Diabetes, Hypertension, and Comorbidity among Bangladeshi Adults: Associated Factors and Socio-Economic Inequalities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Study Design
2.2. Outcome Variables
2.3. Explanatory Variables
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.4.1. Descriptive Measures of Association
2.4.2. Measures of Inequality
2.4.3. Decomposition of CIX
2.5. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Study Participants
3.2. Prevalence of Diabetes, Hypertension, and Comorbidity
3.3. Factors Associated with Diabetes, Hypertension, and Comorbidity
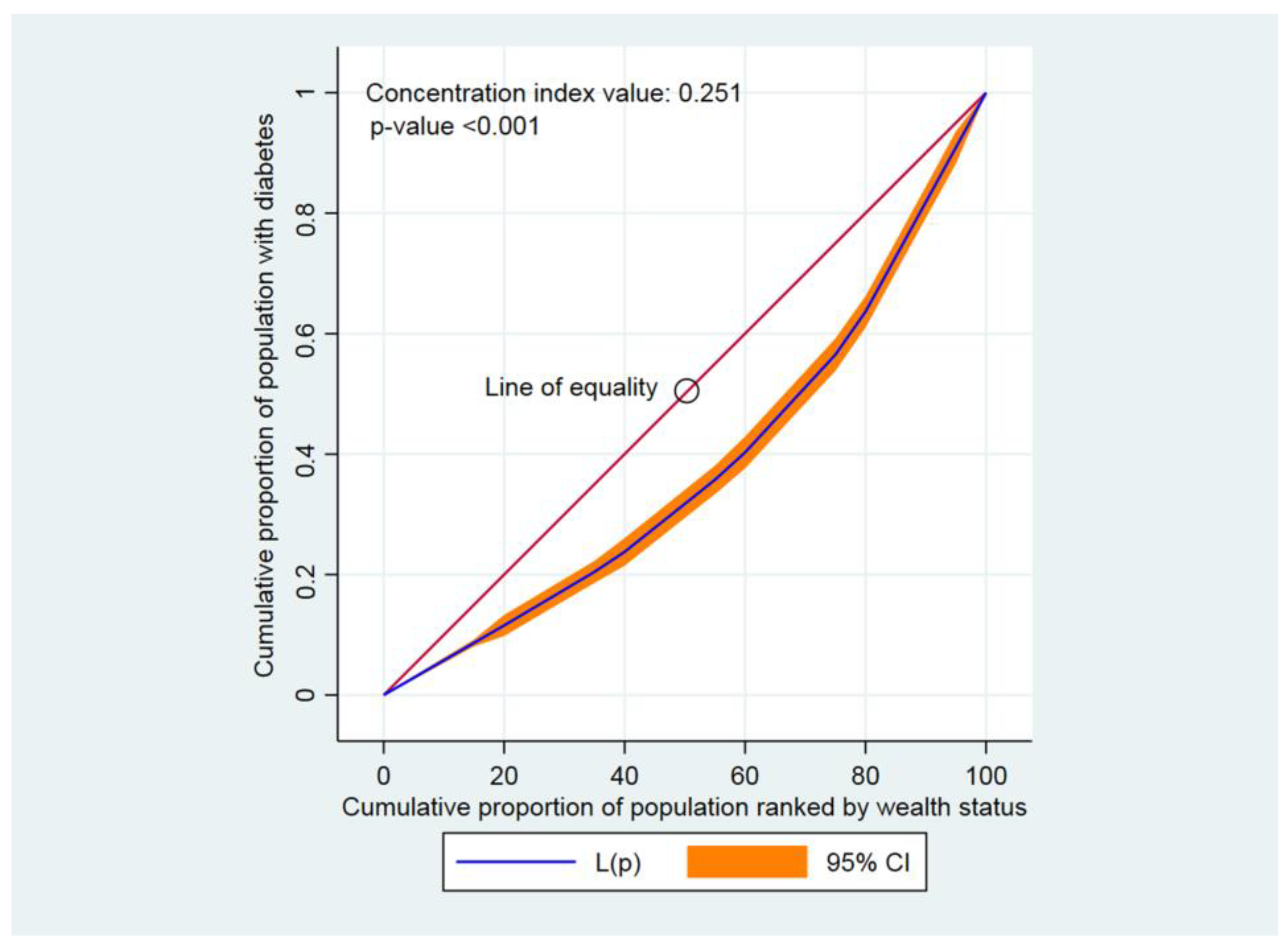
3.4. Socioeconomic Inequality in Diabetes, Hypertension, and Comorbidity
3.5. Decomposing the Socioeconomic Inequality
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BDHS | Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| BP | Blood Pressure |
| CAD | Coronary Artery Disease |
| CC | Concentration Curve |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CIX | Concentration Index |
| EA | Enumeration Area |
| FPG | Fasting Plasma Glucose |
| GBD | Global Burden of Disease |
| HBP | High Blood Pressure |
| ICC | Intra-Class Correlation Coefficient |
| IDF | International Diabetes Federation |
| IQR | Inter-Quartile Range |
| LIMCs | Low-and-Middle-Income Countries |
| NIPORT | National Institute of Population Research and Training |
| NCD | Non-Communicable Disease |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PA | Physical Activity |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Abebe, S.M.; Berhane, Y.; Worku, A.; Getachew, A. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Hypertension: A Crossectional Community Based Study in Northwest Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Rahman, M.; Hasan, R.; Shima, S.A.; Faruquee, M.H.; Islam, T.; Haque, S.E. Hypertension and Associated Risk Factors in Some Selected Rural Areas of Bangladesh. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2014, 2, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erem, C.; Hacihasanoglu, A.; Kocak, M.; Deger, O.; Topbas, M. Prevalence of Prehypertension and Hypertension and Associated Risk Factors among Turkish Adults: Trabzon Hypertension Study. J. Public Health 2009, 31, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xu, Y.; Pan, X.; Xu, J.; Ding, Y.; Sun, X.; Song, X.; Ren, Y.; Shan, P.-F. Global, Regional, and National Burden and Trend of Diabetes in 195 Countries and Territories: An Analysis from 1990 to 2025. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.S.; Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Danaei, G.; Shibuya, K.; Adair-Rohani, H.; AlMazroa, M.A.; Amann, M.; Anderson, H.R.; Andrews, K.G. A Comparative Risk Assessment of Burden of Disease and Injury Attributable to 67 Risk Factors and Risk Factor Clusters in 21 Regions, 1990–2010: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2224–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. A Global Brief on Hypertension: Silent Killer, Global Public Health Crisis: World Health Day 2013; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- International Diabetes Federation IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th Ed.; Brussels, Belgium, 2019. Available online: https://www.diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 6 August 2021).
- Nguyen, T.N.; Chow, C.K. Global and National High Blood Pressure Burden and Control. Lancet 2021, 398, 932–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Carrillo-Larco, R.M.; Danaei, G.; Riley, L.M.; Paciorek, C.J.; Stevens, G.A.; Gregg, E.W.; Bennett, J.E.; Solomon, B.; Singleton, R.K.; et al. Worldwide Trends in Hypertension Prevalence and Progress in Treatment and Control from 1990 to 2019: A Pooled Analysis of 1201 Population-Representative Studies with 104 Million Participants. Lancet 2021, 398, 957–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDF Diabetes Atlas Diabetes around the World in 2021. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/#:~:text=Diabetesaroundtheworldin2021%3A,-andmiddle-incomecountries (accessed on 18 December 2022).
- Thakur, J.S.; Nangia, R.; Singh, S. Progress and Challenges in Achieving Noncommunicable Diseases Targets for the Sustainable Development Goals. FASEB BioAdv. 2021, 3, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global Estimates of Diabetes Prevalence for 2017 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Khan, M.N.; Oldroyd, J.C.; Rana, J.; Chowdhury, E.K.; Karim, M.N.; Hossain, M.B. Prevalence of Diabetes and Prediabetes among Bangladeshi Adults and Associated Factors: Evidence from the Demographic and Health Survey, 2017-18. medRxiv 2021.
- Bishwajit, G.; Yaya, S.; Seydou, I. Diabetes Mellitus and High Blood Pressure in Relation to BMI among Adult Non-Pregnant Women in Bangladesh. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2017, 11, S217–S221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kibria, G.M.; Swasey, K.; Choudhury, A.; Burrowes, V.; Stafford, K.A.; Uddin, S.M.I.; Mirbolouk, M.; Sharmeen, A.; Angela, K.C.; Mitra, D.K. The New 2017 ACC/AHA Guideline for Classification of Hypertension: Changes in Prevalence of Hypertension among Adults in Bangladesh. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2018, 32, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, M.A.B.; Uddin, M.J.; Haque, M.R.; Ibrahimou, B. Hypertension among Adults in Bangladesh: Evidence from a National Cross-Sectional Survey. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2016, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eryd, S.A.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Manhem, K.; Rosengren, A.; Svensson, A.-M.; Miftaraj, M.; Franzén, S.; Björck, S. Blood Pressure and Complications in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes and No Previous Cardiovascular Disease: National Population Based Cohort Study. BMJ 2016, 354, i4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, I.H.; Bangalore, S.; Benetos, A.; Davis, A.M.; Michos, E.D.; Muntner, P.; Rossing, P.; Zoungas, S.; Bakris, G. Diabetes and Hypertension: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrie, J.R.; Guzik, T.J.; Touyz, R.M. Diabetes, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Disease: Clinical Insights and Vascular Mechanisms. Can. J. Cardiol. 2018, 34, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.; Akram, R.; Sheikh, N.; Sarker, A.R.; Sultana, M. Sex-Specific Prevalence, Inequality and Associated Predictors of Hypertension, Diabetes, and Comorbidity among Bangladeshi Adults: Results from a Nationwide Cross-Sectional Demographic and Health Survey. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e029364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Zaman, M.M.; Islam, J.Y.; Chowdhury, J.; Ahsan, H.A.M.N.; Rahman, R.; Hassan, M.; Hossain, Z.; Alam, B.; Yasmin, R. Prevalence, Treatment Patterns, and Risk Factors of Hypertension and Pre-Hypertension among Bangladeshi Adults. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2018, 32, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, T.; Islam, A.; Rawal, L.B.; Islam, S.M.S. Increasing Prevalence of Diabetes in Bangladesh: A Scoping Review. Public Health 2016, 138, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saquib, N.; Khanam, M.A.; Saquib, J.; Anand, S.; Chertow, G.M.; Barry, M.; Ahmed, T.; Cullen, M.R. High Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes among the Urban Middle Class in Bangladesh. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Islam, S.; Pais, P.; Reddy, S.; Dorairaj, P.; Kazmi, K.; Pandey, M.R.; Haque, S.; Mendis, S.; Rangarajan, S. Risk Factors for Early Myocardial Infarction in South Asians Compared with Individuals in Other Countries. Jama 2007, 297, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, A.R.; Sultana, M. Health and Economic Burden of Diabetes in Bangladesh: Priorities for Attention and Control. J. Diabetes 2017, 9, 1118–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Halder, H.R.; Yadav, U.N.; Mistry, S.K. Prevalence of and Factors Associated with Hypertension According to JNC 7 and ACC/AHA 2017 Guidelines in Bangladesh. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talukder, A.; Hossain, M.Z. Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Associated Factors in Bangladesh: Application of Two-Level Logistic Regression Model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.M.; Rahman, M.J.; Abedin, M.M.; Maniruzzaman, M. Investigate the Effect of Diabetes on Hypertension Based on Bangladesh Demography and Health Survey, 2017–18. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kibria, G.M. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Diabetes among Bangladeshi Adults: An Analysis of Demographic and Health Survey 2017–18. Diabetes Epidemiol. Manag. 2021, 2, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.B.; Khan, J.R.; Gupta, R. Das Role of Hypertension in the Association of Overweight and Obesity with Diabetes among Adults in Bangladesh: A Population-Based, Cross-Sectional Nationally Representative Survey. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e050493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization; Public Health Agency of Canada and Canada. Preventing Chronic Diseases: A Vital Investment; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; ISBN 9241563001.
- NIPORT; ICF. Mitra and Associates. Dhaka, Bangladesh: ICF International. Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey 2017-18; NIPORT: Dhaka, Bangladesh; ICF: Rockville, ML, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chobanian, A.V. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure; National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee: The Seventh Report of the Joint National. JAMA 2003, 289, 2560–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. World Health Organization BMI Classification; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Talukder, A.; Akter, N.; Sazzad Mallick, T. Exploring Association between Individuals’ Stature and Type 2 Diabetes Status: Propensity Score Analysis. Environ. Health Insights 2019, 13, 1178630219836975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.R.; Shaw, E. Multilevel Logistic Regression Analysis Applied to Binary Contraceptive Prevalence Data. J. Data Sci. 2011, 9, 93–110. [Google Scholar]
- Talukder, A. Risk Factors Associated with Wasting among Under-5 Children Residing in Urban Areas of Bangladesh: A Multilevel Modelling Approach. J. Public Health 2021, 29, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagstaff, A.; O’Donnell, O.; Van Doorslaer, E.; Lindelow, M. Analyzing Health Equity Using Household Survey Data: A Guide to Techniques and Their Implementation; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; ISBN 0821369342. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donnell, O.; O’Neill, S.; Van Ourti, T.; Walsh, B. Conindex: Estimation of Concentration Indices. Stata J. 2016, 16, 112–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jann, B. Estimating Lorenz and Concentration Curves. Stata J. 2016, 16, 837–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekholuenetale, M.; Tudeme, G.; Onikan, A.; Ekholuenetale, C.E. Socioeconomic Inequalities in Hidden Hunger, Undernutrition, and Overweight among under-Five Children in 35 Sub-Saharan Africa Countries. J. Egypt. Public Health Assoc. 2020, 95, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhusal, U.P. Predictors of Wealth-Related Inequality in Institutional Delivery: A Decomposition Analysis Using Nepal Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey (MICS) 2019. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilger, M.; Sajaia, Z.; Lokshin, M. Health Equity and Financial Protection: Streamlined Analysis with ADePT Software; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; ISBN 0821384597. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, K.T.; Bundy, J.D.; Kelly, T.N.; Reed, J.E.; Kearney, P.M.; Reynolds, K.; Chen, J.; He, J. Global Disparities of Hypertension Prevalence and Control: A Systematic Analysis of Population-Based Studies from 90 Countries. Circulation 2016, 134, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Oldroyd, J.C.; Chowdhury, E.K.; Hossain, M.B.; Rana, J.; Renzetti, S.; Islam, R.M. Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment, and Control of Hypertension in Bangladesh: Findings from National Demographic and Health Survey, 2017–2018. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2021, 23, 1830–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, T.; Pervin, S.; Tanim, M.I.A.; Niessen, L.; Islam, A. Bangladesh Policy on Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases: A Policy Analysis. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Gilmour, S.; Akter, S.; Abe, S.K.; Saito, E.; Shibuya, K. Prevalence and Control of Hypertension in Bangladesh: A Multilevel Analysis of a Nationwide Population-Based Survey. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibria, A.; Muhammed, G.; Gupta, R.D.; Nayeem, J. Prevalence, Awareness, and Control of Hypertension among Bangladeshi Adults: An Analysis of Demographic and Health Survey 2017–18. Clin. Hypertens. 2021, 27, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Ahsan, K.Z.; Jamil, K.; Haider, M.M.; Khan, S.H.; Chakraborty, N.; Streatfield, P.K. Demographic, Socioeconomic, and Biological Correlates of Hypertension in an Adult Population: Evidence from the Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey 2017–18. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Daghri, N.M.; Al-Attas, O.S.; Alokail, M.S.; Alkharfy, K.M.; Yousef, M.; Sabico, S.L.; Chrousos, G.P. Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Other Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases in the Central Region, Saudi Arabia (Riyadh Cohort 2): A Decade of an Epidemic. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akl, C.; Akik, C.; Ghattas, H.; Obermeyer, C.M. Gender Disparities in Midlife Hypertension: A Review of the Evidence on the Arab Region. Women’s Midlife Health 2017, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozanski, A.; Blumenthal, J.A.; Kaplan, J. Impact of Psychological Factors on the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease and Implications for Therapy. Circulation 1999, 99, 2192–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavini, M.; Stidley, C.A.; Shah, V.O.; Narva, A.S.; Tentori, F.; Kessler, D.S.; Bobelu, A.; Albert, C.P.; Bobelu, J.; Jamon, E. Prevalence of Diabetes Is Higher among Female than Male Zuni Indians. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, M.; Chorghade, G.; Crozier, S.; Leary, S.; Fall, C. Socio-Economic Factors, Lifestyle and Gender Differences in Body Mass Index in Rural India. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agho, K.E.; Osuagwu, U.L.; Ezeh, O.K.; Ghimire, P.R.; Chitekwe, S.; Ogbo, F.A. Gender Differences in Factors Associated with Prehypertension and Hypertension in Nepal: A Nationwide Survey. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oparil, S.; Acelajado, M.C.; Bakris, G.L.; Berlowitz, D.R.; Cífková, R.; Dominiczak, A.F.; Grassi, G.; Jordan, J.; Poulter, N.R.; Rodgers, A.; et al. Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, E. Blood Pressure and Ageing. Postgrad. Med. J. 2007, 83, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, J.; Shahjahan, M.; Hossain, S.; Chowdhury, H.A.; Ahmed, K.R.; Fatema, K.; Ara, B.R.; Ali, L. Determinants of Overweight and Obesity among Bangladeshi Diabetic Women of Reproductive Age. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Abdul Baker Chowdhury, M.; Uddin, M.D.; Khan, H.M.R.; Haque, M.D. Type 2 Diabetes and Its Correlates among Adults in Bangladesh: A Population Based Stud. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 1070. [Google Scholar]
- Al Kibria, G.M.; Swasey, K.; Hasan, M.Z.; Choudhury, A.; Gupta, R.D.; Abariga, S.A.; Sharmeen, A.; Burrowes, V. Determinants of Hypertension among Adults in Bangladesh as per the Joint National Committee 7 and 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Hypertension Association Hypertension Guidelines. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2018, 12, e45–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, K.; Fuentes, J.; Márquez, J.L. Physical Inactivity, Sedentary Behavior and Chronic Diseases. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2017, 38, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca-Gómez, L.; Abdeen, Z.A.; Hamid, Z.A.; Abu-Rmeileh, N.M.; Acosta-Cazares, B.; Acuin, C.; Adams, R.J.; Aekplakorn, W.; Afsana, K.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A. Worldwide Trends in Body-Mass Index, Underweight, Overweight, and Obesity from 1975 to 2016: A Pooled Analysis of 2416 Population-Based Measurement Studies in 128· 9 Million Children, Adolescents, and Adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.A.B.; Adnan, M.M.; Hassan, M.Z. Trends, Prevalence and Risk Factors of Overweight and Obesity among Women of Reproductive Age in Bangladesh: A Pooled Analysis of Five National Cross-Sectional Surveys. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e018468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linderman, G.C.; Lu, J.; Lu, Y.; Sun, X.; Xu, W.; Nasir, K.; Schulz, W.; Jiang, L.; Krumholz, H.M. Association of Body Mass Index with Blood Pressure among 1.7 Million Chinese Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e181271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, A.; Jayawardena, R.; Anoop, S. Obesity in South Asia: Phenotype, Morbidities, and Mitigation. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hills, A.P.; Arena, R.; Khunti, K.; Yajnik, C.S.; Jayawardena, R.; Henry, C.J.; Street, S.J.; Soares, M.J.; Misra, A. Epidemiology and Determinants of Type 2 Diabetes in South Asia. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, F.W.; Roberts, C.K.; Laye, M.J. Lack of Exercise Is a Major Cause of Chronic Diseases. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 1143. [Google Scholar]
- Association, A.D. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, S62–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugnara, L.; Murillo, S.; Novials, A.; Rojo-Martínez, G.; Soriguer, F.; Goday, A.; Calle-Pascual, A.; Castaño, L.; Gaztambide, S.; Valdés, S. Low Physical Activity and Its Association with Diabetes and Other Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Nationwide, Population-Based Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Jousilahti, P.; Barengo, N.C.; Qiao, Q.; Lakka, T.A.; Tuomilehto, J. Physical Activity, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and Mortality among Finnish Adults with Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Association, A.D. Physical Activity/Exercise and Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, s58–s62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, Y.D.; Dunstan, D.W. The Effectiveness of Physical Activity Interventions for the Treatment of Overweight and Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2004, 7, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, C.; Kriska, A. Role of Physical Activity in Diabetes Management and Prevention. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2008, 108, S19–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, A.; Bachran, R.; Kapellen, T.; Holl, R.W. Effects of Regular Physical Activity on Control of Glycemia in Pediatric Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2006, 160, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, T.J.; Ford, E.S.; Rolle, I.V.; Wheaton, A.G.; Croft, J.B. Associations of Self-Reported Cigarette Smoking with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Co-Morbid Chronic Conditions in the United States. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2015, 12, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Luo, X.; Xu, S.; Liu, W.; Ding, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, W. Trends in Smoking Prevalence and Implication for Chronic Diseases in China: Serial National Cross-Sectional Surveys from 2003 to 2013. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, K.T.; Fuchs, C.S.; Colditz, G.A.; Stampfer, M.J.; Speizer, F.E.; Willett, W.C.; Curhan, G.C. A Prospective Study of Body Mass Index, Hypertension, and Smoking and the Risk of Renal Cell Carcinoma (United States). Cancer Causes Control 2005, 16, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkiewicz, K.; Kjeldsen, S.E.; Hedner, T. Is Smoking a Causative Factor of Hypertension? Blood Press. 2005, 14, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virdis, A.; Giannarelli, C.; Fritsch Neves, M.; Taddei, S.; Ghiadoni, L. Cigarette Smoking and Hypertension. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 2518–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tareque, M.I.; Koshio, A.; Tiedt, A.D.; Hasegawa, T. Are the Rates of Hypertension and Diabetes Higher in People from Lower Socioeconomic Status in Bangladesh? Results from a Nationally Representative Survey. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangladesh Society of Medicine, World Health Organization, Country Office for Bangladesh. Non-Communicable Disease Risk Factor Survey, Bangladesh 2010; World Health Organization, Country Office for Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2011. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/279484 (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Bureau of Statistic. Ministry of Planning, government of B. In Bangladesh Statistics 2017; 2017. Available online: http://bbs.portal.gov.bd/sites/default/files/files/bbs.portal.gov.bd/page/a1d32f13_8553_44f1_92e6_8ff80a4ff82e/Bangladesh%20%20Statistics-2017.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Mutyambizi, C.; Booysen, F.; Stokes, A.; Pavlova, M.; Groot, W. Lifestyle and Socio-Economic Inequalities in Diabetes Prevalence in South Africa: A Decomposition Analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, A.R.; Khanam, M. Socio-Economic Inequalities in Diabetes and Prediabetes among Bangladeshi Adults. Diabetol. Int. 2021, 13, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Rahman, S.A.; Demirbilek, H.; Güemes, M.; Hussain, K. Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia in Children and Adults. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Tasnim, F.; Tariqujjaman, M.; Ahmed, S. Socioeconomic Inequalities of Undiagnosed Diabetes in a Resource-Poor Setting: Insights from the Cross-Sectional Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey 2011. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Naznin, S.; Halder, H.R.; Khan, U.; Hossain, M.M.; Siddiquee, T. Examining the Prevalence of Hypertension by Urban–Rural Stratification: A Cross-Sectional Study of Nepal Demographic and Health Survey. Asian J. Soc. Health Behav. 2021, 4, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, T.; Islam, M.S.; Linton, N.; Rawal, L.B. Socio-Economic Inequality of Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases in Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167140. [Google Scholar]


| Variables | Unweighted | Weighted | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Percentage | Frequency | Percentage | |
| Individual- and household-level variables | ||||
| Age; Mean (SD) | 39.54 | 16.20 | 39.46 | 16.21 |
| 18–34 years | 5437 | 44.80 | 5381 | 45.07 |
| 35–44 years | 2457 | 20.25 | 2421 | 20.28 |
| 45–54 years | 1712 | 14.11 | 1669 | 13.98 |
| 55–64 years | 1379 | 11.36 | 1348 | 11.30 |
| ≥65 years | 1151 | 9.48 | 1119 | 9.38 |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 5227 | 43.07 | 5111 | 42.81 |
| Female | 6909 | 56.93 | 6827 | 57.19 |
| Employment status | ||||
| Yes | 7551 | 62.22 | 7476 | 62.63 |
| No | 4585 | 37.78 | 4462 | 37.37 |
| Educational level | ||||
| No education | 2948 | 24.29 | 3014 | 25.25 |
| Primary | 3680 | 30.32 | 3596 | 30.12 |
| Secondary | 3516 | 28.97 | 3539 | 29.65 |
| Higher | 1992 | 16.41 | 1789 | 14.99 |
| Body mass index; Mean (SD) | 22.39 | 4.05 | 22.36 | 4.02 |
| Underweight | 2068 | 17.04 | 2056 | 17.22 |
| Normal | 7102 | 58.52 | 6994 | 58.59 |
| Overweight | 2457 | 20.25 | 2395 | 20.06 |
| Obese | 509 | 4.19 | 493 | 4.13 |
| Smoking status | ||||
| Yes | 1857 | 15.30 | 1692 | 14.17 |
| No | 10279 | 84.70 | 10246 | 85.83 |
| Occupation | ||||
| With high physical activity | 4651 | 38.32 | 4736 | 39.67 |
| With low physical activity | 7485 | 61.68 | 7202 | 60.33 |
| Marital status | ||||
| Married | 9720 | 80.09 | 9683 | 81.11 |
| Unmarried | 1252 | 10.32 | 1154 | 9.66 |
| Others | 1164 | 9.59 | 1101 | 9.23 |
| Household wealth status | ||||
| Poorest | 2353 | 19.39 | 2305 | 19.30 |
| Poorer | 2293 | 18.89 | 2346 | 19.65 |
| Middle | 2399 | 19.77 | 2458 | 20.59 |
| Richer | 2381 | 19.62 | 2372 | 19.87 |
| Richest | 2710 | 22.33 | 2457 | 20.58 |
| Media exposure | ||||
| Has access | 378 | 3.11 | 11553 | 96.77 |
| No access | 11758 | 96.89 | 385 | 3.23 |
| Community-level variables | ||||
| Place of residence | ||||
| Rural | 7782 | 64.12 | 8750 | 73.30 |
| Urban | 4354 | 35.88 | 3188 | 26.70 |
| Administrative division | ||||
| Barisal | 1265 | 10.42 | 659 | 5.52 |
| Chittagong | 1643 | 13.54 | 2051 | 17.18 |
| Dhaka | 1597 | 13.16 | 2773 | 23.23 |
| Khulna | 1674 | 13.79 | 1481 | 12.41 |
| Mymensingh | 1377 | 11.35 | 974 | 8.16 |
| Rajshahi | 1585 | 13.06 | 1722 | 14.42 |
| Rangpur | 1565 | 12.90 | 1499 | 12.56 |
| Sylhet | 1430 | 11.78 | 778 | 6.52 |
| Variables | Diabetes % (95% CI) | Hypertension % (95% CI) | Comorbidity % (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 10.04 (9.51–10.59) | 25.70 (24.93–26.49) | 4.47 (4.11–4.85) |
| Individual- and household-level variables | |||
| Age | |||
| 18–34 years | 5.29 (4.73–5.93) | 11.02 (10.21–11.88) | 1.01 (0.78–1.32) |
| 35–44 years | 11.33 (10.12–12.65) | 26.63 (24.91–28.43) | 4.40 (3.66–5.30) |
| 45–54 years | 15.29 (13.64–17.10) | 36.72 (34.44–39.06) | 8.10 (6.88–9.51) |
| 55–64 years | 15.89 (14.03–17.94) | 45.90 (43.25–48.57) | 9.61 (8.15–11.30) |
| ≥65 years | 15.16 (13.18–17.38) | 53.51 (50.58–56.42) | 9.62 (8.02–11.49) |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 10.61 (9.80–11.49) | 24.27 (23.12–25.47) | 4.34 (3.82–4.94) |
| Female | 9.60 (8.93–10.33) | 26.77 (25.74–27.84) | 4.56 (4.09–5.08) |
| Employment status | |||
| Yes | 8.97 (8.35–9.64) | 23.60 (22.65–24.58) | 3.75 (3.35–4.21) |
| No | 11.82 (10.90–12.80) | 29.22 (27.90–30.57) | 5.66 (5.02–6.38) |
| Educational level | |||
| No education | 9.87 (8.86–10.99) | 34.37 (32.69–36.08) | 4.77 (4.06–5.59) |
| Primary | 10.47 (9.51–11.52) | 24.85 (23.47–26.29) | 4.31 (3.70–5.03) |
| Secondary | 9.67 (8.74–10.69) | 21.58 (20.25–22.96) | 4.36 (3.74–5.09) |
| Higher | 10.15 (8.84–11.64) | 20.97 (19.15–22.92) | 4.49 (3.62–5.55) |
| Body mass index | |||
| Underweight | 6.25 (5.28–7.38) | 16.64 (15.09–18.31) | 1.58 (1.12–2.22) |
| Normal | 8.75 (8.11–9.44) | 22.48 (21.51–23.47) | 3.48 (3.08–3.94) |
| Overweight | 15.10 (13.72–16.59) | 39.46 (37.52–41.43) | 8.28 (7.24–9.45) |
| Obese | 19.43 (16.18–23.17) | 42.45 (38.16–46.86) | 11.97 (9.39–15.15) |
| Smoking status | |||
| Yes | 11.12 (9.71–12.71) | 30.19 (28.05–32.42) | 5.08 (4.13–6.24) |
| No | 9.86 (9.29–12.71) | 24.96 (24.13–25.81) | 4.37 (3.99–4.78) |
| Occupation | |||
| With high physical activity | 6.85 (6.16–7.60) | 22.17 (21.01–23.37) | 2.38 (1.99–2.86) |
| With low physical activity | 12.13 (11.40–12.91) | 28.03 (27.00–29.08) | 5.84 (5.32–6.41) |
| Marital status | |||
| Married | 10.41 (9.81–11.03) | 25.08 (24.22–25.95) | 4.55 (4.15–4.98) |
| Unmarried | 4.86 (3.76–6.27) | 9.06 (7.53–10.86) | 0.69 (0.35–1.38) |
| Others | 12.20 (10.40–14.27) | 48.64 (45.69–51.59) | 7.74 (6.30–9.47) |
| Household wealth status | |||
| Poorest | 5.76 (4.88–6.79) | 21.75 (20.12–23.49) | 1.81 (1.34–2.44) |
| Poorer | 6.04 (5.14–7.07) | 23.07 (21.41–24.82) | 2.19 (1.67–2.87) |
| Middle | 7.97 (6.97–9.11) | 25.36 (23.68–27.12) | 3.50 (2.85–4.31) |
| Richer | 11.24 (10.03–12.58) | 26.88 (25.13–28.70) | 4.52 (3.75–5.43) |
| Richest | 18.77 (17.27–20.36) | 31.12 (29.32–32.98) | 10.05 (8.92–11.31) |
| Media exposure | |||
| Has access | 10.14 (9.61–10.71) | 25.51 (24.72–26.31) | 4.54 (4.17–4.93) |
| No access | 6.84 (4.71–9.84) | 31.46 (27.02–36.27) | 2.43 (1.28–4.54) |
| Community-level variables | |||
| Place of residence | |||
| Rural | 8.77 (8.19–9.38) | 25.26 (24.36–26.18) | 3.91 (3.52–4.33) |
| Urban | 13.52 (12.38–14.75) | 26.92 (25.41–28.49) | 6.01 (5.23–6.89) |
| Administrative division | |||
| Barisal | 9.91 (7.85–12.43) | 30.05 (26.67–33.66) | 4.27 (2.97–6.11) |
| Chittagong | 11.13 (9.84–12.57) | 27.78 (25.88–29.75) | 5.81 (4.87–6.90) |
| Dhaka | 14.48 (13.22–15.84) | 22.53 (21.01–24.12) | 5.61 (4.81–6.53) |
| Khulna | 8.31 (7.01–9.83) | 27.42 (25.21–29.75) | 4.57 (3.62–5.76) |
| Mymensingh | 8.15 (6.59–10.05) | 21.61 (19.14–24.31) | 3.17 (2.23–4.47) |
| Rajshahi | 8.10 (6.90–9.49) | 26.05 (24.03–28.18) | 3.46 (2.69–4.43) |
| Rangpur | 5.66 (4.60–6.95) | 28.19 (25.97–30.52) | 2.63 (1.93–3.57) |
| Sylhet | 9.76 (7.87–12.05) | 24.15 (21.27–27.28) | 4.27 (3.06–5.94) |
| Variables | Diabetes | Hypertension | Comorbidity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOR (95% CI) | p Value | AOR (95% CI) | p Value | AOR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Age (years) | ||||||
| 18–34 | Ref | Ref | Ref | |||
| 35–44 | 2.16 (1.77–2.63) | <0.001 | 2.90 (2.52–3.34) | <0.001 | 3.55 (2.53–5.01) | <0.001 |
| 45–54 | 3.32 (2.61–3.96) | <0.001 | 5.13 (4.40–5.98) | <0.001 | 7.51 (5.34–10.54) | <0.001 |
| 55–64 | 3.93 (3.13–4.93) | <0.001 | 8.54 (7.21–10.11) | <0.001 | 10.82 (7.58–15.45) | <0.001 |
| ≥65 | 3.90 (3.01–5.07) | <0.001 | 12.86 (10.60–15.60) | <0.001 | 13.41 (9.04–19.88) | <0.001 |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | Ref | Ref | Ref | |||
| Female | 1.02 (0.87–1.21) | 0.770 | 1.23 (1.10–1.39) | <0.001 | 1.43 (1.12–1.83) | 0.005 |
| Employment status | ||||||
| Yes | 1.07 (0.88–1.28) | 0.502 | 1.01 (0.88–1.15) | 0.944 | 1.32 (1.02–1.73) | 0.038 |
| No | Ref | Ref | Ref | |||
| Educational level | ||||||
| No education | Ref | Ref | Ref | |||
| Primary | 1.24 (1.03–1.49) | 0.022 | 1.06 (0.93–1.20) | 0.378 | 1.15 (0.89–1.48) | 0.287 |
| Secondary | 1.13 (0.92–1.39) | 0.248 | 1.02 (0.88–1.19) | 0.766 | 1.23 (0.92–1.64) | 0.162 |
| Higher | 0.94 (0.73–1.22) | 0.657 | 0.98 (0.81–1.18) | 0.831 | 0.99 (0.70–1.43) | 0.999 |
| Body mass index | ||||||
| Underweight | 0.67 (0.54–0.84) | <0.001 | 0.56 (0.48–0.65) | <0.001 | 0.45 (0.30–0.66) | <0.001 |
| Normal | Ref | Ref | Ref | |||
| Overweight | 1.53 (1.31–1.78) | <0.001 | 2.39 (2.13–2.68) | <0.001 | 1.94 (1.58–2.39) | <0.001 |
| Obese | 1.71 (1.31–2.22) | <0.001 | 2.53 (2.04–3.13) | <0.001 | 2.22 (1.59–3.09) | <0.001 |
| Smoking status | ||||||
| Yes | 1.06 (0.89–1.26) | 0.536 | 1.86 (1.76–1.98) | 0.022 | 1.01 (0.79–1.28) | 0.946 |
| No | Ref | Ref | Ref | |||
| Occupation | ||||||
| With high physical activity | Ref | Ref | Ref | |||
| With low physical activity | 1.41 (1.17–1.69) | <0.001 | 1.34 (1.18–1.52) | <0.001 | 1.72 (1.31–2.26) | <0.001 |
| Marital status | ||||||
| Married | 1.28 (0.93–1.76) | 0.123 | 1.03 (0.82–1.29) | 0.790 | 2.13 (0.96–4.70) | 0.063 |
| Unmarried | Ref | Ref | Ref | |||
| Others | 1.16 (0.78–1.71) | 0.468 | 1.40 (1.06–1.84) | 0.019 | 2.02 (0.87–4.72) | 0.104 |
| Household wealth status | ||||||
| Poorest | Ref | Ref | Ref | |||
| Poorer | 0.96 (0.74–1.25) | 0.747 | 1.12 (0.95–1.31) | 0.176 | 1.11 (0.72–1.71) | 0.647 |
| Middle | 1.15 (0.89–1.49) | 0.282 | 1.27 (1.07–1.49) | 0.005 | 1.60 (1.06–2.40) | 0.025 |
| Richer | 1.45 (1.11–1.90) | 0.006 | 1.38 (1.16–1.66) | <0.001 | 2.05 (1.35–3.11) | 0.001 |
| Richest | 2.14 (1.61–2.86) | <0.001 | 1.40 (1.14–1.71) | 0.001 | 3.44 (2.22–5.33) | <0.001 |
| Media exposure | ||||||
| Has access | 0.95 (0.62–1.45) | 0.800 | 0.83 (0.64–1.07) | 0.158 | 0.99 (0.51–1.96) | 0.999 |
| No access | Ref | Ref | Ref | |||
| Place of residence | ||||||
| Rural | 1.10 (0.92–1.32) | 0.278 | 0.97 (0.85–1.10) | 0.664 | 1.11 (0.90–1.38) | 0.338 |
| Urban | Ref | Ref | Ref | |||
| Administrative division | ||||||
| Barisal | 1.01 (0.73–1.37) | 0.986 | 1.09 (0.88–1.37) | 0.428 | 0.85 (0.58–1.26) | 0.423 |
| Chittagong | 0.93 (0.70–1.24) | 0.623 | 0.99 (0.81–1.22) | 0.940 | 0.91 (0.64–1.28) | 0.578 |
| Dhaka | 1.47 (1.11–1.94) | 0.006 | 0.75 (0.60–0.92) | 0.008 | 1.05 (0.74–1.49) | 0.776 |
| Khulna | 0.81 (0.60–1.10) | 0.176 | 0.90 (0.73–1.11) | 0.318 | 0.87 (0.61–1.25) | 0.462 |
| Mymensingh | 0.98 (0.72–1.34) | 0.910 | 0.78 (0.62–0.97) | 0.029 | 0.75 (0.49–1.13) | 0.164 |
| Rajshahi | 0.95 (0.70–1.29) | 0.747 | 0.98 (0.79–1.22) | 0.890 | 0.87 (0.59–1.28) | 0.473 |
| Rangpur | 0.75 (0.54–1.04) | 0.084 | 1.19 (0.95–1.48) | 0.123 | 0.78 (0.51–1.18) | 0.236 |
| Sylhet | Ref | Ref | Ref | |||
| Measures of variation | ||||||
| Variance (95% CI) | 0.425 (0.327–0.552) | 0.306 (0.233–0.403) | 0.116 (0.001–20.895) | |||
| ICC (95% CI) | 0.052 (0.031–0.085) | 0.028 (0.016–0.047) | 0.004 (<0.001–0.993) | |||
| MOR | 1.86 | 1.69 | 1.38 | |||
| Model fitness | ||||||
| Wald chi2 (p value) | 627.32 (<0.001) | 1737.02 (<0.001) | 598.49 (<0.001) | |||
| AIC | 7136.53 | 11774.48 | 3788.87 | |||
| Cluster number | 675 | 675 | 675 | |||
| Variables | Elasticity | CIX | Contribution to Overall CIX = 0.251 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute Contribution | Percentage Contribution | |||
| Age | ||||
| 18–34 years | Ref | |||
| 35–44 years | 0.135 | −0.021 | −0.003 | −1.143 |
| 45–54 years | 0.142 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.349 |
| 55–64 years | 0.128 | −0.025 | −0.003 | −1.280 |
| ≥65 years | 0.105 | −0.040 | −0.004 | −1.683 |
| Subtotal | −0.009 | −3.757 | ||
| Sex | ||||
| Male | Ref | |||
| Female | −0.018 | −0.005 | <0.001 | 0.035 |
| Employment status | ||||
| Yes | 0.023 | −0.067 | −0.002 | −0.621 |
| No | Ref | |||
| Educational level | ||||
| No education | Ref | |||
| Primary | 0.061 | −0.130 | −0.008 | −3.142 |
| Secondary | 0.024 | 0.127 | 0.003 | 1.218 |
| Higher | −0.009 | 0.398 | −0.004 | −1.397 |
| Subtotal | −0.009 | −3.321 | ||
| Body mass index | ||||
| Underweight | −0.043 | −0.228 | 0.010 | 3.906 |
| Normal | Ref | |||
| Overweight | 0.060 | 0.224 | 0.015 | 5.310 |
| Obese | 0.016 | 0.437 | 0.022 | 8.774 |
| Subtotal | 0.047 | 17.990 | ||
| Smoking status | ||||
| Yes | Ref | |||
| No | 0.002 | −0.136 | <0.001 | −0.104 |
| Occupation | ||||
| With high physical activity | Ref | |||
| With low physical activity | 0.179 | 0.133 | 0.024 | 11.494 |
| Marital status | ||||
| Married | 0.114 | −0.006 | −0.001 | −0.279 |
| Unmarried | Ref | |||
| Others | −0.001 | −0.069 | <0.001 | 0.021 |
| Subtotal | −0.001 | −0.258 | ||
| Household wealth status | ||||
| Poorest | Ref | |||
| Poorer | −0.009 | −0.417 | 0.004 | 1.545 |
| Middle | 0.018 | −0.015 | <0.001 | −0.109 |
| Richer | 0.067 | 0.390 | 0.037 | 15.435 |
| Richest | 0.136 | 0.794 | 0.128 | 48.941 |
| Subtotal | 0.169 | 65.812 | ||
| Media exposure | ||||
| Has access | 0.015 | 0.021 | <0.001 | 0.122 |
| No access | Ref | |||
| Place of residence | ||||
| Rural | 0.036 | −0.138 | −0.005 | −1.999 |
| Urban | Ref | |||
| Administrative division | ||||
| Barisal | 0.001 | −0.233 | −0.001 | −0.114 |
| Chittagong | −0.009 | 0.121 | −0.001 | −0.427 |
| Dhaka | 0.061 | 0.243 | 0.015 | 5.874 |
| Khulna | −0.022 | 0.053 | −0.001 | −0.463 |
| Mymensingh | <0.001 | −0.206 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| Rajshahi | −0.005 | −0.101 | 0.001 | 0.202 |
| Rangpur | −0.028 | −0.297 | 0.008 | 3.325 |
| Sylhet | Ref | |||
| Subtotal | 0.021 | 8.399 | ||
| Explained CIX | 0.235 | 93.792 | ||
| Residual CIX | 0.016 | 6.208 | ||
| Variables | Elasticity | CIX | Contribution to Overall CIX = 0.071 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute Contribution | Percentage Contribution | |||
| Age | ||||
| 18–34 years | Ref | |||
| 35–44 years | 0.133 | −0.021 | −0.003 | −3.991 |
| 45–54 years | 0.140 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 1.231 |
| 55–64 years | 0.147 | −0.025 | −0.004 | −5.245 |
| ≥65 years | 0.143 | −0.040 | −0.006 | −8.195 |
| Subtotal | −0.012 | −16.200 | ||
| Sex | ||||
| Male | Ref | |||
| Female | 0.081 | −0.005 | <0.001 | −0.575 |
| Employment status | ||||
| Yes | 0.023 | −0.067 | −0.002 | −2.179 |
| No | Ref | |||
| Educational level | ||||
| No education | Ref | |||
| Primary | 0.006 | −0.130 | −0.001 | −1.197 |
| Secondary | 0.012 | 0.127 | 0.002 | 2.142 |
| Higher | 0.001 | 0.398 | <0.001 | 0.516 |
| Subtotal | 0.001 | 1.461 | ||
| Body mass index | ||||
| Underweight | −0.064 | −0.228 | 0.015 | 20.731 |
| Normal | Ref | |||
| Overweight | 0.111 | 0.224 | 0.025 | 35.529 |
| Obese | 0.024 | 0.437 | 0.011 | 15.153 |
| Subtotal | 0.051 | 71.413 | ||
| Smoking status | ||||
| Yes | Ref | |||
| No | −0.019 | −0.136 | 0.003 | 3.575 |
| Occupation | ||||
| With high physical activity | Ref | |||
| With low physical activity | 0.114 | 0.133 | 0.015 | 21.539 |
| Marital status | ||||
| Married | 0.009 | −0.006 | <0.001 | −0.075 |
| Unmarried | Ref | |||
| Others | 0.019 | −0.069 | −0.001 | −1.903 |
| Subtotal | −0.001 | −1.978 | ||
| Household wealth status | ||||
| Poorest | Ref | |||
| Poorer | 0.008 | −0.417 | −0.003 | −4.512 |
| Middle | 0.018 | −0.417 | <0.001 | −0.382 |
| Richer | 0.027 | 0.390 | 0.010 | 14.738 |
| Richest | 0.025 | 0.794 | 0.020 | 28.349 |
| Subtotal | 0.027 | 38.193 | ||
| Media exposure | ||||
| Has access | −0.093 | 0.021 | −0.002 | −2.774 |
| No access | Ref | |||
| Place of residence | ||||
| Rural | −0.031 | −0.138 | 0.004 | 6.127 |
| Urban | Ref | |||
| Administrative division | ||||
| Barisal | 0.004 | −0.233 | −0.001 | −1.314 |
| Chittagong | −0.001 | 0.121 | −0.001 | −0.235 |
| Dhaka | −0.044 | 0.243 | −0.011 | −15.078 |
| Khulna | −0.010 | 0.053 | −0.001 | −0.773 |
| Mymensingh | −0.014 | −0.206 | 0.003 | 4.011 |
| Rajshahi | −0.002 | −0.101 | 0.001 | 0.223 |
| Rangpur | 0.010 | −0.297 | −0.003 | −4.310 |
| Sylhet | Ref | |||
| Subtotal | −0.013 | −17.476 | ||
| Explained CIX | 0.072 | 101.126 | ||
| Residual CIX | −0.001 | −1.126 | ||
| Variables | Elasticity | CIX | Contribution to Overall CIX = 0.340 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute Contribution | Percentage Contribution | |||
| Age | ||||
| 18–34 years | Ref | |||
| 35–44 years | 0.253 | −0.021 | −0.005 | −1.575 |
| 45–54 years | 0.269 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.488 |
| 55–64 years | 0.253 | −0.025 | −0.006 | −1.868 |
| ≥65 years | 0.223 | −0.040 | −0.009 | −2.642 |
| Subtotal | −0.018 | −5.597 | ||
| Sex | ||||
| Male | Ref | |||
| Female | 0.169 | −0.005 | −0.001 | −0.249 |
| Employment status | ||||
| Yes | 0.166 | −0.067 | −0.011 | −3.281 |
| No | Ref | |||
| Educational level | ||||
| No education | Ref | |||
| Primary | 0.053 | −0.130 | −0.007 | −2.025 |
| Secondary | 0.073 | 0.127 | 0.009 | 2.715 |
| Higher | 0.011 | 0.398 | 0.005 | 1.323 |
| Subtotal | 0.007 | 2.013 | ||
| Body mass index | ||||
| Underweight | −0.113 | −0.228 | 0.026 | 7.578 |
| Normal | Ref | |||
| Overweight | 0.109 | 0.224 | 0.024 | 7.154 |
| Obese | 0.028 | 0.437 | 0.031 | 10.573 |
| Subtotal | 0.081 | 25.305 | ||
| Smoking status | ||||
| Yes | Ref | |||
| No | −0.012 | −0.136 | 0.002 | 0.471 |
| Occupation | ||||
| With high physical activity | Ref | |||
| With low physical activity | 0.321 | 0.133 | 0.043 | 12.570 |
| Marital status | ||||
| Married | 0.283 | −0.006 | −0.002 | −0.512 |
| Unmarried | Ref | |||
| Others | 0.025 | −0.069 | −0.002 | −0.508 |
| Subtotal | −0.004 | −1.020 | ||
| Household wealth status | ||||
| Poorest | Ref | |||
| Poorer | 0.008 | −0.417 | −0.003 | −1.022 |
| Middle | 0.068 | −0.015 | −0.001 | −0.299 |
| Richer | 0.099 | 0.390 | 0.039 | 11.432 |
| Richest | 0.208 | 0.794 | 0.165 | 48.488 |
| Subtotal | 0.200 | 58.599 | ||
| Media exposure | ||||
| Has access | 0.096 | 0.021 | 0.002 | 0.590 |
| No access | Ref | |||
| Place of residence | ||||
| Rural | 0.076 | −0.138 | −0.011 | −3.095 |
| Urban | Ref | |||
| Administrative division | ||||
| Barisal | −0.005 | −0.233 | 0.001 | 0.337 |
| Chittagong | <0.001 | 0.121 | <0.001 | 0.010 |
| Dhaka | 0.020 | 0.243 | 0.005 | 1.408 |
| Khulna | −0.005 | 0.053 | <0.001 | −0.079 |
| Mymensingh | −0.010 | −0.206 | 0.002 | 0.610 |
| Rajshahi | −0.010 | −0.101 | 0.001 | 0.310 |
| Rangpur | −0.020 | −0.297 | 0.006 | 1.776 |
| Sylhet | Ref | |||
| Subtotal | 0.015 | 4.372 | ||
| Explained CIX | 0.305 | 90.678 | ||
| Residual CIX | 0.035 | 9.322 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kundu, S.; Rahman, M.A.; Kabir, H.; Al Banna, M.H.; Hagan Jr., J.E.; Srem-Sai, M.; Wang, L. Diabetes, Hypertension, and Comorbidity among Bangladeshi Adults: Associated Factors and Socio-Economic Inequalities. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10010007
Kundu S, Rahman MA, Kabir H, Al Banna MH, Hagan Jr. JE, Srem-Sai M, Wang L. Diabetes, Hypertension, and Comorbidity among Bangladeshi Adults: Associated Factors and Socio-Economic Inequalities. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2023; 10(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleKundu, Satyajit, Md. Ashfikur Rahman, Humayun Kabir, Md. Hasan Al Banna, John Elvis Hagan Jr., Medina Srem-Sai, and Lina Wang. 2023. "Diabetes, Hypertension, and Comorbidity among Bangladeshi Adults: Associated Factors and Socio-Economic Inequalities" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 10, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10010007
APA StyleKundu, S., Rahman, M. A., Kabir, H., Al Banna, M. H., Hagan Jr., J. E., Srem-Sai, M., & Wang, L. (2023). Diabetes, Hypertension, and Comorbidity among Bangladeshi Adults: Associated Factors and Socio-Economic Inequalities. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 10(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd10010007








