Obesity-Induced PVAT Dysfunction and Atherosclerosis Development: The Role of GHSR-1a in Increased Macrophage Infiltration and Adipocytokine Secretion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Immunohistochemical Study
2.4. Biochemical Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howard, A.; Feighner, S.; Cully, D.; Arena, J.; Liberator, P.; Rosenblum, C.; Hamelin, M.; Hreniuk, D.; Palyha, O.; Anderson, J.; et al. A Receptor in the Pituitary and Hypothalamus That Functions in Growth Hormone Release. Science 1996, 273, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staes, E.; Absil, P.; Lins, L.; Brasseur, R.; Deleu, M.; Lecouturier, N.; Fievez, V.; Rieux, A.; Mingeot-Leclercq, M.; Raussens, V.; et al. Acylated and Unacylated Ghrelin Binding to Membranes and to Ghrelin Receptor: Towards a Better Understanding of the Underlying Mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1798, 2102–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, J.; Zhou, Y.; Barak, L.; Caron, M. Ghrelin Receptor Signaling in Health and Disease: A Biased View. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 34, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albarrán-Zeckler, R.; Smith, R. The Ghrelin Receptors (GHS-R1a and GHS-R1b). Endocr. Dev. 2013, 25, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, G.; Aguinaga, D.; Angelats, E.; Medrano, M.; Moreno, E.; Mallol, J.; Cortés, A.; Canela, E.; Casadó, V.; McCormick, P.; et al. A Significant Role of the Truncated Ghrelin Receptor GHS-R1b in Ghrelin-Induced Signaling in Neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 13048–13062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, B.; Schwartz, T.W. Ghrelin receptor mutations—Too little height and too much hunger. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katugampola, S.; Pallikaros, Z.; Davenport, A. [125I-His(9)]-Ghrelin, a Novel Radioligand for Localizing GHS Orphan Receptors in Human and Rat Tissue: Up-Regulation of Receptors with Atherosclerosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.; Herrera, M.; Patil, B.; Tan, X.; Wright, G.; Sun, Y. The Expression and Function of Growth Hormone Secretagogue Receptor in Immune Cells: A Current Perspective. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 247, 2184–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qi, M.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W. Ghrelin Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Induced by Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation via Blockade of Kupffer Cell M1 Polarization. J. Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 5121–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Qu, X.; Yuan, F.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Dai, J.; Wang, W.; Fei, J.; Hou, X.; Fang, W. Ghrelin Receptor Deficiency Aggravates Atherosclerotic Plaque Instability. Front. Biosci. 2015, 20, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, F. Ghrelin improves endothelial function and reduces blood pressure in Ang II-induced hypertensive mice: Role of AMPK. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2023, 45, 2208774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, W.; Yu, L. Potential role of ghrelin in the regulation of inflammation. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanetti, M.; Gortan Cappellari, G.; Graziani, A.; Barazzoni, R. Unacylated Ghrelin Improves Vascular Dysfunction and Attenuates Atherosclerosis during High-Fat Diet Consumption in Rodents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tanida, R.; Tsubouchi, H.; Yanagi, S.; Saito, Y.; Toshinai, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Takamura, T.; Nakazato, M. GHS-R1a Deficiency Mitigates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Lung Injury in Mice via the Downregulation of Macrophage Activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 589, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, Q.; Tang, M.; Li, J.; Wu, W.; Wan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bao, S.; Fei, J. Growth Hormone Secretagogue Receptor Is Important in the Development of Experimental Colitis. Cell Biosci. 2015, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Lee, J.; Buras, E.; Yu, K.; Wang, R.; Smith, C.; Wu, H.; Sheikh-Hamad, D.; Sun, Y. Ghrelin Receptor Regulates Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Aging. Aging 2016, 8, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Lin, L.; Yue, J.; Pradhan, G.; Qin, G.; Minze, L.J.; Wu, H.; Sheikh-Hamad, D.; Smith, C.W.; Sun, Y. Ghrelin receptor regulates HFCS-induced adipose inflammation and insulin resistance. Nutr. Diabetes 2013, 3, e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiu, S.N.; Iosep, D.G.; Danciu, M.; Scripcaru, V.; Ianole, V.; Mocanu, V. Ghrelin Expression in Atherosclerotic Plaques and Perivascular Adipose Tissue: Implications for Vascular Inflammation in Peripheral Artery Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.J.; Huang, H.; Huang, C.X. Potential new role of the GHSR-1a-mediated signaling pathway in cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 969–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, J.P.H. Ghrelin and Peripheral Artery Disease. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, G.; Kulkarni, R.; Shah, S.; King, W.; Longchamp, A.; Tao, M.; Ding, K.; Ozaki, C. Local Perivascular Adiponectin Asso-Ciates with Lower Extremity Vascular Operative Wound Complications. Surgery 2016, 160, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiki, N.; Mantzoros, C.; Mikhailidis, D.P. Adiponectin, lipids and atherosclerosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2017, 28, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, V.; Fasshauer, M.; Dalski, A.; Meier, B.; Perwitz, N.; Klein, H.H.; Tschöp, M.; Klein, J. Direct peripheral effects of ghrelin include suppression of adiponectin expression. Horm. Metab. Res. 2002, 34, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Navarro-Jiménez, E.; Laborde-Cárdenas, C.C.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. The Role of Adipokines in Health and Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liao, P.-J.; Ting, M.-K.; Wu, I.-W.; Chen, S.-W.; Yang, N.-I.; Hsu, K.-H. Higher Leptin-to-Adiponectin Ratio Strengthens the Association Between Body Measurements and Occurrence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 678681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Yang, S.; Xiao, H.; Wang, M.; Ye, J.; Cao, L.; Sun, G. Role of Adiponectin in Cardiovascular Diseases Related to Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschöp, M.; Weyer, C.; Tataranni, P.A.; Devanarayan, V.; Ravussin, E.; Heiman, M.L. Circulating ghrelin levels are decreased in human obesity. Diabetes 2001, 50, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyer, C.; Funahashi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Hotta, K.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Pratley, R.E.; Tataranni, P.A. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: Close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 1930–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Ma, J.; Xiang, X.; Lan, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W. Improvement of Adipose Macrophage Polarization in High Fat Diet-Induced Obese GHSR Knockout Mice. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4924325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinetti-Gbaguidi, G.; Colin, S.; Staels, B. Macrophage subsets in atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Qian, L.; Li, J.; Ming, H.; Fang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Ban, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. GHSR Deficiency Exacerbates Cardiac Fibrosis: Role in Macrophage Inflammasome Activation and Myofibroblast Differentiation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibas-Dorna, M.; Nowak, D.; Piatek, J.; Pupek-Musialik, D.; Krauss, H.; Kopczynski, P. Plasma ghrelin and interleukin-6 levels correlate with body mass index and arterial blood pressure in males with essential hypertension. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eder, K.; Baffy, N.; Falus, A.; Fulop, A.K. The major inflammatory mediator interleukin-6 and obesity. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosalski, R.; Guzik, T.J. Perivascular adipose tissue inflammation in vascular disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 3496–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, N. GHSR deficiency suppresses neointimal formation in injured mouse arteries. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 479, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iantorno, M.; Chen, H.; Kim, J.; Tesauro, M.; Lauro, D.; Cardillo, C.; Quon, M. Ghrelin Has Novel Vascular Actions That Mimic PI 3-Kinase-Dependent Actions of Insulin to Stimulate Production of NO from Endothelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 292, E756–E764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, G.; Chen, Q.; Ke, D. Octanoylated Ghrelin Attenuates Angiogenesis Induced by oxLDL in Human Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells via the GHSR1a-Mediated NF-κB Pathway. Metabolism 2015, 64, 1262–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chang, L.; Wang, J.; Xia, L.; Cao, L.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Gao, H. Leptin and Risk Factors for Atherosclerosis: A Review. Medicine 2023, 102, e36076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowers, J.R. Endocrine functions of adipose tissue: Focus on adiponectin. Clin. Cornerstone 2008, 9, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Castro, P.; Pena, L.; Cordido, F. Ghrelin in obesity, physiological and pharmacological considerations. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, C.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Leptin Regulation of Immune Responses. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Becerril, S.; Salvador, J.; Portincasa, P.; Colina, I.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Involvement of the Leptin-Adiponectin Axis in Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in the Metabolic Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Pan, Y.; Yang, G.; Cui, Z.; Yu, W.; Liu, H.; Bai, B. Sfrp5/Wnt5a and leptin/adiponectin levels in the serum and the periarterial adipose tissue of patients with peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 87, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, T.; Li, M.; Tanner, M.A.; Yang, Y.; Sowers, J.R.; Korthuis, R.J.; Hill, M.A. Depletion of dendritic cells in perivascular adipose tissue improves arterial relaxation responses in type 2 diabetic mice. Metabolism 2018, 85, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasshauer, M.; Kralisch, S.; Klier, M.; Lossner, U.; Bluher, M.; Klein, J.; Paschke, R. Adiponectin gene expression and secretion is inhibited by interleukin-6 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 301, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadieh, S.; Kim, H.W.; Weintraub, N.L. Potential role of perivascular adipose tissue in modulating atherosclerosis. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Li, H. The role of perivascular adipose tissue in obesity-induced vascular dysfunction. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 3425–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaoka, M.; Suzuki, H.; Shioda, S.; Sekikawa, K.; Saito, Y.; Nagai, R.; Sata, M. Endovascular injury induces rapid phenotypic changes in perivascular adipose tissue. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukkola, O.; Pöykkö, S.; Päivänsalo, M.; Kesäniemi, Y.A. Interactions between ghrelin, leptin and IGF-I affect metabolic syndrome and early atherosclerosis. Ann. Med. 2008, 40, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hucik, B.; Lovell, A.J.; Hoecht, E.M.; Cervone, D.T.; Mutch, D.M.; Dyck, D.J. Regulation of adipose tissue lipolysis by ghrelin is impaired with high-fat diet feeding and is not restored with exercise. Adipocyte 2021, 10, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Paz-Filho, G.; Mastronardi, C.; Franco, C.B.; Wang, K.B.; Wong, M.L.; Licinio, J. Leptin: Molecular mechanisms, systemic pro-inflammatory effects, and clinical implications. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2012, 56, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.P.; Morris, D.R.; Smith, S.; Moxon, J.V.; Golledge, J. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association Between C-Reactive Protein and Major Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2017, 54, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azul, L.; Leandro, A.; Boroumand, P.; Klip, A.; Seiça, R.; Sena, C.M. Increased inflammation, oxidative stress and a reduction in antioxidant defense enzymes in perivascular adipose tissue contribute to vascular dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 146, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhagen, S.N.; Visseren, F.L. Perivascular adipose tissue as a cause of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2011, 214, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, W.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Ying, R.; Chen, Z.; Wu, M.; Qiu, Q.; et al. C-Reactive Protein Derived from Perivascular Adipose Tissue Accelerates Injury-Induced Neointimal Hyperplasia. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, D.G.; Leuchten, N.; Schaller, G.; Gouya, G.; Kolodjaschna, J.; Schmetterer, L.; Kapiotis, S.; Wolzt, M. C-reactive protein is expressed and secreted by peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2006, 146, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.M.; Lee, J.; Pan, Q.; Han, H.; Shen, Z.; Eshghjoo, S.; Wu, C.; Yang, W.; Noh, J.; Threadgill, D.; et al. Nutrient-Sensing Growth Hormone Secretagogue Receptor in Macrophage Programming and Meta-Inflammation. Mol. Metab. 2024, 79, 101852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, P.L.; Pfeiffenberger, M.; Damerau, A.; Buttgereit, T.; Chen, Y.; Gaber, T.; Buttgereit, F. Production of IL-6 and Phagocytosis Are the Most Resilient Immune Functions in Metabolically Compromised Human Monocytes. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 730672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scerif, M.; Goldstone, A.P.; Korbonits, M. Ghrelin in obesity and endocrine diseases. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2011, 340, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fang, W.; Yuan, F.; Qu, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Shen, Y. Plasma ghrelin levels are closely associated with stenosis severity and morphology of angiographically-detected coronary atherosclerosis in patients with coronary artery disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2011, 151, 122–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildman, R.P.; Mancuso, P.; Wang, C.; Kim, M.; Scherer, P.E.; Sowers, M.R. Adipocytokine and ghrelin levels in relation to cardiovascular disease risk factors in women at midlife: Longitudinal associations. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Francesco, V.; Zamboni, M.; Zoico, E.; Mazzali, G.; Dioli, A.; Omizzolo, F.; Bissoli, L.; Fantin, F.; Rizzotti, P.; Solerte, S.; et al. Unbalanced Serum Leptin and Ghrelin Dynamics Prolong Postprandial Satiety and Inhibit Hunger in Healthy Elderly: Another Reason for the “Anorexia of Aging”. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhen, X.; Tao, S.; Dou, J.; Li, P.; Jiang, G. Perivascular fat tissue and vascular aging: A sword and a shield. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 203, 107140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinz, M.J.; Maguire, J.J.; Skepper, J.N.; Davenport, A.P. Functional and immunocytochemical evidence for a role of ghrelin and des-octanoyl ghrelin in the regulation of vascular tone in man. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 69, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beiras-Fernandez, A.; Kreth, S.; Weis, F.; Ledderose, C.; Pöttinger, T.; Dieguez, C.; Beiras, A.; Reichart, B. Altered myocardial expression of ghrelin and its receptor (GHSR-1a) in patients with severe heart failure. Peptides 2010, 31, 2222–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhou, M.; Cui, X.; Simms, H.H.; Wang, P. Upregulation of cardiovascular ghrelin receptor occurs in the hyperdynamic phase of sepsis. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004, 287, H1296–H1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.L.; Ding, F.; Wang, D.P.; Zhou, L.; Cao, J.M. Hexarelin attenuates atherosclerosis via inhibiting LOX-1-NF-κB signaling pathway-mediated macrophage ox-LDL uptake in ApoE−/− mice. Peptides 2019, 121, 170122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Ke, D.; Li, G. Ghrelin inhibits atherosclerotic plaque angiogenesis and promotes plaque stability in a rabbit atherosclerotic model. Peptides 2017, 90, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, J.P.H.; Pearson, J.T.; Thomas, K.N.; Tsuchimochi, H.; Hosoda, H.; Kojima, M.; Sato, T.; Jones, G.T.; Denny, A.P.; Daniels, L.J.; et al. Dysregulation of ghrelin in diabetes impairs the vascular reparative response to hindlimb ischemia in a mouse model: Clinical relevance to peripheral artery disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fang, W.Y.; Qu, X.K.; Yuan, F.; Wang, W.G.; Fei, J.; Wang, Z.G. AMPK activity is down-regulated in endothelial cells of GHS-R(−/−) mice. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, K.B.; Cheng, C.H.; Wise, H. Anti-inflammatory activity of ghrelin in human carotid artery cells. Inflammation 2009, 32, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, B.; Hunne, B.; Hirayama, H.; Sartor, D.M.; Nguyen, T.V.; Abogadie, F.C.; Ferens, D.; McIntyre, P.; Ban, K.; Baell, J.; et al. Sites of action of ghrelin receptor ligands in cardiovascular control. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 303, H1011–H1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameters | GHSR-1a (−) Men (n = 6) Women (n = 1) | GHSR-1a (+) Men (n = 4) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 66.57 ± 8.89 | 66.75 ± 7.63 | 0.85 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 33.43 ± 2.96 | 31.25 ± 0.50 | 0.09 |
| Central obesity index | 0.48 ± 0.06 | 0.56 ± 0.03 | 0.04 * |
| White blood cell count | 9337.14 ± 1383.29 | 13,440.00 ± 5207.10 | 0.04 * |
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio | 1968.36 ± 968.92 | 3358.38 ± 672.62 | 0.04 * |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 269.71 ± 71.69 | 242.50 ± 29.01 | 0.57 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 296.29 ± 63.13 | 366.25 ± 16.01 | 0.03 * |
| Total Chol/HDL Chol | 5.45 ± 1.67 | 5.02 ± 0.6 | 0.85 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 114.43 ± 32.41 | 119.75 ± 28.19 | 0.45 |
| Hb A1C (%) | 6.79 ± 0.85 | 6.78 ± 0.56 | 0.70 |
| Serum CRP (mg/L) | 27.71 ± 22.32 | 56.50 ± 22.13 | 0.06 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 305.71 ± 120.40 | 461.50 ± 34.58 | 0.06 |
| Parameters | GHSR-1a (−) Men (n = 6) Women (n = 1) | GHSR-1a (+) Men (n = 4) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| In Atherosclerotic plaque | - | - | - |
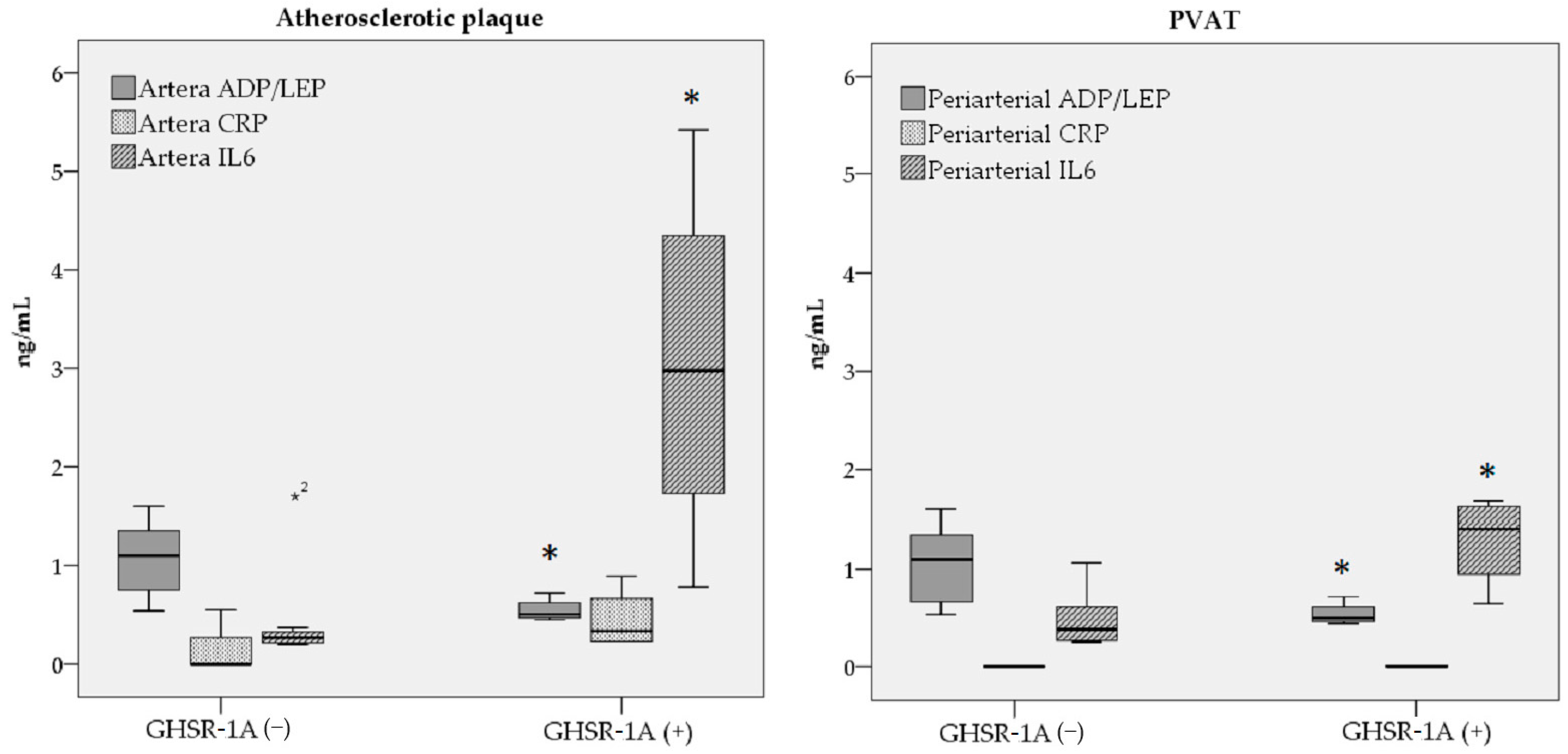
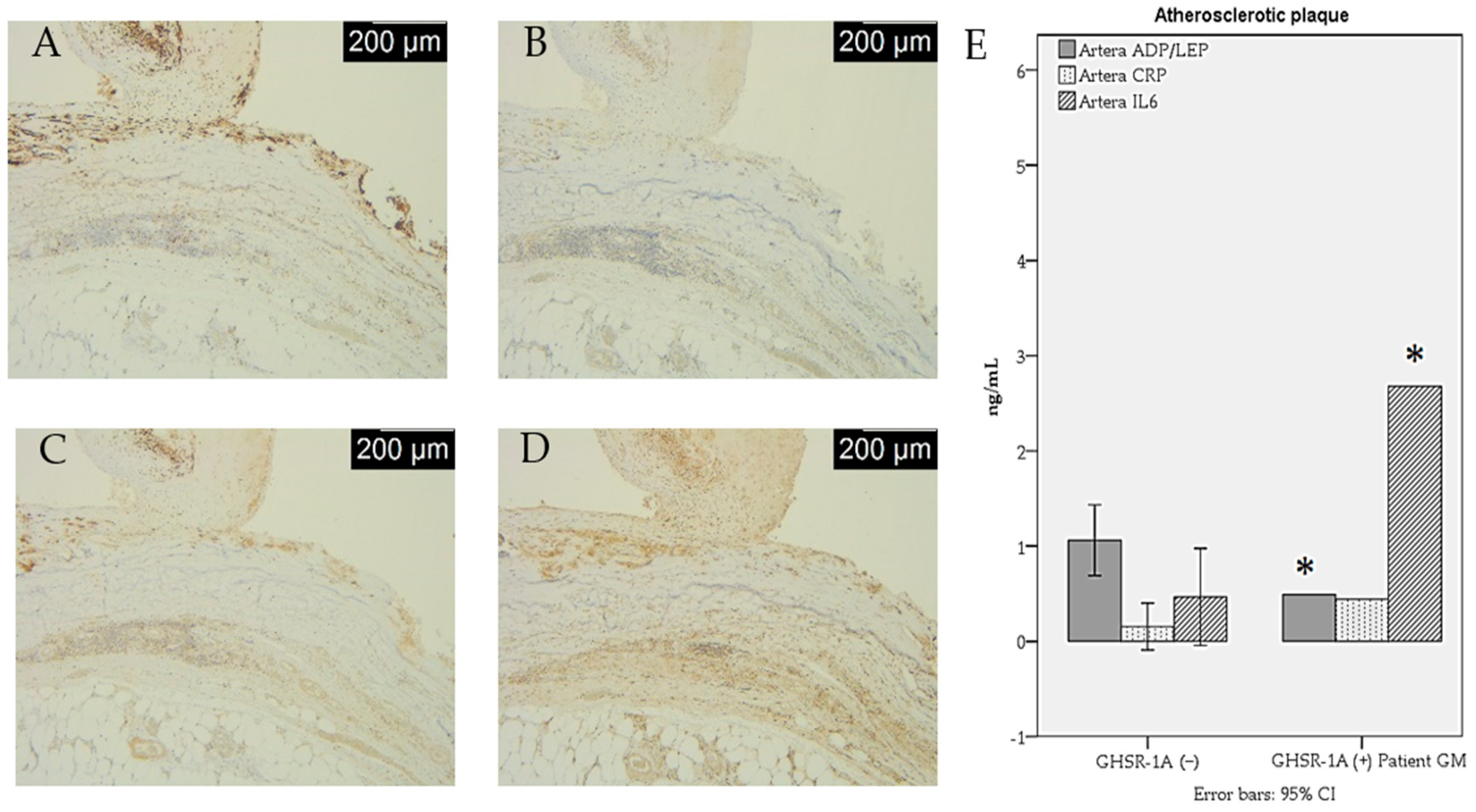
| Adiponectin (ng/dL) | 3.94 ± 2.65 | 4.68 ± 3.67 | 0.85 |
| Leptin (ng/dL) | 5.04 ± 4.48 | 9.44 ± 7.54 | 0.26 |
| ADP/LEP ratio | 1.06 ± 0.40 | 0.55 ± 0.12 | 0.02 * |
| Tissue CRP (ng/dL) | 1.56 ± 2.65 | 4.47 ± 3.11 | 0.12 |
| IL-6 (ng/dL) | 4.65 ± 5.51 | 30.37 ± 19.10 | 0.01 * |
| In PVAT | - | - | - |
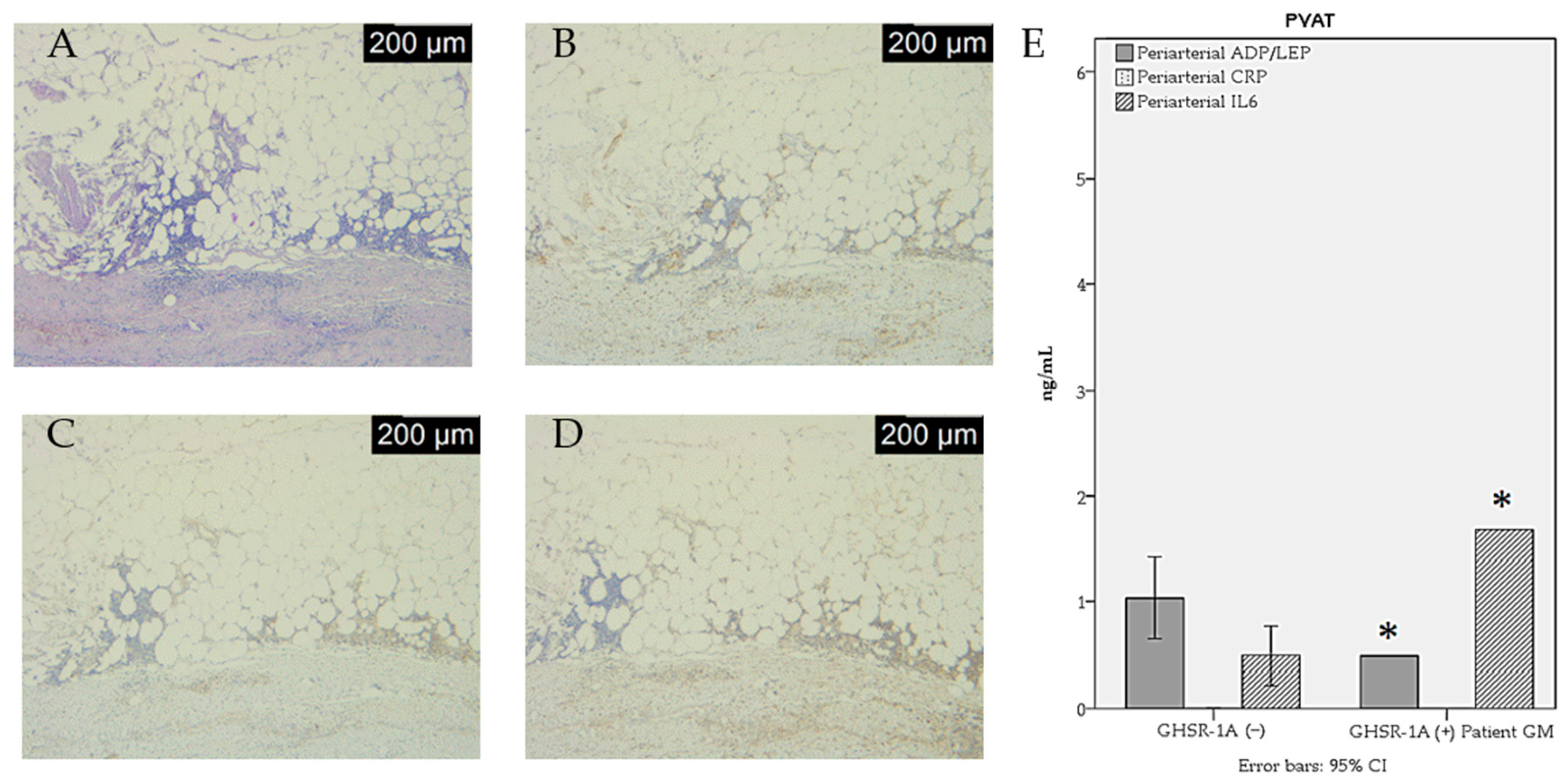
| Adiponectin (ng/dL) | 1.63 ± 0.80 | 1.77 ± 1.03 | 0.64 |
| Leptin (ng/dL) | 1.91 ± 1.60 | 3.43 ± 2.30 | 0.26 |
| ADP/LEP ratio | 1.04 ± 0.42 | 0.55 ± 0.12 | 0.04 * |
| Tissue CRP (ng/dL) | 0 | 0 | 1.00 |
| IL-6 (ng/dL) | 4.94 ± 3.02 | 12.87 ± 4.63 | 0.02 * |
| Histological Examination and IHC | GHSR-1a (−) (n = 7) | GHSR-1a (+) (n = 4) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 * | ≥2 | 0 | 1 | ≥2 | |
| Atherosclerotic plaque | ||||||
| Inflammation intensity | 5 (71.4%) | 2 (28.6) | _ | _ | 2 (50%) | 2 (50%) |
| Calcification | 4 (57.1%) | 3 2.9%) | _ | _ | 4 (100%) | _ |
| Ulceration | 5 (71.4%) | 2 (28.6%) | _ | _ | 4 (100%) | _ |
| Thrombosis | 4 (57.1%) | 3 (42.9%) | _ | _ | 4 (100%) | _ |
| CD68 | 4 (57.1%) | 3 (42.9%) | _ | _ | 4 (100%) | _ |
| CD80 | 5 (71.4%) | 2 (28.6%) | _ | _ | 1 (25%) | 3 (75%) |
| CD14 | 7 (100%) | _ | _ | 2 (50%) | _ | 2 (50%) |
| PVAT | ||||||
| Inflammation intensity | 4 (57.1%) | 3 (42.9) | _ | 1 (25%) | 2 (50%) | 1 (25%) |
| CD68 | 2 (28.6%) | 2 (28.6%) | 3 (42.9%) | 1 (25%) | 1 (25%) | 2 (50%) |
| CD80 | 5 (71.4%) | 2 (28.6%) | _ | 2 (50%) | 1 (25%) | 1 (25%) |
| CD14 | 6 (85.7%) | _ | 1 (14.3%) | 2 (50%) | _ | 2 (50%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peiu, S.N.; Zugun-Eloae, F.; Stoica, B.; Anisie, E.; Iosep, D.G.; Danciu, M.; Silivestru-Crețu, I.; Akad, F.; Avadanei, A.N.; Condur, L.; et al. Obesity-Induced PVAT Dysfunction and Atherosclerosis Development: The Role of GHSR-1a in Increased Macrophage Infiltration and Adipocytokine Secretion. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12030087
Peiu SN, Zugun-Eloae F, Stoica B, Anisie E, Iosep DG, Danciu M, Silivestru-Crețu I, Akad F, Avadanei AN, Condur L, et al. Obesity-Induced PVAT Dysfunction and Atherosclerosis Development: The Role of GHSR-1a in Increased Macrophage Infiltration and Adipocytokine Secretion. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(3):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12030087
Chicago/Turabian StylePeiu, Sorin Nicolae, Florin Zugun-Eloae, Bogdan Stoica, Ecaterina Anisie, Diana Gabriela Iosep, Mihai Danciu, Iustina Silivestru-Crețu, Fawzy Akad, Andrei Nicolae Avadanei, Laura Condur, and et al. 2025. "Obesity-Induced PVAT Dysfunction and Atherosclerosis Development: The Role of GHSR-1a in Increased Macrophage Infiltration and Adipocytokine Secretion" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 3: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12030087
APA StylePeiu, S. N., Zugun-Eloae, F., Stoica, B., Anisie, E., Iosep, D. G., Danciu, M., Silivestru-Crețu, I., Akad, F., Avadanei, A. N., Condur, L., Popa, R. F., & Mocanu, V. (2025). Obesity-Induced PVAT Dysfunction and Atherosclerosis Development: The Role of GHSR-1a in Increased Macrophage Infiltration and Adipocytokine Secretion. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(3), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12030087









