The Impact of Pain on Functionality, Postural Control and Fall Risk in Woman Aged 45 to 64 Years Old
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. Anthropometric Variables
Body Mass Index
Waist Circumference
2.3.2. Physical and Functional Capacity
Five Times Sit-to-Stand Test
Stair Step Test
Six-Minute Walk Distance
Timed-Up and Go
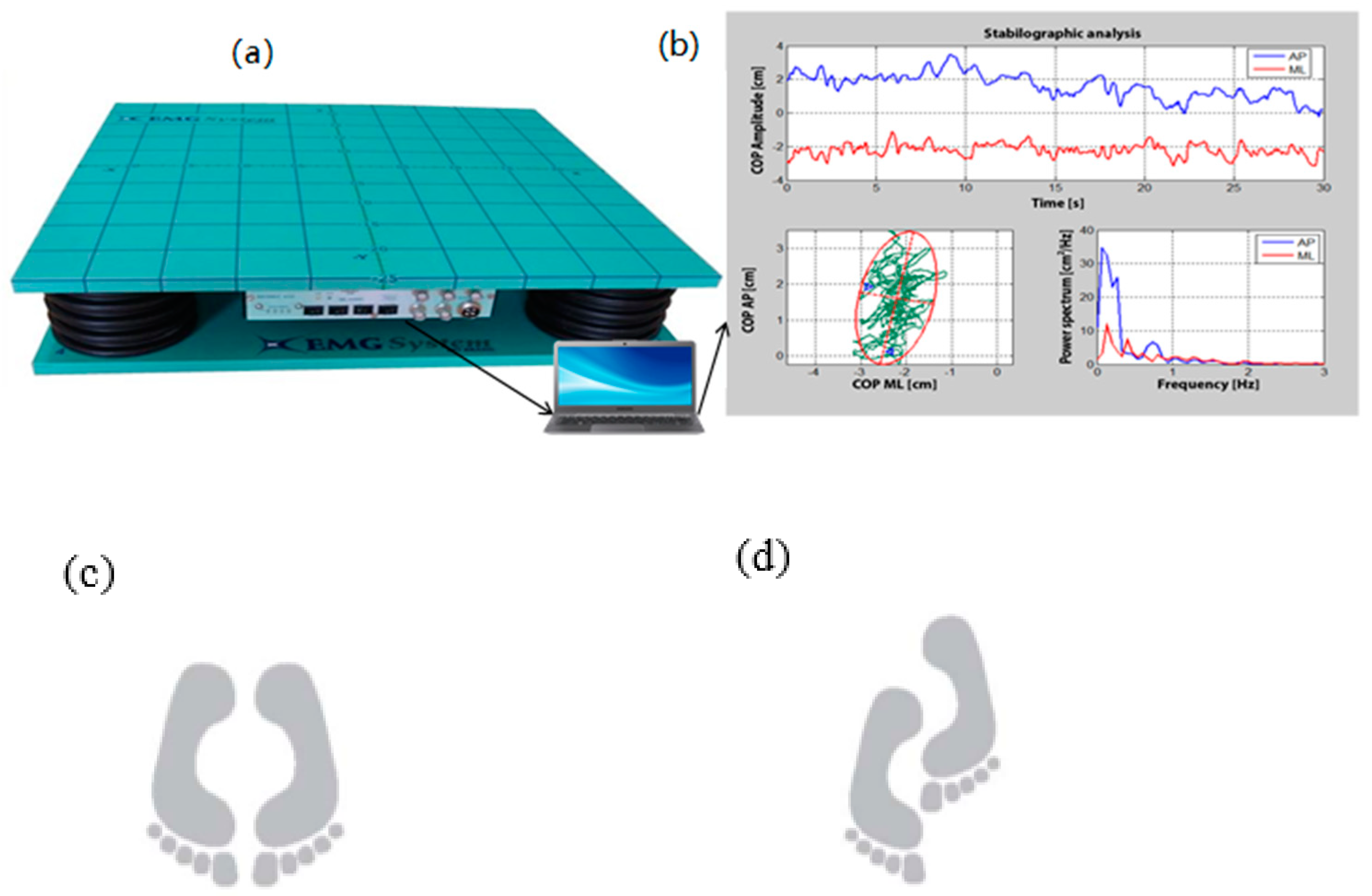
Postural Control Test on the Force Platform
COP Data Processing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical and Functional Capacity and Balance Performance
3.2. Clinical and Functional and Balance Relationship
4. Discussion
Limitation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. World Population Ageing 2019; P.D. Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Ed.; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Salaffi, F.; Carotti, M.; Stancati, A.; Grassi, W. Health-related quality of life in older adults with symptomatic hip and knee osteoarthritis: A comparison with matched healthy controls. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 17, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, R.W. Osteoarthritis: Diagnosis and Medical/Surgical Management; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, D.; Peleteiro, B.; Araujo, J.; Branco, J.; Santos, R.; Ramos, E. The effect of osteoarthritis definition on prevalence and incidence estimates: A systematic review. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2011, 19, 1270–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, L.B.; Helmick, C.G.; Schwartz, T.A.; Renner, J.B.; Tudor, G.; Koch, G.G.; Dragomir, A.D.; Kalsbeek, W.D.; Luta, G.; Jordan, J.M. One in four people may develop symptomatic hip osteoarthritis in his or her lifetime. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Schoor, N.; Lips, P.; Deeg, D. Clinical osteoarthritis of the knee and hip are associated with an increased fall risk. Innov. Aging 2017, 1 (Suppl. 1), 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Altman, R.D. Classification of disease: Osteoarthritis. In Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism; Elsevier: Miami, FL, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, N.J.; Eyles, J.P.; Hunter, D.J. Hip osteoarthritis: Etiopathogenesis and implications for management. Adv. Ther. 2016, 33, 1921–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasch, A.; Byström, A.H.; Dalen, N.; Berg, H.E. Reduced muscle radiological density, cross-sectional area, and strength of major hip and knee muscles in 22 patients with hip osteoarthritis. Acta Orthop. 2007, 78, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arokoski, M.H.; Arokoski, J.P.; Haara, M.; Kankaanpää, M.; Vesterinen, M.; Niemitukia, L.H.; Helminen, H.J. Hip muscle strength and muscle cross sectional area in men with and without hip osteoarthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 2185–2195. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, M.; Wrigley, T.V.; Kasza, J.; Dobson, F.; Pua, Y.H.; Metcalf, B.R.; Bennell, K.L. Cross-sectional association between muscle strength and self-reported physical function in 195 hip osteoarthritis patients. In Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism; Elsevier: Merbourne, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Foucher, K.C.; Aydemir, B.; Huang, C.H.; Horras, M.; Chmell, S.J. Aerobic capacity and fatigability are associated with activity levels in women with hip osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Res. 2021, 39, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philbin, E.F.; Groff, G.D.; Ries, M.D.; Miller, T.E. Cardiovascular fitness and health in patients with end-stage osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. Off. J. Am. Coll. Rheumatol. 1995, 38, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picorelli, A.M.; Hatton, A.L.; Gane, E.M.; Smith, M.D. Balance performance in older adults with hip osteoarthritis: A systematic review. Gait Posture 2018, 65, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.O.; Higson, E.; Pearson, M.; Mansfield, M. Is there an increased risk of falls and fractures in people with early diagnosed hip and knee osteoarthritis? Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arden, N.K.; Nevitt, M.C.; Lane, N.E.; Gore, L.R.; Hochberg, M.C.; Scott, J.C.; Pressman, A.R.; Cummings, S.R. Osteoarthritis and risk of falls, rates of bone loss, and osteoporotic fractures. Arthritis Rheum. Off. J. Am. Coll. Rheumatol. 1999, 42, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Nogues, X.; Javaid, M.K.; Wyman, A.; Arden, N.K.; Azagra, R.; Cooper, C.; Adachi, J.D.; Boonen, S.; Chapurlat, R.D. An increased rate of falling leads to a rise in fracture risk in postmenopausal women with self-reported osteoarthritis: A prospective multinational cohort study (GLOW). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doré, A.L.; Golightly, Y.M.; Mercer, V.S.; Shi, X.A.; Renner, J.B.; Jordan, J.M.; Nelson, A.E. Lower-extremity osteoarthritis and the risk of falls in a community-based longitudinal study of adults with and without osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2015, 67, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoop, J.; Van Der Leeden, M.; Van Der Esch, M.; Thorstensson, C.A.; Gerritsen, M.; Voorneman, R.E.; Lems, W.F.; Roorda, L.D.; Dekker, J.; Steultjens, M.P. Association of lower muscle strength with self-reported knee instability in osteoarthritis of the knee: Results from the Amsterdam Osteoarthritis Cohort. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Esch, M.; Knoop, J.; van der Leeden, M.; Voorneman, R.; Gerritsen, M.; Reiding, D.; Romviel, S.; Knol, D.L.; Lems, W.F.; Dekker, J. Self-reported knee instability and activity limitations in patients with knee osteoarthritis: Results of the Amsterdam osteoarthritis cohort. Clin. Rheumatol. 2012, 31, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvin, M.; Hoozemans, M.J.; Burger, B.J.; Rispens, S.M.; Verschueren, S.M.; van Dieën, J.H.; Pijnappels, M. Effects of hip abductor muscle fatigue on gait control and hip position sense in healthy older adults. Gait Posture 2015, 42, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Johnson, V.L.; Hunter, D.J. The epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 28, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, C.; Nguyen, C.; Lefevre-Colau, M.-M.; Rannou, F.; Poiraudeau, S. Risk factors and burden of osteoarthritis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 59, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busija, L.; Hollingsworth, B.; Buchbinder, R.; Osborne, R.H. Role of age, sex, and obesity in the higher prevalence of arthritis among lower socioeconomic groups: A population-based survey. Arthritis Care Res. 2007, 57, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canizares, M.; Power, J.D.; Perruccio, A.V.; Badley, E.M. Association of regional racial/cultural context and socioeconomic status with arthritis in the population: A multilevel analysis. Arthritis Care Res. 2008, 59, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobasheri, A.; Batt, M. An update on the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 59, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Rong, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, F.; Bao, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y. The relationship between body mass index and hip osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Jt. Bone Spine 2011, 78, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeanmaire, C.; Mazières, B.; Verrouil, E.; Bernard, L.; Guillemin, F.; Rat, A.-C. Body composition and clinical symptoms in patients with hip or knee osteoarthritis: Results from the KHOALA cohort. In Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism; Elsevier: Nancy, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- National Heart, L.; Institute, B. Quality assessment tool for observational cohort and cross-sectional studies. Bethesda Natl. Inst. Health Dep. Health Hum. Serv. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequesne, M.; Mery, C.; Samson, M.; Gerard, P. Indexes of severity for osteoarthritis of the hip and knee: Validation–value in comparison with other assessment tests. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1987, 16 (Suppl. 65), 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitney, S.L.; Wrisley, D.M.; Marchetti, G.F.; Gee, M.A.; Redfern, M.S.; Furman, J.M. Clinical measurement of sit-to-stand performance in people with balance disorders: Validity of data for the Five-Times-Sit-to-Stand Test. Phys. Ther. 2005, 85, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinova, É.; Leone, M. Tests D’évaluation de la Capacité Fonctionnelle Chez L’adulte de 55 Ans et Mieux; PUQ: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Enright, P.L.; Sherill, D. ATS Statement: Guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am. Thorac. Soc. AMJ Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Shumway-Cook, A.; Brauer, S.; Woollacott, M. Predicting the probability for falls in community-dwelling older adults using the Timed Up & Go Test. Phys. Ther. 2000, 80, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, R.A.; Vieira, E.R.; Fernandes, K.B.; Andraus, R.A.; Oliveira, M.R.; Sturion, L.A.; Calderon, M.G. People with chronic low back pain have poorer balance than controls in challenging tasks. Disabil. Rehabil. 2018, 40, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutin, I. In BMI We Trust: Reframing the Body Mass Index as a Measure of Health. Soc. Theory Health 2018, 16, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Initiative, N.O.E. The Practical Guide: Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults; National Institutes of Health: New York, NY, USA, 2000.
- Klein, S.; Allison, D.B.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Kelley, D.E.; Leibel, R.L.; Nonas, C.; Kahn, R. Waist circumference and cardiometabolic risk: A consensus statement from shaping America’s health: Association for Weight Management and Obesity Prevention; NAASO, the Obesity Society; the American Society for Nutrition; and the American Diabetes Association. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, M.R.; Vieira, E.R.; Gil, A.W.; Teixeira, D.C.; Amorim, C.F.; da Silva, R.A. How many balance task trials are needed to accurately assess postural control measures in older women? J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2019, 23, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, R.A.; Bilodeau, M.; Parreira, R.B.; Teixeira, D.C.; Amorim, C.F. Age-related differences in time-limit performance and force platform-based balance measures during one-leg stance. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2013, 23, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paillard, T. Plasticity of the postural function to sport and/or motor experience. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 72, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadri, M.A.; Chevalier, G.; Mecheri, H.; Ngomo, S.; Lavallière, M.; da Silva, R.A.; Beaulieu, L.-D. Time course and variability of tendinous vibration-induced postural reactions in forward and backward directions. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2020, 51, 102386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, G.; Hopkins, K. Statistical methods in education and psychology. Psyccritiques 1996, 41, 1224. [Google Scholar]
- Hedges, L.V. Distribution theory for Glass’s estimator of effect size and related estimators. J. Educ. Stat. 1981, 6, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Hillsdale, N.J., Ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum: New York, NY, USA, 1988; 567p. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, F.; Laslett, L.; Blizzard, L.; Cicuttini, F.; Winzenberg, T.; Ding, C.; Jones, G. Associations between fat mass and multisite pain: A five-year longitudinal study. Arthritis Care Res. 2017, 69, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydevik, K.; Fernandes, L.; Nordsletten, L.; Risberg, M.A. Functioning and disability in patients with hip osteoarthritis with mild to moderate pain. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2010, 40, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosler, A.B.; Kemp, J.; King, M.; Lawrenson, P.R.; Semciw, A.; Freke, M.; Jones, D.M.; Casartelli, N.C.; Wörner, T.; Ishøi, L. Standardised measurement of physical capacity in young and middle-aged active adults with hip-related pain: Recommendations from the first International Hip-related Pain Research Network (IHiPRN) meeting, Zurich, 2018. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerez-Mayorga, D.; Ríos, L.J.C.; Reyes, A.; Delgado-Floody, P.; Payer, R.M.; Requena, I.M.G. Muscle quality index and isometric strength in older adults with hip osteoarthritis. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronti, T.; Lupattelli, G.; Mannarino, E. The endocrine function of adipose tissue: An update. Clin. Endocrinol. 2006, 64, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartvigsen, J.; Natvig, B.; Ferreira, M. Is it all about a pain in the back? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 27, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neogi, T. The epidemiology and impact of pain in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loureiro, A.; Mills, P.M.; Barrett, R.S. Muscle weakness in hip osteoarthritis: A systematic review. Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 65, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, A.; Pizzari, T.; English, D.; Kapakoulakis, T.; Green, R. Hip abductor muscle volume in hip osteoarthritis and matched controls. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinikorena, I.; Martínez-Ramírez, A.; Gómez, M.; Lecumberri, P.; Casas-Herrero, A.; Cadore, E.L.; Millor, N.; Zambom-Ferraresi, F.; Idoate, F.; Izquierdo, M. Gait variability related to muscle quality and muscle power output in frail nonagenarian older adults. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zwart, A.H.; van der Esch, M.; Pijnappels, M.A.; Hoozemans, M.J.; van der Leeden, M.; Roorda, L.D.; Dekker, J.; Lems, W.F.; van Dieën, J.H. Falls associated with muscle strength in patients with knee osteoarthritis and self-reported knee instability. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damen, J.; van Rijn, R.M.; Emans, P.J.; Hilberdink, W.K.; Wesseling, J.; Oei, E.H.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M. Prevalence and development of hip and knee osteoarthritis according to American College of Rheumatology criteria in the CHECK cohort. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Outcomes | Low-PI (n = 14) | Strong-PI (n = 7) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 56.6 ± 4.7 | 57.6 ± 5.3 | 0.66 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.4 ± 4.4 | 34.4 ± 9.4 | 0.11 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 98.0 ± 9.9 | 108.1 ± 13.5 | 0.39 |
| Occupation | |||
| Remunerated job | 8 (57.1%) | 3 (49.2%) | 0.44 |
| Retired | 5 (35.7%) | 2 (28.6%) | |
| Self-employed | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (14.3%) | |
| Housewife | 1 (7.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Disable | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (14.3%) | |
| Education level | |||
| Secondary | 1 (7.1%) | 2 (28.6%) | 0.57 |
| Professional | 4 (28.6%) | 0 (0.0) | |
| College | 2 (14.3%) | 1 (14.3%) | |
| Bachelor | 5 (35.7%) | 3 (42.9%) | |
| Graduate and more | 2 (14.3%) | 1 (14.3%) | |
| Household income (CAN$) | |||
| <15,000$ | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (14.3%) | 0.06 |
| 15,000 to 34,999$ | 3 (30.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| 35,000 to 79,999$ | 1 (10.0%) | 4 (57.1%) | |
| ≥80,000$ | 6 (60.0%) | 2 (28.6%) | |
| Matrimonial status | |||
| Single | 1 (7.1%) | 2 (28.6%) | 0.70 |
| Married | 8 (57.1%) | 4 (57.1%) | |
| Common-law partner | 4 (28.6%) | 1 (14.3%) | |
| Divorced | 1 (7.1%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Variable | Low-PI n = 14 Mean ± SD | Strong-PI n = 7 Mean ± SD | Differences (%) | Hedge’s g | p Value | Pearson’s r (p Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropometric | ||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.78 ± 7.36 | 32.95 ± 9.58 | +18.61 | −0.57 | 0.11 | 0.36 (0.13) |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 99.59 ± 8.34 | 104.34 ± 16.43 | +4.77 | −0.36 | 0.39 | 0.17 (0.49) |
| Physical and functional capacity | ||||||
| FTSST (seconds) | 9.73 ± 2.38 | 13.64 ± 5.17 | +40.18 | −0.97 | 0.08 | 0.53 * (0.02) |
| Stair Step Test (repetitions) | 27.92 ± 5.01 | 19.88 ± 5.26 | −40.44 | 1.44 | 0.001 ** | −0.72 ** (0.001) |
| 6MWD (meters) | 631.82 ± 74.55 | 517.50 ± 78.61 | −22.09 | 1.31 | 0.003 ** | −0.64 ** (0.003) |
| TUG (seconds) | 5.63 ± 0.95 | 7.00 ± 1.83 | +24.33 | −0.93 | 0.04 * | 0.50 * (0.03) |
| Low-PI n = 12 | Strong-PI n = 7 | |||||
| Postural control (force platform) | ||||||
| VEL-COP Bipodal AP EO (cm/s) | 0.69 ± 0.11 | 0.83 ± 0.17 | +20.29 | −0.94 | 0.03 * | 0.49 * (0.03) |
| VEL-COP Bipodal ML EO (cm/s) | 0.72 ± 0.09 | 0.78 ± 0.18 | +8.33 | −0.50 | 0.37 | 0.22 (0.37) |
| VEL-COP Bipodal AP EC (cm/s) | 0.85 ± 0.15 | 0.99 ± 0.21 | +16.47 | −0.73 | 0.11 | 0.38 (0.11) |
| VEL-COP Bipodal ML EC (cm/s) | 0.77 ± 0.09 | 0.80 ± 0.16 | +3.90 | −0.23 | 0.68 | 0.10 (0.68) |
| VEL-COP Semi-tandem AP EO (cm/s) | 1.00 ± 0.17 | 1.07 ± 0.24 | +7.00 | −0.32 | 0.46 | 0.18 (0.46) |
| VEL-COP Semi-tandem ML EO (cm/s) | 1.34 ± 0.26 | 1.43 ± 0.32 | +6.72 | −0.29 | 0.49 | 0.17 (0.49) |
| VEL-COP Semi-tandem AP EC (cm/s) | 1.46 ± 0.37 | 1.58 ± 0.38 | +8.22 | −0.29 | 0.51 | 0.16 (0.51) |
| VEL-COP Semi-tandem ML EC (cm/s) | 2.08 ± 0.60 | 2.29 ± 0.74 | +10.10 | −0.29 | 0.51 | 0.16 (0.51) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beaupré, P.; da Silva, R.A.; Chevrette, T. The Impact of Pain on Functionality, Postural Control and Fall Risk in Woman Aged 45 to 64 Years Old. Geriatrics 2022, 7, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7010010
Beaupré P, da Silva RA, Chevrette T. The Impact of Pain on Functionality, Postural Control and Fall Risk in Woman Aged 45 to 64 Years Old. Geriatrics. 2022; 7(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeaupré, Priscilla, Rubens A. da Silva, and Tommy Chevrette. 2022. "The Impact of Pain on Functionality, Postural Control and Fall Risk in Woman Aged 45 to 64 Years Old" Geriatrics 7, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7010010
APA StyleBeaupré, P., da Silva, R. A., & Chevrette, T. (2022). The Impact of Pain on Functionality, Postural Control and Fall Risk in Woman Aged 45 to 64 Years Old. Geriatrics, 7(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics7010010






