The Protective Efficacy of an Inactivated Vaccine against Avibacterium paragallinarum Field Isolates
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacteria and Media
2.2. Vaccine
2.3. Immunization Procedures
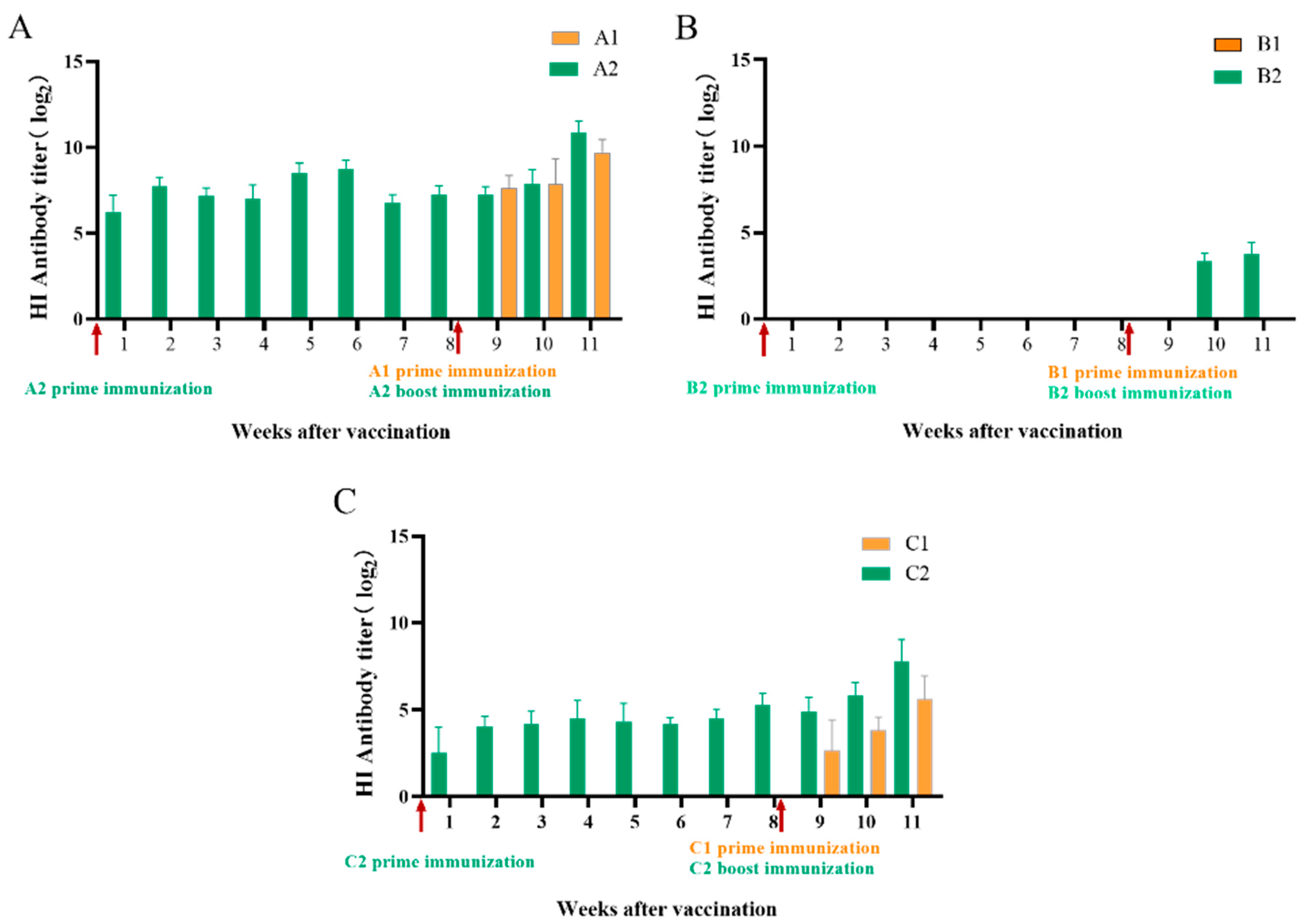
2.4. Antibody Titers Detected by Hemagglutination Inhibition Test
2.5. Challenge Infection Experiments
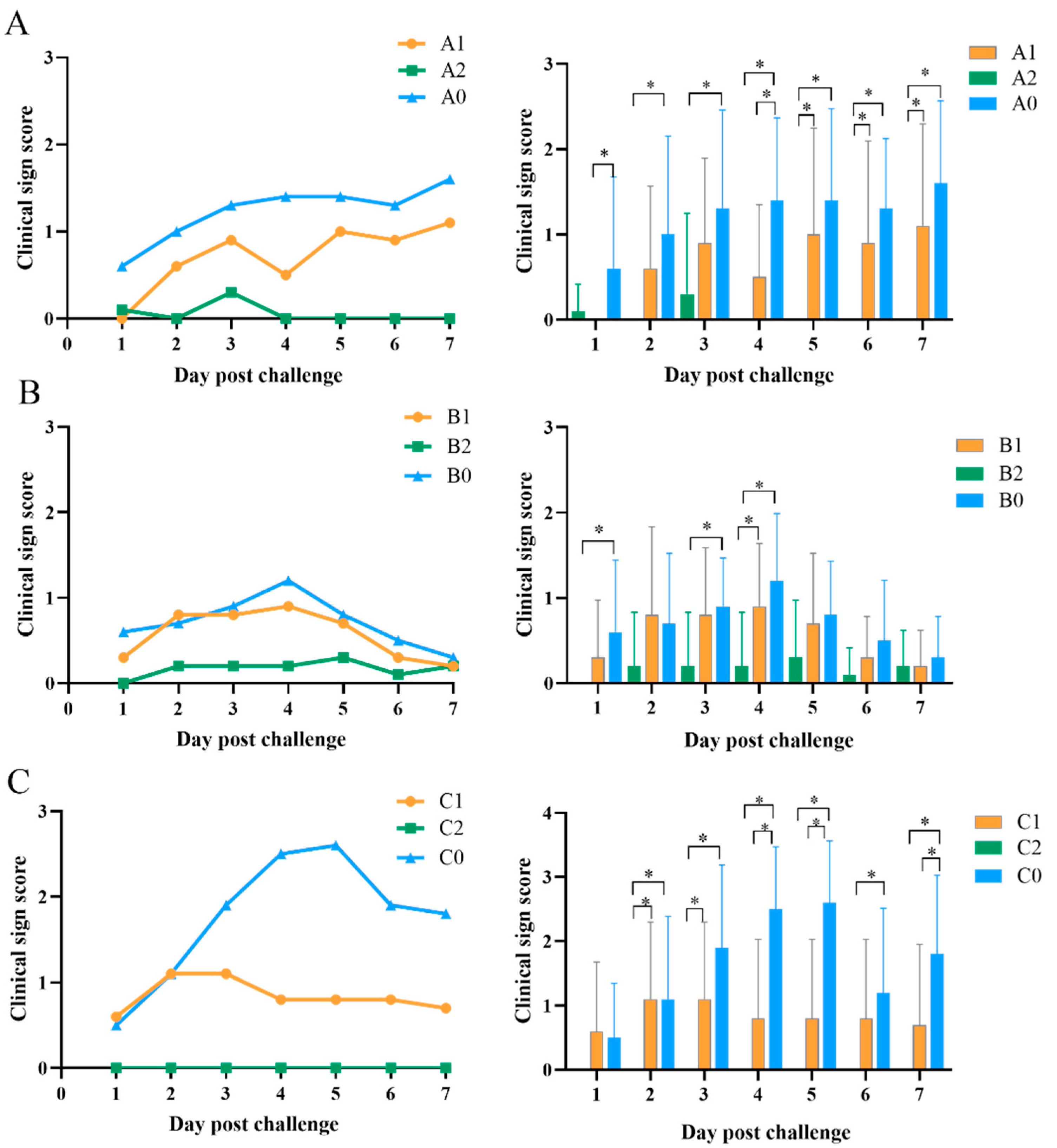
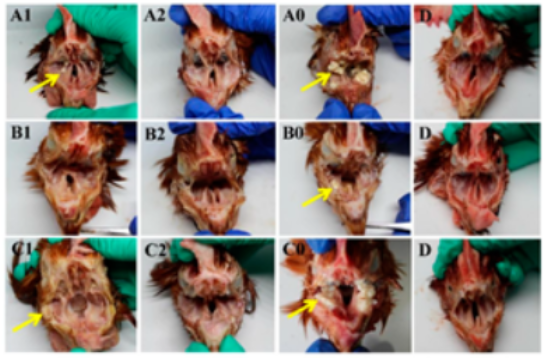
2.6. Clinical Scoring and Necropsy
2.7. Av. paragallinarum Quantification by Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antibody Titers Detected by Hemagglutination Inhibition Test
3.2. Clinical Sign Score
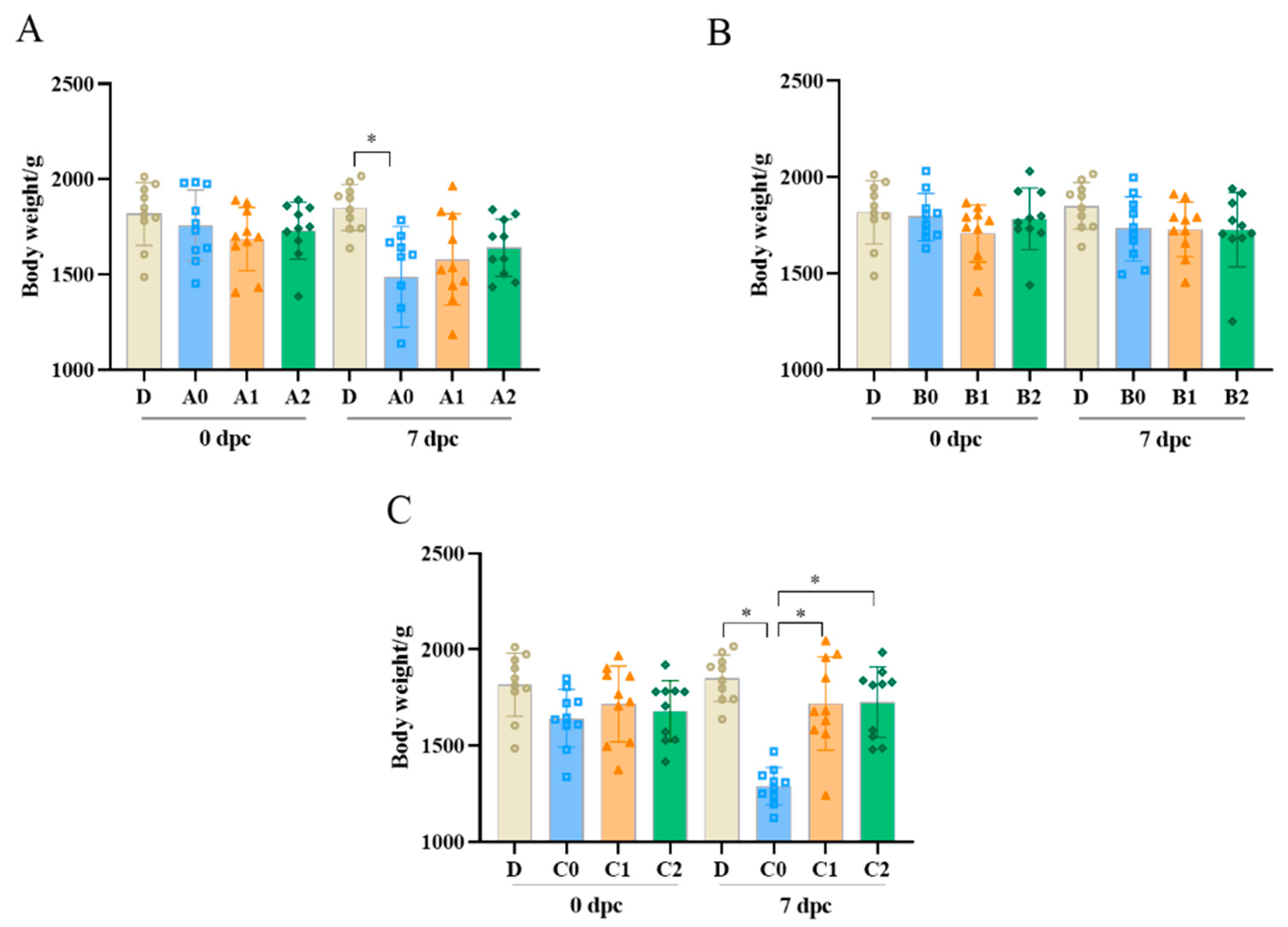
3.3. Body Weight
3.4. Egg Production
3.5. Pathological Changes of Infraorbital Sinus and Trachea
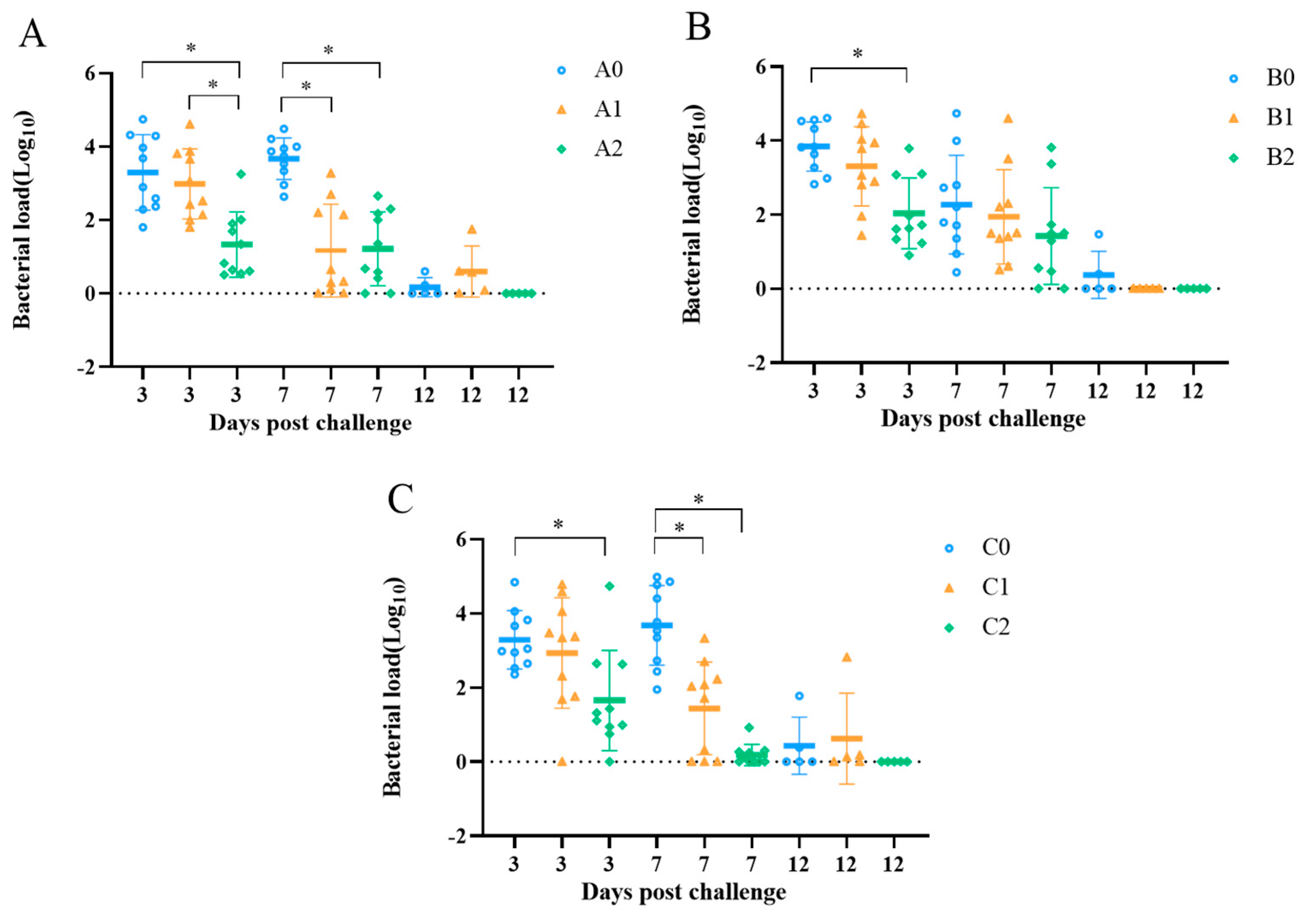
3.6. Bacterial Shedding Quantification
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blackall, P.J. The avian haemophili. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1989, 2, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackall, P.J.; Christensen, H.; Beckenham, T.; Blackall, L.L.; Bisgaard, M. Reclassification of Pasteurella gallinarum, [Haemophilus] paragallinarum, Pasteurella avium and Pasteurella volantium as Avibacterium gallinarum gen. nov., comb. nov., Avibacterium paragallinarum comb. nov., Avibacterium avium comb. nov. and Avibacterium volantium comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55 Pt 1, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blackall, P.J.; Soriano-Vargas, E. Infectious coryza and related bacterial infections. In Diseases of Poultry; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 890–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, S.; Hess, M.; Hess, C. Coinfection of Avibacterium paragallinarum and Gallibacterium anatis in Specific-Pathogen-Free Chickens Complicates Clinical Signs of Infectious Coryza, Which Can Be Prevented by Vaccination. Avian Dis. 2017, 61, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispo, M.; Blackall, P.; Khan, A.; Shivaprasad, H.L.; Clothier, K.; Sentíes-Cué, C.G.; Cooper, G.; Blakey, J.; Pitesky, M.; Mountainspring, G.; et al. Characterization of an Outbreak of Infectious Coryza (Avibacterium paragallinarum) in Commercial Chickens in Central California. Avian Dis. 2019, 63, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Erasto, V.; Falconi-Agapito, F.; Luna-Galaz, G.A.; Saravia, L.E.; Montalvan-Avalos, A.; Soriano-Vargas, E.E.; Fernández-Díaz, M. Coinfection of Avibacterium paragallinarum and Ornithobacterium rhinotracheale in Chickens from Peru. Avian Dis. 2016, 60, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, R.A.; Da Silva, A.P.; Egaña-Labrin, S.; Stoute, S.; Kern, C.; Zhou, H.; Cutler, G.; Corsiglia, C. Infectious Coryza: Persistence, Genotyping, and Vaccine Testing. Avian Dis. 2020, 64, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispo, M.; Sentíes-Cué, C.G.; Cooper, G.L.; Mountainspring, G.; Corsiglia, C.; Bickford, A.A.; Stoute, S.T. Otitis and meningoencephalitis associated with infectious coryza (Avibacterium paragallinarum) in commercial broiler chickens. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyuni, A.; Tabbu, C.R.; Artanto, S.; Setiawan, D.C.B.; Rajaguguk, S.I. Isolation, identification, and serotyping of Avibacterium paragallinarum from quails in Indonesia with typical infectious coryza disease symptoms. Vet. World 2018, 11, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Welchman, D.B.; King, S.A.; Wragg, P.; Wood, A.M.; Irvine, R.M.; Pepper, W.J.; Dijkman, R.; de Wit, J.J. Infectious coryza in chickens in Great Britain. Vet. Rec. 2010, 167, 912–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.V.; Mishra, D.; Mane, D.V. 16S ribosomal RNA sequencing and molecular serotyping of Avibacterium paragallinarum isolated from Indian field conditions. Vet. World 2017, 10, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Xie, S.; Li, X.; Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Boucher, C.E.; Chen, X. Selection of Avibacterium paragallinarum Page serovar B strains for an infectious coryza vaccine. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2018, 199, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X. Isolation, Serovar Identification, and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Avibacterium paragallinarum from Chickens in China from 2019 to 2020. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Page, L.A. Haemophilus infections in chickens. I. Characteristics of 12 Haemophilus isolates recovered from diseased chickens. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1962, 23, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Page, L.A.; Rosenwald, A.S.; Price, F.C. Haemophilus infections in chickens. IV. Results of laboratory and fieldtrials of formalinized bacterins for the prevention of disease caused by Haemophilus gallinarum. Avian Dis. 1963, 7, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, K.; Sawata, A.; Nakai, T.; Matsumoto, M. Serological classification of Haemophilus paragallinarum with a hemagglutinin system. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1983, 17, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackall, P.J.; Eaves, L.E.; Rogers, D.G. Proposal of a new serovar and altered nomenclature for Haemophilus paragallinarum in the Kume hemagglutinin scheme. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 1185–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackall, P.J. Infectious coryza: Overview of the disease and new diagnostic options. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, E.V.; Garduño, M.L.; Téllez, G.; Rosas, P.F.; Suárez-Güemes, F.; Blackall, P.J. Cross-protection study of the nine serovars of Haemophilus paragallinarum in the Kume haemagglutinin scheme. Avian Pathol. 2004, 33, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Blackall, P.J.; Takigami, S.; Iritani, Y.; Hayashi, Y. Immunogenicity of Haemophilus paragallinarum serovar B strains. Avian Dis. 1991, 35, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, A.A.; van den Berg, K.; Malo, A. Efficacy of a new tetravalent coryza vaccine against emerging variant type B strains. Avian Pathol. 2003, 32, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Erasto, V.; Fernández-Rosas, P.; Negrete-Abascal, E.; Salazar-García, F.; Blackall, P.J.; Soriano-Vargas, E. Genotyping, pathogenicity, and immunogenicity of Avibacterium paragallinarum serovar B-1 isolates from the Americas. Avian Dis. 2014, 58, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Huang, X.; Xu, M.; Feng, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, G. Characterization of emergent Avibacterium paragallinarum strains and the protection conferred by infectious coryza vaccines against them in China. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 6463–6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Miflin, J.K.; Zhang, P.; Blackall, P.J. Development and application of DNA probes and PCR tests for Haemophilus paragallinarum. Avian Dis. 1996, 40, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragg, R. Virulence of South African isolates of Haemophilus paragallinarum. Part 1: NAD-dependent field isolates. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2002, 69, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, H.; Zhu, W.; Sun, H.; He, Y.; Shao, Q.; Blackall, P.J. Safety and efficacy studies on trivalent inactivated vaccines against infectious coryza. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 158, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Chen, X.; Xu, F.; Sun, H. Validation of Reference Genes for Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Analysis of Avibacterium paragallinarum. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, K.; Sawata, A.; Nakase, Y. Relationship between protective activity and antigen structure of Haemophilus paragallinarum serotypes 1 and 2. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1980, 41, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, M.; Hirayama, N.; Makie, H.; Ohta, S. Production, characterization and protective effect of monoclonal antibodies to Haemophilus paragallinarum serotype A. Vet. Microbiol. 1991, 27, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Erasto, V.; Maruri-Esteban, E.; Trujillo-Ruíz, H.H.; Talavera-Rojas, M.; Blackall, P.J.; Soriano-Vargas, E. Protection Conferred by Infectious Coryza Vaccines Against Emergent Avibacterium paragallinarum Serovar C-1. Avian Dis. 2015, 59, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Romo, F.; Ortiz, A.M.; Blackall, P.J. The vaccination-challenge trial: The gold standard test to evaluate the protective efficacy of infectious coryza vaccines. Avian Pathol. 2008, 37, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, R.; Baba, S.; Ushijima, T.; Kino, Y.; Honda, T.; Mizokami, H.; Sakaguchi, M. Development of a recombinant vaccine against infectious coryza in chickens. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 94, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.S.; Kim, J.N.; Jeon, E.O.; Lee, H.R.; Koo, B.S.; Min, K.C.; Lee, S.B.; Bae, Y.J.; Mo, J.S.; Cho, S.H.; et al. The current epidemiological status of infectious coryza and efficacy of PoulShot Coryza in specific pathogen-free chickens. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 17, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, T.A.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Stinn, J.P.; Hayes, M.D.; Xin, H. Environmental assessment of three egg production systems—Part II. Ammonia, greenhouse gas, and particulate matter emissions. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, D.; Ma, H.; Liu, K.; Atilgan, A.; Xin, H. Environmental assessment of three egg production systems—Part III: Airborne bacteria concentrations and emissions. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Shepherd, T.A.; Li, H.; Xin, H. Environmental assessment of three egg production system—Part I: Monitoring system and indoor air quality. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 518–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Groups | Number of Chickens | Times of Vaccination | Age of Vaccination | Strain for Challenge | Age of Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 10 | 1 | 110 d | 2019−HB65 | 130 d |
| B1 | 10 | 1 | 110 d | 2019−HB68 | 130 d |
| C1 | 10 | 1 | 110 d | 2020−JS80 | 130 d |
| A2 | 10 | 2 | 53 d and 110 d | 2019−HB65 | 130 d |
| B2 | 10 | 2 | 53 d and 110 d | 2019−HB68 | 130 d |
| C2 | 10 | 2 | 53 d and 110 d | 2020−JS80 | 130 d |
| A0 | 10 | / | / | 2019−HB65 | 130 d |
| B0 | 10 | / | / | 2019−HB68 | 130 d |
| C0 | 10 | / | / | 2020−JS80 | 130 d |
| D | 10 | / | / | / | / |
| Groups | 7 dpc | 14 dpc |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | 15.71 ± 12.94 a | 20.00 ± 15.12 b |
| A2 | 28.57 ± 15.52 | 25.71 ± 20.60 |
| A0 | 15.71 ± 12.94 a | 6.29 ± 8.78 b |
| B1 | 30.00 ± 16.90 | 22.86 ± 12.78 |
| B2 | 45.71 ± 11.78 | 22.86 ± 16.66 |
| B0 | 32.86 ± 12.78 | 22.86 ± 7.00 |
| C1 | 24.29 ± 10.50 | 24.29 ± 15.91 |
| C2 | 30.00 ± 7.56 | 37.14 ± 16.66 |
| C0 | 11.43 ± 9.90 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 b |
| D | 37.14 ± 13.85 | 34.29 ± 9.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, M.; Liu, D.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Y.; Tan, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X. The Protective Efficacy of an Inactivated Vaccine against Avibacterium paragallinarum Field Isolates. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9090458
Guo M, Liu D, Xu H, Zhang H, Jin Y, Tan H, Wu Y, Zhang X. The Protective Efficacy of an Inactivated Vaccine against Avibacterium paragallinarum Field Isolates. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(9):458. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9090458
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Mengjiao, Donghui Liu, Hengli Xu, Hao Zhang, Yikun Jin, Huihui Tan, Yantao Wu, and Xiaorong Zhang. 2022. "The Protective Efficacy of an Inactivated Vaccine against Avibacterium paragallinarum Field Isolates" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 9: 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9090458
APA StyleGuo, M., Liu, D., Xu, H., Zhang, H., Jin, Y., Tan, H., Wu, Y., & Zhang, X. (2022). The Protective Efficacy of an Inactivated Vaccine against Avibacterium paragallinarum Field Isolates. Veterinary Sciences, 9(9), 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9090458







