Biophysics and Clinical Effectiveness of Irreversible Electroporation for Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Biophysical Mechanisms of Pulsed Field Ablation
3.1. Basics of Cell Electrophysiology
3.2. Irreversible Electroporation
4. Field Strength and Tissue Effects
4.1. Parameters That Define Electric Field Strength and Electroporation Effects
4.1.1. Voltage
4.1.2. Waveform Shape
4.1.3. Pulse Parameters and Duration
4.2. Catheter and Electrodes
4.3. Resistance and the Impact of Tissue Contact and Contact Force
4.4. Repetition Dependence
4.5. Clinical Implications and Future Directions—Combined Energy Lesion
5. Safety Profile
5.1. Possible Complications Associated with Pulsed Field Ablation
5.2. Microembolism and the Fear of (Silent) Brain Lesions
6. Further Benefits/Advantages
7. Limitations of PFA and Further Questions for Science
7.1. Effectiveness and How to Further Increase It
7.2. Determining PFA Parameters for Prediction of Durable Lesions
7.3. PFA for Ventricular Ablations
8. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | atrial fibrillation |
| CA | catheter ablation |
| CF | contact force |
| CM | cell membrane |
| EF | electric field |
| EGM | electrogram |
| I | current |
| IRE | irreversible electroporation |
| OCT | optical coherence tomography |
| PEF | pulsed electric field |
| PFA | pulsed field ablation |
| PS-OCR | polarization-sensitive optical coherence reflectometry |
| PV | pulmonary vein |
| R | resistance |
| RE | reversible electroporation |
| RF | radiofrequency |
| T | time |
| V | voltage |
References
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Rienstra, M.; Bunting, K.V.; Casado-Arroyo, R.; Caso, V.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; De Potter, T.J.R.; Dwight, J.; Guasti, L.; Hanke, T.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3314–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, D.; Lee, K.L.; Camm, A.J.; Guerra, P.G.; O’Hara, G.; Stevenson, L.W. Rhythm Control versus Rate Control for Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2667–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, D.L.; Piccini, J.P.; Monahan, K.H.; Al-Khalidi, H.R.; Silverstein, A.P.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Poole, J.E.; Bahnson, T.D.; Lee, K.L.; Mark, D.B.; et al. Ablation Versus Drug Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation in Heart Failure: Results from the CABANA Trial. Circulation 2021, 143, 1377–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzeis, S. 2024 European Heart Rhythm Association/Heart Rhythm Society/Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society/Latin American Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. EP Europace. 2024, 26, euae043. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhof, P.; Camm, A.J.; Goette, A.; Brandes, A.; Eckardt, L.; Elvan, A.; Fetsch, T.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Haase, D.; Haegeli, L.M.; et al. Early Rhythm-Control Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turagam, M.K.; Musikantow, D.; Whang, W.; Koruth, J.S.; Miller, M.A.; Langan, M.-N.; Sofi, A.; Choudry, S.; Dukkipati, S.R.; Reddy, V.Y. Assessment of Catheter Ablation or Antiarrhythmic Drugs for First-line Therapy of Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanem, E.; Reddy, V.Y.; Schmidt, B.; Reichlin, T.; Neven, K.; Metzner, A.; Hansen, J.; Blaauw, Y.; Maury, P.; Arentz, T.; et al. Multi-national survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety on the post-approval clinical use of pulsed field ablation (MANIFEST-PF). EP Eur. 2022, 24, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.; Bordignon, S.; Neven, K.; Reichlin, T.; Blaauw, Y.; Hansen, J. EUropean Real World Outcomes with Pulsed Field AblatiOn in Patients with Symptomatic 2 AtRIAl Fibrillation—Lessons from the multicenter EU-PORIA Registry. EP Eur. 2023, 25, euad185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Gerstenfeld, E.P.; Natale, A.; Whang, W.; Cuoco, F.A.; Patel, C.; Mountantonakis, S.E.; Gibson, D.N.; Harding, J.D.; Ellis, C.R.; et al. Pulsed Field or Conventional Thermal Ablation for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1660–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benali, K.; Vlachos, K.; Reddy, V.Y.; Verma, A.; Chun, J.; Andrade, J.; Macle, L.; Da Costa, A.; Jaïs, P.; Hocini, M. Pulsed field ablation for atrial fibrillation in real-life settings: Efficacy, safety, and lesion durability in patients with recurrences. Heart Rhythm 2024, 21, 962–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckes, D.; Emami, M.; Fong, I.; Lau, D.H.; Sanders, P. Pulsed-field ablation: Computational modeling of electric fields for lesion depth analysis. Heart Rhythm O2 2022, 3, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambricht, L.; Lopes, A.; Kos, S.; Sersa, G.; Préat, V.; Vandermeulen, G. Clinical potential of electroporation for gene therapy and DNA vaccine delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabaja, C.; Younis, A.; Hussein, A.A.; Taigen, T.L.; Nakagawa, H.; Saliba, W.I.; Sroubek, J.; Santangeli, P.; Wazni, O.M. Catheter-Based Electroporation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 2008–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.C.G.; Kwon, D.; Chalikonda, S.; Sellers, M.; Kotz, E.; Scoggins, C.; McMasters, K.M.; Watkins, K. Treatment of 200 Locally Advanced (Stage III) Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Patients with Irreversible Electroporation: Safety and Efficacy. Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, K.-R.J.; Miklavčič, D.; Vlachos, K.; Bordignon, S.; Scherr, D.; Jais, P.; Schmidt, B. State-of-the-art pulsed field ablation for cardiac arrhythmias: Ongoing evolution and future perspective. Europace 2024, 26, euae134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J.C.; Chizmadzhev, Y.A. Theory of electroporation: A review. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1996, 41, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maor, E.; Sugrue, A.; Witt, C.; Vaidya, V.R.; DeSimone, C.V.; Asirvatham, S.J.; Kapa, S. Pulsed electric fields for cardiac ablation and beyond: A state-of-the-art review. Heart Rhythm 2019, 16, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista Napotnik, T.; Polajžer, T.; Miklavčič, D. Cell death due to electroporation—A review. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 141, 107871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, F.D.; Reddy, V.Y.; Viswanathan, R.; Hocini, M.; Jaïs, P. Emerging Technologies for Pulmonary Vein Isolation. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaigne, S.; Sigg, D.C.; Stewart, M.T.; Hocini, M.; Batista Napotnik, T.; Miklavčič, D.; Bernus, O.; Benoist, D. Reversible and Irreversible Effects of Electroporation on Contractility and Calcium Homeostasis in Isolated Cardiac Ventricular Myocytes. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2022, 15, e011131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Zudans, I.; Weber, E.A.; Olofsson, J.; Orwar, O.; Weber, S.G. Effect of Cell Size and Shape on Single-Cell Electroporation. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 3589–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Asivatham, S.J.; Deneke, T.; Castellvi, Q.; Neal, R.E. Primer on Pulsed Electrical Field Ablation: Understanding the Benefits and Limitations. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2021, 14, e010086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geboers, B.; Scheffer, H.J.; Graybill, P.M.; Ruarus, A.H.; Nieuwenhuizen, S.; Puijk, R.S.; Van Den Tol, P.M.; Davalos, R.V.; Rubinsky, B.; De Gruijl, T.D.; et al. High-Voltage Electrical Pulses in Oncology: Irreversible Electroporation, Electrochemotherapy, Gene Electrotransfer, Electrofusion, and Electroimmunotherapy. Radiology 2020, 295, 254–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varró, A.; Tomek, J.; Nagy, N.; Virág, L.; Passini, E.; Rodriguez, B.; Baczkó, I. Cardiac transmembrane ion channels and action potentials: Cellular physiology and arrhythmogenic behavior. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1083–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittkampf, F.H.M.; Van Es, R.; Neven, K. Electroporation and its Relevance for Cardiac Catheter Ablation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 4, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroki, K.; Tada, H. Catheter ablation using pulsed-field energy: Advantages and limitations compared with conventional energy. J. Arrhythmia 2025, 41, e70011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koruth, J.S.; Kuroki, K.; Kawamura, I.; Brose, R.; Viswanathan, R.; Buck, E.D.; Donskoy, E.; Neuzil, P.; Dukkipati, S.R.; Reddy, V.Y. Pulsed Field Ablation Versus Radiofrequency Ablation: Esophageal Injury in a Novel Porcine Model. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e008303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Koruth, J.; Jais, P.; Petru, J.; Timko, F.; Skalsky, I.; Hebeler, R.; Labrousse, L.; Barandon, L.; Kralovec, S.; et al. Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation with Pulsed Electric Fields. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 4, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochet, H.; Nakatani, Y.; Sridi-Cheniti, S.; Cheniti, G.; Ramirez, F.D.; Nakashima, T.; Eggert, C.; Schneider, C.; Viswanathan, R.; Derval, N.; et al. Pulsed field ablation selectively spares the oesophagus during pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation. EP Eur. 2021, 23, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, Y.; Sridi-Cheniti, S.; Cheniti, G.; Ramirez, F.D.; Goujeau, C.; André, C.; Nakashima, T.; Eggert, C.; Schneider, C.; Viswanathan, R.; et al. Pulsed field ablation prevents chronic atrial fibrotic changes and restrictive mechanics after catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. EP Eur. 2021, 23, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrous, N.; Blaschke, F.; Schöppenthau, D.; Hindricks, G.; Boldt, L.-H.; Parwani, A.S. LA PULSE: Evaluating Left Atrial Function Pre- and Post-Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Using PULSEd Field Ablation. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 14, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminska, I.; Kotulska, M.; Stecka, A.; Saczko, J.; Drag-Zalesinska, M.; Wysocka, T.; Choromanska, A.; Skolucka, N.; Nowicki, R.; Marczak, J.; et al. Electroporation-induced changes in normal immature rat myoblasts (H9C2). Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2012, 31, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, D.W.; Kostecki, G.; Fish, J.M.; Jensen, J.A.; Tandri, H. In Vitro Cell Selectivity of Reversible and Irreversible: Electroporation in Cardiac Tissue. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2021, 14, e008817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baena-Montes, J.M.; O’Halloran, T.; Clarke, C.; Donaghey, K.; Dunne, E.; O’Halloran, M.; Quinlan, L.R. Electroporation Parameters for Human Cardiomyocyte Ablation In Vitro. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zheng, J.; Fan, L. Nonthermal Irreversible Electroporation to the Esophagus: Evaluation of Acute and Long-Term Pathological Effects in a Rabbit Model. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e020731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Gu, K.; Zhou, T.; Si, P.; Ji, X.; Zhang, H.; Yan, S.; Wu, X. Investigate the relationship between pulsed field ablation parameters and ablation outcomes. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Neuzil, P.; Koruth, J.S.; Petru, J.; Funosako, M.; Cochet, H.; Sediva, L.; Chovanec, M.; Dukkipati, S.R.; Jais, P. Pulsed Field Ablation for Pulmonary Vein Isolation in Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavee, J.; Onik, G.; Mikus, P.; Rubinsky, B. A Novel Nonthermal Energy Source for Surgical Epicardial Atrial Ablation: Irreversible Electroporation. Heart Surg. Forum 2007, 10, E162–E167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Lv, C.; Cui, Y.; Lu, C.; Cai, H.; Xue, Z.; Xu, X.; Su, S. A pilot clinical assessment of biphasic asymmetric pulsed field ablation catheter for pulmonary vein isolation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1266195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Jia, F.; Lv, C.; He, Q.; Xu, X.; Xue, Z.; Su, S. Preclinical Study of Biphasic Asymmetric Pulsed Field Ablation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 859480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotnik, T.; Kramar, P.; Pucihar, G.; Miklavcic, D.; Tarek, M. Cell membrane electroporation- Part 1: The phenomenon. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2012, 28, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperetti, A.; Assis, F.; Tripathi, H.; Suzuki, M.; Gonuguntla, A.; Shah, R.; Sampognaro, J.; Schiavone, M.; Karmarkar, P.; Tandri, H. Determinants of acute irreversible electroporation lesion characteristics after pulsed field ablation: The role of voltage, contact, and adipose interference. Europace 2023, 25, euad257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattay, F. Analysis of Models for External Stimulation of Axons. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1986, BME-33, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobie, E.A.; Susil, R.C.; Tung, L. A generalized activating function for predicting virtual electrodes in cardiac tissue. Biophys. J. 1997, 73, 1410–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A.; Zilberman, I.; Krywanczyk, A.; Higuchi, K.; Yavin, H.D.; Sroubek, J.; Anter, E. Effect of Pulsed-Field and Radiofrequency Ablation on Heterogeneous Ventricular Scar in a Swine Model of Healed Myocardial Infarction. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2022, 15, e011209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofig, B.J.; Lukac, P.; Nielsen, J.M.; Hansen, E.S.S.; Tougaard, R.S.; Jensen, H.K.; Nielsen, J.C.; Kristiansen, S.B. Radiofrequency ablation lesions in low-, intermediate-, and normal-voltage myocardium: An in vivo study in a porcine heart model. EP Eur. 2019, 21, 1919–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nies, M.; Watanabe, K.; Kawamura, I.; Santos-Gallego, C.G.; Reddy, V.Y.; Koruth, J.S. Preclinical Study of Pulsed Field Ablation of Difficult Ventricular Targets: Intracavitary Mobile Structures, Interventricular Septum, and Left Ventricular Free Wall. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2024, 17, e012734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A.; Santangeli, P.; Garrott, K.; Buck, E.; Tabaja, C.; Wass, S.Y.; Lehn, L.; Kleve, R.; Hussein, A.A.; Nakhla, S.; et al. Impact of Contact Force on Pulsed Field Ablation Outcomes Using Focal Point Catheter. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2024, 17, e012723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, S.K.; Flaherty, M.C.; Laughner, J.; Quan, M.; Anic, A. Catheter–tissue contact optimizes pulsed electric field ablation with a large area focal catheter. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2024, 35, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Biase, L.; Marazzato, J.; Gomez, T.; Byun, E.; Zou, F.; Grupposo, V.; Mohanty, S.; La Fazia, V.M.; Ammirati, G.; Lin, A.; et al. Application repetition and electrode–tissue contact result in deeper lesions using a pulsed-field ablation circular variable loop catheter. Europace 2024, 26, euae220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Castellvi, Q.; Neal, R.; Girouard, S.; Laughner, J.; Ikeda, A.; Sugawara, M.; An, Y.; Hussein, A.A.; Nakhla, S.; et al. Effects of Contact Force on Lesion Size During Pulsed Field Catheter Ablation: Histochemical Characterization of Ventricular Lesion Boundaries. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2024, 17, e012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukharev, S.I.; Klenchin, V.A.; Serov, S.M.; Chernomordik, L.V.; Chizmadzhev, Y. Electroporation and electrophoretic DNA transfer into cells. The effect of DNA interaction with electropores. Biophys. J. 1992, 63, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klenchin, V.A.; Sukharev, S.I.; Serov, S.M.; Chernomordik, L.V.; Chizmadzhev, Y. Electrically induced DNA uptake by cells is a fast process involving DNA electrophoresis. Biophys. J. 1991, 60, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, J.; Xiong, Q.; Kong, Q.; Xiong, L.; Huang, Q.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Hu, J.; Si, P.; Zhou, T.; et al. A novel contact force sensing pulsed field ablation catheter in a porcine model. Clin. Cardiol. 2024, 47, e24220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anić, A.; Phlips, T.; Brešković, T.; Koopman, P.; Girouard, S.; Mediratta, V.; Jurišić, Z.; Sikirić, I.; Lisica, L.; Vijgen, J. Pulsed field ablation using focal contact force-sensing catheters for treatment of atrial fibrillation: Acute and 90-day invasive remapping results. Europace 2023, 25, euad147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Nies, M.; Reddy, V.Y.; Koruth, J.S. Lesion Morphometry of the Pentaspline Pulsed Field Ablation Catheter: Understanding Catheter Pose, Rotation, and Dosing. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2024, 17, e013208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, N.A.; McClennen, L.; Bilenker, J.; Patino, C.; Matos, C.D.; Sauer, K.M.; Hoyas, C.; Tedrow, U.B.; Zei, P.C.; Romero, J.E.; et al. Evaluation of pulsed field ablation lesion characteristics using an in vitro vegetable model. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, I.; Reddy, V.Y.; Wang, B.J.; Dukkipati, S.R.; Chaudhry, H.W.; Santos-Gallego, C.G.; Koruth, J.S. Pulsed Field Ablation of the Porcine Ventricle Using a Focal Lattice-Tip Catheter. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2022, 15, e011120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavin, H.D.; Higuchi, K.; Younis, A.; Anter, E. Lattice-tip catheter for single-shot pulmonary vein isolation with pulsed field ablation. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2023, 66, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turagam, M.K.; Neuzil, P.; Petru, J.; Funasako, M.; Koruth, J.S.; Reinders, D.; Skoda, J.; Kralovec, S.; Reddy, V.Y. PV Isolation Using a Spherical Array PFA Catheter. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Feld, G.K.; Cox, J.L.; Dewland, T.A.; Babkin, A.; De Potter, T.; Raju, N.; Haissaguerre, M. Combined pulsed field ablation with ultra-low temperature cryoablation: A preclinical experience. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2023, 34, 2124–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Maffre, J.; Sharma, T.; Farshchi-Heydari, S. Effect of Sequential, Colocalized Radiofrequency and Pulsed Field Ablation on Cardiac Lesion Size and Histology. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2025, 18, e013143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, C.; Rubinsky, B. Electrical Field and Temperature Model of Nonthermal Irreversible Electroporation in Heterogeneous Tissues. J. Biomech. Eng. 2009, 131, 071006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nies, M.; Watanabe, K.; Kawamura, I.; Koruth, J.S. Endocardial Pulsed Field Ablation and the Oesophagus: Are Atrio-oesophageal Fistulas Now History? Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. Rev. 2024, 13, e02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirstein, B.; Heeger, C.; Vogler, J.; Eitel, C.; Feher, M.; Phan, H.; Mushfiq, I.; Traub, A.; Hatahet, S.; Samara, O.; et al. Impact of pulsed field ablation on intraluminal esophageal temperature. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2024, 35, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duytschaever, M.; De Potter, T.; Grimaldi, M.; Anic, A.; Vijgen, J.; Neuzil, P.; Van Herendael, H.; Verma, A.; Skanes, A.; Scherr, D.; et al. Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Using a Novel Variable-Loop Biphasic Pulsed Field Ablation Catheter Integrated with a 3-Dimensional Mapping System: 1-Year Outcomes of the Multicenter inspIRE Study. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2023, 16, e011780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.S.; Lee, S.-R.; Black-Maier, E.; Jackson, K.P.; Friedman, D.J.; Pokorney, S.D.; Loring, Z.; Febre, J.; Piccini, J.P. Complications associated with pulsed field ablation vs radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm, 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanem, E.; Neuzil, P.; Reichlin, T.; Kautzner, J.; Van Der Voort, P.; Jais, P.; Chierchia, G.-B.; Bulava, A.; Blaauw, Y.; Skala, T.; et al. Safety of pulsed field ablation in more than 17,000 patients with atrial fibrillation in the MANIFEST-17K study. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2020–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Wang, J.; Deng, Q.; Feng, H.; Xie, M.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, S.; et al. Effects of pulsed field ablation on autonomic nervous system in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: A pilot study. Heart Rhythm 2023, 20, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojadinović, P.; Wichterle, D.; Peichl, P.; Nakagawa, H.; Čihák, R.; Hašková, J.; Kautzner, J. Autonomic Changes Are More Durable After Radiofrequency than Pulsed Electric Field Pulmonary Vein Ablation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2022, 8, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Casella, M.; Compagnucci, P.; Torlapati, P.G.; Della Rocca, D.G.; La Fazia, V.M.; Gianni, C.; Chierchia, G.-B.; MacDonald, B.; Mayedo, A.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury Resulting from Hemoglobinuria After Pulsed-Field Ablation in Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2024, 10, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, M.A.; Venier, S.; Menè, R.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Sacher, F.; Derval, N.; Hocini, M.; Dulucq, S.; Caluori, G.; Combes, S.; et al. Characterization and Clinical Significance of Hemolysis After Pulsed Field Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation: Results of a Multicenter Analysis. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2024, 17, e012732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nies, M.; Koruth, J.S.; Mlček, M.; Watanabe, K.; Tibenská, V.C.; Královec, Š.; Tejkl, L.; Neuzil, P.; Reddy, V.Y. Hemolysis After Pulsed Field Ablation: Impact of Lesion Number and Catheter-Tissue Contact. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2024, 17, e012765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Petru, J.; Funasako, M.; Kopriva, K.; Hala, P.; Chovanec, M.; Janotka, M.; Kralovec, S.; Neuzil, P. Coronary Arterial Spasm During Pulsed Field Ablation to Treat Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2022, 146, 1808–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davong, B.; Adeliño, R.; Delasnerie, H.; Albenque, J.-P.; Combes, N.; Cardin, C.; Voglimacci-Stephanopoli, Q.; Combes, S.; Boveda, S. Pulsed-Field Ablation on Mitral Isthmus in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: Preliminary Data on Efficacy and Safety. Focal Atr. Fibrillation 2023, 9, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Neuzil, P.; Petru, J.; Funasako, M.; Hala, P.; Kopriva, K.; Koruth, J.S.; Dukkipati, S.R.; Reddy, V.Y. Coronary Artery Spasm During Pulsed Field vs. Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of the Mitral Isthmus. JAMA Cardiol. 2024, 9, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, D.A.; Garrott, K.; Garlitski, A.; Koop, B. Coronary Spasm due to Pulsed Field Ablation: A State-of-the-Art Review. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, S.; Im, S.I.; Stillson, C.; Buck, E.D.; Jerrell, S.; Schneider, C.W.; Speltz, M.; Gerstenfeld, E.P. Effect of Epicardial Pulsed Field Ablation Directly on Coronary Arteries. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2022, 8, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.; Gerstenfeld, E.P.; Gupta, S.K.; Winterfield, J.; Woods, C.; Natale, A.; Schneider, C.W.; Achyutha, A.B.; Holland, S.K.; Richards, E.; et al. Comparison of cerebral safety after atrial fibrillation using pulsed field and thermal ablation: Results of the neurological assessment subgroup in the ADVENT trial. Heart Rhythm 2024, 21, 2103–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Peichl, P.; Anter, E.; Rackauskas, G.; Petru, J.; Funasako, M.; Minami, K.; Koruth, J.S.; Natale, A.; Jais, P.; et al. A Focal Ablation Catheter Toggling Between Radiofrequency and Pulsed Field Energy to Treat Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 1786–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenegger, C. Incidence of acute pericarditis after pulsed-field ablation for the treatment of atrial fibrillation. Europace 2024, 26, euae180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.S.; Miller, J.; Foreman, J.; Golden, K.; Shah, A.; Field, J.; Gilge, J.; Clark, B.; Joshi, S.; Nair, G.; et al. Prophylactic Colchicine After Radiofrequency Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, R.; Satti, D.I.; Malwankar, J.; Lopez-Silva, C.; Xu, L.; Liebow-Feeser, E.; Akhtar, T.; Marine, J.E.; Berger, R.; Calkins, H.; et al. Pericarditis After Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2024, 10, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erhard, N.; Frison, E.; Asselineau, J.; Aouar, B.; Boveda, S.; Cochet, H.; Deisenhofer, I.; Deneke, T.; Gimbert, A.; Kautzner, J.; et al. Comparing pulsed field electroporation and radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: Design and rationale of the BEAT PAROX-AF randomized clinical trial. Europace 2024, 26, euae103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, B.; Reilly, J.; Coffey, K.; González-Suárez, A.; Quinlan, L.; Van Zyl, M. Cardioneuroablation Using Epicardial Pulsed Field Ablation for the Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duytschaever, M.F.; Firth, K.; Leonard, O.; Paamand, R.; Knecht, S. AB-452675-3 Characteristics of Residual Signals After Pulsed Field Ablation of the Pulmonary Veins. Heart Rhythm 2023, 20, S75–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sanchez, T.; Amoros-Figueras, A.; Casabella-Ramon, S.; Moreno-Weidmann, Z.; Guerra, J.M.; Ivorra, A. Dynamics of local unipolar electrograms during epicardial pulsed field ablation (PFA). Europace 2023, 25, euad122.726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štublar, J.; Jarm, T.; Mattison, L.; Martin, B.D.; Schmidt, M.; Jan, M.; Verma, A.; Iaizzo, P.A.; Sigg, D.C.; Miklavčič, D. Intracardiac electrogram analysis may allow for prediction of lesion transmurality after pulsed field ablation of atria in a porcine model. Heart Rhythm O2 2024, 6, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.P.; Papiashvili, G.; Sabirov, A.; Sabirov, S.; Herranz, D.; Bailleul, C.; Verma, A. First-in-human trial of atrial fibrillation ablation using real-time tissue optical assessment to predict pulsed field lesion durability. Europace 2025, 27, euaf009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherr, D.; Turagam, M.K.; Maury, P.; Blaauw, Y.; van der Voort, P.; Neuzil, P.; Reichlin, T.; Metzner, A.; Vijgen, J.; Kautzner, J.; et al. Repeat Procedures After Pulsed Field Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation: MANIFEST-REDO Study. EP Eur. 2025, 17, euaf012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


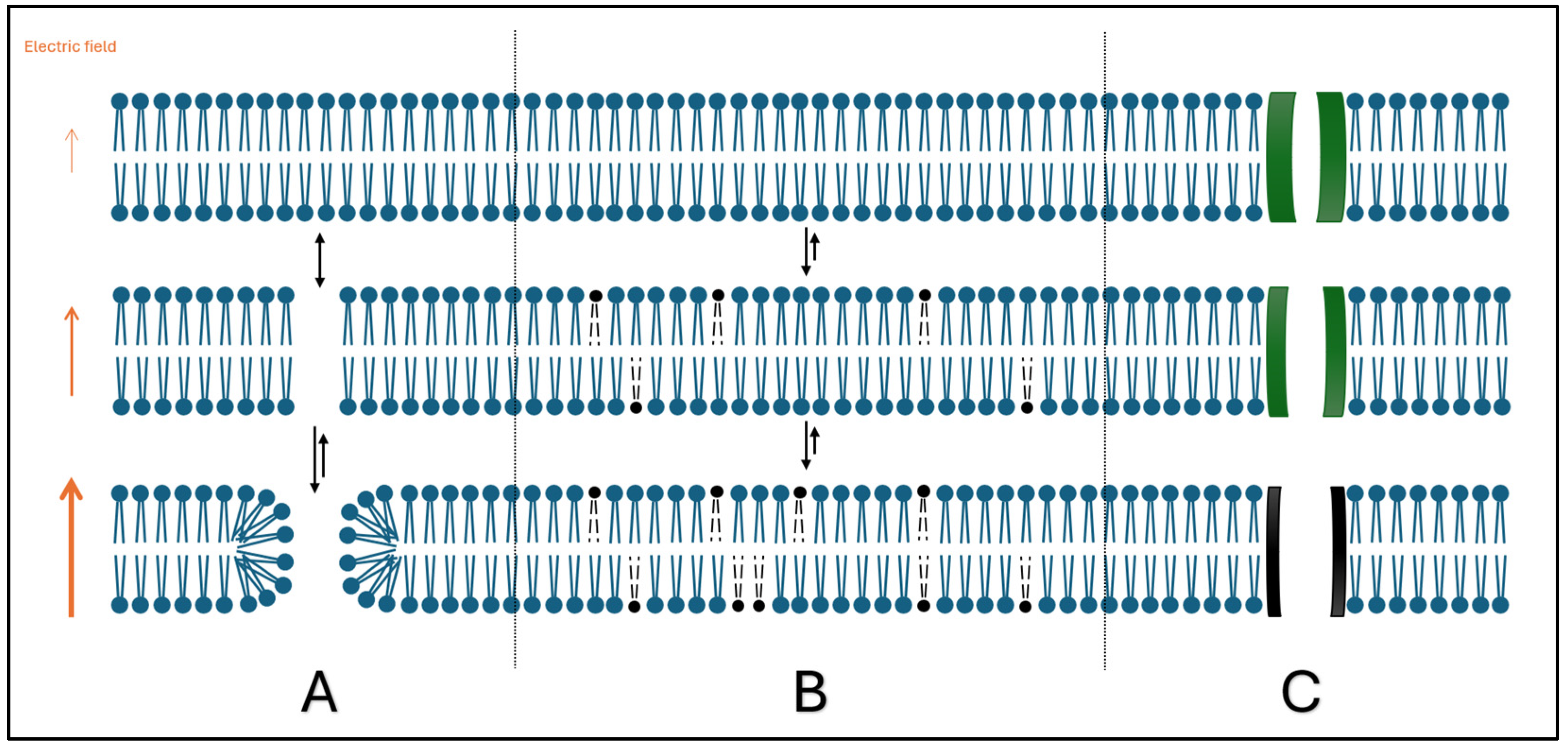
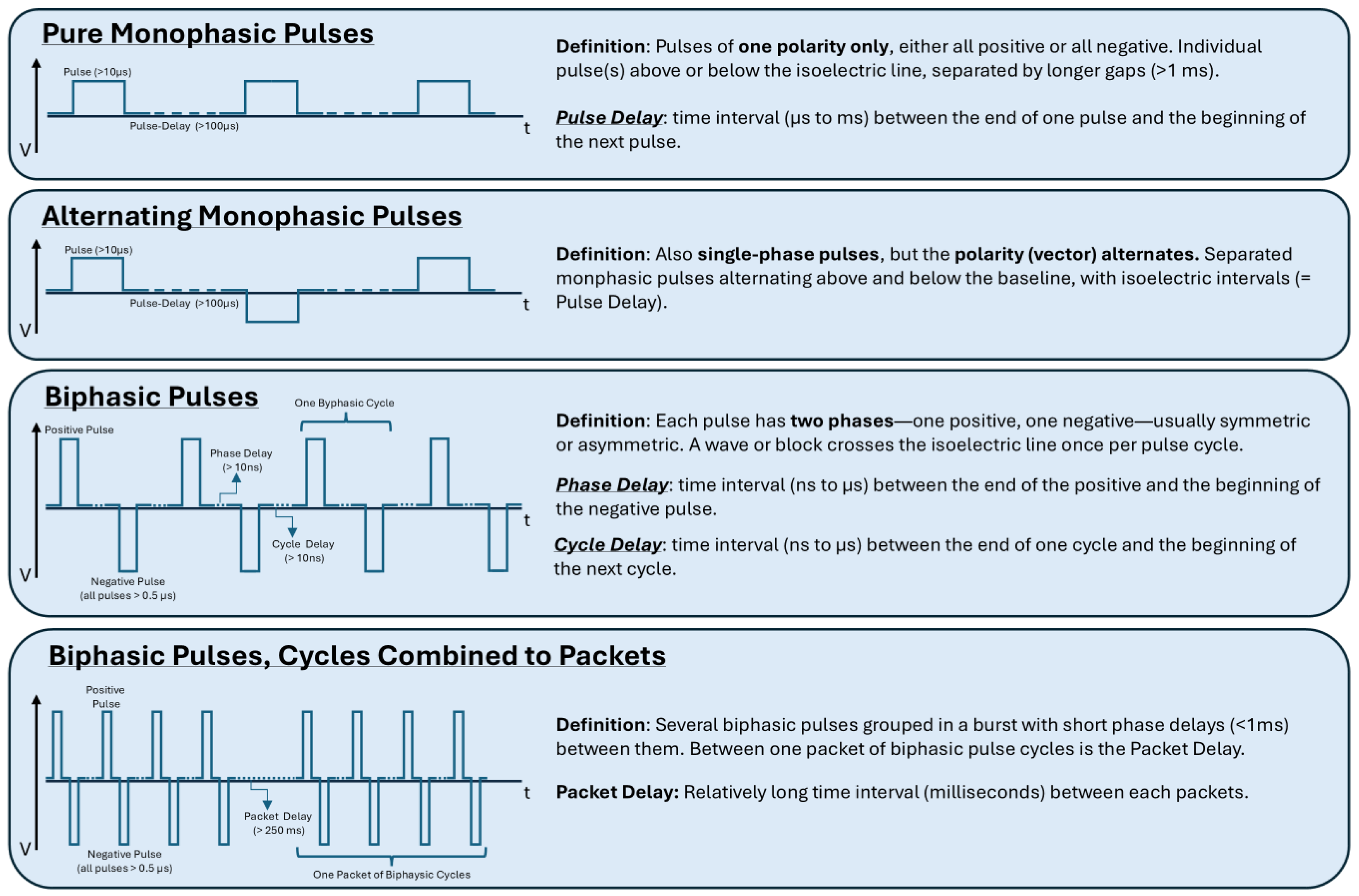
| Tissue | Electric Field Threshold for IRE (V/cm) |
|---|---|
| Nerve | 3800 |
| Vascular smooth muscle | 1750 |
| Red blood cells | 1600 |
| Liver | 700 |
| Kidney | 600 |
| Pancreas | 500 |
| Myocardium | 400 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eberl, A.-S.; Plank, G.; Manninger, M.; Rohrer, U.; Stix, L.; Kurath-Koller, S.; Zirlik, A.; Scherr, D. Biophysics and Clinical Effectiveness of Irreversible Electroporation for Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12060218
Eberl A-S, Plank G, Manninger M, Rohrer U, Stix L, Kurath-Koller S, Zirlik A, Scherr D. Biophysics and Clinical Effectiveness of Irreversible Electroporation for Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(6):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12060218
Chicago/Turabian StyleEberl, Anna-Sophie, Gernot Plank, Martin Manninger, Ursula Rohrer, Laura Stix, Stefan Kurath-Koller, Andreas Zirlik, and Daniel Scherr. 2025. "Biophysics and Clinical Effectiveness of Irreversible Electroporation for Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 6: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12060218
APA StyleEberl, A.-S., Plank, G., Manninger, M., Rohrer, U., Stix, L., Kurath-Koller, S., Zirlik, A., & Scherr, D. (2025). Biophysics and Clinical Effectiveness of Irreversible Electroporation for Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(6), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12060218






