Activation of AcvR1-Mediated Signaling Results in Semilunar Valve Defects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
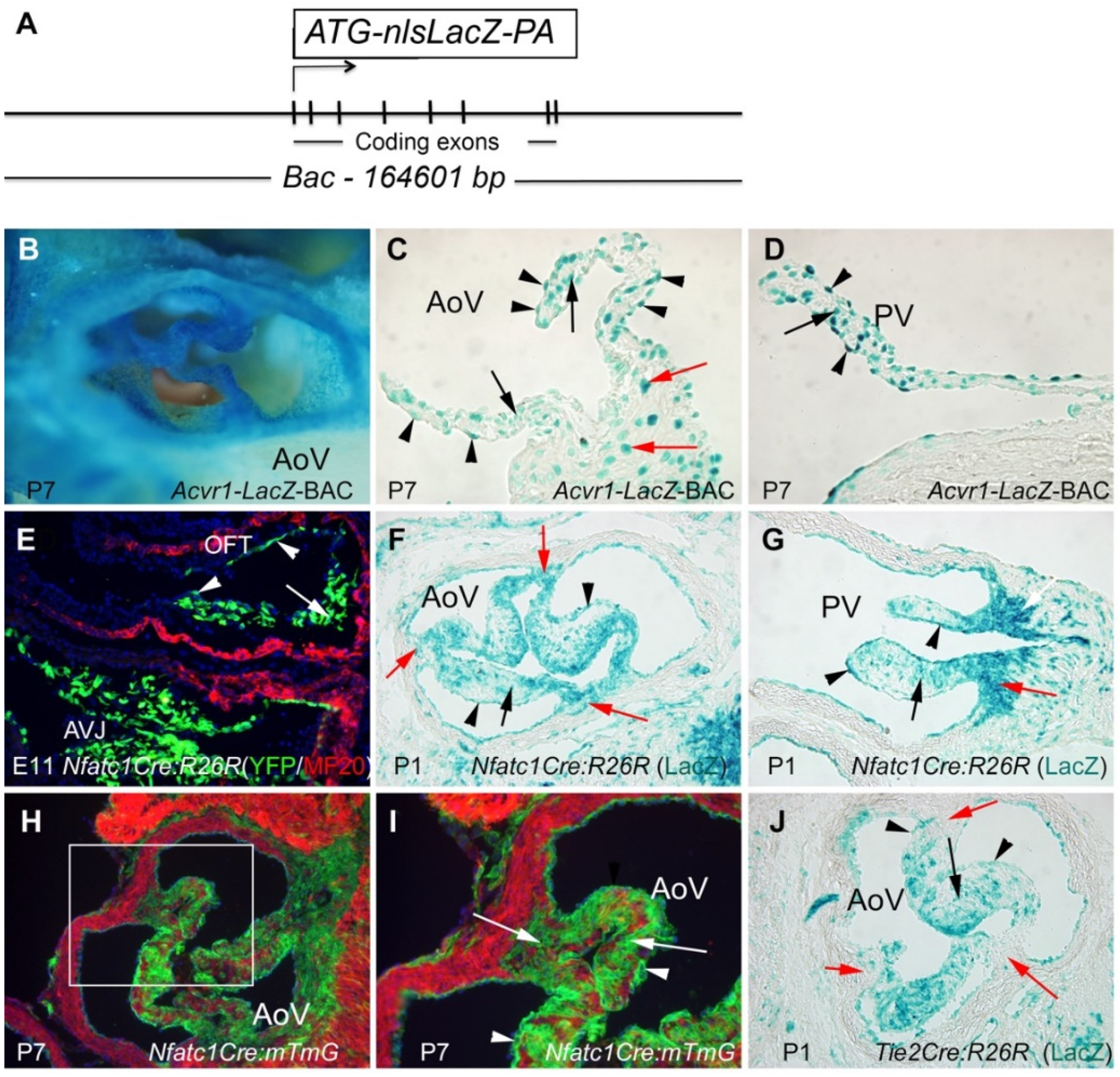
3.1. Acvr1 Is Expressed in Adult Semilunar Valves
3.2. caAcvr1:Nfatc1Cre Mutants Are Viable, but Show Functional Defects in the Heart
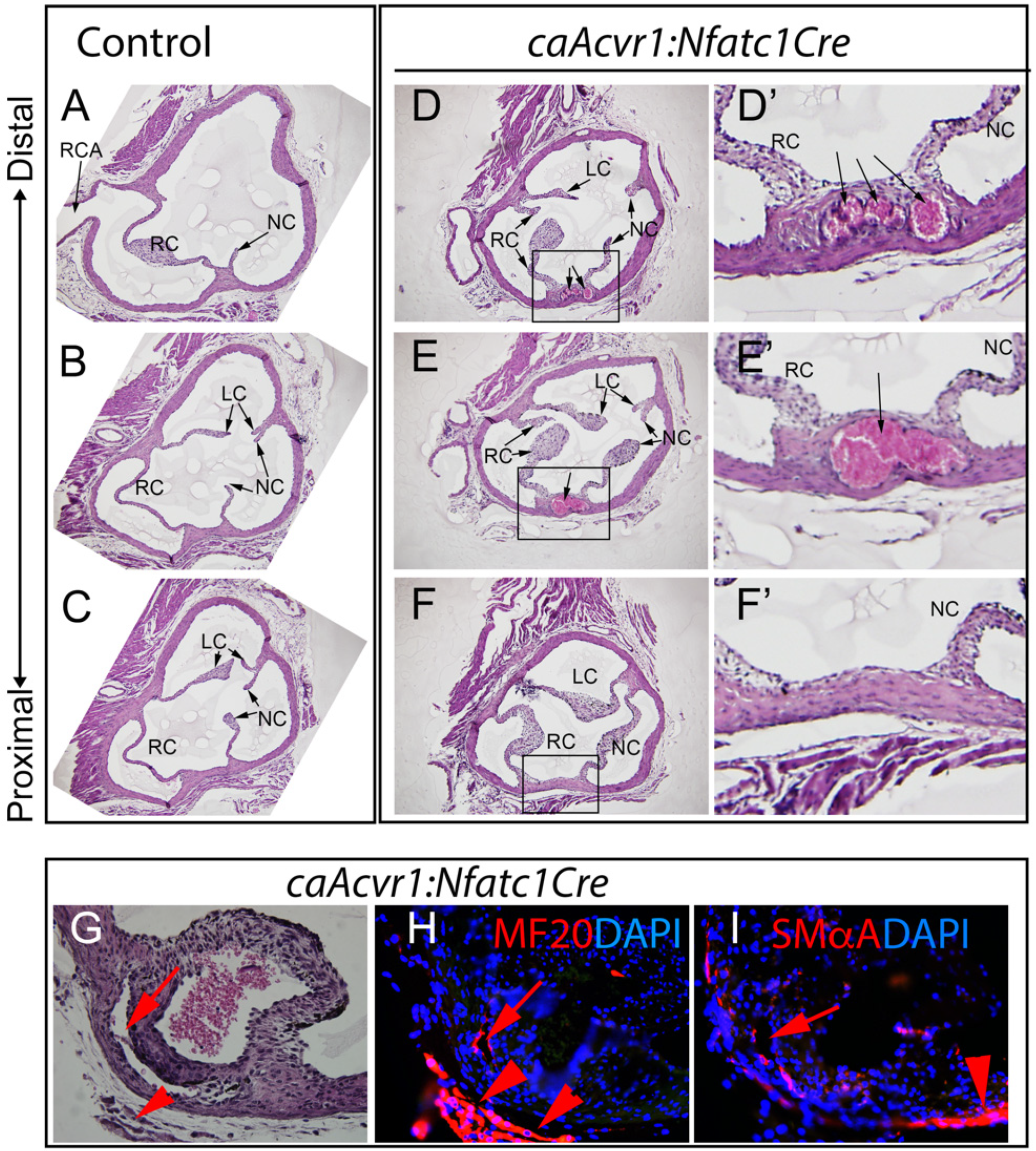
3.3. caAcvr1:Nfatc1Cre Mutants Show Thickened Valve Leaflets and Wall Defects
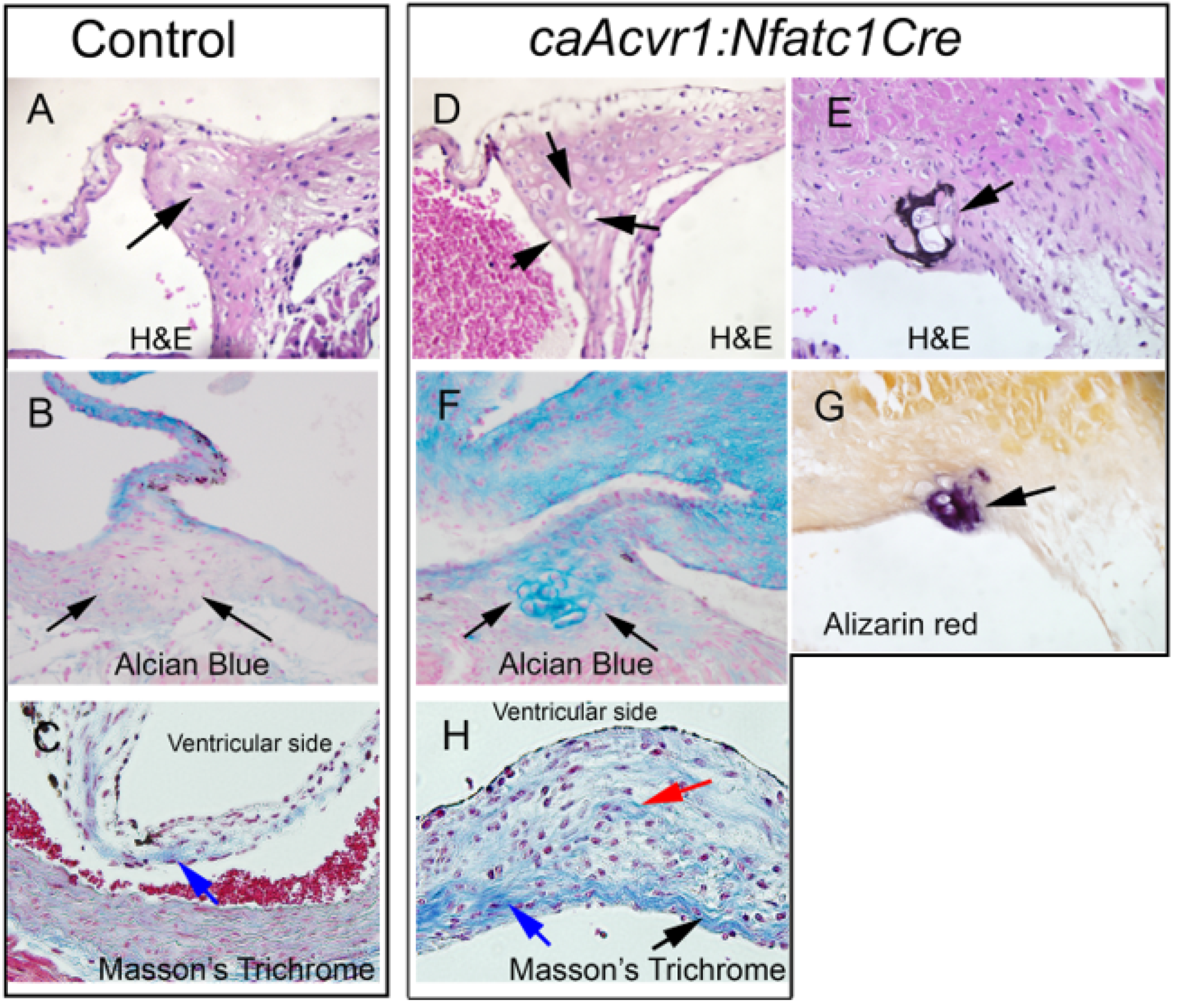
3.4. Hypertrophic Cartilage-like Cells and Calcification in caAcvr1:Nfatc1Cre Mutant Valves
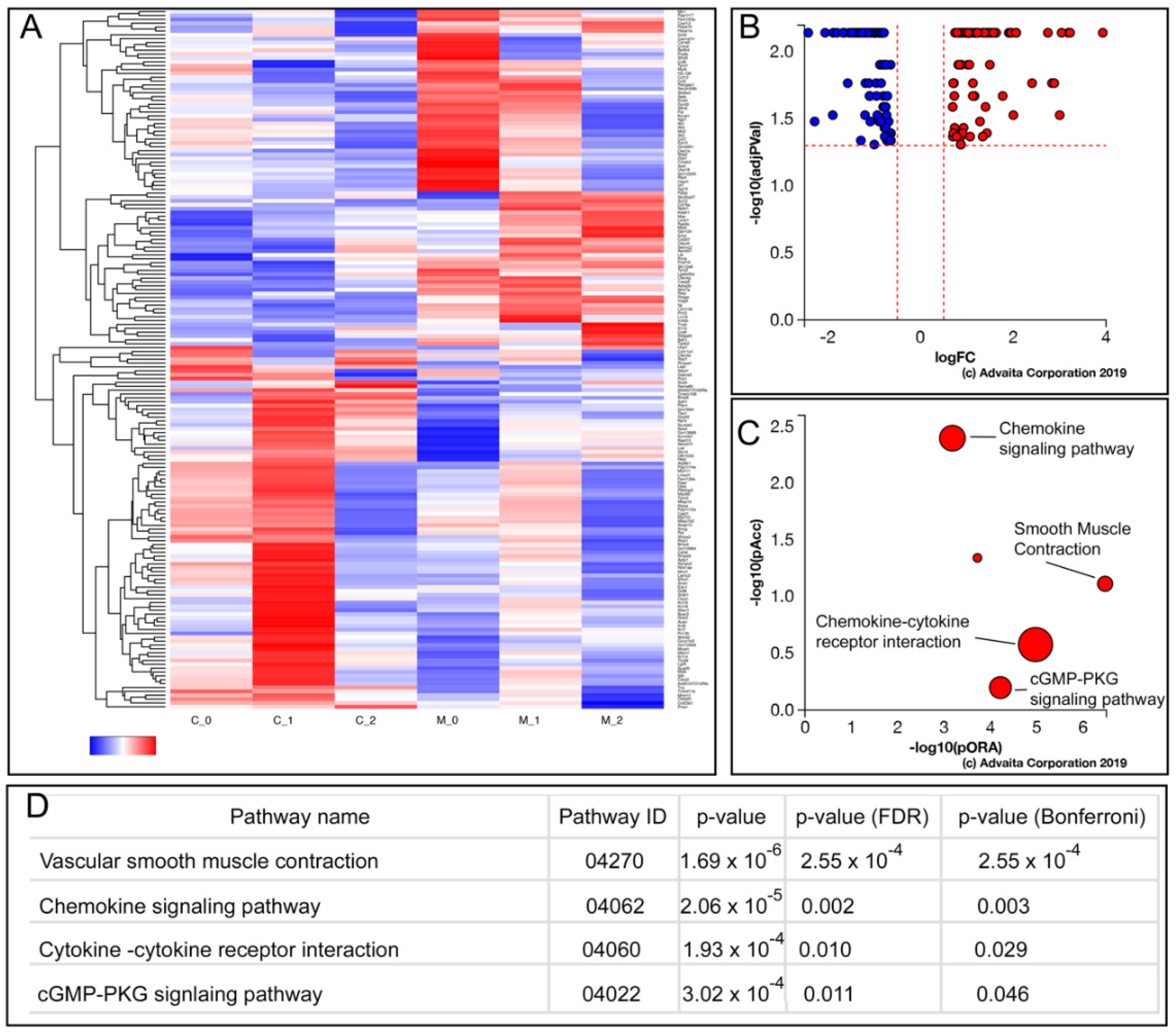
3.5. Enhanced AcvRI Signaling Resulted in Changes in the Gene Sets Associated with Cytokine Signaling, Vascular Smooth Muscle Contraction, and cGMP Signaling
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lincoln, J.; Yutzey, K.E. Molecular and developmental mechanisms of congenital heart valve disease. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2011, 91, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierpont, M.E.; Basson, C.T.; Benson, D.W., Jr.; Gelb, B.D.; Giglia, T.M.; Goldmuntz, E.; McGee, G.; Sable, C.A.; Srivastava, D.; Webb, C.L. Genetic basis for congenital heart defects: Current knowledge: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Congenital Cardiac Defects Committee, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young: Endorsed by the American Academy of Pediatrics. Circulation 2007, 115, 3015–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niessen, K.; Karsan, A. Notch signaling in cardiac development. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 1169–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, R.A. Down syndrome. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1990, 34, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scambler, P.J. The 22q11 deletion syndromes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 2421–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.H.; Tynan, M. Tetralogy of Fallot—A centennial review. Int. J. Cardiol. 1988, 21, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miquerol, L.; Kelly, R.G. Organogenesis of the vertebrate heart. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2013, 2, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sizarov, A.; Lamers, W.H.; Mohun, T.J.; Brown, N.A.; Anderson, R.H.; Moorman, A.F. Three-dimensional and molecular analysis of the arterial pole of the developing human heart. J. Anat. 2012, 220, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eley, L.; Alqahtani, A.M.; MacGrogan, D.; Richardson, R.V.; Murphy, L.; Salguero-Jimenez, A.; San Pedro, M.S.R.; Tiurma, S.; McCutcheon, L.; Gilmore, A.; et al. A novel source of arterial valve cells linked to bicuspid aortic valve without raphe in mice. eLife 2018, 7, e34110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, R.B.; Yutzey, K.E. Heart valve structure and function in development and disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2011, 73, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lincoln, J.; Kist, R.; Scherer, G.; Yutzey, K.E. Sox9 is required for precursor cell expansion and extracellular matrix organization during mouse heart valve development. Dev. Biol. 2007, 305, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lincoln, J.; Alfieri, C.M.; Yutzey, K.E. BMP and FGF regulatory pathways control cell lineage diversification of heart valve precursor cells. Dev. Biol. 2006, 292, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massague, J. TGF-beta signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 753–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derynck, R.; Zhang, Y.E. Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature 2003, 425, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Chen, D. The BMP signaling and in vivo bone formation. Gene 2005, 357, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzler, B.; Foreman, R.K.; Labosky, P.A.; Mallo, M. BMP signaling is essential for development of skeletogenic and neurogenic cranial neural crest. Development 2000, 127, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishina, Y. Function of bone morphogenetic protein signaling during mouse development. Front. Biosci. 2003, 8, 855–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Pardali, E.; Sanchez-Duffhues, G.; ten Dijke, P. BMP signaling in vascular diseases. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, F.S.; Chakkalakal, S.A.; Shore, E.M. Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: Mechanisms and models of skeletal metamorphosis. Dis. Model Mech. 2012, 5, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thawani, J.P.; Wang, A.C.; Than, K.D.; Lin, C.Y.; La Marca, F.; Park, P. Bone morphogenetic proteins and cancer: Review of the literature. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derynck, R.; Feng, X.H. TGF-beta receptor signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1333, F105–F150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joziasse, I.C.; Smith, K.A.; Chocron, S.; van Dinther, M.; Guryev, V.; van de Smagt, J.J.; Cuppen, E. ALK2 mutation in a patient with Down’s syndrome and a congenital heart defect. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 19, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.A.; Joziasse, I.C.; Chocron, S.; van Dinther, M.; Guryev, V.; Verhoeven, M.C.; Rehmann, H.; van der Smagt, J.J.; Doevendans, P.A.; Cuppen, E.; et al. Dominant-negative ALK2 allele associates with congenital heart defects. Circulation 2009, 119, 3062–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shore, E.M.; Xu, M.; Feldman, G.J.; Fenstermacher, D.A.; Cho, T.J.; Choi, I.H.; Connor, J.M.; Delai, P.; Glaser, D.L.; LeMerrer, M.; et al. A recurrent mutation in the BMP type I receptor ACVR1 causes inherited and sporadic fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Loder, S.J.; Brownley, C.; Eboda, O.; Peterson, J.R.; Hayano, S.; Wu, B.; Zhao, B.; Kaartinen, V.; Wong, V.C.; et al. BMP signaling mediated by constitutively active Activin type 1 receptor (ACVR1) results in ectopic bone formation localized to distal extremity joints. Dev. Biol. 2015, 400, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.B.; Deng, D.Y.; Lai, C.S.; Hong, C.C.; Cuny, G.D.; Bouxsein, M.L.; Hong, D.W. BMP type I receptor inhibition reduces heterotopic ossification. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaartinen, V.; Dudas, M.; Nagy, A.; Sridurongrit, S.; Lu, M.M.; Epstein, J.A. Cardiac outflow tract defects in mice lacking ALK2 in neural crest cells. Development 2004, 131, 3481–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, P.S.; Rajderkar, S.; Lane, J.; Mishina, Y.; Kaartinen, V. AcvR1-mediated BMP signaling in second heart field is required for arterial pole development: Implications for myocardial differentiation and regional identity. Dev. Biol. 2014, 390, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lees-Shepard, J.B.; Yamamoto, M.; Biswas, A.A.; Stoessel, S.J.; Nicholas, S.E.; Cogswell, C.A.; Devarakonda, P.M.; Schneider, M.J., Jr.; Cummins, S.M.; Legendre, N.P.; et al. Activin-dependent signaling in fibro/adipogenic progenitors causes fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Nagy, A.; Larsson, J.; Dudas, M.; Sucov, H.M.; Kaartinen, V. Defective ALK5 signaling in the neural crest leads to increased postmigratory neural crest cell apoptosis and severe outflow tract defects. BMC Dev. Biol. 2006, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, P.S.; Sridurongrit, S.; Ruiz-Lozano, P.; Kaartinen, V. Deficient signaling via Alk2 (Acvr1) leads to bicuspid aortic valve development. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, T.; Scott, G.; Komatsu, Y.; Araya, R.; Kawano, M.; Ray, M.K.; Yamada, M.; Mishina, Y. Generation of a mouse with conditionally activated signaling through the BMP receptor, ALK2. Genesis 2006, 44, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Lui, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Chamberlain, A.A.; Moreno-Rodriguez, R.A.; Markwald, R.R.; O’Rourke, B.P.; Sharp, D.J.; et al. Endocardial cells form the coronary arteries by angiogenesis through myocardial-endocardial VEGF signaling. Cell 2012, 151, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, A.; Gertsenstein, M.; Vintersten, K.; Behringer, R. Manipulating the Mouse Embryo—A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Sridurongrit, S.; Dudas, M.; Thomas, P.; Nagy, A.; Schneider, M.D.; Epstein, J.A.; Kaartinen, V. Atrioventricular cushion transformation is mediated by ALK2 in the developing mouse heart. Dev. Biol. 2005, 286, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, J.A. Cellular mechanisms of aortic valve calcification. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2012, 5, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez Stallons, M.V.; Wirrig-Schwendeman, E.E.; Fang, M.; Cheek, J.D.; Alfieri, C.M.; Hinton, R.B.; Yetzey, K.E. Molecular Mechanisms of Heart Valve Development and Disease. In Etiology and Morphogenesis of Congenital Heart Disease: From Gene Function and Cellular Interaction to Morphology; Nakanishi, T., Markwald, R.R., Baldwin, H.S., Keller, B.B., Srivastava, D., Yamagishi, H., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; pp. 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, V.; Muth, A.N.; Ransom, J.F.; Schluterman, M.K.; Barnes, R.; King, I.N.; Grossfeld, P.D.; Srivastava, D. Mutations in NOTCH1 cause aortic valve disease. Nature 2005, 437, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Lu, M.F.; Schwartz, R.J.; Martin, J.F. Bmp2 is essential for cardiac cushion epithelial-mesenchymal transition and myocardial patterning. Development 2005, 132, 5601–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Fassler, R.; Mishina, Y.; Jiao, K.; Baldwin, H.S. Essential functions of Alk3 during AV cushion morphogenesis in mouse embryonic hearts. Dev. Biol. 2007, 301, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prados, B.; Del Toro, R.; MacGrogan, D.; Gómez-Apiñániz, P.; Papoutsi, T.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P.; Méndez-Ferrer, S.; de la Pompa, J.L. Heterotopic ossification in mice overexpressing Bmp2 in Tie2+ lineages. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Guo, H.; Chou, D.W.; Berndt, A.; Sundberg, J.P.; Uitto, J. Mutant Enpp1asj mice as a model for generalized arterial calcification of infancy. Dis. Model Mech. 2013, 6, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohukainen, P.; Ruskoaho, H.; Rysa, J. Cellular Mechanisms of Valvular Thickening in Early and Intermediate Calcific Aortic Valve Disease. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2018, 14, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulin, A.; Moore, V.; James, J.M.; Yutzey, K.E. Loss of Axin2 results in impaired heart valve maturation and subsequent myxomatous valve disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017, 113, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.I.; Sakuma, I.; Sohn, I.S.; Jo, S.H.; Koh, K.K. Inflammatory and metabolic mechanisms underlying the calcific aortic valve disease. Atherosclerosis 2018, 277, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, T.; Tsukada, N.; Okano, M.; Ishida, T.; Hirata, K.I.; Shiomi, M. Progression of calcific aortic valve sclerosis in WHHLMI rabbits. Atherosclerosis 2018, 273, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, M.C.; Wei, K.; Adams, R.L.E.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Caruso, L.L.; Mirzaei, Z.; Lam, A.Y.-L.; Tam, R.K.K.; Zhang, H.; Heximer, S.P.; et al. Deficiency of Natriuretic Peptide Receptor 2 Promotes Bicuspid Aortic Valves, Aortic Valve Disease, Left Ventricular Dysfunction, and Ascending Aortic Dilatations in Mice. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, O.E.; Wader, K.F.; Hella, H.; Mylin, A.K.; Turesson, I.; Nesthus, I.; Waage, N.; Sundan, A.; Holien, T. Activin A inhibits BMP-signaling by binding ACVR2A and ACVR2B. Cell Commun. Signal. 2015, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, K.L.; Makanji, Y.; Harrison, C.A. New insights into the mechanisms of activin action and inhibition. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2012, 359, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatsell, S.J.; Idone, V.; Wolken, D.M.; Huang, L.; Kim, H.J.; Wang, L.; Wen, X.; Nannuru, K.C.; Jimenez, J.; Xie, L.; et al. ACVR1R206H receptor mutation causes fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva by imparting responsiveness to activin A. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 303ra137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.R.; Mackay, A.; Truffaux, N.; Butterfield, Y.; Morozova, O.; Philippe, C.; Castel, D.; Grasso, C.S.; Vinci, M.; Carvalho, D.; et al. Recurrent activating ACVR1 mutations in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeman, C.M.; Cordero, F.J.; Hu, G.; Misuraca, K.; Romero, M.M.; Cardona, H.J.; Hazarian, J.; Hashizume, R.; McLendon, R.; Yu, P.; et al. ACVR1 R206H cooperates with H3.1K27M in promoting diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma pathogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Syed, S.; Rajderkar, S.; Mann, J.M.; Hawkins, T.; Wu, B.; Zhou, B.; Sugi, Y.; Mishina, Y.; Kaartinen, V. Activation of AcvR1-Mediated Signaling Results in Semilunar Valve Defects. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd9080272
Syed S, Rajderkar S, Mann JM, Hawkins T, Wu B, Zhou B, Sugi Y, Mishina Y, Kaartinen V. Activation of AcvR1-Mediated Signaling Results in Semilunar Valve Defects. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2022; 9(8):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd9080272
Chicago/Turabian StyleSyed, Shabber, Sudha Rajderkar, Jeffrey M. Mann, Travis Hawkins, Bingrou Wu, Bin Zhou, Yukiko Sugi, Yuji Mishina, and Vesa Kaartinen. 2022. "Activation of AcvR1-Mediated Signaling Results in Semilunar Valve Defects" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 9, no. 8: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd9080272
APA StyleSyed, S., Rajderkar, S., Mann, J. M., Hawkins, T., Wu, B., Zhou, B., Sugi, Y., Mishina, Y., & Kaartinen, V. (2022). Activation of AcvR1-Mediated Signaling Results in Semilunar Valve Defects. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 9(8), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd9080272





