Deepening Physical Exercise Intervention Protocols for Older People with Sarcopenia Following Establishment of the EWGSOP2 Consensus: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Risk of Bias
2.5. Quality Appraisal
2.6. Data Extraction
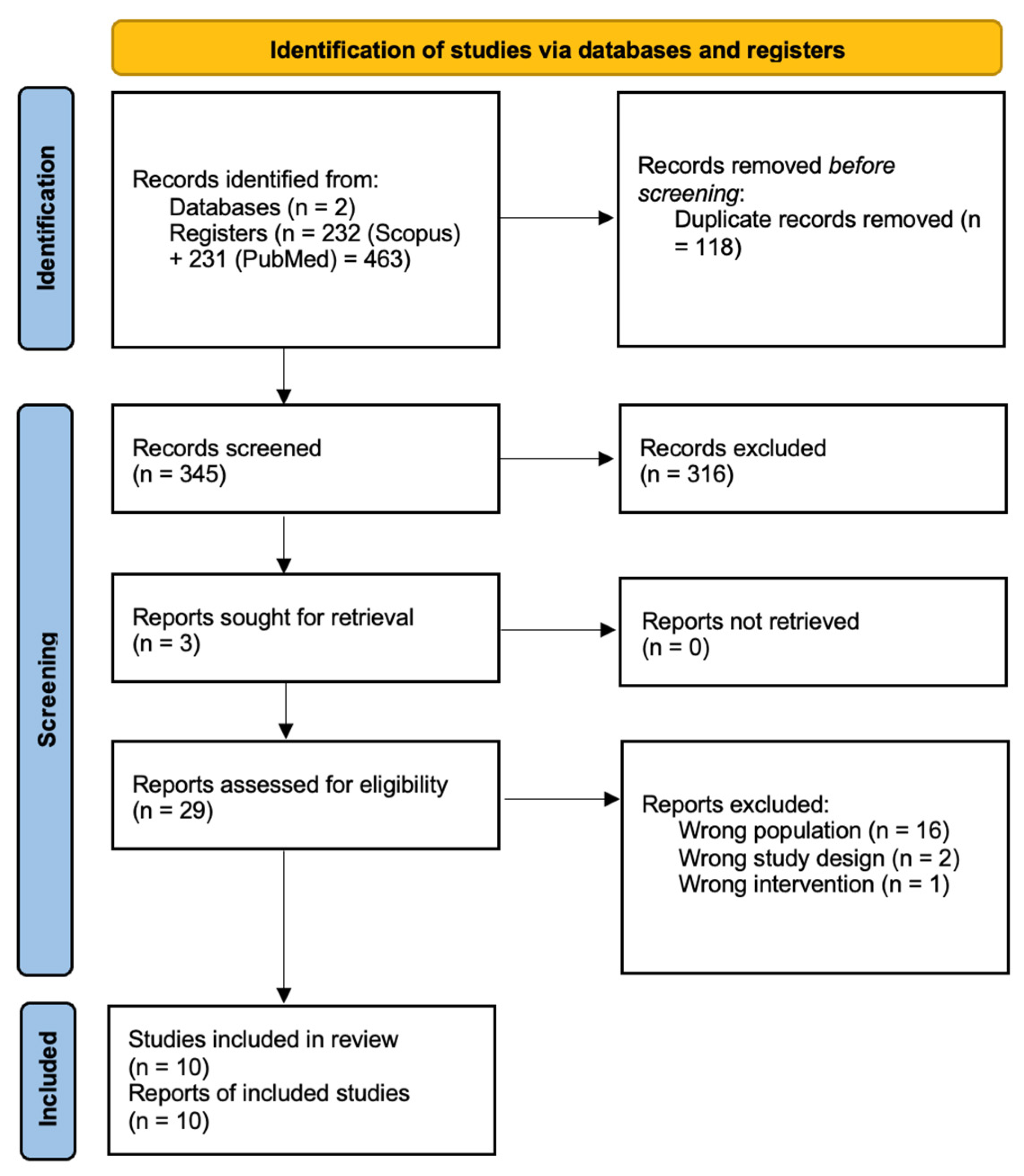
3. Results
3.1. Overview of Studies
3.2. Methodological Quality
3.3. Characteristics of the Studies
3.4. Outcome Measurements
3.4.1. Effectiveness of Physical Exercise Protocols
3.4.2. Tailoring of Exercise Protocols to Individual Needs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EWGSOP | European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People |
| SARC-F | Strength, Assistance in walking, Rise from chair, climb stairs and Falls |
| BIA | Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis |
| SPPB | Short Physical Performance Battery |
| TUG | Timed Up and Go |
| RoB | Cochrane Risk of Bias |
| CERT | Consensus on Exercise Reporting Template |
| 1RM | One-repetition maximum |
References
- Öztürk, Z.A.; Türkbeyler, İ.H.; Abiyev, A.; Kul, S.; Edizer, B.; Yakaryılmaz, F.D.; Soylu, G. Health-related Quality of Life and Fall Risk Associated with Age-related Body Composition Changes; Sarcopenia, Obesity and Sarcopenic Obesity. Intern. Med. J. 2018, 48, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Baeyens, J.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Landi, F.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.-P.; Rolland, Y.; Schneider, S.M.; et al. Sarcopenia: European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, J.E. Sarcopenia in the Elderly. Fam. Pract. 2012, 29, i44–i48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Fernández, I.A.; Torres-Obregón, R.; Esparza-González, S.C.; Delabra-Salinas, M.M. Ejercicios que apoyan el funcionamiento físico en adultos mayores con sarcopenia. SANUS 2019, 3, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Rodríguez, L.; Szlejf, C.; García-González, A.I.; Malmstrom, T.K.; Cruz-Arenas, E.; Rosas-Carrasco, O. Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Validation of the Spanish-Language Version of the SARC-F to Assess Sarcopenia in Mexican Community-Dwelling Older Adults. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urzi, F.; Šimunič, B.; Buzan, E. Basis for Sarcopenia Screening with the SARC-CalF in Nursing Homes. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 991.E5–991.E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshima, N.; Shimada, K.; Islam, M.M.; Kanehisa, H.; Ishida, Y.; Brechue, W.F. Progressive, Site-Specific Loss of Muscle Mass in Older, Frail Nursing Home Residents. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2015, 23, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Newman, A.B.; Simonsick, E.M.; Harris, T.B.; Penninx, B.W.; Brach, J.S.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Satterfield, S.; Bauer, D.C.; et al. Added Value of Physical Performance Measures in Predicting Adverse Health-Related Events: Results from the Health, Aging and Body Composition Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2009, 57, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, J.W.; Senior, H.; Beller, E.M.; Henwood, T. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Low Habitual Walking Speed in Nursing Home Residents: An Observational Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 96, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, B.P.; Batista, A.K.M.S.; Gomes, I.B.; Olivieri, F.M.; Camelier, F.W.R.; Camelier, A.A. Frequency of Sarcopenia and Associated Factors among Hospitalized Elderly Patients. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, E.V.; Dong, X.; Hassan, M. Resistance Training for Activity Limitations in Older Adults with Skeletal Muscle Function Deficits: A Systematic Review. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barajas-Galindo, D.E.; González Arnáiz, E.; Ferrero Vicente, P.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.D. Effects of Physical Exercise in Sarcopenia. A Systematic Review. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. Engl. Ed. 2021, 68, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Shi, Q.; Nong, K.; Li, S.; Yue, J.; Huang, J.; Dong, B.; Beauchamp, M.; Hao, Q. Exercise for Sarcopenia in Older People: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 1199–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chan, H.; Evans, C.; Maddocks, M. The Association between Sedentary Behaviour and Sarcopenia in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Mayer, P.K.; Wu, M.-Y.; Liu, D.-H.; Wu, P.-C.; Yen, H.-R. The Effect of Tai Chi in Elderly Individuals with Sarcopenia and Frailty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 82, 101747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanker, J.; Sim, M.; Anderson, K.; Balogun, S.; Brennan-Olsen, S.L.; Dent, E.; Duque, G.; Girgis, C.M.; Grossmann, M.; Hayes, A.; et al. Consensus Guidelines for Sarcopenia Prevention, Diagnosis and Management in Australia and New Zealand. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguibao, C.; Ajraoui, S.; Centra, J.; Reid, K.F.; Daskalopoulou, C.; Freniche, A.C.; Hamilton, A.L.; Horstman, A.M.H.; Collins, B.X.; Dunn, J.; et al. Identifying Concepts of Physical Activity Which Are Clinically Meaningful to Patients and Care Providers: A Systematic Review of Qualitative Research. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2025, 18, e70191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Juni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, S.C.; Dionne, C.E.; Underwood, M.; Buchbinder, R. Consensus on Exercise Reporting Template (CERT): Explanation and Elaboration Statement. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 1428–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flor-Rufino, C.; Barrachina-Igual, J.; Pérez-Ros, P.; Pablos-Monzó, A.; Martínez-Arnau, F.M. Resistance Training of Peripheral Muscles Benefits Respiratory Parameters in Older Women with Sarcopenia: Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2023, 104, 104799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flor-Rufino, C.; Barrachina-Igual, J.; Pérez-Ros, P.; Pablos-Monzó, A.; Sanz-Requena, R.; Martínez-Arnau, F.M. Fat Infiltration and Muscle Hydration Improve after High-Intensity Resistance Training in Women with Sarcopenia. A Randomized Clinical Trial. Maturitas 2023, 168, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, H.; Chen, K.; Huang, K.; Hsu, H.; Chou, C.; Kuo, C. Effects of Vitality Acupunch Exercise on Functional Fitness and Activities of Daily Living among Probable Sarcopenic Older Adults in Residential Facilities. J. Nurs. Scholarsh. 2022, 54, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.-S.; Kim, Y.-Y.; Park, H.-Y. Circuit Training Improvements in Korean Women with Sarcopenia. Percept. Mot. Skills 2019, 126, 828–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, E.I.; Eyigor, S.; Dikici Yagli, M.; Ozcete, Z.A.; Aydin, T.; Kesiktas, F.N.; Aydin, F.Y.; Vural, M.; Sahin, N.; Karan, A. Effect of Home-Based Exercise Program on Physical Function and Balance in Older Adults with Sarcopenia: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Study. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2021, 29, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sá Souza, H.; De Melo, C.M.; Piovezan, R.D.; Miranda, R.E.E.P.C.; Carneiro-Junior, M.A.; Silva, B.M.; Thomatieli-Santos, R.V.; Tufik, S.; Poyares, D.; D’Almeida, V. Resistance Training Improves Sleep and Anti-Inflammatory Parameters in Sarcopenic Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.-W.; Jung, S.-W.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, J.-M.; Jung, H.C.; Song, J.-K. Effects of 16 Weeks of Resistance Training on Muscle Quality and Muscle Growth Factors in Older Adult Women with Sarcopenia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courel-Ibáñez, J.; Buendía-Romero, Á.; Pallarés, J.G.; García-Conesa, S.; Martínez-Cava, A.; Izquierdo, M. Impact of Tailored Multicomponent Exercise for Preventing Weakness and Falls on Nursing Home Residents’ Functional Capacity. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2022, 23, 98–104.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, R.; Jiang, J.; Tan, L.; Yang, M. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Resistance and Balance Exercise for Sarcopenic Patients Aged 80–99 Years. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Cao, J.; He, S.; Wei, M.; Meng, D.; Yu, I.; Wang, Z.; Chang, X.; Yang, G.; Wang, Z. Quantifying the Enhancement of Sarcopenic Skeletal Muscle Preservation Through a Hybrid Exercise Program: Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Aging 2024, 7, e58175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.-W.; Chou, M.-Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Mao, L.; Feng, Y.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Liu, Y.; Chen, N. Effects of Different Exercise Training Modes on Muscle Strength and Physical Performance in Older People with Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Cheng, R.; Song, G.; Teng, J.; Shen, S.; Fu, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, C. The Effect of Resistance Training on the Rehabilitation of Elderly Patients with Sarcopenia: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, M.; De Souto Barreto, P.; Arai, H.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Cadore, E.L.; Cesari, M.; Chen, L.-K.; Coen, P.M.; Courneya, K.S.; Duque, G.; et al. Global Consensus on Optimal Exercise Recommendations for Enhancing Healthy Longevity in Older Adults (ICFSR). J. Nutr. Health Aging 2025, 29, 100401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, R.; Van Loon, L.J.C. Aging, Exercise, and Muscle Protein Metabolism. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 2040–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragala, M.S.; Cadore, E.L.; Dorgo, S.; Izquierdo, M.; Kraemer, W.J.; Peterson, M.D.; Ryan, E.D. Resistance Training for Older Adults: Position Statement from the National Strength and Conditioning Association. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 2019–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, B.; Mooney, K.; Amirabdollahian, F.; Khaiyat, O. Exercise and Dietary-Protein as a Countermeasure to Skeletal Muscle Weakness: Liverpool Hope University—Sarcopenia Aging Trial (LHU-SAT). Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, L.H.; Slentz, C.A.; Bateman, L.A.; Shields, A.T.; Piner, L.W.; Bales, C.W.; Houmard, J.A.; Kraus, W.E. Effects of Aerobic and/or Resistance Training on Body Mass and Fat Mass in Overweight or Obese Adults. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 113, 1831–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dent, E.; Morley, J.E.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Arai, H.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Guralnik, J.; Bauer, J.M.; Pahor, M.; Clark, B.C.; Cesari, M.; et al. International Clinical Practice Guidelines for Sarcopenia (ICFSR): Screening, Diagnosis and Management. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 1148–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, Y.; Dray, C.; Vellas, B.; Barreto, P.D.S. Current and Investigational Medications for the Treatment of Sarcopenia. Metabolism 2023, 149, 155597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isiktas, O.; Guzel, F.B.; Ozturk, I.; Topal, K.; Sahin, M.; Altunoren, O.; Gungor, O. The Frequency of Sarcopenia Has Increased in Patients with Glomerulonephritis. Nephrology 2023, 28, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altinkaynak, M.; Ozturk, C.K.; Goksoy, Y.; Eryigit, O.Y.; Akpinar, T.S.; Erten, S.N.; Saka, B. The Prevalence of Sarcopenic Obesity and Its Relationship with Type 2 Diabetes in Nursing Home. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 2858–2864. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Escribà-Salvans, A.; Jerez-Roig, J.; Molas-Tuneu, M.; Farrés-Godayol, P.; Moreno-Martin, P.; Goutan-Roura, E.; Güell-Masramon, H.; Amblàs-Novellas, J.; De Souza, D.L.B.; Skelton, D.A.; et al. Sarcopenia and Associated Factors According to the EWGSOP2 Criteria in Older People Living in Nursing Homes: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.A.; Cooper, R.; Arai, H.; Cawthon, P.M.; Ntsama Essomba, M.J.; Fielding, R.A.; Grounds, M.D.; Witham, M.D.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. Sarcopenia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2024, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Authors (Year) | Randomization Process | Deviations from Intended Interventions | Missing Outcome Data | Measurement of the Outcome | Selection of the Reported Result | Overall Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Courel-Ibáñez, J. (2022) [29] | + | + | + | ? | + | ? |
| De Sá Souza, H. (2022) [27] | ? | ? | + | + | ? | ? |
| Flor-Rufino, C. (2023a) [22] | + | + | - | + | ? | - |
| Flor-Rufino, C. (2023b) [23] | + | + | - | + | ? | - |
| Guo, H. (2024) [31] | ? | + | + | + | + | ? |
| Hsiao-Ting, T (2021) [24] | + | + | + | ? | - | - |
| Ilke-Sen, E. (2021) [26] | ? | + | + | - | + | - |
| Liang, Y. (2020) [30] | ? | + | + | + | + | ? |
| Myong-Won, S. (2021) [28] | + | + | + | ? | + | ? |
| Sang-Jung, W. (2019) [25] | + | + | + | - | + | - |
| Authors (Year) | Items from the Modified CERT Template | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | |
| Courel-Ibáñez, J. (2022) [29] | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| De Sá Souza, H. (2022) [27] | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Flor-Rufino, C. (2023a) [22] | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Flor-Rufino, C. (2023b) [23] | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Guo, H. (2024) [31] | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| Hsiao-Ting, T. (2021) [24] | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| Ilke-Sen, E. (2021) [26] | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Myong-Won, S. (2021) [28] | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Liang, Y. (2020) [30] | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Sang-Jung, W. (2019) [25] | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Authors (Year) | Participant Profiles/Severity of Sarcopenia * | Number of Participants and Groups | Details of the Intervention | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Setting | Tailored Intervention | Type | Session Duration | Frequency | Duration of Intervention | |||
| Courel-Ibáñez, J. (2022) [29] | Men and women between 84–87 years/NA | n = 24 (2 groups) IG = 12 CG = 12 | Nursing Home | Yes | IG: Multicomponent intervention CG: Multicomponent intervention | 30–60 min | 5 days/week | 30 weeks |
| de Sá Souza, H. (2022) [27] | Men and women 65 years/NA | n = 28 (2 groups) IG = 14 CG = 14 | Home | Yes | IG: Resistance intervention CG: Education | Based on sets and repetitions | 3 days/ week | 12 weeks |
| Flor-Rufino, C. (2023a) [22] | Women 70 years/NA | n = 51 (2 groups) IG = 24 CG = 27 | Physical performance laboratory | Yes | IG: Multicomponent intervention CG: Phone follow-ups | 65 min | IG = 2 days/week recovery time = 72 h | 30 weeks |
| Flor-Rufino, C. (2023b) [23] | Women 70 years/NA | n = 51 (2 groups) IG = 24 CG = 27 | Physical performance laboratory | Yes | IG: Multicomponent intervention CG: No intervention. Encouraged to stay active | 65 min | IG = 2 days/week 72 h recovery period | 30 weeks |
| Guo, H. (2024) [31] | Men and women between 65–75 years/NA | n = 93 (2 groups) IG = 63 CG = 30 | Hospital | Yes | IG: Multicomponent intervention CG: Education | 30 min | 3 days /week | 24 weeks |
| Hsiao-Ting, T. (2021) [24] | Men and women 65 years/probable sarcopenia | n = 103 (2 groups) IG = 52 CG = 51 | Nursing home | No | IG: Multicomponent intervention CG: Routine daily activities | 40 min | 3 days/week | 31 weeks |
| Ilke-Sen, E. (2021) [26] | Men and women between 65–80 years/confirmed sarcopenia | n = 100 (2 groups) IG = 50 CG = 50 | Home | No | IG: Multicomponent intervention CG: Education + usual physical activity lifestyle | 60 min | 3 days /week | 12 weeks |
| Liang, Y. (2020) [30] | Men and women between 80–90 years/NA | n = 60 (2 groups) IG = 30 CG = 30 | Hospital (post-acute care unit) | Yes | IG: Multicomponent intervention CG: Education + resistance exercise program | 50 min | 2 days /week | 12 weeks |
| Myong-Won, S. (2021) [28] | Women 65 years/NA | n = 22 (2 groups) IG = 12 CG = 10 | Gym | Yes | IG: Resistance intervention CG: No intervention | 60 min | 3 days/ week | 16 weeks |
| Sang Jung, W. (2019) [25] | Women between 75–80 years/NA | n = 26 (2 groups) IG = 13 CG = 13 | Physical performance laboratory | Yes | IG: Multicomponent intervention CG: Usual physical activity lifestyle | 25–75 min | IG: 3 days /week CG: 2 days /week | 12 weeks |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minobes-Molina, E.; Rierola-Fochs, S.; Parés-Martínez, C.; Farrés-Godayol, P.; Ochandorena-Acha, M.; Heras, E.; Missé, J.; Zambom-Ferraresi, F.; Zambom-Ferraresi, F.; Ars, J.; et al. Deepening Physical Exercise Intervention Protocols for Older People with Sarcopenia Following Establishment of the EWGSOP2 Consensus: A Systematic Review. Geriatrics 2025, 10, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10040091
Minobes-Molina E, Rierola-Fochs S, Parés-Martínez C, Farrés-Godayol P, Ochandorena-Acha M, Heras E, Missé J, Zambom-Ferraresi F, Zambom-Ferraresi F, Ars J, et al. Deepening Physical Exercise Intervention Protocols for Older People with Sarcopenia Following Establishment of the EWGSOP2 Consensus: A Systematic Review. Geriatrics. 2025; 10(4):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10040091
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinobes-Molina, Eduard, Sandra Rierola-Fochs, Carles Parés-Martínez, Pau Farrés-Godayol, Mirari Ochandorena-Acha, Eva Heras, Jan Missé, Fabricio Zambom-Ferraresi, Fabiola Zambom-Ferraresi, Joan Ars, and et al. 2025. "Deepening Physical Exercise Intervention Protocols for Older People with Sarcopenia Following Establishment of the EWGSOP2 Consensus: A Systematic Review" Geriatrics 10, no. 4: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10040091
APA StyleMinobes-Molina, E., Rierola-Fochs, S., Parés-Martínez, C., Farrés-Godayol, P., Ochandorena-Acha, M., Heras, E., Missé, J., Zambom-Ferraresi, F., Zambom-Ferraresi, F., Ars, J., Terradas-Monllor, M., & Escribà-Salvans, A. (2025). Deepening Physical Exercise Intervention Protocols for Older People with Sarcopenia Following Establishment of the EWGSOP2 Consensus: A Systematic Review. Geriatrics, 10(4), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10040091








