Abstract
Physical activity is an important factor in achieving healthy aging, offering older persons multiple benefits in terms of maintaining and improving their health and wellbeing. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of physical activity on the quality of life of older adults. A cross-sectional study was conducted from February to May 2022, using the Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36) and the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ). A total of 124 people aged 65 and over participated in the survey. The average age of the participants was 71.6 years, and 62.1% were women. Participants showed a moderate quality of life with regard to the physical health dimension (mean score 52.4) and a higher quality of life with regard to the mental health dimension (mean score 63.1) compared to the expected values of the population. Low levels of physical activity were recorded among older adults, reaching a rate of 83.9%. A moderate or high level of physical activity has been found to contribute to a better physical functioning (p = 0.03), vitality (p = 0.02) and general health (p = 0.01). Finally, comorbidity had a negative impact on physical activity (p = 0.03) and quality of life regarding mental and physical health in older adults. The study showed very low levels of physical activity in older Greek adults. The management of this problem, which was intensified during the COVID-19 pandemic, should be a high priority in public health programs focusing on healthy aging, as physical activity affects and promotes many of the basic aspects of quality of life.
1. Introduction
Aging is a complex, normal and inevitable process in human life, characterized by biological, psychological and social changes which occur in each person at different rates due to various influencing factors [1]. The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared that every person—in every country in the world—should be given the opportunity to live a long life in good health and full participation in society. Healthy aging has been the focus of WHO’s work between 2015 and 2030 and has been defined as “the process of developing and maintaining the functional ability that enables well-being in older age” [2].
In an effort to support older people to be active and obtain a satisfactory level of good health and mood, many interventions have been sought. An important factor in achieving healthy aging is physical activity (PA), which has been positively associated with a number of benefits for maintaining and promoting the health-related quality of life (HRQoL) of the older population [3,4,5,6,7,8,9].
Despite the sudden demographic, epidemiological and anthropological changes triggered by the aging process, physical activity contributes to healthy and quality life years. The American College of Sports Medicine in cooperation with the American Medical Association have established the «Exercise is Medicine» health initiative, which aims to promote the value of physical activity and highlight its multiple benefits. These benefits are more pronounced in people who give up inactivity and a sedentary lifestyle and adopt a more active one [10].
Physical activity is a significant strategy for achieving healthy aging, reducing early mortality by 20–30%, while it beneficially impacts wellbeing (mental, emotional and physical) [5]. Hamer et al., (2014) claim that even a delayed start in physical activity results in remarkable health benefits [11]. According to a study conducted by Balboa-Castillo et al. in 2011 on Spanish people over 60, even light, leisure physical activity such as walking has a positive impact on older adults’ physical, mental and social sphere of life [3]. Other studies similarly claim that light or moderate activities such as walking, gardening, swimming, cycling and dancing benefit the physical, emotional and social wellbeing of older persons [4,8].
Additionally, a study of older persons in Seoul, Korea, conducted by Park et al., (2020) determined that activities boosting physical strength, during which low- or medium-level energy was expended, such as gardening, were beneficial to physical and cognitive health, the psychological state and the prevention of depression [12]. Older persons in Australia who spent time tending to their gardens, and therefore had the opportunity for mental and physical activity, developed, as a result, a positive attitude towards aging and by extension had a better quality of life [13]. Finally, the use of bicycles by older adults brings spectacular results as it increases physical strength, stimulates cognitive function, promotes wellness and enhances their mental health [14].
Participation in primary health and social care centers for older people can promote network growth and access to social resources, increase self-esteem, reduce loneliness and increase physical activity [15]. Participation in community centers where older persons can attend recreational activities and physical exercise programs such as aerobic exercise or traditional dance programs have been found to promote physical health and social interaction and positively affect their mental wellbeing, thus improving their quality of life [16,17]. Older persons who were deprived of the beneficial effects of activities in community centers during the COVID-19 pandemic presented an increased level of loneliness and depression [18]. Thus, innovative exercise programs are suggested and applied, making use of applications and the Internet of Things (IoT) so as to promote older persons’ quality of life. Wearable biomedical sensors can help monitor the older person’s mobility and physiological parameters. A smart home system may include smart fitness equipment in order to help older people perform rehabilitation and exercise programs [19].
Published findings continuously confirm that higher physical activity in the work and home environment or during leisure time can promote people’s quality of life, regardless of existing ailments [20]. Badicu (2018) reports a very positive correlation between the physical activity and quality of life of an adult, regardless of the type of exercise [21]. Subramaniam et al., (2019), while studying the relation between physical activity and quality of life in people with comorbidities, found a strong positive correlation and noted that the lower the levels of physical activity, the poorer the HRQoL [22].
The literature includes little evidence regarding older adults and reveals heterogeneous results regarding physical activity and HRQoL in older people, partly because of the different research designs and different research tools used in order to measure physical activity and HRQoL. In addition, many of the studies concerned older people living in nursing homes instead of community dwellers [23,24]. Studies conducted in Greece investigating the relationship between certain types of physical activity (i.e., traditional dancing) and quality of life and how these affect the life of older people are few in number, making it difficult to extract meaningful and valid conclusions [16,17,25,26]. Moreover, they were conducted before the COVID-19 pandemic, which affected older persons’ lives and created another “pandemic” of inactivity and sedentary lifestyle [27]. The current study comes to fill in the gap in the existing literature by examining the relationship between PA and HRQoL using standard measures of all the dimensions of HRQoL.
2. Objective
The aim of this study was to explore the relationship between physical activity and quality of life in community-dwelling older adults in Greece during the third year of the pandemic so as to utilize the results towards promoting healthy and active aging.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Materials
The current study is an exploratory cross-sectional study carried out through self-report questionnaires. The sample of the study was a convenience sample of 124 participants > 65 years who could speak, read and write in Greek. Older persons with cognitive impairment (according to their medical file) or serious mobility problems who were not able to be physically active were excluded from the study. The study took place in walk-in day centers for older people and primary health care and social care services in the south and central sector of the Athens region during the period February–May 2022. Although community centers for older people remained closed for quite a long period during the pandemic in Greece, during the study period, vaccinated persons only, wearing face masks, could visit public services. Walk-in day centers were accepting only small numbers of older people who had been vaccinated. No recreational activities such as aerobic exercise or traditional dance were taking place during that period, just medical prescriptions and physiotherapy sessions. Wearing face masks was still obligatory when walking in open public places, which was also an inhibiting factor for physical activity outdoors.
3.2. Ethical Approval
Written permission for the study was granted by the health regions and the corresponding municipality services. Permission was also granted by the Ethics Committee of the University of West Attica (protocol number 17349; date: 23 February 2022).
Participants were informed about the scope and the possible benefits of the study. They were assured of the confidentiality of personal data, and that they were free to withdraw at any stage. Finally, they signed an informed consent form.
3.3. Data Collection
The main researcher recruited participants who were visiting the primary health and social care services and examined the eligibility criteria in collaboration with local healthcare professionals. After participants signed the consent form, the first author, who was the main researcher, personally distributed the questionnaires in a quiet and private area of the facilities. Out of the 130 participants recruited, 124 completed the questionnaires, yielding a response rate of 95%. According to the G-power program, the number of 130 participants was found to be sufficient for a correlation study in which a multivariate linear regression analysis will be performed with a power of 95%, an error level of α = 0.05, an effect size of at least 0.16 and a total number of controlled predictors of 5. A post hoc analysis revealed that the actual sample size provided a level of power of 95% to detect an effect size of at least 0.167, a value that is almost identical to our initially intended one.
3.4. Instruments
A sociodemographic and clinical characteristics questionnaire as well as the following scales were used.
3.4.1. Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36)
The SF-36 is a generic research tool used for the assessment of physical, cognitive and mental health of populations and patient groups (Medical Outcomes Trust, Boston, MA, USA) [28,29]. License for use was granted by the RAND Health Care company without any need for written permission. SF-36 has been validated in the Greek population [30,31] and it has been found to be a reliable tool with Cronbach’s α coefficient ranging from 0.79 to 0.95. It includes 36 questions, which make up 8 subscales, with 2 to 10 questions each: The individual subscales/dimensions of physical health are: (1) Physical Functioning (PF), (2) Role Functioning/Physical (RP) (Role limitations due to physical health problems), (3) Bodily Pain (BP) and (4) General Health (GH), while mental health includes the additional subscales/dimensions: (5) Vitality (VT), (6) Social Functioning (SF), (7) Role Functioning/Emotional (RE) (role limitation due to emotional problems) and (8) Mental Health (MH). The answer choices range from 2 to 5 ratings. Two summary component scales, the Physical Component Summary and the Mental Component Summary, derive from the 8 subscales. The score of the SF-36 subscales and components ranges from 0 to 100, while the mean value is 50 [32]. Expected score values for the mental health component vary between 17 to 62, while for the physical health component they vary from 20 to 58 [33]. The mean value of the Greek general population is 51.99 for PCS and 49,73 for MCS. Lower values are associated with worse mental and physical quality of life, respectively, and the higher the score, the better the health [34].
3.4.2. International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)
The International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ), developed by Craig et al., (2003), was validated on adults across twelve countries (Spearman’s ρ averaged around 0.8 and the criterion validity median ρ was about 0.30) [35]. The Greek version presented good to high reliability properties (intra-class correlation coefficients (ICCs) of 0.69 to 0.93) [36]. The IPAQ contains questions related to physical activity in both leisure time and at the workplace, at home and during participants’ daily commutes. Participants report the number of days (frequency) and the number of minutes per day (duration) that they spend in all kinds of vigorous, moderate and walking physical activities during the past week. In addition, a seventh question records the time that subjects spend sitting during an average weekday. The total number of questions is 7 and the grading classifies the level of physical activity into (1) low, (2) moderate and (3) high [36]. Participants who do not meet the criteria of level 2 and 3 are characterized as inactive [37]. Although IPAQ was originally constructed for use in adults 18–65 years old, it has also been used for the measurement of physical activity and sedentary behavior in older adults. Research has shown that IPAQ is a valid tool for the measurement of physical activity and sedentary behavior in older adults in South Africa, showing good reliability and criterion validity (r = 0.46 to 0.77) [38]; in Belgium (moderate validity, r = 0.33–0.40) [39]; Japan (adequate validity, r = 0.42–0.53) [40]; Hong Kong (acceptable reliability and validity, r = 0.47) [41] and the United Kingdom (moderate/acceptable levels of validity (r = 0.430–0.557) for moderate/vigorous physical activity (PA) [42]. It has also been tested by qualitative methodologies, showing its usefulness in older populations provided that clear explanations and directions are given to older participants [43]. The IPAQ is an open access questionnaire and the team that developed it notes that no permission is required in order to use it.
3.5. Data Analysis
Categorical variables are presented with absolute (n) and relative (%) values, while quantitative variables are presented with standard deviations, means, medians and range of values. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test and normality diagrams were used to examine the normal distribution of quantitative variables. Statistical tests such as the x2 test, t-test and Pearson’s and Spearman’s correlation coefficients were employed for data analysis. Multivariate linear regression was performed to identify variables associated with quality of life, employing the backward stepwise entry method. Beta coefficients, 95% confidence intervals and p values are presented. Multivariate logistic regression was performed to identify variables associated with physical activity. Odds ratios with corresponding 95% confidence intervals and p values are presented. Statistical significance level was set at 0.05. Data analysis was performed with the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) v.21.
4. Results
Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
The sample under study consisted of 124 older adults whose sociodemographic and clinical profile is presented in Figure 1. Their average age was 71.6 years, and 62.1% were women. Of the participants, 32.3% were high school (lyceum) graduates, while 17.7% also had a higher education degree. The majority of participants (54.5%) were married, had children (80.3%) and were living with other people (66.9%). Most of the participants were retired (65%), had a health insurance (89.4%) and regarded their financial state as moderate (52%). Half of them had a hobby (50.4%) and participated in community programs for older people (47.6%) (Figure 1).
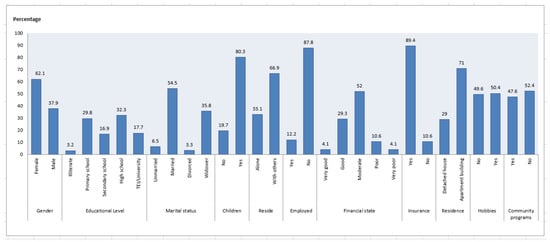
Figure 1.
Sociodemographic characteristics of the participants.
The clinical characteristics of the older persons are presented in Figure 2. The majority of participants (75.2%) had a chronic disease, most commonly, hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease and vision problems. Most of them (83.1%) were taking medication for their chronic disease (Figure 2).
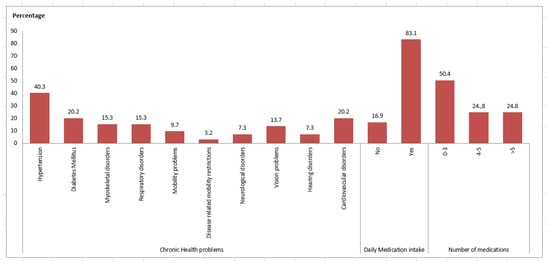
Figure 2.
Clinical characteristics of the participants.
The level of physical activity of the older adults is presented in Table 1. Of the participants, 83% presented a low level of physical activity, 8.9% a moderate level and 7.3% a high level. The scale presents a good level of split-half reliability (0.889).

Table 1.
Level of physical activity of older adults.
The descriptive results of the SF-36 subscales as well as each subscale’s Cronbach’s α value are presented in Table 2. Cronbach’s α values ranged between 0.76 and 0.94, which indicates a very good reliability of the SF-36. Higher scores of the SF-36 indicate a better quality of life.

Table 2.
Descriptive results of SF-36 subscales.
Scores on the Mental and Physical Component Summary dimensions were 52.4 for PCS (expected mean value of PCS: 51.99 in the Greek general population) and 63.1 for MCS (expected mean value of MCS: 49.73 in the Greek general population) (Table 2).
Comparisons between participants’ low and moderate/high activity levels (IPAQ) and SF-36 subscales are presented in Table 3. Participants with a moderate or high level of physical activity had higher scores with regard to Physical Functioning (p = 0.03), Physical Role (0.03), Vitality (p = 0.02) and General Health (p = 0.01) compared to participants with a low level of physical activity (Table 3).

Table 3.
Comparisons between participants’ low and moderate/high activity levels (IPAQ) and SF-36 subscales.
According to the results of the multivariate linear regression analysis, with general health as the dependent variable, it emerged that older persons with a higher educational level (p = 0.048), those who had hobbies (p < 0.001) and those who had children (p < 0.039) had better general health. In contrast, the older adults with more comorbidities (p = 0.003) had worse general health (Table 4).

Table 4.
Multivariate linear regression analyses’ results of SF-36 for the sample.
The MCS dimension was found to be positively associated with higher educational level (p = 0.001) and negatively associated with comorbidity (p = 0.013) (Table 4). No statistically significant results were found in the multivariate linear regression analysis with the PCS as the dependent variable.
According to the results of the multivariate linear regression analysis, for Physical Functioning, it appears that high school graduates and married people had better physical functioning (p = 0.004 and p = 0.0019, respectively), while the persons with more comorbidities had worse physical functioning (p < 0.001) (Table 4).
An important finding of the study is the fact that comorbidity was negatively associated with Physical Functioning (p < 0.001), Physical Role (p < 0.001), MCS scale (p = 0.013), Body Pain (p = 0.002), General Health (p = 0.003), Vitality (p < 0.0010, Social Functioning (p = 0.001), Emotional Functioning (p < 0.001) and Mental Health (p = 0.005).
Finally, with regard to the level of physical activity, according to the results of the multivariate logistic regression, it appears that the older persons who had hobbies had a higher level of physical activity. Older adults with hobbies were 3.5 times more likely to have a moderate/high level of physical activity than older adults without hobbies, and older adults with fewer comorbidities had a higher level of physical activity. The odds ratio of a high level of physical activity decreased by 0.6 for each additional disease from which the older persons suffered (Table 5).

Table 5.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis of physical activity as dependent variable.
5. Discussion
The present study was undertaken to investigate the relationship between physical activity and quality of life in community-dwelling older adults over 65 years old.
Following the analysis of quality of life data derived from the SF-36 scale, it was found that the mean value of the summary mental health dimension was 63.1 (mean value of MCS: 49.73 in the Greek general population), while the mean value of the summary physical health dimension was 52.4 (mean value of PCS: 51.99 in the Greek general population). This shows that older adults had better quality of life with regard to mental health than physical health. The norms suggested by Papa et al., (2005) [31] and Karapanou et al., (2012) [44] that were used in the present study derived from a validation and norming study in a large sample of the urban Greek population which revealed similar norms with the reference study of Ware, thus allowing comparisons with other countries [31]. The lower level of physical compared to mental health is a finding consistent with studies on older populations. Sun et al., (2015) found similar values for mental and physical health (58.9 and 53.7, respectively) [45]. This finding is also similar to the results of Attafuah et al., (2022), who found a poor level of physical health and a moderate level of mental health [46].
The level of quality of life with regard to the mental health of the participants in our study was found to be higher than that of the general Greek population (mean value of MCS: 63.1 compared to MCS: 49.73 in the Greek general population). This finding is in accordance with the findings of other studies which showed that the levels of anxiety and depression of older people during the COVID-19 pandemic were lower than those of younger adults [47,48,49]. Although the levels of depression and anxiety were higher than those in the pre-COVID era [50,51], they were lower than those of younger adults, probably because younger people had to face unemployment, childcare and distance learning [50]. A study in Singapore showed that older adults were more psychosocially adaptable, which may also explain the better mental health of older adults [49].
The better mental health of older people in our study compared to the expected score values in the US general population (expected scores for mental health component are 17 to 62) may be related to stronger family ties, which reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation resulting in fewer depressive symptoms even in the last period of the pandemic. In fact, at the time the study was conducted, a very large part of the older population had been vaccinated and the number of deaths had significantly decreased, which had reduced the negative effects on the mental health of older people during that period [18]. Quality of life in relation to physical health, on the contrary, seems to have remained at moderate levels, obviously affected by the restrictive measures and the effects of the pandemic, since, as already mentioned, the walk-in centers for the elderly operated with restrictions and activities such as creative activities, exercise and recreation were not carried out.
An important finding in the current study is the very high percentage (83.9%) of inactive older people, which poses serious risks to their health, compared to only 7.3% who presented a high activity level. This finding is in accordance with another study using IPAQ on Greek older adults on hemodialysis, in the third year of the pandemic, which found that the majority of older persons presented inactivity (69.7%). Persons exhibiting moderate and high activity represented 28.8% and 1.5% of the sample, respectively [52]. Another study conducted in Greece during the COVID-19 pandemic, also using IPAQ, highlighted the insufficient level of older adults’ physical activity (low 44%, moderate 42.6 and high activity 13.4% [53]. All studies mentioned showed insufficient levels of physical activity among older adults compared to the suggested levels by WHO (2020) (150–300 min of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity weekly) [54]. The level of physical activity of older adults decreased during the pandemic in Greece; research data collected before the pandemic present a higher level of regular activity, although still insufficient [55]. Other studies carried out on an international level before the pandemic also indicate that the vast majority of older people present a lack of daily exercise, resulting in comorbidities and the deterioration of their general health [56,57]. The inactivity pandemic, though, that followed the COVID-19 pandemic was a worldwide phenomenon which deteriorated the activity of older persons [27,58]. It is noteworthy that women in our study reported lower levels of physical activity than men, a finding, of course, open to interpretation; men usually have more free personal time at their disposal, contrary to women who, even at older ages, spend most of their time in household activities or looking after their children and grandchildren, showing the gender gap regarding different amounts of free personal time [55,59]. Similar conclusions have also been obtained in the research of Souza et al., (2015), where physical inactivity was found to be increased in older women compared to men [60].
In the present research, a moderate or high level of physical activity was found to contribute to a better physical functioning (p = 0.03), vitality (p = 0.02) and general health (p = 0.01) compared to a low level of physical activity. However, further analysis by multivariate linear regression has not found physical activity to be an independent predictor of quality of life. This is probably due to the particularly high percentage of older people with low levels of physical activity (83.9% low and 8.9% moderate), a result which was expected due to the ongoing effects of the pandemic during the period of the study (February–May 2022), where vaccinations had progressed and death rates had decreased, but the negative effects on the physical condition and psychology of the elderly were still intense. Additionally, the walk-in centers for older people did not carry out creative exercise and leisure activities, and the use of masks was still mandatory outdoors, where older people could exercise, both significant inhibiting factors for physical activity. Therefore, activity levels recorded during the present study were not sufficient to increase the quality of life of older persons in this time period. In line with our results, the study by Sepúlveda-Loyola et al., (2020) also determined the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the mental and physical health of the elderly. Increased physical inactivity and high levels of loneliness, depression, anxiety and poor sleep quality were observed [61]. Furthermore, Ghram et al., (2020) clarified that the isolation of the elderly during this period increased sedentary behavior and resulted in the presence of functional disorders, an increase in morbidity and the risk of falls [62]. Encouraging participation in physical activity addresses the health problems of the elderly related to physical inactivity by significantly improving physical fitness, cognitive performance and quality of life [63,64].
Another finding of the present study was that about half of the elderly (47.6%) participated in community programs or spent time partaking in a favorite hobby (50.4%), which simultaneously develops social functioning (p = 0.002). It has been reported that a wide range of activities, such as hobbies, traveling, going out and participating in group activities give older people joy and meaning in their lives, removing sadness and apathy [65]. In our study, it was found that the older persons who had included some favorite occupation in their daily life recorded satisfactory levels of physical activity, showing 3.5 times more frequent moderate- or high-level physical activity compared to older people who did not have hobbies. Participating in physical activity helps maintain and improve health, physical function and quality of life [16,17,66,67], while physical inactivity is considered one of the most powerful factors for the deterioration of physical and mental health in older people [68].
In the present study, a higher educational level was associated with better mental health (MCS), better physical functioning (PF) and better general health (GH). This could be attributed to the fact that older people with a satisfactory level of education acquire a higher level of health literacy and thus have the ability to deal with and manage issues related to their health better [69]. These findings are in line with the international literature, as evidence shows that people with a good educational level engage in healthy behaviors, which leads to improvement in their physical health [70]. In addition, educational level can positively contribute to the psychological state of older persons and their social relationships. In numerous studies, a higher educational level was associated with a better quality of life [71,72,73,74,75]. Through education, cognitive abilities are increased, unhealthy habits are prevented, diseases can be managed and the quality of life is holistically improved [76].
Another important factor that affects older persons’ perception of quality of life are comorbidities. A possible explanation could be the fact that chronic diseases and geriatric syndromes in older people contribute to their subjective perception of poor health status [77]. In the current study, the observed levels in mental health, physical, social and emotional role, vitality, general health and physical activity were all found to be affected by comorbidities. The negative impact of multiple and chronic diseases on various aspects related to the quality of life of older persons is evident in many studies [78,79,80,81,82].
Finally, the current study revealed a noticeable negative correlation between comorbidity and physical activity, a fact that can be justified since the progressive deterioration of bodily functions limits mobility and creates fragile health, and the pain that occurs causes psychological discomfort and a lack of desire to exercise. Specifically, older adults with fewer comorbidities had a higher level of physical activity. This finding contradicts the results of the research of Sadrollahi et al., (2016), where older people with chronic conditions had a higher level of physical activity in effort to change their attitude towards the way of dealing with their illness and life in general [83]. Research data show that during the pandemic, older adults with comorbidities decreased their physical activity levels and were more likely to be hospitalized [84,85].
Study Limitations
The results of the current study are subject to some limitations, as the research was not conducted at a nationwide level, but at specific primary health and social care services in the prefecture of Attica, using convenience sampling, and as a result, their generalizability is reduced. At the time of the study, older people were still reluctant to visit primary health and social care services because there was still a fear of COVID-19, and convenient sampling was the most appropriate technique in order to recruit all available eligible persons.
Additionally, the physical activity and quality of life of older persons were only assessed using self-administered questionnaires. In addition, the mental health of participants was not assessed prior the questionnaires’ completion. Moreover, norms used to compare the findings of the current study with regard to the physical and mental health component were derived from a Greek general population instead of a geriatric population. In addition, it is worth considering that the research was carried out during a particularly difficult period where, due to the pandemic, physical activity had been significantly decreased and the physical and psychological condition of older people had been affected. Finally, the use of IPAQ, which is not a tool specifically designed for older adults, is a possible limitation of the study. It should be mentioned that older adults present more difficulties recalling physical-activity-related data, especially lower-intensity and unstructured physical activity, adding a bias in the results [86,87]. However, younger adults may have similar difficulties in recalling activities of low intensity and duration [43]. The main researcher who conducted the interviews was specially trained and used all recommended techniques to minimize error possibly deriving from the use of a non-geriatric tool in older adults (careful explanation of questions, repetition of intensity and time criteria and provision of examples) [43].
Despite any limitations and difficulties, the results obtained from similar research are considered particularly useful for understanding how physical activity is linked to quality of life and for conducting further research work aiming to develop sustainable interventions in public health.
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
Aging is an inevitable process of human nature; however, there are approaches that can promote healthy aging by slowing down the negative effects, postponing degeneration, preserving activeness and sociability and securing an independent life, with physical activity being one of them.
Focusing on the results of the present study, we conclude that physical activity influences and promotes many key aspects of quality of life. Physical activity seems to have an influence on physical functioning as well as a positive impact on general health and vitality of the participants.
The beneficial effect of physical activity on the overall health and quality of life renders it highly important as a public health strategy. The adoption of an active lifestyle must be part of the planning and promotion of healthy aging as a factor that provides independence, functionality, longevity and quality of life among older people.
The activation of institutions (family, city, community, associations and clubs), the design of successful interventions focusing on the increase in physical activity, the enhancement of health literacy of older adults on the benefits of physical activity and the encouragement and motivation for the improvement in physical fitness are useful strategies for the preservation of the physical and mental health of this population as well as their ability to experience healthy and active aging.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P. and M.M.; Data curation, A.P., D.M. and M.M.; Formal analysis, A.P., T.A., P.A. and M.M.; Funding acquisition, A.K., S.P. (Sotirios Plakas) and M.M.; Investigation, A.P.; Methodology, A.P.; Project administration, M.M.; Resources, S.P. ( Stelios Parissopoulos) and A.Z.; Software, A.M. and A.Z.; Supervision, M.M.; Validation, T.A., P.A., S.P. ( Sotirios Plakas) and D.M.; Visualization, P.A., A.K., M.D. and A.M.; Writing—original draft, A.P., P.A., A.K. and M.M.; Writing—review and editing, T.A., P.A., A.K., M.D., S.P. (Sotirios Plakas), D.M., A.M., S.P. (Stelios Parissopoulos), A.Z. and M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript and have agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Funding
The publication costs of this study were funded by the Special Account for Research Grants (ELKE), University of West Attica, Athens, Greece.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of West Attica (protocol number 17349, date: 23 February 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy reasons.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the participants as well as the collaborators of the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gkouvas, K.C.; Soulis, G.; Panagiotakos, D.B. The Multiple Dimensions of the Ageing Process; What Do We Know about Them? Arch. Hell. Med. 2018, 35, 757–764. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Healthy Ageing and Functional Ability. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/healthy-ageing-and-functional-ability (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Balboa-Castillo, T.; León-Muñoz, L.M.; Graciani, A.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F.; Guallar-Castillón, P. Longitudinal Association of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior during Leisure Time with Health-Related Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2011, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, K.; Ihira, H.; Mizumoto, A.; Shimizu, K.; Ishida, T.; Furuna, T. Associations between the Settings of Exercise Habits and Health-Related Outcomes in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 2207–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburton, D.E.R.; Bredin, S.S.D. Health Benefits of Physical Activity: A Systematic Review of Current Systematic Reviews. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2017, 32, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daimiel, L.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Schröder, H.; Vioque, J.; Romaguera, D.; Martínez, J.A.; Wärnberg, J.; Lopez-Miranda, J.; et al. Physical Fitness and Physical Activity Association with Cognitive Function and Quality of Life: Baseline Cross-Sectional Analysis of the PREDIMED-Plus Trial. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepsy, E.; Radwańska, E.; Żurek, G.; Żurek, A.; Kaczorowska, A.; Radajewska, A.; Kołcz, A. Association of Physical Fitness with Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Older Adults Aged 80 and over in Poland: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psarrou, A.; Adamakidou, T.; Plakas, S.; Mastrogiannis, D.; Drakopoulou, M.; Mantzorou, M. Physical Activity and Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2022, 13 (Suppl. S1), 299. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, M.B.; Oliveira, J.S.; Baldwin, J.N.; Hassett, L.; Costa, N.; Gilchrist, H.; Wang, B.; Kwok, W.; Albuquerque, B.S.; Pivotto, L.R.; et al. Impact of Physical Activity Programs and Services for Older Adults: A Rapid Review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2022, 19, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, A.P.; Street, S.J.; Byrne, N.M. Physical Activity and Health. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 75, pp. 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, M.; Lavoie, K.L.; Bacon, S.L. Taking up Physical Activity in Later Life and Healthy Ageing: The English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-A.; Son, S.Y.; Lee, A.-Y.; Park, H.-G.; Lee, W.-L.; Lee, C.H. Metabolite Profiling Revealed That a Gardening Activity Program Improves Cognitive Ability Correlated with BDNF Levels and Serotonin Metabolism in the Elderly. IJERPH 2020, 17, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, T.L.; Masser, B.M.; Pachana, N.A. Positive Ageing Benefits of Home and Community Gardening Activities: Older Adults Report Enhanced Self-Esteem, Productive Endeavours, Social Engagement and Exercise. SAGE Open. Med. 2020, 8, 205031212090173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyland, L.-A.; Spencer, B.; Beale, N.; Jones, T.; Van Reekum, C.M. The Effect of Cycling on Cognitive Function and Well-Being in Older Adults. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, B.; Laumann, E.O. The Health Benefits of Network Growth: New Evidence from a National Survey of Older Adults. Soc. Sci. Med. 2015, 125, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilidou, B.; Duka, S.; Tsolaki, M. The Results of an Intervention Program of Traditional Dances, as a Recreational Activity, Improving the Quality of Life of Senior Citizens at the Municipality of Thessaloniki. Hell. J. Sport. Recreat. Manag. 2015, 12, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Douka, S.; Zilidou, V.I.; Lilou, O.; Tsolaki, M. Greek Traditional Dances: A Way to Support Intellectual, Psychological, and Motor Functions in Senior Citizens at Risk of Neurodegeneration. Front. Ageing Neurosci. 2019, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustakopoulou, L. Study of Fear, Loneliness and Depression in Older Adults during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Master’s Thesis, University of West Attica, Athens, Greece, 2022. Available online: https://polynoe.lib.uniwa.gr/xmlui/handle/11400/3539?locale-attribute=en (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Liu, Y.; Tamura, R.; Song, Y. Constructing a Smart Home for Future Elders toward All-around Happiness: Taking Connectivity as the Core Element. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarabottolo, C.C.; Cyrino, E.S.; Nakamura, P.M.; Tebar, W.R.; da Canhin, D.S.; Gobbo, L.A.; Christofaro, D.G.D. Relationship of Different Domains of Physical Activity Practice with Health-Related Quality of Life among Community-Dwelling Older People: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e027751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bădicu, G. Physical Activity and Health-Related Quality of Life in Adults from Braşov, Romania. Educ. Sci. 2018, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lau, J.H.; Vaingankar, J.A.; Abdin, E.; Chong, S.A.; Lee, E.S. Patterns of Physical Activity and Health-Related Quality of Life amongst Patients with Multimorbidity in a Multi-Ethnic Asian Population. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechamps, A. Effects of Exercise Programs to Prevent Decline in Health-Related Quality of Life in Highly Deconditioned Institutionalized Elderly Persons: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, N.; Higaki, Y.; Inoue, S.; Kimura, H.; Tanaka, K. Effects of a 12-Month Multicomponent Exercise Program on Physical Performance, Daily Physical Activity, and Quality of Life in Very Elderly People With Minor Disabilities: An Intervention Study. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 20, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrovouniotis, F.H.; Argiriadou, E.A.; Papaioannou, C.S. Greek Traditional Dances and Quality of Old People’s Life. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2010, 14, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzonichaki, I.; Malikiosi-Loizos, M.; Kleftaras, G. The Role of Level of Functioning, Life Satisfaction and Leisure Activities in Elderly Depressive Symptomatology. Rostrum Asclepius 2013, 12, 409–427. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, G.; Laddu, D.R.; Phillips, S.A.; Lavie, C.J.; Arena, R. A Tale of Two Pandemics: How Will COVID-19 and Global Trends in Physical Inactivity and Sedentary Behavior Affect One Another? Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 64, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J.Ε.; Sherbourne, C.D. The MOS 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36): I. Conceptual Framework and Item Selection. Med. Care 1992, 30, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, J.E. The SF-36 Health Survey. A Manual and Interpretation Guide; The Health Institute, New England Medical Center: Boston, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Anagnostopoulos, F.; Niakas, D.; Pappa, E. Construct Validation of the Greek SF-36 Health Survey. Qual. Life Res. 2005, 14, 1959–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappa, E.; Kontodimopoulos, N.; Niakas, D. Validating and Norming of the Greek SF-36 Health Survey. Qual. Life Res. 2005, 14, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwar, A.; Sahni, S.; Kim, E.J.; Verma, S.; Kohn, N. Dyspnea, Depression and Health Related Quality of Life in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patients. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2015, 11, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taft, C.; Karlsson, J.; Sullivan, M. Do SF-36 Summary Component Scores Accurately Summarize Subscale Scores? Qual. Life Res. 2001, 10, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J. SF-36 Health Survey Update. Spine 2000, 25, 3130–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International Physical Activity Questionnaire: 12-Country Reliability and Validity. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanasiou, G.; Georgoudis, G.; Papandreou, M.; Spyropoulos, P.; Georgakopoulos, D.; Kalfakakou, V.; Evangelou, A. Reliability Measures of the Short International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) in Greek Young Adults. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2009, 50, 283–294. [Google Scholar]
- IPAQ Research Committee Guidelines for Data Processing and Analysis of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)—Short form. Physiopedia. 2004. Available online: https://www.physiopedia.com/images/c/c7/Quidelines_for_interpreting_the_IPAQ.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Kolbe-Alexander, T.L.; Lambert, E.V.; Harkins, J.B.; Ekelund, U. Comparison of Two Methods of Measuring Physical Activity in South African Older Adults. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2006, 14, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Holle, V.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Deforche, B.; Van Cauwenberg, J.; Van Dyck, D. Assessment of Physical Activity in Older Belgian Adults: Validity and Reliability of an Adapted Interview Version of the Long International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ-L). BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomioka, K.; Iwamoto, J.; Saeki, K.; Okamoto, N. Reliability and Validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) in Elderly Adults: The Fujiwara-Kyo Study. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerin, E.; Barnett, A.; Cheung, M.; Sit, C.H.P.; Macfarlane, D.J.; Chan, W. Reliability and Validity of the IPAQ-L in a Sample of Hong Kong Urban Older Adults: Does Neighborhood of Residence Matter? J. Aging Phys. Act. 2012, 20, 402–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, C.; Ferguson, S.; Ellis, G.; Hunter, R.F. Validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) for Assessing Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour of Older Adults in the United Kingdom. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2018, 18, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heesch, K.C.; Van Uffelen, J.G.; Hill, R.L.; Brown, W.J. What Do IPAQ Questions Mean to Older Adults? Lessons from Cognitive Interviews. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2010, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapanou, O.; Papadopoulos, A.; Vlassopoulou, B.; Vassilopoulos, C.; Pappa, E.; Tsagarakis, S.; Niakas, D. Health status of Greek thyroid cancer patients after radioiodine administration compared to a demographically matched general population sample. Hell. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 15, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Aodeng, S.; Tanimoto, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Han, J.; Wang, B.; Yu, L.; Kono, K. Quality of Life (QOL) of the Community-Dwelling Elderly and Associated Factors: A Population-Based Study in Urban Areas of China. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2015, 60, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attafuah, P.Y.A.; Everink, I.; Abuosi, A.A.; Lohrmann, C.; Schols, J.M.G.A. Quality of Life of Older Adults and Associated Factors in Ghanaian Urban Slums: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e057264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández, L.; Romero-Ferreiro, V.; López-Roldán, P.D.; Padilla, S.; Rodriguez-Jimenez, R. Mental Health in Elderly Spanish People in Times of COVID-19 Outbreak. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2020, 28, 1040–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, L.M.; Chen, C.Y. The COVID-19 Pandemic’s Impact on Older Adults’ Mental Health: Contributing Factors, Coping Strategies, and Opportunities for Improvement. Int. J. Geriat. Psychiatry 2022, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.C.; Tou, N.X.; Low, J.A. A Comparative Study on Mental Health and Adaptability between Older and Younger Adults during the COVID-19 Circuit Breaker in Singapore. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koma, W.; True, S.; Fuglesten Biniek, J.; Cubanski, J.; Orgera, K.; Garfield, R. One in Four Older Adults Report Anxiety or Depression Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic. Medicare. 2020. Available online: https://www.kff.org/medicare/issue-brief/one-in-four-older-adults-report-anxiety-or-depression-amid-the-covid-19-pandemic/ (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Meng, H.; Xu, Y.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Yang, H. Analyze the Psychological Impact of COVID-19 among the Elderly Population in China and Make Corresponding Suggestions. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 289, 112983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsekoura, M.; Kalampakos, N.; Fousekis, K.; Mylonas, K.; Angelopoulos, P.; Matzaroglou, C.; Bita, T.; Gliatis, J.; Tsepis, E.; Billis, E. Risk of Sarcopenia, Fear of COVID-19, Anxiety, Depression and Physical Activity Levels: Associations across Patients on Hemodialysis within Greece. JFSF 2023, 8, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roukounaki, M. Activity Levels of the Elderly in the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Research Study. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Patras, Aigio, Greece, 2022. Available online: http://repository.library.teiwest.gr/xmlui/bitstream/handle/123456789/9904/%CE%A1%CE%9F%CE%A5%CE%9A%CE%9F%CE%A5%CE%9D%CE%91%CE%9A%CE%97.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 6 April 2022).
- WHO Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour: At a Glance. 2020. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/337001/9789240014886-eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 25 March 2022).
- Babatsikou, F.; Gerogianni, G.; Zyga, S.; Koutis, C. Physical Activity in a Sample of Elderly Greek People: A Research Study. Health Sci. J. 2012, 6, 518–533. [Google Scholar]
- McPhee, J.S.; French, D.P.; Jackson, D.; Nazroo, J.; Pendleton, N.; Degens, H. Physical Activity in Older Age: Perspectives for Healthy Ageing and Frailty. Biogerontology 2016, 17, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.E.; Rejeski, W.J.; Blair, S.N.; Duncan, P.W.; Judge, J.O.; King, A.C.; Macera, C.A.; Castaneda-Sceppa, C. Physical Activity and Public Health in Older Adults: Recommendation from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2007, 39, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.R.; Sudati, I.P.; Konzen, V.D.M.; De Campos, A.C.; Wibelinger, L.M.; Correa, C.; Miguel, F.M.; Silva, R.N.; Borghi-Silva, A. COVID-19 and the Impact on the Physical Activity Level of Elderly People: A Systematic Review. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 159, 111675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, J.R.; McGill, B.S.; Bianchi, S.M. Help to Family and Friends: Are There Gender Differences at Older Ages? J. Marriage Fam. 2011, 73, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.M.R.; Fillenbaum, G.G.; Blay, S.L. Prevalence and Correlates of Physical Inactivity among Older Adults in Rio Grande Do Sul, Brazil. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepúlveda-Loyola, W.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, I.; Pérez-Rodríguez, P.; Ganz, F.; Torralba, R.; Oliveira, D.V.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L. Impact of Social Isolation Due to COVID-19 on Health in Older People: Mental and Physical Effects and Recommendations. J. Nutr. Health Ageing 2020, 24, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghram, A.; Briki, W.; Mansoor, H.; Al-Mohannadi, A.S.; Lavie, C.J.; Chamari, K. Home-Based Exercise Can Be Beneficial for Counteracting Sedentary Behavior and Physical Inactivity during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Older Adults. Postgrad. Med. 2021, 133, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D. Physical Activity Is Medicine for Older Adults. Postgrad. Med. J. 2014, 90, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loprinzi, P.D.; Davis, R.E. Bouted and Non-Bouted Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity with Health-Related Quality of Life. Prev. Med. Rep. 2016, 3, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, K.M.; Van Loon, M.S.; Van Nes, F.A.; Bosmans, J.E.; De Vet, H.C.W.; Ket, J.C.F.; Widdershoven, G.A.M.; Ostelo, R.W.J.G. What Does Quality of Life Mean to Older Adults? A Thematic Synthesis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, B.; Kifley, A.; Flood, V.M.; Mitchell, P. Physical Activity as a Determinant of Successful Ageing over Ten Years. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Thomas, S.M.; Veroniki, A.A.; Hamid, J.S.; Cogo, E.; Strifler, L.; Khan, P.A.; Robson, R.; Sibley, K.M.; MacDonald, H.; et al. Comparisons of Interventions for Preventing Falls in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA 2017, 318, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, R.A.; Guralnik, J.M.; King, A.C.; Pahor, M.; McDermott, M.M.; Tudor-Locke, C.; Manini, T.M.; Glynn, N.W.; Marsh, A.P.; Axtell, R.S.; et al. Dose of Physical Activity, Physical Functioning and Disability Risk in Mobility-Limited Older Adults: Results from the LIFE Study Randomized Trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zisopoulou, S.; Plakas, S.; Mastrogiannis, D.; Adamakidou, T.; Mantzorou, M. The Effect of E-Health Literacy on Adherence with Medication in Chronically Ill Patients. Intersci. Healthc. 2020, 12, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, M.; Kc, H.; Bhattarai, P.; Mishra, A.; Parajuli, S.B. Quality of Life of Elderly People Living with Family and in Old Age Home in Morang District, Nepal. BIBECHANA 2018, 16, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde-Sala, J.L.; Portellano-Ortiz, C.; Calvó-Perxas, L.; Garre-Olmo, J. Quality of Life in People Aged 65+ in Europe: Associated Factors and Models of Social Welfare—Analysis of Data from the SHARE Project (Wave 5). Qual. Life Res. 2017, 26, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Labra, C.; Maseda, A.; Lorenzo-López, L.; López-López, R.; Buján, A.; Rodríguez-Villamil, J.L.; Millán-Calenti, J.C. Social Factors and Quality of Life Aspects on Frailty Syndrome in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: The VERISAÚDE Study. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, N.T.; Duy, H.T.; Le, N.H.; Khanal, V.; Moorin, R. Quality of Life among People Living with Hypertension in a Rural Vietnam Community. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skevington, S.M. Qualities of Life, Educational Level and Human Development: An International Investigation of Health. Soc. Psychiat. Epidemiol. 2010, 45, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, L.P.; Schneider, I.J.C.; d’Orsi, E. Quality of Life and Its Association with Work, the Internet, Participation in Groups and Physical Activity among the Elderly from the EpiFloripa Survey, Florianópolis, Santa Catarina State, Brazil. Cad. Saúde Pública 2016, 32, e00143615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutler, D.M.; Lleras-Muney, A. Understanding Differences in Health Behaviors by Education. J. Health Econ. 2010, 29, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doležalová, J.; Tóthová, V.; Neugebauer, J.; Sadílek, P. Impact of Selected Geriatric Syndromes on the Quality of Life in the Population Aged 60 and Older. Healthcare 2021, 9, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponirou, P.; Diomidous, M.; Kalokairinou, A.; Mantas, J.; Tsimahidou, C.; Tzavara, C. Document Details—Health Related Quality of Life in a Sample of Older People Who Are Members of Open Care Centers for the Elderly. In Studies in Health Technology and Informatics; Elsevier: Athens, Greece, 2014; Volume 202, pp. 269–272. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, Y.R.; Lee, I.S.; Lee, H.Y. Effects of Hypertension, Diabetes, and/or Cardiovascular Disease on Health-Related Quality of Life in Elderly Korean Individuals: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Survey. Asian Nurs. Res. 2014, 8, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camelo, L.D.V.; Giatti, L.; Barreto, S.M. Qualidade de Vida Relacionada à Saúde Em Idosos Residentes Em Região de Alta Vulnerabilidade Para Saúde de Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2016, 19, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.R. Factors Determining Quality of Life of Elderly People in Rural Nepal. J. Gerontol. Geriatr. Res. 2020, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, A.; Champion, V.L.; Von Ah, D. Comorbidity, Cognitive Dysfunction, Physical Functioning, and Quality of Life in Older Breast Cancer Survivors. Support. Care Cancer 2022, 30, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadrollahi, A.; Hosseinian, M.; Masoudi Alavi, N.; Khalili, Z.; Esalatmanesh, S. Physical Activity Patterns in the Elderly Kashan Population. Iran. Red. Crescent Med. J. 2016, 18, e25008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Sánchez, G.F.; López-Bueno, R.; Gil-Salmerón, A.; Zauder, R.; Skalska, M.; Jastrzębska, J.; Jastrzębski, Z.; Schuch, F.B.; Grabovac, I.; Tully, M.A.; et al. Comparison of Physical Activity Levels in Spanish Adults with Chronic Conditions before and during COVID-19 Quarantine. Eur. J. Public Health 2021, 31, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, R.Y.C.; Liu, J.Y.W.; Yin, Y.-H.; Lee, P.H.; Ng, S.Y.; Cheung, D.S.K.; Kor, P.P.K.; Lam, S.C.; Lo, S.K.L.; Yang, L.; et al. Sarcopenia and Its Association with Objectively Measured Life-Space Mobility and Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity in the Oldest-Old amid the COVID-19 Pandemic When a Physical Distancing Policy Is in Force. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, N.D.; Chiu, V.; King, A.C.; Stewart, A.L. An Evaluation of Three Self-Report Physical Activity Instruments for Older Adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.L.; Mills, K.M.; King, A.C.; Haskell, W.L.; Gillis, D.; Ritter, P.L. CHAMPS Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Adults: Outcomes for Interventions. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 1126–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).