Genomic Variants, Transcriptomic Profile, Ultrasonographic Findings, and Antioxidant and Immunological Biomarkers Linked to Pregnancy Toxemia Susceptibility in Goats
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Study Design
Blood Sampling
2.2. Ultrasonographic Examination
2.3. Total RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.4. DNA Sequencing and SNP Analysis
2.5. Biochemical, Immunological, and Antioxidant Parameters
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
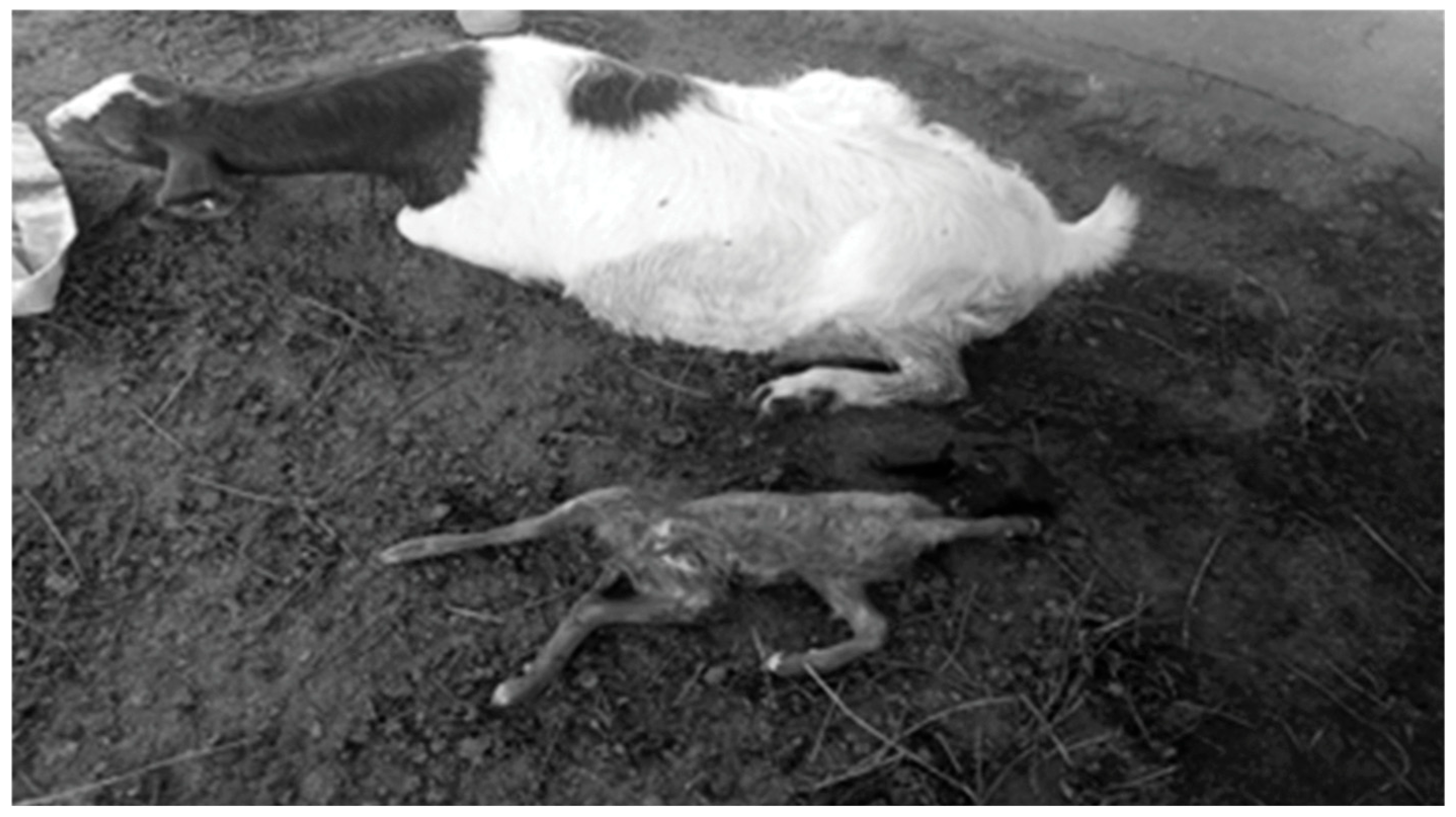
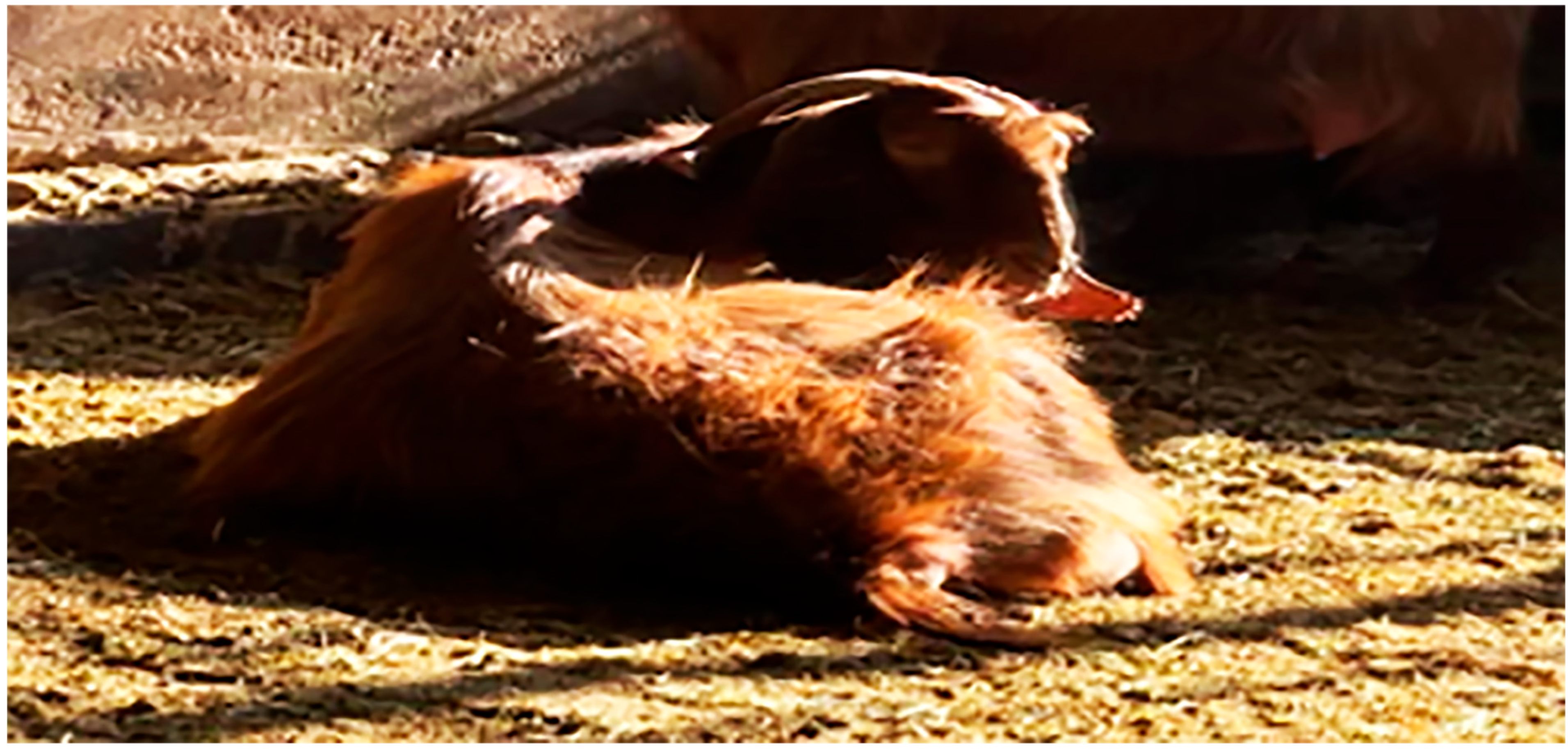
3.1. Clinical Findings
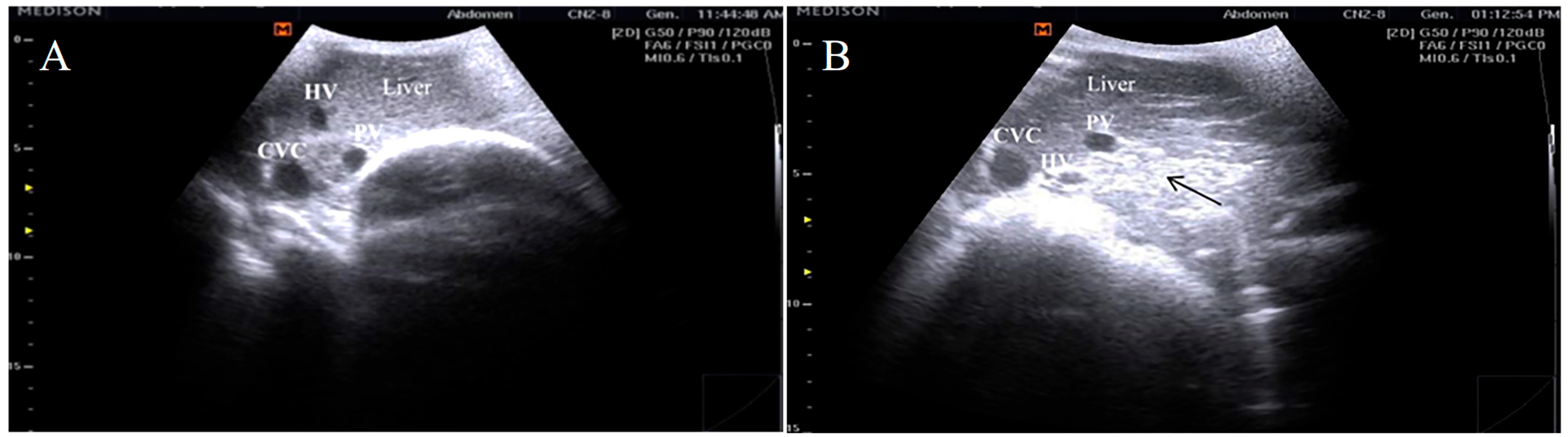
3.2. Ultrasonographic Findings
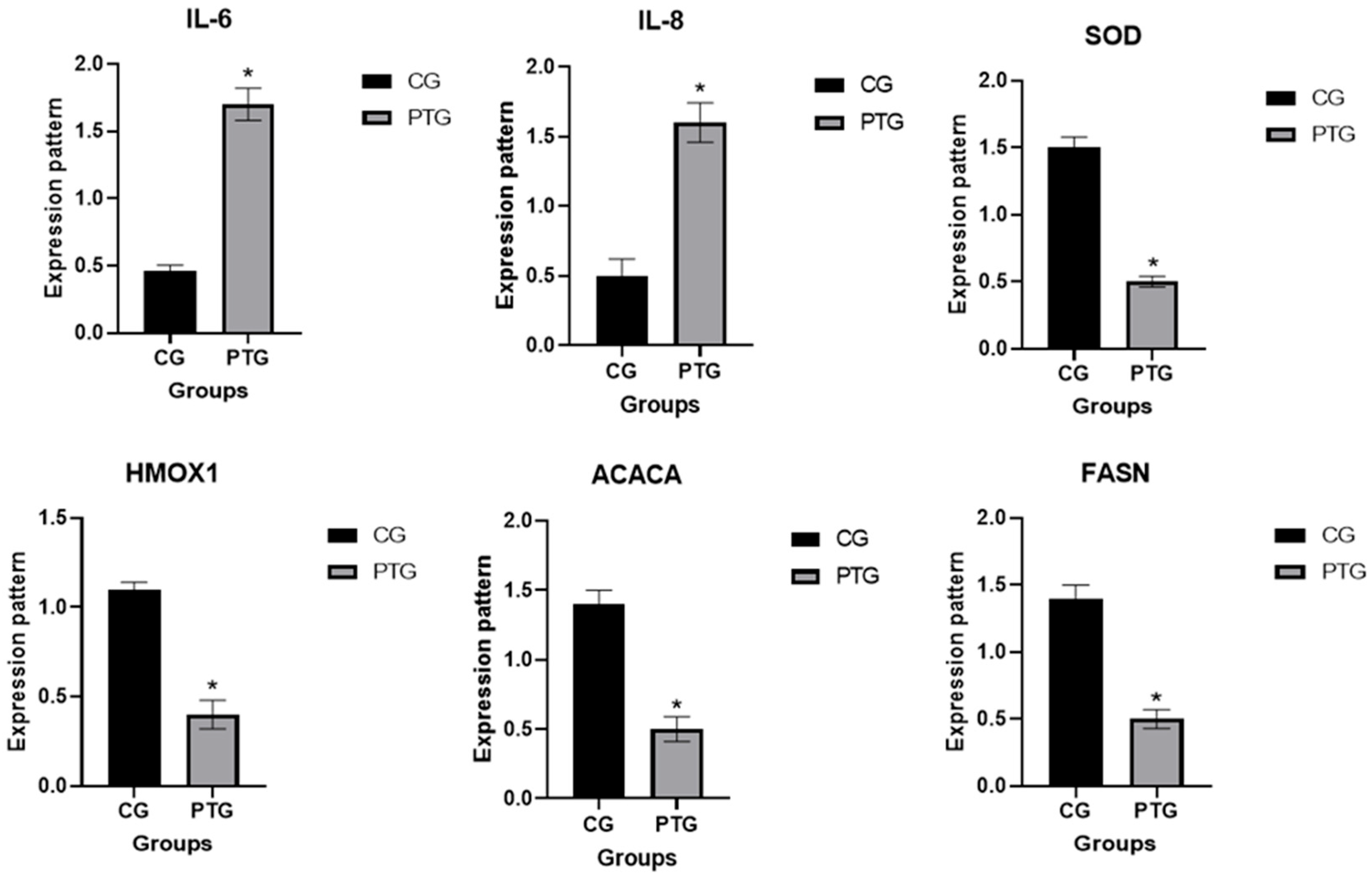
3.3. Patterns for Transcript Levels of Immune, Antioxidant, and Lipogenic Indicators
3.4. Genetic Polymorphisms of Immune, Antioxidant, and Lipogenic Genes
3.5. Hematological, Biochemical, Immunological, and Antioxidant Profile
4. Discussion
Diagnostic Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khameis, A.S.; Atteya, L.F.; Mansour, A.H.; Abdelhady, H.; Saad, A. Molecular detection and phylogenetic analysis of sheep pox virus in El Menofiya Governorate. J. Virol. Sci. 2018, 3, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Joint, F. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Caramel Colours Comb. Compend. Food Addit. Specif. Monogr. 2011, 11, 1817–7077. [Google Scholar]
- Khazaal, K. Comparison of the performance of Shami (Damascus) and Saanen goats raised under similar environmental conditions in Lebanon. In Options Mediterranean; Citeseer: State College, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Barıtçı, I.; Adıgüzel, C. Aleppo (Damascus) goat breeding. Dicle Univ. J. Inststitute Nat. Applied Sci. 2017, 6, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Mavrogenis, A.; Antoniades, N.; Hooper, R. The Damascus (Shami) goat of Cyprus. Anim. Genet. Resour. Inf. 2006, 38, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharwat, M. Serum concentration of bone metabolism biomarkers in goats during the transition period. Vet. Med. Int. 2020, 2020, 4064209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharwat, M.; Al-Hawas, A. Liver diseases in sheep and goats: Parallel sonographic and pathologic findings. Int. J. Vet. Sci. 2024, 13, 284–290. [Google Scholar]
- Mongini, A.; Van Saun, R.J. Pregnancy toxemia in sheep and goats. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. Pract. 2023, 39, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Guo, C.; Hu, F.; Sun, D.; Liu, J.; Mao, S. Molecular mechanisms of lipid metabolism disorder in livers of ewes with pregnancy toxemia. Animal 2019, 13, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takci, A.; Kivrak, M.B. Determination of the efficacy of human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) administrations on reproductive performance, placentation, parturition, and neonatal parameters on different post–mating days in Kangal ewes sexually induced during anestrus. Rev. Cient. De La Fac. De Vet. 2023, 33, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takci, A.; Kivrak, M.; Murat, H.; Cizmeci, S. Reproductive and economic evaluation of sexual stimulation during the anestrous period in a commercial farm with neonatal lamb losses. Arq. Bras. De Med. Veterinária E Zootec. 2023, 75, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Liu, N.; Wang, Y.; Ding, K.; Huang, S.; Zhang, C. Pregnancy Toxemia in ewes: A review of Molecular Metabolic mechanisms and Management Strategies. Metabolites 2023, 13, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rook, J.S. Pregnancy toxemia of ewes, does, and beef cows. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2000, 16, 293–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duehlmeier, R.; Fluegge, I.; Schwert, B.; Ganter, M. Insulin sensitivity during late gestation in ewes affected by pregnancy toxemia and in ewes with high and low susceptibility to this disorder. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 27, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Wang, R.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xue, G.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Analysis of fecal microbiome and metabolome changes in goats with pregnant toxemia. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, M.; Takcı, A.; Kıvrak, M.B. Comparison of some hematological and serum biochemical variables in Kangal Akkaraman, Texel and Île De France ewes in lactation period within Sivas province. Eurasian J. Veter.-Sci. 2021, 37, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faye, B.; Bengoumi, M. Camel Clinical Biochemistry and Hematology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Faraz, A.; Younas, M.; Waheed, A.; Yaqoob, M.; Ishaq, K. Growth performance and hair mineral status of Marecha (Camelus dromedarius) calves reared under different management systems. Pak. J. Zool. 2019, 51, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffield, T. Subclinical ketosis in lactating dairy cattle. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2000, 16, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, W.; Getinet, A.; Mekonnen, H. Study on live weight, carcass weight and dressing percentage of Issa camels in Ethiopia. École Natl. Vétérinaire De Toulouse 2002, 153, 713–716. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, N.; Singh, N.; Singh, O.; Pandey, V.; Verma, P. Oxidative stress and antioxidant status during transition period in dairy cows. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 24, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surai, P.F.; Earle-Payne, K. Antioxidant defences and redox homeostasis in animals. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.H.; Khalphallah, A.; Nakada, K.; Elmeligy, E.; Hassan, D.; Ebissy, E.A.; Ghandour, R.A.; Mousa, S.A.; Hassaneen, A.S.A. Clinical and correlated responses among steroid hormones and oxidant/antioxidant biomarkers in pregnant, non-pregnant and lactating CIDR-pre-synchronized dromedaries (Camelus dromedarius). Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Na, Y.; Jinyou, Z.; Khudhair, N.; Guixue, Z. Responses of Chicken Sertoli Cells and Fibroblasts after Transfection with Plasmids pEGFP-N3-HNP-1. Pak. Vet. J. 2015, 35, 504. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, D.P.; Bermingham, M.L.; Good, M.; More, S.J. Genetics of animal health and disease in cattle. Ir. Vet. J. 2011, 64, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, A.M.; Reyer, H.; Wimmers, K.; Bertolini, F.; Aboul-Naga, A.; Braz, C.U.; Rabee, A.E. Genome-wide landscape of runs of homozygosity and differentiation across Egyptian goat breeds. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, M.; Ajadi, A.A.; Atata, J.A.; Olaniyi, M.O.; Raufu, I.A.; Lawal, F.M.; Bashir, A.; Odetokun, I.O.; Raji, L.O.; Balogun, R.B.; et al. Pathology and oxidative stress changes associated with pregnancy toxaemia in ewes. Sahel J. Vet. Sci. 2024, 21, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (US); Committee on Nutrient Requirements of Small Ruminants. Nutrient Requirements of Small Ruminants: Sheep, Goats, Cervids, and New World Camelids; China Legal Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pugh, D. Sheep and Goat Medicine, 2nd ed.; Pugh, D.G., Baird, A.N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Available online: https://www.elsevier.com (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Al-Sharif, M.; Ateya, A. New insights on coding mutations and mRNA levels of candidate genes associated with diarrhea susceptibility in Baladi goat. Agriculture 2023, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebissy, E.; Darwish, A.; Hafez, A.A.; Ateya, A.; El-Sayed, A. Individual genomic loci, transcript level, and biochemical profile of immune and antioxidant markers associated with genetically identified bacterial mastitis in Shami goats in Egypt. Open Vet. J. 2024, 14, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, A.; Ebissy, E.; Hafez, A.; Ateya, A.; El-Sayed, A. Nucleotide sequence variants, gene expression and serum profile of immune and antioxidant markers associated with bacterial diarrhea susceptibility in Barki lambs. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesenberg-Smith, K.A.; Pessarakli, M.M.; Wolk, D.M. Assessment of DNA yield and purity: An overlooked detail of PCR troubleshooting. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2012, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, B.; Al-Sharif, M.; Abdo, M.; Fericean, L.; Ateya, A. New insights on nucleotide sequence variants and mRNA levels of candidate genes assessing resistance/susceptibility to mastitis in Holstein and Montbéliarde dairy cows. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6. 0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.G.; Cockcroft, P.D.; Elmhurst, S. Clinical Examination of Farm Animals; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 331. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, N.H. Mutation and the evolution of recombination. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 1281–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kala, D.; Dhiman, G.; Yadav, V.; Krokhotin, A.; Dokholyan, N.V. Predicting the functional consequences of non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms in IL8 gene. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, D.-F.; Huang, J.-H.; Zhu, Q.-H.; Luo, L.-Y.; Lu, R.; Xie, X.-L.; Salehian-Dehkordi, H.; Esmailizadeh, A.; Liu, G.E.; et al. Structural variant landscapes reveal convergent signatures of evolution in sheep and goats. Genome Biol. 2024, 25, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwish, A.A.; El-Ebissy, I.A. The diagnostic value of acute phase proteins in Barki ewes with pregnancy toxemia. Alex. J. Veter.-Sci. 2019, 62, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akraiem, A.; Zaid, A.; Arhaiem, A.; Abd Elghany, H. Evaluation of clinical, hematological and biochemical parameters in goats with subclinical and clinical pregnancy toxemia in Libya. J. Anim. Sci. Vet. Med. 2020, 5, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, R.; Beigh, S.; Mir, A.; Shaheen, M.; Hussain, S.; Nisar, M.; Dar, A. Evaluation of metabolic and oxidative profile in ovine pregnancy toxemia and to determine their association with diagnosis and prognosis of disease. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2022, 54, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Kamr, A.; Elkholy, A.; Arbaga, A. Conventional and Doppler ultrasonographic diagnosis of subclinical pregnancy toxemia with altered serum cortisol and biochemical parameters in pregnant does. Res. Vet. Sci. 2024, 176, 105337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türk, S.; Keleş, İ. Adipokine concentrations in sheep with experimental pregnancy toxemia. A randomized, controlled clinical trial. Rev. Científica De La Fac. De Cienc. Vet. 2024, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Tharwat, M.; Alkheraif, A.A.; Marzok, M. Pregnancy toxemia in small ruminants: Clinical, sonographic, hematobiochemical and pathologic findings. Int. J. Vet. Sci. 2024, 14, 204–2011. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, M.A.; Elshahawy, I.I. Clinico-biochemical diagnosis of pregnancy toxemia in ewes with special reference to novel biomarkers. Alex. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 48, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Tharwat, M. Clinical, ultrasonographic, and postmortem findings in sheep and goats with urinary tract disorders. Vet. World 2021, 14, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharwat, M.; Hegazy, Y.; Alkheraif, A.A. Discolored urine in sheep and goats: Clinical, etiological, hematobiochemical, sonographic and postmortem findings. Open Vet. J. 2024, 14, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, S.; Sharma, M.; Singh, A.; Sharma, V.; Thakur, S. Clinical management of pregnancy toxaemia in a goat—A case report. Indian J. Anim. Health 2020, 59, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbaga, A.; Hassan, H.; Elkholy, A.; Kamr, A. Hepatic B-mode Ultrasonography for the Diagnosis of Does Subclinical Pregnancy Toxemia with Special Reference to Hematological Alterations. J. Curr. Vet. Res. 2023, 5, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, T.; Oikawa, S.; Kurosawa, T.; Takehana, K.; Hosaka, Y.; Okada, H.; Koiwa, M.; Sato, H. Focal fatty liver in a heifer: Utility of ultrasonography in diagnosis. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2004, 66, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.A.; El-sheikh, K.; Deheidy, N.; Tharwat, M. Diagnostic investigations for fatty liver syndrome in Egyptian buffaloes. Global Vet. 2014, 12, 682–686. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, M.A.; El-Ashker, M.R.; El-Sayed, A.A.; Ibrahim, F.A.; Awad, M.E. Hepatic ultrasonography and biochemical alterations in Barki sheep under negative energy balance. Egypt. J. Chem. Environ. Health 2016, 2, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasimanickam, R.K. Subclinical pregnancy toxemia-induced gene expression changes in ovine placenta and uterus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodall, C.; Maclaren, L.; Watt, N. Differential levels of mRNAs for cytokines, the interleukin-2 receptor and class II DR/DQ genes in ovine interstitial pneumonia induced by maedi visna virus infection. Vet. Pathol. 1997, 34, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasauer, A.; Chandel, N.S. Targeting antioxidants for cancer therapy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 92, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consoli, V.; Sorrenti, V.; Grosso, S.; Vanella, L. Heme oxygenase-1 signaling and redox homeostasis in physiopathological conditions. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannen, H. Identification and utilization of genes associated with beef qualities. Anim. Sci. J. 2011, 82, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Harten, S.; Brito, R.; Almeida, A.; Scanlon, T.; Kilminster, T.; Milton, J.; Greeff, J.; Oldham, C.; Cardoso, L. Gene expression of regulatory enzymes involved in the intermediate metabolism of sheep subjected to feed restriction. Animal 2013, 7, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticiani, E.; Urio, M.; Ferreira, R.; Harvatine, K.; De Oliveira, D. Transcriptional regulation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase α isoforms in dairy ewes during conjugated linoleic acid induced milk fat depression. Animal 2016, 10, 1677–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadi, M.S.; Naserian, A.A.; Nasiri, M.R.; Heravi, R.M.; Valizadeh, R. Evaluation of SCD and FASN gene expression in Baluchi, Iran-Black, and Arman Sheep. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 5, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhou, R.; Wu, J.; Brown, M. Effects of tail docking on the expression of genes related to lipid metabolism in Lanzhou fat-tailed sheep. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.; Ateya, A.; Hamed, M.; Shoieb, S.; Ibrahim, H.; El-Ashker, M.; Youssef, M.; Ibrahim, F. Gene expression pattern of acetyl-coA carboxylase alpha, fatty acid synthase, and stearoyl-CoA desaturase in pregnant Barki sheep under complete feed deprivation. Mansoura Vet. Med. J. 2019, 20, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.E.; Lashinger, L.M.; Hursting, S.D. The growing challenge of obesity and cancer: An inflammatory issue. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2011, 1229, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khames Mustafa, M.; Shareef Saed, O.; Abdulealah Ismaeel, M. Clinical and Biochemical Study of Pregnancy Toxemia in Iraqi Ewes. Arch Razi Inst. 2023, 78, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky, J.M.; Glass, C.K. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Y.R.; Durrani, A.Z.; Muhammad, I.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, R.L.; Hussain, K.; Rabbani, A.H. Determination of hemato-biochemical biomarkers, associated risk factors and therapeutic protocols for pregnancy toxemia in Beetal goats. Kafkas Üniversitesi Vet. Fakültesi Derg. 2021, 27, 525–535. [Google Scholar]
- Constable, P.D.; Hinchcliff, K.W.; Done, S.H.; Grünberg, W. Veterinary Medicine: A Textbook of the Diseases of Cattle, Horses, Sheep, Pigs and Goats; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mg El-Din, I.; El-Sangery, F. Clinicobiochemical studies on pregnancy toxaemia in sheep in sharkia governorate. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2005, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Găvan, C.; Retea, C.; Motorga, V. Changes in the hematological profile of Holstein primiparous in periparturient period and in early to mid lactation. Sci. Pap. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 43, 244. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, K.M.; Taylor, J.D.; Streeter, R.N. Evaluation of prognostic indicators for goats with pregnancy toxemia. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2019, 254, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.E.; Kuthiala, S.; Liu, H.L.; Durosier, D.L.; Cao, M.; Burns, P.; Desrochers, A.; Fecteau, G.; Frasch, M.G. Effect of maternal ketoacidosis on the ovine fetus. Can. Vet. J. 2015, 56, 863. [Google Scholar]
- Marutsova, V. Changes in blood enzyme activities in ewes with ketosis. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 3, 462–473. [Google Scholar]
- Vasava, P.R.; Jani, R.; Goswami, H.; Rathwa, S.; Tandel, F. Studies on clinical signs and biochemical alteration in pregnancy toxemic goats. Vet. World 2016, 9, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefnawy, A.; Shousha, S.; Youssef, S. Hematobiochemical profile of pregnant and experimentally pregnancy toxemic goats. J. Basic Appl. Chem. 2011, 1, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Balikci, E.; Yildiz, A.; Gurdogan, F. Investigation on some biochemical and clinical parameters for pregnancy toxemia in Akkaraman ewes. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2009, 8, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, A.A.R. The effect of ovine pregnancy toxemia on acid base balance, oxidative stress, some hormonal assays and matrix metalloproteinases. Europ J. Biomed Pharm. Sci. 2019, 6, 393–400. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Ghani, M.; El-Sherry, T.; Hayder, M.; Abou-Khalil, N. Profile of peroxidative injury and antioxidant indicators in singleton, twins and multiple bearing goats throughout pregnancy. Asian Pac. J. Reprod. 2016, 5, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarczyk, B.; Jankowiak, D.; Tomza-Marciniak, A.; Pilarczyk, R.; Sablik, P.; Drozd, R.; Tylkowska, A.; Skólmowska, M. Selenium concentration and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) activity in serum of cows at different stages of lactation. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 147, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, O.A.; El-Boshy, M.E.; El-Khodary, S.A.; Reisha, E.F.; Gadalla, H.A. Selective serum oxidant, antioxidant and trace elements profile in Ossimi sheep affected with pregnancy toxemia. Life Sci. J. 2013, 10, 2833–2837. [Google Scholar]
- Gurdogan, F.; Balikci, E.; Yildiz, A. Some acute phase proteins, oxidative stress biomarkers and antioxidant enzyme activities in ewes with pregnancy toxemia (short paper). Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 15, 297–299. [Google Scholar]
- El-Deeb, W. Novel biomarkers for pregnancy toxemia in ewes: Acute phase proteins and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Open Access Sci. Rep. 2012, 243, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Albay, M.K.; Karakurum, M.; Sahınduran, S.; Sezer, K.; Yıldız, R.; Buyukoglu, T. Selected serum biochemical parameters and acute phase protein levels in a herd of Saanen goats showing signs of pregnancy toxaemia. Vet. Med. 2014, 59, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, N.; Tribe, R. Cytokine networks and the regulation of uterine function in pregnancy and parturition. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 20, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Sengupta, P. Defining pregnancy phases with cytokine shift. J. Pregnancy Reprod 2017, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ingredient | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Corn | 530 kg |
| Wheat bran | 240 kg |
| Soya bean | 230 kg |
| Sodium chloride | 5 kg |
| Calcium carbonate | 10 kg |
| Premix | 1 kg |
| Netro-Nill | 0.5 kg |
| Fylax | 0.5 kg |
| Investigated Marker | Primer | Product Size (bp) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | GenBank Isolate | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | F5′-ATGAACTCCCTCTTCACAAGCG-3′ R5′-CTACTTCATCCGAATAGCTCTCA-3′ | 627 | 60 | NM_001285640.1 | Current study |
| IL-8 | F5′-CTGCTCTCTGCAGCTCTGTGTG-3′ R5′-TGGATCTTGCTTCTCAGCTCT-3′ | 264 | 58 | XM_005681749.3 | |
| SOD3 | F5′-GCGGCGCTCCATGCGGTCTGCC-3′ R5′-CAGGTCGTCCTCGCCCGCGTGGA-3′ | 393 | 58 | NM_001285675.1 | |
| HMOX1 | F5′-CTGGAGGAGGAGATCGAACGCA-3′ R5′-ACAGCTGGATGTTGAGCAGGAA-3′ | 460 | 58 | NM_001285567.1 | |
| ACACA | F5′-GCTGAGCTTCACACAGGCAGTC-3′ R5′-CACCACAGCCTTCATGTGTCCT-3′ | 477 | 60 | DQ370054.1 | |
| FASN | F5′-TACGCCGTGCTGGGCAGCCAGG-3′ R5′-CTCCTGAGAGATGCAGCCGTCG-3′ | 381 | 58 | NM_001285629.1 | |
| ß. actin | F5′-TGGCACCACACCTTCTACAACG-3′ R5′-GGCTTCCTTGATGTCACGGACGA-3′ | 30 | 60 | AF481159.1 |
| Variable | Control Group | Pregnancy Toxemic Group | p Value | Reference Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 39.1 ± 0.05 | 37.2 ± 0.1 * | 0.001 | 38.5–40 [37] |
| Pulse (beats/min) | 84.3 ± 2.3 | 52.3 ± 1.4 * | 0.001 | 70–90 [37] |
| Respiration (breaths/min) | 27 ± 0.5 | 37 ± 0.5 * | 0.001 | 15–30 [37] |
| Gene | SNPs | Healthy n = 33 | Pregnancy Toxemia n = 17 | Total n = 50 | Chi-Square Value X2 | p Value | Kind of Inherited Change | Amino Acid Order and Sort |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | G111A | 18/33 | -/17 | 18/50 | 14.4 | 0.001 | Synonymous | 37 K |
| IL-8 | T115C | 21/33 | -/17 | 21/50 | 18.6 | 0.001 | Synonymous | 39 L |
| G196A | -/33 | 11/17 | 11/50 | 27.3 | 0.001 | Non-synonymous | 66 D to N | |
| SOD3 | T245C | 13/33 | -/17 | 13/50 | 9 | 0.001 | Non-synonymous | 82 L to P |
| HMOX1 | T81C | 17/33 | -/17 | 17/50 | 13.2 | 0.001 | Synonymous | 27 A |
| G309C | -/33 | 13/17 | 13/50 | 34.1 | 0.001 | Synonymous | 103 G | |
| ACACA | G166C | -/33 | 10/17 | 10/50 | 24.2 | 0.001 | Non-synonymous | 56 G to R |
| G186A | 24/33 | -/17 | 24/50 | 23.7 | 0.001 | Synonymous | 62 R | |
| FASN | C48G | -/33 | 9/17 | 9/50 | 21.3 | 0.001 | Synonymous | 16 V |
| T57C | 14/33 | -/17 | 14/50 | 10 | 0.001 | Synonymous | 19 S | |
| G214A | 18/33 | -/17 | 18/50 | 14.4 | 0.001 | Non-synonymous | 72 A to T |
| Predicted Group Membership | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy | Diseased | |||
| Count | Healthy | 35 | 0 | 100 |
| Diseased | 0 | 35 | 100 | |
| % | Healthy | 35 | 0.0 | 100.0 |
| Diseased | 0.0 | 35 | 100.0 | |
| Parameter | Healthy Does | Pregnancy Toxemic Does | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| RBC (×1012/L) | 10.8 ± 0.5 | 8.5 ± 0.4 * | 0.03 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 9.8 ± 0.2 | 8 ± 0.3 * | 0.01 |
| PCV% | 36.3 ± 0.8 | 30.2 ± 0.5 * | 0. 007 |
| MCV (fL) | 40.1 ± 0.6 | 33 ± 0.5 * | 0.001 |
| MCH (pg) | 9.1 ± 0.4 | 6.2 ± 0.1 * | 0.01 |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 29.5 ± 0.4 | 20.8 ± 0.7 * | 0.002 |
| WBC (×109/L) | 7.9 ± 0.5 | 10 ± 0.08 * | 0.001 |
| Neutrophil (×109/L) | 6 ± 0.05 | 7.3 ± 0.08 * | 0.003 |
| lymphocyte (×109/L) | 3.3 ± 0.1 | 3.9 ± 0.05 * | 0.001 |
| Parameter | Normal Does | Pregnancy Toxemic Does | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 90 ± 7.6 | 53.3 ± 6 * | 0.02 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 70.3 ± 8.9 | 47 ± 7.2 | 0.01 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 40 ± 0.5 | 62 ± 1.7 * | 0.003 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 47 ± 7.2 | 31 ± 1 * | 0.001 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 38.2 ± 0.3 | 30 ± 0.5 * | 0.01 |
| Total protein P (g/dL) | 7.4 ± 0.2 | 5.2 ± 0.3 * | 0.01 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.8 ± 0.1 | 3 ± 0.05 * | 0.009 |
| Globulin (g/dL) | 3.8 ± 0.05 | 1.8 ± 0.05 * | 0.001 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 45 ± 0.5 | 64 ± 2 * | 0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.6 ± 0.01 | 1 ± 0.03 * | 0.001 |
| NEFAs (mmol/L) | 0.2 ± 0.01 | 0.5 ± 0.008 * | 0.001 |
| BHBA (mmol/L) | 0.5 ± 0.01 | 2.5 ± 0.04 * | 0.001 |
| AST (U/L) | 51 ± 0.5 | 81 ± 1.8 * | 0.002 |
| ALT (U/L) | 25 ± 0.5 | 44 ± 1.1 * | 0.001 |
| Parameters | Healthy Does | Pregnancy Toxemic Does | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL1α (pg/mL) | 39.7 ± 1.1 | 102.1 ± 1.6 * | 0.001 |
| IL 1β (pg/mL) | 49.2 ± 0.5 | 115.4 ± 1.4 * | 0.001 |
| IL 6 (pg/mL) | 28.9 ± 0.6 | 99.2 ± 0.3 * | 0.001 |
| IL10 (pg/mL) | 133 ± 0.5 | 67.9 ± 0.6 * | 0.001 |
| TNFα (pg/mL) | 53 ± 0.5 | 142.1 ± 1.2 * | 0.001 |
| GPx (U/gHb) | 35.5 ± 0.3 | 22.2 ± 0.6 * | 0.001 |
| GSH (mg/dL) | 43.3 ± 2.1 | 28.8 ± 0.4 * | 0.001 |
| CAT (U/mL) | 35.4 ± 0.4 | 20.5 ± 0.4 * | 0.001 |
| SOD (U/mL) | 49.3 ± 0.7 | 33.2 ± 1 * | 0.001 |
| MDA (nmol/mL) | 5.6 ± 0.4 | 12.7 ± 0.6 * | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Sayed, A.; Marzok, M.; Alqahtani, H.A.; Tahoun, A.; Almubarak, A.I.; Elkhidr, R.Y.; Al Mohamed, Z.; Abdelnaby, E.A.; Babiker, H.; Alharbi, H.M.; et al. Genomic Variants, Transcriptomic Profile, Ultrasonographic Findings, and Antioxidant and Immunological Biomarkers Linked to Pregnancy Toxemia Susceptibility in Goats. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090891
El-Sayed A, Marzok M, Alqahtani HA, Tahoun A, Almubarak AI, Elkhidr RY, Al Mohamed Z, Abdelnaby EA, Babiker H, Alharbi HM, et al. Genomic Variants, Transcriptomic Profile, Ultrasonographic Findings, and Antioxidant and Immunological Biomarkers Linked to Pregnancy Toxemia Susceptibility in Goats. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(9):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090891
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Sayed, Ahmed, Mohamed Marzok, Huda A. Alqahtani, Amin Tahoun, Adel I. Almubarak, Rasha Yassin Elkhidr, Zakriya Al Mohamed, Elshymaa A. Abdelnaby, Hussein Babiker, Hanan M. Alharbi, and et al. 2025. "Genomic Variants, Transcriptomic Profile, Ultrasonographic Findings, and Antioxidant and Immunological Biomarkers Linked to Pregnancy Toxemia Susceptibility in Goats" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 9: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090891
APA StyleEl-Sayed, A., Marzok, M., Alqahtani, H. A., Tahoun, A., Almubarak, A. I., Elkhidr, R. Y., Al Mohamed, Z., Abdelnaby, E. A., Babiker, H., Alharbi, H. M., Alwutayd, K. M., & Ateya, A. (2025). Genomic Variants, Transcriptomic Profile, Ultrasonographic Findings, and Antioxidant and Immunological Biomarkers Linked to Pregnancy Toxemia Susceptibility in Goats. Veterinary Sciences, 12(9), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090891







