The Role of Serum Uric Acid and Serum Creatinine Ratio as Possible Markers of Autonomic Dysfunction and Left Ventricular Mass Index in Atherosclerotic Renal Artery Stenosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Heart Rate Variability and QTc Interval
2.3. Left Ventricular Mass and Left Ventricular Mass Index
2.4. Statistical Analysis
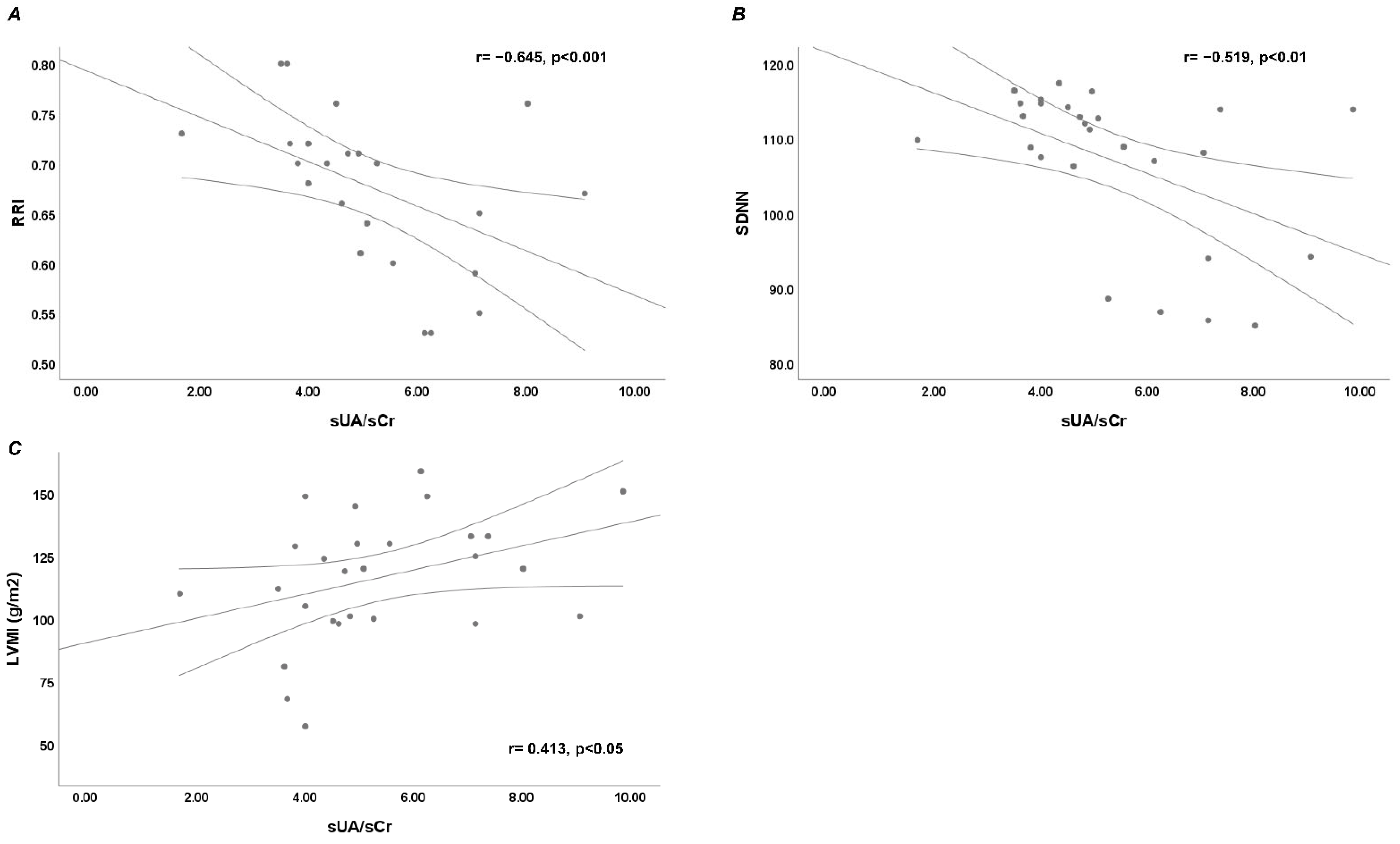
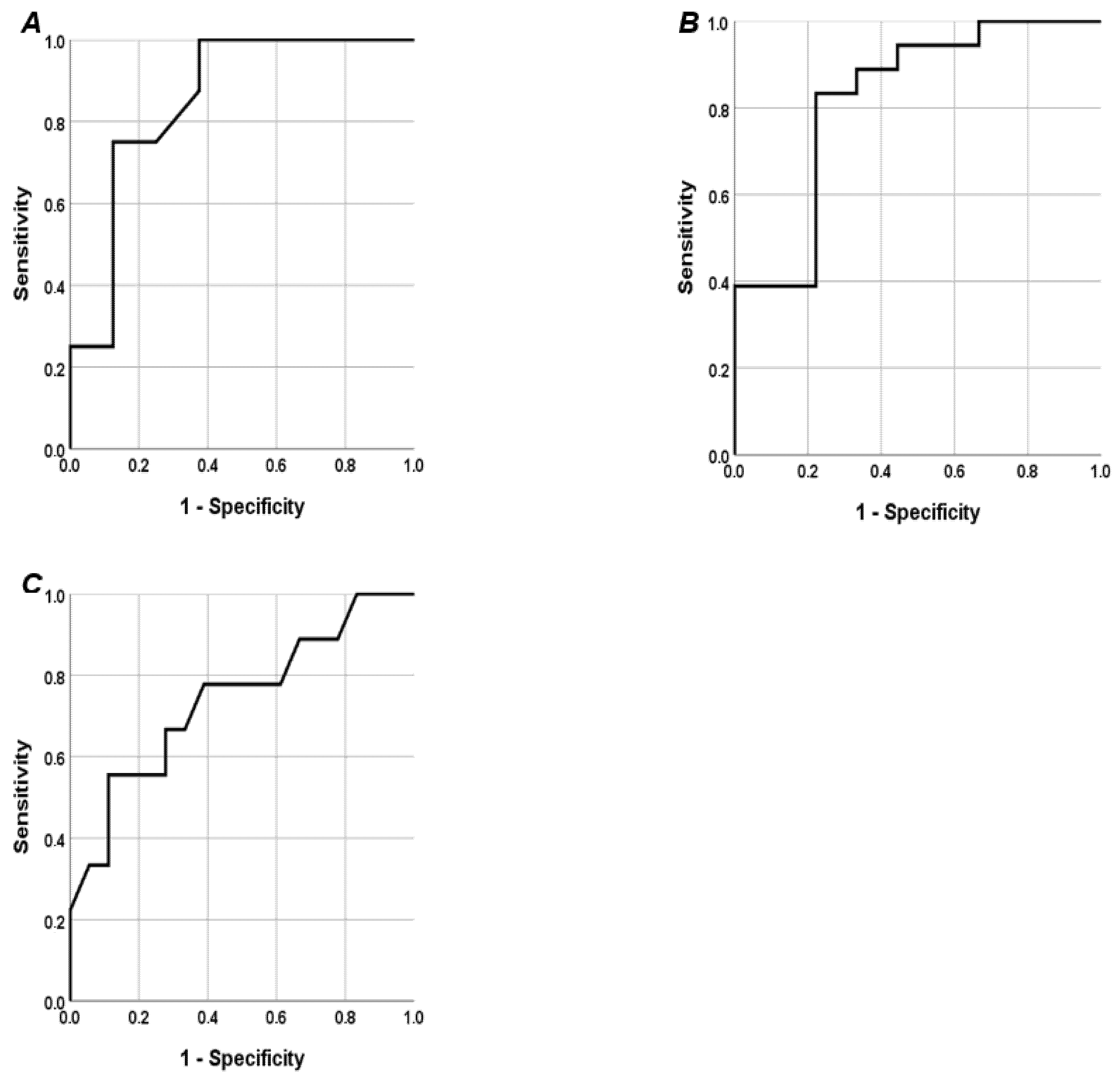
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lan, R.; Ran, T.; He, J.; Li, J.; Shi, Q.; Mao, M.; Zuo, Z. Atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis, mediating biomarkers, and risk of cardiac among individuals with hypertension: A real-world study. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2024, 55, 101556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mast, Q.; Beutler, J.J. The prevalence of atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis in risk groups: A systematic literature review. J. Hypertens. 2009, 27, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safian, R.D.; Textor, S.C. Renal-artery stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virdis, A.; Masi, S.; Casiglia, E.; Tikhonoff, V.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Ungar, A.; Rivasi, G.; Salvetti, M.; Barbagallo, C.M.; Bombelli, M.; et al. Identification of the Uric Acid Thresholds Predicting an Increased Total and Cardiovascular Mortality over 20 Years. Hypertension 2020, 75, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.J.; Eirin, A.; Kane, G.C.; Misra, S.; Textor, S.C.; Lerman, A.; Lerman, L.O. Impact of Serum Uric Acid Levels on Outcomes following Renal Artery Revascularization in Patients with Renovascular Disease. Int. J. Hypertens. 2019, 2019, 3872065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deswal, A. Diastolic dysfunction and diastolic heart failure: Mechanisms and epidemiology. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2005, 7, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, S.E.; Mariampillai, J.E.; Høieggen, A. Uric acid and left ventricular mass in prediction of cardiovascular risk-New insight from the URRAH study. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 114, 45–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulleryd, M.A.; Prahl, U.; Börsbo, J.; Schmidt, C.; Nilsson, S.; Bergström, G.; Johansson, M.E. The association between autonomic dysfunction, inflammation and atherosclerosis in men under investigation for carotid plaques. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, A.; Zingaretti, V.; Proietti, M.; Rosato, E.; Cianci, R. Autonomic dysfunction and cardiovascular risk in patients with atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis: A pilot study. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 52, e19–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M. Heart rate variability: Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation 1996, 93, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, A.J. Measurement of the QT interval and the risk associated with QTc in interval prolongation: A review. Am. J. Cardiol. 1993, 72, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.M.; Bierig, M.; Devereux, R.B.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Pellikka, P.A.; Picard, M.H.; Roman, M.J.; Seward, J.; Shanewise, J.; et al. Recommendations for chamber quantification. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2006, 7, 79–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, M.; Hisatome, I.; Ae, R.; Kosami, K.; Aoki, Y.; Andres-Hernando, A.; Kanbay, M.; Lanaspa, M.A. Hyperuricemia, A new cardiovascular risk. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2025, 35, 103796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiglia, E.; Tikhonoff, V.; Virdis, A.; Grassi, G.; Angeli, F.; Barbagallo, C.M.; Bombelli, M.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Cirillo, M.; Cirillo, P.; et al. Serum uric acid/serum creatinine ratio as a predictor of cardiovascular events. Detection of prognostic cardiovascular cut-off values. J. Hypertens. 2023, 41, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Elia, L.; Masulli, M.; Cirillo, P.; Virdis, A.; Casiglia, E.; Tikhonoff, V.; Angeli, F.; Barbagallo, C.M.; Bombelli, M.; Cappelli, F.; et al. Serum uric acid/serum creatinine ratio and cardiovascular mortality in diabetic individuals-the uric acid right for heart health (URRAH) project. Metabolites 2024, 14, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Bertolotto, M.; Zanetti, V.; Picciotto, D.; Esposito, P.; Carbone, F.; Montecucco, F.; Pontremoli, R.; Garibotto, G.; Viazzi, F.; et al. Role of uric acid in vascular remodeling: Cytoskeleton changes and migration in VSMCs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofue, T. Hyperuricemia: The third key player for nephrosclerosis with ischemia. Hypertens. Res. 2023, 46, 1707–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, R.; Hong, H.; Zhang, J. Serum uric acid level is associated with glomerular ischemic lesions in patients with primary membranous nephropathy: An analytical, cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, A.; Pellicano, C.; Gallicchio, C.; Melena, M.; Fiorino, M.; Rosato, E.; Giannakakis, K.; Ascione, A.; Muscaritoli, M.; Cianci, R. Serum Uric Acid/Serum Creatinine Ratio and Chronic Vascular Lesions on Renal Biopsy: A Retrospective Observational Study. High. Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2025, 32, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Cui, L.; Shu, R.; Song, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Han, Y.; Yu, P.; Yuan, W.; Wang, J.; et al. Associations of uric acid with the risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality among individuals with chronic kidney disease: The Kailuan Study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2024, 31, 2058–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Bagordo, D.; Perrotta, A.M.; Gigante, A.; Gasperini, M.L.; Muscaritoli, M.; Mazzaferro, S.; Cianci, R. Autonomic dysfunction in kidney diseases. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 8458–8468. [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer, F.; Ginsberg, J.P. An Overview of Heart Rate Variability Metrics and Norms. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunikullaya, K.U.; Purushottam, N.; Prakash, V.; Mohan, S.; Chinnaswamy, R. Correlation of serum uric acid with heart rate variability in hypertension. Hipertens. Riesgo Vasc. 2015, 32, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erden, M.; Kocaman, S.A.; Poyraz, F.; Topal, S.; Sahinarslan, A.; Boyacı, B.; Cengel, A.; Yalçın, M.R. Incremental effects of serum uric acid levels, autonomic dysfunction, and low-grade inflammation on nocturnal blood pressure in untreated hypertensive patients and normotensive individuals. Turk. Kardiyol. Dern. Ars. 2011, 39, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liao, X.P.; Zhu, H.W.; Zeng, F.; Tang, Z.H. The association and interaction analysis of hypertension and uric acid on cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, C.W.; Clark, T.W.I.; Cooper, C.J.; de Bhailís, Á.M.; De Carlo, M.; Green, D.; Małyszko, J.; Miglinas, M.; Textor, S.C.; Herzog, C.A.; et al. Atherosclerotic Renovascular Disease: A KDIGO (Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes) Controversies Conference. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 79, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Pi, X.; Ma, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, H.; Chi, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Liu, N. Relationship between serum uric acid and clustering of cardiovascular disease risk factors and renal disorders among Shanghai population: A multicentre and cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e025453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianci, R.; Martina, P.; Gigante, A.; Di Donato, D.; Polidori, L.; Presta, P.; Labbadia, R.; Amoroso, D.; Zaccaria, A.; Barbano, B.; et al. Predictor factors for renal outcome in renal artery stenosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 507–512. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, E.; Viazzi, F.; Pontremoli, R.; Barbagallo, C.M.; Bombelli, M.; Casiglia, E.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Cirillo, M.; Cirillo, P.; Desideri, G.; et al. Association of uric acid with kidney function and albuminuria: The Uric Acid Right for heArt Health (URRAH) Project. J. Nephrol. 2022, 35, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B. Concentration of serum uric acid in patients with Renal Artery Stenosis and Hypertension prEdict Future nephropathy and death: C-RASHEF study. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2023, 25, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muiesan, M.L.; Agabiti Rosei, C.; Paini, A.; Casiglia, E.; Cirillo, M.; Grassi, G.; Iaccarino, G.; Mallamaci, F.; Maloberti, A.; Mazza, A.; et al. Serum uric acid and left ventricular mass index independently predict cardiovascular mortality: The uric acid right for heart health (URRAH) project. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 114, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viazzi, F.; Parodi, D.; Leoncini, G.; Parodi, A.; Falqui, V.; Ratto, E.; Vettoretti, S.; Bezante, G.P.; Del Sette, M.; Deferrari, G.; et al. Serum uric acid and target organ damage in primary hypertension. Hypertension 2005, 45, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catena, C.; Colussi, G.; Capobianco, F.; Brosolo, G.; Sechi, L.A. Uricaemia and left ventricular mass in hypertensive patients. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 44, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, V.; Pascale, A.V.; Virtuoso, N.; Mongiello, F.; Cinque, F.; Gioia, R.; Finelli, R.; Mazzeo, P.; Manzi, M.V.; Morisco, C.; et al. Serum uric acid and left ventricular mass in essential hypertension. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 570000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age, years | 67 (60–77) |
| Female/Male | 16 (59)/11 (41) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.3 (23.2–27.8) |
| SBP, mmHg | 130 (125–140) |
| DBP, mmHg | 80 (75–80) |
| eGFR (CKD-EPI), mL/min | 67.5 (53.7–89.2) |
| sCr, mg/dL | 1.05 (0.8–1.3) |
| SUA, mg/dL | 5.3 (4.6–6.3) |
| SUA ≥ 5.6, mg/dL | 9 (33.3) |
| SUA/sCr | 4.92 (4–7.06) |
| SUA/sCr ≥ 4.05 | 19 (70.4) |
| Na | 140 (139–143) |
| K | 4.5 (4.27–4.9) |
| Ca | 9.67 (9.4–10) |
| P | 3.75 (3.4–4) |
| RRI | 0.7 (0.63–0.72) |
| RRI ≥ 0.7 | 15 (55.5) |
| SDNN | 111.2 (106.3–114.2) |
| HR mean | 78.6 (73.9–83.6) |
| HR min | 73.5 (70–79) |
| HR max | 113 (104–118) |
| QTc mean | 436 (418–458) |
| LVMI, g/m2 | 120 (100–133) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gigante, A.; Cascone, R.; Pellicano, C.; Iannazzo, F.; Gadaleta, F.R.; Rosato, E.; Cianci, R. The Role of Serum Uric Acid and Serum Creatinine Ratio as Possible Markers of Autonomic Dysfunction and Left Ventricular Mass Index in Atherosclerotic Renal Artery Stenosis. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12060202
Gigante A, Cascone R, Pellicano C, Iannazzo F, Gadaleta FR, Rosato E, Cianci R. The Role of Serum Uric Acid and Serum Creatinine Ratio as Possible Markers of Autonomic Dysfunction and Left Ventricular Mass Index in Atherosclerotic Renal Artery Stenosis. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(6):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12060202
Chicago/Turabian StyleGigante, Antonietta, Rosa Cascone, Chiara Pellicano, Francesco Iannazzo, Francesca Romana Gadaleta, Edoardo Rosato, and Rosario Cianci. 2025. "The Role of Serum Uric Acid and Serum Creatinine Ratio as Possible Markers of Autonomic Dysfunction and Left Ventricular Mass Index in Atherosclerotic Renal Artery Stenosis" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 6: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12060202
APA StyleGigante, A., Cascone, R., Pellicano, C., Iannazzo, F., Gadaleta, F. R., Rosato, E., & Cianci, R. (2025). The Role of Serum Uric Acid and Serum Creatinine Ratio as Possible Markers of Autonomic Dysfunction and Left Ventricular Mass Index in Atherosclerotic Renal Artery Stenosis. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(6), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12060202







