Dexmedetomidine or Butorphanol for Co-Induction of General Anaesthesia with Propofol in Unpremedicated Healthy Dogs: Clinical and Echocardiographic Assessment
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
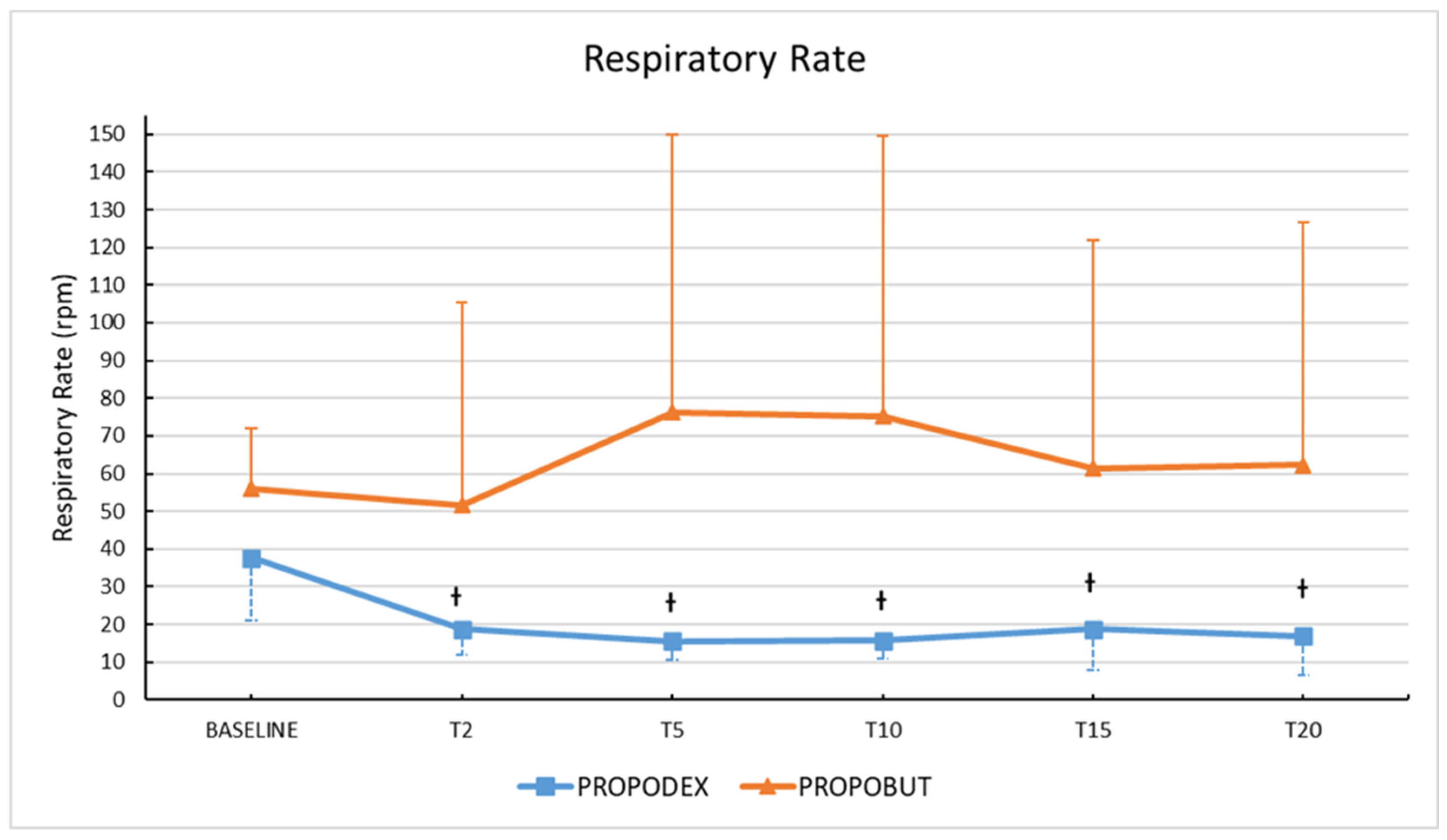
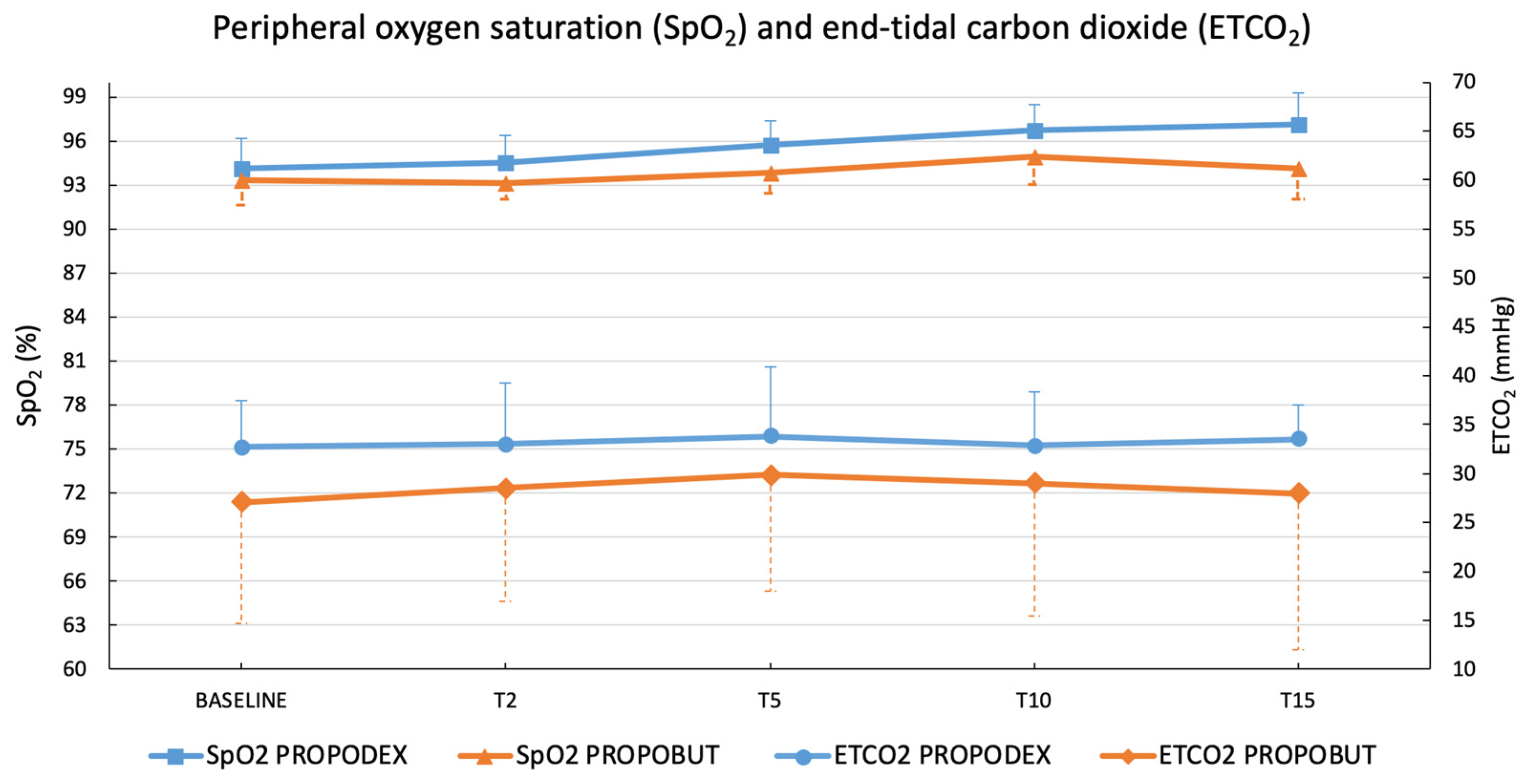
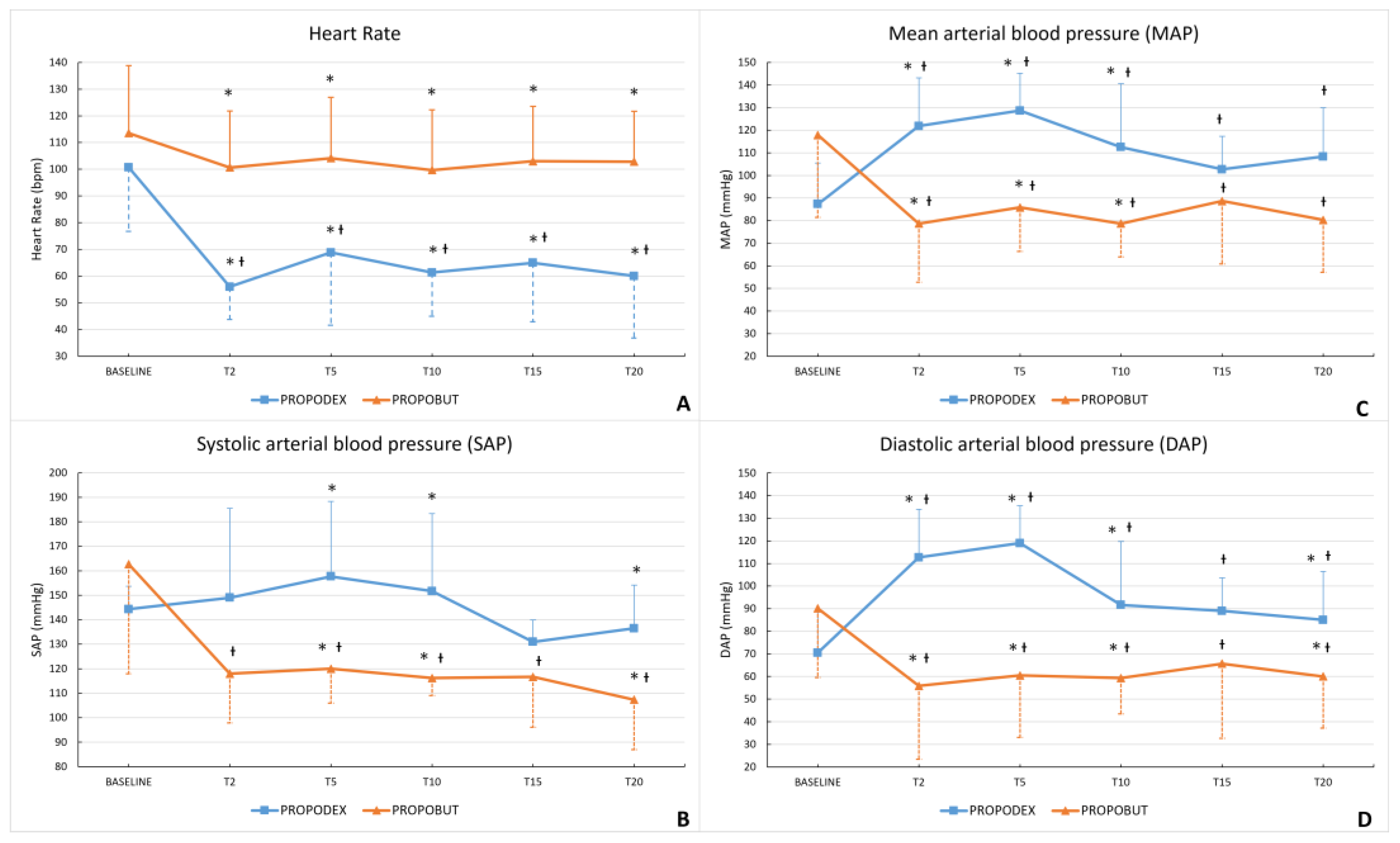
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2-D | Two-dimensional |
| ANOVA | Repeated-measures analysis of variance |
| AO | Aortic diameter |
| ARJ | Regurgitant Jet Area |
| ARJ/LAA ratio | Regurgitant Jet Area to Left Atrium Area Ratio |
| ASA | American Society of Anaesthesiologists |
| A-V max | A peak velocity |
| BCS | Body condition score |
| BPM | Beats per minute |
| BSA | Body surface area |
| bECHO | Baseline echocardiography |
| BUT | Butorphanol |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CO | Cardiac output |
| DAP | Diastolic arterial pressure |
| DEX | Dexmedetomidine |
| E/A | E peak velocity to A peak velocity ratio |
| EDVI | End diastolic volume index |
| EF | Ejection fraction |
| ESVI | End-systolic volume index |
| ETCO2 | End-tidal carbon dioxide |
| E-V max | E peak velocity |
| FS | Fractional shortening |
| HR | Heart rate |
| IV | Intravenous |
| LA | Left atrial |
| LA/Ao | Left atrial-to-aortic ratio |
| LAA | Left atrium area |
| LV | Left ventricular |
| LVEDV | Left ventricular end diastolic volume |
| LVESV | Left ventricular end-systolic volume |
| LVIDd | Left ventricular internal diastolic diameter |
| LVIDs | Left ventricular internal systolic diameter |
| MAP | Mean arterial pressure |
| pECHO | Post-induction echocardiography |
| PPF | Propofol |
| PPF-I | Propofol required for intubation |
| PPF-M | Propofol required for maintenance |
| PROPOBUT | Propofol-butorphanol group |
| PROPODEX | Propofol-dexmedetomidine group |
| RPM | Rest per minute |
| RR | Respiratory rate |
| SAP | Systolic arterial pressure |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SMOD | Simpson’s method of discs |
| SpO2 | Peripheral oxygen saturation |
| SV | Stroke volume |
| T0 | Baseline time (induction time) |
| T2 | Two minutes from induction |
| T5 | Five minutes from induction |
| T10 | Ten minutes from induction |
| T15 | Fifteen minutes from induction |
| T20 | Twenty minutes from induction |
| VTD | Telediastolic volume |
| VTIAo | Aortic velocity time integral |
| VTIPv | Pulmonary velocity time integral |
References
- Lundy, J.S. Balanced Anaesthesia. Minn. Med. J. 1926, 9, 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickx, J.F.A.; Eger, E.I.; Sonner, J.M.; Shafer, S.L. Is Synergy the Rule? A Review of Anesthetic Interactions Producing Hypnosis and Immobility. Anesth. Analg. 2008, 107, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covey-Crump, G.L.; Murison, P.J. Fentanyl or Midazolam for Co-Induction of Anaesthesia with Propofol in Dogs. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2008, 35, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, C.E.; Bufalari, A. Propofol Anesthesia. Vet. Clin. N. Am.-Small Anim. Pract. 1999, 29, 747–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.K.; Seddighi, R.; Cox, S.K.; Sun, X.; Knych, H.K.; Doherty, T.J. Effect of Dexmedetomidine on the Minimum Infusion Rate of Propofol Preventing Movement in Dogs. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2017, 44, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattai, A.; Rabozzi, R.; Ferasin, H.; Isola, M.; Franci, P. Haemodynamic Changes during Propofol Induction in Dogs: New Findings and Approach of Monitoring. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, S.H. Injectable Anesthetics. In Veterinary Anesthesia and Analgesia: The Fifth Edition of Lumb and Jones; Grimm, K.A., Lamont, L.A., Tranquilli, W.J., Greene, S.A., Robertson, S.A., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2015; pp. 277–296. ISBN 9781118526231. [Google Scholar]
- Geel, J.K. The Effect of Premedication on the Induction Dose of Propofol in Dogs and Cats. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 1991, 62, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Bhardwaj, N.; Jain, K. Efficacy of Ketamine and Midazolam as Co-Induction Agents with Propofol for Laryngeal Mask Insertion in Children. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2008, 18, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravasio, G.; Gallo, M.; Beccaglia, M.; Comazzi, S.; Gelain, M.E.; Fonda, D.; Bronzo, V.; Zonca, A. Evaluation of a Ketamine-Propofol Drug Combination with or without Dexmedetomidine for Intravenous Anesthesia in Cats Undergoing Ovariectomy. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2012, 241, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springfield, D.; KuKanich, B.; Gray, M.; KuKanich, K.; Lai, P. Dosing Protocols to Increase the Efficacy of Butorphanol in Dogs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 45, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pircio, A.W.; Gylys, J.A.; Cavanagh, R.L.; Buyniski, J.P.; Bierwagen, M.E. The Pharmacology of Butorphanol, a 3,14-Dihydroxymorphinan Narcotic Antagonist Analgesic. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1976, 220, 231–257. [Google Scholar]
- Hosgood, G. Pharmacologic Features of Butorphanol in Dogs and Cats. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1990, 196, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantino, S.C.; Kleine, S.A.; Smith, C.K.; Smith, S.M.; Zhu, X.; Seddighi, R. Effects of Intravenous Acepromazine and Butorphanol on Propofol Dosage for Induction of Anesthesia in Healthy Beagle Dogs. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2022, 49, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, T.; Nishimura, R.; Mochizuki, M.; Sasaki, N. Effects of Midazolam-Butorphanol, Acepromazine-Butorphanol and Medetomidine on an Induction Dose of Propofol and Their Compatibility in Dogs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2003, 65, 1141–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, M.B.; Nagrale, M.; Dwivedi, S.; Singh, H. What Happens to the Hemodynamic Responses for Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion When We Supplement Propofol with Butorphanol or Fentanyl for Induction of Anesthesia: A Comparative Assessment and Critical Review. Int. J. Crit. Illn. Inj. Sci. 2016, 6, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagalakshmi, P.; Leo, S.; Uthirapathi, S. Use of Butorphanol, Fentanyl, and Ketamine as Co-Induction Agents with Propofol for Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion: A Comparative Study. Anesth. Essays Res. 2018, 12, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, J.C.; Hellebrekers, L.J. Medetomidine and Dexmedetomidine: A Review of Cardiovascular Effects and Antinociceptive Properties in the Dog. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2005, 32, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustagi, P.S.; Nellore, S.S.; Kudalkar, A.G.; Sawant, R. Comparative Evaluation of I-Gel® Insertion Conditions Using Dexmedetomidine-Propofol versus Fentanyl-Propofol—A Randomised Double-Blind Study. Indian. J. Anaesth. 2019, 63, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, J.; Prabhudesai, A.; Datta, C. Dexmedetomidine with Propofol versus Fentanyl with Propofol for Insertion of Proseal Laryngeal Mask Airway: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 35, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groppetti, D.; Di Cesare, F.; Pecile, A.; Cagnardi, P.; Merlanti, R.; D’Urso, E.S.; Gioeni, D.; Boracchi, P.; Ravasio, G. Maternal and Neonatal Wellbeing during Elective C-Section Induced with a Combination of Propofol and Dexmedetomidine: How Effective Is the Placental Barrier in Dogs? Theriogenology 2019, 129, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgeat, A.; Wilder-Smith, O.H.G.; Saiah, M.; Rifat, K. Subhypnotic Doses of Propofol Possess Direct Antiemetic Properties. Anesth. Analg. 1992, 74, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dent, B.T.; Aarnes, T.K.; Wavreille, V.A.; Lakritz, J.; Lerche, P.; KuKanich, B.; Riccò Pereira, C.H.; Bednarski, R.M. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamic Effects of Oral Transmucosal and Intravenous Administration of Dexmedetomidine in Dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 80, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, W.W.; Gadawski, J.E. Respiratory Depression and Apnea Induced by Propofol in Dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1998, 59, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Gaynor, J.S.; Bednarski, R.M.; Muir, W.W. Adverse Effects of Administration of Propofol with Various Preanesthetic Regimens in Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1993, 202, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, G.B. The Role of Alpha2 Agonists in Pediatric Anesthesia. Can. J. Anesth./J. Can. D’anesthésie 2005, 52, R42–R44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pan, S.-Y.; Liu, G.; Lin, J.-H.; Jin, Y.-P. Efficacy and Safety of Dexmedetomidine Premedication in Balanced Anesthesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis in Dogs. Animals 2021, 11, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michou, J.N.; Leece, E.A.; Brearley, J.C. Comparison of Pain on Injection during Induction of Anaesthesia with Alfaxalone and Two Formulations of Propofol in Dogs. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2012, 39, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keene, B.W.; Atkins, C.E.; Bonagura, J.D.; Fox, P.R.; Häggström, J.; Fuentes, V.L.; Oyama, M.A.; Rush, J.E.; Stepien, R.; Uechi, M. ACVIM Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Myxomatous Mitral Valve Disease in Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laflamme, D. Development and Validation of a Body Condition Score System for Dogs. Canine Pract. 1997, 22, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Maddern, K.; Adams, V.J.; Hill, N.A.T.; Leece, E.A. Alfaxalone Induction Dose Following Administration of Medetomidine and Butorphanol in the Dog. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2010, 37, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.P.; Gaber, C.E.; Jacobs, G.J.; Kaplan, P.M.; Lombard, C.W.; Sydney Moise, N.; Moses, B.L. Recommendations for Standards in Transthoracic Two-Dimensional Echocardiography in the Dog and Cat. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1993, 7, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, L.C.; Borkovec, M.; Bauer, A.; Häggström, J.; Wess, G. Left Ventricular M-Mode Prediction Intervals in 7651 Dogs: Population-Wide and Selected Breed-Specific Values. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 2242–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishniw, M.; Caivano, D.; Dickson, D.; Vatne, L.; Harris, J.; Matos, J.N. Two-Dimensional Echocardiographic Left- Atrial-to-Aortic Ratio in Healthy Adult Dogs: A Reexamination of Reference Intervals. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wess, G.; Bauer, A.; Kopp, A. Echocardiographic Reference Intervals for Volumetric Measurements of the Left Ventricle Using the Simpson’s Method of Discs in 1331 Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 724–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetboul, V.; Tissier, R. Echocardiographic Assessment of Canine Degenerative Mitral Valve Disease. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2012, 14, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Belda, E.; Escobar, M.; Agut, A.; Soler, M.; Laredo, F.G. Effects of Altering the Sequence of Midazolam and Propofol during Co-Induction of Anaesthesia. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2013, 40, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigby, S.E.; Beths, T.; Bauquier, S.; Carter, J.E. Effect of Rate of Administration of Propofol or Alfaxalone on Induction Dose Requirements and Occurrence of Apnea in Dogs. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2017, 44, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society of Anesthesiologists. Practice Guidelines for Moderate Procedural Sedation and Analgesia 2018: A Report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Moderate Procedural Sedation and Analgesia, the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons, American College of Radiology, American Dental Association, American Society of Dentist Anesthesiologists, and Society of Interventional Radiology. Anesthesiology 2018, 128, 437–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auckburally, A.; Pawson, P.; Flaherty, D. A Comparison of Induction of Anaesthesia Using a Target-Controlled Infusion Device in Dogs with Propofol or a Propofol and Alfentanil Admixture. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2008, 35, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubb, T.; Sager, J.; Gaynor, J.S.; Montgomery, E.; Parker, J.A.; Shafford, H.; Tearney, C. 2020 AAHA Anesthesia and Monitoring Guidelines for Dogs and Cats. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2020, 56, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, C.E.; Riebold, T.W.; Mandsager, R.E. Recovery Characteristics of Dogs Following Anesthesia Induced with Tiletamine-Zolazepam, Alfaxalone, Ketamine-Diazepam, or Propofol and Maintained with Isoflurane. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2019, 254, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sams, L.; Braun, C.; Allman, D.; Hofmeister, E. A Comparison of the Effects of Propofol and Etomidate on the Induction of Anesthesia and on Cardiopulmonary Parameters in Dogs. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2008, 35, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.; Borer-Weir, K. A Dose Titration Study into the Effects of Diazepam or Midazolam on the Propofol Dose Requirements for Induction of General Anaesthesia in Client Owned Dogs, Premedicated with Methadone and Acepromazine. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2013, 40, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonca, A.; Ravasio, G.; Gallo, M.; Montesissa, C.; Carli, S.; Villa, R.; Cagnardi, P. Pharmacokinetics of Ketamine and Propofol Combination Administered as Ketofol via Continuous Infusion in Cats. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, F.; Brioschi, F.A.; Ravasio, G.; Groppetti, D.; Amari, M.; Giussani, E.; Draghi, S.; Sala, G.; Pecile, A.; Cagnardi, P. Dexmedetomidine and Alfaxalone Intravenous Co-Administration for the Induction of General Anaesthesia in Bitches Undergoing C-Section: Impact on Newborn Viability and Pharmacokinetics. Theriogenology 2025, 247, 117578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuusela, E.; Raekallio, M.; Anttila, M.; Falck, I.; Mölsä, S.; Vainio, O. Clinical Effects and Pharmacokinetics of Medetomidine and Its Enantiomers in Dogs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 23, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Villamandos, R.J.; Palacios, C.; Benitez, A.; Granados, M.M.; Dominguez, J.M.; Lopez, I.; Ruiz, I.; Aguilera, E.; Santisteban, J.M. Dexmedetomidine or Medetomidine Premedication before Propofol-Desflurane Anaesthesia in Dogs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Therap. 2006, 29, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuusela, E.; Raekallio, M.; Vaisanen, M.; Mykkanen, K.; Ropponen, H.; Vainio, O. Comparison of Medetomidine and Dexmedetomidine as Premedicants in Dogs Undergoing Propofol-Isoflurane Anesthesia. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Kong, X. Comparative Evaluation of Remifentanil and Dexmedetomidine in General Anesthesia for Cesarean Delivery. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 3806–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KuKanich, B.; Wiese, A.J. Opioids. In Veterinary Anesthesia and Analgesia: The Fifth Edition of Lumb and Jones; Grimm, K.A., Lamont, L.A., Tranquilli, W.J., Greene, S.A., Robertson, S.A., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2015; pp. 207–226. ISBN 9781118526231. [Google Scholar]
- KuKanich, B.; Papich, M.G. Opioid Analgesic Drugs. In Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics; Riviere, J.E., Papich, M.G., Adams, H.R., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2006; pp. 589–611. [Google Scholar]
- Lerche, P.; Muir, W.W. Effect of Medetomidine on Breathing and Inspiratory Neuromuscular Drive in Conscious Dogs. AJVR 2004, 65, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granholm, M.; McKusick, B.C.; Westerholm, F.C.; Aspegren, J.C. Evaluation of the Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Intramuscular and Intravenous Doses of Dexmedetomidine and Medetomidine in Dogs and Their Reversal with Atipamezole. Vet. Rec. 2007, 160, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bufalari, A.; Miller, S.M.; Short, C.E.; Giannoni, G. The Use of Propofol for Induction of Anaesthesia in Dogs Premeditated with Acepromazine, Butorphanol and Acepromazine-Butorphanol. N. Z. Vet. J. 2011, 45, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprung, J.; Ogletree-hughes, M.L.; Mcconnell, B.K.; Zakhary, D.R.; Smolsky, S.M.; Moravec, C.S. The Effects of Propofol on the Contractility of Failing and Nonfailing Human Heart Muscles. Anesth. Analg. 2001, 93, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, L.; Mitter, N.; Berkowitz, D.E.; Nyhan, D. Pharmacology of Anesthetic Drugs. In Kaplan’s Cardiac Anesthesia for Cardiac and Noncardiac Surgery; Kaplan, J.A., Augoustides, J.G.T., Manecke, G.R., Maus, T., Reich, D.L., Eds.; ELS: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 247–291. [Google Scholar]
- Flacke, W.E.; Flacke, J.W.; Blow, K.D.; Mclntee, D.F.; Bloor, B.C. Effect of Dexmedetomidine, an A2-Adrenergic Agonist, in the Isolated Heart. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 1992, 6, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuusela, E.; Raekallio, M.; Hietanen, H.; Huttula, J.; Vainio, O. 24-Hour Holter-Monitoring in the Perianaesthetic Period in Dogs Premedicated with Dexmedetomidine. Vet. J. 2002, 164, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, B.A. Opioid Peptides and the Heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 1999, 43, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, K.K.; Jin, W.Q.; Chan, T.K.Y.; Wong, T.M. Characterization of [3H]U69593 Binding Sites in the Rat Heart by Receptor Binding Assays. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1991, 23, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonagura, J.D.; Visser, L.C. Echocardiographic Assessment of Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Dogs. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2022, 40, 15–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Hung, C.T.; Lee, W.M.; Chang, K.M.; Chen, K.S. Effects of Intravenous Dexmedetomidine on Cardiac Characteristics Measured Using Radiography and Echocardiography in Six Healthy Dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2016, 57, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, B.; Harel, M.; Fourel, I.; Micieli, F.; Cataldi, M.; Segard-Weisse, E.; Portier, K. Intranasal Dexmedetomidine in Healthy Beagles: An Echocardiographic and Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Study. Vet. J. 2019, 251, 105346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarelli, G.; Lopez, J.T.; del Palacio, J.F. Effects of a Combination of Acepromazine Maleate and Butorphanol Tartrate on Conventional and Two-Dimensional Speckle Tracking Echocardiography in Healthy Dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res 2017, 78, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzarini, E.; Martinelli, E.; Brioschi, F.A.; Gioeni, D.; Corneliani, R.T.; Carotenuto, A.M. Intramuscular Alfaxalone and Methadone with or without Ketamine in Healthy Cats: Effects on Sedation and Echocardiographic Measurements. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2020, 47, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Scores | Quality of Anaesthesia Induction |
|---|---|
| 0 (smooth) | Patient safely assumed sternal decubitus Induction occurred gradually and quietly without excitement Presence of ventro-rotation of the eyeball No periods of apnoea were observed Orotracheal intubation was possible. |
| 1 (fair) | Patient assumed sternal or lateral decubitus Slight excitement, muscle twitching, or mild and transient limb movement No ventro-rotation of the eyeball Less than 30 s periods of polypnoea or apnoea were observed Orotracheal intubation required additional propofol to be achieved. |
| 2 (poor) | Patient was ataxic Marked excitement, myoclonus, or prolonged paddling, and possible vocalizations No ventro-rotation of the eyeball More than 30 s periods of polypnoea or apnoea were observed Orotracheal intubation required additional propofol to be achieved |
| Variable | Time | PROPODEX | PROPOBUT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ||
| LVIDd (mm) | bECHO | 37.38 ± 11 | 39.7 ± 5.82 |
| pECHO | 36.75 ± 12.17 | 37.18 ± 5.09 | |
| LVIDs (mm) | bECHO | 22.22 ± 8.36 † | 26.2 ± 4.88 |
| pECHO | 25.7 ± 9.03 † | 25.2 ± 4.77 | |
| FS (%) | bECHO | 41 ± 8.83 † | 34 ± 6.7 |
| pECHO | 29.83 ± 7.08 † | 32.5 ± 6.44 | |
| LVEDV (mL) | bECHO | 50.88 ± 37.44 | 55.6 ± 27.9 † |
| pECHO | 58.4 ± 42.1 | 45.43 ± 22.4 † | |
| LVESV (mL) | bECHO | 19.65 ± 16.08 † | 21.32 ± 10.97 |
| pECHO | 32.3 ± 25.73 † | 20.22 ± 12.71 | |
| EDVI (mL/m2) | bECHO | 50.26 ± 24.23 | 63.98 ± 19.55 † |
| pECHO | 59.47 ± 25.13 | 49.22 ± 15.47 † | |
| ESVI (mL/m2) | bECHO | 19.13 ± 11.18 † | 22.82 ± 8.87 |
| pECHO | 35.51 ± 16.9 † | 21.24 ± 9.43 | |
| EF (%) | bECHO | 62.5 ± 11.47 | 64.5 ± 8.07 |
| pECHO | 46 ± 14.91 | 58.5 ± 7.74 | |
| LA/Ao | bECHO | 1.25 ± 0.18 | 1.20 ± 0.17 |
| pECHO | 1.38 ± 0.35 | 1.15 ± 0.19 | |
| SV (mL) | bECHO | 31.25 ± 22.41 | 34.33 ± 19.48 |
| pECHO | 26.1 ± 19.8 | 25.23 ± 10.02 | |
| CO (L/min) | bECHO | 2.34 ± 1.83 | 3.52 ± 2.32 |
| pECHO | 1.91 ± 1.58 | 2.66 ± 1.19 | |
| E-Vmax (m/second) | bECHO | 0.62 ± 0.11 | 0.75 ± 0.15 |
| pECHO | 0.67 ± 0.22 | 0.71 ± 0.13 | |
| A-Vmax (m/second) | bECHO | 0.62 ± 0.16 | 0.7 ± 0.24 |
| pECHO | 0.54 ± 0.15 | 0.52 ± 0.11 | |
| E/A | bECHO | 1.04 ± 0.22 | 1.19 ± 0.41 † |
| pECHO | 1.25 ± 0.30 | 1.43 ± 0.44 † | |
| VTIPv (cm) | bECHO | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.15 ± 0.02 |
| pECHO | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | |
| VTIAo (cm) | bECHO | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 0.16 ± 0.02 |
| pECHO | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.13 ± 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ravasio, G.; Amari, M.; Locatelli, C.; Ferrari, F.; Jacchetti, A.; Bronzo, V.; Brioschi, F.A. Dexmedetomidine or Butorphanol for Co-Induction of General Anaesthesia with Propofol in Unpremedicated Healthy Dogs: Clinical and Echocardiographic Assessment. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090885
Ravasio G, Amari M, Locatelli C, Ferrari F, Jacchetti A, Bronzo V, Brioschi FA. Dexmedetomidine or Butorphanol for Co-Induction of General Anaesthesia with Propofol in Unpremedicated Healthy Dogs: Clinical and Echocardiographic Assessment. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(9):885. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090885
Chicago/Turabian StyleRavasio, Giuliano, Martina Amari, Chiara Locatelli, Francesco Ferrari, Andrea Jacchetti, Valerio Bronzo, and Federica Alessandra Brioschi. 2025. "Dexmedetomidine or Butorphanol for Co-Induction of General Anaesthesia with Propofol in Unpremedicated Healthy Dogs: Clinical and Echocardiographic Assessment" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 9: 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090885
APA StyleRavasio, G., Amari, M., Locatelli, C., Ferrari, F., Jacchetti, A., Bronzo, V., & Brioschi, F. A. (2025). Dexmedetomidine or Butorphanol for Co-Induction of General Anaesthesia with Propofol in Unpremedicated Healthy Dogs: Clinical and Echocardiographic Assessment. Veterinary Sciences, 12(9), 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090885







