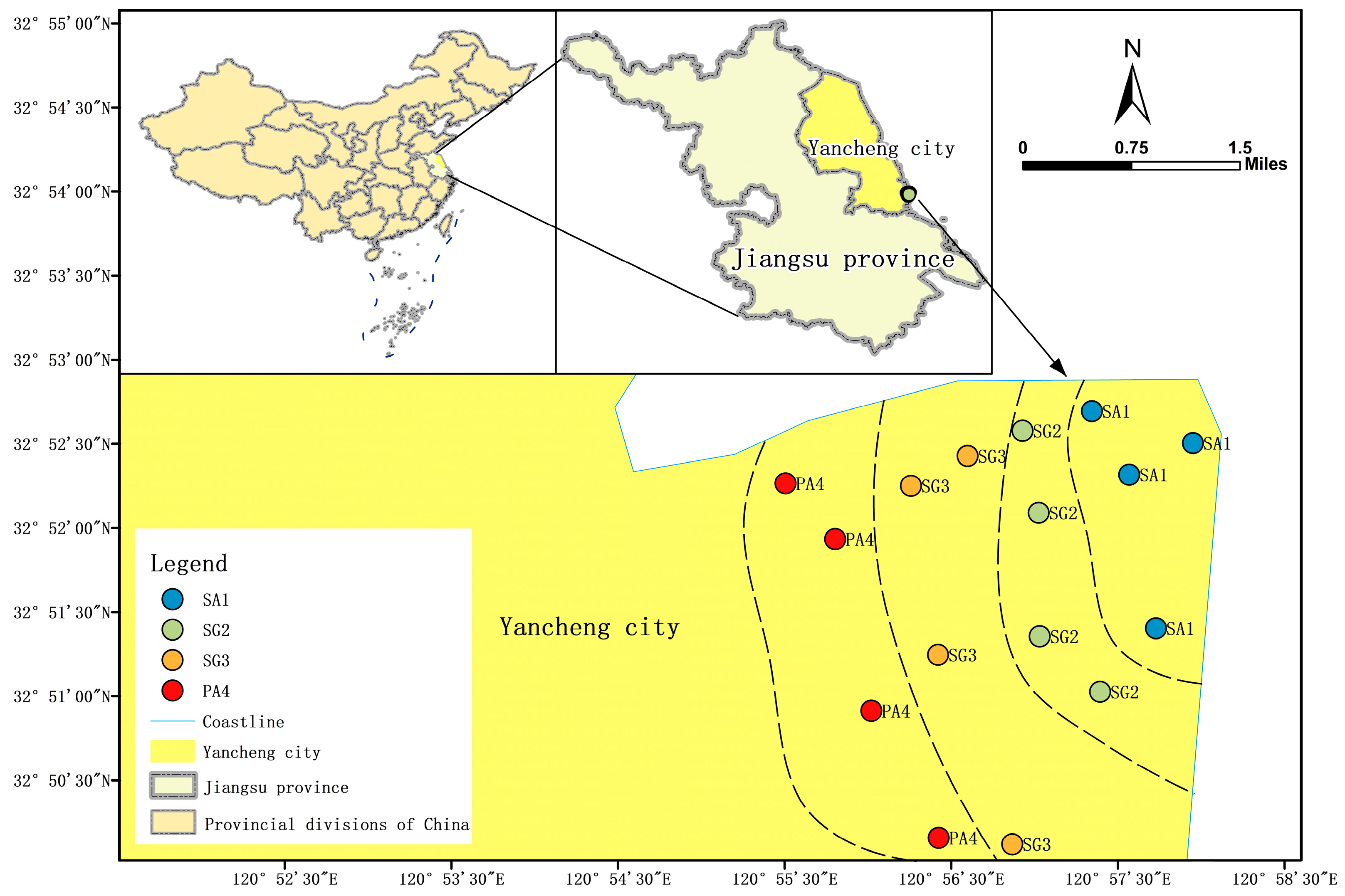
2.1. Site Description and Sample Collection
2.2. Soil Physiochemical Properties
2.3. Extraction and Amplification of Soil Microbial DNA
2.4. Illumina Miseq Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Properties
3.2. Soil Microbial Alpha-Diversity
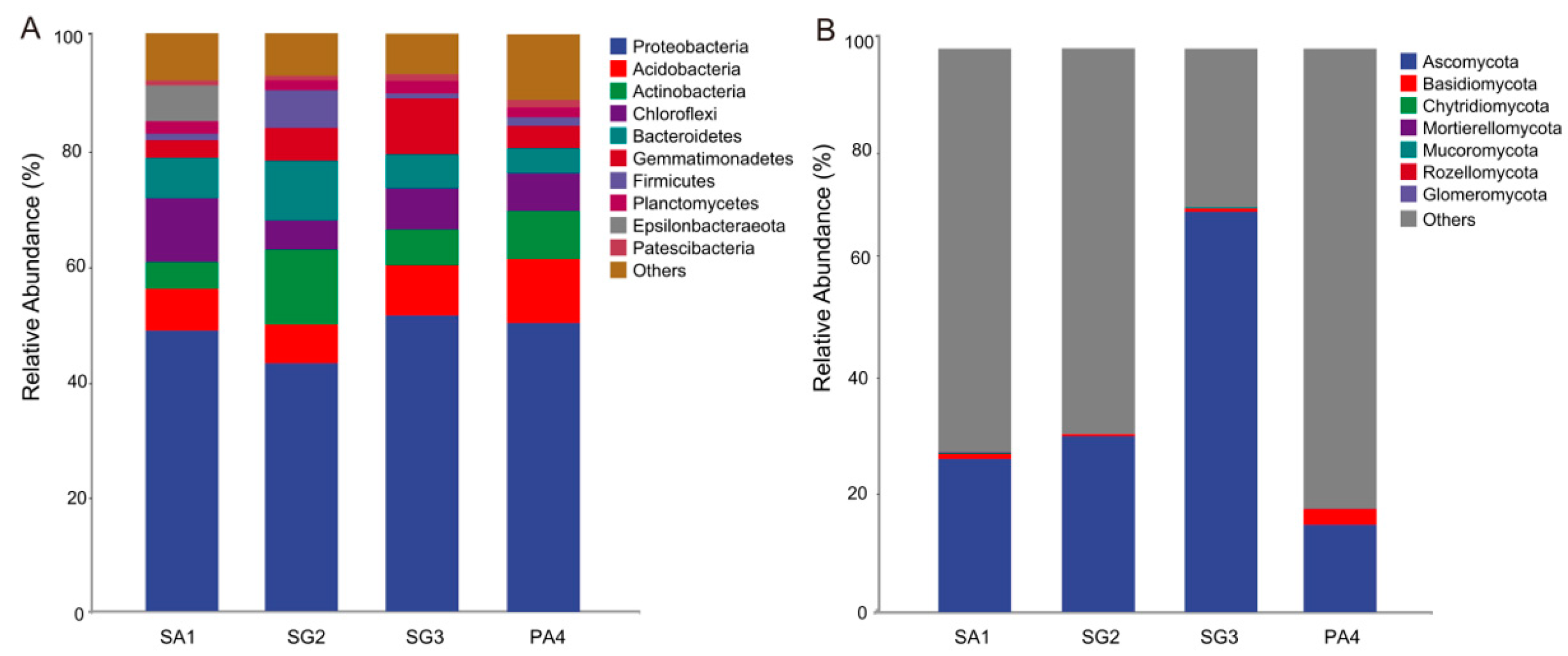
3.3. Soil Microbial Community Structure
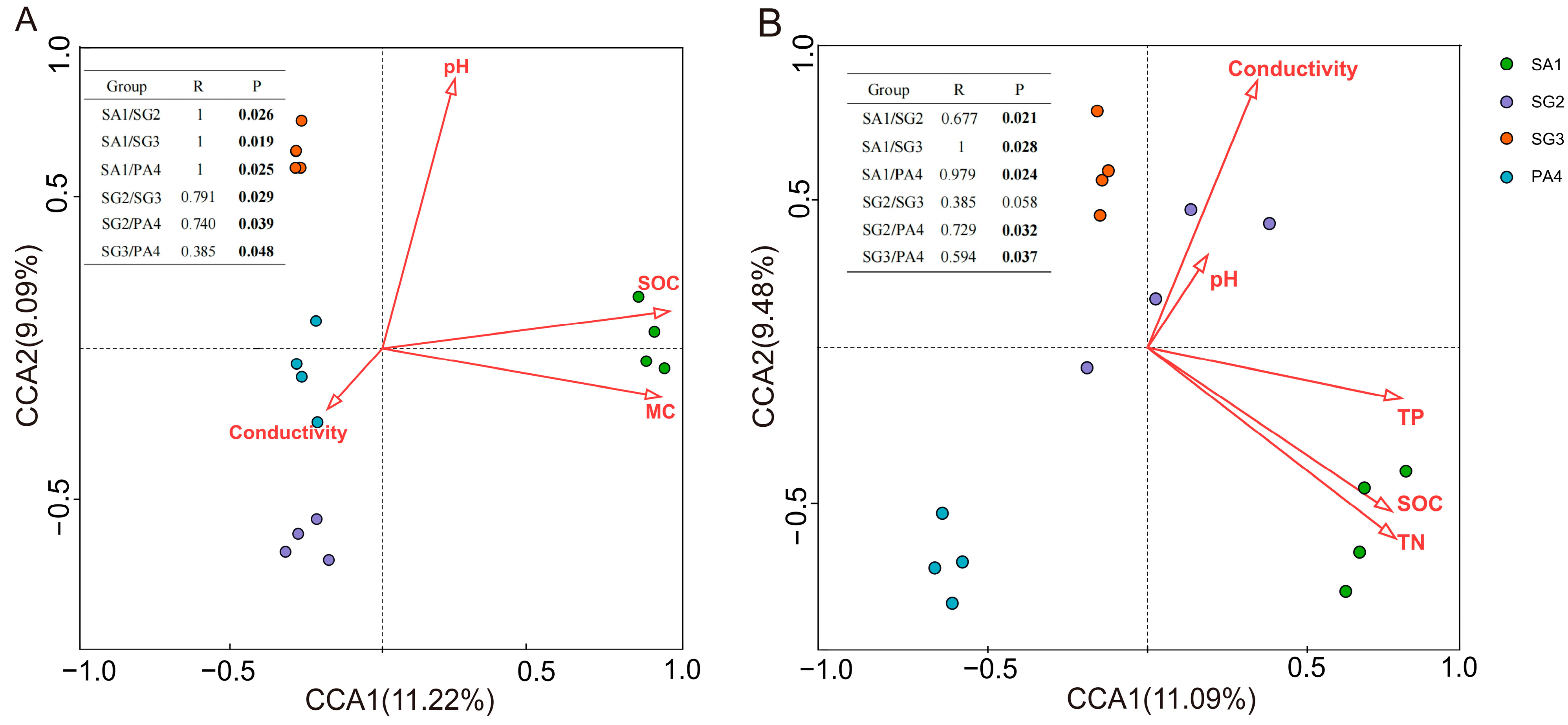
3.4. Environmental Determinants of Soil Microbial Community Structures
4. Discussion
4.1. Variations in Soil Properties Across Different Wetlands
4.2. Drivers of Soil Bacterial Diversity Across Different Wetlands
4.3. Soil Nutrients and Salinity Determine Fungal Diversity Across Different Wetlands
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.Y.; Chen, Q.F.; Li, Q.; Zhao, C.S.; Feng, Y. Influence of plants and environmental variables on the diversity of soil microbial communities in the Yellow River Delta Wetland, China. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.L.; Chang, H.P.; Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, W.L. Salinity and nutrient modulate soil bacterial communities in the coastal wetland of the Yellow River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2021, 28, 14621–14631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Guo, Y.T.; Zhang, M.X.; Pan, W.B.; Wang, J.J. Stronger network connectivity with lower diversity of soil fungal community was presented in coastal marshes after sixteen years of freshwater restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Chi, Q.; Sui, X.; Zhang, M.M.; Jia, H.; Sun, G.S. Metabolic diversity and seasonal variation of soil microbial communities in natural forested wetlands. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 2619–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Pedro, L.; Ling, X.X.; Zhou, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Pu, Z.H.; Wang, Y.L.; Deng, Z.F. Spartina alterniflora invasion alters soil microbial metabolism in coastal wetland of China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 245, 106982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noval, R.M.; Burton, O.T.; Wise, P.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Hobson, S.A.; Lloret, M.G.; Chehoud, C.; Kuczynski, J.; DeSantis, T.; Warrington, J.; et al. A microbiota signature associated with experimental food allergy promotes allergic sensitization and anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.G.; Su, J.; Wang, J.S.; Dai, N.; Li, J.; Song, L.T.; Zuo, R. Soil microbial community response to seawater intrusion into coastal aquifer of Donghai Island, South China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 3329–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Feng, D.F.; Yang, G.; Deng, Z.M.; Rui, J.P.; Chen, H. Soil water content and ph drive archaeal distribution patterns in sediment and soils of water-level-fluctuating zones in the East Dongting Lake Wetland, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2019, 26, 29127–29137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.F.; Liu, L.L.; Zhu, P.C.; Yang, S.R.; Guo, W.H.; Yu, X.N. Patterns and dynamics of the soil microbial community with gradual vegetation succession in the Yellow River Delta, China. Wetlands 2021, 41, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.D.; Li, S.P.; Yang, X.; Zhou, J.Z.; Shu, W.S.; Jiang, L. Mechanisms of soil bacterial and fungal community assembly differ among and within islands. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1559–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Müller, T.; Joergensen, R.G. Relationships between soil biological and other soil properties in saline and alkaline arable soils from the Pakistani Punjab. J. Arid Environ. 2008, 72, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.J.; Su, J.Q.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y.G.; Cao, Z.H. Bacterial succession along a long-term chronosequence of paddy soil in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, Z.; Zak, D.R. Soil bacterial communities are shaped by temporal and environmental filtering: Evidence from a long-term chronosequence. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3208–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kang, E.; Song, B.; Wang, J.S.; Zhang, X.D.; Wang, J.Z.; Li, M.; Yan, L.; Yan, Z.Q.; Zhang, K.R. Soil salinity and nutrients availability drive patterns in bacterial community and diversity along succession gradient in the Yellow River Delta. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 262, 107621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasooriya, W.K.; Denef, K.; Peters, J.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Boeckx, P. Vegetation composition and soil microbial community structural changes along a wetland hydrological gradient. Hydrol. Earth Syst Sci. 2008, 12, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Lauber, C.L.; Ramirez, K.S.; Zaneveld, J.; Bradford, M.A.; Knight, R. Comparative metagenomic, phylogenetic and physiological analyses of soil microbial communities across nitrogen gradients. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, B.M.; Fry, E.L.; Eldridge, D.J.; De Vries, F.T.; Manning, P.; Hamonts, K.; Kattge, J.; Boenisch, G.; Singh, B.K.; Bardgett, R.D. Plant attributes explain the distribution of soil microbial communities in two contrasting regions of the globe. New Phytol. 2018, 219, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Clark, M.; Su, J.Q.; Xiao, C.W. Litter decomposition and soil microbial community composition in three Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) forests along an altitudinal gradient. Plant Soil 2015, 386, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.D.; Wu, H.D.; Li, M.; Yan, L.; Zhang, K.R.; Wang, J.Z.; Kang, X.M. Soil pH and nutrients shape the vertical distribution of microbial communities in an alpine wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, B.M.; Oliverio, A.M.; Brewer, T.E.; Benavent, G.A.; Lez, A.; Eldridge, D.J.; Bardgett, R.D.; Maestre, F.T.; Singh, B.K.; Fierer, N. A global atlas of the dominant bacteria found in soil. Science 2018, 359, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Wu, Y.M.; Yin, M.Q.; Ma, X.Y.; Yu, X.N.; Guo, X.; Du, N.; Eller, F.; Guo, W.H. Soil salinity, not plant genotype or geographical distance, shapes soil microbial community of a reed wetland at a fine scale in the Yellow River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Hua, J.N.; Zhang, J.B.; Liu, D.; Bhople, P.; Li, X.X.; Zhang, Y.; Ruan, H.H.; Xing, W.; Mao, L.F. Soil nutrients and plant diversity affect ectomycorrhizal fungal community structure and functional traits across three subalpine coniferous forests. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1016610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.R.; Xie, B.; Cagle, G.A.; Wang, X.H.; Han, G.X.; Wang, X.J.; Hou, A.X.; Guan, B. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on soil microbial community diversity in coastal wetland of the Yellow River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulskamp, R.; Luijendijk, A.; Maren, B.V.; Rodenas, A.M.; Calkoen, F.; Kras, E.; Lhermitte, S.; Aarninkhof, S. Global distribution and dynamics of muddy coasts. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. Impacts of expansion of Spartina alterniflora on Yancheng Tidal flat wetland in Jiangsu province of China. Landsc. Res. 2017, 1, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, D.M.; Jiang, H.; Ding, J.J. Evaluation of coastal wetland ecosystem services in Jiangsu province. Ecol. Sci. 2016, 35, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantel, S.; Dondeyne, S.; Deckers, S. World reference base for soil resources (WRB). In Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 4, pp. 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Alva, A.K.; Appel, T. An evaluation of plant-available soil nitrogen in selected sandy soils by electro-Ultrafiltration, KCl, and CaCl2 extraction methods. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 30, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Agricultural Chemical Analysis of Soil, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades, J.D.; Shouse, P.J.; Alves, W.J.; Manteghi, N.A.; Lesch, S.M. Determining soil salinity from soil electrical conductivity using different models and estimates. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1990, 54, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.M.; Yang, J.S.; Jiang, Y. Salinity characters of soils and gmundwater in typical coastal area in Jiangsu province. Soils 2005, 37, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, K.; Zaprjanova, P.; Petkova, M.; Stefanova, V.; Kmetov, V.; Georgieva, D.; Angelova, V. Comparison of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and colorimetric determination of total and extractable phosphorus in soils. Spectroc. Acta Part B-Atom. Spectr. 2012, 71–72, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Wang, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Li, X.X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.M.; Peng, S.L.; Ge, Z.W.; Mao, L.F.; et al. Long-term nitrogen deposition alters ectomycorrhizal community composition and function in a poplar plantation. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg, L.D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16s rrna diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, S.i.; Senda, Y.; Nakaguchi, S.; Hashimoto, T. Multiplex pcr using internal transcribed spacer 1 and 2 regions for rapid detection and identification of yeast strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 3617–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Li, X.X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, B.; Hua, J.N.; Zhang, J.B.; Peng, S.L.; Ge, Z.W.; et al. Diversity patterns and drivers of soil bacterial and fungal communities along elevational gradients in the southern Himalayas, China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 178, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using Qiime 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. Dada2: High-resolution sample inference from illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Toh, H. Recent developments in the mafft multiple sequence alignment program. Brief. Bioinform. 2008, 9, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The silva ribosomal rna gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kõljalg, U.; Nilsson, R.H.; Abarenkov, K.; Tedersoo, L.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Bahram, M.; Bates, S.T.; Bruns, T.D.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Callaghan, T.M.; et al. Towards a unified paradigm for sequence-based identification of fungi. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 5271–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Gregory Caporaso, J. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with qiime 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, B.B. Levene’s test for relative variation. Syst. Biol. 1985, 34, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St, L.; Wold, S. Analysis of variance (ANOVA). Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1989, 6, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Wagner, H.H. Vegan Community Ecology Package, Version 2.5-7; Comprehensive R Archive Network. 2020. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/346579465_vegan_community_ecology_package_version_25-7_November_2020 (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- McKight, P.E.; Najab, J. Kruskal-Wallis Test. In The Corsini Encyclopedia of Psychology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; p. 1-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarland, T.W.; Yates, J.M.; MacFarland, T.W.; Yates, J.M. Spearman’s Rank-Difference Coefficient of Correlation. In Introduction to Nonparametric Statistics for the Biological Sciences Using R; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 249–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grömping, U. Estimators of relative importance in linear regression based on variance decomposition. Am. Stat. 2007, 61, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Wang, Y.C.; Liu, B.R.; Zhang, J.B.; Hua, J.N.; Liu, D.; Bhople, P.; Zhang, Y.R.; Zhang, H.G.; Zhang, C.H.; et al. Exploration of soil microbial diversity and community structure along mid-subtropical elevation gradients in southeast China. Forests 2023, 14, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.F.; Luo, Y.Q.; Chen, J.K.; Li, B. Ecophysiological characteristics of invasive Spartina alterniflora and native species in salt marshes of Yangtze River Estuary, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 81, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Deng, W.; Yang, J.F.; Zang, G.X.; Li, X.J. Effects of soil moisture and electrical conductivity on growthand population distribution of phragmites australis. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2006, 1, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Sarker, M.R.H.; Mia, M.Y. Spatial and temporal variation of soil and water salinity in the south-western and south-central coastal region of Bangladesh. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 66, 854–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, M.I.; Mia, S.; Supit, I.; Ludwig, F. Spatio-temporal variability in soil and water salinity in the south-central coast of Bangladesh. Catena 2023, 222, 106786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LI, W.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, L.Q.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.J.; Pan, J.L.; Chen, Y.H. Responses of Scirpus mariqueter and Spartina alterniflora to simulated salt stress and salt-tolerance thresholds. Chin. J. Ecol. 2018, 37, 2596–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, J.J.; Banerjee, S.; Zhou, N.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhang, K.; Tian, C.Y. Soil pH is equally important as salinity in shaping bacterial communities in saline soils under halophytic vegetation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Lv, D.T.; Jiang, S.Y.; Lin, H.; Sun, J.Q.; Li, K.J.; Sun, J. Soil salinity regulation of soil microbial carbon metabolic function in the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.F.; Xiang, Q.; Wu, T.; Jiang, G.J.; Sun, X.M.; Zhu, M.; Pu, L. Progress and prospect of soil microorganisms and their influencing factors in coastal wetland ecosystem. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.L.; Xu, Z.C.; Zou, P.; Tang, Q.; Li, Y.Q.; You, X.W.; Zhang, C.S. Coastal halophytes alter properties and microbial community structure of the saline soils in the Yellow River Delta, China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 134, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisseler, D.G.; Horwath, W.R.; Scow, K.M. Soil moisture and plant residue addition interact in their effect on extracellular enzyme activity. Pedobiologia 2011, 54, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, P.L.; Mu, H.X.; Cao, B.H.; Qin, Y.J.; Shao, H.B.; Wang, S.M.; Tai, X.G. Dynamic characteristics of soil properties in a robinia pseudoacacia vegetation and coastal eco-restoration. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 92, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.M.; Jiang, S.H.; Liu, Q.N.; Zhou, C.L.; Tang, B.P. Density, but not distribution pattern of assiminea latericea varies on tidal flats with smooth cordgrass Spartina alterniflora invasion stage. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 27, 100528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.X.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Yao, M.J.; Rui, J.P.; Zhang, S.H.; Li, X.Z. Soil bacterial community structure in chinese wetlands. Geoderma 2019, 337, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.E.; Wallenstein, M.D. Soil microbial community response to drying and rewetting stress: Does historical precipitation regime matter? Biogeochemistry 2012, 109, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, D.D.; Li, Q.; Huo, L.L.; Xu, Q.; Chen, X.; He, F.Q.; Zhao, L. Soil nutrients directly drive soil microbial biomass and carbon metabolism in the Sanjiangyuan alpine grassland. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 3548–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.T.; Peng, X.; Deng, G.H.; Sheng, H.F.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.W.; Tam, N.F.Y. Illumina sequencing of 16s rrna tag revealed spatial variations of bacterial communities in a mangrove wetland. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.L.; Ju, Y.W.; Deng, Y.C.; Zhang, H.X. Bacterial community structure in two permafrost wetlands on the tibetan plateau and Sanjiang plain, China. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 68, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.C.; Liu, D.; An, S.S. Decoupled diversity patterns in microbial geographic distributions on the arid area (the Loess Plateau). Catena 2021, 196, 104922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, B.M.; Maestre, F.T.; Reich, P.B.; Trivedi, P.; Osanai, Y.; Liu, Y.R.; Hamonts, K.; Jeffries, T.C.; Singh, B.K. Carbon content and climate variability drive global soil bacterial diversity patterns. Ecol. Monogr. 2016, 86, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Anderson, I.C.; Singh, B.K. Microbial Modulators of Soil Carbon Storage: Integrating genomic and metabolic knowledge for global prediction. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; He, N.P.; Hale, L.; Niu, S.L.; Yu, G.R.; Liu, Y.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhou, J.Z. Soil organic matter availability and climate drive latitudinal patterns in bacterial diversity from tropical to cold temperate forests. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.B.; Shen, Z.H.; Li, C.N.; Kou, Y.P.; Wang, Y.S.; Tu, B.; Zhang, S.H.; Li, X.Z. Stair-step pattern of soil bacterial diversity mainly driven by ph and vegetation types along the elevational gradients of Gongga mountain, China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevarez, L.; Vasseur, V.; Le Madec, A.; Le Bras, M.A.; Coroller, L.; Legueacuterinel, I.; Barbier, G. Physiological traits of penicillium glabrum strain lcp 08.5568, a filamentous fungus isolated from bottled aromatised mineral water. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 130, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, I.R. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH in bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 1985, 49, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.B.; Liu, Y.Q.; Lin, X.G.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zeng, J.; Hou, J.Z.; Yang, Y.P.; Yao, T.D.; Knight, R.; Chu, H.Y. Geographic distance and pH drive bacterial distribution in Alkaline lake sediments across Tibetan plateau. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 9, 2457–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Samaddar, S.; Chatterjee, P.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Jeon, S.; Sa, T. Structural and functional responses of microbial community with respect to salinity levels in a coastal reclamation land. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 137, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Bai, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, G.; Cui, B. Shifts in the soil bacterial community along a salinity gradient in the Yellow River Delta. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2255–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, K.M.; Rousk, J. Salt effects on the soil microbial decomposer community and their role in organic carbon cycling: A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 81, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macêdo, W.V.; Sakamoto, I.K.; Azevedo, E.B.; Damianovic, M.H.R.Z. The effect of cations (Na+, Mg2+, and Ca2+) on the activity and structure of nitrifying and denitrifying bacterial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 679, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, J.B.; Hua, J.N.; Song, B.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Xing, W.; Wang, G.B.; Mao, L.F.; Ruan, H.H. Differentiation of fungal trophic guilds to long-term nitrogen addition in a poplar plantation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 555, 121699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.N.; Zhang, J.B.; Song, B.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Li, J.J.; Yang, N.; Mao, L.F. Diverse responses of fungal functional groups to desertification in forest soils of Pinus densata on the Chinese Tibetan plateau. J. For. Res. 2024, 35, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yuan, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Butterly, C.R.; Tong, D.L.; Zhou, B.; Li, X.Z.; Zhang, H.B. Effects of exotic Spartina alterniflora invasion on soil phosphorus and carbon pools and associated soil microbial community composition in coastal wetlands. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 5730–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunuen, T.T.; Maria, D.R.T.; James, E.; Africa, I.; Valeria, S.; Felipe, G.O.; Gabriela, O.Á. How to live with phosphorus scarcity in soil and sediment: Lessons from bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4652–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elena, F.F.; Francisco, J.R.D.; Patricia, F.; Dan, C. Comparative genomics of ceriporiopsis subvermispora and phanerochaete chrysosporium provide insight into selective ligninolysis. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5458–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanna, B.; Manuela, F.; Helmut, B.; Gessner, M.O. Microbial communities in contrasting freshwater marsh microhabitats. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 69, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Hu, W.G.; Zhang, X.; Qi, X.Y.; He, B.; Chen, X.M. Composition and diversity of the fungal community in the rhizosphere soil of halophytic vegetation in Ebinur Lake wetland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2023, 30, 86097–86109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, T.; Keiblinger, K.M.; Schmid, E.; Gleixner, K.S.; Ellersdorfer, G.; Roschitzki, B.; Richter, A.; Eberl, L.; Boltenstern, S.Z.; Riedel, K. Who is who in litter decomposition? metaproteomics reveals major microbial players and their biogeochemical functions. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1749–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C.; Li, Y.F.; Chang, S.X.; Xu, Q.F.; Guo, Z.Y.; Gao, Q.; Qin, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.F.; Chen, J.H.; Liang, X. Bamboo invasion of broadleaf forests altered soil fungal community closely linked to changes in soil organic c chemical composition and mineral n production. Plant Soil 2017, 418, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, E.W.; Frey, S.D.; Sadowsky, J.J.; Diepen, L.T.A.; Thomas, W.K.; Pringle, A. Chronic nitrogen additions fundamentally restructure the soil fungal community in a temperate forest. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 23, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Wang, B.; Liu, D.; Bai, H.; Jin, L.; Wang, B.T.; Ruan, H.H.; Mao, L.F.; Jin, F.J.; et al. Effects of Nitrogen addition on rhizospheric soil microbial communities of poplar plantations at different ages. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 494, 119328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenlord, S.D.; Zak, D.R. Simulated atmospheric nitrogen deposition alters actinobacterial community composition in forest soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.X.; Yan, L.J.; Korpelainen, H.; Niinemets, U.; Li, C.Y. Plant-plant interactions and n fertilization shape soil bacterial and fungal communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 128, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.; Marschner, P.; Burns, R. Response of microbial activity and community structure to decreasing soil osmotic and matric potential. Plant Soil 2011, 344, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmajdoub, B.; Marschner, P. Responses of soil microbial activity and biomass to salinity after repeated additions of plant residues. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, X.Z.; Miao, F.H.; Li, Z.Y.; Tang, W.; Sun, J. Assessing the effect of soil salinization on soil microbial respiration and diversities under incubation conditions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 155, 103671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, R.; Kim, K.; Kim, C.; Sa, T. Changes of arbuscular mycorrhizal traits and community structure with respect to soil salinity in a coastal reclamation land. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 72, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.S.; Zhou, M.X.; Zai, X.M.; Zhao, F.G.; Qin, P. Spatio-temporal dynamics of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and soil organic carbon in coastal saline soil of China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Xiang, L.; Jiang, W.; Chen, X.; Yin, C.M.; Mao, Z.Q. Soil arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community structure and diversity in apple orchards with different replant disease severity around bohai bay, China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 177, 104524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazard, C.; Gosling, P.; Van Der Gast, C.J.; Mitchell, D.T.; Doohan, F.M.; Bending, G.D. The role of local environment and geographical distance in determining community composition of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi at the landscape scale. ISME J. 2013, 7, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiiesalu, I.; Pärtel, M.; Davison, J.; Gerhold, P.; Metsis, M.; Moora, M.; Öpik, M.; Vasar, M.; Zobel, M.; Wilson, S.D. Species richness of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: Associations with grassland plant richness and biomass. New Phytol. 2014, 203, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Gai, S.S.; He, X.Y.; Zhang, W.; Hu, P.L.; Soromotin, A.V.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Wang, K. Habitat heterogeneity drives arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and shrub communities in karst ecosystems. Catena 2023, 233, 107513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.C.; Wang, D.Z.; Guo, X.S.; Yang, T.; Xiang, X.J.; Walder, F.; Chu, H.Y. Differential responses of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities to long-term fertilization in the wheat rhizosphere and root endosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e00349-00321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausing, S.; Polle, A. Mycorrhizal phosphorus efficiencies and microbial competition drive root p uptake. Front. For. Glob. Chang. 2020, 3, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.E.; Read, D.J. Mycorrhizal Symbiosis; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]


| Variables | SA1 | SG2 | SG3 | PA4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conductivity (mS/cm) | 4.64 ± 0.21 c | 7.21 ± 0.31 a | 6.02 ± 0.08 b | 3.03 ± 0.12 d |
| pH | 8.45 ± 0.03 b | 7.90 ± 0.02 d | 8.69 ± 0.01 a | 8.08 ± 0.03 c |
| MC (%) | 71.48 ± 0.42 a | 30.97 ± 0.46 c | 22.25 ± 0.20 d | 37.67 ± 0.20 b |
| AP (mg/kg) | 17.53 ± 0.29 b | 15.93 ± 0.05 c | 18.99 ± 0.17 a | 15.70 ± 0.06 c |
| TP (mg/kg) | 111.07 ± 0.51 a | 109.36 ± 0.75 a | 102.20 ± 0.79 b | 103.45 ± 0.71 b |
| NH4+ (mg/kg) | 1.77 ± 0.07 a | 0.67 ± 0.06 d | 1.06 ± 0.05 c | 1.30 ± 0.03 b |
| NO3− (mg/kg) | 1.21 ± 0.07 a | 0.89 ± 0.03 c | 1.04 ± 0.04 b | 0.74 ± 0.03 d |
| SOC (g/kg) | 12.71 ± 0.28 a | 1.58 ± 0.34 d | 2.84 ± 0.15 c | 3.47 ± 0.25 b |
| TC (g/kg) | 24.83 ± 0.69 a | 10.80 ± 0.20 d | 12.70 ± 0.26 c | 15.45 ± 0.18 b |
| TN (g/kg) | 2.93 ± 0.08 a | 2.08 ± 0.05 b | 1.87 ± 0.10 b | 2.10 ± 0.04 b |
| Variables | Bacteria | Fungi | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed_Species | Shannon | Observed_Species | Shannon | |
| Conductivity | −0.191 | −0.104 | 0.197 | 0.584 |
| pH | 0.016 | −0.05 | 0.259 | 0.066 |
| MC | 0.586 | 0.372 | 0.186 | 0.167 |
| AP | −0.162 | −0.107 | 0.384 | 0.482 |
| TP | 0.461 | 0.495 | 0.303 | 0.635 |
| NH4+ | 0.375 | 0.107 | 0.194 | −0.032 |
| NO3− | 0.065 | −0.064 | 0.101 | 0.508 |
| TC | 0.507 | 0.123 | 0.320 | 0.085 |
| TN | 0.525 | 0.287 | 0.339 | 0.297 |
| SOC | 0.491 | 0.016 | 0.271 | 0.005 |
| Type | Predictor Variables | Slope (SE) | t-Value | p | RI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Observed_species | (intercept) | −5.733 × 10−17 (0.219) | 0.000 | 1.000 | |
| MC | 0.881 (0.384) | 3.331 | 0.037 | |||
| Shannon | (intercept) | −0.000 (0.222) | −0.002 | 0.999 | ||
| TP | 0.495 (0.241) | 2.051 | 0.061 | |||
| Fungi | Observed_species | (intercept) | −2.897 (0.282) | −1.000 | 1.000 | |
| AP | 0.262 (0.162) | 4.246 | 0.027 | |||
| Shannon | (intercept) | −0.000 (0.129) | −0.003 | 0.998 | ||
| TP | 0.526 (0.148) | 3.559 | 0.005 | 0.336 | ||
| conductivity | 0.575 (0.206) | 2.748 | 0.019 | 0.269 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, B.; Wang, T.; Wan, C.; Cai, Y.; Mao, L.; Ge, Z.; Yang, N. Diversity Patterns and Drivers of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities in a Muddy Coastal Wetland of China. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10110770
Song B, Wang T, Wan C, Cai Y, Mao L, Ge Z, Yang N. Diversity Patterns and Drivers of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities in a Muddy Coastal Wetland of China. Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(11):770. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10110770
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Baohan, Tianyi Wang, Cheng Wan, Yuan Cai, Lingfeng Mao, Zhiwei Ge, and Nan Yang. 2024. "Diversity Patterns and Drivers of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities in a Muddy Coastal Wetland of China" Journal of Fungi 10, no. 11: 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10110770
APA StyleSong, B., Wang, T., Wan, C., Cai, Y., Mao, L., Ge, Z., & Yang, N. (2024). Diversity Patterns and Drivers of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities in a Muddy Coastal Wetland of China. Journal of Fungi, 10(11), 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10110770






