Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Older People with Functional and Nutritional Impairment and Depressive Symptoms: A Comparative Cross-Sectional Study in Brazil and Portugal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Ethical Aspects
2.3. Study Location
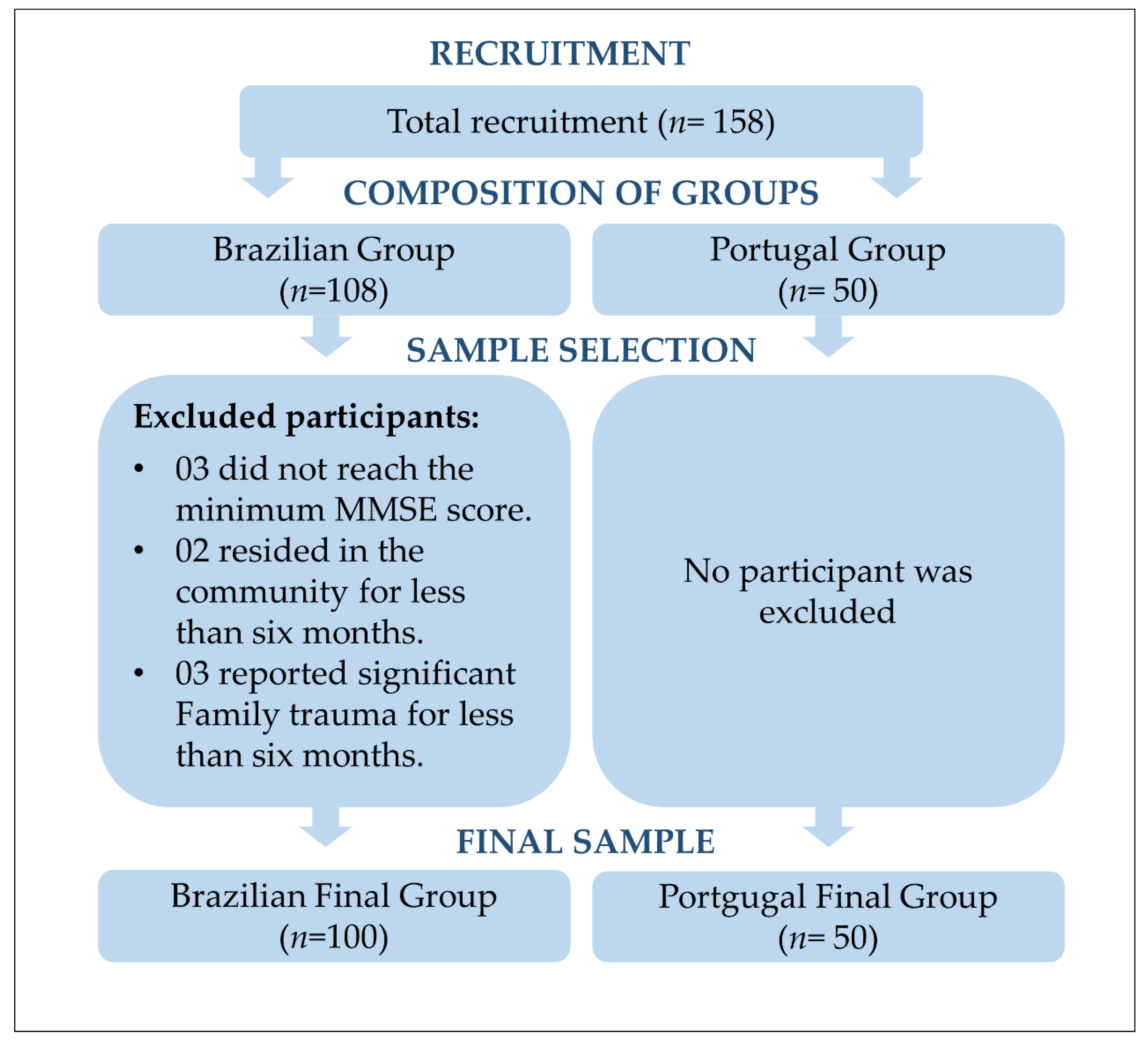
2.4. Population and Sample
2.5. Data Collection and Availability
2.6. Instruments and Variables
2.7. Data Analysis and Treatment
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The World Health Organization Quality of Life Assessment (WHOQOL). Position Paper from the World Health Organization. Soc. Sci. Med. 1995, 41, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Age-Friendly Cities: A Guide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Sampaio, A.; Marques-Aleixo, I.; Seabra, A.; Mota, J.; Marques, E.; Carvalho, J. Physical Fitness in Institutionalized Older Adults with Dementia: Association with Cognition, Functional Capacity and Quality of Life. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 32, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, M.J.; Pinho, L.G.; Fonseca, C.; Goes, M.; Oliveira, H.; Garcia-Alonso, J.; Afonso, A. Functioning and Cognition of Portuguese Older Adults Attending in Residential Homes and Day Centers: A Comparative Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reber, E.; Gomes, F.; Vasiloglou, M.F.; Schuetz, P.; Stanga, Z. Nutritional Risk Screening and Assessment. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maseda, A.; Diego-Diez, C.; Lorenzo-Lopez, L.; Lopez-Lopez, R.; Regueiro-Folgueira, L.; Millan-Calenti, J.C. Quality of Life, Functional Impairment and Social Factors as Determinants of Nutritional Status in Older Adults: The VERISAUDE Study. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faxen-Irving, G.; Luiking, Y.; Gronstedt, H.; Franzen, E.; Seiger, A.; Vikstrom, S.; Wimo, A.; Bostrom, A.M.; Cederholm, T. Do Malnutrition, Sarcopenia and Frailty Overlap in Nursing-Home Residents? J. Frailty Aging 2021, 10, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumye, S.; Belayneh, Z.; Mengistu, N. Health Related Quality of Life and Its Correlates Among People with Depression Attending Outpatient Department in Ethiopia: A Cross Sectional Study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2019, 17, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.V.; Noronha, K.; Cardoso, C.S.; Oliveira, C.D.L.; Calazans, J.A.; Souza, M.N. Challenges and Lessons from a Primary Care Intervention in a Brazilian Municipality. Rev. Saude. Pública 2019, 53, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.M.; Alvarez, A.M.; Rauch, K.C. Trends in Hospitalization and Mortality for Ambulatory Care Sensitive Conditions Among Older Adults. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2019, 22, e190010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil. Percepção do Estado de Saúde, Estilos de Vida, Doenças Crônicas E Saúde Bucal; Fundação SEADE: São Paulo, Brazil, 2020; 113p. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, L.F.; Soranz, D.; Scardua, M.T.; Silva, I.M. Ambulatory Municipal Regulation of the Unified Health System Services in Rio de Janeiro: Advances, Limitations and Challenges. Ciência Saúde Coletiva 2017, 22, 1257–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estatística. I.N.d. Inquérito Nacional de Saúde 2019; Instituto Nacional de Estadística: Madrid, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Beard, J.R.; Officer, A.; de Carvalho, I.A.; Sadana, R.; Pot, A.M.; Michel, J.P.; Lloyd-Sherlock, P.; Epping-Jordan, J.E.; Peeters, G.; Mahanani, W.R.; et al. The World Report on Ageing and Health: A Policy Framework for Healthy Ageing. Lancet 2016, 387, 2145–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenco, R.A.; Veras, R.P. Mini-Mental State Examination: Psychometric Characteristics in Elderly Outpatients. Rev. Saúde Pública 2006, 40, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciconelli, R.M.; Ferraz, M.B.; dos Santos, W.S.; Meinão, I.M.; Quaresma, M.R. Traducao Para a Lingua Portuguesa e Validacao do Questionario Generico de Avaliacao de Qualidade de Vida SF-36 (Brasil SF-36). Rev. Bras. Reumatol. 1999, 39, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Saenger, A.L.; Caldas, C.P.; Motta, L.B. Cross-Cultural Adaptation of the PRISMA-7 Instrument for Use in Brazil: Evaluation of Conceptual, Item, and Semantic Equivalences. Cad. Saúde Pública 2016, 32, e00072015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, M.P.; Brody, E.M. Assessment of Older People: Self-Maintaining and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living. Gerontologist 1969, 9, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenstein, L.Z.; Harker, J.O.; Salva, A.; Guigoz, Y.; Vellas, B. Screening for Undernutrition in Geriatric Practice: Developing the Short-Form Mini-Nutritional Assessment (MNA-SF). J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M366–M372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuna, K.; Cruz, T. Nutritional Assessment of Adults and Elderly and the Nutritional Status of the Brazilian Population. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2004, 48, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradela, E.M.; Lourenco, R.A.; Veras, R.P. Validation of Geriatric Depression Scale in a General Outpatient Clinic. Rev. Saude Pública 2005, 39, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, O.P.; Almeida, S.A. Reliability of the Brazilian Version of the Abbreviated Form of Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS) Short Form. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 1999, 57, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Ghimire, S.; Baral, B.K.; Pokhrel, B.R.; Pokhrel, A.; Acharya, A.; Amatya, D.; Amatya, P.; Mishra, S.R. Depression, Malnutrition, and Health-Related Quality of Life Among Nepali Older Patients. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Albuquerque-Araujo, L.; Quintiliano-Scarpelli, D.; Masferrer Riquelme, D.; Ferreira Santos, J.L. Influence of Sociodemographic, Health-Related, and Behavioral Factors on Food Guidelines Compliance in Older Adults: A Hierarchical Approach from the Chilean National Health Survey 2016–2017 Data. Geriatrics 2022, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, A.T.M.; Nguyen, V.T.; Nguyen, H.V.; Nguyen, L.T.K. Factors Associated with Depression among the Elderly Living in Urban Vietnam. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2370284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velazquez-Alva, M.C.; Irigoyen-Camacho, M.E.; Cabrer-Rosales, M.F.; Lazarevich, I.; Arrieta-Cruz, I.; Gutierrez-Juarez, R.; Zepeda-Zepeda, M.A. Prevalence of Malnutrition and Depression in Older Adults Living in Nursing Homes in Mexico City. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Ge, Y.; Meng, N.; Xie, T.; Ding, H. Correlation Between Depressive Symptoms and Quality of Life, And Associated Factors for Depressive Symptoms Among Rural Elderly in Anhui, China. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 1901–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goates, S.; Du, K.; Arensberg, M.B.; Gaillard, T.; Guralnik, J.; Pereira, S.L. Economic Impact of Hospitalizations in US Adults with Sarcopenia. J. Frailty Aging 2019, 8, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez Gomez, M.A.; Fernandez Dominguez, M.J.; Blanco Ramos, M.A.; Alves Perez, M.T.; Fernandez Dominguez, M.J.; Souto Ramos, A.I.; Gonzalez Iglesias, M.P.; Claveria Fontan, A. Depression and Burden in the Caretaking of Elderly. Rev. Esp. Salud Pública 2019, 93, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Zwi, A.B.; Shen, C.; Wu, Y.; Gao, J. Exploring the Relationship Between Functional Limitations of the Older Adults and the Health-Related Quality of Life of Their Spouse in Shaanxi Province, China. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2021, 19, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopsawang, I.; Aree-Ue, S.; Baurangthienthong, S.; Boontham, J.; Phiboonleetrakun, Y. Path Model Factors Associated with Depressive Symptoms among Older Thais Living in Rural Areas. Geriatrics 2022, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billett, M.C.; Campanharo, C.R.V.; Lopes, M.; Batista, R.E.A.; Belasco, A.G.S.; Okuno, M.F.P. Functional Capacity and Quality of Life of Hospitalized Octogenarians. Rev. Bras. Enferm. 2019, 72, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacador, C.; Teixeira-Lemos, E.; Oliveira, J.; Pinheiro, J.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F.; Ramos, F. The Relationship between Nutritional Status and Functional Capacity: A Contribution Study in Institutionalised Portuguese Older Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, F.; Shafiee, G.; Kamali, K.; Ebrahimi, M.; Azimi, M.; Ahadi, Z.; Sharifi, F.; Tanjani, P.T.; Heshmat, R. Correlation between Malnutrition and Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQOL) in Elderly Iranian Adults. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060519863497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamoureux-Lamarche, C.; Berbiche, D.; Vasiliadis, H.M. Treatment Adequacy and Remission of Depression and Anxiety Disorders and Quality of Life in Primary Care Older Adults. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2021, 19, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Blanch, C.; Hernandez-de-Hita, F.; Munoz-Navarro, R.; Ruiz-Rodriguez, P.; Medrano, L.A.; Cano-Vindel, A. The Association Between Different Domains of Quality of Life and Symptoms in Primary Care Patients with Emotional Disorders. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas, B.; de Miranda, J.M.A.; Cavalcante, A.C.V.; Toscano, G.; Torres, L.S.S.; Rossignolo, S.C.O.; Nobre, T.T.X.; Maia, E.M.C.; de Miranda, F.A.N.; Torres, G.V. Impact of Multidimensional Interventions on Quality of Life and Depression Among Older Adults in a Primary Care Setting in Brazil: A Quasi-Experimental Study. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2020, 42, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.P.; Nyunt, M.S.Z.; Feng, L.; Kumar, R.; Fones, C.S.L.; Ko, S.M. Collaborative Care for Primary Care Treatment of Late-Life Depression in Singapore: Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2020, 35, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever-van Milligen, B.A.; Verhoeven, J.E.; Schmaal, L.; van Velzen, L.S.; Revesz, D.; Black, C.N.; Han, L.K.M.; Horsfall, M.; Batelaan, N.M.; van Balkom, A.; et al. The Impact of Depression and Anxiety Treatment on Biological Aging and Metabolic Stress: Study Protocol of the Mood Treatment with Antidepressants or Running (MOTAR) Study. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, S.G.; Curtiss, J.; Carpenter, J.K.; Kind, S. Effect of Treatments for Depression on Quality of Life: A Meta-Analysis. Cogn. Behav. Ther. 2017, 46, 265–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresden, S.M.; McCarthy, D.M.; Engel, K.G.; Courtney, D.M. Perceptions and Expectations of Health-Related Quality of Life Among Geriatric Patients Seeking Emergency Care: A Qualitative Study. BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, E.; Wright, O.; Hoogendijk, E.O.; Hubbard, R.E. Nutritional Screening and Dietitian Consultation Rates in a Geriatric Evaluation and Management Unit. Nutr. Diet 2018, 75, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Dantas, B.A.; Cavalcante, A.C.V.; de Miranda, J.M.A.; da Silva Toscano, G.A.; Nobre, T.T.X.; Mendes, F.R.P.; de Miranda, F.A.N.; Maia, E.M.C.; Torres, G.V. Depression and Quality of Life in Brazilian and Portuguese Older People Communities: Analysis of Association. Medicine 2021, 100, e27830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onocko-Campos, R.T.; Amaral, C.E.M.; Saraceno, B.; de Oliveira, B.D.C.; Treichel, C.; Delgado, P.G.G. Functioning of Psychosocial Care Centers in Four Cities in BrazilActuacion de Los Centros de Atencion Psicosocial en Cuatro Centros Urbanos en Brasil. Rev. Panam. Salud Pública 2018, 42, e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapao, L.V.; Arcencio, R.A.; Popolin, M.P.; Rodrigues, L.B. The role of Primary Healthcare in the coordination of Health Care Networks in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and Lisbon region, Portugal. Ciência Saúde Coletiva 2017, 22, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinto, L.F.; Rocha, C.M.; Lapao, L.V.; Pisco, L.A. Comparative Health Systems: Primary Health Care in the cities of Lisbon and Rio de Janeiro. Ciência Saúde Coletiva 2017, 22, 676–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prazeres, F.; Santiago, L. Prevalence of Multimorbidity in the Adult Population Attending Primary Care in Portugal: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e009287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Variable | Brazil (n = 100) n (%) | Portugal (n = 50) n (%) | Total (n = 150) n (%) | p Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Female | 73 (73%) | 41 (82%) | 114 (76%) | 0.224 |
| Male | 27 (27%) | 9 (18%) | 36 (24%) | ||
| Age range, yr | 65–80 | 89 (89%) | 43 (86%) | 132 (88%) | 0.594 |
| 81–100 | 11 (11%) | 7 (14%) | 18 (12%) | ||
| Educational attainment, yr | ≤5 | 79 (79%) | 26 (52%) | 105 (70%) | 0.001 |
| >5 | 21 (21%) | 24 (48%) | 45 (30%) | ||
| Marital status | Married/cohabitating | 51 (51%) | 22 (44%) | 73 (48.7%) | 0.419 |
| Single/widowed/divorced | 49 (49%) | 28 (56%) | 77 (51.3%) | ||
| Household income, ** minimum wage | ≤1 | 42 (42%) | 50 (100%) | 92 (61.3%) | <0.001 |
| >1 | 58 (58%) | - | 58 (38.7%) | ||
| Chronic Diseases | Yes | 79 (79%) | 46 (92%) | 125 (83.3%) | 0.062 *** |
| No | 21 (21%) | 4 (8%) | 25 (16.7%) | ||
| QoL (SF-36) | Brazil (n = 100) | Portugal (n = 50) | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Percentiles | Percentiles | ||
| 25-50-75 | 25-50-75 | ||
| Domains | |||
| Physical role Functioning | 35.0–67.5–90.0 | 50.0–75.0–90.0 | 0.174 |
| Physical Functioning | 0–50–100 | 75–100–100 | <0.001 |
| Emotional Role Functioning | 33.3–100–100 | 66.7–100–100 | 0.359 |
| Mental Health | 52–56–60 | 48–56–64 | 0.332 |
| General Health Perceptions | 30–35–55 | 35–50–56.2 | 0.043 |
| Pain | 20–40–60 | 20–30–40 | 0.076 |
| Vitality | 45–50–60 | 43.7–50–56.2 | 0.348 |
| Social Role Functioning | 50–50–50 | 37.5–50–50 | 0.022 |
| Total Score | 44.2–55–61 | 53.9–60.8–63.9 | 0.006 |
| Dimensions | |||
| Mental Health | 47.2–57–61 | 49.9–58.3–61.9 | 0.235 |
| Physical Health | 40–50–57 | 49.7–57–63 | <0.001 |
| Evaluated Variables | Rating | Brazil (n = 100) | Portugal (n = 50) | Total (n = 150) | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Functionality | |||||
| Prisma 7 | I ** | 56 (56%) | 41 (82%) | 97 (64.7%) | 0.002 |
| P *** | 44 (44%) | 9 (18%) | 53 (35.3%) | ||
| Lawton & Brody | I | 75 (75%) | 12 (24%) | 87 (58%) | <0.001 |
| P | 25 (25%) | 38 (76%) | 63 (42%) | ||
| Nutrition | |||||
| MNA | I | 90 (90%) | 32 (64%) | 122 (81.3%) | <0.001 |
| P | 10 (10%) | 18 (36%) | 28 (18.7%) | ||
| Depressive Symptoms | |||||
| GDS-15 | I | 59 (59%) | 19 (38%) | 78 (52%) | 0.015 |
| P | 41 (41%) | 31 (62%) | 72 (48%) | ||
| QoL (SF-36) | Risk of Functional Decline (Prisma 7) | Nutrition (MNA) | Depressive Symptoms (GDS-15) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil (n = 56) | Portugal (n = 41) | Brazil (n = 90) | Portugal (n = 32) | Brazil (n = 59) | Portugal (n = 19) | |
| Percentiles | Percentiles | Percentiles | ||||
| 25–50–75 | 25–50–75 | 25–50–75 | 25–50–75 | 25–50–75 | 25–50–75 | |
| Domains | ||||||
| Physical Functioning | 50–100–100 | 100–100–100 | 0–50–100 | 37.5–100–100 | 0–25–100 | 25–100–100 |
| p value * | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.054 | |||
| Mental Health | 56–58–60 | 50–60–64 | 52–56–60 | 45–52–60 | 52–56–60 | 40–48–56 |
| p value | 0.677 | 0.098 | 0.016 | |||
| General Health Perceptions | 30–35–50 | 30–45–55 | 30–37–55 | 36.2–50–60 | 30–40–60 | 40–50–65 |
| 0.093 | ||||||
| p value | 0.042 | 0.041 | ||||
| Vitality | 45–50–60 | 45–50–60 | 45–50–60 | 40–45–55 | 45–50–60 | 40–45–50 |
| p value | 0.827 | 0.049 | 0.050 | |||
| Social Role Functioning | 50–50–50 | 43.7–50–50 | 50–50–53 | 37–50–50 | 50–50–62 | 37.5–50–50 |
| p value | 0.072 | 0.013 | 0.016 | |||
| Dimensions | ||||||
| Physical Health | 49.2–55–59 | 52–58–63 | 39–50–57 | 45.2–53.5–62.5 | 38–45–56 | 43–52–58 |
| p value | 0.031 | 0.032 | 0.147 | |||
| Mental Health | 49–57–60 | 51.6–59.9–62.6 | 45.7–57–61 | 48.1–57.7–61 | 43–56–61 | 40.6–50.2–61.2 |
| p value | 0.042 | 0.848 | 0.608 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Miranda, J.M.A.; Viana, D.M.d.O.; dos Santos, A.A.L.; Costa, Á.F.d.A.; Dantas, B.A.d.S.; de Miranda, F.A.N.; Mendes, F.R.P.; Torres, G.d.V. Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Older People with Functional and Nutritional Impairment and Depressive Symptoms: A Comparative Cross-Sectional Study in Brazil and Portugal. Geriatrics 2022, 7, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7050096
de Miranda JMA, Viana DMdO, dos Santos AAL, Costa ÁFdA, Dantas BAdS, de Miranda FAN, Mendes FRP, Torres GdV. Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Older People with Functional and Nutritional Impairment and Depressive Symptoms: A Comparative Cross-Sectional Study in Brazil and Portugal. Geriatrics. 2022; 7(5):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7050096
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Miranda, Jéssica Maria Arouca, Dalyanna Mildred de Oliveira Viana, Anderson Antônio Lima dos Santos, Áquila Filêmon de Andrade Costa, Bruno Araújo da Silva Dantas, Francisco Arnoldo Nunes de Miranda, Felismina Rosa Parreira Mendes, and Gilson de Vasconcelos Torres. 2022. "Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Older People with Functional and Nutritional Impairment and Depressive Symptoms: A Comparative Cross-Sectional Study in Brazil and Portugal" Geriatrics 7, no. 5: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7050096
APA Stylede Miranda, J. M. A., Viana, D. M. d. O., dos Santos, A. A. L., Costa, Á. F. d. A., Dantas, B. A. d. S., de Miranda, F. A. N., Mendes, F. R. P., & Torres, G. d. V. (2022). Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Older People with Functional and Nutritional Impairment and Depressive Symptoms: A Comparative Cross-Sectional Study in Brazil and Portugal. Geriatrics, 7(5), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7050096








