Impact of Intrapericardial Fluid on Lesion Size During Epicardial Radiofrequency Ablation: A Computational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
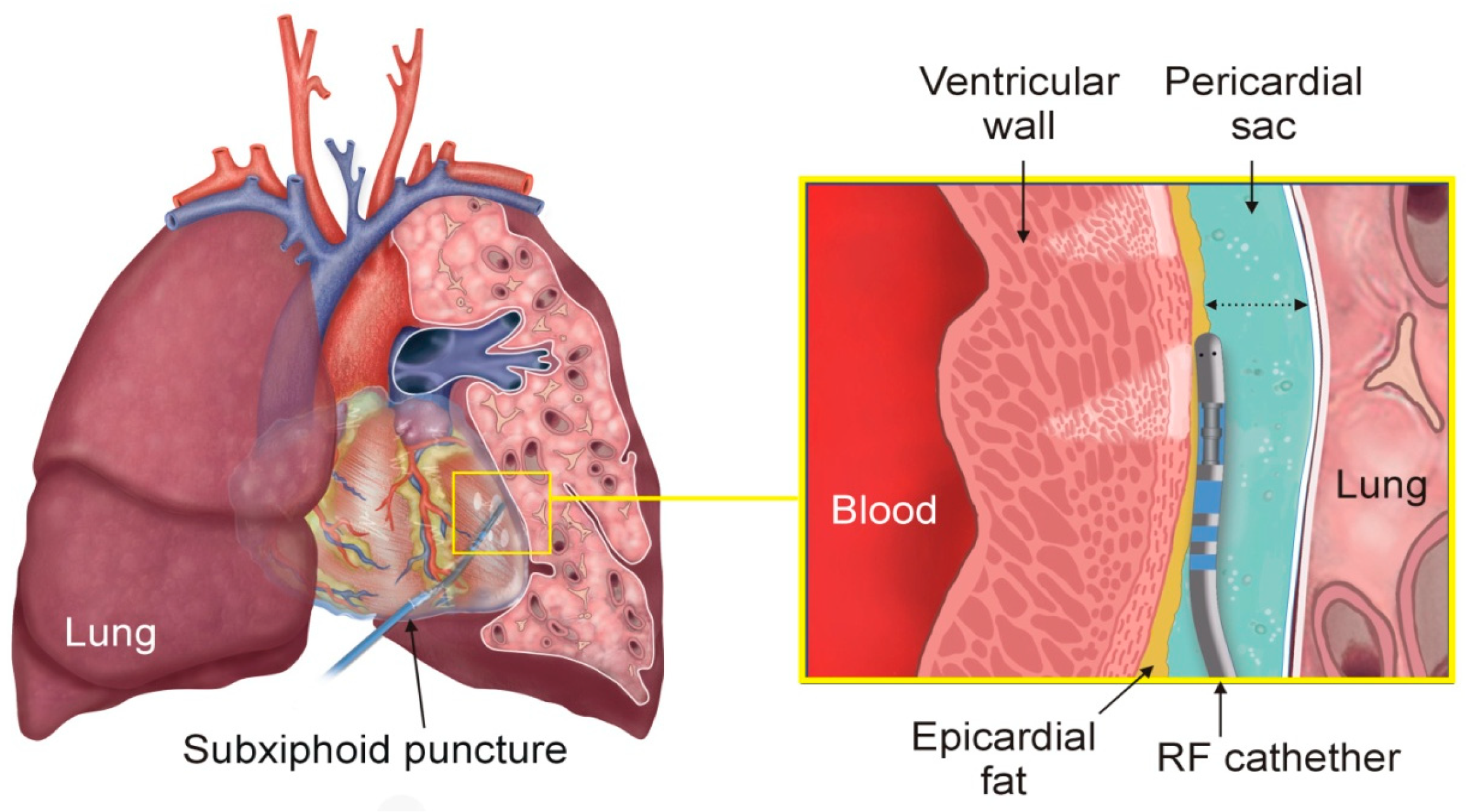
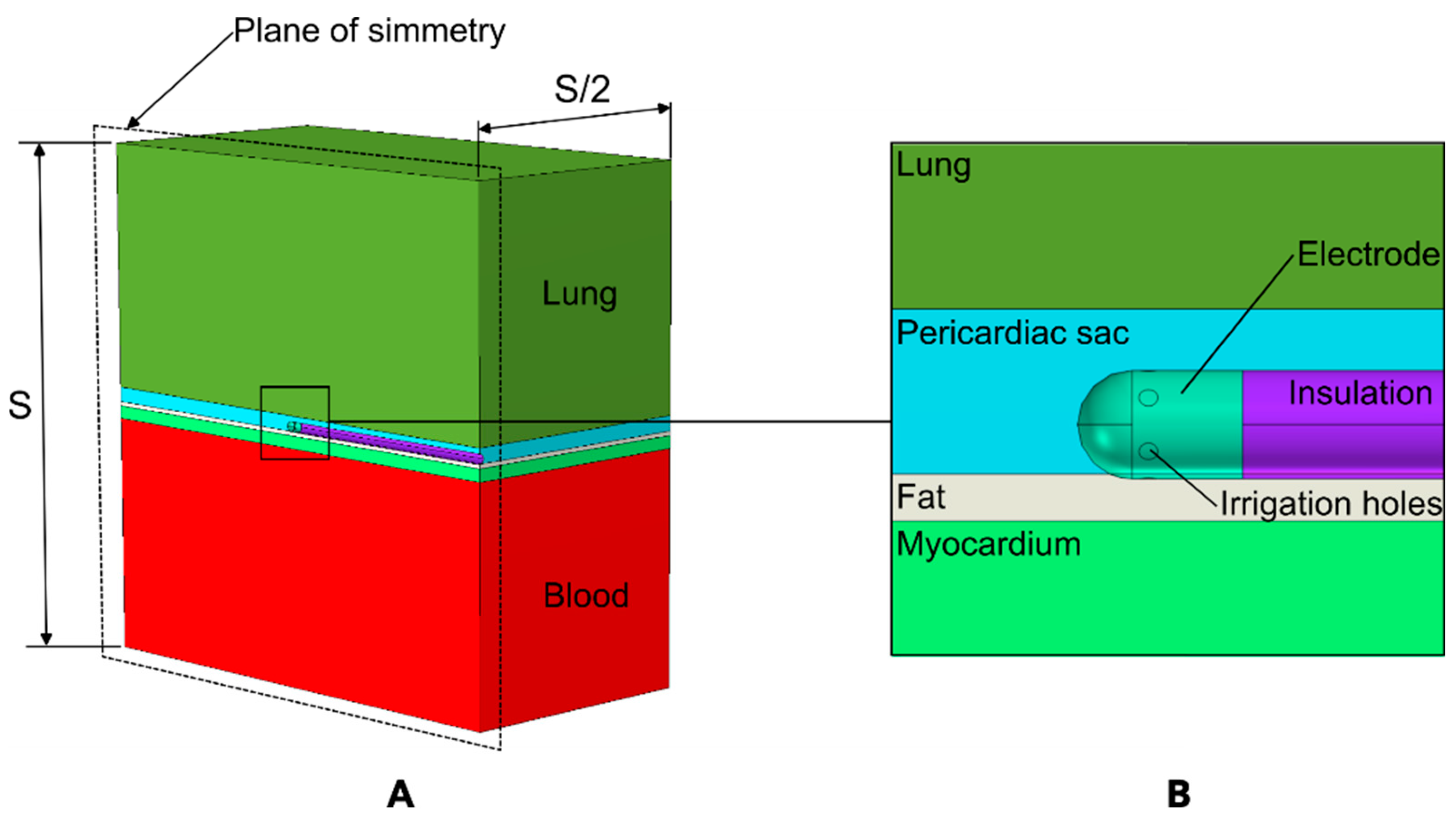
2.1. Model Geometry
2.2. Underlying Biophysics
2.3. Properties of Materials and Tissues
3. Results
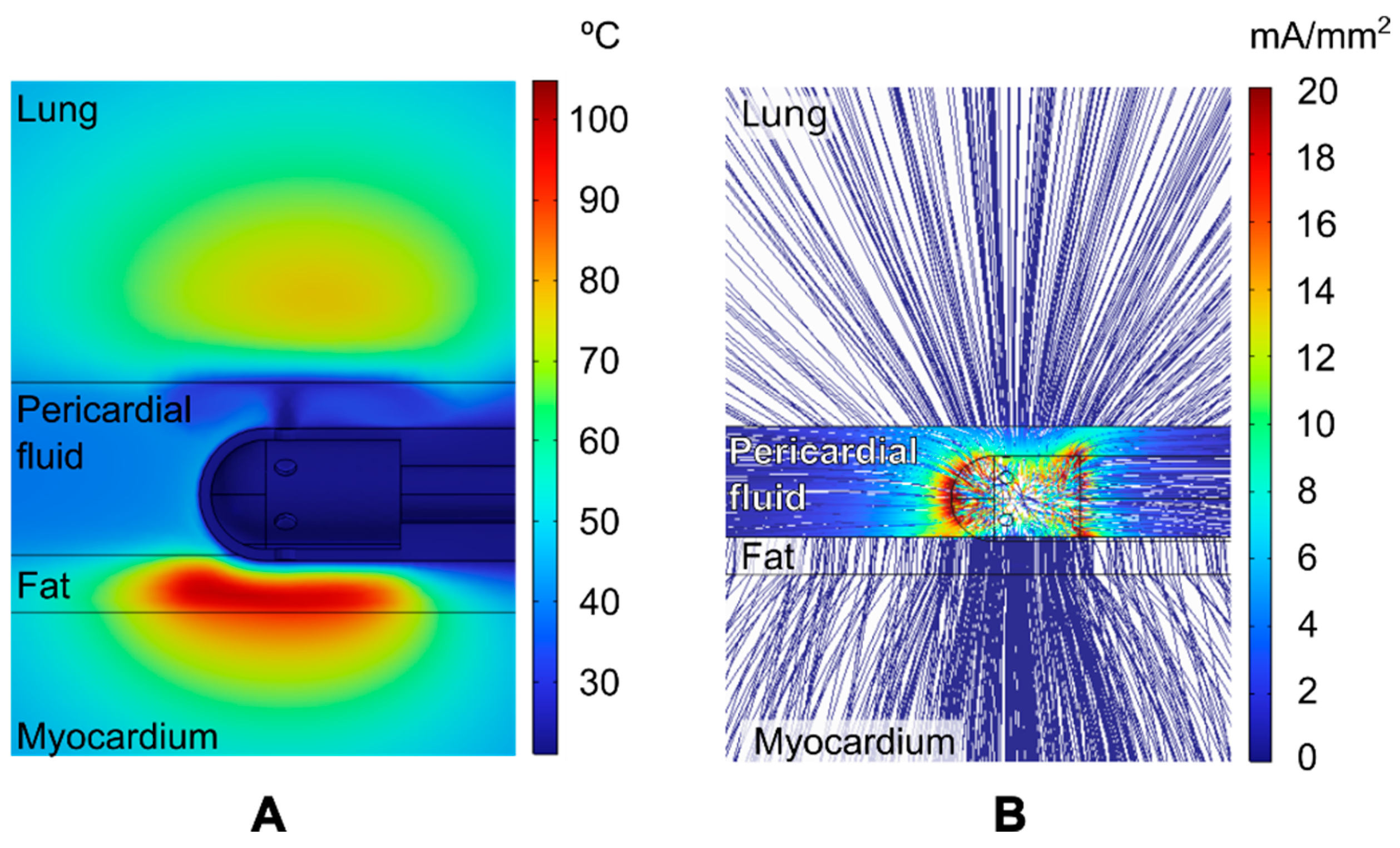
3.1. Overview of the Thermal and Electrical Performance
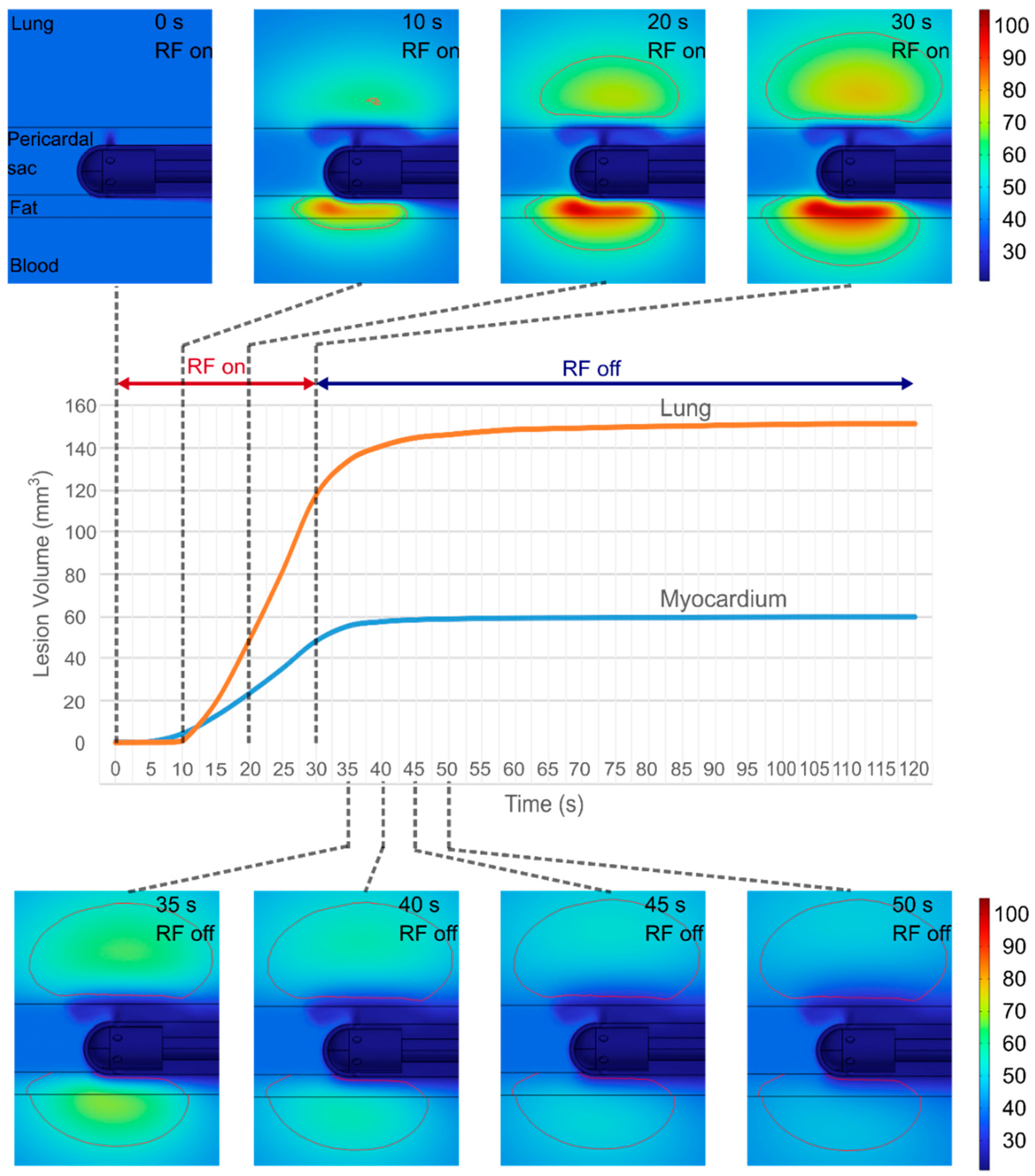
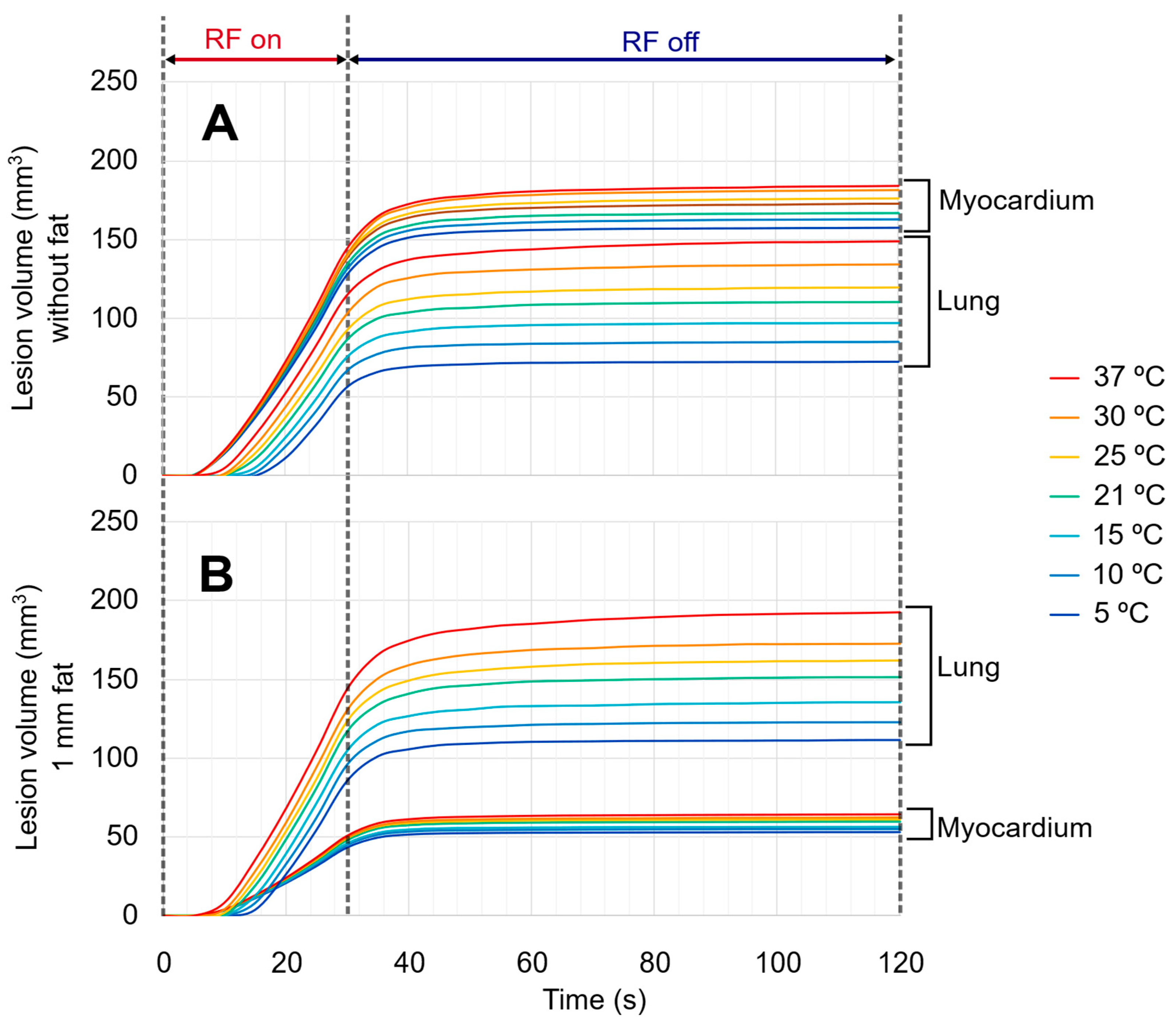
3.2. Evolution of Lesion Volume in Myocardium and Lung
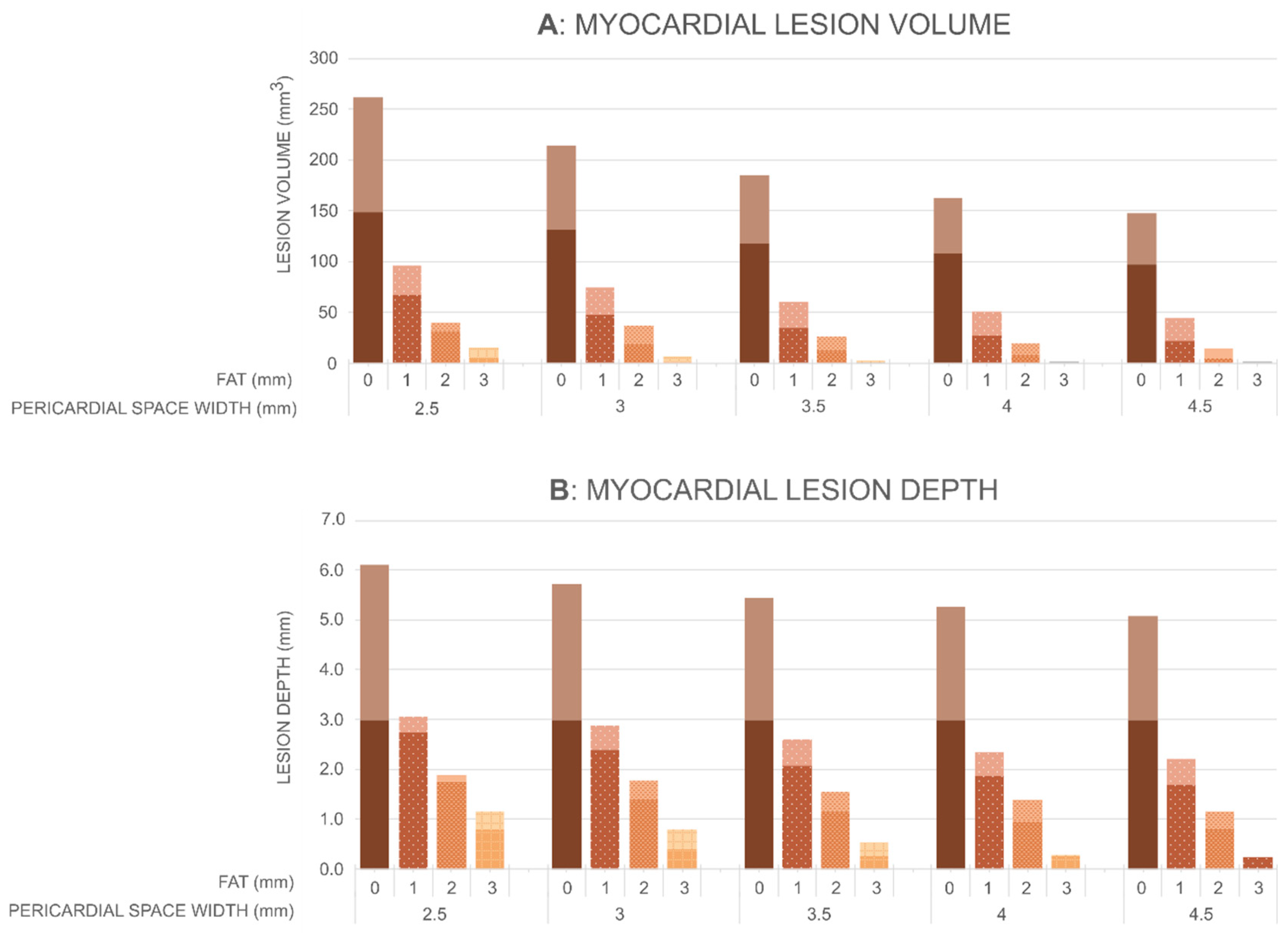
3.3. Effect of the Anatomical Parameters on Myocardium and Lung Lesion
3.4. Effect of Irrigation Fluid Temperature
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Pericardial Space on the Myocardial Lesion Size
4.2. Impact of Pericardial Space on the Heating in the Lung
4.3. Effect of Irrigation Fluid Temperature
4.4. Comparison with Experimental Data
4.5. Clinical Implications
4.6. Study Limitations
4.6.1. Impact of Intrapericardial Fluid Volume
4.6.2. Excluded Ultra-Thin Anatomical Layers and Small Structures
4.6.3. Irrigation Flow Rate
4.6.4. Catheter Orientation and Irrigation Holes Position
4.6.5. Constant Dynamic Viscosity
4.6.6. Specific Energy Setting
4.6.7. Single-Lesion Modeling
4.6.8. Effect of the Beating Heart
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sosa, E.; Scanavacca, M.; d’Avila, A.; Pilleggi, F. A new technique to perform epicardial mapping in the electrophysiology laboratory. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 1996, 7, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa, E.; Scanavacca, M.; D’Avila, A.; Piccioni, J.; Sanchez, O.; Velarde, J.L.; Silva, M.; Reolão, B. Endocardial and epicardial ablation guided by nonsurgical transthoracic epicardial mapping to treat recurrent ventricular tachycardia. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 1998, 9, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryana, A.; d’Avila, A. Epicardial Catheter Ablation of Ventricular Tachycardia. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2017, 9, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, A.; Di Biase, L.; Bazán, V.; Berruezo, A.; d’Avila, A.; Della Bella, P.; Enriquez, A.; Hocini, M.; Kautzner, J.; Pak, H.N.; et al. Epicardial ventricular arrhythmia ablation: A clinical consensus statement of the European Heart Rhythm Association of the European Society of Cardiology and the Heart Rhythm Society, the Asian Pacific Heart Rhythm Society, the Latin American Heart Rhythm Society, and the Canadian Heart Rhythm Society. Europace 2025, 27, euaf055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryana, A.; O’Neill, P.G.; Pujara, D.K.; Singh, S.K.; Bowers, M.R.; Allen, S.L.; d’Avila, A. Impact of irrigation flow rate and intrapericardial fluid on cooled-tip epicardial radiofrequency ablation. Heart Rhythm 2016, 13, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Avila, A.; Houghtaling, C.; Gutierrez, P.; Vragovic, O.; Ruskin, J.N.; Josephson, M.E.; Reddy, V.Y. Catheter ablation of ventricular epicardial tissue: A comparison of standard and cooled-tip radiofrequency energy. Circulation 2004, 109, 2363–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipse, M.M.; Edward, J.A.; Zheng, L.; Tzou, W.S.; Borne, R.T.; Sauer, W.H.; Nguyen, D.T. Impact of epicardial adipose tissue and catheter ablation strategy on biophysical parameters and ablation lesion characteristics. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2020, 31, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesel, L.; Sacher, F.; Komatsu, Y.; Daly, M.; Zellerhoff, S.; Lim, H.S.; Derval, N.; Denis, A.; Ambri, W.; Ramoul, K.; et al. Characterization of contact force during endocardial and epicardial ventricular mapping. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2014, 7, 1168–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacher, F.; Wright, M.; Derval, N.; Denis, A.; Ramoul, K.; Roten, L.; Pascale, P.; Bordachar, P.; Ritter, P.; Hocini, M.; et al. Endocardial versus epicardial ventricular radiofrequency ablation: Utility of in vivo contact force assessment. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2013, 6, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano Granero, C.; Franco, E.; Matía Francés, R.; Hernández-Madrid, A.; Sánchez-Pérez, I.; Zamorano Gómez, J.L.; Moreno, J. Impact of power and contact force on index-guided radiofrequency lesions in an ex vivo porcine heart model. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2022, 63, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junarta, J.; Rodriguez, S.; Ullah, W.; Siddiqui, M.U.; Riley, J.M.; Patel, A.; O’Neill, P.; Dikdan, S.J.; Fradin, J.J.; Rosen, J.L.; et al. Comparison of very high-power short-duration, high-power short-duration, and low-power long-duration radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 46, 1609–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ito, H.; Onuki, T.; Miyoshi, F.; Matsuyama, T.A.; Watanabe, N.; Ryu, S.; Asano, T.; Miyata, A.; et al. Epicardial ablation with cooled tip catheter close to the coronary arteries is effective and safe in the porcine heart if the ventricular potential is being monitored in the epicardium and endocardium. Circ. J. 2006, 70, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, K.; Watanabe, I.; Okumura, Y.; Sonoda, K.; Kofune, M.; Mano, H.; Ohkubo, K.; Nakai, T.; Kunimoto, S.; Kasamaki, Y.; et al. Epicardial ablation with irrigated electrodes: −Effect of bipolar vs. unipolar ablation on lesion formation−. Circ. J. 2012, 76, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yokoyama, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Wittkampf, F.H.; Pitha, J.V.; Lazzara, R.; Jackman, W.M. Comparison of electrode cooling between internal and open irrigation in radiofrequency ablation lesion depth and incidence of thrombus and steam pop. Circulation 2006, 113, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenelon, G.; Pereira, K.P.; de Paola, A.A. Epicardial radiofrequency ablation of ventricular myocardium: Factors affecting lesion formation and damage to adjacent structures. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2006, 15, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, J. A mathematical model for irrigated epicardial radiofrequency ablation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 30, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berjano, E.J.; Hornero, F. Thermal-electrical modeling for epicardial atrial radiofrequency ablation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 1348–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, A.G.; Hornero, F.; Berjano, E.J. Mathematical modeling of epicardial RF ablation of atrial tissue with overlying epicardial fat. Open Biomed. Eng. J. 2010, 4, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawel, N.; Turkbey, E.B.; Carr, J.J.; Eng, J.; Gomes, A.S.; Hundley, W.G.; Johnson, C.; Masri, S.C.; Prince, M.R.; van der Geest, R.J.; et al. Normal left ventricular myocardial thickness for middle-aged and older subjects with steady-state free precession cardiac magnetic resonance: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 5, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maron, B.J.; Desai, M.Y.; Nishimura, R.A.; Spirito, P.; Rakowski, H.; Towbin, J.A.; Rowin, E.J.; Maron, M.S.; Sherrid, M.V. Diagnosis and Evaluation of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 372–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younis, A.; Tabaja, C.; Kleve, R.; Garrott, K.; Lehn, L.; Buck, E.; Hussein, A.A.; Nakhla, S.; Nakagawa, H.; Krywanczyk, A.; et al. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Pulsed Field Ablation Versus Radiofrequency Ablation of Idiopathic LV Arrhythmias. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2024, 10, 1998–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balt, J.C.; Abeln, B.G.S.; van Dijk, V.F.; Wijffels, M.C.E.F.; Liebregts, M.; Boersma, L.V.A. Predictors of long-term success after high-density mapping-guided substrate ablation procedures for ventricular tachycardia in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. J. Arrhythm. 2024, 40, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TactiCath™ Contact Force Ablation Catheter, Sensor Enabled™. Instructions for Use. 2019. Available online: https://manuals.eifu.abbott/content/dam/av/manuals-eifu/global/US/en/ARTEN600077656_A.PDF (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- González-Suárez, A.; Pérez, J.J.; Irastorza, R.M.; D’Avila, A.; Berjano, E. Computer modeling of radiofrequency cardiac ablation: 30 years of bioengineering research. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2022, 214, 106546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irastorza, R.M.; d’Avila, A.; Berjano, E. Thermal latency adds to lesion depth after application of high-power short-duration radiofrequency energy: Results of a computer-modeling study. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2018, 29, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasgall, P.A.; Di Gennaro, F.; Baumgartner, C.; Neufeld, E.; Lloyd, B.; Gosselin, M.C.; Payne, D.; Klingenböck, A.; Kuster, N. IT’IS Database for Thermal and Electromagnetic Parameters of Biological Tissues, Version 4.1; IT’IS Foundation: Zürich, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://itis.swiss/virtual-population/tissue-properties/overview/ (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Haynes, W.M. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 95th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; ISBN 9781315380476. [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo, M.; Berjano, E. Review of the mathematical functions used to model the temperature dependence of electrical and thermal conductivities of biological tissue in radiofrequency ablation. Int. J. Hyperth. 2013, 29, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, K.R.; Schwan, H.P. Dielectric properties of tissues and biological materials: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 1989, 17, 25–104. [Google Scholar]
- Guyton, A.C.; Hall, J.E. Textbook of Medical Physiology, 20th ed.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011; ISBN 9781416045748. [Google Scholar]
- Sacher, F.; Roberts-Thomson, K.; Maury, P.; Tedrow, U.; Nault, I.; Steven, D.; Hocini, M.; Koplan, B.; Leroux, L.; Derval, N.; et al. Epicardial ventricular tachycardia ablation a multicenter safety study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrda, K.; Piers, S.R.; van Huls van Taxis, C.F.; Schalij, M.J.; Zeppenfeld, K. Influence of steroid therapy on the incidence of pericarditis and atrial fibrillation after percutaneous epicardial mapping and ablation for ventricular tachycardia. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2014, 7, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.J.; Nadal, E.; Berjano, E.; González-Suárez, A. Computer modeling of radiofrequency cardiac ablation including heartbeat-induced electrode displacement. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 144, 105346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berjano, E.J. Theoretical modeling for radiofrequency ablation: State-of-the-art and challenges for the future. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 2006, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, D.E. Letter by Haines regarding article, “Direct measurement of the lethal isotherm for radiofrequency ablation of myocardial tisssue”. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2011, 4, e67; author reply e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irastorza, R.M.; Gonzalez-Suarez, A.; Pérez, J.J.; Berjano, E. Differences in applied electrical power between full thorax models and limited-domain models for RF cardiac ablation. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, F.M.; Majdalani, J. Viscous Fluid Flow, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill Higher Education: New York, NY, USA, 2021; ISBN 9781260597806. [Google Scholar]
- Parés, C.; Berjano, E.; González-Suárez, A. Effect of intracardiac blood flow pulsatility during radiofrequency cardiac ablation: Computer modeling study. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Element/Material | ρ kg/m3 | k W/(m·K) | c J/(kg·K) | σ (S/m) | μ (Pa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiac chamber/blood | 1050 | 0.52 | 3617 | 0.748 | 0.0033 |
| Cardiac wall/myocardium | 1081 | 0.56 | 3686 | 0.281 | - |
| Visceral fat/adipose tissue | 911 | 0.21 | 2348 | 0.044 | - |
| Lung/pulmonary tissue * | 722 | 0.39 | 3890 | 0.215 | - |
| Pericardial sac/irrigation fluid (0.9% NaCl) | 1009 | 0.6 | 3670 | 1.44 | 0.001 |
| Electrode/Pt-Ir | 21,500 | 71 | 132 | 4.6×106 | - |
| Catheter/polyurethane | 1440 | 23 | 1050 | 105 | - |
| Power (W) | Lesion Depth (mm) | Lesion Volume (mm3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Computer results | 50 | 5.1–6.1 | 130–262 | |
| Aryana et al. [5] | Without intrapericardial fluid | 38.9 ± 0.9 | 5.5 ± 0.52 | 177.7 ± 42.7 |
| With intrapericardial fluid | 39.1 ± 0.9 | 4.5 ± 0.59 | 100.7 ± 26.0 | |
| Fenelon et al. [15] | 43.0 ± 6.1 | 6.4 ± 2.1 | Not reported | |
| D’Avila et al. [6] | 44.8 ± 6.8 | 6.7 ± 1.7 | Not reported | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cuenca-Dacal, L.; Mercado-Montoya, M.; Gómez-Bustamante, T.; Berjano, E.; Izquierdo, M.; Lozano, J.M.; Pérez, J.J.; González-Suárez, A. Impact of Intrapericardial Fluid on Lesion Size During Epicardial Radiofrequency Ablation: A Computational Study. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12080283
Cuenca-Dacal L, Mercado-Montoya M, Gómez-Bustamante T, Berjano E, Izquierdo M, Lozano JM, Pérez JJ, González-Suárez A. Impact of Intrapericardial Fluid on Lesion Size During Epicardial Radiofrequency Ablation: A Computational Study. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(8):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12080283
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuenca-Dacal, Luis, Marcela Mercado-Montoya, Tatiana Gómez-Bustamante, Enrique Berjano, Maite Izquierdo, José M. Lozano, Juan J. Pérez, and Ana González-Suárez. 2025. "Impact of Intrapericardial Fluid on Lesion Size During Epicardial Radiofrequency Ablation: A Computational Study" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 8: 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12080283
APA StyleCuenca-Dacal, L., Mercado-Montoya, M., Gómez-Bustamante, T., Berjano, E., Izquierdo, M., Lozano, J. M., Pérez, J. J., & González-Suárez, A. (2025). Impact of Intrapericardial Fluid on Lesion Size During Epicardial Radiofrequency Ablation: A Computational Study. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(8), 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12080283










