Identification of Changes in Rumination Behavior Registered with an Online Sensor System in Cows with Subclinical Mastitis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Location and Animals
2.3. Experiment Design
2.4. Measurements
2.5. Periods of Measurements
2.6. Data Analysis and Statistics
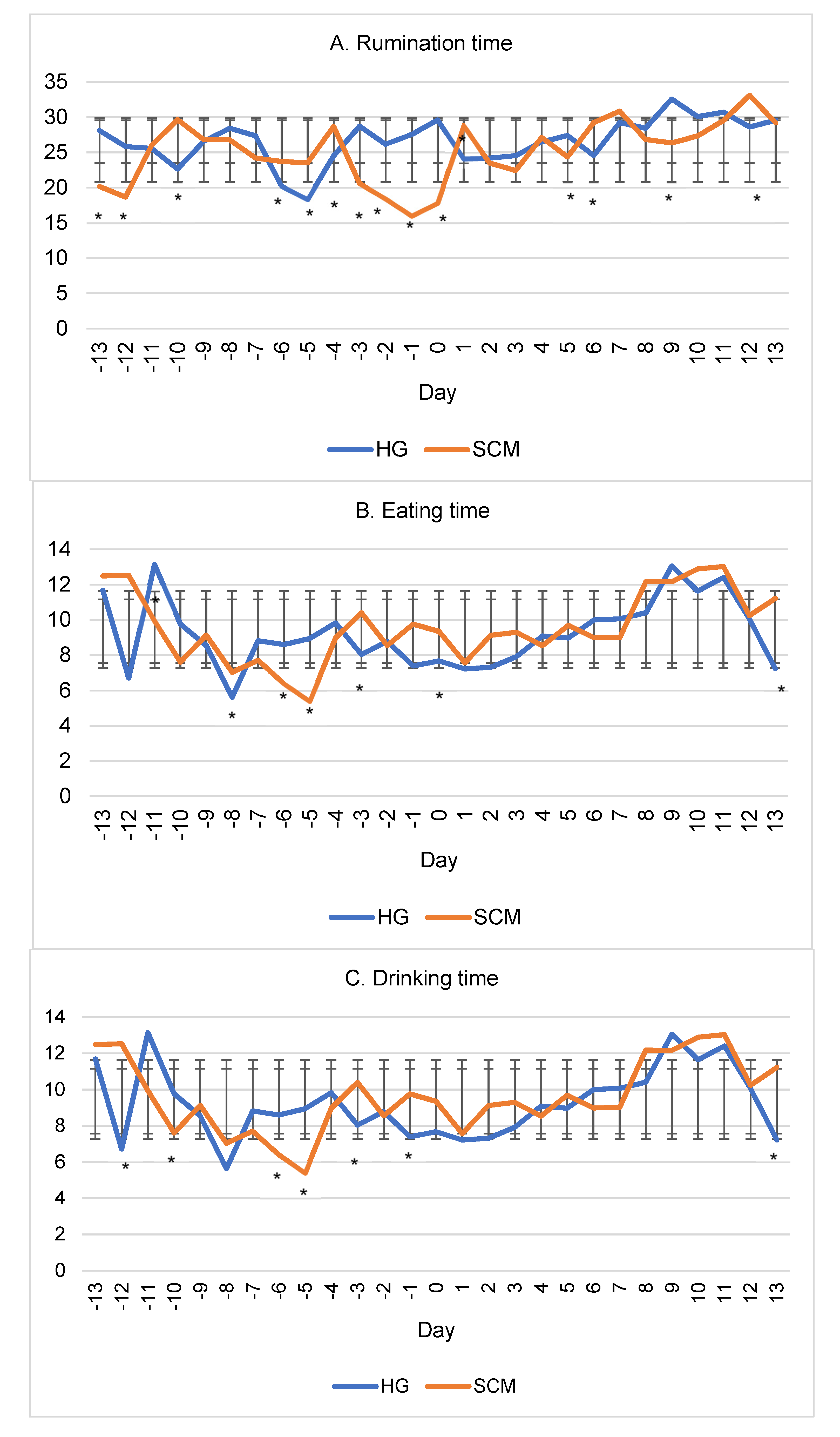
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Etiologia Das Mastites: Pesquisa de Micro-Organismos Da Classe Mollicutes|Veterinária e Zootecnia. Available online: https://rvz.emnuvens.com.br/rvz/article/view/41 (accessed on 6 August 2022).
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; Wen, X.; Ran, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Qi, Y.; Xue, N. Prevalence of Subclinical Mastitis among Dairy Cattle and Associated Risks Factors in China during 2012–2021: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022, 148, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, P.R.F.; Middleton, J.R. Methods for Diagnosing Mastitis. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. Pract. 2018, 34, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, K.A.E.; Sparks, L.G.; Lyman, R.L.; Washburn, S.P.; Anderson, K.L. Comparisons of Milk Quality on North Carolina Organic and Conventional Dairies. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 6753–6762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballou, M.A. Growth and development symposium: Inflammation: Role in the Etiology and Pathophysiology of Clinical Mastitis in Dairy Cows. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, M.R.; Peñagaricano, F.; Santos, J.E.P.; DeVries, T.J.; McBride, B.W.; Ribeiro, E.S. Long-Term Effects of Postpartum Clinical Disease on Milk Production, Reproduction, and Culling of Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 11701–11717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viguier, C.; Arora, S.; Gilmartin, N.; Welbeck, K.; O’Kennedy, R. Mastitis Detection: Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatun, M.; Clark, C.E.F.; Lyons, N.A.; Thomson, P.C.; Kerrisk, K.L.; García, S.C. Early Detection of Clinical Mastitis from Electrical Conductivity Data in an Automatic Milking System. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2017, 57, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.P.; Luoreng, Z.M.; Zan, L.S.; Raza, S.H.A.; Li, F.; Li, N.; Liu, S. Expression Patterns of MiR-146a and MiR-146b in Mastitis Infected Dairy Cattle. Mol. Cell. Probes 2016, 30, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutten, C.J.; Velthuis, A.G.J.; Steeneveld, W.; Hogeveen, H. Invited Review: Sensors to Support Health Management on Dairy Farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 1928–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukas, J.M.; Reneau, J.K.; Wallace, R.L.; De Vries, A. A Study of Methods for Evaluating the Success of the Transition Period in Early-Lactation Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, M.T.M.; LeBlanc, S.J.; Pajor, E.A.; Wright, T.C.; DeVries, T.J. Behavior and Productivity of Cows Milked in Automated Systems before Diagnosis of Health Disorders in Early Lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4343–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stangaferro, M.L.; Wijma, R.; Caixeta, L.S.; Al-Abri, M.A.; Giordano, J.O. Use of Rumination and Activity Monitoring for the Identification of Dairy Cows with Health Disorders: Part III. Metritis. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 7422–7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McArt, J.A.A.; Nydam, D.V.; Oetzel, G.R. Epidemiology of Subclinical Ketosis in Early Lactation Dairy Cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 5056–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reis, E.M.B.; Lopes, M.A. Métodos automatizados de diagnóstico de mastite em vacas leiteiras: Uma revisão. Arq. Ciênc. Vet. Zool. UNIPAR 2014, 17, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beauchemin, K.A. Invited Review: Current Perspectives on Eating and Rumination Activity in Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4762–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calamari, L.; Soriani, N.; Panella, G.; Petrera, F.; Minuti, A.; Trevisi, E. Rumination Time around Calving: An Early Signal to Detect Cows at Greater Risk of Disease. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 3635–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.M.; Sharpe, K.T.; Heins, B.J. Evaluation of the RumiWatch System as a Benchmark to Monitor Feeding and Locomotion Behaviors of Grazing Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 3736–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaissa, S.; Tuyttens, F.A.M.; Plets, D.; Cattrysse, H.; Martens, L.; Vandaele, L.; Joseph, W.; Sonck, B. Classification of Ingestive-Related Cow Behaviours Using RumiWatch Halter and Neck-Mounted Accelerometers. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2019, 211, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zehner, N.; Umstätter, C.; Niederhauser, J.J.; Schick, M. System Specification and Validation of a Noseband Pressure Sensor for Measurement of Ruminating and Eating Behavior in Stable-Fed Cows. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 136, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antanaitis, R.; Juozaitienė, V.; Televičius, M.; Malašauskienė, D.; Urbutis, M.; Baumgartner, W. Relation of Subclinical Ketosis of Dairy Cows with Locomotion Behaviour and Ambient Temperature. Animals 2020, 10, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antanaitis, R.; Juozaitienė, V.; Jonike, V.; Baumgartner, W.; Paulauskas, A. Milk Lactose as a Biomarker of Subclinical Mastitis in Dairy Cows. Animals 2021, 11, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielen, M.; Schukken, Y.H.; Brand, A.; Deluyker, H.A.; Maatje, K. Detection of Subclinical Mastitis from On-Line Milking Parlor Data. J. Dairy Sci. 1995, 78, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaaod, M.; Niederhauser, J.J.; Beer, G.; Zehner, N.; Schuepbach-Regula, G.; Steiner, A. Development and Validation of a Novel Pedometer Algorithm to Quantify Extended Characteristics of the Locomotor Behavior of Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 6236–6242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chagunda, M.G.; Larsen, T.; Bjerring, M.; Ingvartsen, K.L. L-Lactate Dehydrogenase and N-Acetyl-β-D-Glucosaminidase Activities in Bovine Milk as Indicators of Non-Specific Mastitis. J. Dairy Res. 2006, 73, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, E.I.; LeBlanc, S.J.; McBride, B.W.; Duffield, T.F.; DeVries, T.J. Association of Rumination Time with Subclinical Ketosis in Transition Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5604–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weary, D.M.; Huzzey, J.M.; von Keyserlingk, M.A.G. Board-invited review: Using Behavior to Predict and Identify Ill Health in Animals1. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Boever, J.L.; Andries, J.I.; De Brabander, D.L.; Cottyn, B.G.; Buysse, F.X. Chewing Activity of Ruminants as a Measure of Physical Structure—A Review of Factors Affecting It. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1990, 27, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Keyserlingk, M.A.G.; Weary, D.M. Review: Feeding Behaviour of Dairy Cattle: Meaures and Applications. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 90, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.P.; Vieira, L.V.; Barbosa, A.A.; Marins, L.; Corrêa, M.N.; Pino, F.A.B.D.; Brauner, C.C.; Rabassa, V.R.; Feijó, J.d.O.; Schmitt, E. Use of the Rumination Profile Through Collar Sensors for Mastitis Diagnosis in Dairy Cows. Acta Sci. Vet. 2021, 49, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gáspárdy, A.; Efrat, G.; Bajcsy, Á.; Fekete, S. Electronic Monitoring of Rumination Activity as an Indicator of Health Status and Production Traits in High-Yielding Dairy Cows. Acta Vet. Hung. 2014, 62, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watt, L.J.; Clark, C.E.F.; Krebs, G.L.; Petzel, C.E.; Nielsen, S.; Utsumi, S.A. Differential Rumination, Intake, and Enteric Methane Production of Dairy Cows in a Pasture-Based Automatic Milking System. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 7248–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.S.; Tranchina, D.; Ohta, Y.; Flajnik, M.F.; Hsu, E. Hypermutation in Shark Immunoglobulin Light Chain Genes Results in Contiguous Substitutions. Immunity 2002, 16, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soriani, N.; Trevisi, E.; Calamari, L. Relationships between Rumination Time, Metabolic Conditions, and Health Status in Dairy Cows during the Transition Period1. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 4544–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.D.P.; Silveira, I.D.B.; Fischer, V. Impact of Subclinical and Clinical Mastitis on Sensitivity to Pain of Dairy Cows. Animal 2015, 9, 2024–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- González, L.A.; Tolkamp, B.J.; Coffey, M.P.; Ferret, A.; Kyriazakis, I. Changes in Feeding Behavior as Possible Indicators for the Automatic Monitoring of Health Disorders in Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dollinger, J.; Kaufmann, O. Feeding Behaviour in Dairy Cows with and without the Influence of Clinical Diseases or Subclinical Disorders. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2013, 56, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kume, S.; Nonaka, K.; Oshita, T.; Kozakai, T. Evaluation of Drinking Water Intake, Feed Water Intake and Total Water Intake in Dry and Lactating Cows Fed Silages. Livest. Sci. 2010, 128, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tolkamp, B.J.; D’Eath, R.B. Hunger Associated with Restricted Feeding Systems. In Nutrition and the Welfare of Farm Animals; Phillips, C.J.C., Ed.; Animal Welfare; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 11–27. ISBN 978-3-319-27356-3. [Google Scholar]
- Huzzey, J.M.; DeVries, T.J.; Valois, P.; von Keyserlingk, M.A.G. Stocking Density and Feed Barrier Design Affect the Feeding and Social Behavior of Dairy Cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siivonen, J.; Taponen, S.; Hovinen, M.; Pastell, M.; Lensink, B.J.; Pyörälä, S.; Hänninen, L. Impact of Acute Clinical Mastitis on Cow Behaviour. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2011, 132, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano-Galarza, C.; Gibbons, J.; Wagner, S.; de Passillé, A.M.; Rushen, J. Behavioral Changes in Dairy Cows with Mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 6994–7002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jadhav, P.V.; Das, D.N.; Suresh, K.P.; Shome, B.R. Threshold Somatic Cell Count for Delineation of Subclinical Mastitis Cases. Vet. World 2018, 11, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madouasse, A.; Huxley, J.N.; Browne, W.J.; Bradley, A.J.; Green, M.J. Somatic Cell Count Dynamics in a Large Sample of Dairy Herds in England and Wales. Prev. Vet. Med. 2010, 96, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhoudt, A.; van Hees-Huijps, K.; van Knegsel, A.T.M.; Sampimon, O.C.; Vernooij, J.C.M.; Nielen, M.; van Werven, T. Effects of Reduced Intramammary Antimicrobial Use during the Dry Period on Udder Health in Dutch Dairy Herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3248–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lipkens, Z.; Piepers, S.; De Visscher, A.; De Vliegher, S. Evaluation of Test-Day Milk Somatic Cell Count Information to Predict Intramammary Infection with Major Pathogens in Dairy Cattle at Drying Off. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 4309–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, L.; Piccioli-Cappelli, F.; Lopreiato, V.; Lovotti, G.; Arrigoni, N.; Minuti, A.; Trevisi, E. Drying-off Cows with Low Somatic Cell Count with or without Antibiotic Therapy: A Pilot Study Addressing the Effects on Immunometabolism and Performance in the Subsequent Lactation. Livest. Sci. 2021, 254, 104740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reith, S.; Brandt, H.; Hoy, S. Simultaneous Analysis of Activity and Rumination Time, Based on Collar-Mounted Sensor Technology, of Dairy Cows over the Peri-Estrus Period. Livest. Sci. 2014, 170, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, C.; Michie, C.; Hamilton, A.; Tachtatzis, C.; Andonovic, I.; Gilroy, M. Detecting Heat Stress in Dairy Cattle Using Neck-Mounted Activity Collars. Agriculture 2020, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müschner-Siemens, T.; Hoffmann, G.; Ammon, C.; Amon, T. Daily Rumination Time of Lactating Dairy Cows under Heat Stress Conditions. J. Therm. Biol. 2020, 88, 102484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeni, F.; Galli, A. Monitoring Cow Activity and Rumination Time for an Early Detection of Heat Stress in Dairy Cow. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2017, 61, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antanaitis, R.; Juozaitienė, V.; Urbonavičius, G.; Malašauskienė, D.; Televičius, M.; Urbutis, M.; Baumgartner, W. Impact of Lameness on Attributes of Feeding Registered with Noseband Sensor in Fresh Dairy Cows. Agriculture 2021, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Rumination time (RT) | Time spent on ruminating chews, including chewing breaks of up to 5 s |
| Eating time (ET) | Time spent chewing food, including breaks of up to 5 s |
| Drinking time (DT) | Time spent drinking, including delays between gulps of up to 5 s |
| Rumination chews (RC) | Molars chewing during rumination for mechanical reduction of regurgitated materials into smaller bits |
| Eating chews (EC) | Total number of trepidation bites and mastication chews made when eating |
| Drinking gulps (DG) | Total amount of gulps taken while drinking |
| Bolus (B) | Total amount of gulps taken while drinking |
| RumiWatch NoseBand Indicator | HG | SCM |
|---|---|---|
| Period 1 (−13–0 days) | ||
| Mean ± standard deviation | Mean ± standard deviation | |
| Rumination time (min/h) | 25.70 ±2.02 a | 22.97 ± 1.99 b |
| Eating time (min/h) | 8.87 ± 1.94 a | 8.91 ± 2.07 a |
| Drinking time (min/h) | 1.24 ± 0.20 a | 1.18 ± 0.18 b |
| Rumination chews (n/h) | 1704.54 ± 235.67 a | 1501.58 ± 276.92 b |
| Eating chews (n/h) | 504.89 ± 88.02 a | 522.19 ± 127.073 a |
| Drinking gulps (n/h) | 164.87 ± 40.03 a | 168.03 ± 48.927 a |
| Bolus (n/rumination) | 26.46 ± 1.97 a | 25.90 ± 2.30 a |
| Activity | 66.91 ± 2.03 a | 67.58 ± 2.77 a |
| Downtime | 34.01 ± 1.05 a | 34.36 ± 2.54 a |
| Uptime | 31.37 ± 1.26 a | 33.16 ± 2.01 b |
| Average temperature | 11.68 ± 0.99 a | 11.62 ± 1.01 a |
| Period 2 (1–13 days) | ||
| Mean ± standard deviation | Mean ± standard deviation | |
| Rumination time (min/h) | 27.74 ± 2.03 a | 27.59 ± 0.79 a |
| Eating time (min/h) | 9.62 ± 1.91 a | 10.33 ± 1.79 a |
| Drinking time (min/h) | 1.17 ± 0.23 a | 1.07 ± 0.06 b |
| Rumination chews (n/h) | 1798.68 ± 184.91 a | 1776.95 ± 168.97 a |
| Eating chews (n/h) | 621.20 ± 151.34 a | 643.63 ± 113.18 a |
| Drinking gulps (n/h) | 226.05 ± 64.61 a | 237.37 ± 67.44 a |
| Bolus (n/rumination) | 27.97 ± 3.114 a | 28.94 ± 2.70 a |
| Activity | 65.52 ± 2.32 a | 63.66 ± 2.44 a |
| Downtime | 32.17 ± 1.01 a | 35.68 ± 1.45 b |
| Uptime | 41.06 ± 2.58 a | 38.37 ± 1.61 b |
| Average temperature | 9.38 ± 0.72 a | 9.57 ± 0.56 a |
| Indicators | Rumination Time | Eating Time | Drinking Time | Rumination Chews | Eating Chews | Drinking Gulps | Bolus | Activity | DownTime | UpTime | Average Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rumination time | × | 0.276 ** | −0.100 ** | 0.933 ** | 0.318 ** | 0.340 ** | 0.935 ** | −0.460 ** | −0.008 | 0.118 ** | −0.353 ** |
| Eating time | −0.021 | × | −0.176 ** | 0.205 ** | 0.798 ** | 0.687 ** | 0.328 ** | −0.011 | 0.009 | 0.114 ** | −0.189 ** |
| Drinking time | −0.066 * | −0.037 | × | −0.087 * | −0.099 ** | −0.151 ** | −0.164 ** | −0.105 ** | 0.244 ** | −0.128 ** | 0.187 ** |
| Rumination chews | 0.779 ** | −0.037 | −0.119 ** | × | 0.259 ** | 0.249 ** | 0.881 ** | −0.533 ** | −0.066 * | 0.018 | −0.249 ** |
| Eating chews | 0.007 | 0.960 ** | −0.075 * | −0.016 | × | 0.875 ** | 0.330 ** | 0.114 ** | −0.077 | 0.201 ** | −0.288 ** |
| Drinking gulps | 0.010 | 0.777 ** | −0.076 * | 0.009 | 0.844 ** | × | 0.428 ** | 0.314 ** | −0.003 | 0.271 ** | −0.530 ** |
| Bolus | 0.766 ** | 0.025 | −0.150 ** | 0.699 ** | 0.031 | 0.133 ** | × | −0.406 ** | 0.088 ** | 0.004 | −0.407 ** |
| Activity | 0.498 ** | 0.290 ** | −0.088 ** | 0.490 ** | 0.270 ** | 0.306 ** | −0.580 ** | × | −0.203 ** | 0.009 | −0.191 ** |
| Downtime | 0.149 ** | −0.088 ** | −0.201 ** | 0.224 ** | 0.068 * | 0.047 | 0.215 ** | −0.006 | × | −0.100 ** | −0.020 |
| Uptime | 0.321 ** | −0.012 | 0.045 | 0.072 * | 0.092 | 0.167 ** | 0.081 * | 0.078 * | 0.036 | × | −0.235 ** |
| Average temperature | −0.139 ** | −0.569 ** | 0.127 ** | −0.342 ** | −0.658 ** | −0.747 ** | −0.329 ** | 0.003 | −0.077 * | 0.065* | × |
| Risk Indicators | Classes of Explanatory Variables | B | S.E. | Wald χ2 | df | p | OR (95% CI OR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rumination time | G0 ≤ 23.80 | 2.905 | 1.082 | 7.203 | 1 | 0.007 | 18.271 (8.756–31.117) |
| G1 > 23.80 | |||||||
| Rumination chews | G0 ≤ 1627.88 | −1.323 | 0.609 | 4.714 | 1 | 0.030 | 0.266 (0.081–0.879) |
| G1 > 1627.88 | |||||||
| Boluses | G0 ≤ 27.63 | 2.771 | 1.111 | 6.225 | 1 | 0.013 | 15.976 (7.248–30.223) |
| G1 > 27.63 | |||||||
| Constant | −2.283 | 1.113 | 4.208 | 1 | 0.040 | 0.102 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antanaitis, R.; Juozaitienė, V.; Malašauskienė, D.; Televičius, M.; Urbutis, M.; Rutkaukas, A.; Šertvytytė, G.; Baumgartner, W. Identification of Changes in Rumination Behavior Registered with an Online Sensor System in Cows with Subclinical Mastitis. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9090454
Antanaitis R, Juozaitienė V, Malašauskienė D, Televičius M, Urbutis M, Rutkaukas A, Šertvytytė G, Baumgartner W. Identification of Changes in Rumination Behavior Registered with an Online Sensor System in Cows with Subclinical Mastitis. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(9):454. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9090454
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntanaitis, Ramūnas, Vida Juozaitienė, Dovilė Malašauskienė, Mindaugas Televičius, Mingaudas Urbutis, Arūnas Rutkaukas, Greta Šertvytytė, and Walter Baumgartner. 2022. "Identification of Changes in Rumination Behavior Registered with an Online Sensor System in Cows with Subclinical Mastitis" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 9: 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9090454
APA StyleAntanaitis, R., Juozaitienė, V., Malašauskienė, D., Televičius, M., Urbutis, M., Rutkaukas, A., Šertvytytė, G., & Baumgartner, W. (2022). Identification of Changes in Rumination Behavior Registered with an Online Sensor System in Cows with Subclinical Mastitis. Veterinary Sciences, 9(9), 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9090454







