Acute Kidney Injury in Cardiogenic Shock: An Updated Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
3. Pathogenesis
3.1. Role of Inflammation
3.1.1. C-Reactive Protein
3.1.2. Angiopoietin and Interleukin
3.1.3. Nitric Oxide
3.1.4. Role of Novel Biomarkers
3.2. Role of Right Ventricular Failure/Renal Vein Congestion
3.3. Role of Thromboembolism
3.4. Contrast-Induced AKI
3.5. Role of Mechanical Circulatory Support
4. Outcomes
4.1. In-Hospital Outcomes
4.2. Long-Term Outcomes
5. Management
5.1. Cardiac Management
5.2. Renal Management
5.3. Supportive Therapies
6. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMI | acute myocardial infarction |
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| CS | cardiogenic shock |
| CI | cardiac index |
| CRRT | continuous renal replacement therapy |
| CVVH | continuous veno-venous hemofiltration |
| CVP | central venous pressure |
| ECMO | extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| HF | heart failure |
| hs-CRP | high sensitivity C-reactive protein |
| IABP | intra-aortic balloon pump |
| MCS | mechanical circulatory support |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| PMR | papillary muscle rupture |
| pVADs | percutaneous ventricular assist devices |
| PCI | primary percutaneous intervention |
| RRT | renal replacement therapy |
| RV | right ventricle/right ventricular |
| STEMI | ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction |
| VSD | ventricular septal defect |
References
- Vallabhajosyula, S.; Dunlay, S.M.; Prasad, A.; Kashani, K.; Sakhuja, A.; Gersh, B.J.; Jaffe, A.S.; Holmes, D.R.; Barsness, G.W. Acute Noncardiac Organ Failure in Acute Myocardial Infarction with Cardiogenic Shock. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhajosyula, S.; Dunlay, S.M.; Barsness, G.W.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Sundaragiri, P.R.; Gersh, B.J.; Jaffe, A.S.; Kashani, K. Temporal trends, predictors, and outcomes of acute kidney injury and hemodialysis use in acute myocardial infarction-related cardiogenic shock. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhajosyula, S.; Dunlay, S.M.; Kashani, K.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Sundaragiri, P.R.; Jaffe, A.S.; Barsness, G.W. Temporal trends and outcomes of prolonged invasive mechanical ventilation and tracheostomy use in acute myocardial infarction with cardiogenic shock in the United States. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 285, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Patil, S.; Patel, B.; Agarwal, M.; Davila, C.D.; Garg, L.; Agrawal, S.; Kapur, N.K.; Jorde, U.P. Causes and Predictors of 30-Day Readmission in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction and Cardiogenic Shock. Circ. Heart Fail. 2018, 11, e004310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarvasmäki, T.; Haapio, M.; Mebazaa, A.; Sionis, A.; Silva-Cardoso, J.; Tolppanen, H.; Lindholm, M.G.; Pulkki, K.; Parissis, J.; Harjola, V.-P.; et al. Acute kidney injury in cardiogenic shock: Definitions, incidence, haemodynamic alterations, and mortality. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marenzi, G.; Assanelli, E.; Campodonico, J.; De Metrio, M.; Lauri, G.; Marana, I.; Moltrasio, M.; Rubino, M.; Veglia, F.; Montorsi, P.; et al. Acute kidney injury in ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock at admission*. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puymirat, E.; Fagon, J.Y.; Aegerter, P.; Diehl, J.L.; Monnier, A.; Hauw-Berlemont, C.; Boissier, F.; Chatellier, G.; Guidet, B.; Danchin, N.; et al. Cardiogenic shock in intensive care units: Evolution of prevalence, patient profile, management and outcomes, 1997–2012. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, P.; Brillet, G.; Catella, L.; Schmidt, A.; Bénard, S. Outcomes, risk factors and health burden of contrast-induced acute kidney injury: An observational study of one million hospitalizations with image-guided cardiovascular procedures. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delmas, C.; Puymirat, E.; Leurent, G.; Elbaz, M.; Manzo-Silberman, S.; Bonello, L.; Gerbaud, E.; Bataille, V.; Levy, B.; Lamblin, N.; et al. Design and preliminary results of FRENSHOCK 2016: A prospective nationwide multicentre registry on cardiogenic shock. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 112, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhajosyula, S.; Ya’Qoub, L.; Dunlay, S.M.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Sundaragiri, P.R.; Jaffe, A.S.; Gersh, B.J.; Kashani, K. Sex disparities in acute kidney injury complicating acute myocardial infarction with cardiogenic shock. ESC Heart Fail. 2019, 6, 874–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elbadawi, A.; Elgendy, I.Y.; Mahmoud, K.; Barakat, A.F.; Mentias, A.; Mohamed, A.H.; Ogunbayo, G.O.; Megaly, M.; Saad, M.; Omer, M.; et al. Temporal Trends and Outcomes of Mechanical Complications in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 12, 1825–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rewa, O.; Bagshaw, S.M. Acute kidney injury—epidemiology, outcomes and economics. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, M.; Mullens, W.; Tang, W.H.W. Impact of Systemic Venous Congestion in Heart Failure. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2011, 8, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain-Syed, F.; McCullough, P.A.; Birk, H.-W.; Renker, M.; Brocca, A.; Seeger, W.; Ronco, C. Cardio-Pulmonary-Renal Interactions: A Multidisciplinary Approach. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 2433–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, N.; Genovese, S.; Campodonico, J.; Bonomi, A.; Lucci, C.; Milazzo, V.; Moltrasio, M.; Biondi, M.L.; Riggio, D.; Veglia, F.; et al. High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein and Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Prospective Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McFadyen, J.D.; Kiefer, J.; Braig, D.; Loseff-Silver, J.; Potempa, L.A.; Eisenhardt, S.U.; Peter, K. Dissociation of C-Reactive Protein Localizes and Amplifies Inflammation: Evidence for a Direct Biological Role of C-Reactive Protein and Its Conformational Changes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baer, P.; Gauer, S.; Wegner, B.; Schubert, R.; Geiger, H. C-reactive protein induced activation of MAP-K and RANTES in human renal distal tubular epithelial cells in vitro. Clin. Nephrol. 2006, 66, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Tang, Y.; Huang, X.R.; Tang, P.M.K.; Xu, A.; Szalai, A.J.; Lou, T.-Q.; Lan, H.Y. C-reactive protein promotes acute kidney injury via Smad3-dependent inhibition of CDK2/cyclin E. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 610–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shacham, Y.; Rubinow, E.L.-; Steinvil, A.; Keren, G.; Roth, A.; Arbel, Y. High sensitive C-reactive protein and the risk of acute kidney injury among ST elevation myocardial infarction patients undergoing primary percutaneous intervention. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2014, 19, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pöss, J.; Fuernau, G.; Denks, D.; Desch, S.; Eitel, I.; De Waha, S.; Link, A.; Schuler, G.; Adams, V.; Böhm, M.; et al. Angiopoietin-2 in acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock-a biomarker substudy of the IABP-SHOCK II-Trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrié, R.P.; Becher, U.M.; Frommold, R.; Tiyerili, V.; Schrickel, J.W.; Nickenig, G.; Schwab, J.O. Interleukin-6 is the strongest predictor of 30-day mortality in patients with cardiogenic shock due to myocardial infarction. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geppert, A.; Dorninger, A.; Delle-Karth, G.; Zorn, G.; Heinz, G.; Huber, K. Plasma concentrations of interleukin-6, organ failure, vasopressor support, and successful coronary revascularization in predicting 30-day mortality of patients with cardiogenic shock complicating acute myocardial infarction*. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 2035–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geppert, A.; Steiner, A.; Zorn, G.; Delle-Karth, G.; Koreny, M.; Haumer, M.; Siostrzonek, P.; Huber, K.; Heinz, G. Multiple organ failure in patients with cardiogenic shock is associated with high plasma levels of interleukin-6. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 30, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunwald, E. Biomarkers in Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2148–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gimbrone, M.A.; García-Cardeña, G. Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and the Pathobiology of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parenica, J.; Kala, P.; Mebazaa, A.; Littnerova, S.; Benesova, K.; Tomandl, J.; Pavkova, M.G.; Jarkovský, J.; Spinar, J.; Tomandlova, M.; et al. Activation of the Nitric Oxide Pathway and Acute Myocardial Infarction Complicated by Acute Kidney Injury. Cardiorenal Med. 2020, 10, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, M.; Zarbock, A.; Goldstein, S.; Kashani, K.; Macedo, E.; Murugan, R.; Bell, M.; Forni, L.; Guzzi, L.; Joannidis, M.; et al. Recommendations on Acute Kidney Injury Biomarkers from the Acute Disease Quality Initiative Consensus Conference. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2019209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Sun, S.; Lin, L.; Han, M.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Su, B.; Huang, S.; et al. Predictive Factors Upon Discontinuation of Renal Replacement Therapy for Long-Term Chronic Dialysis and Death in Acute Kidney Injury Patients: Predictive Factors Upon Disccontinuation of RRT. Artif. Organs 2017, 41, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, S.J.; Zarbock, A.; Meersch, M.; Küllmar, M.; Kellum, J.A.; Schmit, D.; Wagner, M.; Triem, S.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Gröne, H.-J.; et al. Association between urinary dickkopf-3, acute kidney injury, and subsequent loss of kidney function in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: An observational cohort study. Lancet 2019, 394, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mårtensson, J.; Martling, C.-R.; Bell, M. Novel biomarkers of acute kidney injury and failure: Clinical applicability. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 109, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kashani, K.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Ronco, C. Biomarkers of acute kidney injury: The pathway from discovery to clinical adoption. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 1074–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meersch, M.; Schmidt, C.; Hoffmeier, A.; Van Aken, H.; Wempe, C.; Gerss, J.; Zarbock, A. Prevention of cardiac surgery-associated AKI by implementing the KDIGO guidelines in high risk patients identified by biomarkers: The PrevAKI randomized controlled trial. Intensiv. Care Med. 2017, 43, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Göcze, I.; Jauch, D.; Götz, M.; Kennedy, P.; Jung, B.; Zeman, F.; Gnewuch, C.; Graf, B.M.; Gnann, W.; Banas, B.; et al. Biomarker-guided Intervention to Prevent Acute Kidney Injury After Major Surgery: The Prospective Randomized BigpAK Study. Ann. Surg. 2018, 267, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Use of Cell Cycle Arrest Biomarkers in Conjunction with Clas.: Critical Care Medicine. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/ccmjournal/Fulltext/2019/10000/Use_of_Cell_Cycle_Arrest_Biomarkers_in_Conjunction.38.aspx (accessed on 25 July 2021).
- Pipili, C.; Ioannidou, S.; Tripodaki, E.-S.; Parisi, M.; Douka, E.; Vasileiadis, I.; Joannidis, M.; Nanas, S. Prediction of the renal replacement therapy requirement in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients by combining biomarkers for glomerular filtration and tubular damage. J. Crit. Care 2014, 29, 692.e7–692.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäntti, T.; for the CardShock Investigators; Tarvasmäki, T.; Harjola, V.-P.; Pulkki, K.; Turkia, H.; Sabell, T.; Tolppanen, H.; Jurkko, R.; Hongisto, M.; et al. Predictive value of plasma proenkephalin and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in acute kidney injury and mortality in cardiogenic shock. Ann. Intensiv. Care 2021, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marenzi, G.; Cosentino, N.; Genovese, S.; Campodonico, J.; De Metrio, M.; Rondinelli, M.; Cornara, S.; Somaschini, A.; Camporotondo, R.; Demarchi, A.; et al. Reduced Cardio-Renal Function Accounts for Most of the In-Hospital Morbidity and Mortality Risk Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Undergoing Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akker, J.P.V.D.; Bakker, J.; Groeneveld, A.; Uil, C.D. Risk indicators for acute kidney injury in cardiogenic shock. J. Crit. Care 2019, 50, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binanay, C.; Califf, R.M.; Hasselblad, V.; O’Connor, C.M.; Shah, M.R.; Sopko, G.; Stevenson, L.W.; Francis, G.S.; Leier, C.V.; Miller, L.W.; et al. Evaluation Study of Congestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Effectiveness: The ESCAPE trial. JAMA 2005, 294, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jentzer, J.C.; Ahmed, A.M.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Burstein, B.; Tabi, M.; Barsness, G.W.; Murphy, J.G.; Best, P.J.; Bell, M.R. Shock in the cardiac intensive care unit: Changes in epidemiology and prognosis over time. Am. Heart J. 2021, 232, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanberg, J.S.; Sury, K.; Wilson, F.; Brisco, M.A.; Ahmad, T.; ter Maaten, J.M.; Broughton, J.S.; Assefa, M.; Tang, W.W.; Parikh, C.; et al. Reduced Cardiac Index Is Not the Dominant Driver of Renal Dysfunction in Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 2199–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matějka, J.; Varvařovský, I.; Rozsíval, V.; Herman, A.; Bláha, K.; Večeřa, J.; Lazarák, T.; Novotný, V.; Mužáková, V.; Vojtíšek, P. Heart failure is the strongest predictor of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Kardiol. Pol. 2016, 74, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullens, W.; Abrahams, Z.; Francis, G.S.; Sokos, G.; Taylor, D.O.; Starling, R.C.; Young, J.B.; Tang, W.W. Importance of Venous Congestion for Worsening of Renal Function in Advanced Decompensated Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damman, K.; Van Deursen, V.M.; Navis, G.; Voors, A.A.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Hillege, H.L. Increased Central Venous Pressure Is Associated With Impaired Renal Function and Mortality in a Broad Spectrum of Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doty, J.M.; Saggi, B.H.; Sugerman, H.J.; Blocher, C.R.; Pin, R.; Fakhry, I.; Gehr, T.W.B.; Sica, D.A. Effect of Increased Renal Venous Pressure on Renal Function. J. Trauma Inj. Infect. Crit. Care 1999, 47, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K.B.; Penalver, J.; Toroghi, H.M.; Jeon, H.D.; Habib, N.; Pinto, W.H.; Ram, P.; Gupta, S.; Rangaswami, J. Invasive Hemodynamic Predictors of Renal Outcomes after Percutaneous Coronary Interventions. Cardiorenal Med. 2019, 9, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damman, K.; Voors, A.A.; Navis, G.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Hillege, H.L. The Cardiorenal Syndrome in Heart Failure. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 54, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.-A.; Sanchez-Lozada, L.-G.; Johnson, R.J.; Kang, D.-H. Oxidative stress with an activation of the renin–angiotensin system in human vascular endothelial cells as a novel mechanism of uric acid-induced endothelial dysfunction. J. Hypertens. 2010, 28, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korabathina, R.; Heffernan, K.S.; Paruchuri, V.; Patel, A.; Mudd, J.O.; Prutkin, J.M.; Orr, N.M.; Weintraub, A.; Kimmelstiel, C.D.; Kapur, N.K. The pulmonary artery pulsatility index identifies severe right ventricular dysfunction in acute inferior myocardial infarction. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2012, 80, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guven, G.; Brankovic, M.; Constantinescu, A.A.; Brugts, J.J.; Hesselink, D.A.; Akin, S.; Struijs, A.; Birim, O.; Ince, C.; Manintveld, O.C.; et al. Preoperative right heart hemodynamics predict postoperative acute kidney injury after heart transplantation. Intensiv. Care Med. 2018, 44, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pavasini, R.; Tebaldi, M.; Bugani, G.; Tonet, E.; Campana, R.; Cimaglia, P.; Maietti, E.; Grazzi, G.; Pompei, G.; Fabbri, G.; et al. Contrast Associated Acute Kidney Injury and Mortality in Older Adults with Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Pooled Analysis of the FRASER and HULK Studies. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Maekawa, Y.; Miyata, H.; Inoue, S.; Ishikawa, S.; Sueyoshi, K.; Noma, S.; Kawamura, A.; Kohsaka, S.; Fukuda, K. Impact of Periprocedural Bleeding on Incidence of Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Treated With Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyman, U.; Björk, J.; Aspelin, P.; Marenzi, G. Contrast medium dose-to-gfr ratio: A measure of systemic exposure to predict contrast-induced nephropathy after percutaneous coronary intervention. Acta Radiol. 2008, 49, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, A.V.; Barsness, G.W.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Vallabhajosyula, S. Complications of Temporary Percutaneous Mechanical Circulatory Support for Cardiogenic Shock: An Appraisal of Contemporary Literature. Cardiol. Ther. 2019, 8, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallabhajosyula, S.; Prasad, A.; Bell, M.R.; Sandhu, G.S.; Eleid, M.F.; Dunlay, S.M.; Schears, G.J.; Stulak, J.M.; Singh, M.; Gersh, B.J.; et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Use in Acute Myocardial Infarction in the United States, 2000 to 2014. Circ. Heart Fail. 2019, 12, e005929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askenazi, D.J.; Selewski, D.T.; Paden, M.L.; Cooper, D.; Bridges, B.C.; Zappitelli, M.; Fleming, G.M. Renal Replacement Therapy in Critically Ill Patients Receiving Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, R.; Hachamovitch, R.; Kittleson, M.; Patel, J.; Arabia, F.; Moriguchi, J.; Esmailian, F.; Azarbal, B. Complications of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Treatment of Cardiogenic Shock and Cardiac Arrest: A Meta-Analysis of 1866 Adult Patients. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 97, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, G.; Kofman, N.; Gal-Oz, A.; Arbel, Y.; Khoury, S.; Keren, G.; Shacham, Y. Relation of positive fluid balance to the severity of renal impairment and recovery among ST elevation myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock. J. Crit. Care 2017, 40, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, K.-I.; Shiono, M.; Orime, Y.; Hata, M.; Sezai, A.; Saitoh, T.; Sezai, Y. Effect of Pulsatile and Nonpulsatile Assist on Heart and Kidney Microcirculation with Cardiogenic Shock. Artif. Organs 1996, 20, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keckler, S.J.; Laituri, C.A.; Ostlie, D.J.; Peter, S.D.S. A Review of Venovenous and Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Neonates and Children. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2009, 20, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhne, I. Haemolysis induced by mechanical circulatory support devices: Unsolved problems. Perfusion 2020, 35, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhajosyula, S.; Subramaniam, A.V.; Jr, D.H.M.; Patlolla, S.H.; Ya’Qoub, L.; Kumar, V.; Verghese, D.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Jentzer, J.C.; Sandhu, G.S.; et al. Complications from percutaneous-left ventricular assist devices versus intra-aortic balloon pump in acute myocardial infarction-cardiogenic shock. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadeer, A.I.; Kurlansky, P.; Chiuzan, C.; Truby, L.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Garan, R.; Topkara, V.; Yuzefpolskaya, M.; Colombo, P.; Takeda, K.; et al. Importance of stratifying acute kidney injury in cardiogenic shock resuscitated with mechanical circulatory support therapy. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 154, 856–864.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adegbala, O.; Inampudi, C.; Adejumo, A.; Otuonye, G.; Akintoye, E.; Elsayed, R.; Williams, K.; Alvarez, P.; Afonso, L.; Briasoulis, A. Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with Cardiogenic Shock Utilizing Hemodialysis for Acute Kidney Injury. Am. J. Cardiol. 2019, 123, 1816–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marenzi, G.; Cosentino, N.; Marinetti, A.; Leone, A.M.; Milazzo, V.; Rubino, M.; De Metrio, M.; Cabiati, A.; Campodonico, J.; Moltrasio, M.; et al. Renal replacement therapy in patients with acute myocardial infarction: Rate of use, clinical predictors and relationship with in-hospital mortality. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 230, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, M.D.; Gammelager, H.; Schmidt, M.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Shaw, R.E.; Bøtker, H.E.; Sørensen, H.T.; Christiansen, C.F. Acute kidney injury treated with renal replacement therapy and 5-year mortality after myocardial infarction-related cardiogenic shock: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallabhajosyula, S.; Verghese, D.; Desai, V.K.; Sundaragiri, P.R.; Miller, V.M. Sex differences in acute cardiovascular care: A review and needs assessment. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhajosyula, S.; Ya’Qoub, L.; Singh, M.; Bell, M.R.; Gulati, R.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Sundaragiri, P.R.; Miller, V.M.; Jaffe, A.S.; Gersh, B.J.; et al. Sex Disparities in the Management and Outcomes of Cardiogenic Shock Complicating Acute Myocardial Infarction in the Young. Circ. Heart Fail. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallabhajosyula, S.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Dunlay, S.M.; Hayes, S.N.; Best, P.J.; Brenes-Salazar, J.A.; Lerman, A.; Gersh, B.J.; Jaffe, A.S.; Bell, M.R.; et al. Sex and Gender Disparities in the Management and Outcomes of Acute Myocardial Infarction–Cardiogenic Shock in Older Adults. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 1916–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bărcan, A.; Chițu, M.; Benedek, E.; Rat, N.; Korodi, S.; Morariu, M.; Kovacs, I. Predictors of Mortality In Patients With ST-Segment Elevation Acute Myocardial Infarction And Resuscitated Out-Of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest. J. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 2, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kouraki, K.; Schneider, S.; Uebis, R.; Tebbe, U.; Klein, H.H.; Janssens, U.; Zahn, R.; Senges, J.; Zeymer, U. Characteristics and clinical outcome of 458 patients with acute myocardial infarction requiring mechanical ventilation. Results of the BEAT registry of the ALKK-study group. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2010, 100, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, J.W.; Blunt, I.R.H.; Than, M.P. Acute Kidney Injury and mortality prognosis in Acute Coronary Syndrome patients: A meta-analysis. Nephrol Carlton Vic. 2018, 23, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayıroğlu, M.İ. Pehlivano Effect of Acute Kidney Injury on Long-Term Mortality in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Complicated with Cardiogenic Shock and Underwent Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in a High-Volume Tertiary Center. Turk Kardiyol. Dernegi Arsivi-Arch. Turk. Soc. Cardiol. 2019, 47, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patlolla, S.H.; Kanwar, A.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Doshi, R.P.; Stulak, J.M.; HolmesJr, D.R.; Bell, M.R.; Singh, M.; Vallabhajosyula, S. Temporal Trends, Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Emergent Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting for Acute Myocardial Infarction in the United States. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, e020517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homorodean, C.; Iancu, A.C.; Dregoesc, I.M.; Spînu, M.; Ober, M.C.; Tãtaru, D.; Leucuţa, D.; Olinic, M.; Olinic, D.M. Renal Failure Impact on the Outcomes of ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients Due to a Left Main Coronary Culprit Lesion Treated Using a Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Backhaus, T.; Fach, A.; Schmucker, J.; Fiehn, E.; Garstka, D.; Stehmeier, J.; Hambrecht, R.; Wienbergen, H. Management and predictors of outcome in unselected patients with cardiogenic shock complicating acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: Results from the Bremen STEMI Registry. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2017, 107, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanic, V.; Kompara, G.; Suran, D.; Ekart, R.; Bevc, S.; Hojs, R. Impact of KDIGO-Defined Acute Kidney Injury on Mortality after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for Acute Myocardial Infarction. Cardiorenal Med. 2018, 8, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koreny, M.; Karth, G.D.; Geppert, A.; Neunteufl, T.; Priglinger, U.; Heinz, G.; Siostrzonek, P. Prognosis of patients who develop acute renal failure during the first 24 hours of cardiogenic shock after myocardial infarction. Am. J. Med. 2002, 112, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlFaleh, H.F.; Alsuwaida, A.O.; Ullah, A.; Hersi, A.; Alhabib, K.F.; AlNemer, K.; AlSaif, S.; Taraben, A.; Kashour, T.; Balghith, M.A.; et al. The prognostic impact of in-hospital worsening of renal function in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Haapio, M.; House, A.A.; Anavekar, N.; Bellomo, R. Cardiorenal Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, T.D.; Tomey, M.I.; Tamis-Holland, J.E.; Thiele, H.; Rao, S.V.; Menon, V.; Klein, D.G.; Naka, Y.; Piña, I.L.; Kapur, N.K.; et al. Invasive Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction Complicated by Cardiogenic Shock: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Diepen, S.; Katz, J.N.; Albert, N.M.; Henry, T.D.; Jacobs, A.K.; Kapur, N.K.; Kilic, A.; Menon, V.; Ohman, E.M.; Sweitzer, N.K.; et al. Contemporary Management of Cardiogenic Shock: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 136, e232–e268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, H.; Akin, I.; Sandri, M.; Fuernau, G.; De Waha, S.; Meyer-Saraei, R.; Nordbeck, P.; Geisler, T.; Landmesser, U.; Skurk, C.; et al. PCI Strategies in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction and Cardiogenic Shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2419–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Procyrion. An Evaluation of the Safety and Performance of the Aortix System for Intra-Aortic Mechanical Circulatory Support in Patients with Cardiorenal Syndrome. clinicaltrials.gov. 2021. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04145635 (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- De Backer, D.; Biston, P.; Devriendt, J.; Madl, C.; Chochrad, D.; Aldecoa, C.; Brasseur, A.; Defrance, P.; Gottignies, P.; Vincent, J.-L. Comparison of Dopamine and Norepinephrine in the Treatment of Shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levy, B.; Clere-Jehl, R.; Legras, A.; Morichau-Beauchant, T.; Leone, M.; Frederique, G.; Quenot, J.-P.; Kimmoun, A.; Cariou, A.; Lassus, J.; et al. Epinephrine Versus Norepinephrine for Cardiogenic Shock After Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigger, O.; Bloechlinger, S.; Berger, D.; Häner, J.; Zanchin, T.; Windecker, S.; Räber, L.; Schefold, J.C. Baseline serum bicarbonate levels independently predict short-term mortality in critically ill patients with ischaemic cardiogenic shock. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2018, 7, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zante, B.; Reichenspurner, H.; Kubik, M.; Kluge, S.; Schefold, J.C.; Pfortmueller, C. Base excess is superior to lactate-levels in prediction of ICU mortality after cardiac surgery. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prowle, J.; Bellomo, R. Fluid administration and the kidney. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2010, 16, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, C.; Reuter, H.; Seck, C.; Hellmich, M.; Zobel, C. Fluid therapy and acute kidney injury in cardiogenic shock after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2013, 84, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, S.; Calderon, J.; Tafer, N.; Pouquet, O.; Fournet, N.; Richebé, P.; Barandon, L.; Janvier, G. Evaluation of continuous veno-venous hemofiltration for the treatment of cardiogenic shock in conjunction with acute renal failure after cardiac surgery? Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2009, 36, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.-Y.; Yang, W.-C.; Chuang, C.-L. Effect of early and intensive continuous venovenous hemofiltration on patients with cardiogenic shock and acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 1628–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rude, R.E. Pharmacologic support in cardiogenic shock. Adv. Shock. Res. 1983, 10, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Solomon, S.D. Optimizing care of heart failure after acute MI with an aldosterone receptor antagonist. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2007, 4, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghionzoli, N.; Sciaccaluga, C.; Mandoli, G.; Vergaro, G.; Gentile, F.; D’Ascenzi, F.; Mondillo, S.; Emdin, M.; Valente, S.; Cameli, M. Cardiogenic shock and acute kidney injury: The rule rather than the exception. Heart Fail. Rev. 2020, 26, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhajosyula, S.; Sakhuja, A.; Geske, J.B.; Kumar, M.; Kashyap, R.; Kashani, K.; Jentzer, J.C. Clinical profile and outcomes of acute cardiorenal syndrome type-5 in sepsis: An eight-year cohort study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotecha, A.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Coville, H.H.; Kashani, K. Cardiorenal syndrome in sepsis: A narrative review. J. Crit. Care 2018, 43, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentzer, J.C.; Bihorac, A.; Brusca, S.B.; Del Rio-Pertuz, G.; Kashani, K.; Kazory, A.; Kellum, J.A.; Mao, M.; Moriyama, B.; Morrow, D.A.; et al. Contemporary Management of Severe Acute Kidney Injury and Refractory Cardiorenal Syndrome: JACC Council Perspectives. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1084–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallabhajosyula, S.; Shankar, A.; Patlolla, S.H.; Prasad, A.; Bell, M.R.; Jentzer, J.C.; Arora, S.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Gersh, B.J.; Jaffe, A.S.; et al. Pulmonary artery catheter use in acute myocardial infarction-cardiogenic shock. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhajosyula, S.; Barsness, G.W.; Vallabhajosyula, S. Multidisciplinary teams for cardiogenic shock. Aging 2019, 11, 4774–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
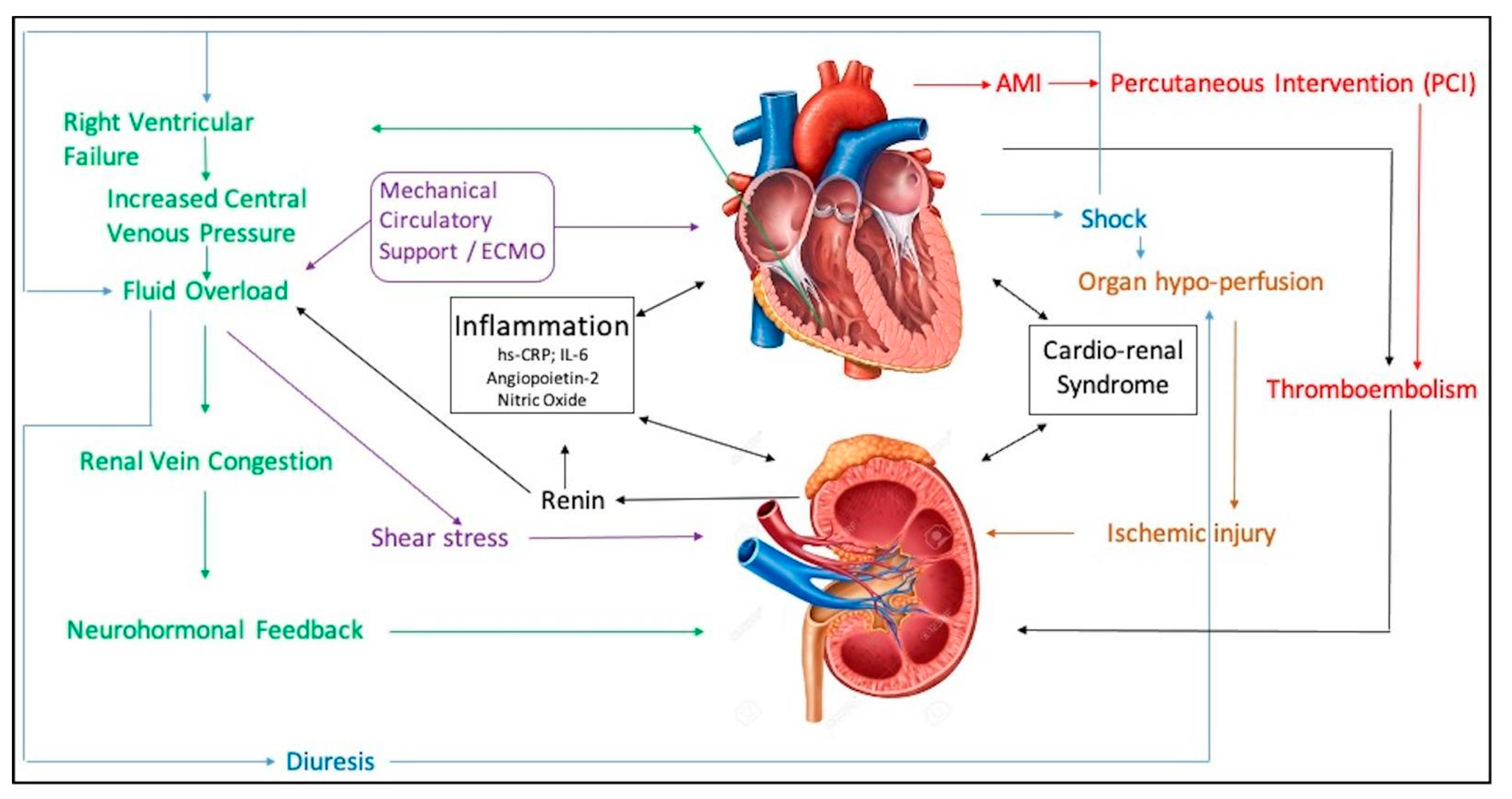
| Mechanism | Markers | Pathogenesis |
|---|---|---|
| Inflammation | hs-CRP, IL-6, angiopoietin-2, nitric oxide | MAPK → impairs tubular epithelial cell regeneration → impairs tubular epithelial cell regeneration pathway Capillary leakage |
| Right ventricular failure | Central venous pressure | Renal vein congestion → neurohormonal feedback → tubular cell injury → inflammation Cardio-renal syndrome |
| Mechanical circulatory support | NT-ProBNP | Loss of pulsatile flow → shear stress Fluid overload → renal vein congestion Hemolysis in extracorporeal circuit Impella (intracorporeal motor)-related hemolysis |
| Decreased cardiac index | Serum bicarbonate, lactate | Organ hypoperfusion leading to ischemic injury |
| Thromboembolism/contrast-induced nephropathy | Contrast medium dose-to-eGFR ratio | Cell-mediated injury Thromboembolic shower during PCI |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, S.; Kanwar, A.; Sundaragiri, P.R.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Truesdell, A.G.; Rab, S.T.; Singh, M.; Vallabhajosyula, S. Acute Kidney Injury in Cardiogenic Shock: An Updated Narrative Review. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2021, 8, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8080088
Singh S, Kanwar A, Sundaragiri PR, Cheungpasitporn W, Truesdell AG, Rab ST, Singh M, Vallabhajosyula S. Acute Kidney Injury in Cardiogenic Shock: An Updated Narrative Review. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2021; 8(8):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8080088
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Sohrab, Ardaas Kanwar, Pranathi R. Sundaragiri, Wisit Cheungpasitporn, Alexander G. Truesdell, Syed Tanveer Rab, Mandeep Singh, and Saraschandra Vallabhajosyula. 2021. "Acute Kidney Injury in Cardiogenic Shock: An Updated Narrative Review" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 8, no. 8: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8080088
APA StyleSingh, S., Kanwar, A., Sundaragiri, P. R., Cheungpasitporn, W., Truesdell, A. G., Rab, S. T., Singh, M., & Vallabhajosyula, S. (2021). Acute Kidney Injury in Cardiogenic Shock: An Updated Narrative Review. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 8(8), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8080088







