Scoping Review of Factors Affecting Antimicrobial Use and the Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance in the Poultry Production Chain
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Review Approach
2.2. Review Team
2.3. Review Question, Scope, and Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Search Strategy
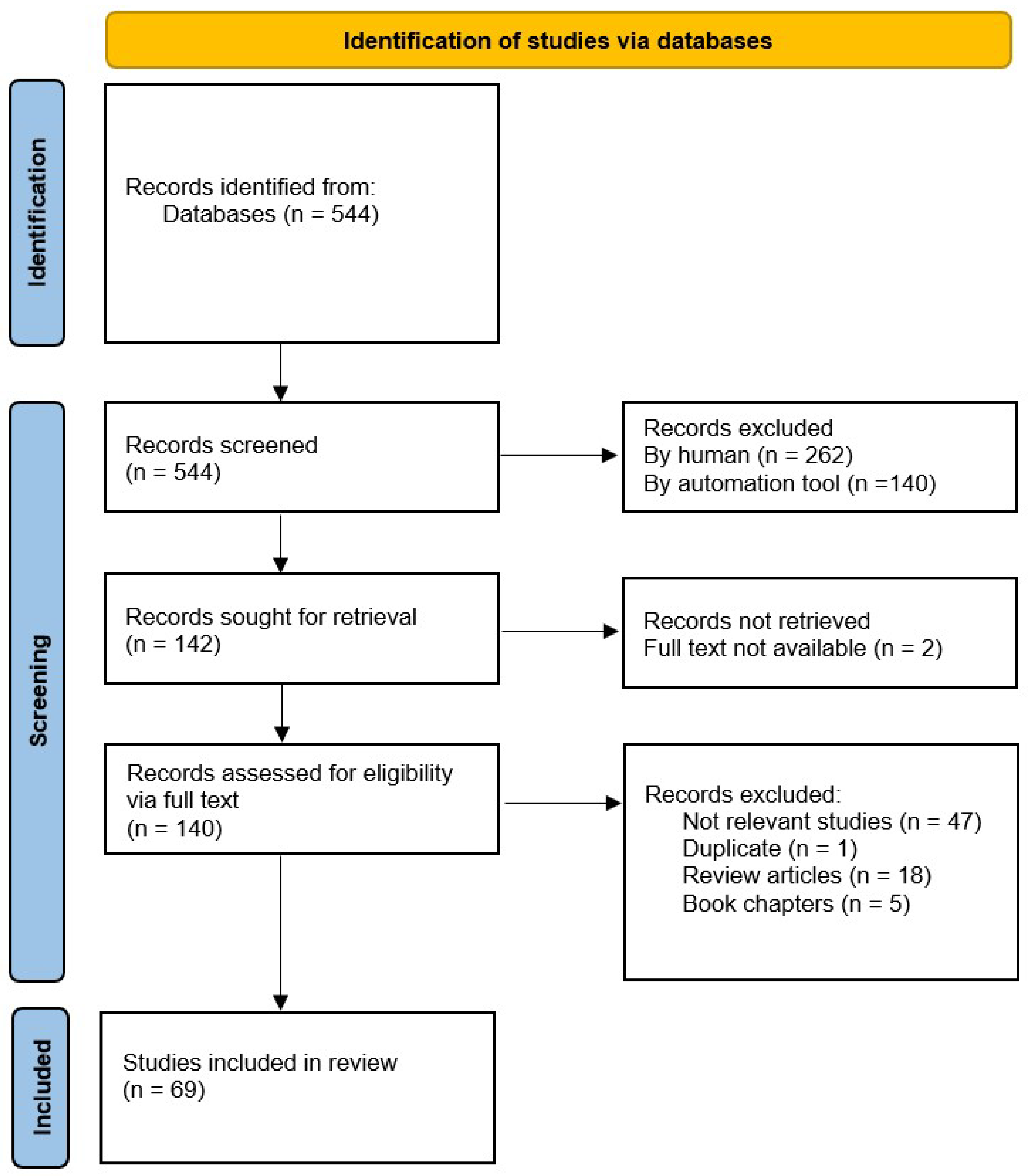
2.5. Title and Abstract Relevance Screening (AS)
2.6. Relevance Confirmation During Full Text Screening
2.7. Content/Information Extraction
3. Results
3.1. Results of the Review Process
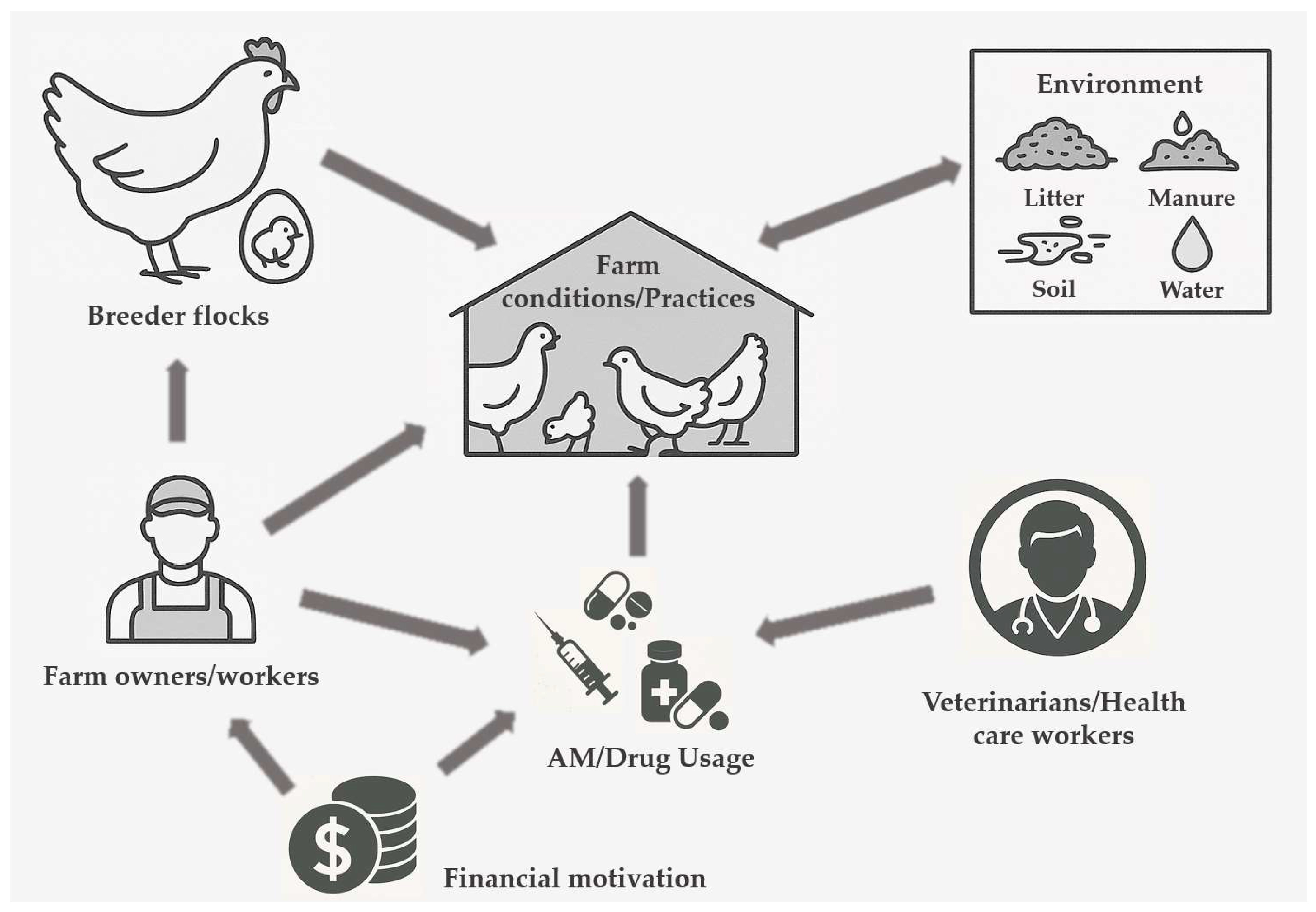
3.2. Classification of Factors Affecting AMU and the Spread of AMR
3.3. Discussion on Factors Affecting AMU and the Spread of AMR
3.3.1. Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice
Farm Workers’ Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice
- Knowledge and attitude
- 2.
- Education and training
- 3.
- Unexpected results regarding the effect of education and training on AMU and AMR
- 4.
- Farm workers’ experience
- 5.
- Farm workers’ personal characteristics (age, gender, marital status, income, location, and health status)
Farming Practices
- Management of sewage, litter, manure, bedding, carcasses, and water
- 2.
- Flock/herd related effects (arrangement, size, density)
- 3.
- Farm-related effects (size, location, number of farm workers, equipment used, feeding practices)
- 4.
- Breed selection
- 5.
- Species per farm
- 6.
- Administration/record keeping
Animal Health Management
AMU Practices and Their Impact on AMR (Excluding Intentional Misuse)
Hygiene and Biosecurity
- -
- Absence of a lavatory for workers [46];
- -
- -
- Use of hydrogen peroxide to disinfect water lines during the growing period [50];
- -
- Transport personnel entering the room where the broilers are raised [80];
- -
- Personal movement, vehicles, and instruments (considered as vectors) [57];
- -
- Disposal of solid wastes from the household [31];
- -
- Uncontrolled disposal of human and veterinary drugs [31];
- -
- Lack of observance of an empty period of the flock house [43];
- -
- Positive status for diseases of the previous flock in the broiler house [80];
- -
Financial Motivation
Operational Issues
Allowing Visitors/Transport Personnel
3.3.2. Intentional Misuse or Bad Practices of AMU
- -
- -
- -
- Mistreatment of illness, misuse [29,86] such as no differentiation between antimicrobials and other type of medicines [84], infrequent use of antibiotics to treat parasites or animals not eating [34], use it as painkillers or for treatment of viral diseases [39], administering antibiotics at the first indication of disease [38], constant use of broad-spectrum antibiotic more frequently [87], or use of human antimicrobials in animal treatment [31];
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- Poor handling of drugs at purchase and administration practices [87] *.
3.3.3. Other Factors
Environmental Factors (Soil, Seasonality, Geographical Location)
Vectors
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Health Status/Age of the Animals
Veterinarians/Health Care Workers’ Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice
Drug/Feed Sellers’ Knowledge and Motivation
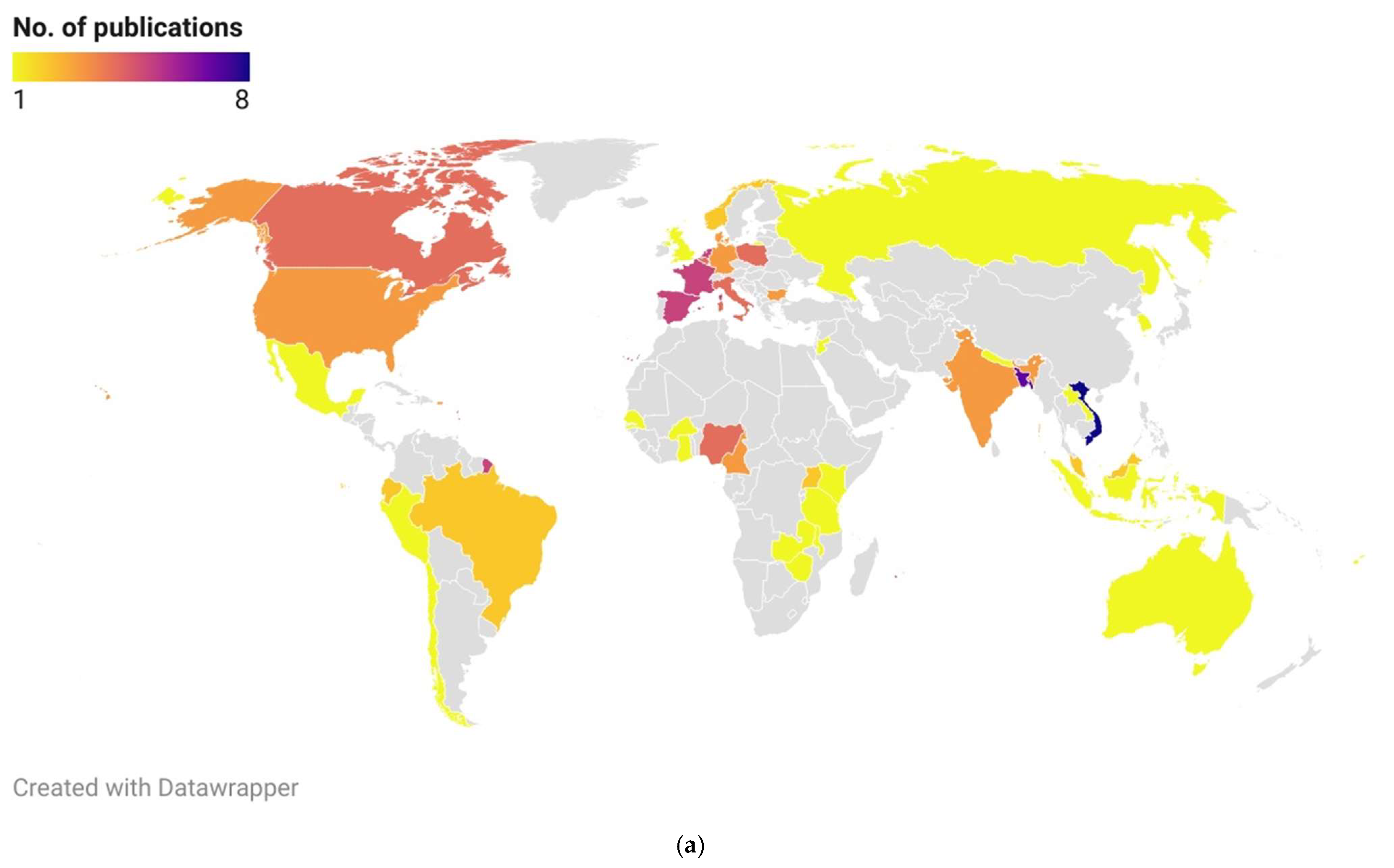
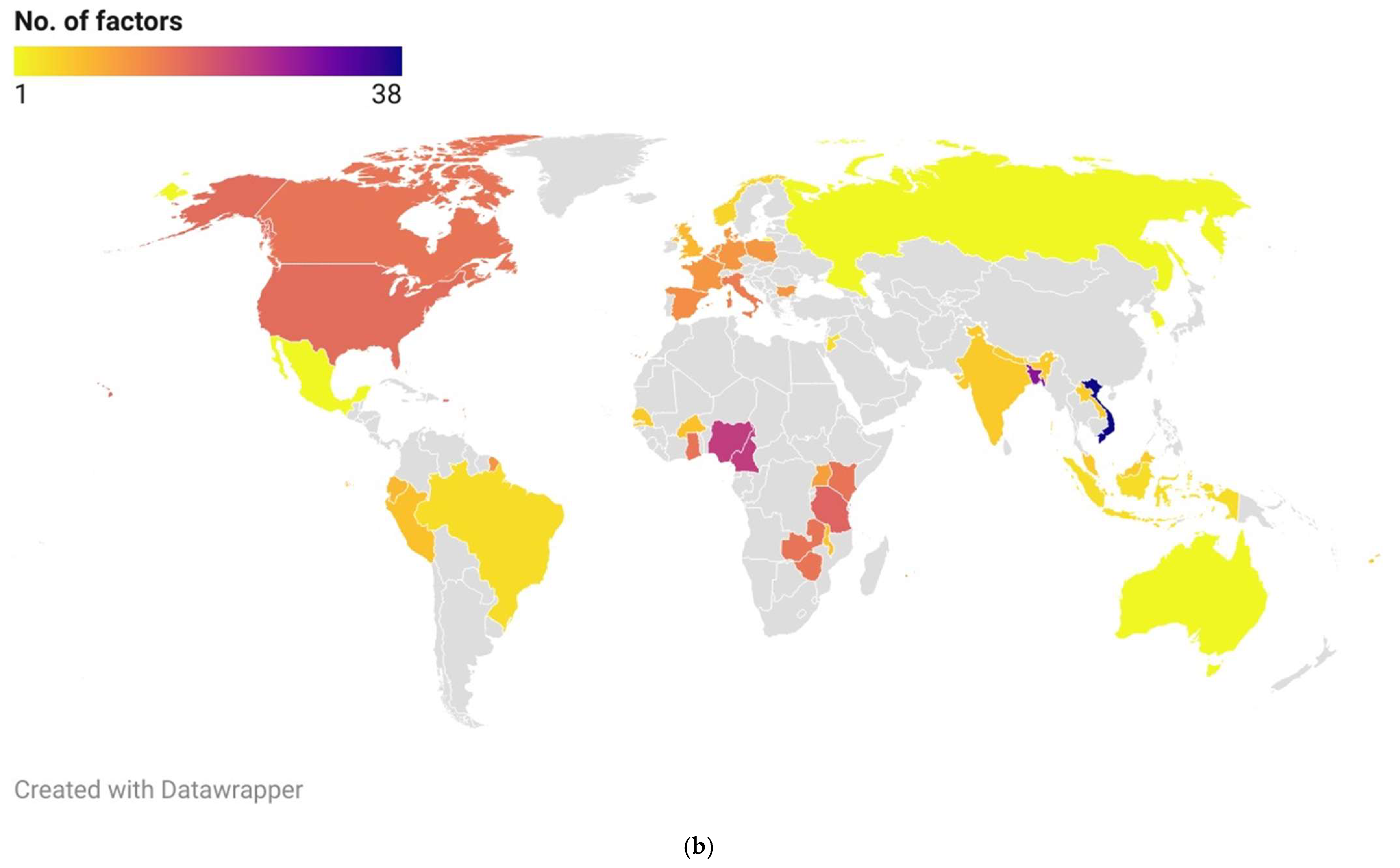
3.4. Geographical Representation
3.5. Knowledge/Evidence Synthesis Based on Identified Factors and Conclusions of the Studies
- Paradox of education: higher farmer education inconsistently reduced AMR (12 studies from the total of 24). In Burkina Faso/Senegal, it increased prophylaxis due to financial capacity;
- Flock management: high density (5 studies) and large size (5 studies) were major AMR drivers, while biosecurity interventions reduced risk (7 studies);
- Economic drivers: financial constraints (11 studies) led to underdosing, non-veterinary AMU, and preventive misuse;
- Environmental transmission: environmental vectors (e.g., flies, wild birds) facilitated AMR gene spread in 8 studies;
- Intentional misuse: prophylaxis (12 studies) and growth promotion (5 studies) dominated, especially in countries where regulations were weak.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. General Overview Based on Findings of the Study
4.2. Core Insights Based on Knowledge/Evidence Synthesis
4.3. Limitations of the Study
4.4. Final Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| AMU | Antimicrobial use |
| KAP | Knowledge, attitudes, and practices |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| LMICs | Low-to-middle income countries |
| FAO | Food and Agricultural Organization |
| ESC | Extended-spectrum cephalosporin |
| ESBL/AmpC | Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases and AmpC beta-lactamases |
| ARGs | Antimicrobial resistance genes |
| PICO | Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome |
| BPS | Backyard production systems |
| FQr | Fluoroquinolone-resistant |
| MDR | Multidrug-resistant |
Appendix A. Search Strategy Details
| Date | 10 February 2023 |
| Performed by | Zsuzsa Farkas |
| Databases | Scopus |
| Institution | University of Veterinary Medicine; Budapest, Hungary |
| Search string: | (antimicrobial resistance OR AMR AND poultry OR chicken OR gallus OR broiler AND factor OR driver) in TI (Title) in AB (Abstract or Author-Supplied Abstract) in KW (Author-Supplied Keywords) |
| Hits | 544 |
| Limits | Published since 2013 |
Appendix B. Title and Abstract Relevance Screening Form
| Question | Options |
|---|---|
| Is the article written in English? | Yes → Proceed No → Exclude |
| Is the study about antimicrobial resistance? | Yes → Proceed No → Exclude |
| Is the study about poultry production chain? | Yes → Proceed No → Exclude |
Appendix C. Full Text Relevance Confirmation Form
| Question | Options |
|---|---|
| Is publication type other than peer reviewed scientific article or primary research (e.g., review article, book chapter)? | Yes → Exclude |
| Is the publication about drivers and/or factors contributing to AMR in the poultry production chain? | Yes → Proceed No, it investigated the drivers and/or factors resulted in antibiotic usage → Proceed No → Exclude |
| Is the text in English? | Yes → Proceed No → Exclude |
Appendix D. Data/Information Extraction Form
| Field | Attributes |
|---|---|
| Authors | |
| Title | |
| Published | |
| Driver (affecting more than 1 factor) | free text |
| Factor | free text |
| Bacterium | free text |
| Antibiotic or antibiotic group | free text |
| Disease type | free text |
| AMR extent | free text |
| Sample | free text |
| Region of the study conducted | values: Europe, North America, South America and Caribbean, Africa, Asia, Australia |
| Comment | free text |
References
- Cassini, A.; Högberg, L.D.; Plachouras, D.; Quattrocchi, A.; Hoxha, A.; Simonsen, G.S.; Colomb-Cotinat, M.; Kretzschmar, M.E.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Cecchini, M.; et al. Attributable Deaths and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years Caused by Infections with Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A Population-Level Modelling Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations; Review on Antimicrobial Resistance: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hedman, H.D.; Vasco, K.A.; Zhang, L. A Review of Antimicrobial Resistance in Poultry Farming within Low-Resource Settings. Animals 2020, 10, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eurostat. Agricultural Production—Livestock and Meat; Eurostat: Luxembourg, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Meat Market Review: Overview of Global Market Developments in 2023; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Nhung, N.T.; Chansiripornchai, N.; Carrique-Mas, J.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacterial Poultry Pathogens: A Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mesquita Souza Saraiva, M.; Lim, K.; do Monte, D.F.M.; Givisiez, P.E.N.; Alves, L.B.R.; de Freitas Neto, O.C.; Kariuki, S.; Júnior, A.B.; de Oliveira, C.J.B.; Gebreyes, W.A. Antimicrobial Resistance in the Globalized Food Chain: A One Health Perspective Applied to the Poultry Industry. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 465–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin-Guyomard, A.; Jouy, E.; Urban, D.; Chauvin, C.; Granier, S.A.; Mourand, G.; Chevance, A.; Adam, C.; Moulin, G.; Kempf, I. Decrease in Fluoroquinolone Use in French Poultry and Pig Production and Changes in Resistance among E. coli and Campylobacter. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 243, 108637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, G.; Cobean, J.; Snyder, R.P.; Barta, J.R.; Boerlin, P. Extended-Spectrum Cephalosporin Resistance in Escherichia coli from Broiler Chickens Raised with or without Antibiotics in Ontario, Canada. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 258, 109116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Urmi, U.L.; Rana, M.; Sultana, F.; Jahan, N.; Hossain, B.; Iqbal, S.; Hossain, M.; Mosaddek, A.S.; Nahar, S. High Abundance of the Colistin Resistance Gene Mcr-1 in Chicken Gut-Bacteria in Bangladesh. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, K.; Masaki, T.; Kawaguchi, T.; Kuroda, M. Persistence of Colistin Resistance and Mcr-1.1-Positive E. coli in Poultry Despite Colistin Ban in Japan. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldea, I.; Gibello, A.; Hernández, M.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Bortolaia, V.; Moreno, M.A. Clonal and Plasmid-Mediated Flow of ESBL/AmpC Genes in Escherichia coli in a Commercial Laying Hen Farm. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 270, 109453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoumanis, K.; Allende, A.; Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Bolton, D.; Bover-Cid, S.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; De Cesare, A.; Herman, L.; Hilbert, F.; et al. Transmission of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) during Animal Transport. EFSA J. 2022, 20, 7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endale, H.; Mathewos, M.; Abdeta, D. Potential Causes of Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance and Preventive Measures in One Health Perspective—A Review. Infect Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 7515–7545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Li, M.; Jing, Y.; Liu, K.; Wu, Y.; Peng, Z. What Are the Drivers Triggering Antimicrobial Resistance Emergence and Spread? Outlook from a One Health Perspective. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Kalam, M.A.; Alim, M.A.; Shano, S.; Nayem, M.R.K.; Badsha, M.R.; Mamun, M.A.A.; Hoque, A.; Tanzin, A.Z.; Nath, C.; et al. Knowledge, Attitude, and Practices on Antimicrobial Use and Antimicrobial Resistance among Commercial Poultry Farmers in Bangladesh. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, B.M.; Levy, S.B. Food Animals and Antimicrobials: Impacts on Human Health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Pires, J.; Silvester, R.; Zhao, C.; Song, J.; Criscuolo, N.G.; Gilbert, M.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Resistance in Animals in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Science 2019, 365, eaaw1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. FDA. 2018 Summary Report On Antimicrobials Sold or Distributed for Use in Food-Producing Animals; U.S. Food and Drug Administration Center for Veterinary Medicine: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Mulchandani, R.; Wang, Y.; Gilbert, M.; Boeckel, T.P.V. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food-Producing Animals: 2020 to 2030. PLoS Glob. Public Health 2023, 3, e0001305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Guidance for those carrying out systematic reviews European Food Safety Authority Application of Systematic Review Methodology to Food and Feed Safety Assessments to Support Decision Making. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajić, A.; Young, I. Knowledge Synthesis, Transfer and Exchange in Agri-Food Public Health: A Handbook for Science-to-Policy Professionals; University of Guelph: Guelph, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Handbook for Guideline Development, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; ISBN 978-92-4-154896-0. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.scopus.com (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- van de Schoot, R.; de Bruin, J.; Schram, R.; Zahedi, P.; de Boer, J.; Weijdema, F.; Kramer, B.; Huijts, M.; Hoogerwerf, M.; Ferdinands, G.; et al. An Open Source Machine Learning Framework for Efficient and Transparent Systematic Reviews. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2021, 3, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.zotero.org (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Khan, X.; Lim, R.H.M.; Rymer, C.; Ray, P. Fijian Farmers’ Attitude and Knowledge Towards Antimicrobial Use and Antimicrobial Resistance in Livestock Production Systems—A Qualitative Study. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 838457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenstein, C.; Waters, W.F.; Roess, A.; Leibler, J.H.; Graham, J.P. Animal Husbandry Practices and Perceptions of Zoonotic Infectious Disease Risks among Livestock Keepers in a Rural Parish of Quito, Ecuador. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 1450–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koju, P.; Shrestha, R.; Shrestha, A.; Tamrakar, S.; Rai, A.; Shrestha, P.; Madhup, S.K.; Katuwal, N.; Shrestha, A.; Shrestha, A.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance in E. coli Isolated from Chicken Cecum Samples and Factors Contributing to Antimicrobial Resistance in Nepal. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimera, Z.I.; Frumence, G.; Mboera, L.E.G.; Rweyemamu, M.; Mshana, S.E.; Matee, M.I.N. Assessment of Drivers of Antimicrobial Use and Resistance in Poultry and Domestic Pig Farming in the Msimbazi River Basin in Tanzania. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speksnijder, D.C.; Jaarsma, A.D.C.; van der Gugten, A.C.; Verheij, T.J.M.; Wagenaar, J.A. Determinants Associated with Veterinary Antimicrobial Prescribing in Farm Animals in the Netherlands: A Qualitative Study. Zoonoses Public Health 2015, 62, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poupaud, M.; Goutard, F.L.; Phouthana, V.; Muñoz Viera, F.; Caro, D.; Patriarchi, A.; Paul, M.C. Different Kettles of Fish: Varying Patterns of Antibiotic Use on Pig, Chicken and Fish Farms in Lao PDR and Implications for Antimicrobial Resistance Strategies. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 3940–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, J.A.; Streicker, D.G.; Gonzales, M.S.; Rojas-Paniagua, E.; Shiva, C. Knowledge and Use of Antibiotics among Low-Income Small-Scale Farmers of Peru. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 189, 105287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaji, N.B.; Haruna, A.E.; Muhammad, B.; Lawan, M.K.; Isola, T.O. Antimicrobials Usage Assessments in Commercial Poultry and Local Birds in North-Central Nigeria: Associated Pathways and Factors for Resistance Emergence and Spread. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 154, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, Q.H.; Nguyen, T.L.A.; Pham, T.N.; Vo, N.G.; Padungtod, P. Antimicrobial Use in Household, Semi-Industrialized, and Industrialized Pig and Poultry Farms in Viet Nam. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 189, 105292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawadogo, A.; Kagambèga, A.; Moodley, A.; Ouedraogo, A.A.; Barro, N.; Dione, M. Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices Related to Antibiotic Use and Antibiotic Resistance among Poultry Farmers in Urban and Peri-Urban Areas of Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham-Duc, P.; Cook, M.A.; Cong-Hong, H.; Nguyen-Thuy, H.; Padungtod, P.; Nguyen-Thi, H.; Dang-Xuan, S. Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices of Livestock and Aquaculture Producers Regarding Antimicrobial Use and Resistance in Vietnam. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffo, F.; Mouliom Mouiche, M.M.; Kochivi, F.L.; Dongmo, J.B.; Djomgang, H.K.; Tombe, P.; Mbah, C.K.; Mapiefou, N.P.; Mingoas, J.-P.K.; Awah-Ndukum, J. Knowledge, Attitudes, Practices and Risk Perception of Rural Poultry Farmers in Cameroon to Antimicrobial Use and Resistance. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 182, 105087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, Z.; Islam, S.; Kundu, L.R.; Ahmed, A.; Hsan, K.; Pardhan, S.; Driscoll, R.; Hossain, S.; Hossain, M. Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices Regarding Antimicrobial Usage, Spread and Resistance Emergence in Commercial Poultry Farms of Rajshahi District in Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oloso, N.O.; Odetokun, I.A.; Ghali-Mohammed, I.; Fasina, F.O.; Olatoye, I.O.; Adetunji, V.O. Knowledge, Attitudes, and Risk Perception of Broiler Grow-Out Farmers on Antimicrobial Use and Resistance in Oyo State, Nigeria. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudell, M.A.; Dorado-Garcia, A.; Eckford, S.; Creese, C.; Byarugaba, D.K.; Afakye, K.; Chansa-Kabali, T.; Fasina, F.O.; Kabali, E.; Kiambi, S.; et al. Towards a Bottom-up Understanding of Antimicrobial Use and Resistance on the Farm: A Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices Survey across Livestock Systems in Five African Countries. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0220274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vounba, P.; Arsenault, J.; Bada-Alambédji, R.; Fairbrother, J.M. Prevalence of Antimicrobial Resistance and Potential Pathogenicity, and Possible Spread of Third Generation Cephalosporin Resistance, in Escherichia coli Isolated from Healthy Chicken Farms in the Region of Dakar, Senegal. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhung, N.T.; Cuong, N.V.; Campbell, J.; Hoa, N.T.; Bryant, J.E.; Truc, V.N.T.; Kiet, B.T.; Jombart, T.; Trung, N.V.; Hien, V.B.; et al. High Levels of Antimicrobial Resistance among Escherichia coli Isolates from Livestock Farms and Synanthropic Rats and Shrews in the Mekong Delta of Vietnam. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffo, F.; Mouiche, M.M.M.; Djomgang, H.K.; Tombe, P.; Wade, A.; Kochivi, F.L.; Dongmo, J.B.; Mbah, C.K.; Mapiefou, N.P.; Ngogang, M.P.; et al. Poultry Litter Contamination by Escherichia coli Resistant to Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human and Animal Use and Risk for Public Health in Cameroon. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aworh, M.K.; Kwaga, J.; Okolocha, E.; Mba, N.; Thakur, S. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Multi-Drug Resistant Escherichia coli among Poultry Workers in the Federal Capital Territory, Abuja, Nigeria. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrique-Mas, J.J.; Trung, N.V.; Hoa, N.T.; Mai, H.H.; Thanh, T.H.; Campbell, J.I.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Hardon, A.; Hieu, T.Q.; Schultsz, C. Antimicrobial Usage in Chicken Production in the Mekong Delta of Vietnam. Zoonoses Public Health 2015, 62, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankhomwa, J.; Tolhurst, R.; M’biya, E.; Chikowe, I.; Banda, P.; Mussa, J.; Mwasikakata, H.; Simpson, V.; Feasey, N.; MacPherson, E.E. A Qualitative Study of Antibiotic Use Practices in Intensive Small-Scale Farming in Urban and Peri-Urban Blantyre, Malawi: Implications for Antimicrobial Resistance. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 876513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmi, S.A.; Simons, D.; Elton, L.; Haider, N.; Hamid, M.M.A.; Shuaib, Y.A.; Khan, M.A.; Othman, I.; Kock, R.; Osman, A.Y. Identification of Risk Factors Associated with Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates from Poultry Farms in the East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia: A Cross Sectional Study. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffrey, N.; Nekouei, O.; Gow, S.; Agunos, A.; Checkley, S. Risk Factors Associated with the A2C Resistance Pattern among E. coli Isolates from Broiler Flocks in Canada. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 148, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Devendec, L.; Mourand, G.; Bougeard, S.; Léaustic, J.; Jouy, E.; Keita, A.; Couet, W.; Rousset, N.; Kempf, I. Impact of Colistin Sulfate Treatment of Broilers on the Presence of Resistant Bacteria and Resistance Genes in Stored or Composted Manure. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 194, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Heederik, D.J.J.; Mevius, D.J.; Scherpenisse, P.; Luiken, R.E.C.; Van Gompel, L.; Skarżyńska, M.; Wadepohl, K.; Chauvin, C.; Van Heijnsbergen, E.; et al. Risk Factors for the Abundance of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes Aph(3′)-III, Erm(B), Sul2 and Tet(W) in Pig and Broiler Faeces in Nine European Countries. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwini, A.; Jamwal, P.; Vanak, A.T. Environmental Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in a Rapidly Developing Catchment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulianne, M.; Arsenault, J.; Daignault, D.; Archambault, M.; Letellier, A.; Dutil, L. Drug Use and Antimicrobial Resistance among Escherichia coli and Enterococcus Spp. Isolates from Chicken and Turkey Flocks Slaughtered in Quebec, Canada. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 80, 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Saraiva, M.M.S.; Silva, N.M.V.; Ferreira, V.A.; Moreira Filho, A.L.B.; Givisiez, P.E.N.; Freitas Neto, O.C.; Berchieri Júnior, A.; Gebreyes, W.A.; de Oliveira, C.J.B. Residual Concentrations of Antimicrobial Growth Promoters in Poultry Litter Favour Plasmid Conjugation among Escherichia coli. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 74, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luiken, R.E.; Heederik, D.J.; Scherpenisse, P.; Van Gompel, L.; van Heijnsbergen, E.; Greve, G.D.; Jongerius-Gortemaker, B.G.; Tersteeg-Zijderveld, M.H.; Fischer, J.; Juraschek, K.; et al. Determinants for Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Farm Dust on 333 Poultry and Pig Farms in Nine European Countries. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.A.; Cryer, T.L.; Lafi, S.Q.; Basha, E.-A.; Good, L.; Tarazi, Y.H. Identification of Escherichia coli from Broiler Chickens in Jordan, Their Antimicrobial Resistance, Gene Characterization and the Associated Risk Factors. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, A.B.; Saleha, A.A.; Jalila, A.; Zunita, Z. Risk Factors and Spatial Distribution of Extended Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing- Escherichia coli at Retail Poultry Meat Markets in Malaysia: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, E.P.; Golding, S.E.; van Rosmalen, J.; Vinueza-Burgos, C.; Verbon, A.; van Schaik, G. Antibiotic Prescription Patterns and Non-Clinical Factors Influencing Antibiotic Use by Ecuadorian Veterinarians Working on Cattle and Poultry Farms: A Cross-Sectional Study. Prev. Vet. Med. 2023, 213, 105858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, V.L.; Scandorieiro, S.; Vespero, E.C.; Oba, A.; De Brito, B.G.; De Brito, K.C.T.; Nakazato, G.; Kobayashi, R.K.T. Comparison of Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Factors among Escherichia coli Isolated from Conventional and Free-Range Poultry. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 618752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakooza, S.; Munyiirwa, D.; Ssajjakambwe, P.; Kayaga, E.; Tayebwa, D.S.; Ndoboli, D.; Basemera, L.; Nabatta, E.; Tumwebaze, M.A.; Kaneene, J.B. Epidemiological Dynamics of Extended-Spectrum β -Lactamase- or AmpC β -Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Screened in Apparently Healthy Chickens in Uganda. Scientifica 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Carrique-Mas, J.J.; Ngo, T.H.; Ho, H.M.; Ha, T.T.; Campbell, J.I.; Nguyen, T.N.; Hoang, N.N.; Pham, V.M.; Wagenaar, J.A.; et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Carriage of Antimicrobial-Resistant Escherichia coli on Household and Small-Scale Chicken Farms in the Mekong Delta of Vietnam. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 2144–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargavi, D.; Sahu, R.; Nishanth, M.A.D.; Doijad, S.P.; Niveditha, P.; Kumar, O.R.V.; Sunanda, C.; Girish, P.S.; Naveena, B.M.; Vergis, J.; et al. Genetic Diversity and Risk Factor Analysis of Drug-Resistant Escherichia coli Recovered from Broiler Chicken Farms. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 93, 101929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffrey, N.; Agunos, A.; Gow, S.; Liljebjelke, K.; Waldner, C.L.; Mainali, C.; Checkley, S.L. A Cross-Sectional Study of the Prevalence Factors Associated with Fluoroquinolone Resistant Campylobacter Jejuni in Broiler Flocks in Canada. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 186, 105164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouiche, M.M.M.; Wouembe, F.D.K.; Mpouam, S.E.; Moffo, F.; Djuntu, M.; Toukam, C.M.W.; Kameni, J.M.F.; Okah-Nnane, N.H.; Awah-Ndukum, J. Cross-Sectional Survey of Prophylactic and Metaphylactic Antimicrobial Use in Layer Poultry Farming in Cameroon: A Quantitative Pilot Study. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 646484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caucci, C.; Di Martino, G.; Dalla Costa, A.; Santagiuliana, M.; Lorenzetto, M.; Capello, K.; Mughini-Gras, L.; Gavazzi, L.; Bonfanti, L. Trends and Correlates of Antimicrobial Use in Broiler and Turkey Farms: A Poultry Company Registry-Based Study in Italy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 2784–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavez-Muñoz, E.; González, C.; Fernández-Sanhueza, B.; Sánchez, F.; Escobar, B.; Ramos, R.; Fuenzalida, V.; Galarce, N.; Arriagada, G.; Neira, V.; et al. Antimicrobial Usage Factors and Resistance Profiles of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli in Backyard Production Systems From Central Chile. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 595149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buberg, M.L.; Witsø, I.L.; L’Abée-Lund, T.M.; Wasteson, Y. Zinc and Copper Reduce Conjugative Transfer of Resistance Plasmids from Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoro-Dasi, L.; Villagra, A.; Sevilla-Navarro, S.; Pérez-Gracia, M.T.; Vega, S.; Marin, C. The Dynamic of Antibiotic Resistance in Commensal Escherichia coli throughout the Growing Period in Broiler Chickens: Fast-Growing vs. Slow-Growing Breeds. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bythwood, T.N.; Soni, V.; Lyons, K.; Hurley-Bacon, A.; Lee, M.D.; Hofacre, C.; Sanchez, S.; Maurer, J.J. Antimicrobial Resistant Salmonella Enterica Typhimurium Colonizing Chickens: The Impact of Plasmids, Genotype, Bacterial Communities, and Antibiotic Administration on Resistance. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarzynska, M.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Wasyl, D. A Metagenomic Glimpse into the Gut of Wild and Domestic Animals: Quantification of Antimicrobial Resistance and More. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastard, J.; Nhung, N.T.; Hien, V.B.; Kiet, B.T.; Temime, L.; Opatowski, L.; Carrique-Mas, J.; Choisy, M. Modelling the Impact of Antimicrobial Use and External Introductions on Commensal E. coli Colistin Resistance in Small-Scale Chicken Farms of the Mekong Delta of Vietnam. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e2185–e2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, D.A.; Ivanova, O.E.; Pomazkova, A.V.; Egoreva, M.A.; Prasolova, O.V.; Lenev, S.V.; Gergel, M.A.; Bukova, N.K.; Karabanov, S.Y. Antimicrobial Resistance of Commensal Enterococcus Faecalis and Enterococcus Faecium from Food-Producing Animals in Russia. Vet. World 2022, 15, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oloso, N.O.; Adeyemo, I.A.; Heerden, H.V.; Fasanmi, O.G.; Fasina, F.O. Antimicrobial Drug Administration and Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella Isolates Originating from the Broiler Production Value Chain in Nigeria. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiken, R.E.C.; Van Gompel, L.; Munk, P.; Sarrazin, S.; Joosten, P.; Dorado-García, A.; Borup Hansen, R.; Knudsen, B.E.; Bossers, A.; Wagenaar, J.A.; et al. Associations between Antimicrobial Use and the Faecal Resistome on Broiler Farms from Nine European Countries. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 2596–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, K.; Wei, B.; Kang, M. Distribution and Dissemination of Antimicrobial-Resistant Salmonella in Broiler Farms with or without Enrofloxacin Use. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, N.M.; Wales, A.D.; Ridley, A.M.; Davies, R.H. Farm Level Risk Factors for Fluoroquinolone Resistance in E. coli and Thermophilic campylobacter spp. on Poultry Farms. Avian Pathol. 2016, 45, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, L.; Agunos, A.; Gow, S.P.; Carson, C.A.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Reduction in Antimicrobial Use and Resistance to Salmonella, Campylobacter, and Escherichia coli in Broiler Chickens, Canada, 2013–2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2434–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.K.; Talukder, S.; Hasan, M.M.; Tasmim, S.T.; Parvin, M.S.; Ali, M.Y.; Islam, M.T. Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli in Broiler Chickens, Farmworkers, and Farm Sewage in Bangladesh. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.S.; Kristoffersen, A.B.; Sunde, M.; Nødtvedt, A.; Norström, M. Risk Factors for Occurrence of Cephalosporin-Resistant Escherichia coli in Norwegian Broiler Flocks. Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 130, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezhoud, H.; Chantziaras, I.; Iguer-Ouada, M.; Moula, N.; Garmyn, A.; Martel, A.; Touati, A.; Smet, A.; Haesebrouck, F.; Boyen, F. Presence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Coliform Bacteria from Hatching Broiler Eggs with Emphasis on ESBL/AmpC-Producing Bacteria. Avian Pathol. 2016, 45, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, L.; Patrick, I.; Arief, R.; Benigno, C.; Kalpravidh, W.; McGrane, J.; Schoonman, L.; Sukarno, A.H.; Rushton, J. The Costs, Benefits and Human Behaviours for Antimicrobial Use in Small Commercial Broiler Chicken Systems in Indonesia. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalam, M.A.; Rahman, M.S.; Alim, M.A.; Shano, S.; Afrose, S.; Jalal, F.A.; Akter, S.; Khan, S.A.; Islam, M.M.; Uddin, M.B.; et al. Knowledge, Attitudes, and Common Practices of Livestock and Poultry Veterinary Practitioners Regarding the AMU and AMR in Bangladesh. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, X.; Rymer, C.; Lim, R.; Ray, P. Factors Associated with Antimicrobial Use in Fijian Livestock Farms. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bâtie, C.; Ha, L.T.T.; Loire, E.; Truong, D.B.; Tuan, H.M.; Cuc, N.T.K.; Paul, M.; Goutard, F. Characterisation of Chicken Farms in Vietnam: A Typology of Antimicrobial Use among Different Production Systems. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 208, 105731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Fournié, G.; Blake, D.; Henning, J.; Conway, P.; Hoque, A.; Ghosh, S.; Parveen, S.; Biswas, P.K.; Akhtar, Z.; et al. Antibiotic Usage Practices and Its Drivers in Commercial Chicken Production in Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dione, M.M.; Amia, W.C.; Ejobi, F.; Ouma, E.A.; Wieland, B. Supply Chain and Delivery of Antimicrobial Drugs in Smallholder Livestock Production Systems in Uganda. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 611076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltholth, M.; Govindaraj, G.; Das, B.; Shanabhoga, M.B.; Swamy, H.M.; Thomas, A.; Cole, J.; Shome, B.R.; Holmes, M.A.; Moran, D. Factors Influencing Antibiotic Prescribing Behavior and Understanding of Antimicrobial Resistance Among Veterinarians in Assam, India. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 864813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoola, M.B.; Pillai, N.; Nanduri, B.; Rothrock, M.J.; Ramkumar, M. Preharvest Environmental and Management Drivers of Multidrug Resistance in Major Bacterial Zoonotic Pathogens in Pastured Poultry Flocks. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.T.L.; Ngo, T.H.H.; Tran, T.M.H.; Vu, T.N.B.; Le, V.T.; Tran, H.A.; Pham, D.T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Tran, D.L.; Nguyen, T.P.L.; et al. Genomic Epidemiological Analysis of Mcr-1-Harboring Escherichia coli Collected from Livestock Settings in Vietnam. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1034610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, S.; Sahibzada, S.; Hewson, K.; Laird, T.; Abraham, R.; Pavic, A.; Truswell, A.; Lee, T.; O’Dea, M.; Jordan, D. Emergence of Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Campylobacter Jejuni and Campylobacter Coli among Australian Chickens in the Absence of Fluoroquinolone Use. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02765-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Belenguer, A.; Doménech, E.; Villagrá, A.; Fenollar, A.; Ferrús, M.A. Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli Isolated in Newly-Hatched Chickens and Effect of Amoxicillin Treatment during Their Growth. Avian Pathol. 2016, 45, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladeinde, A.; Abdo, Z.; Press, M.O.; Cook, K.; Cox, N.A.; Zwirzitz, B.; Woyda, R.; Lakin, S.M.; Thomas Iv, J.C.; Looft, T.; et al. Horizontal Gene Transfer Is the Main Driver of Antimicrobial Resistance in Broiler Chicks Infected with Salmonella Enterica Serovar Heidelberg. Msystems 2021, 6, e00729-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talavera-González, J.M.; Talavera-Rojas, M.; Soriano-Vargas, E.; Vázquez-Navarrete, J.; Salgado-Miranda, C. In Vitro Transduction of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes into Escherichia coli Isolates from Backyard Poultry in Mexico. Can. J. Microbiol. 2021, 67, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, S.; Hasan, M.M.; Mandal, A.K.; Tasmim, S.T.; Parvin, M.S.; Ali, M.Y.; Nahar, A.; Islam, M.Z.; Islam, M.T. Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Salmonella in Chickens, Sewage, and Workers of Broiler Farms in Selected Areas of Bangladesh. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2021, 15, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, A.; Alim, A.; Shano, S.; Nayem, R.K.; Badsha, R.; Mamun, A.A.; Hoque, A.; Tanzin, A.Z.; Khan, S.A.; Islam, A.; et al. Knowledge, Attitude, and Practices on Antimicrobial Use and Antimicrobial Resistance among Poultry Drug and Feed Sellers in Bangladesh. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Category | Subcategory | Direction | Studies (n) | Example Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmer KAP | Education/Training | ↑↓ | 24 | Higher education → ↑prophylaxis/growth promotion (Burkina Faso); Training → ↓prudent dispensing (Zambia) |
| Experience | ↑↓ | 7 | Longer experience → ↓AMR (Cameroon); ↑cautious use (Tanzania) | |
| Age | ↑↓ | 7 | Younger farmers → ↑AMU (Lao PDR); Older farmers → ↓AMR (Vietnam) | |
| Income | ↑ | 6 | Low income → ↑AMR (Nigeria, Malawi) | |
| Gender | ↑ | 2 | Male farmers → ↑AMU (Vietnam) | |
| Farming Practices | Litter/Manure Management | ↑ | 6 | Chicken litter → ↑resistant bacteria (India, Brazil) |
| ↓ | 4 | Composting manure → ↓AMR (France) | ||
| Flock Density/Confinement | ↑ | 5 | High density → ↑AMR (Vietnam, Cameroon) | |
| Flock Size | ↑ | 5 | Large flocks (5,000–10,000 hens) → ↑AMU/AMR (Cameroon, Canada) | |
| Water Management | ↑ | 4 | River/pump water use → ↑AMR (Tanzania, Malaysia) | |
| Biosecurity/Hygiene | ↑ | 10 | Poor hygiene → ↑AMR (India, Tanzania); Wild bird access → ↑AMR (UK) | |
| ↓ | 7 | Sanitation/disinfection → ↓AMR (Malaysia, EU) | ||
| Feed Practices | ↑ | 4 | Low-quality/commercial feed → ↑AMR (Vietnam, Ecuador) | |
| Intentional Misuse | Prophylactic Use | ↑ | 12 | Antibiotics for disease prevention (Vietnam, Tanzania, Burkina Faso) |
| Growth Promotion | ↑ | 5 | Antibiotics to enhance growth (Bangladesh, Indonesia) | |
| Non-Prescription Use | ↑ | 6 | Access without prescription (Bangladesh, Nepal) | |
| Improper Dosing | ↑ | 5 | Underdosing/overdosing (Nigeria, Cameroon) | |
| Economic Factors | Financial Pressure | ↑ | 11 | Livelihood precarity → ↑AMU (Malawi); Cost avoidance → ↓veterinary consultations (Ecuador) |
| Environmental Factors | Vectors/Wildlife | ↑ | 8 | Fly-mediated gene transfer (Vietnam); Wild birds → ↑fluoroquinolone resistance (Australia) |
| Seasonality/Geography | ↑ | 5 | Winter → ↑AMR (Bangladesh); Southern regions → ↑AMU (Italy) | |
| Veterinary Practices | Prescription Behavior | ↑ | 5 | Non-diagnostic prescriptions (Ecuador); Client pressure (Netherlands) |
| Drug/Feed Sellers | Knowledge Gaps | ↑ | 5 | Lack of policy awareness (Uganda); Role as non-professional prescribers (Ecuador) |
| Regulatory Gaps | Drug Access | ↑ | 6 | Over-the-counter sales (Nepal); Unrestricted availability (Tanzania) |
| Core Insight 1: Economic Pressures Override Knowledge | |||||
| Driver | Category | Subcategory | Direction | Studies (n) | Example Factor |
| Farmer Decision-Making Drivers | Financial Pressures | Livelihood Protection | ↑ | 11 | Trained farmers using antibiotics preventively to avoid income loss (Burkina Faso, Senegal) |
| Cost-Driven Practices | ↑ | 9 | Economic constraints → Underdosing/slaughter vs. veterinary care (Malawi, Ecuador) | ||
| Production Risks | Flock Security | ↑ | 7 | Prophylactic antibiotic use to protect large flocks (Cameroon, Indonesia) | |
| Core Insight 2: Regulatory Gaps Enable Misuse | |||||
| Driver | Category | Subcategory | Direction | Studies (n) | Example Factor |
| Systemic Vulnerabilities | Drug Access | Non-Prescription Sales | ↑ | 12 | 57/327 factors involved intentional misuse (e.g., black market antibiotics in Nepal, Tanzania) |
| Policy Enforcement | Weak Implementation | ↑ | 8 | Low enforcement → Growth promoter use despite bans (Nigeria, Bangladesh) | |
| Prescription Practices | Non-Veterinary Advice | ↑ | 6 | Drug sellers as primary prescribers (Zambia, Ecuador) | |
| Core Insight 3: Environmental/Structural Understudied | |||||
| Driver | Category | Subcategory | Direction | Studies (n) | Example Factor |
| Emerging Risk Pathways | Environmental Exposure | Vectors and Seasonality | ↑ | 5 | Fly-mediated gene transfer (Vietnam); winter → ↑AMR (Bangladesh, Italy) |
| Farm Infrastructure | Waste Management | ↑↓ | 7 | Litter composting ↓AMR (France); improper carcass disposal ↑AMR (Senegal) | |
| Wildlife Interface | Cross-Species Transmission | ↑ | 4 | Wild birds spreading fluoroquinolone resistance (Australia) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farkas, Z.; Strang, O.; Zentai, A.; Csorba, S.; Farkas, M.; Bittsánszky, A.; Tóth, A.; Süth, M.; Jóźwiak, Á. Scoping Review of Factors Affecting Antimicrobial Use and the Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance in the Poultry Production Chain. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090881
Farkas Z, Strang O, Zentai A, Csorba S, Farkas M, Bittsánszky A, Tóth A, Süth M, Jóźwiak Á. Scoping Review of Factors Affecting Antimicrobial Use and the Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance in the Poultry Production Chain. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(9):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090881
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarkas, Zsuzsa, Orsolya Strang, Andrea Zentai, Szilveszter Csorba, Máté Farkas, András Bittsánszky, András Tóth, Miklós Süth, and Ákos Jóźwiak. 2025. "Scoping Review of Factors Affecting Antimicrobial Use and the Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance in the Poultry Production Chain" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 9: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090881
APA StyleFarkas, Z., Strang, O., Zentai, A., Csorba, S., Farkas, M., Bittsánszky, A., Tóth, A., Süth, M., & Jóźwiak, Á. (2025). Scoping Review of Factors Affecting Antimicrobial Use and the Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance in the Poultry Production Chain. Veterinary Sciences, 12(9), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090881







