Evolution of the Sinus Venosus from Fish to Human
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Molecular Identification and Characterization of the Sinus Venosus
3. The Sinus Venosus is Maintained in Evolution
4. The Dominant Pacemaker Generally is Located at the Sinuatrial Border
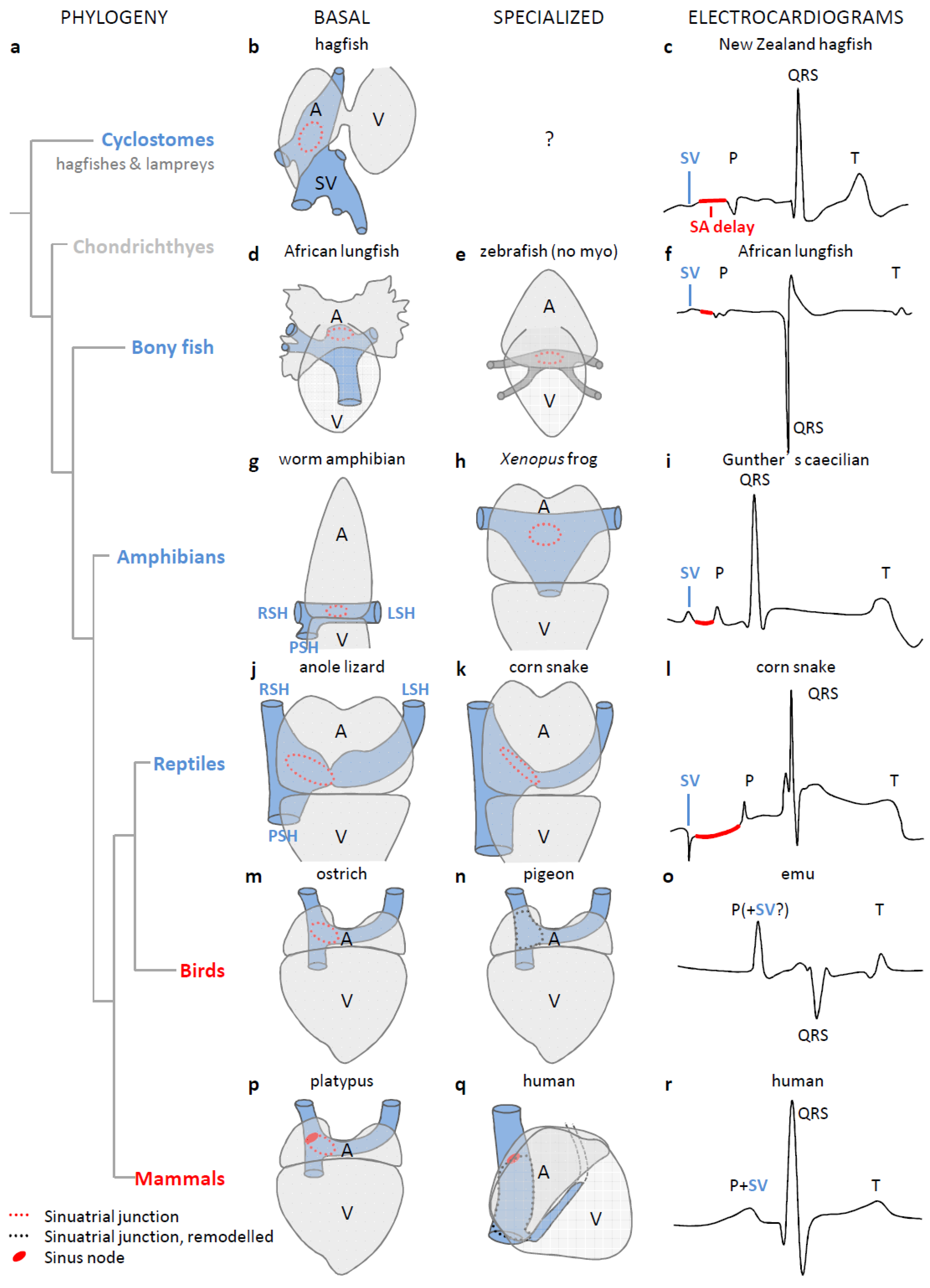
5. In Ectotherms, the Sinus Venosus Promotes Cardiac Output through Atrial Filling
6. The Sinus Venosus is Atrialized in Endotherms
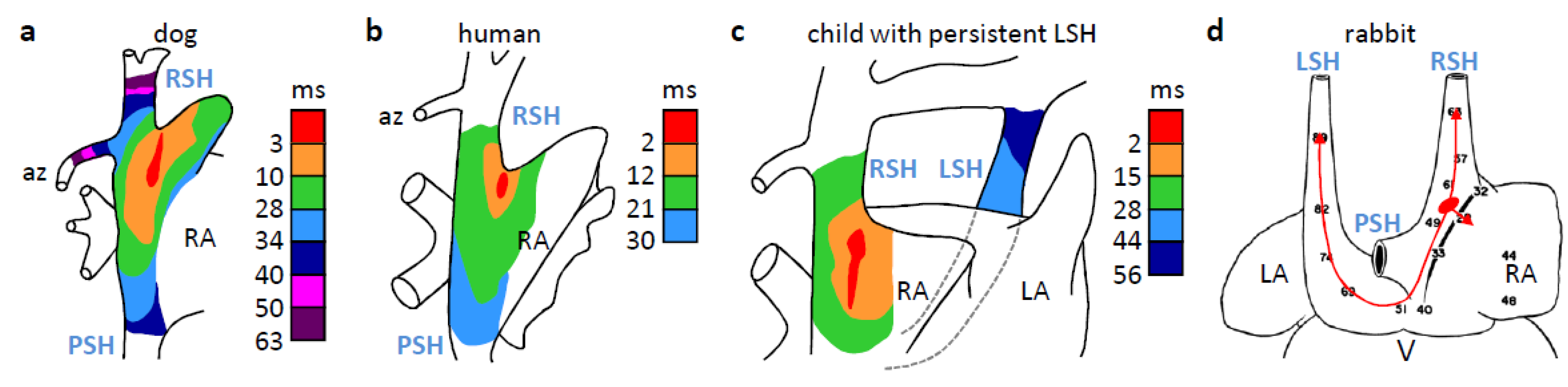
7. Why is the Sinus Venosus Atrialized in Mammals?
8. Arrhythmias Originate from Sinus Venosus-Derived Myocardium
9. Why is the Sinus Venosus-Derived Myocardium Retained in the Mammalian Heart?
10. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaskell, W.H. On the Innervation of the Heart, with especial reference to the Heart of the Tortoise. J. Physiol. 1883, 4, 43–230. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, A.; Flack, M. The Form and Nature of the Muscular Connections between the Primary Divisions of the Vertebrate Heart. J. Anat. Physiol. 1907, 41, 172–189. [Google Scholar]
- Sizarov, A.; Anderson, R.H.; Christoffels, V.M.; Moorman, A.F. Three-dimensional and molecular analysis of the venous pole of the developing human heart. Circulation 2010, 122, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzynski, H.; Anderson, R.H.; Atkinson, A.; Borbas, Z.; D'Souza, A.; Fraser, J.F.; Inada, S.; Logantha, S.J.; Monfredi, O.; Morris, G.M.; Moorman, A.F.; Nikolaidou, T.; Schneider, H.; Szuts, V.; Temple, I.P.; Yanni, J.; Boyett, M.R. Structure, function and clinical relevance of the cardiac conduction system, including the atrioventricular ring and outflow tract tissues. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 139, 260–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.S.; Tai, C.T.; Hsieh, M.H.; Tsai, C.F.; Lin, Y.K.; Tsao, H.M.; Huang, J.L.; Yu, W.C.; Yang, S.P.; Ding, Y.A.; Chang, M.S.; Chen, S.A. Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation initiated by non-pulmonary vein ectopy. Circulation 2003, 107, 3176–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, J.A.; Sanchez-Quintana, D. Cardiac anatomy: What the electrophysiologist needs to know. Heart 2013, 99, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes-Costa, M.S.; Vasconcelos, M.; Sampaio, A.C.; Cravo, R.M.; Linhares, V.L.; Hochgreb, T.; Yan, C.Y.; Davidson, B.; Xavier-Neto, J. The evolutionary origin of cardiac chambers. Dev. Biol. 2005, 277, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Xavier-Neto, J.; Davidson, B.; Simoes-Costa, M.S.; Castro, R.A.; Castillo, H.A.; Sampaio, A.C.; Azambuja, A.P. Evolutionary origins of hearts. In Heart Development and Regeneration; Nadia, R., Richard, P.H., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 3–45. [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich, E.S. Studies on the Structure and Development of Vertebrates; Macmillan & Co.: London, UK, 1930. [Google Scholar]
- Benninghoff, A. Das Herz. In Handbuch der vergleichende Anatomie der Wirbeltiere; Bolk, L., Göppert, E., Kallius, E., Lubosch, W., Eds.; Urban & Schwarzenberg: Berlin, Germany, 1933; pp. 467–555. [Google Scholar]
- Kardong, K.V. Vertebrates: Comparative Anatomy, Function, Evolution; McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Blaschke, R.J.; Hahurij, N.D.; Kuijper, S.; Just, S.; Wisse, L.J.; Deissler, K.; Maxelon, T.; Anastassiadis, K.; Spitzer, J.; Hardt, S.E.; Scholer, H.; Feitsma, H.; Rottbauer, W.; Blum, M.; Meijlink, F.; Rappold, G.; Gittenberger-de Groot, A.C. Targeted mutation reveals essential functions of the homeodomain transcription factor Shox2 in sinoatrial and pacemaking development. Circulation 2007, 115, 1830–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza-Lewis, R.A.; Yu, L.; He, F.; Liu, H.; Tang, R.; Shi, J.; Sun, X.; Martin, J.F.; Wang, D.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y. Shox2 is essential for the differentiation of cardiac pacemaker cells by repressing Nkx2–5. Dev. Biol. 2009, 327, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, S.; Berger, I.M.; Glaser, A.; Bacon, C.; Li, L.; Gretz, N.; Steinbeisser, H.; Rottbauer, W.; Just, S.; Rappold, G. Islet1 is a direct transcriptional target of the homeodomain transcription factor Shox2 and rescues the Shox2-mediated bradycardia. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2013, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffels, V.M.; Mommersteeg, M.T.; Trowe, M.O.; Prall, O.W.; de Gier-de, V.C.; Soufan, A.T.; Bussen, M.; Schuster-Gossler, K.; Harvey, R.P.; Moorman, A.F.; Kispert, A. Formation of the venous pole of the heart from an Nkx2–5-negative precursor population requires Tbx18. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommersteeg, M.T.; Dominguez, J.N.; Wiese, C.; Norden, J.; de Gier-de, V.C.; Burch, J.B.; Kispert, A.; Brown, N.A.; Moorman, A.F.; Christoffels, V.M. The sinus venosus progenitors separate and diversify from the first and second heart fields early in development. Cardiovas. Res. 2010, 87, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessadori, F.; van Weerd, J.H.; Burkhard, S.B.; Verkerk, A.O.; de, P.E.; Boukens, B.J.; Vink, A.; Christoffels, V.M.; Bakkers, J. Identification and functional characterization of cardiac pacemaker cells in zebrafish. PLoS One 2012, 7, e47644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, F.; Mehrkens, D.; Friedrich, F.W.; Stubbendorff, M.; Hua, X.; Muller, J.C.; Schrepfer, S.; Evans, S.M.; Carrier, L.; Eschenhagen, T. Localization of Islet-1-positive cells in the healthy and infarcted adult murine heart. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, M.L.; Boink, G.J.; Boukens, B.J.; Verkerk, A.O.; van den Boogaard, M.; den Haan, A.D.; Hoogaars, W.M.; Buermans, H.P.; de Bakker, J.M.; Seppen, J.; Tan, H.L.; Moorman, A.F.; 't Hoen, P.A.; Christoffels, V.M. T-box transcription factor TBX3 reprogrammes mature cardiac myocytes into pacemaker-like cells. Cardiovas. Res. 2012, 94, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, R.M. Morphology and Innervation of the Fish Heart; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Satchell, G.H. Physiology and Form of Fish Circulation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, J.A.; Graham, J.B.; Cech, J.J., Jr.; Dalton, N.; Michaels, J.; Chin, L.N. Pericardial and pericardioperitoneal canal relationships to cardiac function in the white sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2004, 138, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, J.; Millot, J.; Robineau, D. Le coeur et l'aorte ventrale de Latimeria chalumnae (Poisson, Coelocanthidae). Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences 1965, 261, 223–226. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, A.P. Cardiovascular Systems in Primitive Fishes. Fish Physiol. 2007, 26, 53–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amemiya, C.T.; Alfoldi, J.; Lee, A.P.; Fan, S.; Philippe, H.; Maccallum, I.; Braasch, I.; Manousaki, T.; Schneider, I.; Rohner, N.; Organ, C.; Chalopin, D.; Smith, J.J.; Robinson, M.; Dorrington, R.A.; Gerdol, M.; Aken, B.; Biscotti, M.A.; Barucca, M.; Baurain, D.; Berlin, A.M.; Blatch, G.L.; Buonocore, F.; Burmester, T.; Campbell, M.S.; Canapa, A.; Cannon, J.P.; Christoffels, A.; De, M.G.; Edkins, A.L.; Fan, L.; Fausto, A.M.; Feiner, N.; Forconi, M.; Gamieldien, J.; Gnerre, S.; Gnirke, A.; Goldstone, J.V.; Haerty, W.; Hahn, M.E.; Hesse, U.; Hoffmann, S.; Johnson, J.; Karchner, S.I.; Kuraku, S.; Lara, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Litman, G.W.; Mauceli, E.; Miyake, T.; Mueller, M.G.; Nelson, D.R.; Nitsche, A.; Olmo, E.; Ota, T.; Pallavicini, A.; Panji, S.; Picone, B.; Ponting, C.P.; Prohaska, S.J.; Przybylski, D.; Saha, N.R.; Ravi, V.; Ribeiro, F.J.; Sauka-Spengler, T.; Scapigliati, G.; Searle, S.M.; Sharpe, T.; Simakov, O.; Stadler, P.F.; Stegeman, J.J.; Sumiyama, K.; Tabbaa, D.; Tafer, H.; Turner-Maier, J.; van, H.P.; White, S.; Williams, L.; Yandell, M.; Brinkmann, H.; Volff, J.N.; Tabin, C.J.; Shubin, N.; Schartl, M.; Jaffe, D.B.; Postlethwait, J.H.; Venkatesh, B.; Di, P.F.; Lander, E.S.; Meyer, A.; Lindblad-Toh, K. The African coelacanth genome provides insights into tetrapod evolution. Nature 2013, 496, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, H.; Kurohmaru, M.; Nishida, T.; Hayashi, Y. Cardiac musculature of the cranial and caudal venae cavae and the pulmonary vein in the fowl. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1992, 54, 479–484. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, B.; van den Berg, G.; van den Doel, R.; Oostra, R.J.; Wang, T.; Moorman, A.F. Development of the hearts of lizards and snakes and perspectives to cardiac evolution. PLoS One 2013, 8, e63651. [Google Scholar]
- Opthof, T. The mammalian sinoatrial node. Cardiovas. Drugs Ther. 1988, 1, 573–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzynski, H.; Boyett, M.R.; Anderson, R.H. New insights into pacemaker activity: Promoting understanding of sick sinus syndrome. Circulation 2007, 115, 1921–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, V.V.; Glukhov, A.V.; Chang, R.; Kostecki, G.; Aferol, H.; Hucker, W.J.; Wuskell, J.P.; Loew, L.M.; Schuessler, R.B.; Moazami, N.; Efimov, I.R. Optical mapping of the isolated coronary-perfused human sinus node. JACC 2010, 56, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, F.; Francis, E.T.B. The conducting system of the vertebrate heart. Biol. Rev. 1946, 21, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, W.H.; De Jong, F.; De Groot, I.J.M.; Moorman, A.F.M. The Development of the Avian Conduction System, A Review. Eur. J. Morphol. 1991, 29, 233–253. [Google Scholar]
- Hoogaars, W.M.H.; Tessari, A.; Moorman, A.F.M.; de Boer, P.A.J.; Hagoort, J.; Soufan, A.T.; Campione, M.; Christoffels, V.M. The transcriptional repressor Tbx3 delineates the developing central conduction system of the heart. Cardiovas. Res. 2004, 62, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Steijn, R.; Kolditz, D.P.; Mahtab, E.A.; Askar, S.F.; Bax, N.A.; Van der Graaf, L.M.; Wisse, L.J.; Passier, R.; Pijnappels, D.A.; Schalij, M.J.; Poelmann, R.E.; Gittenberger-de Groot, A.C.; Jongbloed, M.R. Electrical activation of sinus venosus myocardium and expression patterns of RhoA and Isl-1 in the chick embryo. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2010, 21, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverinen, J.; Vornanen, M. Temperature acclimation modifies sinoatrial pacemaker mechanism of the rainbow trout heart. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R1023–R1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batulevicius, D.; Skripkiene, G.; Batuleviciene, V.; Skripka, V.; Dabuzinskiene, A.; Pauza, D.H. Distribution, structure and projections of the frog intracardiac neurons. Auton. Neurosci. 2012, 168, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, B.; Moorman, A.F.; Wang, T. Structure and function of the hearts of lizards and snakes. Biol. Rev. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, C.M.; Stoyek, M.R.; Croll, R.P.; Smith, F.M. Regional innervation of the heart in the goldfish, Carassius auratus: A confocal microscopy study. J. Comp. Neurol. 2014, 522, 456–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.I. The development of the heart and vascular system of Lepidosiren paradoxa. Q. J. Microsc. Sci. 1913, 2, 53–132. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, F. The Conducting System of the Monotreme Heart. J. Anat. 1931, 65, 339–351. [Google Scholar]
- Romanoff, A.L. The Avian Embryo. Structural and Functional Development; The Macmillan Company: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Bugge, J. The heart of the African lungfish, Protopterus. Videnskabelige Meddelelser fra Dansk Naturhistorisk Forening 1961, 123, 193–210. [Google Scholar]
- Dowd, D.A. The coronary vessels and conducting system in the heart of monotremes. Acta Anat. 1969, 74, 547–573. [Google Scholar]
- Klitgaard, T. Morphology and Histology of the Heart of the Australian Lungfish, Neoceratodus-Forsteri (Krefft). Acta Zool. 1978, 59, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezuidenhout, A.J. The anatomy of the heart of the ostrich Struthio camelus (Linn). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, N.; Yost, H.J.; Clark, E.B. Cardiac morphology and blood pressure in the adult zebrafish. Anat. Rec. 2001, 264, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.X.; Liang, D.; Wen, J.Z.; Zhang, P. Multiple genome alignments facilitate development of NPCL markers: A case study of tetrapod phylogeny focusing on the position of turtles. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 3237–3252. [Google Scholar]
- De Simone, C.V.; Noheria, A.; Lachman, N.; Edwards, W.D.; Gami, A.S.; Maleszewski, J.J.; Friedman, P.A.; Munger, T.M.; Hammill, S.C.; Packer, D.L.; Asirvatham, S.J. Myocardium of the superior vena cava, coronary sinus, vein of Marshall, and the pulmonary vein ostia: Gross anatomic studies in 620 hearts. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2012, 23, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushing, A.; Linney, C.; McClean, M.; Stanford, M.; Rishniw, M. The electrocardiogram of anesthetized captive adult emus (Dromaius novaehollandiae). J. Vet. Cardiol. 2013, 15, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oisi, Y.; Ota, K.G.; Kuraku, S.; Fujimoto, S.; Kuratani, S. Craniofacial development of hagfishes and the evolution of vertebrates. Nature 2013, 493, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, J.A.; Mullen, R.K. Electrocardiography in Caecilia guentheri (Peters). Physiol. Zool. 1966, 39, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Valentinuzzi, M.E.; Hoff, H.E. Catheterization in the snake: Correlation of cardiac events. Cardiovasc. Res. Cent. Bull. 1970, 8, 102–118. [Google Scholar]
- Arbel, E.R.; Liberthson, R.; Langendorf, R.; Pick, A.; Lev, M.; Fishman, A.P. Electrophysiological and anatomical observations on the heart of the African lungfish. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 1977, 232, H24–H34. [Google Scholar]
- Davie, P.S.; Forster, M.E.; Davison, B.; Satchell, G.H. Cardiac function in the New Zealand hagfish, Eptatretus cirrhatus. Physiol. Zool. 1987, 60, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Chiodi, V.; Bortolami, R. The Conducting System of the Vertebrate Heart; Edizioni Calderini: Bologna, Italy, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Arrenberg, A.B.; Stainier, D.Y.; Baier, H.; Huisken, J. Optogenetic control of cardiac function. Science 2010, 330, 971–974. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, G.; Lu, H.H.; Tsumuraya, Y.; Brooks, C.M. Pacemaker actions in the turtle heart. Am. J. Physiol. 1966, 210, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Boineau, J.P.; Canavan, T.E.; Schuessler, R.B.; Cain, M.E.; Corr, P.B.; Cox, J.L. Demonstration of a widely distributed atrial pacemaker complex in the human heart. Circulation 1988, 77, 1221–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, V.V.; Glukhov, A.V.; Chang, R. Conduction barriers and pathways of the sinoatrial pacemaker complex: Their role in normal rhythm and atrial arrhythmias. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H1773–H1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Mierop, L.H. Location of pacemaker in chick embryo heart at the time of initiation of heartbeat. Am. J. Physiol. 1967, 212, 407–415. [Google Scholar]
- Kamino, K.; Hirota, A.; Fujii, S. Localization of pacemaking activity in early embryonic heart monitored using voltage-sensitive dye. Nature 1981, 290, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommersteeg, M.T.; Hoogaars, W.M.; Prall, O.W.; de Gier-de, V.C.; Wiese, C.; Clout, D.E.; Papaioannou, V.E.; Brown, N.A.; Harvey, R.P.; Moorman, A.F.; Christoffels, V.M. Molecular pathway for the localized formation of the sinoatrial node. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffels, V.M.; Moorman, A.F. Development of the cardiac conduction system: Why are some regions of the heart more arrhythmogenic than others? Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2009, 2, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Steijn, R.; Passier, R.; Wisse, L.J.; Schalij, M.J.; Poelmann, R.E.; Gittenberger-de Groot, A.C.; Jongbloed, M.R. Funny current channel HCN4 delineates the developing cardiac conduction system in chicken heart. Heart Rhythm. 2011, 8, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, M.; Liu, G.; Mikawa, T. Early mesodermal cues assign avian cardiac pacemaker fate potential in a tertiary heart field. Science 2013, 340, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Yeh, H.I.; Lin, C.I.; Chen, S.A. Electrophysiology and arrhythmogenic activity of single cardiomyocytes from canine superior vena cava. Circulation 2002, 105, 2679–2685. [Google Scholar]
- Burggren, W.; Farrell, A.P.; Lillywhite, H.B. Vertebrate cardiovascular systems. Compr. Physiol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, K.; Burggren, W.W. Venous return and cardiac filling in varanid lizards. J. Exp. Biol. 1984, 113, 389–399. [Google Scholar]
- Sandblom, E.; Axelsson, M. The venous circulation: A piscine perspective. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 148, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, K.J. Valves in Veins: An Historical Survey. Proc. Roy. Soc. Med. 1927, 21, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Rowlatt, U. Comparative Anatomy of the Heart of Mammals. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 1990, 98, 73–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlett, W.C.; Schwartz, F.J.; Schmeinda, R.; Cuevas, E. Anatomy, histology, and development of the cardiac valvular system in elasmobranchs. J. Exp. Zool. 1996, 275, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, A.; Duran, A.C.; de Andres, A.V.; Navarro, P.; Munoz-Chapuli, R. Anatomy and development of the sinoatrial valves in the dogfish (Scyliorhinus canicula). Anat. Rec. 1997, 248, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steding, G.; Xu, J.W.; Seidl, W.; Manner, J.; Xia, H. Developmental aspects of the sinus valves and the sinus venosus septum of the right atrium in human embryos. Anat. Embryol. 1990, 181, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvin, M.; Shah, D.C.; Haissaguerre, M.; Marcellin, L.; Brechenmacher, C. The anatomic basis of connections between the coronary sinus musculature and the left atrium in humans. Circulation 2000, 101, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, H.; Mifune, H.; Kurohmaru, M.; Hayashi, Y. Cardiac musculature of the cranial vena cava in the rat. Acta Anat. 1994, 151, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, H.; Maeda, S.; Kimura, J.; Yamada, J.; Rerkamnuaychoke, W.; Chungsamarnyart, N.; Tanigawa, M.; Kurohmaru, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Nishida, T. Cardiac musculature of the cranial vena cava in the common tree shrew (Tupaia glis). J. Anat. 1995, 187, 347–352. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, H.; Yamada, T.K.; Suzuki, N.; Suwa, G.; Uetsuka, K.; Hashimoto, O.; Kurohmaru, M.; Hayashi, Y. Ultrastructure of cardiac myocyte in the Asian elephant (Elephas maximus). J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1995, 57, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.I.; Lai, Y.J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.N.; Ko, Y.S.; Chen, S.A.; Severs, N.J.; Tsai, C.H. Heterogeneity of myocardial junctions in canine sleeve morphology and gap superior vena cava. Circulation 2001, 104, 3152–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, H.; Gloobe, H. Myocardial atrio-venous junctions and extensions (sleeves) over the pulmonary and caval veins. Anatomical observations in various mammals. Thorax 1970, 25, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholova, I.; Kautzner, J. Morphology of atrial myocardial extensions into human caval veins: A postmortem study in patients with and without atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2004, 110, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.; Meakins, J.; White, P.D. The Excitatory Process in the Dog's Heart. Part I. The Auricles. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. Series B 1914, 205, 375–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spach, M.S.; Barr, R.C.; Jewett, P.H. Spread of excitation from the atrium into thoracic veins in human beings and dogs. Ame. J. Cardiol. 1972, 30, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Arita, M.; Saeki, K.; Tanoue, M.; Fukushima, I. Functional properties of sinocaval conduction. Jap. J. Physiol. 1967, 17, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimov, I.R.; Fedorov, V.V.; Joung, B.; Lin, S.F. Mapping cardiac pacemaker circuits: Methodological puzzles of the sinoatrial node optical mapping. Circ. Res. 2010, 106, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, M.; Saeki, K.; Tanoue, M.; Ito, M.; Yanaga, T.; Mashiba, H. Studies on transmembrane action potentials and mechanical responses of the venae cavae and atria of the rabbit. Jap. J. Physiol. 1966, 16, 462–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, M.; Saeki, K.; Tanoue, M.; Fukushima, I.; Ito, M. Effects of catecholamines, propranolol, acetylcholine and ouabain on the transmembrane action potentials and contractility of the isolated venae cavae proximal to the heart of the rabbit. Jap. J. Physiol. 1967, 17, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, B.; Wang, T.; Christoffels, V.M.; Moorman, A.F. Evolution and development of the building plan of the vertebrate heart. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2013, 1833, 783–794. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, A.P. Features heightening cardiovascular performance in fishes, with special reference to tunas. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Physiol. 1996, 113, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haissaguerre, M.; Jais, P.; Shah, D.C.; Takahashi, A.; Hocini, M.; Quiniou, G.; Garrigue, S.; Le, M.A.; Le, M.P.; Clementy, J. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N. Eng. J. Med. 1998, 339, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.F.; Tai, C.T.; Hsieh, M.H.; Lin, W.S.; Yu, W.C.; Ueng, K.C.; Ding, Y.A.; Chang, M.S.; Chen, S.A. Initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating from the superior vena cava—Electrophysiological characteristics and results of radiofrequency ablation. Circulation 2000, 102, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, H.; Zipes, D.P.; Morita, S.T.; Wu, J. The role of coronary sinus musculature in the induction of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2012, 9, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Holm, H.; Gretarsdottir, S.; Thorleifsson, G.; Walters, G.B.; Thorgeirsson, G.; Gulcher, J.; Mathiesen, E.B.; Njolstad, I.; Nyrnes, A.; Wilsgaard, T.; Hald, E.M.; Hveem, K.; Stoltenberg, C.; Kucera, G.; Stubblefield, T.; Carter, S.; Roden, D.; Ng, M.C.; Baum, L.; So, W.Y.; Wong, K.S.; Chan, J.C.; Gieger, C.; Wichmann, H.E.; Gschwendtner, A.; Dichgans, M.; Kuhlenbaumer, G.; Berger, K.; Ringelstein, E.B.; Bevan, S.; Markus, H.S.; Kostulas, K.; Hillert, J.; Sveinbjornsdottir, S.; Valdimarsson, E.M.; Lochen, M.L.; Ma, R.C.; Darbar, D.; Kong, A.; Arnar, D.O.; Thorsteinsdottir, U.; Stefansson, K. A sequence variant in ZFHX3 on 16q22 associates with atrial fibrillation and ischemic stroke. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 876–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.; Chinchilla, A.; Aranega, A.E. Transgenic insights linking Pitx2 and atrial arrhythmias. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, B.; Boukens, B.J.; Postma, A.V.; Gunst, Q.D.; van den Hoff, M.J.; Moorman, A.F.; Wang, T.; Christoffels, V.M. Identifying the evolutionary building blocks of the cardiac conduction system. PLoS One 2012, 7, e44231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Mierop, L.H.; Bertuch, C.J., Jr. Development of arterial blood pressure in the chick embryo. Am. J. Physiol. 1967, 212, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Altimiras, J.; Crossley, D.A. Control of blood pressure mediated by baroreflex changes of heart rate in the chicken embryo (Gallus gallus). Am. J. Physiol. Reg. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2000, 278, R980–R986. [Google Scholar]
- Fanaroff, J.M.; Fanaroff, A.A. Blood pressure disorders in the neonate: Hypotension and hypertension. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2006, 11, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Raj, J.U. Regulation of the pulmonary circulation in the fetus and newborn. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 1291–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.G.; Ye, H.; Zhao, B.; Pizzatto, L.; Ji, X.; Shine, R. Patterns of interspecific variation in the heart rates of embryonic reptiles. PLoS One 2011, 6, e29027. [Google Scholar]
- Sedmera, D.; Ostadal, B. Ontogenesis of myocardial function. In Ontogeny and Phylogeny of the Vertebrate Heart; Sedmera, D., Wang, T., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 147–175. [Google Scholar]
- Eme, J.; Elsey, R.M.; Crossley, D.A. Development of sympathetic cardiovascular control in embryonic, hatchling, and yearling female American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis). Com. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 165, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jensen, B.; Boukens, B.J.D.; Wang, T.; Moorman, A.F.M.; Christoffels, V.M. Evolution of the Sinus Venosus from Fish to Human. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2014, 1, 14-28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd1010014
Jensen B, Boukens BJD, Wang T, Moorman AFM, Christoffels VM. Evolution of the Sinus Venosus from Fish to Human. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2014; 1(1):14-28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd1010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleJensen, Bjarke, Bastiaan J. D. Boukens, Tobias Wang, Antoon F. M. Moorman, and Vincent M. Christoffels. 2014. "Evolution of the Sinus Venosus from Fish to Human" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 1, no. 1: 14-28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd1010014
APA StyleJensen, B., Boukens, B. J. D., Wang, T., Moorman, A. F. M., & Christoffels, V. M. (2014). Evolution of the Sinus Venosus from Fish to Human. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 1(1), 14-28. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd1010014