Abstract
Despite its high frequency and clinical relevance, the pathogenesis of canine pyometra remains poorly understood. The most accepted hypothesis is that bacteria involved ascend from the intestinal tract, causing the uterine infection. Extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) is the most frequent pathogen in canine pyometra, accounting for 57–100% of cases. The aim of the present study was to determine the frequency of phylogenetic groups and virulence factors in E. coli strains isolated from the uterine and rectal swabs of bitches with pyometra (n = 72) and from rectal swabs from healthy bitches fed commercial dry feed (n = 53) or a raw meat-based diet (RMBD; n = 38). A total of 512 strains of E. coli were isolated and divided into five categories according to the origin of the sample: 120 isolates from the uterine content of dogs with E. coli pyometra, 102 from the feces of bitches with E. coli pyometra, 75 from the feces of bitches without E. coli pyometra, 130 feces samples from healthy dogs fed commercial feed, and 85 feces samples from healthy dogs fed a raw meat-based diet. E. coli strains belonging to the B2 phylogroup and positive for virulence factor genes associated with adhesion (fimbriae type P [papC]) and production of toxins (α-hemolysin [hlyA] and uropathogenic specific protein [usp]) predominated in the uterine content and rectal swabs of bitches with E. coli pyometra. Interestingly, a lower growth rate of E. coli from the B2 phylogroup was observed in dogs fed a RMBD than in those fed commercial dry feed. The present study suggests that intestinal colonization by certain types of E. coli could be a risk factor for the occurrence of E. coli pyometra in bitches and that diet can influence intestinal colonization by such strains.
1. Introduction
Pyometra is the most frequently occurring reproductive disease in bitches, affecting up to 25% of uncastrated females [1,2]. The disease is characterized by bacterial infection of the uterus with local and systemic clinical manifestations that can lead to death [3,4,5]. However, despite its relevance, the pathogenesis of this disease remains poorly understood. It is believed that bacterial species causing pyometra ascend from the intestinal tract of females, causing infections [1,2,5,6].
Extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) is the most common pathogen involved in canine pyometra and has been reported in 57–100% of cases [1,2,6,7]. These isolates are phylogenetically and epidemiologically distinct from E. coli strains commonly found in intestinal commensals that cause diarrhea and other gastrointestinal disorders [8,9,10]. In canine pyometra, E. coli strains found in uterine contents are commonly associated with phylogroup B2 and less frequently with phylogroup D [11,12,13]. In contrast, commensal intestinal strains of E. coli in dogs are mostly classified into phylogenetic groups B1 and A [5,9,12]. In addition, E. coli recovered from pyometra have specific virulence factors, such as adhesins, toxins, iron acquisition systems, and protectins [7,14,15], which are commonly classified as endometrial pathogenic E. coli (EnPEC), a subgroup of the ExPEC pathotype. These virulence factors may confer a selective advantage over commensal strains [16], playing a key role in the development of canine pyometra [11,14,17] as well as in other extraintestinal infections in humans and animals [16,17,18].
Although the intestinal ascension of E. coli strains is currently the most accepted hypothesis in the pathogenesis of canine pyometra [1,2,7], no studies have evaluated the influence of the dog diet on the specific colonization of ExPEC strains. In the last decade, an increasing number of owners have been feeding their dogs and cats raw meat-based diets (RMBDs), instead of regular commercial dry feed [19]. Dogs fed an RMBD shed an increased amount of some pathogens in their feces, including Salmonella spp. and diarrheagenic E. coli [19,20,21]. However, specific virulence factors related to extraintestinal infections have not yet been investigated. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of phylogroups and virulence factors in E. coli isolates obtained from the uterine contents and feces of bitches with pyometra infection. In addition, we compared these E. coli isolates with those obtained from the feces of healthy dogs fed commercial dry feed or an RMBD to evaluate the possible influence of diet on colonization by E. coli strains.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
Three groups of bitches were sampled in the present study: dogs with pyometra (uterine and rectal swabs), healthy dogs fed commercial dry feed (rectal swab), and healthy dogs fed a RMBD (rectal swab). A total of 72 bitches with pyometra who underwent ovariohysterectomy (OH) surgery at the Veterinary Hospital of the Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (VH-UFMG) between January 2017 and December 2020 were included. Immediately following surgery, aspiration puncture of the uterine contents was performed and a swab was introduced into the rectal ampulla of the bitches. The samples were refrigerated at 4 °C until processing for a maximum of 24 h. Rectal swabs from 91 healthy dogs were included, of which 53 were fed commercial dry feed, and 38 were fed a RMBD. The samples were kept in a cooler with ice packs and transported for processing within a maximum of 24 h. This study was approved by the Ethical Committee on Animal Use of UFMG (protocol no. 51/2015).
2.2. Isolation and Identification of E. coli
The uterine contents were plated on Mueller Hinton (MH) agar (Kasvi, Maharashtra, India) supplemented with equine blood (5%) and MacConkey (MC) agar (Difco, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA), and the plates were incubated at 37 °C for 48 h under aerobiosis and anaerobiosis. Plating of rectal swab samples from female dogs subjected to OH and healthy dogs was performed on MC agar and incubated at 37 °C for 48 h under aerobiosis. For each clinical specimen, up to three lactose-fermenting colonies were subjected to species-specific polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to identify E. coli [22]. Strains not identified as E. coli was identified by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-ToF MS; Bruker Daltonics, Billerica, USA). A cutoff log score of 2 was used to validate the identification at the species level, as recommended by the manufacturer.
2.3. Characterization of E. coli
E. coli strains were subjected to PCR to determine phylogroups (A, B1, B2, C, D, E, F, or clade I) [23], and identify virulence genes corresponding to the ExPEC pathotype, namely, fimbriae type I (fimH), fimbriae type I central region (focG), fimbriae type P (papC and papG, allele II and III), fimbriae type S (sfaS), cytotoxic necrotizing factor type 1 (cnf1), uropathogenic specific protein (usp), α-hemolysin (hlyA), aerobactin (iutA), and serum resistance (traT) [18,24].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The results were analyzed using EngineRoom software [25]. To analyze the association between E. coli phylogroups, virulence factors, and categorical variables related to the group origin of the samples (uterine content of bitches with E. coli pyometra, rectal swabs of bitches with E. coli pyometra, or without E. coli pyometra, and healthy dogs fed commercial dry feed or a RMBD) a multiple proportion comparison test was conducted. This test is based on the chi-square distribution and the pooled estimate of the population proportion to estimate the standard error of the test statistic. If a significant difference was found in the overall test, the pairwise comparisons method with Marascuillo procedure was used to identify the specific pairs of proportions which differ significantly. Statistical significance of the results was set at p ≤ 0.05 for the analyzed characteristics [26].
3. Results
3.1. E. coli Isolation
A total of 40 (56%) of the 72 dogs tested positive for E. coli in the uterine content; up to three colonies were obtained from each, totaling 120 E. coli strains, while 21 (29%) had only other pathogens, and no bacterial growth was seen in 11 (15%) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Bacterial species isolated from the uterus in bitches with pyometra.
Up to three colonies of E. coli were obtained from rectal swabs of 59 bitches with pyometra, totaling 177 E. coli strains: 102 from dogs that tested positive for E. coli content (E. coli pyometra) and 75 from bitches that tested negative for E. coli (without E. coli pyometra) in the uterine contents.
From healthy bitches, at least one E. coli isolate was recovered from 91 dogs sampled, totaling 215 strains: 130 and 85 from dogs fed commercial feed or RMBD, respectively.
3.2. E. coli Phylogroups
Phylogroup B2 was the most common E. coli phylogroup detected in the uterine contents of bitches infected with E. coli pyometra (85%) and also in the rectal swab isolates of bitches with E. coli pyometra (58.8%), whereas B1 was most frequent in the rectal swabs of bitches without E. coli pyometra (41.3%). Bitches with E. coli pyometra showed a higher frequency of phylogroup B2 in the rectal swab than females without E. coli pyometra (p < 0.05). Phylogroup B2 was also the most frequent in E. coli isolates from rectal swabs of dogs fed commercial dry feed (34.6%), whereas B1 was the most common in dogs fed RMBD (34.1%). Dogs fed commercial dry feed showed a higher frequency of phylogroup B2 in rectal swabs than dogs fed RMBD (p < 0.05) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Number of isolates and frequency of E. coli phylogroups identified in the uterine content, rectal swabs of bitches with pyometra and rectal swabs of healthy dogs.
3.3. Frequency of Virulence Genes Associated with the ExPEC Pathotype
All the virulence genes tested were detected in E. coli isolates from all groups at different frequencies. Virulence genes associated with adhesion (papC) and toxin production (hlyA and usp) were more frequent in the rectal swabs of bitches with E. coli pyometra than in those without E. coli pyometra (p < 0.05). In addition, two virulence genes associated with adhesion (focG and sfaS) were more frequent in isolates from dogs fed commercial dry feed than in those from dogs fed RMBD (p < 0.05). In contrast, the serum resistance gene (traT) was found at a higher frequency in isolates from dogs fed RMBD than in those from dogs fed commercial dry feed (p < 0.05) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Number of isolates and frequency of E. coli virulence genes identified in the uterine content, rectal swabs of bitches with pyometra and rectal swabs of healthy dogs.
4. Discussion
As expected, E. coli was isolated from most of the uterine contents of dogs with pyometra. This result is in accordance with previous studies showing that E. coli is the main bacterium involved in pyometra [6,27,28].
Differentiation into phylogenetic groups and the detection of virulence factors have been widely used in studies on E. coli, helping to elucidate the epidemiology of infections and the colonization dynamics of these bacteria [5,23,29]. Previous studies have demonstrated that ExPEC strains isolated from canine pyometra tend to cluster mainly in phylogroup B2, whereas those isolated from the intestinal microbiota of healthy dogs cluster mainly in phylogenetic groups B1 and A [9,12,30]. In the present study, phylogroup B2 was the most frequent in the uterine contents of bitches, with clinical cases of pyometra caused by E. coli (Figure 1), corresponding to 85% of the isolates. This frequency is similar to that found in previous studies on pyometra, suggesting a high capacity of phylogroup B2 strains to colonize the canine uterus [7,11,31].
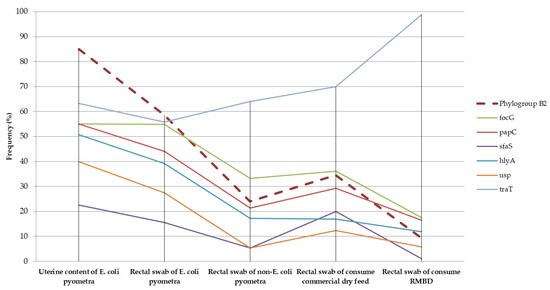
Figure 1.
Frequency of the phylogroup B2 and the main virulence factors identified in E. coli isolated from the uterine content, rectal swabs of bitches with pyometra and rectal swabs of healthy dogs fed commercial dry feed and raw meat-based diet (RMBD).
Although the pathogenesis of pyometra is poorly understood, previous studies have suggested that the intestine is the main source of E. coli strains that ascend into the uterus [1,2,7]. This study reinforces this hypothesis, as bitches with E. coli pyometra were more likely to harbor E. coli strains from phylogroup B2 in the rectal swab when compared to the group of bitches without E. coli pyometra. This finding indicates that intestinal colonization by E. coli from phylogroup B2 increases the risk of pyometra in female dogs.
Another interesting aspect of ExPEC is the presence of certain virulence factors that enable infection at different locations [5]. Virulence factors that promote adhesion and colonization, especially fimbriae, are considered to be of great relevance for the establishment of E. coli infections in the canine uterus [18,32,33]. Previous studies demonstrated that simple inactivation of some adhesins, such as type 1 (fim), P (papGIII), and S (sfa/foc) fimbriae, results in a considerable reduction in bacterial binding to cell lines of the canine endometrium, reinforcing the importance of these factors in the pathogenesis of the disease [34]. In the present study, four adhesin-encoding virulence genes were found more frequently in E. coli samples obtained from the uterine contents, similar to the findings of previous studies [11,18,31]. This finding reinforces the hypothesis that some adherent virulence factors are associated with pyometra caused by E. coli in female dogs. It is noteworthy that the gene encoding type P fimbriae (papC), which is considered important for the adhesion and colonization of E. coli in the canine endometrium [6,7], was found in 55% of the isolates from the uterine contents. This frequency is similar to that identified in other studies on canine pyometra isolates [5,18]. In addition, strains isolated from the rectal swabs of bitches with E. coli pyometra were more commonly positive for the type P fimbriae gene (papC) than strains isolated from the rectal swabs of dogs without E. coli pyometra. Notably, the frequency of papC-positive E. coli strains in dogs without E. coli pyometra was similar to that reported in a previous study on E. coli from rectal swabs of healthy dogs [17].
Although E. coli is known to be the main bacterium involved in pyometra [1,2], and recent studies have suggested that diet can influence E. coli colonization [8,35,36], current studies have evaluated how different diets would affect the frequency of ExPEC in bitches. In the present study, the papC gene showed no statistical difference between the groups of healthy bitches under different types of feeding. In contrast, the genes encoding type 1 adhesin (focG) and S (sfaS) fimbriae were found less frequently in E. coli strains recovered from dogs fed RMBD. These adhesins are considered important in the pathogenesis of canine pyometra [11,32,37]. However, it is important to note that the frequency of these two adhesin-encoding genes was similar in strains isolated from rectal swabs of dogs with or without E. coli pyometra, raising doubts regarding the role of these virulence factors in disease development.
Previous studies have indicated that ExPEC obtained from the uterine content of bitches with pyometra commonly expresses genes encoding toxins that may provide a selective advantage [1,2,7,38]. We observed that all toxin-coding virulence genes were found more frequently in E. coli samples obtained from the uterine content, which is in agreement with previous studies [6,18,31], which reinforces the hypothesis that, in addition to adhesins, ExPEC toxin virulence factors are associated with the occurrence of E. coli pyometra. Among the E. coli isolates from rectal swabs, the α-hemolysin (hlyA) toxin, which is capable of lysing erythrocytes and leukocytes [31,38,39], was found more frequently in strains isolated from bitches with E. coli pyometra than in strains isolated from rectal swabs of dogs without E. coli pyometra. Additionally, the uropathogenic specific protein (usp), which acts as a bacteriocin and assists in the migration of strains into the bloodstream [18,33,40], was more frequent in strains isolated from the rectal swabs of bitches with E. coli pyometra than in strains isolated from dogs without E. coli pyometra.
ExPEC obtained from the uterine contents of bitches with pyometra is commonly positive for the aerobactin gene (iutA), a virulence factor responsible for iron acquisition [5,38], and for the serum resistance gene (traT), a virulence factor associated with the inhibition of the immune response of the host in cases of translocation of the pathogen into the bloodstream [31,39]. In the present study, both virulence genes were detected in all groups, and the frequency was similar among E. coli strains obtained from uterine content and rectal swabs from bitches with E. coli and without E. coli pyometra. In contrast, traT was more frequently detected in E. coli strains from rectal swabs of dogs fed RMBD than in those fed commercial dry feed.
Research on phylogroups and virulence factors of E. coli from different origins has increased over the last few years, but many gaps remain, mostly regarding E. coli colonization and infection in dogs [1,7]. In the present study, we demonstrated that, compared to dogs without E. coli pyometra, dogs with E. coli pyometra are more likely to be colonized by E. coli from phylogroup B2, which is positive for specific virulence genes, including type 1 adhesin (papC) and two toxins (hlyA and usp). These results suggest that colonization by these strains is a risk factor for canine pyometra caused by E. coli. Based on these results, we sampled two groups of healthy dogs under different diets to evaluate whether dietary habits altered the intestinal microbiota and further established E. coli in the B2 phylogroup. Our results suggest that dogs fed RMBD are less frequently colonized by E. coli strains from phylogroup B2, raising the hypothesis that diet can be a risk factor for the occurrence of E. coli pyometra, which is the main bacterium responsible for this disease [6,7,41].
Importantly, several studies have indicated public health risks associated with RMBD, such as greater fecal shedding of pathogenic and zoonotic microorganisms, which is a potential risk to animal and human health [19,42]. Therefore, several health agencies have released statements that discourage the inclusion of raw or undercooked animal protein in dog diets [42]. We believe that the results of this study will motivate future evaluations of different diets for dogs that aim to reduce the colonization of ExPEC, however, this study should not be considered as a motivation for the adoption of RMDB, owing to the known risks of this practice.
5. Conclusions
The present study demonstrated the high frequency of E. coli strains belonging to phylogroup B2 and carrying virulence factors associated with ExPEC in isolates from the uterine contents of bitches with pyometra. In addition, this study found a higher frequency of these strains in the intestinal microbiota of bitches with E. coli pyometra than in bitches without E. coli pyometra, suggesting that intestinal colonization by these strains could be a risk factor for the occurrence of E. coli pyometra in dogs. Interestingly, when evaluating the intestinal microbiota of dogs on different types of diets, the present study found a lower frequency of such strains in the intestinal microbiota of dogs subjected to a RMBD than in dogs who consumed commercial dry feed, suggesting that future studies on diet modulation affecting intestinal colonization could find mechanisms to prevent and control E. coli pyometra in dogs.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and samples collection, P.H.S.d.S., H.D.T.; laboratory analysis, R.G.C.X. and G.M.C.; first draft of the manuscript, R.G.C.X., R.R.N., P.M.C.F., and R.O.S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES—Prêmio CAPES 2015—0774/2017), National Council for Scientific and Tech-nological Development (CNPq—406402/2018-3), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG—APQ-00524-17) and Pró-Reitoria de Pesquisa da Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (PRPq/UFMG) and the MCTIC/FNDCT-CNPq/MEC-CAPES/Grant 440593/2016-6. ROSS has a fellowship from CNPq (Brazil).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee on Animal Use of the Federal University of Minas Gerais under protocol no. 51/2015.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the veterinarians and owners that agreed to participate in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hagman, R. Pyometra in Small Animals. Vet. Clin. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 48, 639–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagman, R. Pyometra in Small Animals 2.0. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2022, 52, 631–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fieni, F.; Topie, E.; Gogny, A. Medical Treatment for Pyometra in Dogs. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2014, 49, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitpean, S.; Ström-Holst, B.; Emanuelson, U.; Höglund, O.V.; Pettersson, A.; Alneryd-Bull, C.; Hagman, R. Outcome of Pyometra in Female Dogs and Predictors of Peritonitis and Prolonged Postoperative Hospitalization in Surgically Treated Cases. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müştak, H.K.; Günaydin, E.; Kaya, İ.B.; Salar, M.Ö.; Babacan, O.; Önat, K.; Ata, Z.; Diker, K.S. Phylo-Typing of Clinical Escherichia Coli Isolates Originating from Bovine Mastitis and Canine Pyometra and Urinary Tract Infection by Means of Quadruplex PCR. Vet. Q. 2015, 35, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, Y.M.M.; Wright, P.J.; Lee, C.-S.; Browning, G.F. Uropathogenic Virulence Factors in Isolates of Escherichia Coli from Clinical Cases of Canine Pyometra and Feces of Healthy Bitches. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.E.; De Carli, S.; Riboldi, C.I.; De Lorenzo, C.; Panziera, W.; Driemeier, D.; Siqueira, F.M. Pet Pyometra: Correlating Bacteria Pathogenicity to Endometrial Histological Changes. Pathogens 2021, 10, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenaillon, O.; Skurnik, D.; Picard, B.; Denamur, E. The Population Genetics of Commensal Escherichia Coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coura, F.M.; Diniz, A.N.; Oliveira Junior, C.A.; Lage, A.P.; Lobato, F.C.F.; Heinemann, M.B.; Silva, R.O.S.; Coura, F.M.; Diniz, A.N.; Oliveira Junior, C.A.; et al. Detection of Virulence Genes and the Phylogenetic Groups of Escherichia Coli Isolated from Dogs in Brazil. Ciência Rural 2018, 48, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, K.S.; Cao, Y.; Wei, D.-J. Epidemiologic Investigation of Extra-Intestinal Pathogenic E. Coli (ExPEC) Based on PCR Phylogenetic Group and FimH Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in China. Int. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Genet. 2011, 2, 339–353. [Google Scholar]
- Mateus, L.; Henriques, S.; Merino, C.; Pomba, C.; Lopes da Costa, L.; Silva, E. Virulence Genotypes of Escherichia Coli Canine Isolates from Pyometra, Cystitis and Fecal Origin. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Hao, C. Association between Virulence Profile and Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Escherichia Coli Isolated from Dogs and Cats in China. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2017, 11, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, C.E.; De Carli, S.; Weber, M.N.; Fonseca, A.C.V.; Tagliari, N.J.; Foresti, L.; Cibulski, S.P.; Mayer, F.Q.; Canal, C.W.; Siqueira, F.M. Insights on the Genetic Features of Endometrial Pathogenic Escherichia Coli Strains from Pyometra in Companion Animals: Improving the Knowledge about Pathogenesis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 85, 104453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, S.; Silva, E.; Silva, M.F.; Carvalho, S.; Diniz, P.; Lopes-da-Costa, L.; Mateus, L. Immunomodulation in the Canine Endometrium by Uteropathogenic Escherichia Coli. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maluta, R.P.; Borges, C.A.; Beraldo, L.G.; Cardozo, M.V.; Voorwald, F.A.; Santana, A.M.; Rigobelo, E.C.; Toniollo, G.H.; Ávila, F.A. Frequencies of Virulence Genes and Pulse Field Gel Electrophoresis Fingerprints in Escherichia Coli Isolates from Canine Pyometra. Vet. J. 2014, 202, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salipante, S.J.; Roach, D.J.; Kitzman, J.O.; Snyder, M.W.; Stackhouse, B.; Butler-Wu, S.M.; Lee, C.; Cookson, B.T.; Shendure, J. Large-Scale Genomic Sequencing of Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia Coli Strains. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Johnson, J.R. Proposal for a New Inclusive Designation for Extraintestinal Pathogenic Isolates of Escherichia Coli: ExPEC. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 1753–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, A.K.; Ribeiro, M.G.; da S Leite, D.; Tiba, M.R.; de Moura, C.; Lopes, M.D.; Prestes, N.C.; Salerno, T.; da Silva, A.V. Virulence Factors in Escherichia Coli Strains Isolated from Urinary Tract Infection and Pyometra Cases and from Feces of Healthy Dogs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2009, 86, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, F.M.; Ramos, C.P.; Xavier, R.G.C.; Lopes, E.O.; Júnior, C.A.O.; Bagno, R.M.; Diniz, A.N.; Lobato, F.C.F.; Silva, R.O.S. Fecal Shedding of Salmonella Spp., Clostridium Perfringens, and Clostridioides Difficile in Dogs Fed Raw Meat-Based Diets in Brazil and Their Owners’ Motivation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; An, J.-U.; Kim, W.; Lee, S.; Cho, S. Differences in the Gut Microbiota of Dogs (Canis Lupus Familiaris) Fed a Natural Diet or a Commercial Feed Revealed by the Illumina MiSeq Platform. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.H.; Lawes, J.R.; Wales, A.D. Raw Diets for Dogs and Cats: A Review, with Particular Reference to Microbiological Hazards. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2019, 60, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDaniels, A.E.; Rice, E.W.; Reyes, A.L.; Johnson, C.H.; Haugland, R.A.; Stelma, G.N. Confirmational Identification of Escherichia Coli, a Comparison of Genotypic and Phenotypic Assays for Glutamate Decarboxylase and Beta-D-Glucuronidase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3350–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clermont, O.; Christenson, J.K.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.M. The Clermont Escherichia Coli Phylo-Typing Method Revisited: Improvement of Specificity and Detection of New Phylo-Groups. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.R.; Stell, A.L. Extended Virulence Genotypes of Escherichia Coli Strains from Patients with Urosepsis in Relation to Phylogeny and Host Compromise. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MoreSteam Multiple Proportions Test. Available online: https://moresteam.com/help/engineroom/multiple-proportions-test (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Marascuilo, L.A. Large-Sample Multiple Comparisons. Psychol. Bull. 1966, 65, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.M.; Dockweiler, J.C.; Cheong, S.H.; de Amorim, M.D. Pyometra and Unilateral Uterine Horn Torsion in a Sheep. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2018, 53, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainey, B.; Singh, A.; Valverde, A.; Hoddinott, K.; Beaufrère, H.; Tindal, L.; Smith, D. Laparoscopic-Assisted Ovariohysterectomy for the Treatment of Pyometra in a Bengal Tiger (Panthera Tigris Tigris). Can. Vet. J. 2018, 59, 895–898. [Google Scholar]
- Clermont, O.; Gordon, D.; Denamur, E. Guide to the Various Phylogenetic Classification Schemes for Escherichia Coli and the Correspondence among Schemes. Microbiology 2015, 161, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.M.; Pinchbeck, G.L.; Nuttall, T.; McEwan, N.; Dawson, S.; Williams, N.J. Antimicrobial Resistance Risk Factors and Characterisation of Faecal E. Coli Isolated from Healthy Labrador Retrievers in the United Kingdom. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 119, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, S.; Silva, E.; Lemsaddek, A.; Lopes-da-Costa, L.; Mateus, L. Genotypic and Phenotypic Comparison of Escherichia Coli from Uterine Infections with Different Outcomes: Clinical Metritis in the Cow and Pyometra in the Bitch. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 170, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krekeler, N.; Marenda, M.S.; Browning, G.F.; Holden, K.M.; Charles, J.A.; Wright, P.J. Uropathogenic Virulence Factor FimH Facilitates Binding of Uteropathogenic Escherichia Coli to Canine Endometrium. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 35, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostinho, J.M.A.; de Souza, A.; Schocken-Iturrino, R.P.; Beraldo, L.G.; Borges, C.A.; Ávila, F.A.; Marin, J.M. Escherichia Coli Strains Isolated from the Uteri Horn, Mouth, and Rectum of Bitches Suffering from Pyometra: Virulence Factors, Antimicrobial Susceptibilities, and Clonal Relationships among Strains. Int. J. Microbiol. 2014, 2014, 979584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krekeler, N.; Marenda, M.S.; Browning, G.F.; Holden, K.M.; Charles, J.A.; Wright, P.J. The Role of Type 1, P and S Fimbriae in Binding of Escherichia Coli to the Canine Endometrium. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wotzka, S.Y.; Kreuzer, M.; Maier, L.; Arnoldini, M.; Nguyen, B.; Brachmann, A.O.; Berthold, D.L.; Zünd, M.; Hausmann, A.; Bakkeren, E.; et al. Escherichia Coli Limits Salmonella Typhimurium Infections after Diet-Shifts and Fat-Mediated Microbiota Perturbation in Mice. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2164–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuzer, M.; Hardt, W.-D. How Food Affects Colonization Resistance Against Enteropathogenic Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 74, 787–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarpour, R.; Akhtardanesh, B. Genotype and Antibiotic Resistance Profile of Escherichia Coli Strains Involved in Canine Pyometra. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 21, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggan, J.A.; Melville, P.A.; de Oliveira, C.M.; Faustino, M.; Moreno, A.M.; Benites, N.R. Microbiological and Histopathological Aspects of Canine Pyometra. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2008, 39, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, A.P.; Woodford, N. Extra-Intestinal Pathogenic Escherichia Coli (ExPEC): Disease, Carriage and Clones. J. Infect. 2015, 71, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etefia, E.U.; Ben, S.A. Virulence Markers, Phylogenetic Evolution, and Molecular Techniques of Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli. J. Nat. Sci. Med. 2020, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagman, R. Canine Pyometra: What Is New? Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2017, 52, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, L.M.; Chandler, M.L.; Hamper, B.A.; Weeth, L.P. Current Knowledge about the Risks and Benefits of Raw Meat–Based Diets for Dogs and Cats. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2013, 243, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).