Plasma Fibronectin as a Novel Predictor of Coronary Heart Disease: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Definition
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Biomarker Assays
2.5. Coronary Angiography
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Plasma Biomarkers
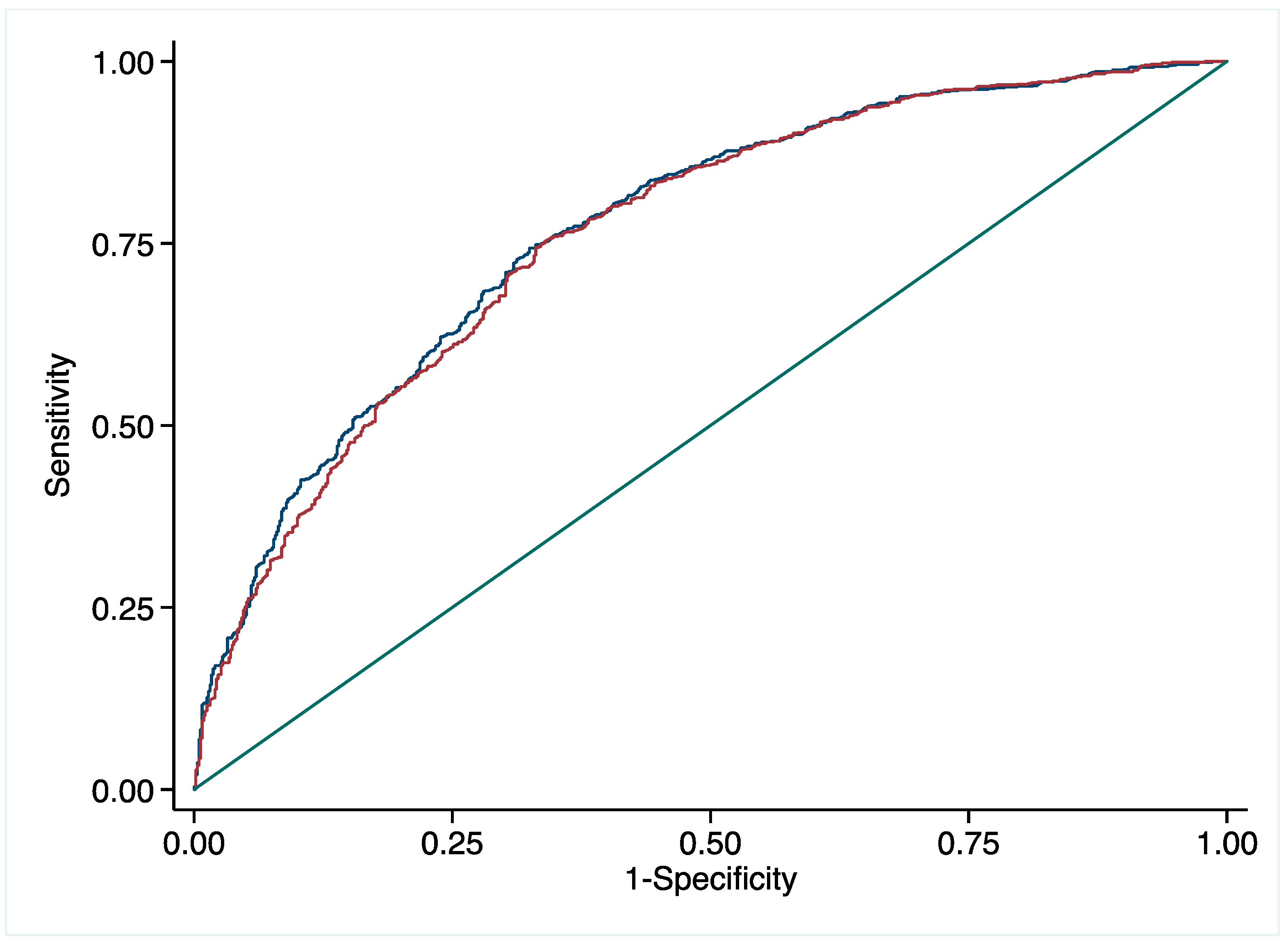
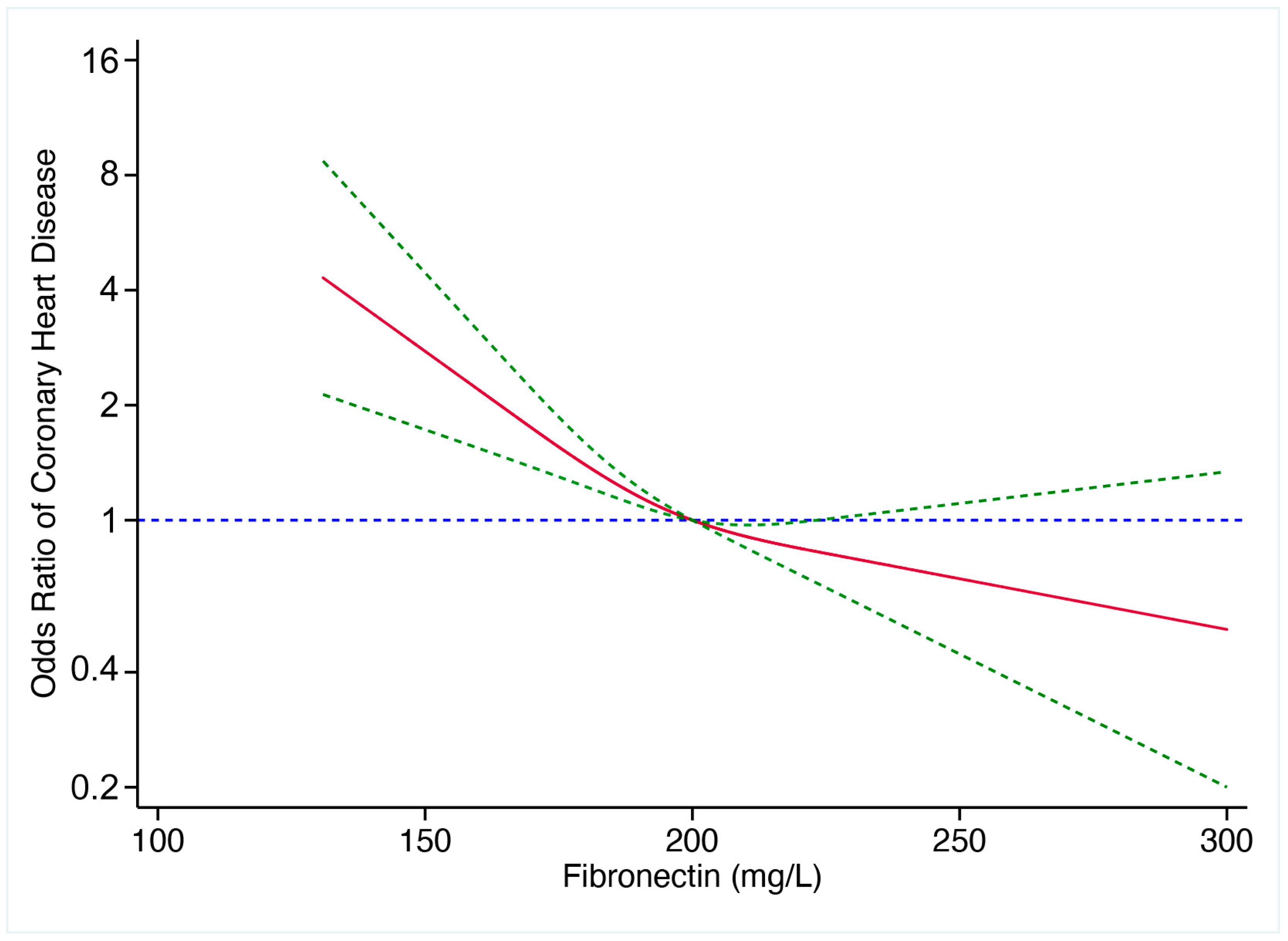
3.3. Predictive Value of pFN for CHD
3.4. Predictive Value of pFN for the Severity of CHD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benjamin, E.J.; Virani, S.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Delling, F.N.; Deo, R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2018 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 137, e67–e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Writing Committee of the Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China. Annual report on cardiovascular health and diseases in China 2020. J. Cardiovasc. Pulm. Dis. 2021, 40, 885–889. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.E.; JebaMercy, G.; Pazhanchamy, K.; Guo, X.; Ngan, S.C.; Liou, K.C.K.; Lynn, S.E.; Ng, S.S.; Meng, W.; Lim, S.C.; et al. Aging-induced isoDGR-modified fibronectin activates monocytic and endothelial cells to promote atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2021, 324, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornblihtt, A.R.; Pesce, C.G.; Alonso, C.R.; Cramer, P.; Srebrow, A.; Werbajh, S.; Muro, A.F. The fibronectin gene as a model for splicing and transcription studies. FASEB J. 1996, 10, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirbhate, U.; Bajaj, P.; Pandher, J.; Durge, K. Fibronectin and Its Applications in Dentistry and Periodontics: A Cell Behaviour Conditioner. Cureus 2022, 14, e30702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.S.; Muro, A.F. Fibronectin splice variants: Understanding their multiple roles in health and disease using engineered mouse models. IUBMB Life 2011, 63, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, W.S.; Midwood, K.S. Plasma and cellular fibronectin: Distinct and independent functions during tissue repair. Fibrogenes. Tissue Repair. 2011, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.; Boekhoven, J.; Dickerson, M.B.; Naik, R.R.; Stupp, S.I. Biopolymers and supramolecular polymers as biomaterials for biomedical applications. MRS Bull. 2015, 40, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, T.L.; Li, H.Y.; Wan, Y.S.; Peng, N.F.; Gui, X.E.; Zhu, Y. Hepatitis B Virus Stimulated Fibronectin Facilitates Viral Maintenance and Replication through Two Distinct Mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, M.K.; Mosher, D.F. Fibronectin: Structure, assembly, and cardiovascular implications. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyberg, J.; Blomgren, K.; Roy, J.; Tran, P.K.; Hedin, U. Phenotypic Modulation of Smooth Muscle Cells after Arterial Injury Is Associated with Changes in the Distribution of Laminin and Fibronectin. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1997, 45, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcelik, F.; Erdogan, O.; Aktoz, M.; Ekuklu, G.; Tatli, E.; Demir, M. Diagnostic value of plasma fibronectin level in predicting the presence and severity of coronary artery disease. Ann. Hematol. 2009, 88, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Krepinsky, J.C.; Wang, C.; Segbo, J.; Zheng, F. Association study between fibronectin and coronary heart disease. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2006, 44, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavalle, J.P.; Wu, S.S.; Hughey, R.; Madamanchi, N.R.; Stouffer, G.A. Plasma fibronectin levels and coronary artery disease. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 864–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.B.; Cui, N.H.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.J.; Ma, J.F.; Ming, L. Leukocyte telomere length, mitochondrial DNA copy number, and coronary artery disease risk and severity: A two-stage case-control study of 3064 Chinese subjects. Atherosclerosis 2019, 284, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; Chaitman, B.R.; Bax, J.J.; Morrow, D.A.; White, H.D. Executive Group on behalf of the Joint European Society of Cardiology/American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/World Heart Federation Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial I. Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (2018). Circulation 2018, 138, e618–e651. [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, e263–e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 75, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, T.; Borghi, C.; Charchar, F.; Khan, N.A.; Poulter, N.R.; Prabhakaran, D.; Ramirez, A.; Schlaich, M.; Stergiou, G.S.; Tomaszewski, M.; et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1334–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Committee for Guideline R. 2018 Chinese Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension-A report of the Revision Committee of Chinese Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 182–241. [Google Scholar]
- American Diabetes A. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S15–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, C.; Ma, X.; Gao, Y.; Song, X.; Xiao, S.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, X.; et al. Recommendations in clinical practice guidelines on gout: Systematic review and consistency analysis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hansson, G.K. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanisaber, H.; Rouleau, L.; Faucheux, N. Effect of BMP-9 on endothelial cells and its role in atherosclerosis. Front. Biosci. Landmark Ed. 2019, 24, 994–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: A perspective for the 1990s. Nature 1993, 362, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudijanto, A. The role of vascular smooth muscle cells on the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Acta Med. Indones. 2007, 39, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Galanakis, D.K.; Protopopova, A.; Li, K.; Yu, Y.; Ahmed, T.; Sensel, L.; Heslin, R.; Gouda, M.; Koo, J.; Weisel, J.; et al. Novel characteristics of soluble fibrin: Hypercoagulability and acceleration of blood sedimentation rate mediated by its generation of erythrocyte-linked fibers. Cell Tissue Res. 2022, 387, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ni, H. Fibronectin maintains the balance between hemostasis and thrombosis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3265–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Wang, B.; Sun, L. Expression and significance of integrin alpha5beta1 and fibronectin in atherosclerotic plaques from autopsy specimens. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2017, 46, 182–186. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, N.; Hou, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, T.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Mu, W.; Lv, X.; Li, A. Increased Fibronectin Impairs the Function of Excitatory/Inhibitory Synapses in Hirschsprung Disease. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 40, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashchekina, Y.; Nikonov, P.; Prasolov, N.; Sulatsky, M.; Chabina, A.; Nashchekin, A. The Structural Interactions of Molecular and Fibrillar Collagen Type I with Fibronectin and Its Role in the Regulation of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Morphology and Functional Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.L.; Zang, Y.M.; Zhu, M.Z. The consumption of fibronectin content in coronary artery stenosis in dogs. Sheng Li Xue Bao 1989, 41, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saba, T.M.; Jaffe, E. Plasma fibronectin (opsonic glycoprotein): Its synthesis by vascular endothelial cells and role in cardiopulmonary integrity after trauma as related to reticuloendothelial function. Am. J. Med. 1980, 68, 577–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmekci, H.; Ekmekci, O.B.; Sonmez, H.; Ozturk, Z.; Domanic, N.; Kokoglu, E. Evaluation of Fibronectin, Vitronectin, and Leptin Levels in Coronary Artery Disease: Impacts on Thrombosis and Thrombolysis. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2005, 11, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Non-CHD | CHD | Single | Double | Triple | Low | Medium-Low | Medium-High | High | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 649 | n = 995 | n = 354 | n = 315 | n = 326 | n = 249 | n = 262 | n = 237 | n = 247 | |
| Age (years) | 59 (50, 67.5) | 67 (58, 74) a | 66 (56, 74) | 68 (57, 75) | 67 (59, 74) | 68 (60, 75) | 68 (60, 76) | 66 (57, 74) d,e | 66 (56, 73) d,e |
| SEX, (%) | |||||||||
| Male | 327 (50.4) | 670 (67.3) a | 231 (65.3) | 216 (68.6) | 223 (68.4) | 143 (57.4) | 183 (69.8) d | 163 (68.8) d | 181 (73.3) d,e,f |
| Female | 322 (49.6) | 325 (32.7) | 123 (34.7) | 99 (31.4) | 103 (31.6) | 106 (42.6) | 79 (30.2) d | 74 (31.2) d | 66 (26.7) d,e,f |
| BMI, (kg/m2) | 23.6 (22.6, 24.6) | 23.8 (22.5, 25.0) | 23.5 (22.3, 24.9) | 23.9 (22.7, 25.0) | 23.8 (22.6, 24.8) | 23.7 (22.6, 25.0) | 23.9 (22.5, 24.9) | 23.8 (22.4, 24.9) | 23.7 (22.4, 24.9) |
| Hypertension (%) | 321 (49.5) | 697 (70.1) a | 222 (62.7) | 224 (71.1) | 251 (77.0) b | 164 (65.9) | 195 (74.4) | 158 (66.7) | 180 (72.9) |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 112 (17.3) | 402 (40.4) a | 112 (31.6) | 128 (40.6) b | 162 (49.7) b | 76 (30.5) | 115 (43.9) d | 92 (38.8) d | 119 (48.2) d,e,f |
| Hyperuricemia (%) | 93 (14.3) | 149 (15.0) | 52 (14.7) | 58 (18.4) | 39 (12.0) | 40 (16.1) | 46 (17.6) | 29 (12.2) | 34 (13.8) |
| AMI (%) | 0 | 282 (28.3) a | 61 (17.2) | 84 (26.7) b | 137 (42.0) b,c | 13 (5.2) | 56 (21.4) d | 87 (36.7) d,e | 126 (51.0) d,e,f |
| AHF (%) | 43 (6.62) | 385 (39.0) a | 107 (30.2) | 142 (45.1) b | 136 (41.7) b | 72 (28.9) | 114 (43.5) d | 91 (38.4) d | 108 (43.7) d |
| History of MI (%) | 0 | 93 (9.35) a | 28 (7.91) | 36 (11.4) | 29 (8.90) | 9 (3.6) | 32 (12.2) d | 25 (10.5) d | 27 (10.9) d |
| History of PCI (%) | 0 | 203 (20.4) a | 61 (17.2) | 75 (23.8) | 67 (20.6) | 30 (12.0) | 71 (27.1) d | 56 (23.6) d,e | 46 (18.6) d,e |
| Non-CHD | CHD | Single | Double | Triple | Low | Medium-Low | Medium-High | High | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 649 | n = 995 | n = 354 | n = 315 | n = 326 | n = 249 | n = 262 | n = 237 | n = 247 | |
| pFN (mg/L) | 197.2 (185.1, 211.5) | 190.2 (174.1, 205.7) a | 189.8 (172.6, 206.0) | 190.6 (175.9, 207.6) | 190.1 (174.2, 204.6) | 191.0 (174.6, 206.9) | 188.6 (173.1, 205.9) | 191.2 (176.6, 207.3) | 190.2 (173.6, 203.0) |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 3.06 (2.38, 3.73) | 2.76 (2.09, 3.61) a | 2.73 (2.05, 3.52) | 2.66 (1.96, 3.59) | 2.87 (2.20, 3.68) | 2.73 (2.07, 3.64) | 2.64 (2.03, 3.35) | 2.82 (2.11, 3.79) | 2.86 (2.08, 3.69) |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.9 (4.1, 5.6) | 4.5 (3.7, 5.4) a | 4.4 (3.7, 5.3) | 4.5 (3.7, 5.6) | 4.5 (3.7, 5.6) | 4.5 (3.7, 5.5) | 4.4 (3.6, 5.2) | 4.5 (3.8, 5.7) | 4.6 (3.7, 5.6) |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.38 (1.05, 1.98) | 1.4 (1.0, 2.0) | 1.33 (0.98, 1.85) | 1.41 (0.99, 2.08) | 1.45 (1.05, 2.09) | 1.34 (1.00, 1.89) | 1.26 (0.96, 1.96) | 1.47 (1.06, 1.91) | 1.50 (1.01, 2.23) |
| CTnI (pg/mL) | 0.012 (0.01, 0.012) | 0.012 (0.01, 0.42) a | 0.012 (0.01, 0.03) | 0.012 (0.01, 0.2) | 0.02 (0.012, 3.13) b,c | 0.012 (0.01, 0.02) | 0.012 (0.01, 0.06) d | 0.013 (0.01, 6.69) d,e | 0.06 (0.01, 12.7) d,e,f |
| CK-MB (ug/L) | 0.6 (0.33, 1.2) | 1.06 (0.55, 3.2) a | 0.84 (0.46, 2.04) | 1.11 (0.54, 2.75) b | 1.44 (0.67, 5.96) b,c | 0.75 (0.43, 1.41) | 0.92 (0.53, 2.23) d | 1.25 (0.61, 11.5) d,e | 1.8 (0.74, 18.1) d,e |
| WBC (*109/L) | 6.41 (5.49, 6.94) | 6.48 (5.68, 6.92) | 6.48 (5.72, 6.86) | 6.48 (5.64, 7.02) | 6.48 (5.71, 7.18) | 6.48 (5.75, 7.39) | 6.48 (5.54, 6.83) | 6.48 (5.60, 6.93) | 6.48 (5.73, 7.19) |
| Variables | OR | Lower 95% CI | Upper 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pFN | 0.987 | 0.982 | 0.992 | <0.001 |
| Age | 1.061 | 1.05 | 1.073 | <0.001 |
| TG Sex Hypertension | 1.243 3.584 1.492 | 1.108 2.791 1.18 | 1.395 4.604 1.887 | <0.001 <0.001 0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 3.18 | 2.437 | 4.15 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, L.; Deng, H.; Li, J.; Lu, G.; Zhai, Y.-S. Plasma Fibronectin as a Novel Predictor of Coronary Heart Disease: A Retrospective Study. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10100415
Peng L, Deng H, Li J, Lu G, Zhai Y-S. Plasma Fibronectin as a Novel Predictor of Coronary Heart Disease: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2023; 10(10):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10100415
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Longyun, Haiwei Deng, Jie Li, Guihua Lu, and Yuan-Sheng Zhai. 2023. "Plasma Fibronectin as a Novel Predictor of Coronary Heart Disease: A Retrospective Study" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 10, no. 10: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10100415
APA StylePeng, L., Deng, H., Li, J., Lu, G., & Zhai, Y.-S. (2023). Plasma Fibronectin as a Novel Predictor of Coronary Heart Disease: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 10(10), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10100415






