Analysis of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme, Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase & Serotonin Gene Polymorphisms among Atrial Septal Defect Subjects with and without Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genetic Analysis
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humbert, M.; Sitbon, O.; Chaouat, A.; Bertocchi, M.; Habib, G.; Gressin, V.; Yaici, A.; Weitzenblum, E.; Cordier, J.F.; Chabot, F.; et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension in france: Results from a national registry. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barst, R.J. Pulmonary hypertension: Past, present and future. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2008, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedford, R.J.; Mudd, J.O.; Girgis, R.E.; Mathai, S.C.; Zaiman, A.L.; Housten-Harris, T.; Boyce, D.; Kelemen, B.W.; Bacher, A.C.; Shah, A.A.; et al. Right ventricular dysfunction in systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ. Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, B.J. Changing demographics of pulmonary arterial hypertension in congenital heart disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2010, 19, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, E.; Kassem, A.; Zakaria, N. The role of the biomarker and the genetic polymorphism of endothelin-1 in pulmonary arterial hypertension among egyptians. Egypt. J. Chest Dis. Tuberc. 2012, 61, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, A.K.; Dean, A.; Morecroft, I.; Hood, K.; Nilsen, M.; Loughlin, L.; Anagnostopoulou, A.; Touyz, R.M.; White, K.; MacLean, M.R. The serotonin transporter promotes a pathological estrogen metabolic pathway in pulmonary hypertension via cytochrome p450 1b1. Pulm. Circ. 2016, 6, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, M.; Xia, J.; Qin, R.Y. Association between serotonin transporter (sert) gene polymorphism and idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension: A meta-analysis and review of the literature. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2013, 62, 1867–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heils, A.; Teufel, A.; Petri, S.; Stober, G.; Riederer, P.; Bengel, D.; Lesch, K.P. Allelic variation of human serotonin transporter gene expression. J. Neurochem. 1996, 66, 2621–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vachharajani, A.; Saunders, S. Allelic variation in the serotonin transporter (5HTT) gene contributes to idiopathic pulmonary hypertension in children. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 334, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, S.; Szamalek-Hoegel, J.; Hersberger, M.; Fischler, M.; Garcia, J.S.; Huber, L.C.; Grunig, E.; Janssen, B.; Speich, R. Sequence variants in bmpr2 and genes involved in the serotonin and nitric oxide pathways in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: Relation to clinical parameters and comparison with left heart disease. Respir. Int. Rev. Thorac. Dis. 2010, 79, 279–287. [Google Scholar]
- Vadapalli, S.; Rani, H.S.; Sastry, B.; Nallari, P. Endothelin-1 and endothelial nitric oxide polymorphisms in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Genet. 2010, 1, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.Q.; Wen, J.G.; Zhou, H.H.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, W. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene g894t polymorphism and myocardial infarction: A meta-analysis of 34 studies involving 21,068 subjects. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, R.; Gonzalez, P.; Batalla, A.; Reguero, J.R.; Iglesias-Cubero, G.; Hevia, S.; Cortina, A.; Merino, E.; Gonzalez, I.; Alvarez, V.; et al. Association between the nos3 (-786 t/c) and the ace (i/d) DNA genotypes and early coronary artery disease. Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem. 2001, 5, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, V.; Ismail, P.; Stanslas, J.; Shamsudin, N.; Moin, S.; Mohd Jas, R. Association of insertion/deletion polymorphism of angiotensin-converting enzyme gene with essential hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus in malaysian subjects. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldost. Syst. JRAAS 2008, 9, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Fan, G.; Sun, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, S.; Niu, W. Association of angiotensin-converting enzyme gene i/d polymorphism with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A meta-analysis. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldost. Syst. JRAAS 2018, 19, 1470320318770546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlak, R.; Homa-Mlak, I.; Powrozek, T.; Mackiewicz, B.; Michnar, M.; Krawczyk, P.; Dziedzic, M.; Rubinsztajn, R.; Chazan, R.; Milanowski, J.; et al. Impact of i/d polymorphism of ace gene on risk of development and course of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Arch. Med. Sci. AMS 2016, 12, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista, L.E.; Ardila, M.E.; Gamarra, G.; Vargas, C.I.; Arenas, I.A. Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphism and risk of myocardial infarction in colombia. Med. Sci. Monit. 2004, 10, CR473–CR479. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bahramali, E.; Rajabi, M.; Jamshidi, J.; Mousavi, S.M.; Zarghami, M.; Manafi, A.; Firouzabadi, N. Association of ace gene d polymorphism with left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with diastolic heart failure: A case-control study. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, W.T.; Raynolds, M.V.; Badesch, D.B.; Wynne, K.M.; Groves, B.M.; Roden, R.L.; Robertson, A.D.; Lowes, B.D.; Zisman, L.S.; Voelkel, N.F.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme dd genotype in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension: Increased frequency and association with preserved haemodynamics. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldost. Syst. JRAAS 2003, 4, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddahibi, S.; Humbert, M.; Fadel, E.; Raffestin, B.; Darmon, M.; Capron, F.; Simonneau, G.; Dartevelle, P.; Hamon, M.; Adnot, S. Serotonin transporter overexpression is responsible for pulmonary artery smooth muscle hyperplasia in primary pulmonary hypertension. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guignabert, C.; Izikki, M.; Tu, L.I.; Li, Z.; Zadigue, P.; Barlier-Mur, A.M.; Hanoun, N.; Rodman, D.; Hamon, M.; Adnot, S.; et al. Transgenic mice overexpressing the 5-hydroxytryptamine transporter gene in smooth muscle develop pulmonary hypertension. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willers, E.D.; Newman, J.H.; Loyd, J.E.; Robbins, I.M.; Wheeler, L.A.; Prince, M.A.; Stanton, K.C.; Cogan, J.A.; Runo, J.R.; Byrne, D.; et al. Serotonin transporter polymorphisms in familial and idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, R.D.; Koehler, R.; Glissmeyer, E.; Veal, C.; Suntharalingam, J.; Kim, M.; Carlquist, J.; Town, M.; Elliott, C.G.; Hoeper, M.; et al. Genetic association of the serotonin transporter in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulasli, S.S.; Eyuboglu, F.O.; Verdi, H.; Atac, F.B. Associations between endothelial nitric oxide synthase A/B, angiotensin converting enzyme I/D and serotonin transporter L/S gene polymorphisms with pulmonary hypertension in COPD patients. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 5625–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, P.; Oflaz, H.; Cine, N.; Erginel-Unaltuna, N.; Erzengin, F.; Yilmaz, V. Gene polymorphisms of endothelial nitric oxide synthase enzyme associated with pulmonary hypertension in patients with copd. Respir. Med. 2003, 97, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, A.; Ram, R.; Baig, M.A.; Pasha, M.A. Ace i allele and enos g allele crosstalk may have a role in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 37, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Tacacs, A.; Stellmacher, U.; Lichtinghagen, R. Lack of association between angiotensin converting enzyme (ace) genotype, serum ace activity, and haemodynamics in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Heart 2003, 89, 445–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togănel, R.; Muntean, I.; Duicu, C.; Făgărăşan, A.; Gozar, L.; Bănescu, C. The role of enos and agt gene polymorphisms in secondary pulmonary arterial hypertension in romanian children with congenital heart disease. Rom. J. Lab. Med. 2013, 21, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kikuchi, S.; Suzuki, H.; Nagase, S.; Koyama, A. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphism in intron 4 affects the progression of renal failure in non-diabetic renal diseases. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1999, 14, 2898–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tkacova, R.; Joppa, P.; Stancak, B.; Salagovic, J.; Misikova, S.; Kalina, I. The link between angiotensin-converting enzyme genotype and pulmonary artery pressure in patients with copd. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift 2005, 117, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togănel, R.; Bănescu, C.; Duicu, C.; Şuteu, C.; Muntean, I.; Făgărăşan, A.; Gozar, L.; Pasc, S. Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphisms in pulmonary arterial hypertension in children. Revista Română Medicină Lab. 2010, 18, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiee, S.M.; Firoozrai, M.; Salimi, S.; Zand, H.; Hesabi, B.; Mohebbi, A. Angiotensin converting enzyme dd genotype not associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease in the iranian population. Pathophysiology 2010, 17, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, K.; Narang, R.; Sreenivas, V.; Das, S.; Das, N. Association of enos glu298asp gene polymorphism with essential hypertension in asian indians. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 387, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, S.; Hersberger, M.; Fischler, M.; Nussbaumer-Ochsner, Y.; Treder, U.; Russi, E.W.; Speich, R. Genetic polymorphisms of the serotonin transporter, but not the 2a receptor or nitric oxide synthetase, are associated with pulmonary hypertension in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Int. Rev. Thorac. Dis. 2010, 79, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vasudevan, R.; Ismail, P.; Jaafar, N.; Mohamad, N.; Etemad, E.; WS, W.A.; Eshkor, S. Analysis of human bradykinin receptor gene and endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphisms in end-stage renal disease among malaysians. Balkan J. Med. Genet. 2014, 17, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baloira, A.; Nunez, M.; Cifrian, J.; Vilarino, C.; Ojeda, M.; Valverde, D. Polymorphisms in the serotonin transporter protein (sert) gene in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2012, 48, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Gu, H.; Qiu, W.; Zuo, W.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Y. Association study of serotonin transporter gene polymorphisms and ventricular septal defects related possible pulmonary arterial hypertension in chinese population. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2009, 31, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
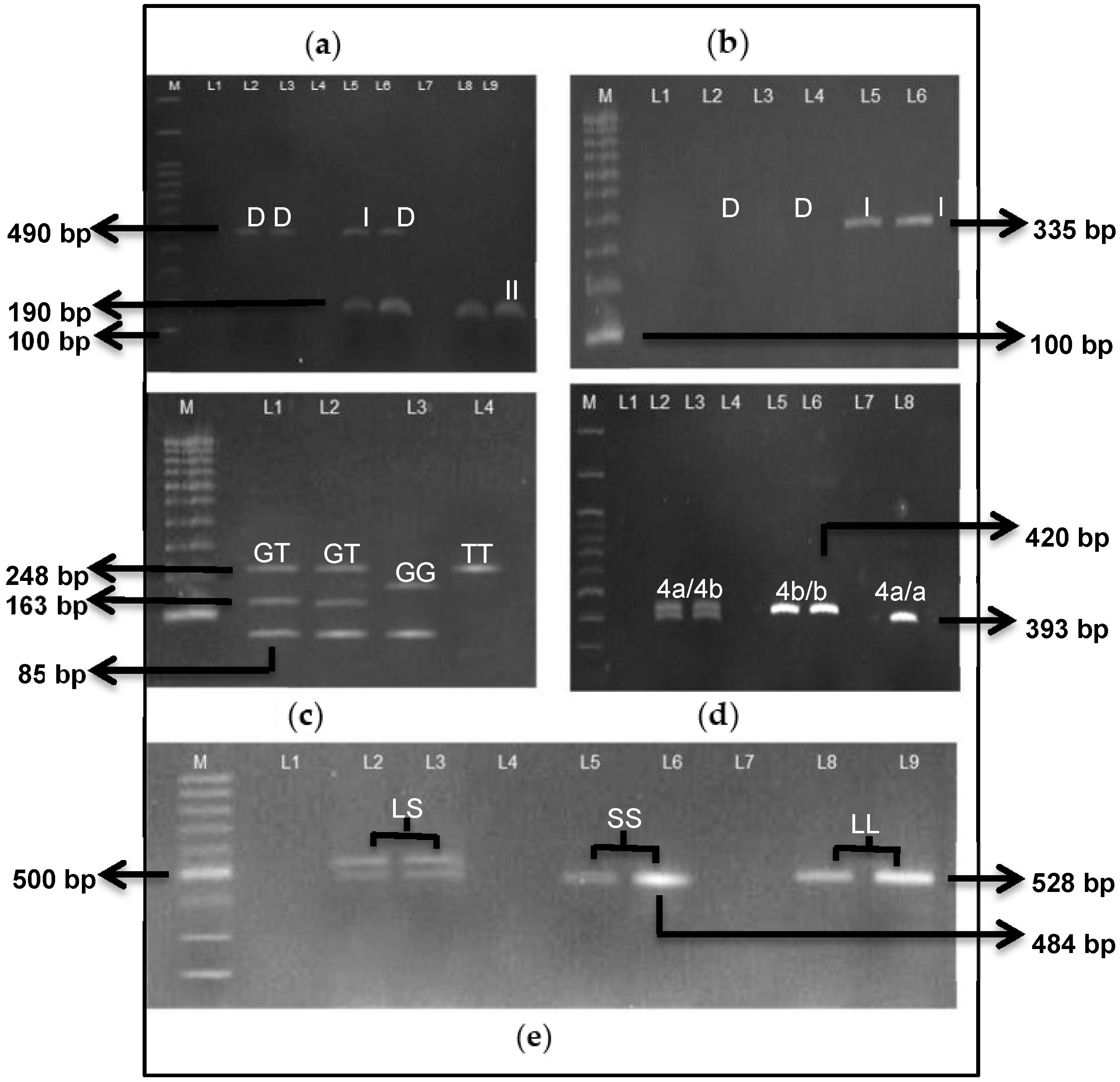
| Gene Polymorphisms | Primers | PCR Cycling Conditions | PCR Products (bp) | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACE I/D (rs4340) | Forward: 5′-CTG GAG ACC ACT CCC ATC CTT TCT-3′ Reverse: 5′-GAT GTG GCC ATC ACA TTC GTC ACG -AT-3′ | Denaturation Annealing Extension Final Extension Number of Cycles | 95 °C, 1 min 58 °C, 2 min 72 °C, 1 min 72 °C, 2 min 30 cycles | 190—DD 490—II 40 & 190—ID | [20] |
| ACE mistyping | Forward: 5′-TGG GAC CAC AGC GCC CGC CAC TAC-3′ Reverse: 5′-TCG CCA GCC CTC CCA TGC CCA TAA-3′ | Denaturation Annealing Extension Final Extension Number of Cycles | 94 °C, 30 s 67 °C, 45 s 72 °C, 2 min 72 °C, 2 min 30 cycles | 353—I allele no band—DD | [21] |
| eNOS G894T (rs1799983) | Forward: 5′-AAG GCA GGA GAC AGT GGA TGG A-3′ Reverse: 5′-CCC AGT CAA TCC CTT TGG TGC TCA-3′ | Denaturation Annealing Extension Final Extension Number of Cycles | 94 °C, 30 s 62.8 °C, 30 s 72 °C, 2 min 72 °C, 5 min 35 cycles | 248 | [22] |
| eNOS 4b/4a | Forward: 5′-AGG CCC TAT GGT AGT GCC TTT-3′ Reverse: 5′-TCT CTT AGT GCT GTG GTC AC-3′ | Denaturation Annealing Extension Final Extension Number of Cycles | 94 °C, 1 min 56 °C, 1 min 72 °C, 2 min 72 °C, 7 min 35 cycles | 393—4a/a 420—4b/b 393 & 420—4a/b | [23] |
| 5-HTTLPR (rs25531) | Forward: 5′-GGC GTT GCC GCT CTG AAT GC-3′ Reverse: 5′-GGC GTT GCC GCT CTG AAT GC-3′ | Denaturation Annealing Extension Final Extension Number of Cycles | 94 °C, 30 s 61 °C, 30 s 72 °C, 1 min 72 °C, 10 min 35 cycles | 528—LL 484—SS 484 & 528—LS | [24] |
| Parameter | Case Subjects (ASD with PAH) | Control Subjects (ASD without PAH) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, M/F | 2/28 | 6/44 | - |
| Age | 33.33 ± 9.316 | 37.50 ± 14.971 | 0.174 |
| Age diagnosed | 28.97 ± 8.838 | 32.80 ± 14.474 | 0.194 |
| Diameter of defects (cm) | 3.19 ± 4.018 | 1.88 ± 0.852 | * 0.028 |
| MAP (mmHg) | 89.30 ± 12.438 | 78.82 ± 18.169 | * 0.007 |
| mPAP (mmHg) | 58.88 ± 14.53 | 22.04 ± 10.517 | * 0.000 |
| Gene Polymorphism | PAH Patients (n = 30) n (%) | Control Subjects (n = 50) n (%) | p Value | Odds Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACE I/D | Genotypes | 0.68 (0.33–1.41) | |||
| II | 17 (56.67%) | 22 (44%) | 0.53 | ||
| ID | 12 (40%) | 25 (50%) | |||
| DD | 1 (3.33%) | 3 (6%) | |||
| Alleles | |||||
| I | 46 (76.67%) | 69 (69%) | 0.30 | ||
| D | 14 (23.33%) | 31 (31%) | |||
| eNOS G894T | Genotypes | ||||
| GG | 0 (0%) | 1 (2%) | 0.63 | 0.98 (0.51–1.85) | |
| GT | 29 (96.67%) | 47 (94%) | |||
| TT | 1 (3.33%) | 2 (4%) | |||
| Alleles | |||||
| G | 29 (48.33%) | 49 (49%) | 0.94 | ||
| T | 31 (51.67%) | 51 (51%) | |||
| eNOS 4b/4a | Genotypes | ||||
| 4b/b (wild type) | 21 (70%) | 35 (70%) | 0.57 | 1.217 (0.56–2.64) | |
| 4a/a (mutant) | 5 (16.7%) | 5 (10%) | |||
| 4a/b | 4 (13.3%) | 10 (20%) | |||
| Alleles | |||||
| a | 14 (23.33%) | 20 (20%) | 0.62 | ||
| b | 46 (76.67%) | 80 (80%) | |||
| 5-HTTLPR | Genotypes | 0.43 (0.22–0.82) | |||
| SS | 6 (20%) | 23 (46%) | 0.06 | ||
| LL | 12 (40%) | 12 (24%) | |||
| LS | 12 (40%) | 15 (30%) | |||
| Alleles | |||||
| S | 24 (40%) | 61 (61%) | * 0.01 | ||
| L | 36 (60%) | 39 (39%) | |||
| Gene Polymorphism | ASD with PAH (Case) | ASD without PAH (Control) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age * | Size of Defect * | MAP * (mmHg) | mPAP * (mmHg) | Age * | Size of Defect * | MAP * (mmHg) | mPAP * (mmHg) | |
| ACE I/D | ||||||||
| II | 32.71 ± 9.51 | 2.59 ± 0.88 | 90.71 ± 10.51 | 59.09 ± 17.53 | 36.95 ± 13.54 | 2.18 ± 0.77 | 72.86 ± 23.51 | 24.23 ± 12.59 |
| ID | 34.42 ± 9.75 | 4.29 ± 6.23 | 87.25 ± 15.48 | 58.92 ± 10.40 | 39.64 ± 16.03 | 1.66 ± 0.83 | 84.20 ± 10.79 | 20.64 ± 8.58 |
| DD | 31.00 ± 0.00 | 0.22 ± 0.00 | 90.00 ± 0.00 | 55.00 ± 0.00 | 23.67 ± 11.59 | 1.44 ± 1.24 | 77.67 ± 11.68 | 17.67 ± 7.64 |
| eNOS G894T | ||||||||
| GG | - | - | - | - | 29.00 ± 0.00 | 1.96 ± 0.00 | 77.00 ± 0.00 | 17.00 ± 0.00 |
| GT | 32.66 ± 8.69 | 3.22 ± 4.09 | 89.10 ± 12.61 | 58.98 ± 14.77 | 38.07 ± 15.48 | 1.91 ± 0.85 | 78.54 ± 18.90 | 35.11 ± 21.98 |
| TT | 53.00 ± 0.00 | 2.30 ± 0.00 | 95.00 ± 0.00 | 56.00 ± 0.00 | 31.67 ± 1.53 | 1.27 ± 0.90 | 83.67 ± 4.04 | 35.75 ± 17.21 |
| eNOS 4b/4a | ||||||||
| 4b/b | 35.48 ± 9.82 | 3.60 ± 4.45 | 89.29 ± 13.17 | 58.07 ± 14.23 | 38.37 ± 16.24 | 1.94 ± 0.87 | 78.91 ± 11.78 | 21.69 ± 9.40 |
| 4a/b | 27.50 ± 8.43 | 3.75 ± 3.59 | 93.25 ± 15.15 | 71.50 ± 13.48 | 36.90 ± 13.34 | 1.85 ± 0.82 | 78.50 ± 24.29 | 26.70 ± 14.47 |
| 4a/a | 29.00 ± 3.54 | 1.05 ± 1.23 | 86.20 ± 7.40 | 52.20 ± 12.76 | 32.60 ± 8.17 | 1.47 ± 0.82 | 78.70 ± 5.40 | 15.20 ± 4.32 |
| 5-HTTLPR | ||||||||
| SS | 36.00 ± 9.80 | 2.77 ± 0.77 | 93.33 ± 8.60 | 52.67 ± 11.38 | 38.52 ± 15.73 | 1.87 ± 0.87 | 78.35 ± 20.18 | 22.65 ± 11.27 |
| LS | 33.50 ± 10.71 | 4.57 ± 6.12 | 88.08 ± 11.57 | 59.08 ± 17.05 | 40.13 ± 14.82 | 1.98 ± 0.71 | 78.87 ± 19.70 | 22.20 ± 10.52 |
| LL | 31.83 ± 8.01 | 2.04 ± 1.09 | 88.50 ± 15.14 | 61.79 ± 13.28 | 32.25 ± 13.51 | 1.76 ± 1.02 | 79.66 ± 12.70 | 20.67 ± 11.45 |
| Population | Disease | No | Genotypes (%) | Allele (%) | Study | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACE I/D | II | ID | DD | p Value | I | D | p Value | |||
| Malaysia | HPT | 65 | 36.9 | 52.3 | 10.8 | * | 63.08 | 36.92 | ** | [14] |
| USA | PPH | 60 | 45 | 35 | 20 | ** | - | - | - | [19] |
| Caucasian | COPD | 66 | 22.73 | 46.97 | 30.3 | * | - | - | - | [30] |
| Romania | PAH | 29 | 6.90 | 58.62 | 34.48 | * | 39.58 | 60.42 | * | [31] |
| German | PPH | 51 | 9.8 | 58.82 | 31.37 | NS | - | - | - | [27] |
| Iran | CAD | 224 | 12.5 | 38.84 | 48.66 | NS | 31.92 | 68.08 | NS | [32] |
| Malaysia | PAH | 30 | 56.67 | 40.0 | 3.33 | NS | 76.67 | 23.33 | NS | Current study |
| eNOS G894T | GG | GT | TT | G | T | |||||
| Germany | IPAH | 16 | 27 | 53 | 20 | NS | 53 | 47 | NS | [10] |
| India | IPAH | 77 | 50.65 | 41.16 | 51.95 | NS | 72.73 | 27.27 | NS | [11] |
| India | EH | 226 | 139 | 82 | 5 | *** | 79.65 | 20.35 | *** | [33] |
| Malaysia | PAH | 30 | 0 | 96.67 | 3.33 | NS | 48.33 | 51.67 | NS | Current study |
| eNOS 4b/4a | bb | ab | Aa | p | a | b | ||||
| Germany | IPAH | 16 | 67 | 33 | - | NS | 83 | 17 | NS | [10] |
| Turkey | PH in COPD | 24 | 83 | 17 | 0 | * | 8.33 | 91.67 | - | [25] |
| Swiss | PH in COPD | 27 | 63 | 33 | 4 | NS | 20.37 | 79.63 | - | [34] |
| Malaysia | ESRD | 150 | 87.33 | 11.33 | 1.33 | NS | 93 | 7 | NS | [35] |
| Malaysia | PAH | 30 | 70 | 16.67 | 13.33 | NS | 23.33 | 58.78 | NS | Current study |
| 5-HTTLPR | SS | LS | LL | p | S | L | ||||
| Caucasian | IPAH | 11 | 81.82 | 0 | 18.18 | * | 18.18 | 81.82 | - | [9] |
| Germany | COPD + PAH | 27 | 18.52 | 59.26 | 22.22 | - | 51.85 | 48.15 | * | [10] |
| Spain | IPAH + 2° PAH | 49 | 26.53 | 28.15 | 20.41 | NS | 46.94 | 53.06 | - | [36] |
| Chinese | VSD-related PAH | 140 | 50.71 | 36.43 | 12.86 | * | 31.07 | 68.93 | - | [37] |
| Malaysia | PAH | 30 | 20 | 40 | 40 | NS | 40 | 60 | * | Current study |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaafar, N.I.; Vasudevan, R.; Ismail, P.; Abdul Aziz, A.F.; Mohamad, N.A.; Kandavello, G.; Raja Adnan, R.N.E.; Balasubramaniam, V. Analysis of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme, Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase & Serotonin Gene Polymorphisms among Atrial Septal Defect Subjects with and without Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2018, 5, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd5030048
Jaafar NI, Vasudevan R, Ismail P, Abdul Aziz AF, Mohamad NA, Kandavello G, Raja Adnan RNE, Balasubramaniam V. Analysis of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme, Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase & Serotonin Gene Polymorphisms among Atrial Septal Defect Subjects with and without Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2018; 5(3):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd5030048
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaafar, Nur Ilyana, Ramachandran Vasudevan, Patimah Ismail, Ahmad Fazli Abdul Aziz, Nur Afiqah Mohamad, Geetha Kandavello, Raja Nurzatul Effah Raja Adnan, and Vinod Balasubramaniam. 2018. "Analysis of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme, Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase & Serotonin Gene Polymorphisms among Atrial Septal Defect Subjects with and without Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 5, no. 3: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd5030048
APA StyleJaafar, N. I., Vasudevan, R., Ismail, P., Abdul Aziz, A. F., Mohamad, N. A., Kandavello, G., Raja Adnan, R. N. E., & Balasubramaniam, V. (2018). Analysis of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme, Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase & Serotonin Gene Polymorphisms among Atrial Septal Defect Subjects with and without Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 5(3), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd5030048






