An Evaluation of Quantitative PCR Assays (TaqMan® and SYBR Green) for the Detection of Babesia bigemina and Babesia bovis, and a Novel Fluorescent-ITS1-PCR Capillary Electrophoresis Method for Genotyping B. bovis Isolates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Parasite and Parasite DNA Samples
2.2. DNA Isolation and Quantification from Purified Parasites
2.3. DNA Isolation from Clinical Samples and Vaccinated Cattle
2.4. Standard PCR
2.5. Optimization of SYBR Green Based Quantitative PCR Assay
2.6. TaqMan qPCR Assay
2.7. Sensitivity and Specificity of Species Specific Assays
2.8. Clinical Evaluation of Assay Sensitivity and Specificity of Species Specific Assays
2.9. Statistical Analysis
2.10. Babesia bovis ITS Genotyping Method
3. Results
3.1. Sensitivity and Specificity
3.2. Clinical Sensitivity of SYBR Green qPCR Assays
3.3. Babesia Bovis ITS Genotyping
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| TFC | Tick Fever Centre |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| qPCR | Quantitative PCR |
| M13 | M13 bacteriophage |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| dNTPs | Deoxynucleotides |
References
- Bock, R.E.; Jackson, L.; DeVos, A.J.; Jorgensen, K. Babesiosis of cattle. Parasitology 2004, 129, S247–S269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackett, D.; Holmes, P.; Abbott, K.; Jephcott, S.; Barber, M. Assessing the Economic Cost of Endemic Disease on the Profitability of Australian Beef Cattle and Sheep Producers; Meat & Livestock Australia Limited: North Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lew-Tabor, A.E.; Rodriguez Valle, M. A review of reverse vaccinology approaches for the development of vaccines against ticks and tick borne diseases. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahrimal, Y.; Goff, W.L.; Jasmer, D.P. Detection of Babesia bovis carrier cattle by using polymerase chain reaction amplification of parasite DNA. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Oura, C.A.; Bishop, R.P.; Wampande, E.M.; Lubega, G.W.; Tait, A. Application of a reverse line blot assay to the study of haemoparasites in cattle in Uganda. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, R.E.; De Vos, A.J. Immunity following use of the Australian tick fever vaccine: A review of the evidence. Aust. Vet. J. 2001, 79, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Castro, J.J. Sustainable tick and tickborne disease control in livestock improvement in developing countries. Vet. Parasitol. 1997, 71, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeria, S.; Castella, J.; Ferrer, D.; Ortuno, A.; Estrada-Pena, A.; Gutierrez, J.F. Bovine piroplasms in Minorca (Balearic Islands, Spain): A comparison of PCR-based and light microscopy detection. Vet. Parasitol. 2001, 99, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, J.A.M.; Reddy, G.R.; Chieves, L.; Courtney, C.H.; Littell, R.; Livengood, J.R.; Norval, R.A.I.; Smith, C.; Dame, J.B. Monitoring Babesia bovis infections in cattle by using PCR-based tests. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 2748–2755. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, J.V.; Chieves, L.P.; Johnson, G.S.; Buening, G.M. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction based assay for the detection of Babesia bigemina, Babesia bovis and Anaplasma marginale DNA in bovine blood. Vet. Parasitol. 1993, 50, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yin, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, D.; Guan, G.; Liu, A.; Ma, M.; Dang, S.; Lu, B.; Sun, C.; et al. Molecular phylogenetic studies on an unnamed bovine Babesia sp. based on small subunit ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 133, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Sequeira, T.C.G.; Oliveira, M.C.S.; Araujo, J.P.; Amarante, A.F.T. PCR-based detection of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina in their natural host Boophilus microplus and cattle. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lew, A.E.; Dalrymple, B.P.; Jeston, P.J.; Bock, R.E. PCR methods for the discrimination of Babesia bovis isolates. Vet. Parasitol. 1997, 71, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francino, O.; Altet, L.; Sanchez-Robert, E.; Rodriguez, A.; Solano-Gallego, L.; Alberola, J.; Ferrer, L.; Sanchez, A.; Roura, X. Advantages of real-time PCR assay for diagnosis and monitoring of canine leishmaniosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 137, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama Iniguez, S.; Dea-Ayuela, M.A.; Sanchez-Brunete, J.A.; Torrado, J.J.; Alunda, J.M.; Bolas-Fernandez, F. Real-time reverse transcription-PCR quantification of cytokine mRNA expression in golden Syrian hamster infected with Leishmania infantum and treated with a new amphotericin B formulation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buling, A.; Criado-Fornelio, A.; Asenzo, G.; Benitez, D.; Barba-Carretero, J.C.; Florin-Christensen, M. A quantitative PCR assay for the detection and quantification of Babesia bovis and B. bigemina. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 147, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Iseki, H.; Herbas, M.S.; Yokoyama, N.; Suzuki, H.; Xuan, X.; Fujisaki, K.; Igarashi, I. Development of TaqMan-based real-time PCR assays for diagnostic detection of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lew, A.E.; Bock, R.E.; Croft, J.M.; Minchin, C.M.; Kingston, T.G.; Dalgliesh, R.J. Genotypic diversity in field isolates of Babesia bovis from cattle with babesiosis after vaccination. Aust. Vet. J. 1997, 75, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, R.E.; DeVos, A.J.; Lew, A.; Kingston, T.G.; Fraser, I.R. Studies on failure of T strain live Babesia bovis vaccine. Aust. Vet. J. 1995, 72, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combrink, M.P.; Troskie, P.C.; Pienaar, R.; Latif, A.A.; Mans, B.J. Genotypic diversity in Babesia bovis field isolates and vaccine strains from South Africa. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 199, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molad, T.; Fleiderovich, L.; Leibovitz, B.; Wolkomirsky, R.; Behar, A.; Markovics, A. Differentiation between Israeli B. bovis vaccine strain and field isolates. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 208, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Llaneza, A.; Caballero, M.; Baravalle, E.; Mesplet, M.; Mosqueda, J.; Suarez, C.E.; Echaide, I.; Katzer, F.; Pacheco, G.M.; Florin-Christensen, M.; et al. Development of a tandem repeat-based multilocus typing system distinguishing Babesia bovis geographic isolates. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 167, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, G.H.; Liu, X.; Johnsrude, J.D.; Dame, J.B.; Roman Reddy, G. Development and evaluation of an extra chromosomal DNA-based PCR test for diagnosing bovine babesiosis. Mol. Cell. Probes 1999, 13, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuelke, M. An economic method for the fluorescent labeling of PCR fragments. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godwin, R.M.; Morgan, J.A. A simple, one-tube assay for the simultaneous detection and diagnosis of ten Australian poultry Eimeria. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolls, P.J.; Bock, R.E.; de Vos, A.J.; Waldron, S.J. Bovine Babesiosis. In OIE Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccine for Terrestrial Animals, 7th ed.; Work Organisation for Animal Health (OIE): Paris, France, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 601–615. [Google Scholar]
- Herndon, D.R.; Palmer, G.H.; Shkap, V.; Knowles, D.P., Jr.; Brayton, K.A. Complete genome sequence of Anaplasma marginale subsp. centrale. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 379–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, J.V.; Chieves, L.P.; Johnson, G.S.; Buening, G.M. Detection of Babesia bigemina-infected carriers by polymerase chain reaction amplification. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 2576–2582. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cawthraw, S.; Saunders, G.C.; Martin, T.C.; Sawyer, J.; Windl, O.; Reaney, S.D. Real-time PCR detection and identification of prohibited mammalian and avian material in animal feeds. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Theiler, A. Further Investigation into Anaplasmosis of South African Cattle; 1st report of the Director of Veterinary Research, Union of South Africa; Government Printer and Stationery Office: Pretoria, South Africa, 1911; pp. 7–46.
- Rogers, R.J.; Shiels, I.A. Epidemiology and control of anaplasmosis in Australia. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 1979, 50, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramos, C.A.; Araujo, F.R.; Souza, I.I.F.; Bacanelli, G.; Luiz, H.L.; Russi, L.S.; Oliveira, R.H.; Soares, C.O.; Rosinha, G.M.; Alves, L.C. Real-time polymerase chain reaction based on msa2c gene for detection of Babesia bovis. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 176, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monis, P.T.; Giglio, S.; Keegan, A.R.; Andrew Thompson, R.C. Emerging technologies for the detection and genetic characterization of protozoan parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2005, 21, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Salas, D.; Mira, A.; Mosqueda, J.; Garcia-Vazquez, Z.; Hidalgo-Ruiz, M.; Vela, N.A.; de Leon, A.A.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Schnittger, L. Molecular and serological detection of Babesia bovis- and Babesia bigemina-infection in bovines and water buffaloes raised jointly in an endemic field. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 217, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adjou Moumouni, P.F.; Aboge, G.O.; Terkawi, M.A.; Masatani, T.; Cao, S.; Kamyingkird, K.; Jirapattharasate, C.; Zhou, M.; Wang, G.; Liu, M.; et al. Molecular detection and characterization of Babesia bovis, Babesia bigemina, Theileria species and Anaplasma marginale isolated from cattle in Kenya. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Cao, S.; Terkawi, M.A.; Lan, D.T.; Long, P.T.; Yu, L.; Zhou, M.; Gong, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. Molecular and seroepidemiological survey of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina infections in cattle and water buffaloes in the central region of Vietnam. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 31, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Terkawi, M.A.; Alhasan, H.; Huyen, N.X.; Sabagh, A.; Awier, K.; Cao, S.; Goo, Y.K.; Aboge, G.; Yokoyama, N.; Nishikawa, Y.; et al. Molecular and serological prevalence of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina in cattle from central region of Syria. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 187, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Terkawi, M.A.; Cruz-Flores, M.J.; Claveria, F.G.; Aboge, G.O.; Yamagishi, J.; Goo, Y.K.; Cao, S.; Masatani, T.; Nishikawa, Y.; et al. Epidemiological survey of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina infections of cattle in Philippines. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combrink, M.P.; Troskie, P.C.; de Klerk, D.G.; Pienaar, R.; Latif, A.A.; Mans, B.J. Co-transmission of the non-transmissible South African Babesia bovis S24 vaccine strain during mixed infection with a field isolate. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2015, 6, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
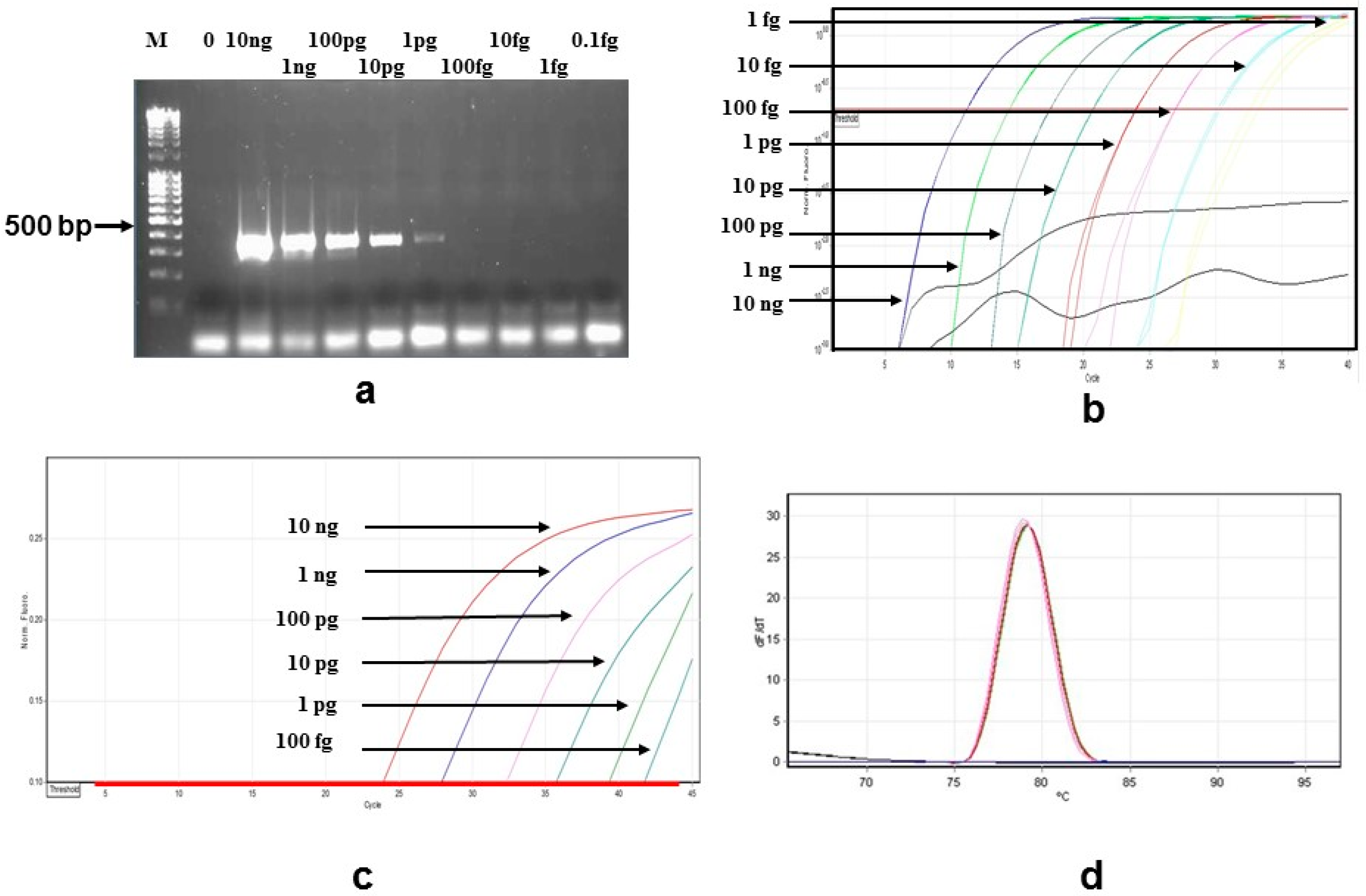
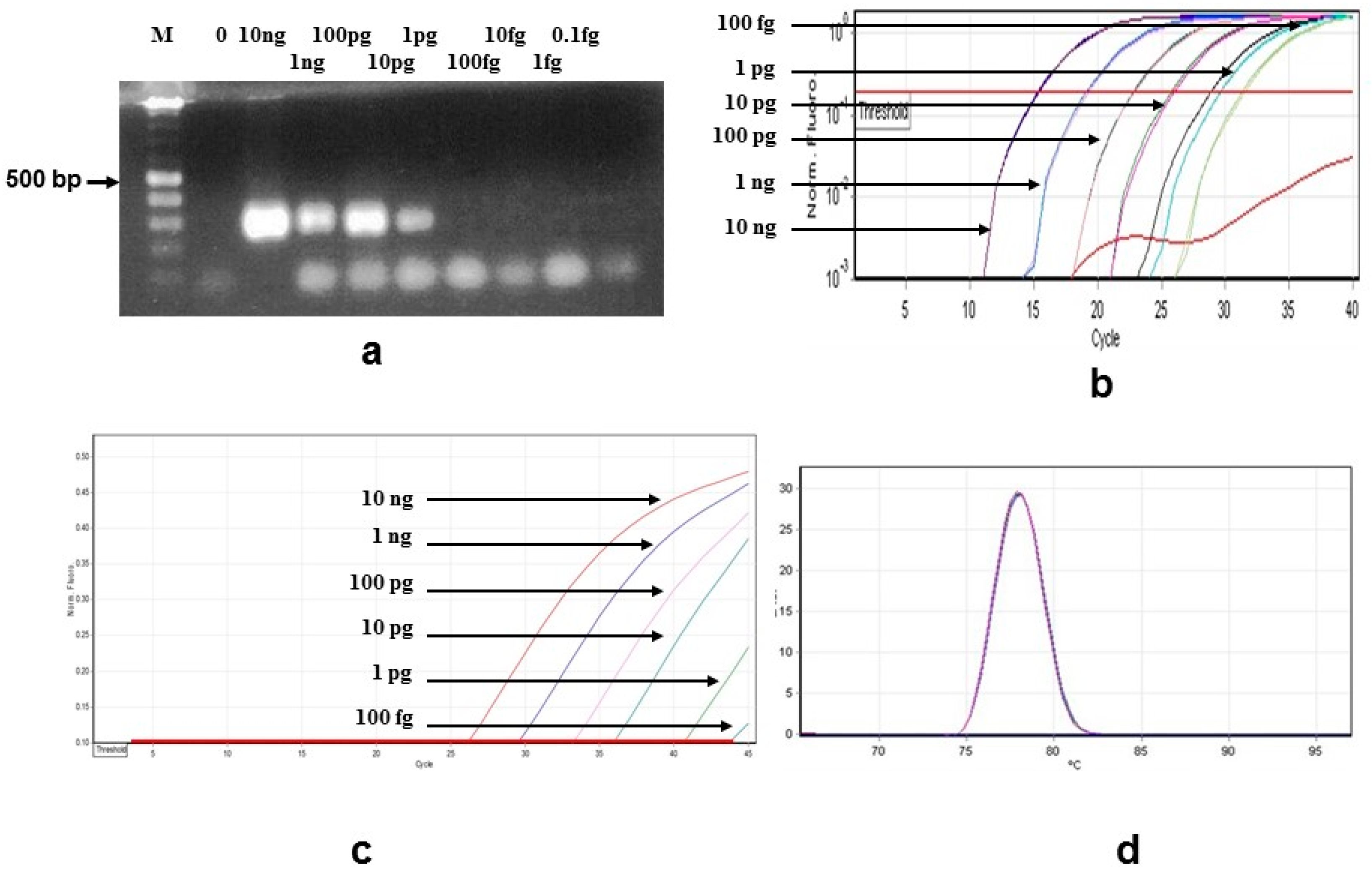
| Species Strain/No. | Sample Source 1 |
|---|---|
| Reference Isolates: | |
| B. microti-1610 | CDC |
| B. microti-1737 | CDC |
| B. microti-1750 | CDC |
| B. microti-1743 | CDC |
| B. microti-1716 | CDC |
| B. duncani-1671 | CDC |
| Babesia spp. 1749 CDC | CDC |
| A. marginale subsp. central 2 | TFC vaccine |
| A. marginale Dawn strain | TFC stabilate |
| B. bovis-Dixie vaccine strain | TFC vaccine calf |
| B. bigemina-G vaccine strain | TFC vaccine calf |
| B. bovis and B. bigemina field isolates (Species specific qPCR assays): | |
| B. bovis—1–31 | TFC field samples |
| B. bigemina—1–14 | TFC stabilates of field strains |
| B. bovis isolates for genotyping evaluation 3: | |
| B. bovis Dixie vaccine passaged through ticks-H03 4, H10 4 | TFC stabilates |
| B. bovis H92 5 | TFC stabilates of field strains |
| B. bovis H97 6 | |
| B. bovis J40 6 | |
| B. bovis J50 6 | |
| B. bovis—32 6 | TFC field samples |
| B. bovis—33 5 | |
| B. bovis—34 6 | |
| Species | Primer/Probe | Sequence 5′-3′ | Product Length (bp) | Target Sequence (Genbank No.) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. bovis | Standard PCR | 356 | (M38218.1) | [10] | |
| BoF | CACGAGGAAGGAACTACCGATGTTGA | 656–681 | |||
| BoR | CCAAGGAGCTTCAACGTACGAGGTCA | 986–1011 | |||
| SYBR Green qPCR | 88 | (GQ214235.1) | [16] | ||
| cbosg-1 (F) | TGTTCCTGGAAGCGTTGATTC | 135–155 | |||
| cbosg-2 (R) | AGCGTGAAAATAACGCATTGC | 202–222 | |||
| TaqMan qPCR | 90 | (AB499088.1) | This study | ||
| bovisF160 | ATATGTTTGCATTTGCTG | 160–178 | |||
| bovisR249 | CTCCAAACCAATATGAAAG | 230–249 | |||
| bovisPb | VIC-CAAACCATAAAGTCATCGGTATATCCTAC-MGB | 196–225 | |||
| Genotyping PCR | 245 | This study (B. bovis) M13 [24] | |||
| M13BbovITSF | 1 GAGCGGATAACAATTTCACACAGGAAGGAGAAGTCGTAACAAGG | (EF458299.1) | |||
| BbovITSR | GGTCGTGGCAGTCACGGC | 9–28 | |||
| M13-FAM | 6FAM-GAGCGGATAACAATTTCACACAGG | 236–253 | |||
| B. bigemina | Standard PCR | 278 | (S45366.1) | [28] | |
| BiIA | CATCTAATTTCTCTCCATACCCCTCC | 6–31 | |||
| BiIB | CCTCGGCTTCAACTCTGATGCCAAAG | 258–283 | |||
| SYBR Green qPCR | 88 | (GQ214234.1) | [16] | ||
| cbisg-1 (F) | TGTTCCAGGAGATGTTGATTC | 182–202 | |||
| cbisg-2 (R) | AGCATGGAAATAACGAAGTGC | 249–269 | |||
| TaqMan qPCR | 146 | (AB499085.1) | This study | ||
| bigemF295 | GGTCTATTTGGTGGAGTT | 295–313 | |||
| bigemR413 | ACAAGACCAAATGCAATT | 395-413 | |||
| bigemPb | 6FAM-CAATTGTTCTTGGAGCAGCT-TAMRA | 329–349 | |||
| Bovine | SYBR Green qPCR 2 | 108 | (V00654) | [29] | |
| MTFB | GCGATTTTAAAGACTAGACCC | 2642–2662 | |||
| MTRBO | TGAATAGGATTGCGCTGT | 2732–2749 |
| Reference | Assay Type | Species | Target Gene | Specificity | Sensitivity | Source of Isolates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [16] | SYBR Green | B. bovis B. bigemina | cytochrome b | 100% | 0.1 fg 1 (1000 target copies) | Spain, Argentina |
| B. bovis | 100% | 1 fg or 0.35 parasites/µL | Australia 2 | |||
| B. bigemina | 100% | 100 fg or 20 parasites/µL | ||||
| This study | TaqMan probes | B. bovis | cytochrome b | 100% | 100 fg or 35 parasites/µL | Australia |
| B. bigemina | 100% | 100 fg or 20 parasites/µL | ||||
| [32] | SYBR Green | B. bovis | msa2c | 100% | 1000 copies/mL | Brazil |
| [17] | TaqMan probes | B. bovis B. bigemina | 18S rRNA genes | 100% | 2.5 parasites/µL | Brazil |
| Clinical Samples 1 | Standard PCR B. bovis | Standard PCR B. bigemina | SYBR qPCR B. bovis | SYBR qPCR B. bigemina |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31 B. bovis | 22/31 | ND | 31/31 | 6/31 |
| 14 B. bigemina | ND | 14/14 | 4/14 | 14/14 |
| B. bovis Isolates 1 | Isolate Description | BvVA1 1,2 kb | ITS Alleles 1,2 bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dixie | Vaccine isolate | 3.5, 6.8 | 224, 234 |
| H03 | Dixie vaccine following tick passage | 6.8 | 224, 234 |
| H10 | Dixie vaccine following tick passage | 3.5, 6.8 | 224, 233, 234, 243 |
| H92 3 | Field isolate 3 | 5.5, 6.1 | 218, 233, 235, 239, 242, 247 |
| H97 | Field isolate | 6.4, 6.8 | 224, 234, 242 |
| J40 | Field isolate | 6.1, (6.2) | 224, 226, 227, 229, 231, 234, 236, 238, 239, 242 |
| J50 | Field isolate | 6.1 | 224, 233, 234 |
| 32 | Field isolate | 6.2, 8.0 | 224, 234, 237, (309), (337) |
| 33 | Field isolate | Nil | (142), (189), 220, 224, 250, 256, 315, 325, 337, 342 |
| 34 | Field isolate | 6.5 | 218, (224), 234, 244, (302), (337) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Sambono, J.L.; Morgan, J.A.T.; Venus, B.; Rolls, P.; Lew-Tabor, A.E. An Evaluation of Quantitative PCR Assays (TaqMan® and SYBR Green) for the Detection of Babesia bigemina and Babesia bovis, and a Novel Fluorescent-ITS1-PCR Capillary Electrophoresis Method for Genotyping B. bovis Isolates. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci3030023
Zhang B, Sambono JL, Morgan JAT, Venus B, Rolls P, Lew-Tabor AE. An Evaluation of Quantitative PCR Assays (TaqMan® and SYBR Green) for the Detection of Babesia bigemina and Babesia bovis, and a Novel Fluorescent-ITS1-PCR Capillary Electrophoresis Method for Genotyping B. bovis Isolates. Veterinary Sciences. 2016; 3(3):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci3030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bing, Jacqueline L. Sambono, Jess A. T. Morgan, Bronwyn Venus, Peter Rolls, and Ala E. Lew-Tabor. 2016. "An Evaluation of Quantitative PCR Assays (TaqMan® and SYBR Green) for the Detection of Babesia bigemina and Babesia bovis, and a Novel Fluorescent-ITS1-PCR Capillary Electrophoresis Method for Genotyping B. bovis Isolates" Veterinary Sciences 3, no. 3: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci3030023
APA StyleZhang, B., Sambono, J. L., Morgan, J. A. T., Venus, B., Rolls, P., & Lew-Tabor, A. E. (2016). An Evaluation of Quantitative PCR Assays (TaqMan® and SYBR Green) for the Detection of Babesia bigemina and Babesia bovis, and a Novel Fluorescent-ITS1-PCR Capillary Electrophoresis Method for Genotyping B. bovis Isolates. Veterinary Sciences, 3(3), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci3030023





