Isolation and Identification of Staphylococcus Species Obtained from Healthy Companion Animals and Humans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Subjects and Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Isolation and Identification
2.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
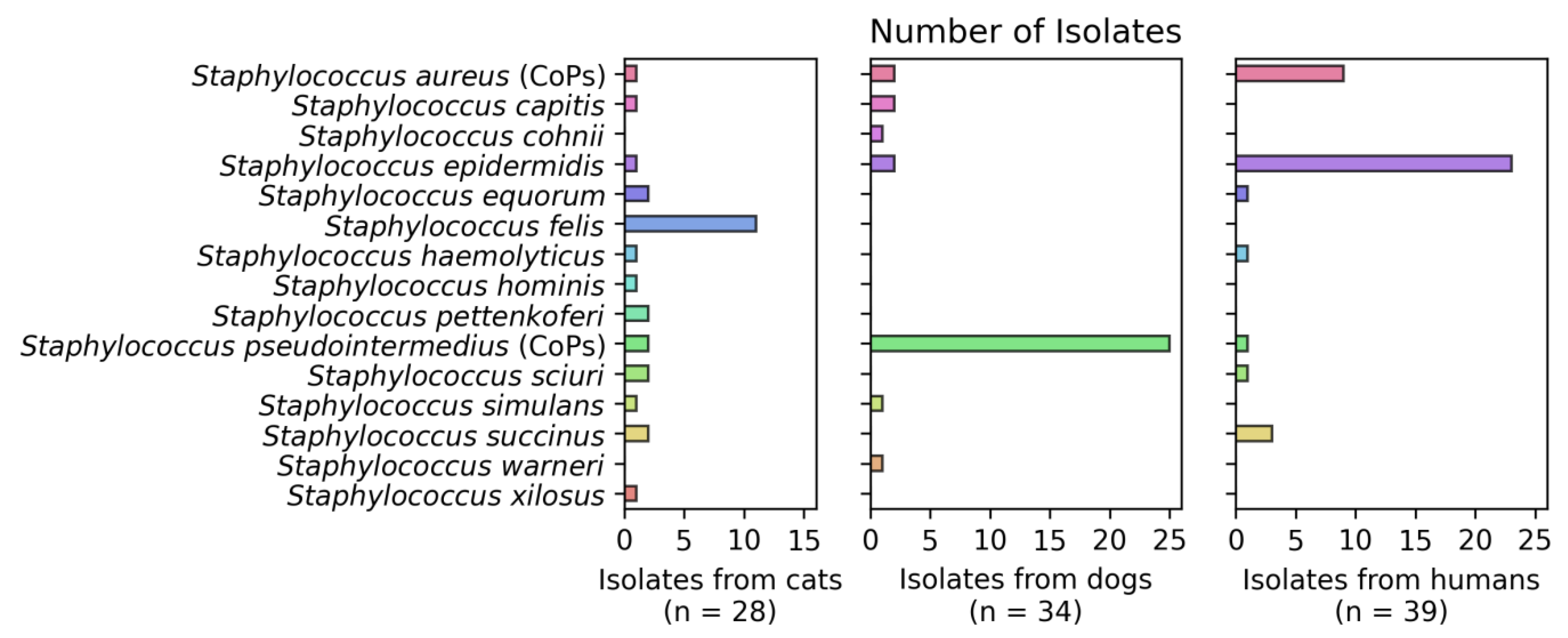
3.2. Detection of Staphylococcus spp.
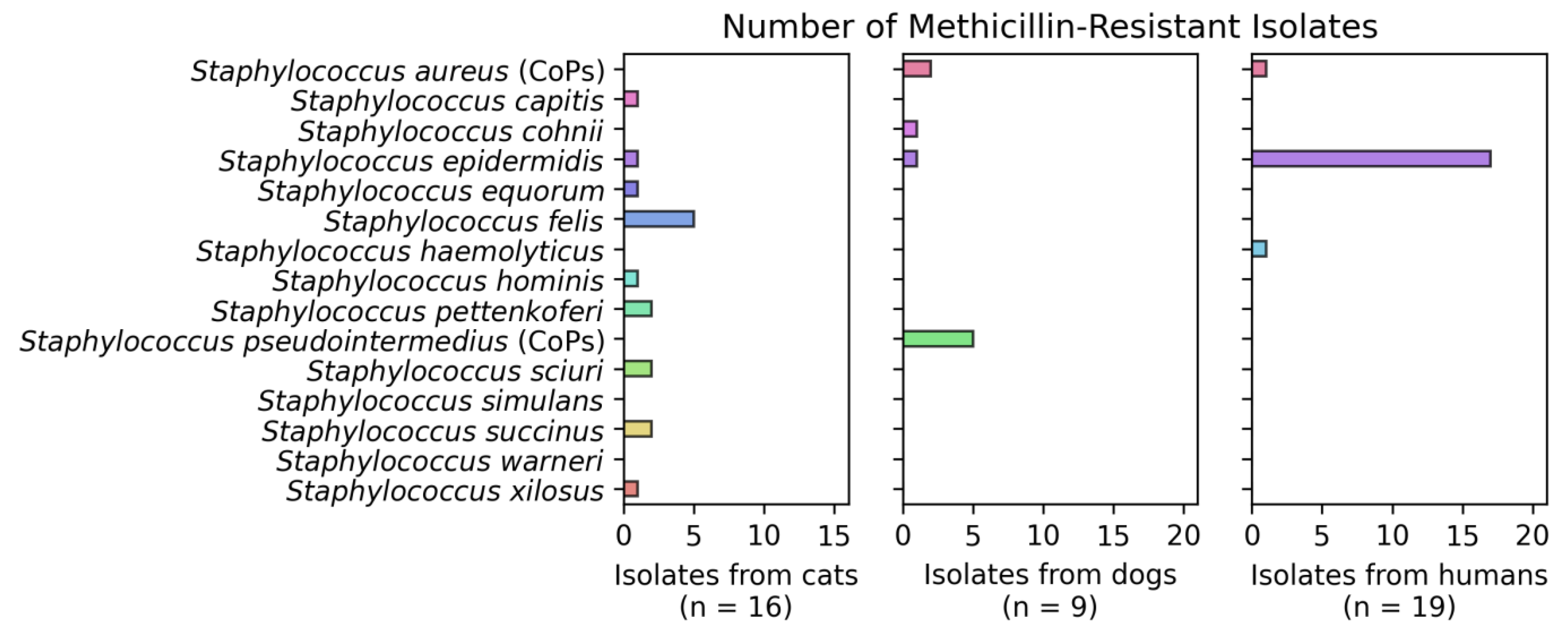
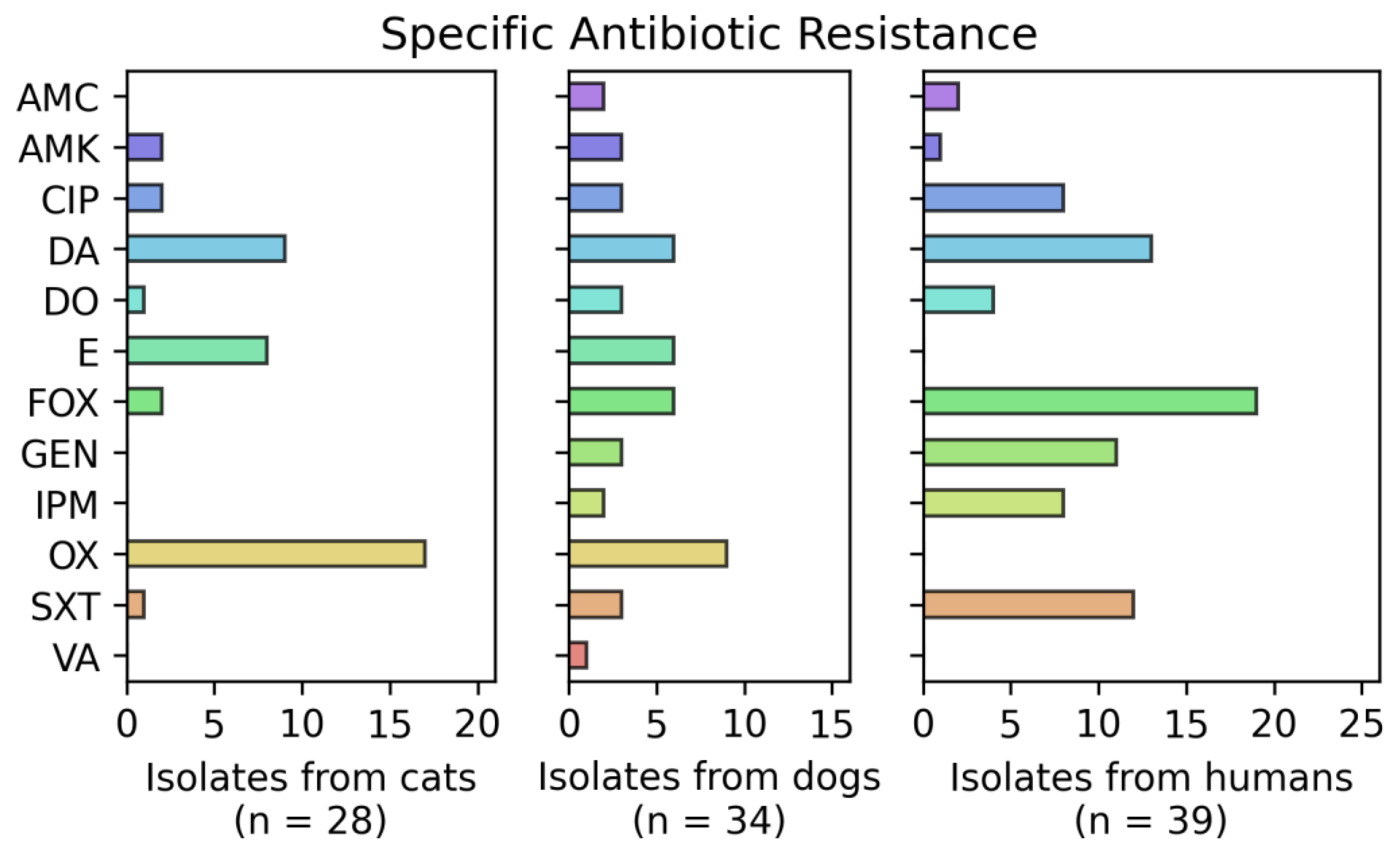
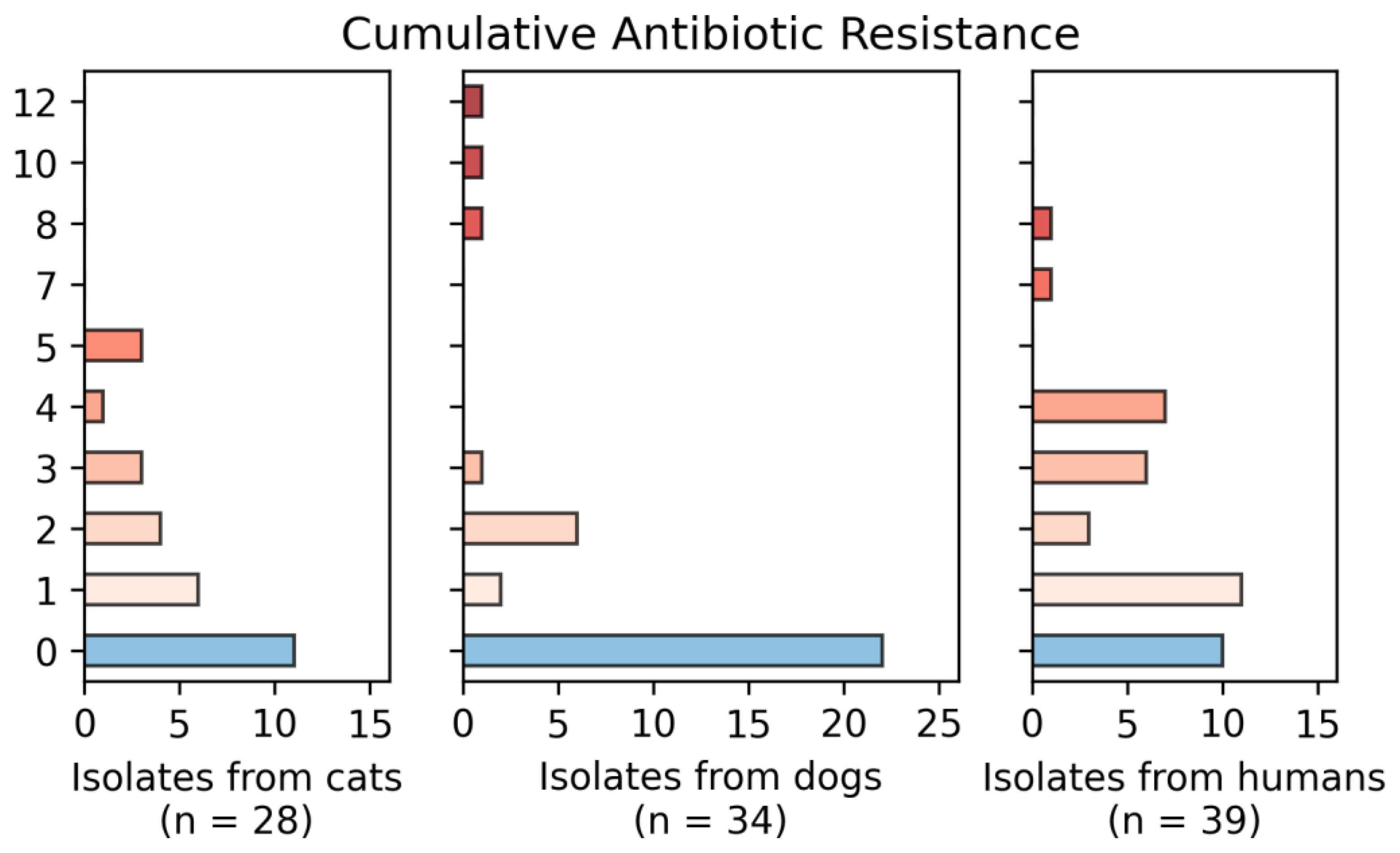
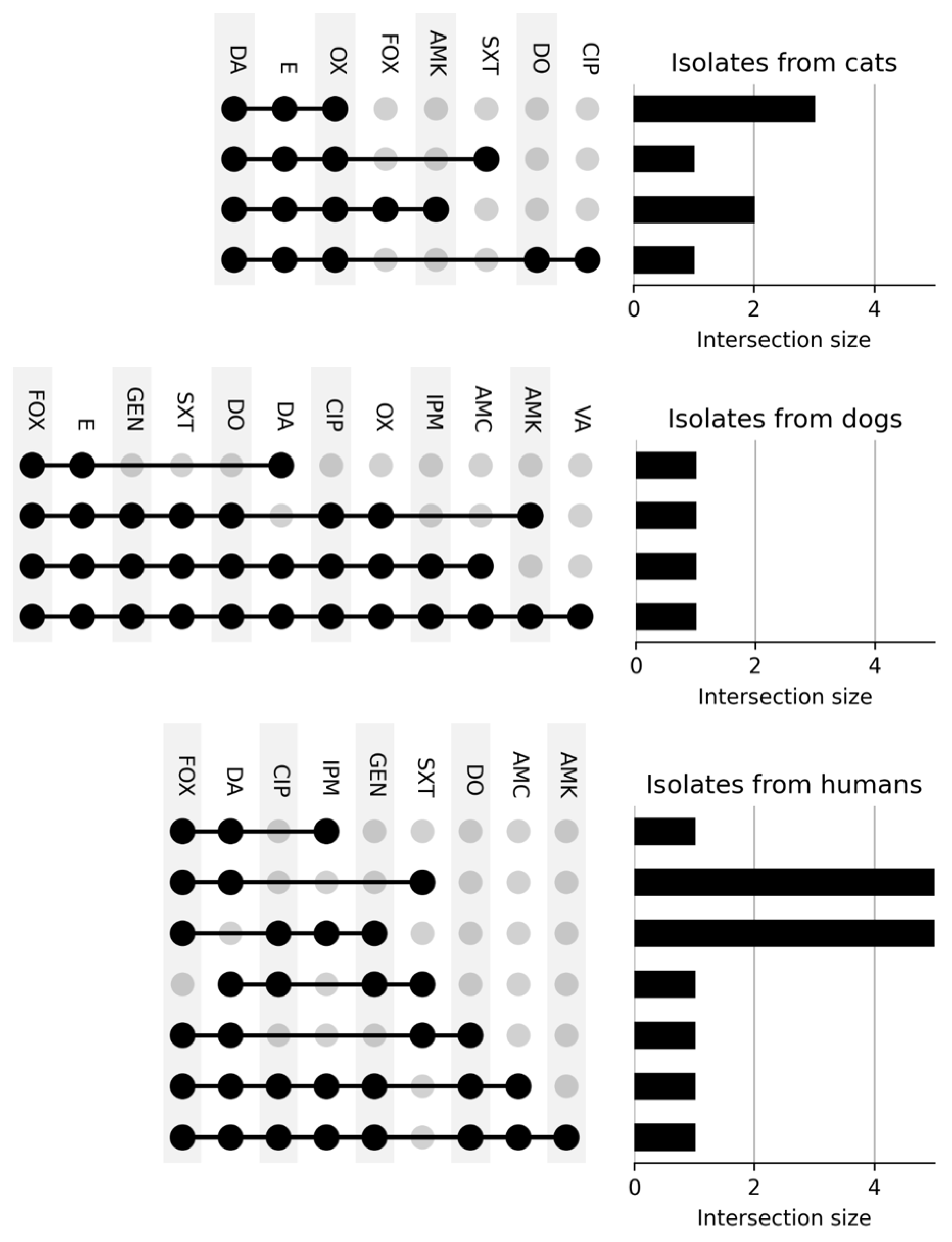
3.3. Resistance Phenotype
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vire, F.P.; Akpaka, P.E.; Unakal, C. Molecular characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from rural community settings in Trinidad and Tobago. Niger J. Clin. Pract. 2018, 21, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortora, G.; Berdell, F.; Case, C.; Weber, D.; Bair, W. Microbiology: An Introduction, 13th ed.; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pasachova, J.; Ramírez, S.; Muñoz, L. Staphylococcus aureus: Generalidades, mecanismos de patogenicidad y colonización celular. Nova 2019, 17, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tam, K.; Torres, V.J. Staphylococcus aureus Secreted Toxins and Extracellular Enzymes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papić, B.; Golob, M.; Zdovc, I.; Kušar, D.; Avberšek, J. Genomic insights into the emergence and spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in veterinary clinics. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 258, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Simón, C.; Ceballos, S.; Ortega, C.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C.; Gómez-Sanz, E. S. pseudintermedius and S. aureus lineages with transmission ability circulate as causative agents of infections in pets for years. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martín, M.; Corbera, J.A.; Suárez-Bonnet, A.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T. Virulence factors in coagulase-positive staphylococci of veterinary interest other than Staphylococcus aureus. Vet. Q. 2020, 40, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steining, E.J.; Duchene, S.; Robinson, D.A. Evolution and Global Transmission of a Multidrug-Resistant, Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Lineage from the Indian Subcontinent. mBio 2019, 10, e01105-19. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, S.; Song, P.I.; Seo, C.H.; Cheong, H.; Park, Y. Colonization and infection of the skin by S. aureus: Immune system evasion and the response to cationic antimicrobial peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 8753–8772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Argudín, M.A.; Vanderhaeghen, W.; Butaye, P. Antimicrobial resistance and population structure of Staphylococcus epidermidis recovered from pig farms in Belgium. Vet. J. 2015, 203, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoPinto, A.; Mohammed, H.; Ledbetter, E. Prevalence and risk factors for isolation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus in dogs with keratitis. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2015, 18, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Moein, K.A.; Zaher, H.M. The Nasal Carriage of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci among Animals and Its Public Health Implication. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 20, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, M. Staphylococci in animals: Prevalence, identification and antimicrobial susceptibility, with an emphasis on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2005, 62, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowy, F.D. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, H.F. The changing epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus? Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seas, C.; Garcia, C.; Salles, M.J.; Labarca, J.; Luna, C.; Alvarez-Moreno, C.; Mejía-Villatoro, C.; Zurita, J.; Guzmán-Blanco, M.; Rodríguez-Noriega, E.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections in Latin America: Results of a multinational prospective cohort study. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, G.; Bae, J.S.; Otto, M. Pathogenicity and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Virulence 2021, 12, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, L.C.; Souza da Cunha, M. Insights into the epidemiology of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in special populations and at the community-healthcare interface. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 25, 101636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, T.; Unakal, C. Staphylococcus aureus; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Algammal, A.M.; Hetta, H.F.; Elkelish, A.; Alkhalifah, D.; Hozzein, W.N.; Batiha, G.E.; El Nahhas, N.; Mabrok, M.A. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): One health perspective approach to the bacterium epidemiology, virulence factors, antibiotic-resistance, and zoonotic impact. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3255–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnageh, H.; Hiblu, M.; Abbassi, M.; Abouzeed, Y.; Ahmed, M. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus species isolated from cats and dogs. Open Vet. J. 2021, 10, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.; Souza-Silva, T.; Araújo-Alves, A.; Giambiagi-deMarval, M. CRISPR-Cas Systems Features and the Gene-Reservoir Role of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanoukon, C.; Argemi, X.; Sogbo, F.; Orekan, J.; Keller, D.; Affolabi, D.; Schramm, F.; Riegel, P.; Baba-Moussa, L.; Prévost, G. Pathogenic features of clinically significant coagulase-negative staphylococci in hospital and community infections in Benin. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 307, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fišarová, L.; Pantůček, R.; Botka, T.; Doškař, J. Variability of resistance plasmids in coagulase-negative staphylococci and their importance as a reservoir of antimicrobial resistance. Res. Microbiol. 2019, 170, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Malinis, A.J.; Milagro, A.; Torres Sopena, L.; Gilaberte, Y. Staphylococcus lugdunensis Skin Infection: Report of 16 Cases. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021, 112, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, E.; Acuña, M.; Álvarez, A.M.; Avilés, C.; Maza, V.; Salgado, C.; Tordecilla, J.; Varas, M.; Venegas, M.; Villarroel, M.; et al. Microorganismos aislados de hemocultivos en niños con cáncer y neutropenia febril de alto riesgo en cinco hospitales de Santiago, Chile, período 2012–2015. Rev. Chil. Infectol. 2018, 35, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rynhoud, H.; Meler, E.; Gibson, J.S.; Price, R.; Maguire, T.; Farry, T.; Bennett, E.; Hartono, J.; Magalhaes, R.J. Epidemiology of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus species carriage in companion animals in the Greater Brisbane Area, Australia. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 136, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshaikh, B.; Yee, W.; Lodha, A.; Henderson, E.; Yusuf, K.; Sauve, R. Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus sepsis in preterm infants and long-term neurodevelopmental outcome. J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chah, K.F.; Gómez-Sanz, E.; Nwanta, J.A.; Asadu, B.; Agbo, I.C.; Lozano, C.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. Methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci from healthy dogs in Nsukka, Nigeria. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2014, 45, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherifi, S.; Byl, B.; Deplano, A.; Nagant, C.; Nonhoff, C.; Denis, O.; Hallin, M. Genetic characteristics and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates from patients with catheter-related bloodstream infections and from colonized healthcare workers in a Belgian hospital. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2014, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, E.M.; Weinert, L.A.; Holden, M.T.; Welch, J.J.; Wilson, K.; Morgan, F.J.; Harris, S.R.; Loeffler, A.; Boag, A.K.; Peacock, S.J.; et al. A shared population of epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus 15 circulates in humans and companion animals. mBio 2014, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, G.C.; Worthing, K.A.; Ward, M.P.; Norris, J.M. Commensal Staphylococci Including Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Dogs and Cats in Remote New South Wales, Australia. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 79, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litster, A.; Moss, S.M.; Honnery, M.; Rees, B.; Trott, D.J. Prevalence of bacterial species in cats with clinical signs of lower urinary tract disease: Recognition of Staphylococcus felis as a possible feline urinary tract pathogen. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 121, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worthing, K.; Pang, S.; Trott, D.J.; Abraham, S.; Coombs, G.W.; Jordan, D.; McIntyre, L.; Davies, M.R.; Norris, J. Characterization of Staphylococcus felis isolated from cats using whole genome sequencing. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 222, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, J.P.; Anderson, K.L.; Correa, M.T.; Lyman, R.; Ruffin, F.; Reller, L.B.; Fowler, V.G., Jr. Transmission of mrsa between companion animals and infected human patients presenting to outpatient medical care facilities. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harvey, R.G.; Marples, R.; Noble, W. Nasal Carriage of Staphylococcus intermedius in Humans in Contact with Dogs. Microb Ecol. Health Dis. 1994, 7, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duijkeren, E.; Wolfhagen, M.J.; Box, A.T.; Heck, M.E.; Wannet, W.J.; Fluit, A.C. Human-to-Dog Transmission of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 2235–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boost, M.; O’Donoghue, M.M.; James, A. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus carriage among dogs and their owners. Epidemiol. Infect. 2008, 136, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Sanz, E.; Torres, C.; Ceballos, S.; Lozano, C.; Zarazaga, M. Clonal Dynamics of Nasal Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in Dog-Owning Household Members. Detection of MSSA ST398. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vengust, M.; Anderson, M.E.; Rousseau, J.; Weese, J.S. Methicillin-resistant staphylococcal colonization in clinically normal dogs and horses in the community. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weese, S.J.; Nichols, J.; Jalali, M.; Litster, A. The oral and conjunctival microbiotas in cats with and without feline immunodeficiency virus infection. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanselman, B.A.; Kruth, S.A.; Rousseau, J.; Weese, J.S. Article Coagulase positive staphylococcal colonization of humans and their household pets. Can. Vet. J. 2009, 50, 954–958. [Google Scholar]
- Van Duijkeren, E.; Kamphuis, M.; Van der Mije, I.C.; Laarhoven, L.M.; Duim, B.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Houwers, D.J. Transmission of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius between infected dogs and cats and contact pets, humans and the environment in households and veterinary clinics. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 150, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suepaul, S.; Georges, K.; Unakal, C.; Boyen, F.; Sookhoo, J.; Ashraph, K.; Yusuf, A.; Butaye, P. Determination of the frequency, species distribution and antimicrobial resistance of staphylococci isolated from dogs and their owners in Trinidad. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gortel, K.; Campbell, K.; Kakoma, I.; Whittem, T.; Schaeffer, D.; Weisiger, R. Methicillin resistance among staphylococci isolated from dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1999, 60, 1526–1530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grönthal, T.; Moodley, A.; Nykäsenoja, S.; Junnila, J.; Guardabassi, L.; Thomson, K.; Rantala, M. Large outbreak caused by methicillin resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius ST71 in a Finnish Veterinary Teaching Hospital—from out-break control to outbreak prevention. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lena, P.; Ishak, A.; Karageorgos, S.A.; Tsioutis, C. Presence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (Mrsa) on healthcare workers’ attire: A systematic review. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loncaric, I.; Tichy, A.; Handler, S.; Szostak, M.P.; Tickert, M.; Diab-Elschahawi, M.; Spergser, J.; Künzel, F. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus sp. (MRS) in different companion animals and determination of risk factors for colonization with MRS. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, E.; Carvalho, A.; Ferreira, A.M.; Moura, L.; Valle, A.; Freitas, D.; Moura, M. Colonization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among healthcare students: An integrative review. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2021, 139, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchamba, C.; Rao, A.S.; Boyen, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; Jean Noel, D.; Theron, L. Comparison of quantitative PCR and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry assays for identification of bacteria in milk samples from cows with subclinical mastitis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uchida-Fujii, E.; Niwa, H.; Kinoshita, Y.; Nukada, T. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization–Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) for Identification of Bacterial Isolates from Horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2020, 95, 103276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI, VET01S. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Test for Bacteria Isolate from Animals, 5th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI, M100. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N.; Strobelt, H.; Vuillemot, R.; Pfister, H. UpSet: Visualization of Intersecting Sets. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput Graph. 2014, 20, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumi, M.V.; Nuske, E.; Mas, J.; Argüello, A.; Gutkind, G.; Di Conza, J. Antimicrobial resistance in bacterial isolates from companion animals in Buenos Aires, Argentina: 2011–2017 retrospective study. Zoonoses Public Health 2021, 68, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlavanzadeh, S.; Khoshbakht, R.; Kaboosi, H.; Moazamian, E. Antibiotic resistance and phylogenetic comparison of human, pet animals and raw milk Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 79, 101717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avedissian, S.N.; Rhodes, N.J.; Shaffer, C.L.; Tran, L.; Bradley, J.S.; Le, J. Antimicrobial prescribing for treatment of serious infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in pediatrics: An expert review. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, X.; García-De-la-Mària, C.; Gasch, O.; Pericàs, J.M.; Soy, D.; Cañas-Pacheco, M.A.; Falces, C.; García-González, J.; Hernández-Meneses, M.; Vidal, B.; et al. Effectiveness of vancomycin plus cloxacillin compared with vancomycin, cloxacillin and dap-tomycin single therapies in the treatment of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in a rabbit model of experimental endocarditis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramatsu, K.; Cui, L.; Kuroda, M. The emergence and evolution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 9, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thomson, P.; García, P.; Miles, J.; Isla, D.; Yáñez, C.; Santibáñez, R.; Núñez, A.; Flores-Yáñez, C.; del Río, C.; Cuadra, F. Isolation and Identification of Staphylococcus Species Obtained from Healthy Companion Animals and Humans. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9020079
Thomson P, García P, Miles J, Isla D, Yáñez C, Santibáñez R, Núñez A, Flores-Yáñez C, del Río C, Cuadra F. Isolation and Identification of Staphylococcus Species Obtained from Healthy Companion Animals and Humans. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(2):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9020079
Chicago/Turabian StyleThomson, Pamela, Patricia García, Jorge Miles, David Isla, Camilo Yáñez, Rodrigo Santibáñez, Andrea Núñez, Carla Flores-Yáñez, Camila del Río, and Françoise Cuadra. 2022. "Isolation and Identification of Staphylococcus Species Obtained from Healthy Companion Animals and Humans" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 2: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9020079
APA StyleThomson, P., García, P., Miles, J., Isla, D., Yáñez, C., Santibáñez, R., Núñez, A., Flores-Yáñez, C., del Río, C., & Cuadra, F. (2022). Isolation and Identification of Staphylococcus Species Obtained from Healthy Companion Animals and Humans. Veterinary Sciences, 9(2), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9020079





