Effect of a Six-Month Dance Intervention on Postural Control and Fall-Related Outcomes in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Intervention
2.3. Balance Measurements
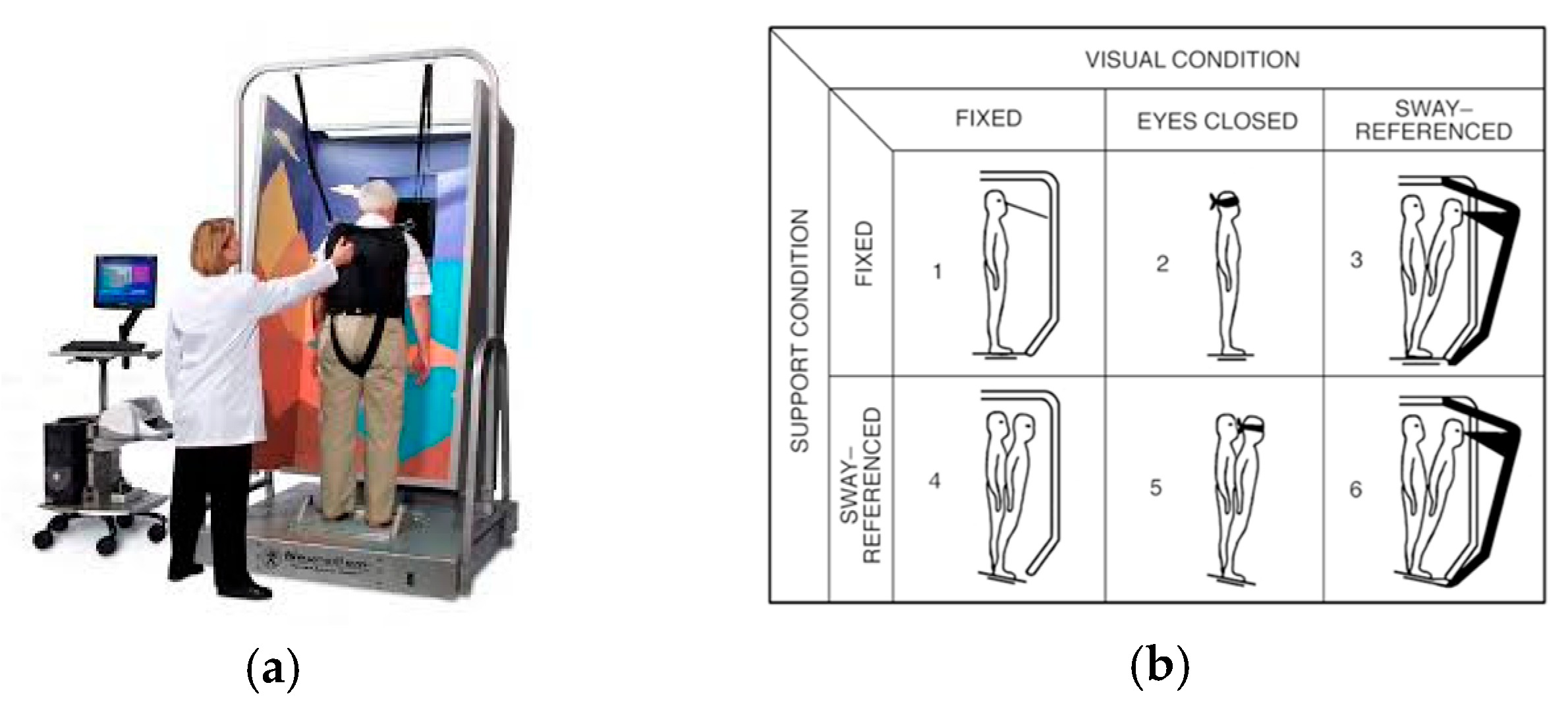
2.3.1. Sensory Organization Test
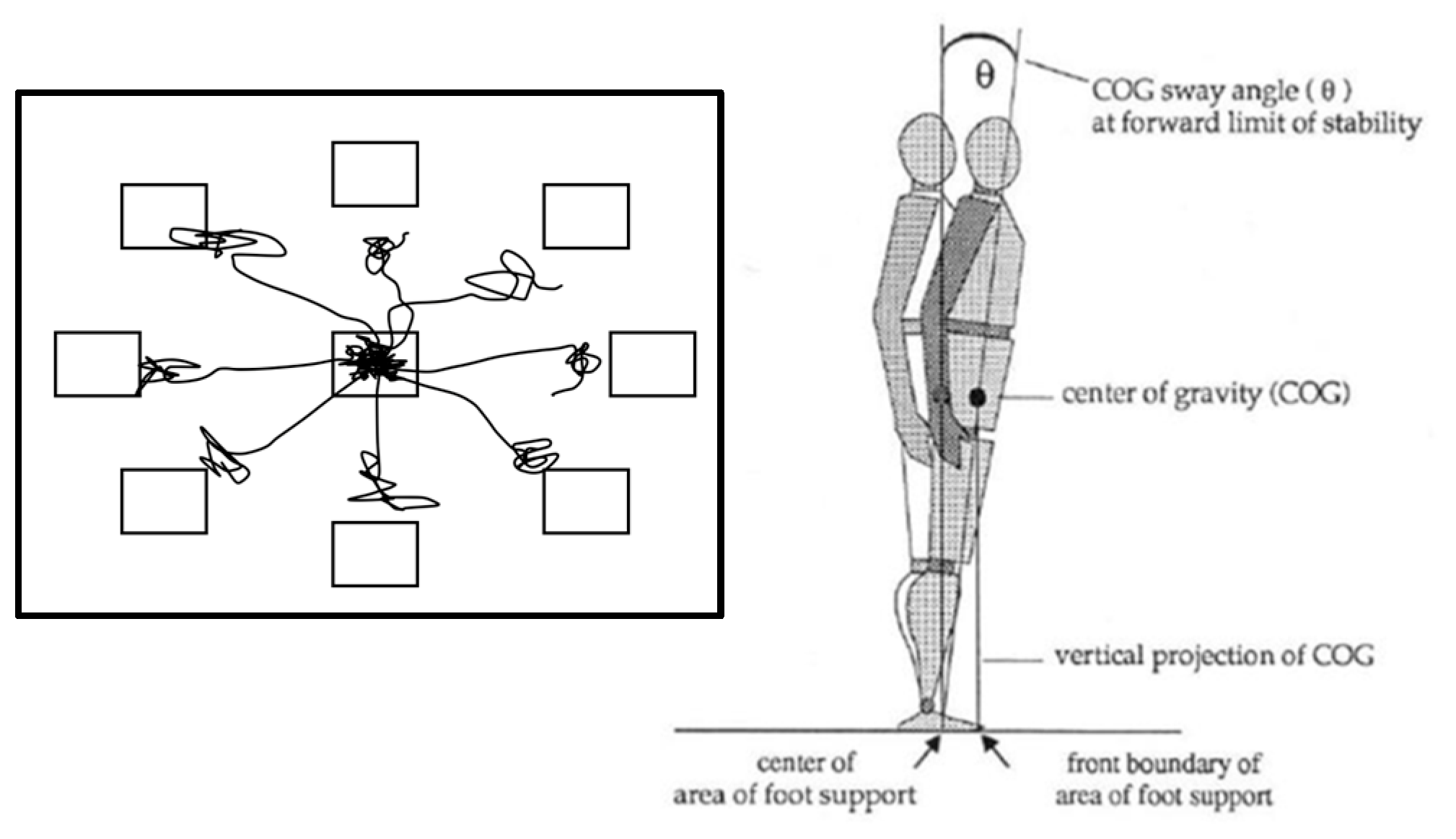
2.3.2. Limits of Stability
2.4. Muscle Contraction Velocity
2.5. Falls Efficacy Scale
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sensory Organization Test
3.2. Limits of Stability
3.3. Muscle Contraction Velocity
3.4. Fear of Falling and Number of Falls
4. Discussion
4.1. Balance
4.2. Muscle Contraction Velocity
4.3. Fear of Falling and Number of Falls
4.4. Limitations
4.5. Suggestions for Further Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MCI | mild cognitive impairment |
| IG | intervention group |
| CG | control group |
| SOT | Sensory Organization Test |
| LOS | Limits of Stability Test |
| Vc | muscle contraction velocity |
| FES-I | Falls Efficacy Scale—International |
| ROF | risk of falling |
| RT | reaction time |
| MVL | movement velocity |
| COG | center of gravity |
| MXE | maximum excursion |
| EPE | endpoint excursion |
| DCL | directional control |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
References
- Horak, F.B. Postural orientation and equilibrium: What do we need to know about neural control of balance to prevent falls? Age Ageing 2006, 35 (Suppl. S2), ii7–ii11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granacher, U.; Gollhofer, A.; Hortobágyi, T.; Kressig, R.W.; Muehlbauer, T. The importance of trunk muscle strength for balance, functional performance, and fall prevention in seniors: A systematic review. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, P.; Rowland, P. Impact of sensory reweighting strategies on postural control using the sensory organization test in older adults with and without fall risks. Physiother. Res. Int. J. Res. Clin. Phys. Ther. 2024, 29, e2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, E.; Battaglia, G.; Patti, A.; Brusa, J.; Leonardi, V.; Palma, A.; Bellafiore, M. Physical activity programs for balance and fall prevention in elderly: A systematic review. Medicine 2019, 98, e16218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittrakul, J.; Siviroj, P.; Sungkarat, S.; Sapbamrer, R. Multi-System Physical Exercise Intervention for Fall Prevention and Quality of Life in Pre-Frail Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granacher, U.; Muehlbauer, T.; Gruber, M. A qualitative review of balance and strength performance in healthy older adults: Impact for testing and training. J. Aging Res. 2012, 2012, 708905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, Y.-C.; Huang, L.-K.; Wang, Y.-H.; Hu, C.-J.; Tseng, I.-J.; Chen, H.-C.; Lin, L.-F. Balance and gait performance in older adults with early-stage cognitive impairment. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 57, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangari, M.; Dehkordi, P.S.; Shams, A. Age and attentional focus instructions effects on postural and supra-postural tasks among older adults with mild cognitive impairments. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 6795–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, W. A Class-Imbalanced Deep Learning Fall Detection Algorithm Using Wearable Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allali, G.; Verghese, J. Management of Gait Changes and Fall Risk in MCI and Dementia. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2017, 19, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.F.; Moore, S.; Woollacott, M.H. Correlation between two clinical balance measures in older adults: Functional mobility and sensory organization test. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 1998, 53, M140–M146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ruhe, A.; Fejer, R.; Walker, B. Center of pressure excursion as a measure of balance performance in patients with non-specific low back pain compared to healthy controls: A systematic review of the literature. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraldo-García, A.; Santos-Pérez, S.; Crujeiras, R.; Soto-Varela, A. Postural changes associated with ageing on the sensory organization test and the limits of stability in healthy subjects. Auris Nasus Larynx 2016, 43, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspersen, C.J.; Powell, K.E.; Christenson, G.M. Physical activity, exercise, and physical fitness: Definitions and distinctions for health-related research. Public Health Rep. 1985, 100, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Nagamatsu, L.S.; Heyn, P.C. The Effects of Physical Activity on Cognitive Function in Older Adults: Evidence From Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2023, 31, 529–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.; Awan-Scully, R.; Ash, G.I.; Pei, Z.; Gu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Cole, A.; Baker, J.S. The effectiveness of dance movement interventions for older adults with mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease, and dementia: A systematic scoping review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 92, 102120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.; Knopman, D.S. Classification and epidemiology of MCI. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2013, 29, 753–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Chan, J.S.Y.; Yan, J.H. Mild cognitive impairment affects motor control and skill learning. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 27, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puts, M.T.E.; Toubasi, S.; Andrew, M.K.; Ashe, M.C.; Ploeg, J.; Atkinson, E.; Ayala, A.P.; Roy, A.; Rodríguez Monforte, M.; Bergman, H.; et al. Interventions to prevent or reduce the level of frailty in community-dwelling older adults: A scoping review of the literature and international policies. Age Ageing 2017, 46, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Step Safely: Strategies for Preventing and Managing Falls Across the Life-Course. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/978924002191-4 (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Nissim, M.; Livny, A.; Barmatz, C.; Tsarfaty, G.; Berner, Y.; Sacher, Y.; Giron, J.; Ratzon, N.Z. Effects of aquatic physical intervention on fall risk, working memory and hazard-perception as pedestrians in older people: A pilot trial. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegl, A.; Hayn, D.; Kastner, P.; Fabiani, E.; Šimunič, B.; Löffler, K.; Weidinger, L.; Brix, B.; Goswami, N.; Günter, S. Quantification of the Link between Timed Up-and-Go Test Subtasks and Contractile Muscle Properties. Sensors 2021, 21, 6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, S.C.; Riege, R.F.F.; Tisborn, K.; Biondo, J.; Martin, L.; Beelmann, A. Effects of Dance Movement Therapy and Dance on Health-Related Psychological Outcomes. A Meta-Analysis Update. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrington, C.; Fairhall, N.J.; Wallbank, G.K.; Tiedemann, A.; Michaleff, Z.A.; Howard, K.; Clemson, L.; Hopewell, S.; Lamb, S.E. Exercise for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2019, CD012424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiros-Rodríguez, R.; García-Soidan, J.L. Balance Training in Elderly Women Using Public Parks. J. Women Aging 2014, 26, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedemann, A.; Sherrington, C.; Close, J.C.T.; Lord, S.R. Exercise and Sports Science Australia Exercise and Sports Science Australia position statement on exercise and falls prevention in older people. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2011, 14, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Rambo, E.; Bandeira-Guimarães, M.; Vieira, A.F.; Pietta-Dias, C.; Izquierdo, M.; Cadore, E.L. Dance as an Intervention to Reduce Fall Risk in Older Adults: A Systematic Review with a Meta-Analysis. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2022, 30, 1118–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong Yan, A.; Nicholson, L.L.; Ward, R.E.; Hiller, C.E.; Dovey, K.; Parker, H.M.; Low, L.-F.; Moyle, G.; Chan, C. The Effectiveness of Dance Interventions on Psychological and Cognitive Health Outcomes Compared with Other Forms of Physical Activity: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2024, 54, 1179–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehfeld, K.; Müller, P.; Aye, N.; Schmicker, M.; Dordevic, M.; Kaufmann, J.; Hökelmann, A.; Müller, N.G. Dancing or Fitness Sport? The Effects of Two Training Programs on Hippocampal Plasticity and Balance Abilities in Healthy Seniors. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauggel, S.; Birkner, B. Validität und Reliabilität einer deutschen Version der Geriatrischen Depressionsskala (GDS). Z. Für Klin. Psychol. Psychotherapie 1999, 28, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.C. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 256, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creavin, S.T.; Wisniewski, S.; Noel-Storr, A.H.; Trevelyan, C.M.; Hampton, T.; Rayment, D.; Thom, V.M.; Nash, K.J.E.; Elhamoui, H.; Milligan, R.; et al. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) for the detection of dementia in clinically unevaluated people aged 65 and over in community and primary care populations. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2016, CD011145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessen, F.; Spottke, A.; Boecker, H.; Brosseron, F.; Buerger, K.; Catak, C.; Fliessbach, K.; Franke, C.; Fuentes, M.; Heneka, M.T.; et al. Design and first baseline data of the DZNE multicenter observational study on predementia Alzheimer’s disease (DELCODE). Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2018, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.-G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/9781134742707 (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Schulz, K.F.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; for the CONSORT Group. CONSORT 2010 Statement: Updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMJ 2010, 340, c332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, C.E.; Blissmer, B.; Deschenes, M.R.; Franklin, B.A.; Lamonte, M.J.; Lee, I.-M.; Nieman, D.C.; Swain, D.P.; American College of Sports Medicine American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: Guidance for prescribing exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1334–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsell, E.M.; Furman, J.M.; Herdman, S.J.; Konrad, H.R.; Shepard, N.T. Computerized dynamic platform posturography. Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. 1997, 117, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trueblood, P.R.; Hodson-Chennault, N.; McCubbin, A.; Youngclarke, D. Performance and Impairment-Based Assessments Among Community Dwelling Elderly: Sensitivity and Specificity. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2001, 24, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterka, R.J.; Loughlin, P.J. Dynamic regulation of sensorimotor integration in human postural control. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 91, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-Y.; Chen, P.-Y.; Hsieh, W.-L.; Cheen, J.-R.; Kao, C.-L. Correlation of the composite equilibrium score of computerized dynamic posturography and clinical balance tests. J. Clin. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2012, 3, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SMART Balance Master. Neurorehabdirectory. Available online: https://www.neurorehabdirectory.com/rehab-products/smart-balance-master-2/ (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Mangus, B.C.; Wallmann, H.W.; Ledford, M. Analysis of postural stability in collegiate soccer players before and after an acute bout of heading multiple soccer balls. Sports Biomech. 2004, 3, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balance Manager Systems: Clinical Interpretation Guide; Natus Medical Incorporated: Clackamas, OR, USA, 2008.
- Alvarez-Otero, R.; Perez-Fernandez, N. The limits of stability in patients with unilateral vestibulopathy. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017, 137, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instruction Manual of the Neurocom Balance Master; Natus Medical Incorporated: Clackamas, OR, USA, 2006.
- García-García, O.; Cuba-Dorado, A.; Álvarez-Yates, T.; Carballo-López, J.; Iglesias-Caamaño, M. Clinical utility of tensiomyography for muscle function analysis in athletes. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2019, 10, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencic, V.; Knez, N. Measuring of skeletal muscles’ dynamic properties. Artif. Organs 1997, 21, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitru, D.; Zwarts, M.J. Special Nerve Conduction Techniques. In Elextrodiagnostic Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 225–256. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9781560534334500146 (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Krizaj, D.; Simunic, B.; Zagar, T. Short-term repeatability of parameters extracted from radial displacement of muscle belly. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2008, 18, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.A.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Martín-Rodríguez, S.; Kobal, R.; Abad, C.C.C.; Arruda, A.F.S.; Guerriero, A.; Loturco, I. Is Tensiomyography-Derived Velocity of Contraction a Sensitive Marker to Detect Acute Performance Changes in Elite Team-Sport Athletes? Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2020, 15, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macgregor, L.J.; Hunter, A.M.; Orizio, C.; Fairweather, M.M.; Ditroilo, M. Assessment of Skeletal Muscle Contractile Properties by Radial Displacement: The Case for Tensiomyography. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 1607–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimunič, B.; Koren, K.; Rittweger, J.; Lazzer, S.; Reggiani, C.; Rejc, E.; Pišot, R.; Narici, M.; Degens, H. Tensiomyography detects early hallmarks of bed-rest-induced atrophy before changes in muscle architecture. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, P.L.; Saco-Ledo, G.; Morales, J.S.; Gallardo-Gómez, D.; Morales-Palomo, F.; López-Ortiz, S.; Rivas-Baeza, B.; Castillo-García, A.; Jiménez-Pavón, D.; Santos-Lozano, A.; et al. Effects of physical exercise on physical function in older adults in residential care: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2023, 4, e247–e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, N.; Kempen, G.I.J.M.; Todd, C.J.; Beyer, N.; Freiberger, E.; Piot-Ziegler, C.; Yardley, L.; Hauer, K. The German version of the Falls Efficacy Scale-International Version (FES-I). Z. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2006, 39, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardley, L.; Beyer, N.; Hauer, K.; Kempen, G.; Piot-Ziegler, C.; Todd, C. Development and initial validation of the Falls Efficacy Scale-International (FES-I). Age Ageing 2005, 34, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, L.; Ferrari-Piloni, C.; Torres, É.; Estrela, C.; Valladares-Neto, J. Effect size: A statistical basis for clinical practice. Rev. Odonto Ciênc. 2018, 33, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, L.Z. Falls in older people: Epidemiology, risk factors and strategies for prevention. Age Ageing 2006, 35 (Suppl. S2), ii37–ii41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trombetti, A.; Reid, K.F.; Hars, M.; Herrmann, F.R.; Pasha, E.; Phillips, E.M.; Fielding, R.A. Age-associated declines in muscle mass, strength, power, and physical performance: Impact on fear of falling and quality of life. Osteoporos. Int. 2016, 27, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Odasso, M.; Verghese, J.; Beauchet, O.; Hausdorff, J.M. Gait and cognition: A complementary approach to understanding brain function and the risk of falling. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 2127–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattenstroth, J.-C.; Kalisch, T.; Holt, S.; Tegenthoff, M.; Dinse, H.R. Six months of dance intervention enhances postural, sensorimotor, and cognitive performance in elderly without affecting cardio-respiratory functions. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2013, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narikbayeva, L.; Klyshbayev, T.; Kalimullin, D.; Mochalov, D. The impact of dance on enhancing social skills and emotional intelligence through creativity. Acta Psychol. 2025, 253, 104736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehfeld, K.; Lüders, A.; Hökelmann, A.; Lessmann, V.; Kaufmann, J.; Brigadski, T.; Müller, P.; Müller, N.G. Dance training is superior to repetitive physical exercise in inducing brain plasticity in the elderly. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamacher, D.; Hamacher, D.; Rehfeld, K.; Hökelmann, A.; Schega, L. The Effect of a Six-Month Dancing Program on Motor-Cognitive Dual-Task Performance in Older Adults. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2015, 23, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamacher, D.; Hamacher, D.; Rehfeld, K.; Schega, L. Motor-cognitive dual-task training improves local dynamic stability of normal walking in older individuals. Clin. Biomech. 2016, 32, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratiglioni, L.; Wang, H.X.; Ericsson, K.; Maytan, M.; Winblad, B. Influence of social network on occurrence of dementia: A community-based longitudinal study. Lancet 2000, 355, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesinski, M.; Hortobágyi, T.; Muehlbauer, T.; Gollhofer, A.; Granacher, U. Effects of Balance Training on Balance Performance in Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1721–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitney, S.L.; Marchetti, G.F.; Schade, A.I. The relationship between falls history and computerized dynamic posturography in persons with balance and vestibular disorders. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 87, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; McCandliss, B.D.; Sommer, T.; Raz, A.; Posner, M.I. Testing the efficiency and independence of attentional networks. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2002, 14, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, M.H.; Yue, G.H. Postural Control Dysfunction and Balance Rehabilitation in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyler, K.; Krause, A.; Gollhofer, A.; Ritzmann, R. Specific Stimuli Induce Specific Adaptations: Sensorimotor Training vs. Reactive Balance Training. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borde, R.; Hortobágyi, T.; Granacher, U. Dose–Response Relationships of Resistance Training in Healthy Old Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1693–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-H.; Su, C.-H.; Wang, D. The Role of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) in Neuromuscular Adaptations: Implications for Strength and Power Development—A Review. Life 2025, 15, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.L.; Blizzard, L.; Wood, A.G.; Srikanth, V.; Thomson, R.; Sanders, L.M.; Callisaya, M.L. Cognitive function, gait, and gait variability in older people: A population-based study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2013, 68, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osoba, M.Y.; Rao, A.K.; Agrawal, S.K.; Lalwani, A.K. Balance and gait in the elderly: A contemporary review. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2019, 4, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, B.; Xu, J.-F.; Wang, F.-B.-H.; Ye, H.; Duan, J.-P.; Cui, X.-W. Home-based strength and balance exercises for fall prevention among older individuals of advanced age: A randomized controlled single-blind study. Ann. Med. 2025, 57, 2459818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batcir, S.; Shani, G.; Shapiro, A.; Melzer, I. Characteristics of step responses following varying magnitudes of unexpected lateral perturbations during standing among older people—A cross-sectional laboratory-based study. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula Simola, R.Á.; Harms, N.; Raeder, C.; Kellmann, M.; Meyer, T.; Pfeiffer, M.; Ferrauti, A. Assessment of neuromuscular function after different strength training protocols using tensiomyography. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loturco, I.; Pereira, L.A.; Kobal, R.; Kitamura, K.; Ramírez-Campillo, R.; Zanetti, V.; Abad, C.C.C.; Nakamura, F.Y. Muscle Contraction Velocity: A Suitable Approach to Analyze the Functional Adaptations in Elite Soccer Players. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2016, 15, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orr, R.; de Vos, N.J.; Singh, N.A.; Ross, D.A.; Stavrinos, T.M.; Fiatarone-Singh, M.A. Power training improves balance in healthy older adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2006, 61, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, D.A.; Kennedy, J.; Rutherford, O.M. Explosive power and asymmetry in leg muscle function in frequent fallers and non-fallers aged over 65. Age Ageing 2002, 31, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, R.; Raymond, J.; Fiatarone Singh, M. Efficacy of progressive resistance training on balance performance in older adults: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 317–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcleod, J.C.; Currier, B.S.; Lowisz, C.V.; Phillips, S.M. The influence of resistance exercise training prescription variables on skeletal muscle mass, strength, and physical function in healthy adults: An umbrella review. J. Sport Health Sci. 2024, 13, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Freire, M.; de Cabo, R.; Studenski, S.A.; Ferrucci, L. The Neuromuscular Junction: Aging at the Crossroad between Nerves and Muscle. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 208. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/aging-neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00208/full (accessed on 28 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, D.J.; Piasecki, M.; Atherton, P.J. The age-related loss of skeletal muscle mass and function: Measurement and physiology of muscle fibre atrophy and muscle fibre loss in humans. Ageing Res. Rev. 2018, 47, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pus, K.; Paravlic, A.H.; Šimunič, B. The use of tensiomyography in older adults: A systematic review. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1213993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gschwind, Y.J.; Kressig, R.W.; Lacroix, A.; Muehlbauer, T.; Pfenninger, B.; Granacher, U. A best practice fall prevention exercise program to improve balance, strength / power, and psychosocial health in older adults: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. BMC Geriatr. 2013, 13, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Fang, Z. The effects of dance interventions on reducing the risk of falls in older adults: A network meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1496692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auais, M.; Alvarado, B.; Guerra, R.; Curcio, C.; Freeman, E.E.; Ylli, A.; Guralnik, J.; Deshpande, N. Fear of falling and its association with life-space mobility of older adults: A cross-sectional analysis using data from five international sites. Age Ageing 2017, 46, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-C.; Li, Y.-T.; Tung, T.-H.; Chen, C.; Tsai, C.-Y. The relationship between falling and fear of falling among community-dwelling elderly. Medicine 2021, 100, e26492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrington, C.; Michaleff, Z.A.; Fairhall, N.; Paul, S.S.; Tiedemann, A.; Whitney, J.; Cumming, R.G.; Herbert, R.D.; Close, J.C.T.; Lord, S.R. Exercise to prevent falls in older adults: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, T.E.; Rochester, L.; Neil, F.; Skelton, D.A.; Ballinger, C. Exercise for improving balance in older people. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 2011, CD004963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpkins, C.; Yang, F. Recreational older ballet dancers fall less with more effective reactive balance control than non-dancers after a slip during gait. Exp. Brain Res. 2025, 243, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, N.; Maggi, S.; Schofield, P.; Stubbs, B. Dance movement therapy and falls prevention. Maturitas 2017, 102, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-N.W.; Mao, H.-F.; Lee, H.-M.; Chi, W.-C. Association between Fear of Falling and Seven Performance-Based Physical Function Measures in Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K. Intention-to-treat concept: A review. Perspect. Clin. Res. 2011, 2, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso Soares, B.; Alves Costa, D.; de Faria Xavier, J.; Alamino Pereira de Viveiro, L.; Pedrozo Campos Antunes, T.; Grazielli Mendes, F.; Assis Kovachich de Oliveira, M.; Petravicius Bomfim, C.; Su Hsien, K.; Silva, E.C.G.E.; et al. Social isolation due to COVID-19: Impact on loneliness, sedentary behavior, and falls in older adults. Aging Ment. Health 2022, 26, 2120–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefferts, E.C.; Saavedra, J.M.; Song, B.K.; Lee, D.-C. Effect of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior in Older Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huy, C. German-PAQ-50+—German-PAQ-50+ Fragebogen zur Erfassung der körperlichen Aktivität. ZPID (Leibniz Institute for Psychology Information)—Testarchiv. 2011. Available online: https://psycharchives.zpid.de/handle/20.500.12034/407 (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Labott, B.K.; Herold, F.; Langhans, C.; Halfpaap, N.; Grässler, B.; Hökelmann, A.; Müller, N.G.; Hamacher, D. Minimum Toe Clearance Variability in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: Differences to Healthy Controls and Effects of a Dance Intervention. 2024. Available online: https://www.ssrn.com/abstract=4825197 (accessed on 13 March 2025).

| Characteristics | Total | Intervention Group | Control Group | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (n) | 50 | 26 | 24 | - |
| Sex (female/male) | 27/23 | 16/10 | 11/13 | - |
| Subtype of MCI (amnestic/non-amnestic) | 25/25 | 15/11 | 10/14 | - |
| Age (years) | 69.9 ± 6.2 | 70.7 ± 5.6 | 69.1 ± 6.8 | 0.373 |
| Height (cm) | 171.5 ± 9.2 | 169.1 ± 8.9 | 174.0 ± 9.0 | 0.060 |
| Body weight (kg) | 74.4 ± 11.3 | 71.8 ± 8.2 | 77.1 ± 13.5 | 0.097 |
| Years of education | 15.6 ± 2.5 | 15.8 ± 2.7 | 15.3 ± 2.1 | 0.396 |
| Score MMSE | 27.2 ± 1.4 | 27.1 ± 1.5 | 27.3 ± 1.2 | 0.651 |
| Control Group | Intervention Group | ANOVA | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | ||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 95% CI | Mean ± SD | 95% CI | Mean ± SD | 95% CI | Mean ± SD | 95% CI | F | p | η2p | |
| Composite Score | 81.2 ± 3.9 | [79.2, 83.1] | 81.0 ± 3.3 | [79.2, 82.8] | 81.5 ± 4.5 | [79.7, 83.4] | 80.7 ± 4.2 | [79.1, 82.4] | 0.208 | 0.651 | 0.005 |
| SOM | 97.7 ± 1.1 | [96.7, 98.6] | 97.6 ± 1.8 | [96.7, 98.6] | 97.1 ± 2.7 | [96.2, 98.0] | 97.3 ± 2.2 | [96.5, 98.2] | 0.137 | 0.714 | 0.003 |
| VIS | 85.9 ± 8.1 | [82.5, 89.3] | 91.4 ± 4.3 | [89.3, 93,4] | 88.3 ± 6.7 | [85.2, 91,5] | 91.1 ± 4.6 | [89.2, 93.0] | 1.346 | 0.253 | 0.033 |
| VEST | 68.1 ± 11.1 | [62.8, 73.3] | 64.5 ± 10.1 | [59.4, 69.6] | 68.5 ± 11.6 | [63.6, 73.4] | 65.3 ± 11.7 | [60.6, 70.0] | 0.005 | 0.942 | 0 |
| PREF | 99.5 ± 6.0 | [96.9, 102.1] | 99.1 ± 7.4 | [95.2, 102.9] | 99.2 ± 5.2 | [96.8, 101.6] | 99.3 ± 9.0 | [95.7, 102.9] | 0.034 | 0.854 | 0.001 |
| Control Group | Intervention Group | ANOVA | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | ||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 95% CI | Mean ± SD | 95% CI | Mean ± SD | 95% CI | Mean ± SD | 95% CI | F | p | η2p | |
| Forward RT | 1.4 ± 0.7 | [1.1, 1.8] | 0.9 ± 0.6 | [0.5, 1.3] | 1.3 ± 0.7 | [1.0, 1.6] | 1.2 ± 0.9 | [0.8, 1.6] | 1.377 | 0.249 | 0.038 |
| Forward MVL | 1.7 ± 1.3 | [1.1, 2.2] | 2.5 ± 1.6 | [1.7, 3.3] | 2.0 ± 0.8 | [1.5, 2.5] | 2.5 ± 1.4 | [1.8, 3.2] | 0.634 | 0.431 | 0.018 |
| Forward EPE | 50.1 ± 21.5 | [40.4, 59.8] | 61.1 ± 28.1 | [48.1, 74.2] | 47.8 ± 17.2 | [39.3, 56.3] | 54.4 ± 23.8 | [43.1, 65.8] | 0.172 | 0.681 | 0.005 |
| Forward MXE | 72.5 ± 13.8 | [64.9, 80.1] | 80.8 ± 15.1 | [72.3, 89.2] | 70.4 ± 15.7 | [63.8, 77.0] | 79.9 ± 17.8 | [72.5, 87.3] | 0.041 | 0.84 | 0.001 |
| Forward DCL | 90.3 ± 7.1 | [86.7, 93.8] | 87.3 ± 8.6 | [82.6, 92.0] | 85.4 ± 6.8 | [82.3, 88.5] | 87.8 ± 9.8 | [83.7, 91.9] | 2.357 | 0.134 | 0.063 |
| Right RT | 1.2 ± 0.4 | [0.9, 1.4] | 0.9 ± 0.4 | [0.7, 1.1] | 1.1 ± 0.5 | [0.9, 1.3] | 1.0 ± 0.5 | [0.7, 1.2] | 0.126 | 0.724 | 0.004 |
| Right MVL | 2.3 ± 0.8 | [1.7, 2.9] | 3.4 ± 1.7 | [2.6, 4.2] | 3.0 ± 1.4 | [2.5, 3.6] | 3.1 ± 1.5 | [2.4, 3.8] | 4.458 | 0.042 † | 0.113 |
| Right EPE | 68.8 ± 12.0 | [63.8, 73.7] | 67.4 ± 17.9 | [58.8, 76.0] | 70.4 ± 7.8 | [66.1, 74.8] | 67.0 ± 16.1 | [59.5, 74.5] | 0.131 | 0.719 | 0.004 |
| Right MXE | 78.6 ± 5.4 | [74.5, 82.8] | 82.7 ± 9.5 | [77.2, 88.2] | 80.4 ± 9.7 | [76.8, 84.0] | 78.3 ± 11.7 | [73.5, 83.1] | 3.567 | 0.067 | 0.092 |
| Right DCL | 87.3 ± 4.4 | [84.4, 90.2] | 84.1 ± 6.3 | [77.4, 90.7] | 84.5 ± 6.5 | [82.0, 87.1] | 79.2 ± 16.4 | [73.4, 85.0] | 0.204 | 0.655 | 0.006 |
| Backward RT | 0.9 ± 0.4 | [0.7, 1.1] | 0.7 ± 0.5 | [0.5, 0.9] | 0.9 ± 0.4 | [0.7, 1.1] | 0.6 ± 0.4 | [0.4, 0.8] | 0.393 | 0.535 | 0.011 |
| Backward MVL | 1.9 ± 0.9 | [−0.2, 3.9] | 2.1 ± 1.0 | [1.5, 2.8] | 3.2 ± 5.3 | [1.4, 5.0] | 2.2 ± 1.4 | [1.6, 2.7] | 0.76 | 0.389 | 0.021 |
| Backward EPE | 39.1 ± 9.5 | [33.1, 45.2] | 46.7 ± 12.1 | [40.0, 53.4] | 44.7 ± 13.5 | [39.4, 49.9] | 43.9 ± 14.0 | [38.1, 49.7] | 2.191 | 0.148 | 0.059 |
| Backward MXE | 72.4 ± 12.3 | [64.6, 80.2] | 70.1 ± 9.0 | [62.7, 77.5] | 70.4 ± 17.3 | [63.6, 77.2] | 62.5 ± 17.7 | [56.0, 68.9] | 0.822 | 0.371 | 0.023 |
| Backward DCL | 78.9 ± 8.4 | [72.5, 85.3] | 72.8 ± 14.8 | [60.6, 85.0] | 71.1 ± 15.0 | [65.6, 76.7] | 64.9 ± 29.1 | [54.2, 75.5] | 0.001 | 0.978 | 0 |
| Left RT | 1.0 ± 0.5 | [0.8, 1.3] | 0.9 ± 0.6 | [0.5, 1.3] | 0.9 ± 0.4 | [0.7, 1.1] | 1.0 ± 0.9 | [0.6, 1.3] | 0.494 | 0.487 | 0.014 |
| Left MVL | 2.8 ± 1.1 | [2.2, 3.5] | 3.4 ± 1.4 | [2.7, 4.2] | 3.1 ± 1.4 | [2.6, 3.7] | 3.3 ± 1.4 | [2.7, 4.0] | 0.696 | 0.41 | 0.019 |
| Left EPE | 73.4 ± 9.4 | [67.0, 79.9] | 72.3 ± 10.5 | [64.7, 79.8] | 64.7 ± 14.7 | [59.1, 70.3] | 70.1 ± 17.5 | [63.5, 76.7] | 1.253 | 0.271 | 0.035 |
| Left MXE | 81.4 ± 5.8 | [75.4, 87.3] | 81.5 ± 9.2 | [76.8, 86.2] | 78.40 ± 14.7 | [73.2, 83.6] | 81.8 ± 9.1 | [77.7, 85.8] | 0.617 | 0.438 | 0.017 |
| Left DCL | 87.8 ± 4.3 | [85.0, 90.6] | 86.4 ± 5.5 | [83.5, 89.3] | 85.7 ± 6.3 | [83.3, 88.2] | 85.4 ± 5.8 | [82.9, 87.9] | 0.167 | 0.685 | 0.005 |
| Control Group | Intervention Group | ANOVA | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | ||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 95% CI | Mean ± SD | 95% CI | Mean ± SD | 95% CI | Mean ± SD | 95% CI | F | p | η2p | |
| Vc m. rectus femoris (left) | 0.3 ± 0.1 | [0.2, 0.3] | 0.2 ± 0.1 | [0.2, 0.3] | 0.3 ± 0.1 | [0.2, 0.3] | 0.2 ± 0.9 | [0.2, 0.2] | 0.587 | 0.448 | 0.013 |
| Vc m. rectus femoris (right) | 0.3 ± 0.1 | [0.3, 0.3] | 0.3 ± 0.1 | [0.2, 0.3] | 0.3 ± 0.1 | [0.2, 0.3] | 0.2 ± 0.1 | [0.2, 0.3] | 0.117 | 0.734 | 0.003 |
| Vc m. semitendinosus (left) | 0.2 ± 0.1 | [0.2, 0.3] | 0.2 ± 0.1 | [0.2, 0.3] | 0.2 ± 0.1 | [0.2, 0.3] | 0.1 ± 0.1 | [0.1, 0.2] | 1.698 | 0.200 | 0.038 |
| Vc m. semitendinosus (right) | 0.2 ± 0.1 | [0.2, 0.2] | 0.2 ± 0.1 | [0.1, 0.2] | 0.2 ± 0.1 | [0.1, 0.2] | 0.1 ± 0.1 | [0.1, 0.2] | 0.498 | 0.484 | 0.011 |
| Vc m. tibialis anterior (left) | 0.1 ± 0.1 | [0.1, 0.1] | 0.1 ± 0.1 | [0.1, 0.1] | 0.1 ± 0.1 | [0.1, 0.1] | 0.1 ± 0.1 | [0.1, 0.1] | 0.133 | 0.717 | 0.003 |
| Vc m. tibialis anterior (right) | 0.1 ± 0.1 | [0.1, 0.1] | 0.1 ± 0.1 | [0.1, 0.1] | 0.1 ± 0.1 | [0.1, 0.1] | 0.1 ± 0.1 | [0.1, 0.1] | 0.02 | 0.889 | 0 |
| Control Group | Paired-Samples t-Test | Intervention Group | Paired-Samples t-Test | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | |||||||
| Mean ± SD | 95% CI | Mean ± SD | 95% CI | p | Mean ± SD | 95% CI | Mean ± SD | 95% CI | p | |
| Score | 19.7 ± 4.3 | [17.5, 21.8] | 19.7 ± 4.9 | [17.3, 22.1] | 1 | 18.9 ± 2.5 | [17.8, 20.0] | 18.3 ± 2.9 | [17.0, 19.5] | 0.032 * |
| Number of Falls | 0.7 ± 2.4 | [−0.4, 1.9] | 0.4 ± 1.3 | [−0.2, 1.1] | 0.593 | 0.4 ± 0.9 | [0.0, 0.7] | 0.00 ± 0.2 | [0.0, 0.13] | 0.088 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thiel, U.; Halfpaap, N.; Labott, B.K.; Herold, F.; Langhans, C.; Heinrichs, K.; Müller, P.; Müller, N.G.; Hökelmann, A. Effect of a Six-Month Dance Intervention on Postural Control and Fall-Related Outcomes in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Geriatrics 2025, 10, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10030067
Thiel U, Halfpaap N, Labott BK, Herold F, Langhans C, Heinrichs K, Müller P, Müller NG, Hökelmann A. Effect of a Six-Month Dance Intervention on Postural Control and Fall-Related Outcomes in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Geriatrics. 2025; 10(3):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10030067
Chicago/Turabian StyleThiel, Ulrich, Nicole Halfpaap, Berit K. Labott, Fabian Herold, Corinna Langhans, Kristinn Heinrichs, Patrick Müller, Notger G. Müller, and Anita Hökelmann. 2025. "Effect of a Six-Month Dance Intervention on Postural Control and Fall-Related Outcomes in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Geriatrics 10, no. 3: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10030067
APA StyleThiel, U., Halfpaap, N., Labott, B. K., Herold, F., Langhans, C., Heinrichs, K., Müller, P., Müller, N. G., & Hökelmann, A. (2025). Effect of a Six-Month Dance Intervention on Postural Control and Fall-Related Outcomes in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Geriatrics, 10(3), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/geriatrics10030067








