Nutritional Intervention Effectiveness on Slowing Time to Dialysis in Elderly Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease—A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
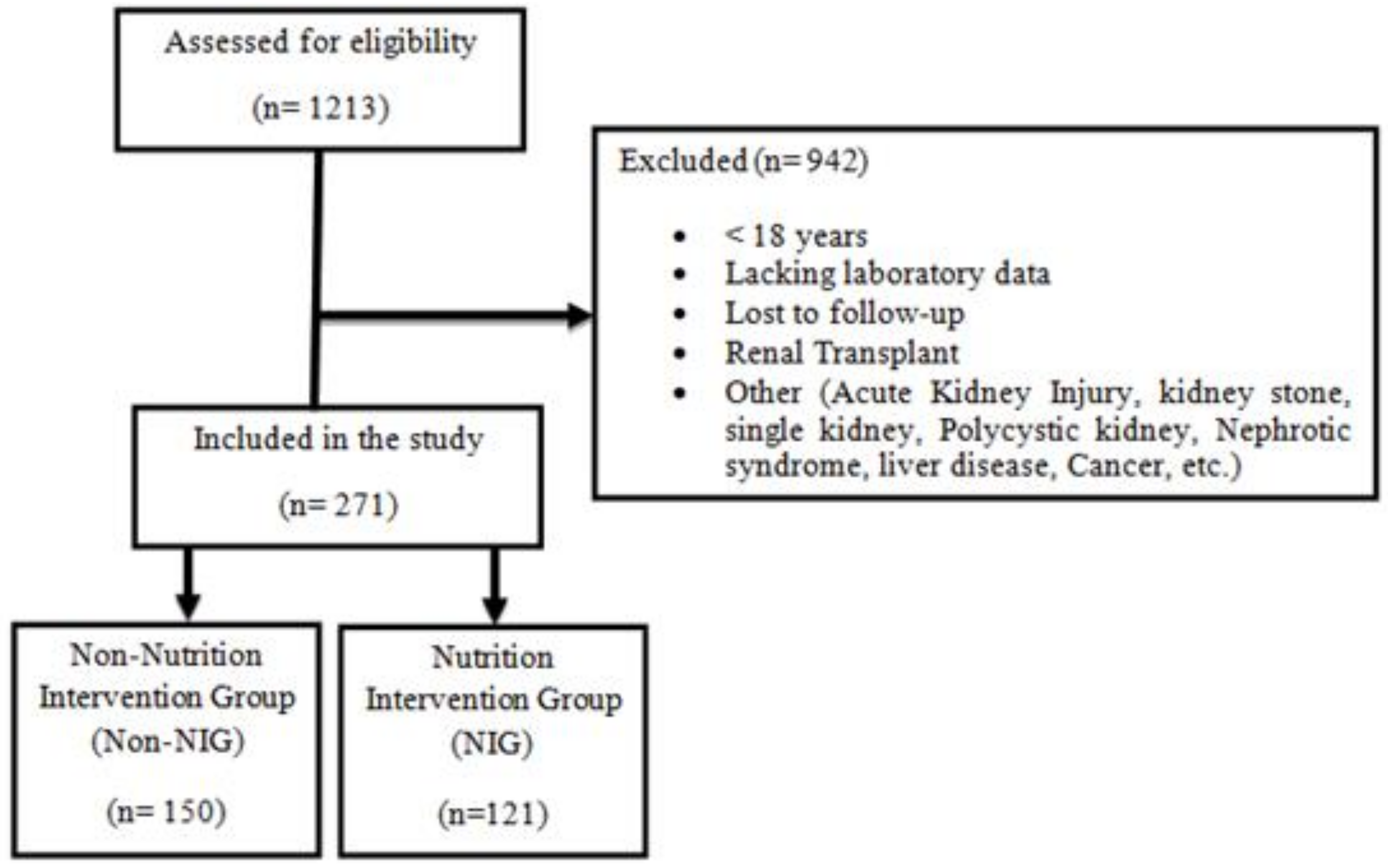
2.1. Setting and Participants
2.2. Data Collection/Procedures
2.3. Nutritional Intervention
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Intervention Effect within Group (Pre-Post Intervention)
3.3. Between-Groups Effects
4. Discussion
Study Strengths and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foreman, K.J.; Marquez, N.; Dolgert, A.; Fukutaki, K.; Fullman, N.; McGaughey, M.; Pletcher, M.A.; Smith, A.E.; Tang, K.; Brown, J.C.; et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: Reference and alternative scenarios for 2016–40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet 2018, 392, 2052–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; Atai, E.; Chan, M.; Phoon, R.K.; Scott, C.; Toussaint, N.D.; Turner, G.L.; Usherwood, T.; Wiggins, K.J. KHA-CARI. Guideline: Early chronic kidney disease: Detection, prevention, and management. Nephrology 2013, 18, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikizler, T.A.; Burrowes, J.D.; Byham-Gray, L.D.; Campbell, K.L.; Carrero, J.-J.; Chan, W.; Fouque, D.; Friedman, A.N.; Ghaddar, S.; Goldstein-Fuchs, D.J.; et al. lePKDOQI clinical practice guideline for nutrition in CKD: 2020 update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, S1–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.L.; Ash, S.; Bauer, J.D. The impact of nutrition intervention on quality of life in pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease patients. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.L.; Yen, M.; Fetzer, S.; Sung, J.M.; Hung, S.Y. Effects of targeted interventions on lifestyle modifications of chronic kidney disease patients: Randomized controlled trial. West. J. Nurs. Res. 2013, 35, 1107–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, F.G.; Goulart, R.M.M.; Prearo, L.C. The impact of a nutrition intervention program targeting elderly people with chronic kidney disease. Cienc. Saudecoletiva 2018, 23, 2555–2564. [Google Scholar]
- Slinin, Y.; Guo, H.; Gilbertson, D.T.; Mau, L.W.; Ensrud, K.; Collins, A.J.; Ishani, A. Prehemodialysis care by dietitians and first-year mortality after initiation of hemodialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2011, 58, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Molfino, A.; Coppola, B.; De Leo, S.; Tommasi, V.; Galani, A.; Muscaritoli, M. Effect of personalized dietary intervention on nutritional, metabolic and vascular indices in patients with chronic kidney disease. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 3351–3359. [Google Scholar]
- Flesher, M.; Woo, P.; Chiu, A.; Charlebois, A.; Warburton, D.E.; Leslie, B. Self-management and biomedical outcomes of a cooking, and exercise program for patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2011, 21, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Waal, D.; Heaslip, E.; Callas, P. Medical nutrition therapy for chronic kidney disease improves biomarkers and slows time to dialysis. J. Ren. Nutr. 2016, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cupisti, A.; D’Alessandro, C.; Di Iorio, B.; Bottai, A.; Zullo, C.; Giannese, D.; Egidi, M.F. Nutritional support in the tertiary care of patients affected by chronic renal insufficiency: Report of a step-wise, personalized, pragmatic approach. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulley, S.B.; Cummings, S.R.; Browner, W.S.; Grady, D.; Newman, T.B. Designing Clinical Research: An Epidemiologic Approach, 4th ed.; Appendix 6A; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, S.-C.; Shao, J.; Wang, H. Sample Size Calculations in Clinical Research, 2nd ed.; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; Chapter 3.2.1; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- National Kidney Foundation (NKF). KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines. 2011. Available online: http://www.kidney.org/PROFESSIONALS/kdoqi/guidelines.cfm (accessed on 17 March 2011).
- National Kidney Foundation. KDOQI clinical practice guideline for diabetes and CKD: 2012 update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 60, 850–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munson, L. Strategies for setting medical nutrition therapy priorities for patients with stage 3 and 4 chronic kidney disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2013, 23, e43–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narva, A.S.; Briggs, M. The National Kidney Disease Education Program: Improving understanding, detection, and management of CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, S115–S120. [Google Scholar]
- Beto, J.A.; Ramirez, W.E.; Bansal, V.K. Medical nutrition therapy in adults with chronic kidney disease: Integrating evidence and consensus into practice for the generalist registered dietitian nutritionist. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 114, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notaras, S.; Galea, L.; Lee, P.; Mak, M.; Lambert, K.; Makris, A. The association between dietetic consultation and time to dialysis for patients attending a pre-dialysis clinic: A retrospective cohort study. Nephrology 2020, 25, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiavaroli, L.; Mirrahimi, A.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; Jenkins, D.J.A.; Darling, P.B. Dietary fiber effects in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled feeding trials. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekki, K.; Bouzidi-bekada, N.; Kaddous, A.; Bouchenak, M. Mediterranean diet improves dyslipidemia and biomarkers in chronic renal failure patients. Food Funct. 2010, 1, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neogi, T. Lifestyle Modification and Other Strategies to Reduce the Risk of Gout Flares and Progression of Gout. 2019. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/lifestyle-modification-and-other-strategies-to-reduce-the-risk-of-gout-flares-and-progression-of-gout (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Kim, S.M.; Jung, J.Y. Nutritional management in patients with chronic kidney disease. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grams, M.E.; Chow, E.K.; Segev, D.L.; Coresh, J. Lifetime incidence of CKD stages 3-5 in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 62, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 163 | 60.1 |
| Female | 108 | 39.9 |
| Co-morbidities | ||
| Diabetes | 216 | 79.7 |
| Hypertension | 238 | 87.8 |
| Heart disease | 52 | 19.3 |
| Follow-up period | ||
| 0–3 Months | 97 | 41.8 |
| 4–6 Months | 97 | 41.8 |
| 7–9 Months | 30 | 12.9 |
| 10–15 Months | 8 | 3.4 |
| CKD stages on the eGFR | ||
| 60–45 mL/min | 65 | 24 |
| 30–44.9 mL/min | 65 | 24 |
| <30 mL/min | 141 | 52 |
| Variable | Non-Nutrition Intervention Group (Non-NIG) (n = 150) 59 F, M 91 | Nutrition Intervention Group (NIG) (n = 121) 49 F, 72 M | Total Sample (n = 271; Non-NIG = 150; NIG = 121) | p-Value between Groups |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age year. | 67.95 ± 14.62 | 64.71 ± 12.01 | 66.51 ± 13.58 | 0.051 |
| Weight kg | 79.66 ± 17.03 | 83.06 ± 16.99 | 81.86 ± 17.03 | 0.235 |
| BMI kg/m2 | 30.18 ± 6.28 | 31.55 ± 7.22 | 31.06 ± 6.91 | 0.256 |
| Hemoglobin g/dL | 11.04 ± 1.86 | 11.33 ± 1.71 | 11.17 ± 1.80 | 0.202 |
| eGFR mL/min/1.73 m2 | 32.87 ± 16.16 | 29.18 ± 13.21 | 31.21 ± 14.99 | 0.044 * |
| T. cholesterol mmol/L | 4.01 ± 1.17 | 4.03 ± 0.95 | 4.02 ± 1.08 | 0.886 |
| HDL mmol/L | 1.13 ± 0.81 | 1.04 ± 0.32 | 1.09 ± 0.64 | 0.237 |
| LDL mmol/L | 2.20 ± 1.11 | 2.22 ± 0.93 | 2.21 ± 1.03 | 0.874 |
| Albumin g/L | 39.69 ± 4.48 | 41.56 ± 3.89 | 40.55 ± 4.31 | p < 0.001 * |
| FBG mmol/L | 6.85 ± 3.13 | 7.17 ± 3.70 | 7.00 ± 3.40 | 0.465 |
| HbA1C mmol/mol | 55.07 ± 19.65 | 53.11 ± 17.22 | 54.14 ± 18.52 | 0.414 |
| BUN mmol/L | 15.10 ± 7.66 | 16.88 ± 8.17 | 15.88 ± 7.92 | 0.079 |
| Creatinine µmol/L | 233.12 ± 310.93 | 224.01 ± 120.58 | 229.06 ± 244.68 | 0.762 |
| Microalbumin mg/g | 339.75 ± 634.34 | 371.48 ± 555.33 | 355.15 ± 595.32 | 0.757 |
| UACR mg/g | 79.91 ± 172.51 | 98.75 ± 170.77 | 90.61 ± 171.24 | 0.489 |
| PTH pmol/L | 19.96 ± 20.69 | 20.00 ± 19.42 | 19.98 ± 20.07 | 0.990 |
| Uric acid µmol/L | 438.00 ± 103.49 | 444.89 ± 123.91 | 441.12 ± 113.02 | 0.628 |
| Sodium mol/L | 149.02 ± 107.22 | 140.25 ± 2.90 | 145.15 ± 80.15 | 0.377 |
| Potassium mol/L | 4.95 ± 0.63 | 5.02 ± 0.70 | 4.98 ± 0.66 | 0.387 |
| Calcium mol/L | 2.42 ± 2.03 | 2.47 ± 1.95 | 2.44 ± 1.99 | 0.830 |
| Phosphorus mol/L | 1.51 ± 1.47 | 1.33 ± 0.31 | 1.43 ± 1.10 | 0.211 |
| Follow-up period months | 6 ± 2 | 6 ± 4 | 6 ± 3 | 0.850 |
| Variable | Non-Nutrition Intervention (Non-NIG), within-Group Δ Change (SD) | p-Value within Group | Nutrition Intervention (NIG), within-Group Δ Change (SD) | p-Value within Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight kg | −0.02 (−1.43; 1.38) | 0.970 | −1.84 * (−2.60; −1.07) | p < 0.001 |
| BMI kg/m2 | −0.01 (−0.61; 0.58) | 0.960 | −0.69 *(−1.00; −0.37) | p < 0.001 |
| Hb g/dL | −0.02 (−0.21; 0.17) | 0.837 | −0.00 (−0.21; 0.20) | 0.951 |
| eGFR mL/min/1.73 m2 | −2.85 * (−4.02; −1.67) | 0.000 | 5.16 * (4.04; 6.28) | p < 0.001 |
| Cholesterol mmol/L | 0.13 (−0.05; 0.31) | 0.155 | −0.17 * (−0.30; −0.05) | 0.006 |
| HDL mmol/L | −0.06 (−0.21; 0.07) | 0.341 | 0.02 (−0.01; 0.05) | 0.219 |
| LDL mmol/L | 0.09 (−0.11; 0.30) | 0.382 | −0.15 (−0.31; 0.00) | 0.060 |
| Triglyceride mmol/L | 0.06 (−0.09; 0.22) | 0.411 | −0.15 * (−0.28; −0.01) | 0.026 |
| Albumin g/L | 0.26 (−0.38; 0.91) | 0.424 | −0.29 (−0.77; 0.18) | 0.229 |
| F.B.S mmol/L | 0.22 (−0.44; 0.89) | 0.513 | −0.70 * (−1.27; −0.13) | 0.016 |
| HbA1c mmol/mol | 0.35 (−2.28;3.00) | 0.789 | 1.10 (−1.58; 3.79) | 0.419 |
| BUN mmol/L | 0.65 (−0.02; 1.33) | 0.059 | −2.19 * (−2.96; −1.42) | p < 0.001 |
| Creatinine µmol/L | −1.72 (−46.83; 43.39) | 0.940 | −25.31 * (−30.63; −19.98) | p < 0.001 |
| Microalbumin mg/g | 18.15 (−164.73; 201.04) | 0.842 | −104.21 (−249.97; 41.53) | 0.157 |
| UACR mg/g | 20.45 (−24.56; 65.47) | 0.365 | −9.13 (−35.21; 16.94) | 0.488 |
| PTH pmol/L | 2.87 (−0.52; 6.27) | 0.097 | −0.83 (−3.34; 1.66) | 0.508 |
| Uric acid µmol/L | 6.90 (−11.44; 25.25) | 0.458 | −28.35 * (−48.55; −8.15) | 0.006 |
| Sodium mmol/L | −9.36 (−27.24; 8.50) | 0.302 | 11.94 (−11.37; 35.27) | 0.312 |
| Potassium mmol/L | 0.04 (−0.05; 0.14) | 0.413 | 0.00 (−0.11; 0.11) | 1.000 |
| Calcium mmol/L | −0.14 (−0.51; 0.23) | 0.453 | −0.20 (−0.58; 0.16) | 0.275 |
| Phosphorus mmol/L | −0.14 (−0.46; 0.18) | 0.393 | −0.05 * (−0.10; −0.00) | 0.025 |
| Variable | Nutrition Intervention Group NIG (Effect of) Minus the Effect of Non-Intervention Group (Non-NIG) Δ Change | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Weight kg | −1.81 * | 0.022 |
| BMI kg/m2 | −0.67 * | 0.021 |
| Hemoglobin g/dL | 0.01 | 0.534 |
| eGFR mL/min/1.73 m2 | 8.01 * | 0.000 |
| T. Cholesterol mmol/L | −0.31 * | 0.031 |
| HDL mmol/L | 0.71 | 0.250 |
| LDL mmol/L | −0.24 | 0.151 |
| Triglycerides mmol/L | 0.22 | 0.100 |
| Albumin g/L | −0.55 | 0.465 |
| FBS mmol/L | −0.92 | 0.086 |
| HbA1C mmol/mol | 0.74 | 0.484 |
| BUN mmol/L | −2.84 * | p < 0.001 |
| Creatinine µmol/L | −23.58 * | p < 0.001 |
| Microalbumin mg/g | −122.36 | 0.499 |
| UACR mg/g | −29.58 | 0.488 |
| PTH pmol/L | −3.70 | 0.098 |
| Uric acid µmol/L | −35.25 * | 0.004 |
| Sodium mol/L | 21.31 | 0.575 |
| Potassium mol/L | −0.04 | 0.955 |
| Calcium mol/L | −0.06 | 0.289 |
| Phosphorus mol/L | 0.08 | 0.856 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perna, S.; Faisal, F.; Spadaccini, D.; Alalwan, T.A.; Ilyas, Z.; Gasparri, C.; Rondanelli, M. Nutritional Intervention Effectiveness on Slowing Time to Dialysis in Elderly Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease—A Retrospective Cohort Study. Geriatrics 2022, 7, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7040083
Perna S, Faisal F, Spadaccini D, Alalwan TA, Ilyas Z, Gasparri C, Rondanelli M. Nutritional Intervention Effectiveness on Slowing Time to Dialysis in Elderly Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease—A Retrospective Cohort Study. Geriatrics. 2022; 7(4):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7040083
Chicago/Turabian StylePerna, Simone, Fatima Faisal, Daniele Spadaccini, Tariq A. Alalwan, Zahra Ilyas, Clara Gasparri, and Mariangela Rondanelli. 2022. "Nutritional Intervention Effectiveness on Slowing Time to Dialysis in Elderly Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease—A Retrospective Cohort Study" Geriatrics 7, no. 4: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7040083
APA StylePerna, S., Faisal, F., Spadaccini, D., Alalwan, T. A., Ilyas, Z., Gasparri, C., & Rondanelli, M. (2022). Nutritional Intervention Effectiveness on Slowing Time to Dialysis in Elderly Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease—A Retrospective Cohort Study. Geriatrics, 7(4), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7040083







