Patent Foramen Ovale—A Not So Innocuous Septal Atrial Defect in Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
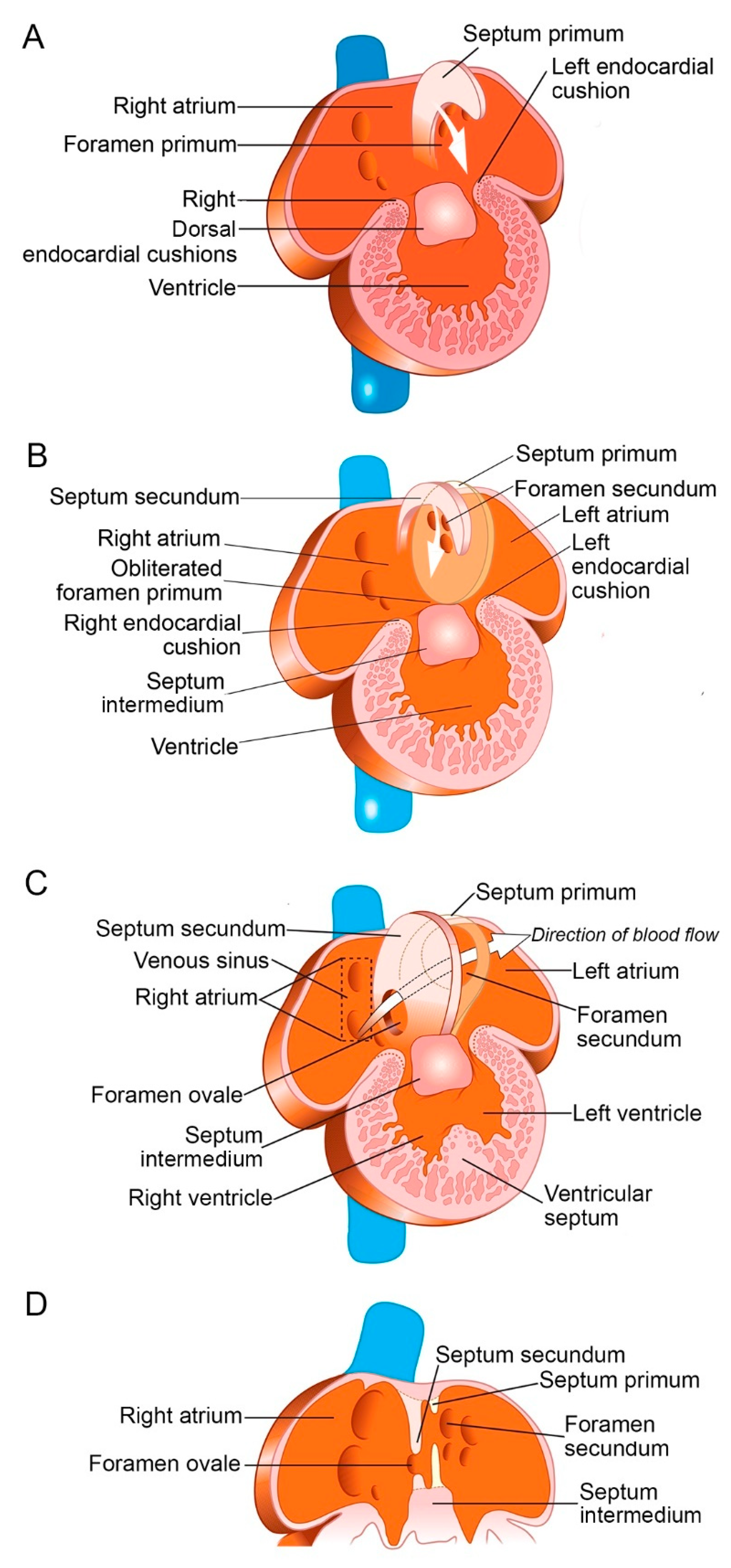
2. Development of Interatrial Septum and Foramen Ovale
3. Foramen Ovale after Birth
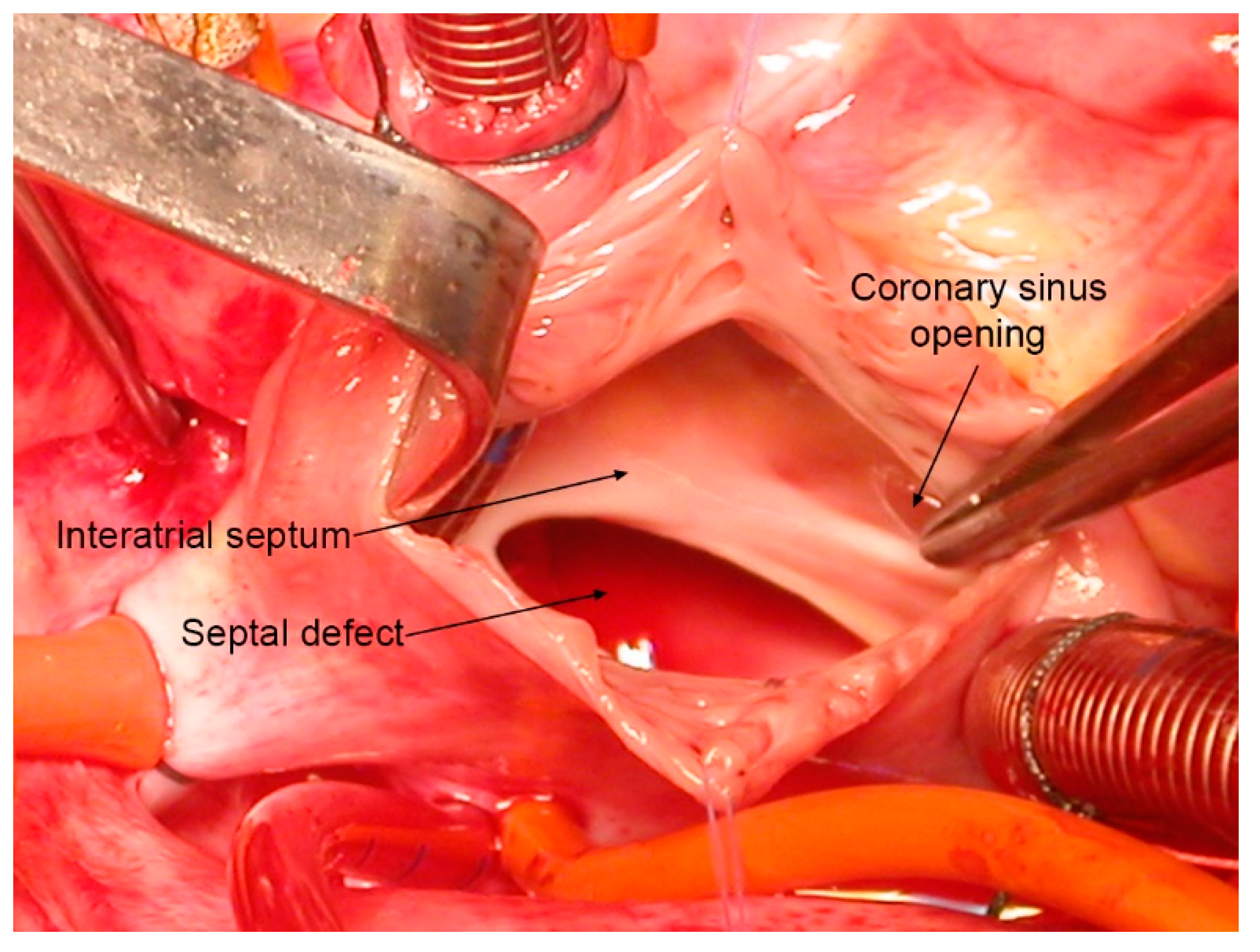
4. Anatomy of PFO
5. Etiology of PFO
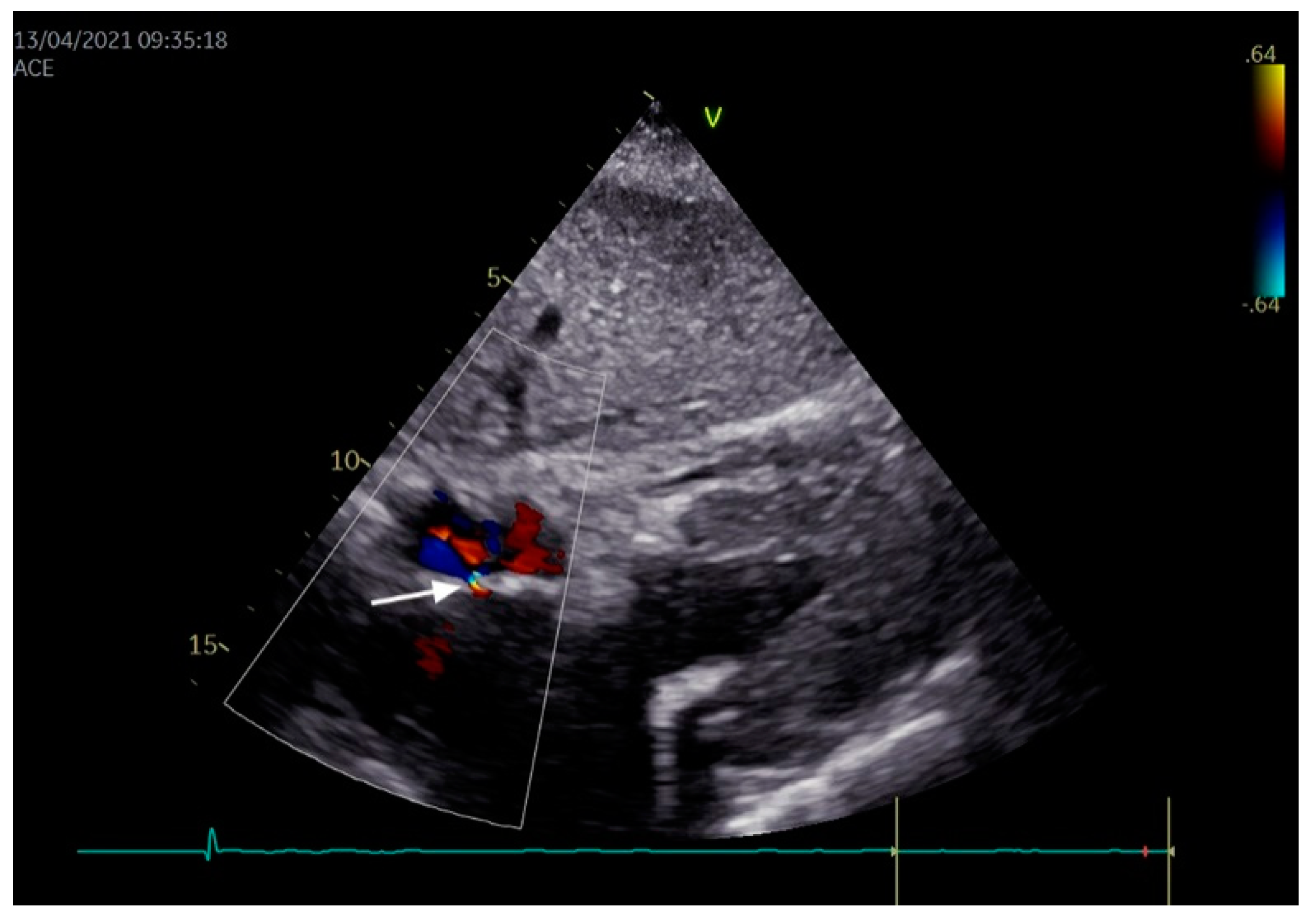
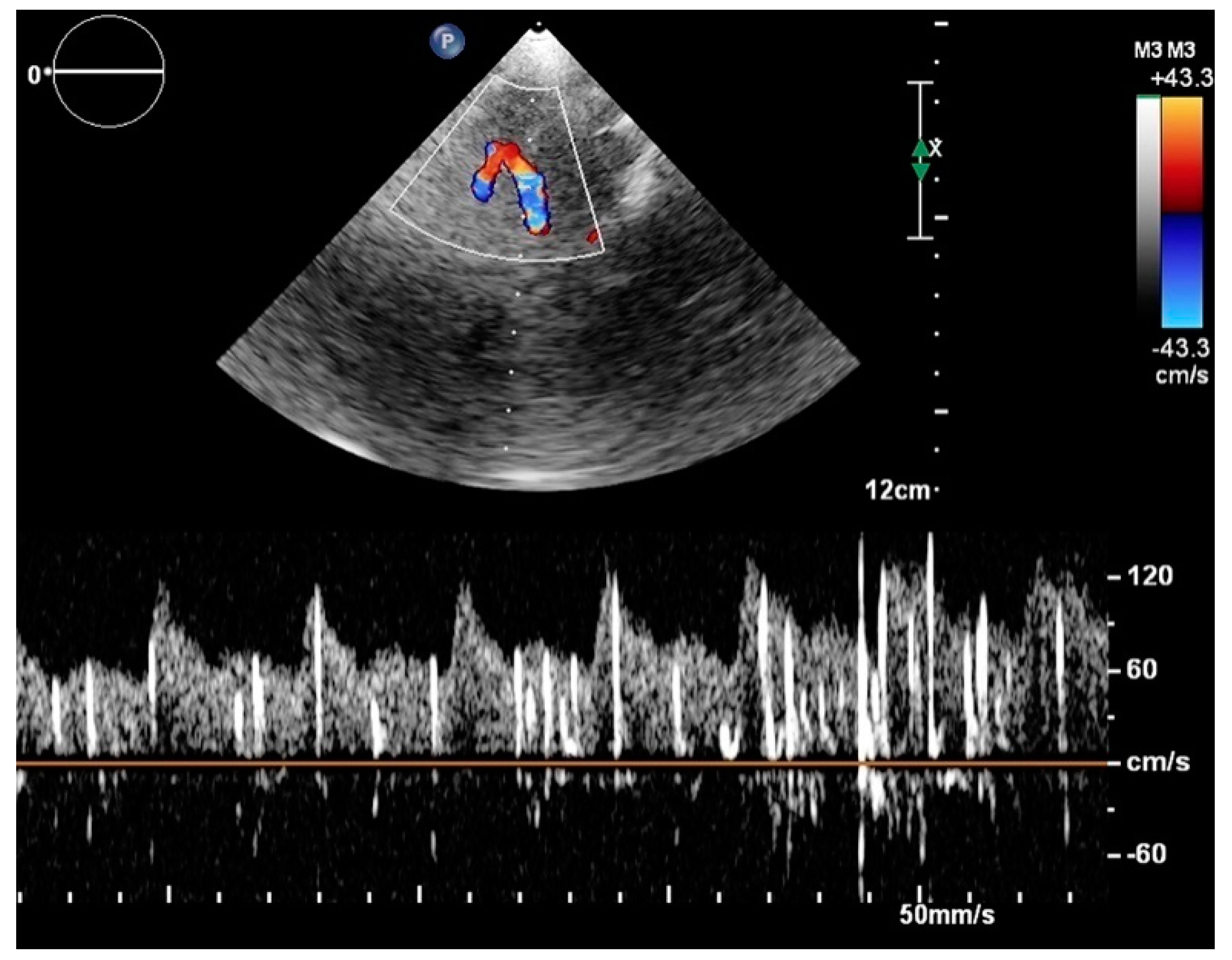
6. Diagnosis of PFO
7. Clinical Features of PFO
8. Diving with PFO
9. Take-Home Message
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teshome, M.K.; Najib, K.; Nwagbara, C.C.; Akinseye, O.A.; Ibebuogu, U.N. Patent foramen ovale: A comprehensive review. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2020, 45, 100392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, K.; Lui, F. Anatomy, Thorax, Heart Foramen Ovale. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31424787/ (accessed on 9 April 2021).
- Jensen, B.; Boukens, B.J.D.; Postma, A.V.; Gunst, Q.D.; van den Hoff, M.J.B.; Moorman, A.F.M.; Wang, T.; Christoffels, V.M. Identifying the evolutionary building blocks of the cardiac conduction system. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.P.; Homma, S. Patent foramen ovale and stroke. Circ. J. 2016, 80, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hołda, M.K.; Koziej, M. Morphometric features of patent foramen ovale as a risk factor of cerebrovascular accidents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pristipino, C.; Sievert, H.; D’Ascenzo, F.; Louis Mas, J.; Meier, B.; Scacciatella, P.; Hildick-Smith, D.; Gaita, F.; Toni, D.; Kyrle, P.; et al. European position paper on the management of patients with patent foramen ovale. General approach and left circulation thromboembolism. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3182–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhouli, M.; Sievert, H.; Holmes, D.R. Patent foramen ovale closure for secondary stroke prevention. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 2339–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.M.; Carroll, J.D. Device closure of patent foramen ovale for cryptogenic stroke: Patient selection and outcomes according to new randomized trials. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2019, 21, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, B.; Fonseca, A.C.; Ferro, J.M. Patent foramen ovale and stroke. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 1943–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.-J.; Lv, J.; Han, X.-T.; Luo, G.-G. Migraine and percutaneous patent foramen ovale closure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2017, 17, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K.; Yoshiyama, M.; Homma, S. Patent foramen ovale and cryptogenic stroke. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 27, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hexdall, E.J.; Cooper, J.S. Patent Foramen Ovale in Diving. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28613763/ (accessed on 9 April 2021).
- Mojadidi, M.K.; Ruiz, J.C.; Chertoff, J.; Zaman, M.O.; Elgendy, I.Y.; Mahmoud, A.N.; Al-Ani, M.; Elgendy, A.Y.; Patel, N.K.; Shantha, G.; et al. Patent foramen ovale and hypoxemia. Cardiol. Rev. 2019, 2, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigatelli, G.; Sharma, S. Patent foramen ovale-obstructive sleep apnea relationships: Pro and cons. Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 2012, 13, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, M. First and Second Heart Field. In Congenital Heart Diseases: The Broken Heart; Rickert-Sperling, S., Kelly, R., Driscoll, D., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, T.; Yang, Y.; Hiriart, E.; Wessels, A. The Dorsal Mesenchymal Protrusion and the Pathogenesis of Atrioventricular Septal Defects. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2016, 3, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.L.; Persaud, T.V.N.; Torchia, M.G. The Developing Human, 10th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 294–298. [Google Scholar]
- Deepe, R.; Fitzgerald, E.; Wolters, R.; Drummond, J.; De Guzman, K.; Van den Hoff, M.J.; Wessels, A. The Mesenchymal Cap of the Atrial Septum and Atrial and Atrioventricular Septation. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2020, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aanhaanen, W.T.J.; Mommersteeg, M.T.M.; Norden, J.; Wakker, V.; de Gier-de Vries, C.; Anderson, R.H.; Kispert, A.; Moorman, A.F.M.; Christoffels, V.M. Developmental origin, growth, and three-dimensional architecture of the atrioventricular conduction axis of the mouse heart. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, N.; McCarthy, K.P.; Ho, S.Y. Anatomy of the atrial septum and interatrial communications. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S2837–S2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standring, S. (Ed.) Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bertini, G. (Ed.) Embriologia Umana; Edizioni Idelson Gnocchi: Napoli, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fazio, G.; Ferro, G.; Barbaro, G.; Fattouch, K.; Ferrara, F.; Novo, G.; Novo, S. Patent foramen ovale and thromboembolic complications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 3497–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, S.; Messé, S.R.; Rundek, T.; Sun, Y.-P.; Franke, J.; Davidson, K.; Sievert, H.; Sacco, R.L.; Di Tullio, M.R. Patent foramen ovale. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 15086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcagni, G.; Unolt, M.; Digilio, M.C.; Baban, A.; Versacci, P.; Tartaglia, M.; Baldini, A.; Marino, B. Congenital heart disease and genetic syndromes: New insights into molecular mechanisms. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 17, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Kartiko, S.; Finnell, R.H. Importance of gene-environment interactions in the etiology of selected birth defects. Clin. Genet. 2009, 75, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, C.; Bevilacqua, G. The prevalence of cardiovascular malformations in offspring of diabetic mothers. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2006, 27, 649–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, I.; Rajakumar, G. Genetics of Congenital Heart Defects: The NKX2-5 Gene, a Key Player. Genes 2016, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granados-Riveron, J.T.; Ghosh, T.K.; Pope, M.; Bu’Lock, F.; Thornborough, C.; Eason, J.; Kirk, E.P.; Fatkin, D.; Feneley, M.P.; Harvey, R.P.; et al. α-Cardiac myosin heavy chain (MYH6) mutations affecting myofibril formation are associated with congenital heart defects. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 4007–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabst, S.; Wollnik, B.; Rohmann, E.; Hintz, Y.; Glänzer, K.; Vetter, H.; Nickenig, G.; Grohé, C. A novel stop mutation truncating critical regions of the cardiac transcription factor NKX2-5 in a large family with autosomal dominant inherited congenital heart disease. Clin. Res.Cardiol. 2008, 97, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basson, C.T.; Cowley, G.S.; Solomon, S.D.; Weissman, B.; Poznanski, A.K.; Traill, T.A.; Seidman, J.G.; Seidman, C.E. The clinical and genetic spectrum of the Holt-Oram syndrome (heart-hand syndrome). N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posch, M.G.; Gramlich, M.; Sunde, M.; Schmitt, K.R.; Lee, S.H.Y.; Richter, S.; Kersten, A.; Perrot, A.; Panek, A.N.; Al Khatib, I.H.; et al. A gain-of-function TBX20 mutation causes congenital atrial septal defects, patent foramen ovale and cardiac valve defects. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 47, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Kasner, S.E. Patent foramen ovale and cryptogenic stroke: Diagnosis and updates in secondary stroke prevention. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2018, 3, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitarelli, A. Patent foramen ovale: Pivotal role of transesophageal echocardiography in the indications for closure, assessment of varying anatomies and post-procedure follow-up. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 1882–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivanovic, Z.; Ruzicka-Kaloci, S.; Jesic, A.; Radovanovic, B.; Lucic-Prokin, A.; Slankamenac, P. Paradoxical emboli: Clinical importance of transcranialdoppler for detection of patent foramen ovale. Med. Pregl. 2010, 63, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeltchev, K.; Mattle, H.P. Contrast-enhanced transcranial doppler ultrasound for diagnosis of patent foramen ovale. Front. Neurol. Neurosci. 2006, 21, 206–215. [Google Scholar]
- Koutroulou, I.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Tsalikakis, D.; Karacostas, D.; Grigoriadis, N.; Karapanayiotides, T. Epidemiology of patent foramen ovale in general population and in stroke patients: A narrative review. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, N.E.; Bangee, M.; Benedetto, V.; Bray, E.P.; Georgiou, R.F.; Gibson, J.M.E.; Lane, D.A.; Al-Khalidi, A.H.; Chatterjee, K.; Chauhan, U.; et al. Etiologic workup in cases of cryptogenicstroke: A systematic review of international clinical practice guidelines. Stroke 2020, 51, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, P.C.; Tajik, A.J.; Hynes, J.K.; Edwards, W.D.; Reeder, G.S.; Hagler, D.J.; Seward, J.B. Diagnosis and classification of atrial septal aneurysm by two-dimensional echocardiography: Report of 80 consecutive cases. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1985, 6, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kijima, Y.; West, B.H.; Tobis, J.M. The connection between patent foramen ovale and migraine. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2019, 29, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayhill, M.; Burch, R. PFO and migraine: Is there a role for closure? Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2017, 17, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Gheewala, N.; Silver, P. Role of patent foramen ovale in migraine etiology and treatment: A review. Echocardiography 2011, 28, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HHoněk, J.; Šrámek, M.; Šefc, L.; Januška, J.; Fiedler, J.; Horváth, M.; Tomek, A.; Novotný, S.; Honěk, T.; Veselka, J. High-grade patent foramen ovale is a risk factor of unprovoked decompression sickness in recreational divers. J. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopsen, R.; Stella, P.R.; Thijs, K.M.; Rienks, R. Persistent foramen ovale closure in divers with a history of decompression sickness. Neth. Heart J. 2018, 26, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.; Ebersole, D.; Covington, D.; Denoble, P.J. The effectiveness of risk mitigation interventions in divers with persistent (patent) foramen ovale. Diving Hyperb. Med. 2019, 49, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torti, S. Risk of decompression illness among 230 divers in relation to the presence and size of patent foramen ovale. Eur. Heart J. 2004, 25, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lairez, O.; Cournot, M.; Minville, V.; Roncalli, J.; Austruy, J.; Elbaz, M.; Galinier, M.; Carrié, D. Risk of neurological decompression sickness in the diver with a right-to-left shunt: Literature review and meta-analysis. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2009, 19, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germonpré, P. Persistent (patent) foramen ovale: Implications for safe diving. Diving Hyperb. Med. 2015, 45, 73–74. [Google Scholar]
- Honěk, J.; Šrámek, M.; Šefc, L.; Januška, J.; Fiedler, J.; Horváth, M.; Tomek, A.; Novotný, S.; Honěk, T.; Veselka, J. Effect of catheter-based patent foramen ovale closure on the occurrence of arterial bubbles in scuba divers. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 7, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pristipino, C.; Germonpré, P.; Toni, D.; Sievert, H.; Meier, B.; D′Ascenzo, F.; Berti, S.; Onorato, E.M.; Bedogni, F.; Mas, J.L.; et al. European position paper on the management of patients with patent for amen ovale. Part II—Decompression sickness, migraine, arterial deoxygenation syndromes and select high-risk clinical conditions. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, B. Permeables foramen ovale (PFO) als todesursache. Med. Klin. Intensivmed. Notfmed. 2020, 115, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honěk, J.; Šrámek, M.; Šefc, L.; Januška, J.; Fiedler, J.; Horváth, M.; Tomek, A.; Novotný, S.; Honěk, T.; Veselka, J. Effect of conservative dive profiles on the occurrence of venous and arterial bubbles in divers with a patent foramen ovale: A pilot study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 176, 1001–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billinger, M.; Zbinden, R.; Mordasini, R.; Windecker, S.; Schwerzmann, M.; Meier, B.; Seiler, C. Patent foramen ovale closure in recreational divers: Effect on decompression illness and is chaemic brain lesions during long-term follow-up. Heart 2011, 97, 1932–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmshurst, P. Risk mitigation in divers with persistent (patent) foramen ovale. Diving Hyperb. Med. J. 2019, 49, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henzel, J.; Rudziński, P.N.; Kłopotowski, M.; Konka, M.; Dzielińska, Z.; Demkow, M. Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale for the secondary prevention of decompression illness in professional divers: A single-centre experience with long-term follow-up. Kardiol. Pol. 2018, 76, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romano, V.; Gallinoro, C.M.; Mottola, R.; Serio, A.; Di Meglio, F.; Castaldo, C.; Sirico, F.; Nurzynska, D. Patent Foramen Ovale—A Not So Innocuous Septal Atrial Defect in Adults. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2021, 8, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8060060
Romano V, Gallinoro CM, Mottola R, Serio A, Di Meglio F, Castaldo C, Sirico F, Nurzynska D. Patent Foramen Ovale—A Not So Innocuous Septal Atrial Defect in Adults. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2021; 8(6):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8060060
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomano, Veronica, Carlo Maria Gallinoro, Rosita Mottola, Alessandro Serio, Franca Di Meglio, Clotilde Castaldo, Felice Sirico, and Daria Nurzynska. 2021. "Patent Foramen Ovale—A Not So Innocuous Septal Atrial Defect in Adults" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 8, no. 6: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8060060
APA StyleRomano, V., Gallinoro, C. M., Mottola, R., Serio, A., Di Meglio, F., Castaldo, C., Sirico, F., & Nurzynska, D. (2021). Patent Foramen Ovale—A Not So Innocuous Septal Atrial Defect in Adults. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 8(6), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd8060060









