Ultrasonographical Assessment of Caudal Vena Cava Size through Different Views in Healthy Calves: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Point of Care Ultrasound Examination
2.3. POCUS Views
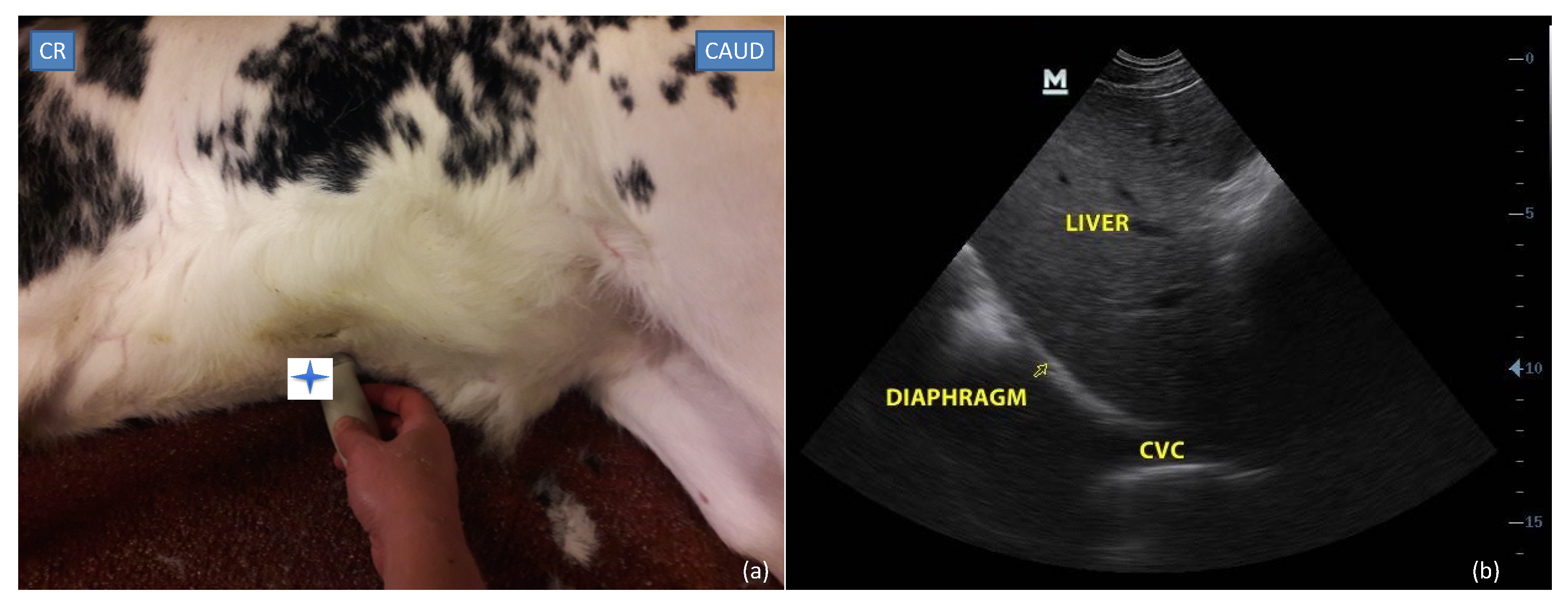
2.3.1. Subxiphoid Window
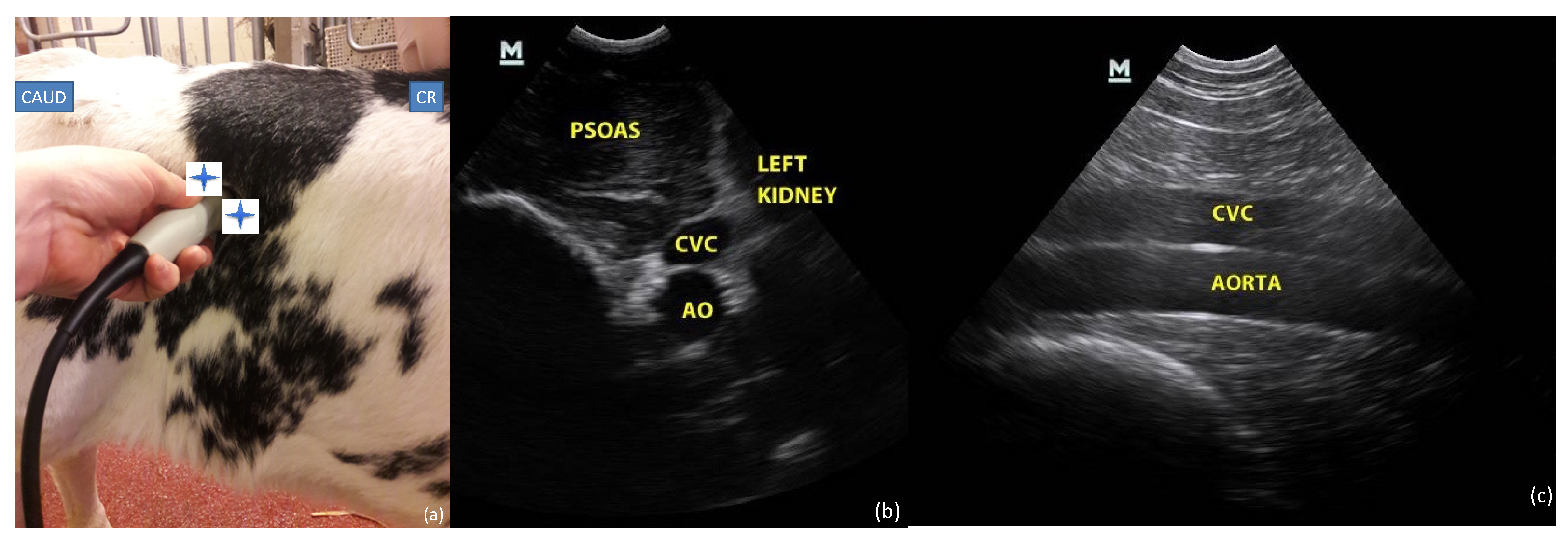
2.3.2. Paralumbar Window
2.4. Measurements
2.4.1. Subxiphoid Window
2.4.2. Paralumbar Transversal and Longitudinal View
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
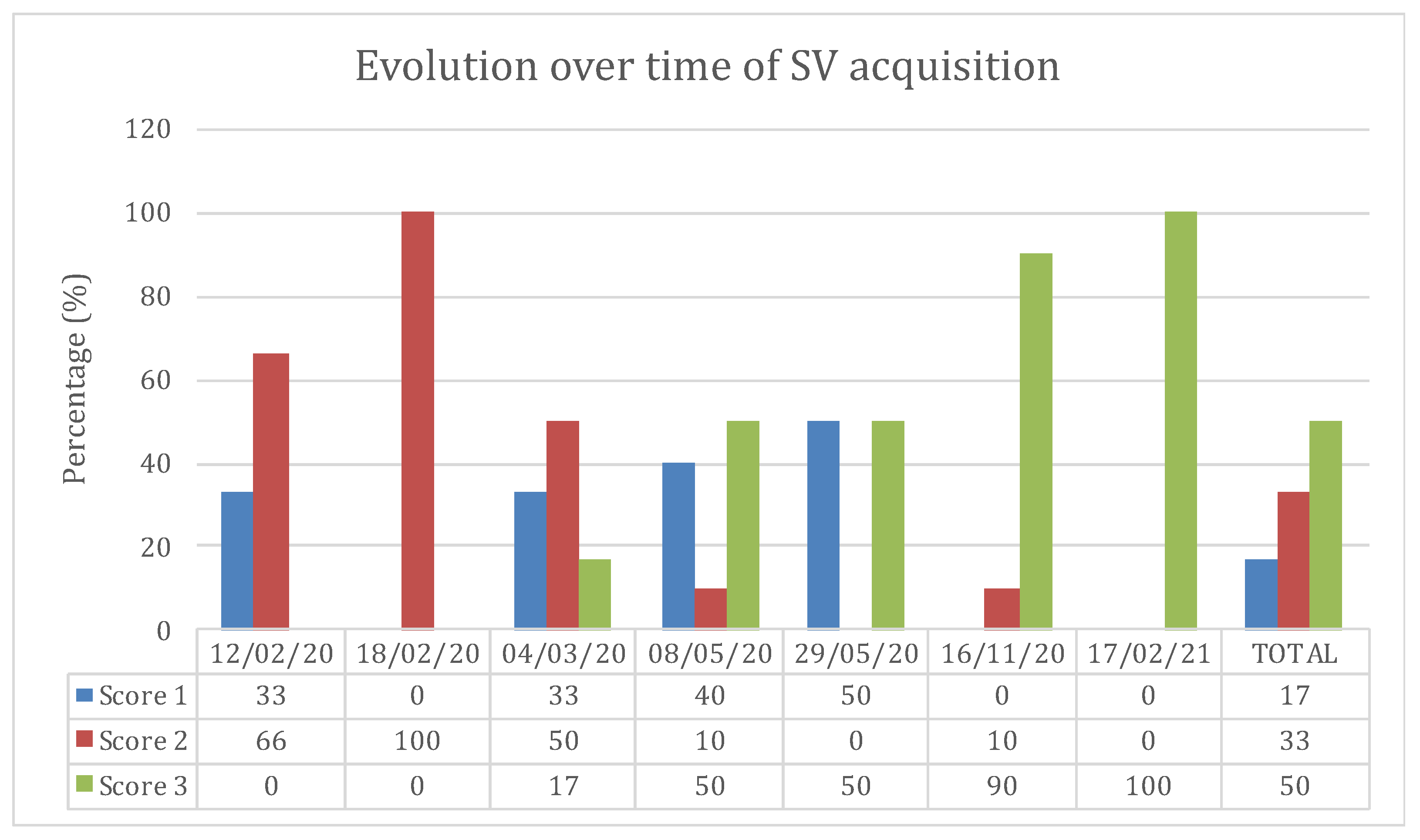
3.2. Intra- Interobserver Agreement
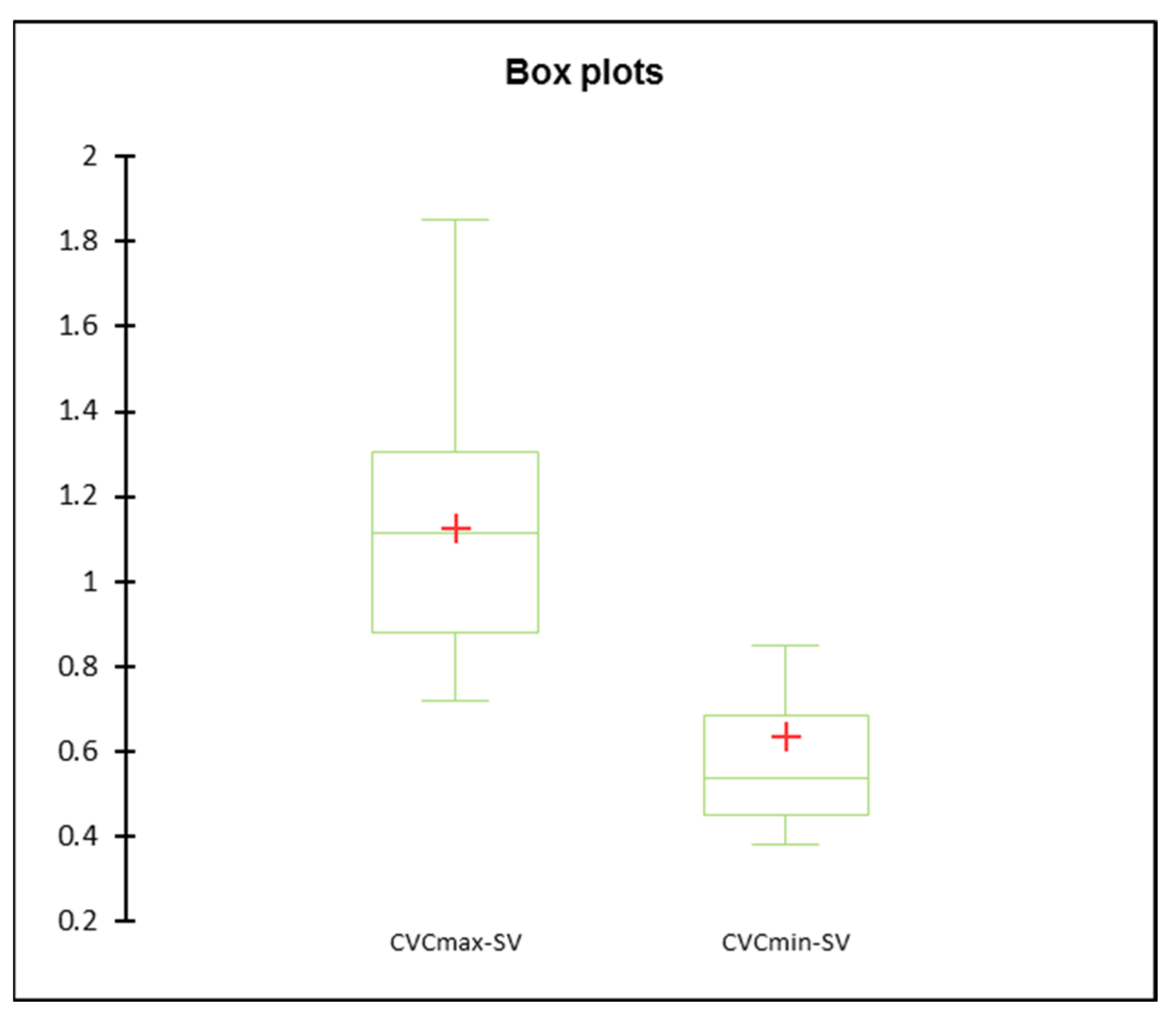
3.3. Point of Care Ultrasound Views and Measurements
3.3.1. Subxiphoid Window
3.3.2. Paralumbar Transversal and Longitudinal View
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fecteau, G.; Desrochers, A.; Francoz, D.; Nichols, S. Diagnostic Approach to the Acute Abdomen. Vet. Clin. N. Am.-Food Anim. Pract. 2018, 34, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulon, P.Y.; Desrochers, A. Surgical Abdomen of the Calf. Vet. Clin. N. Am.-Food Anim. Pract. 2005, 21, 101–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lausch, C.K.; Lorch, A.; Giertzuch, S.; Rieger, A.; Knubben-Schweizer, G.; Trefz, F.M. Prognostic Relevance of Pre- and Postoperative Plasma L-Lactate Measurements in Calves with Acute Abdominal Emergencies. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 1856–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constable, P.D.; Trefz, F.M.; Sen, I.; Berchtold, J.; Nouri, M.; Smith, G.; Grünberg, W. Intravenous and Oral Fluid Therapy in Neonatal Calves With Diarrhea or Sepsis and in Adult Cattle. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 603358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercolini, F.; Di Leo, V.; Bordin, G.; Melotti, R.; Sperotto, F.; Pettenazzo, A.; Amigoni, A.; Tosoni, A. Central Venous Pressure Estimation by Ultrasound Measurement of Inferior Vena Cava and Aorta Diameters in Pediatric Critical Patients: An Observational Study. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 22, e1–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, S.; Robel-Tillig, E. Index from Diameter of Inferior Vena Cava and Abdominal Aorta of Newborns—A Relevant Method for Evaluation of Hypovolemia. Z. Fur Geburtshilfe Und Neonatol. 2020, 224, 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.A.; Kwon, H.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Choi, Y.J. Comparison of Sonographic Inferior Vena Cava and Aorta Indexes during Fluid Administered in Children. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 36, 1529–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sänger, F.; Dorsch, R.; Hartmann, K.; Dörfelt, R. Ultrasonographic Assessment of the Caudal Vena Cava Diameter in Cats during Blood Donation. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2021, 24, 1098612X211028838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneghini, C.; Rabozzi, R.; Franci, P. Correlation of the Ratio of Caudal Vena Cava Diameter and Aorta Diameter with Systolic Pressure Variation in Anesthetized Dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 77, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciozda, W.; Kedan, I.; Kehl, D.W.; Zimmer, R.; Khandwalla, R.; Kimchi, A. The Efficacy of Sonographic Measurement of Inferior Vena Cava Diameter as an Estimate of Central Venous Pressure. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2016, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, B.D.; Schlader, Z.J.; Schaake, M.W.; O’Leary, M.C.; Hostler, D.; Lin, H.; St. James, E.; Lema, P.C.; Bola, A.; Clemency, B.M. Inferior Vena Cava Diameter Is an Early Marker of Central Hypovolemia during Simulated Blood Loss. Prehospital Emerg. Care 2020, 25, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, G.A. POINT: Should Acute Fluid Resuscitation Be Guided Primarily by Inferior Vena Cava Ultrasound for Patients in Shock? Yes. Chest 2017, 151, 531–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corl, K.A.; George, N.R.; Romanoff, J.; Levinson, A.T.; Chheng, D.B.; Merchant, R.C.; Levy, M.M.; Napoli, A.M. Inferior Vena Cava Collapsibility Detects Fluid Responsiveness among Spontaneously Breathing Critically-Ill Patients. J. Crit. Care 2017, 41, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preau, S.; Bortolotti, P.; Colling, D.; Dewavrin, F.; Colas, V.; Voisin, B.; Onimus, T.; Drumez, E.; Durocher, A.; Redheuil, A.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of the Inferior Vena Cava Collapsibility to Predict Fluid Responsiveness in Spontaneously Breathing Patients with Sepsis and Acute Circulatory Failure. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, e290–e297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Jung, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kwak, Y.H.; Kim, D.K.; Jung, J.H.; Chang, I.W.; Kim, K. Sonographic Aorta/IVC Cross-Sectional Area Index for Evaluation of Dehydration in Children. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 34, 1840–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnis, E.; Boysen, S.; Merveille, A.C.; Desquilbet, L.; Chalhoub, S.; Gommeren, K. Establishment of Reference Values of the Caudal Vena Cava by Fast-Ultrasonography through Different Views in Healthy Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1308–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.; Yoon, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Eom, K. Ultrasonographic Measurement of Caudal Vena Cava to Aorta Ratios for Determination of Volume Depletion in Normal Beagle Dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2018, 59, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultman, T.M.; Boysen, S.R.; Owen, R.; Yozova, I.D. Ultrasonographically Derived Caudal Vena Cava Parameters Acquired in a Standing Position and Lateral Recumbency in Healthy, Lightly Sedated Cats: A Pilot Study. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2021, 1098612X2110646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prete, C.; Freccero, F.; Lanci, A.; Hallowell, G.D.; Bullone, C.; Castagnetti, C.; Pasolini, M.P. Transabdominal Ultrasonographic Measurement of Caudal Vena Cava to Aorta Derived Ratios in Clinically Healthy Neonatal Foals. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuplin, M.C.; Romero, A.E.; Boysen, S.R. Influence of the Respiratory Cycle on Caudal Vena Cava Diameter Measured by Sonography in Healthy Foals: A Pilot Study. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braun, U.; Krüger, S. Ultrasonography of the Spleen, Liver, Gallbladder, Caudal Vena Cava and Portal Vein in Healthy Calves from Birth to 104 Days of Age. Acta Vet. Scand. 2013, 55, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orso, D.; Paoli, I.; Piani, T.; Cilenti, F.L.; Cristiani, L.; Guglielmo, N. Accuracy of Ultrasonographic Measurements of Inferior Vena Cava to Determine Fluid Responsiveness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 35, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnis, E.; Merveille, A.C.; Desquilbet, L.; Boysen, S.; Gommeren, K. Interobserver Agreement between Non-Cardiologist Veterinarians and a Cardiologist after a 6-Hour Training Course for Echographic Evaluation of Basic Echocardiographic Parameters and Caudal Vena Cava Diameter in 15 Healthy Beagles. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2019, 29, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kory, P. COUNTERPOINT: Should Acute Fluid Resuscitation Be Guided Primarily by Inferior Vena Cava Ultrasound for Patients in Shock? No. Chest 2017, 151, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gui, J.; Zhou, B.; Liu, J.; Ou, B.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Tang, W.; Luo, B.; Yang, Z. Impact of Body Characteristics on Ultrasound-Measured Inferior Vena Cava Parameters in Chinese Children. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kathuria, N.; Ng, L.; Saul, T.; Lewiss, R.E. The Baseline Diameter of the Inferior Vena Cava Measured by Sonography Increases with Age in Normovolemic Children. J. Ultrasound Med. 2015, 34, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenson, E.K.; Punn, R.; Ramsi, M.; Kache, S. A Retrospective Evaluation of Echocardiograms to Establish Normative Inferior Vena Cava and Aortic Measurements for Children Younger than 6 Years. J. Ultrasound Med. 2018, 37, 2225–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mannarino, S.; Bulzomì, P.; Codazzi, A.C.; Rispoli, G.A.; Tinelli, C.; De Silvestri, A.; Manzoni, F.; Chiapedi, S. Inferior Vena Cava, Abdominal Aorta, and IVC-to-Aorta Ratio in Healthy Caucasian Children: Ultrasound Z-Scores According to BSA and Age. J. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häggström, J.; Andersson, O.; Falk, T.; Nilsfors, L.; OIsson, U.; Kresken, J.G.; Höglund, K.; Rishniw, M.; Tidholm, A.; Ljungvall, I. Effect of Body Weight on Echocardiographic Measurements in 19,866 Pure-Bred Cats with or without Heart Disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lorenzo, R.A.; Morris, M.J.; Williams, J.B.; Haley, T.F.; Straight, T.M.; Holbrook-Emmons, V.L.; Medina, J.S. Does a Simple Bedside Sonographic Measurement of the Inferior Vena Cava Correlate to Central Venous Pressure? J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 42, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagdev, A.D.; Merchant, R.C.; Tirado-Gonzalez, A.; Sisson, C.A.; Murphy, M.C. Emergency Department Bedside Ultrasonographic Measurement of the Caval Index for Noninvasive Determination of Low Central Venous Pressure. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2010, 55, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, S.; Come, P.C.; McKay, R.G.; Ransil, B.J. Effects of Positional Changes on Inferior Vena Caval Size and Dynamics and Correlations with Right-Sided Cardiac Pressure. Am. J. Cardiol. 1987, 59, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panebianco, N.L.; Shofer, F.; Cheng, A.; Fischer, J.; Cody, K.; Dean, A.J. The Effect of Supine versus Upright Patient Positioning on Inferior Vena Cava Metrics. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 32, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelista, M.C.; Benito, J.; Monteiro, B.P.; Watanabe, R.; Doodnaught, G.M.; Pang, D.S.J.; Steagall, P.V. Clinical Applicability of the Feline Grimace Scale: Real-Time versus Image Scoring and the Influence of Sedation and Surgery. PeerJ 2020, 2020, e8967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cambournac, M.; Goy-Thollot, I.; Violé, A.; Boisvineau, C.; Pouzot-Nevoret, C.; Barthélemy, A. Sonographic Assessment of Volaemia: Development and Validation of a New Method in Dogs. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 59, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, U.; Krüger, S.; Hässig, M. Ultrasonographic Examination of the Reticulum, Rumen, Omasum and Abomasum during the First 100days of Life in Calves. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 95, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| POCUS Views | OBS1 | OBS2 | OBS3 | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OBS | REP | OBS/REP | |||||
| PV-long | Ao diameter (cm) | 1.17±0.03 | 1.15 ± 0.03 | 1.21 ± 0.03 | 0.45 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| CVC diameter (cm) | 1.06 ± 0.08 | 1.00 ± 0.12 | 0.94 ± 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.99 | 1.00 | |
| CVC/Ao diameter index | 0.91 ± 0.03 | 0.88 ± 0.03 | 0.77 ± 0.03 | 0.002 | 0.98 | 0.99 | |
| PV-trans | Ao area (cm2) | 0.91 ± 0.03 | 0.88 ± 0.03 | 0.77 ± 0.03 | 0.79 | 0.87 | 0.99 |
| CVC area (cm2) | 1.08 ± 0.03 | 1.02 ± 0.03 | 1.02 ± 0.03 | 0.41 | 0.61 | 0.99 | |
| CVC/Ao area index | 0.99 ± 0.04 | 0.86 ± 0.04 | 1.02 ± 0.04 | 0.006 | 0.98 | 1.00 | |
| SV | CVCmin (cm) | 0.33 ± 0.02 | 0.39 ± 0.02 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 0.92 |
| CVCmax (cm) | 0.74 ± 0.04 | 0.89 ± 0.04 | 0.85 ± 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| POCUS Views | Ao Diameter (cm) | CVC Diameter (cm) | CVC/Ao Diameter Index | Ao Area (cm2) | CVC Area (cm2) | CVC/Ao Area Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PV-long | 1.20 (1.09–1.35) | 0.86 ± 0.23 | 0.71 ± 0.22 | - | - | - |
| PV-trans | 1.25 (1.08–1.39) | - | - | 1.26 ± 0.39 | 1.06 ± 0.42 | 0.89 ± 0.34 |
| POCUS View | T1 | T2 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PV-long | Ao diameter (cm) | 1.09 ± 0.10 | 1.24 ± 0.14 | 0.0004 |
| CVC diameter (cm) | 0.92 ± 0.14 | 1.25 ± 0.24 | 0.00005 | |
| CVC/Ao diameter index | 0.84 ± 0.09 | 0.97 ± 0.19 | 0.009 | |
| PV-trans | Ao diameter (cm) | 1.13 ± 0.12 | 1.28 ± 0.13 | 0.00001 |
| Ao area (cm2) | 0.99 ± 0.23 | 1.05 ± 0.3 | 0.3269 | |
| CVC area (cm2) | 1.04 ± 0.35 | 1.55 ± 0.6 | 0.002 | |
| CVC/Ao area index | 1.05 ± 0.26 | 0.97 ± 0.19 | 0.002 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Casalta, H.; Busoni, V.; Eppe, J.; Grulke, S.; Merveille, A.-C.; Moula, N.; Gommeren, K. Ultrasonographical Assessment of Caudal Vena Cava Size through Different Views in Healthy Calves: A Pilot Study. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9070308
Casalta H, Busoni V, Eppe J, Grulke S, Merveille A-C, Moula N, Gommeren K. Ultrasonographical Assessment of Caudal Vena Cava Size through Different Views in Healthy Calves: A Pilot Study. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(7):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9070308
Chicago/Turabian StyleCasalta, Hélène, Valeria Busoni, Justine Eppe, Sigrid Grulke, Anne-Christine Merveille, Nassim Moula, and Kris Gommeren. 2022. "Ultrasonographical Assessment of Caudal Vena Cava Size through Different Views in Healthy Calves: A Pilot Study" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 7: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9070308
APA StyleCasalta, H., Busoni, V., Eppe, J., Grulke, S., Merveille, A.-C., Moula, N., & Gommeren, K. (2022). Ultrasonographical Assessment of Caudal Vena Cava Size through Different Views in Healthy Calves: A Pilot Study. Veterinary Sciences, 9(7), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9070308







