Development of Reverse Transcriptase Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Combined with Lateral Flow Dipstick for Rapid Detection of Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV): Pilot Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Preparation
2.2. Primer Design
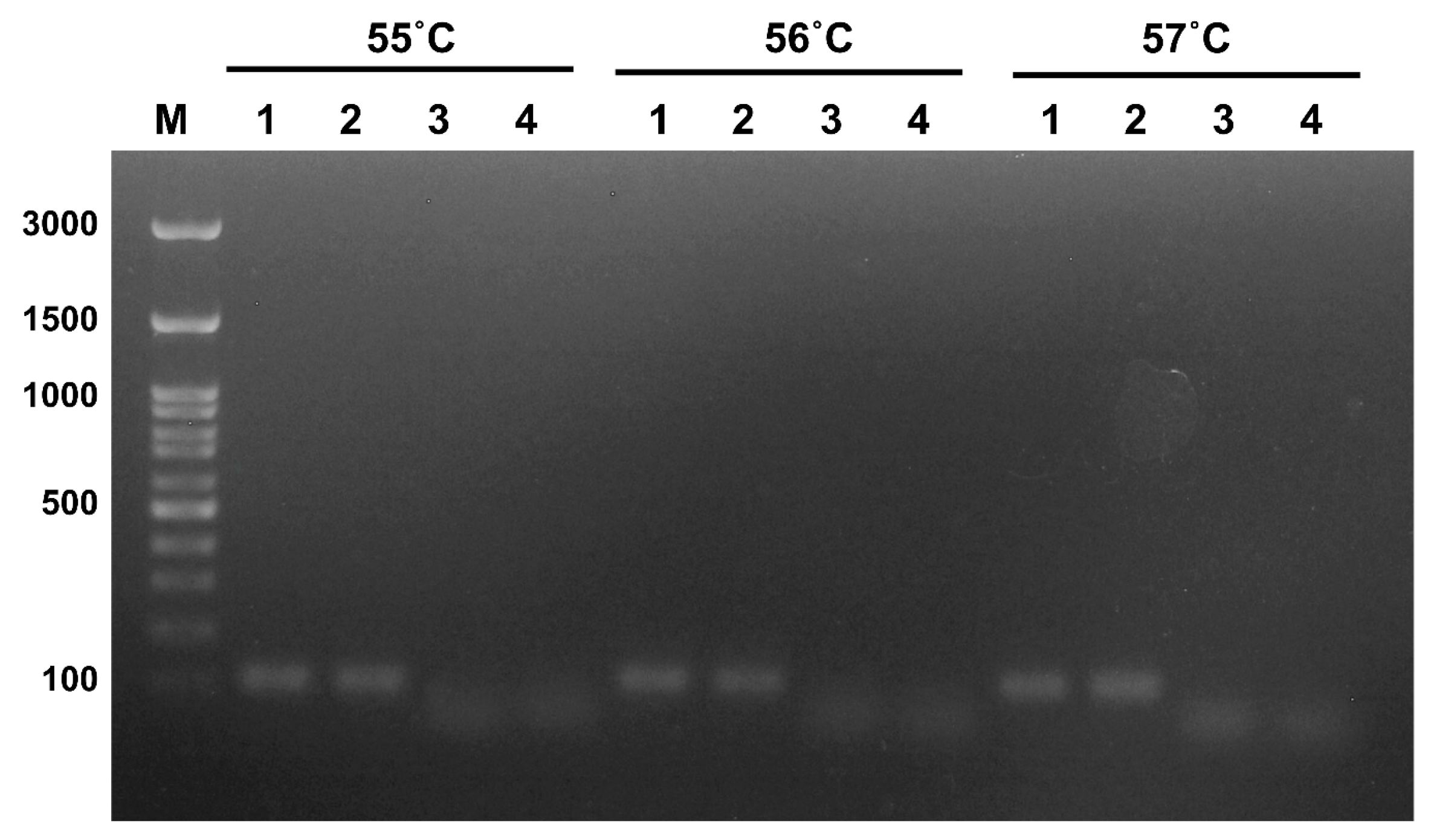
2.3. RT-PCR for Primer Screening
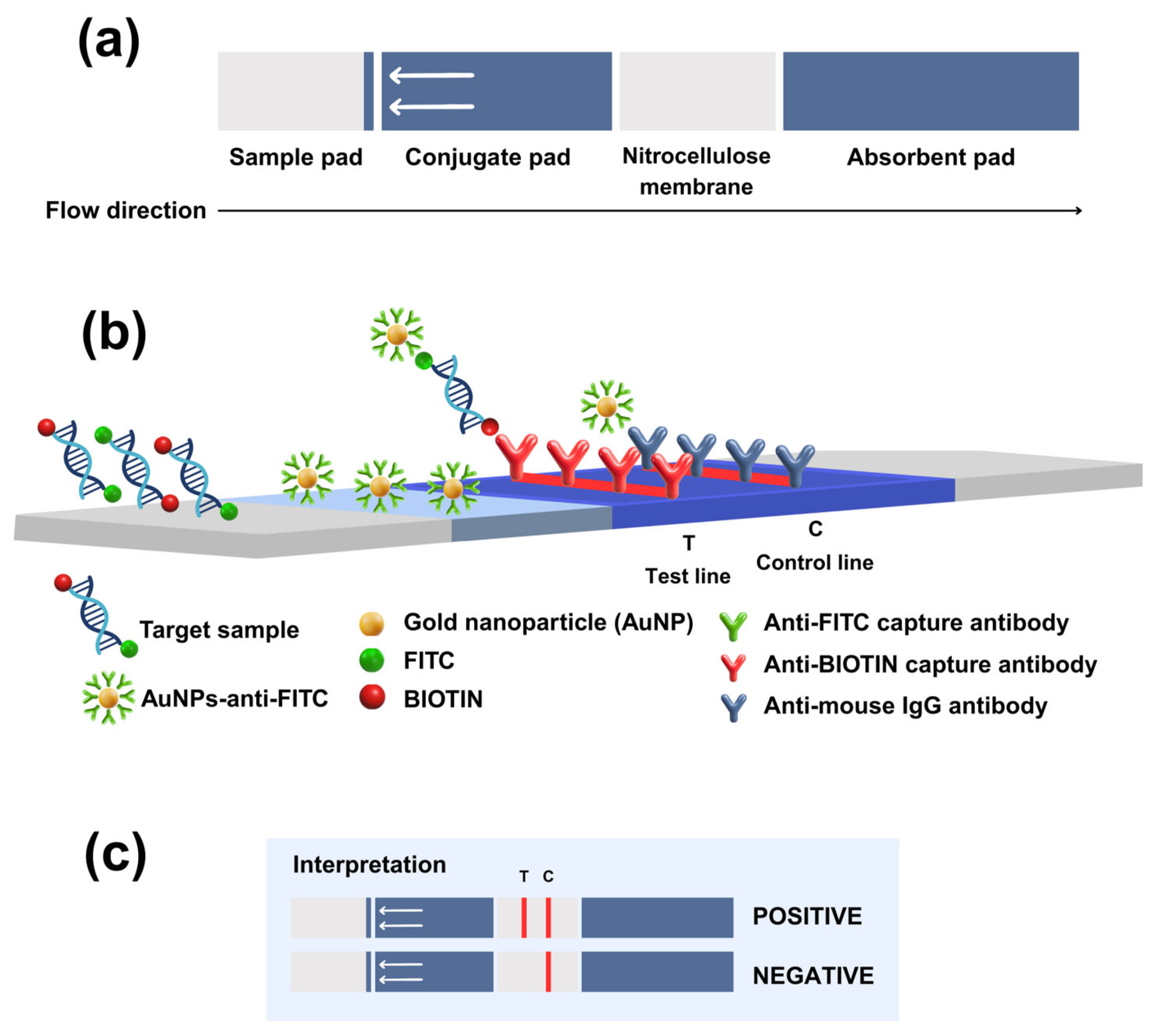
2.4. Development of RT-RPA-LFD Assay
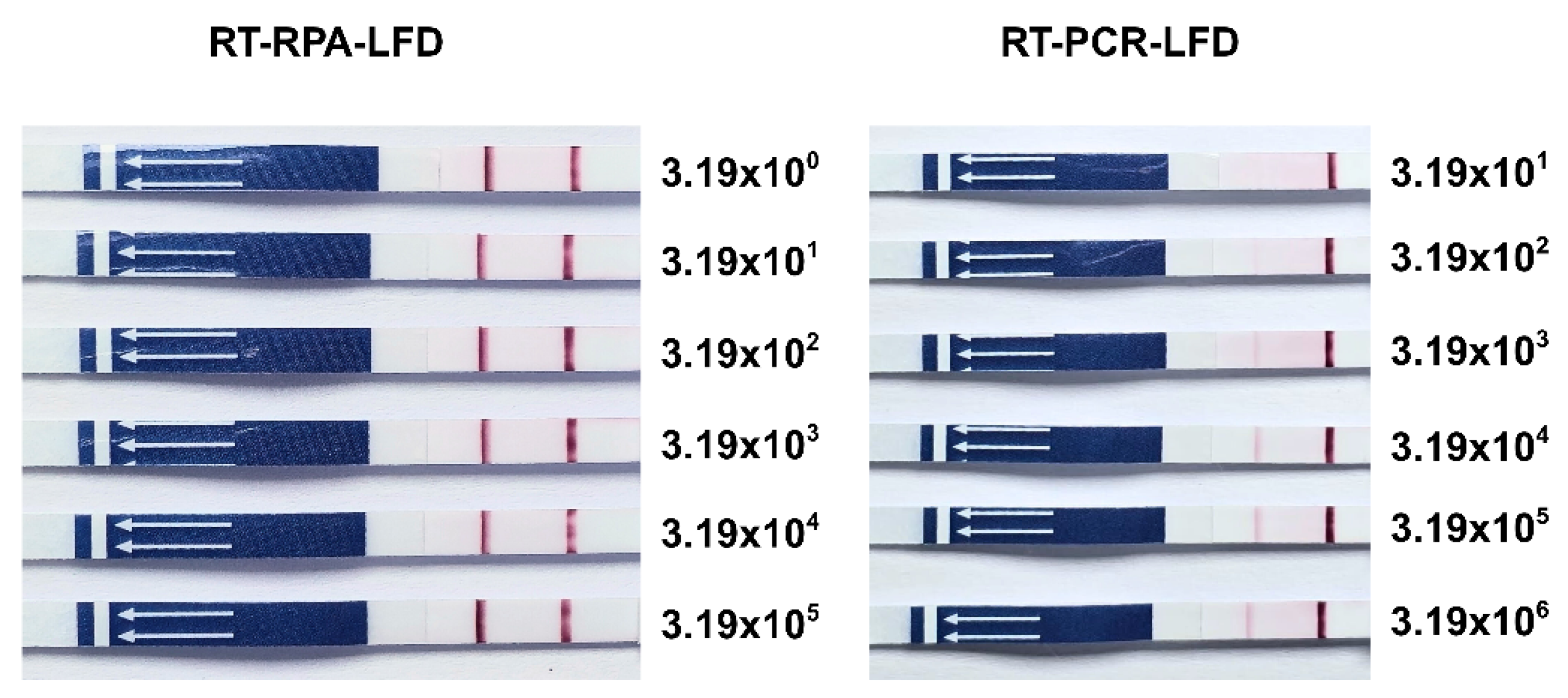
2.5. Determination of the Limit of Detection (LOD)
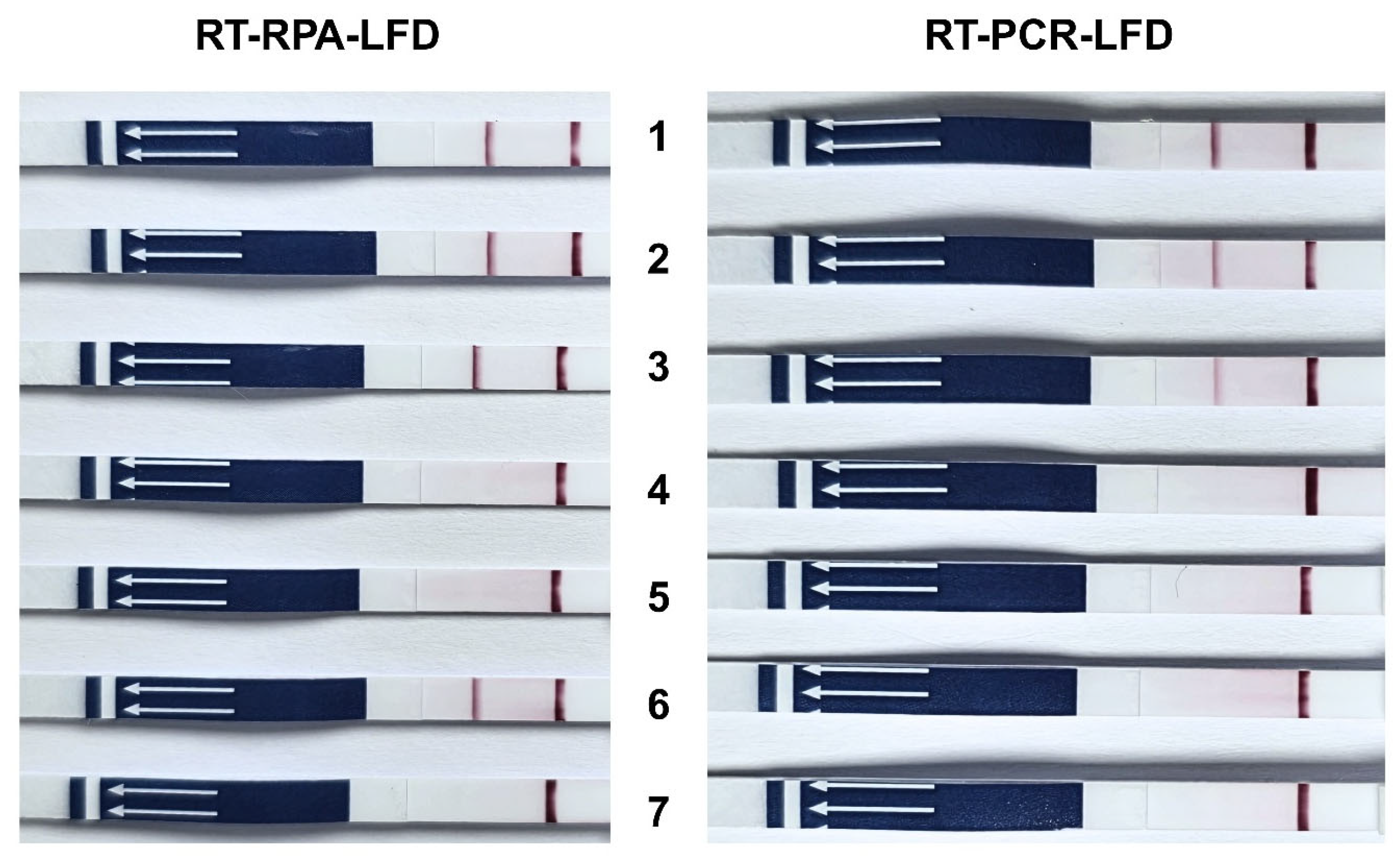
2.6. Validation LFD in TiLV-Infected Tissues
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of the Reaction
3.2. Limit of Detection (LOD)
3.3. Application of RT-RPA-LFD in Tilapia Tissues
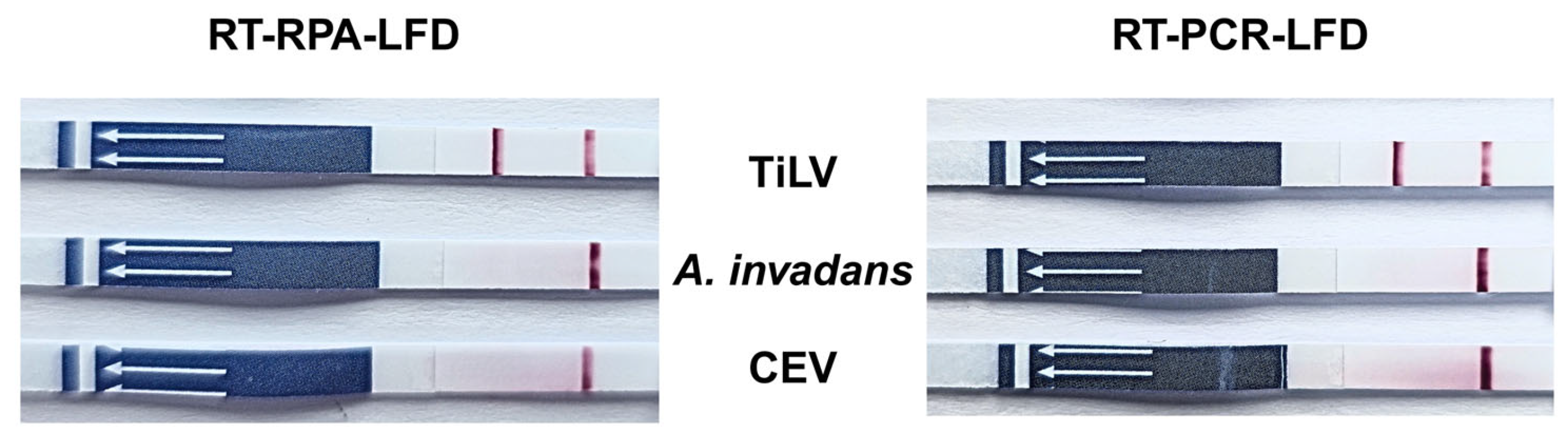
3.4. Determination of Specificity of RT-RPA-LFD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AuNPs | Gold nanoparticles |
| A. invadans | Aphanomyces invadans |
| CEV | Carp Edema Virus |
| FITC | Fluorescein Isothiocyanate |
| LFD | Lateral flow dipstick |
| LOD | Limit of Detection |
| pTiLV | Plasmid Tilapia Lake Virus |
| RT-RPA | Reverse Transcriptase Recombinase Polymerase Amplification |
| RT-PCR | Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| TiLV | Tilapia Lake Virus |
References
- Eyngor, M.; Zamostiano, R.; Kembou Tsofack, J.E.; Berkowitz, A.; Bercovier, H.; Tinman, S.; Lev, M.; Hurvitz, A.; Galeotti, M.; Bacharach, E.; et al. Identification of a Novel RNA Virus Lethal to Tilapia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4137–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surachetpong, W.; Roy, S.R.K.; Nicholson, P. Tilapia lake virus: The story so far. J. Fish. Dis. 2020, 43, 1115–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.R.K.; Yamkasem, J.; Tattiyapong, P.; Surachetpong, W. Weight-dependent susceptibility of tilapia to tilapia lake virus infection. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.T.; Siriroob, S.; Meemetta, W.; Santimanawong, W.; Gangnonngiw, W.; Pirarat, N.; Khunrae, P.; Rattanarojpong, T.; Vanichviriyakit, R.; Senapin, S. Emergence of tilapia lake virus in Thailand and an alternative semi-nested RT-PCR for detection. Aquaculture 2017, 476, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyde, C.W.; Tan, J.P.; Yeap, S.K.; Yong, C.Y. Current updates on viral infections affecting tilapia. Aquac. Fish. Fish. 2025, 10, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugimba, K.K.; Lamkhannat, M.; Dubey, S.; Mutoloki, S.; Munang’andu, H.M.; Evensen, Ø. Tilapia lake virus downplays innate immune responses during early stage of infection in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierezan, F.; Yun, S.; Piewbang, C.; Surachetpong, W.; Soto, E. Pathogenesis and immune response of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to Tilapia lake virus by intragastric route. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. Rep. 2020, 107, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamkasem, J.; Tattiyapong, P.; Kamlangdee, A.; Surachetpong, W. Evidence of potential vertical transmission of tilapia lake virus. J. Fish. Dis. 2019, 42, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.K.; Pradhan, P.K.; Swaminathan, T.R.; Sood, N.; Paria, P.; Das, A.; Verma, D.K.; Kumar, R.; Yadav, M.K.; Dev, A.K.; et al. Emergence of Tilapia Lake Virus associated with mortalities of farmed Nile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus 1758) in India. Aquaculture 2017, 484, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattiyapong, P.; Dachavichitlead, W.; Surachetpong, W. Experimental infection of Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV) in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and red tilapia (Oreochromis spp.). Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 207, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, P.P.; Delamare-Deboutteville, J.; Jansen, M.D.; Phiwsaiya, K.; Dalia, A.; Hasan, M.A.; Senapin, S.; Mohan, C.V.; Dong, H.T.; Rodkhum, C. Two-year surveillance of tilapia lake virus (TiLV) reveals its wide circulation in tilapia farms and hatcheries from multiple districts of Bangladesh. J. Fish. Dis. 2020, 43, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierezan, F.; Yun, S.; Surachetpong, W.; Soto, E. Intragastric and intracoelomic injection challenge models of tilapia lake virus infection in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) fingerlings. J. Fish. Dis. 2019, 42, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del-Pozo, J.; Mishra, N.; Kabuusu, R.; Cheetham, S.; Eldar, A.; Bacharach, E.; Lipkin, W.I.; Ferguson, H.W. Syncytial Hepatitis of Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) is Associated With Orthomyxovirus-Like Virions in Hepatocytes. Vet. Pathol. 2016, 54, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Ye, C.; Cao, J.; Zhou, X.; Xie, M.; Qing, J.; Chen, Z. Application of recombinase polymerase amplification with lateral flow assay to pathogen point-of-care diagnosis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1475922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preena, P.G.; Kumar, T.V.A.; Johny, T.K.; Dharmaratnam, A.; Swaminathan, T.R. Quick hassle-free detection of cyprinid herpesvirus 2 (CyHV-2) in goldfish using recombinase polymerase amplification-lateral flow dipstick (RPA-LFD) assay. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacharoje, S.; Techangamsuwan, S.; Chaichanawongsaroj, N. Rapid characterization of feline leukemia virus infective stages by a novel nested recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) and reverse transcriptase-RPA. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, I.M.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Recombinase polymerase amplification: Basics, applications and recent advances. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2018, 98, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Wang, S.; Chi, T.; Song, F.; et al. Clinical Validation of Two Recombinase-Based Isothermal Amplification Assays (RPA/RAA) for the Rapid Detection of African Swine Fever Virus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.R.; Yang, Z.X.; Li, Z.H.; Gao, X.; Hu, Z.Y.; Yang, H.; Liao, D.F. Development and evaluation of recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick assays for co-detection of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus and the Palyam serogroup virus. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Zhang, L.; Chang, J.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Yuan, G.; Su, J. Rapid and sensitive detection of pathogenic Elizabethkingia miricola in black spotted frog by RPA-LFD and fluorescent probe-based RPA. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. Rep. 2022, 3, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukonta, T.; Senapin, S.; Taengphu, S.; Hannanta-anan, P.; Kitthamarat, M.; Aiamsa-at, P.; Chaijarasphong, T. An RT-RPA-Cas12a platform for rapid and sensitive detection of tilapia lake virus. Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Bergmann, S.M.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Lv, Y.; Yin, J.; Yang, G.; Qv, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Development and comparative evaluation of real-time PCR and real-time RPA assays for detection of tilapia lake virus. Mol. Cell Probes 2021, 60, 101776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, P.; Fathi, M.A.; Fischer, A.; Mohan, C.; Schieck, E.; Mishra, N.; Heinimann, A.; Frey, J.; Wieland, B.; Jores, J. Detection of Tilapia Lake Virus in Egyptian fish farms experiencing high mortalities in 2015. J. Fish. Dis. 2017, 40, 1925–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattiyapong, P.; Sirikanchana, K.; Surachetpong, W. Development and validation of a reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction for tilapia lake virus detection in clinical samples and experimentally challenged fish. J. Fish. Dis. 2018, 41, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Wahed, A.; Sanabani, S.S.; Faye, O.; Pessôa, R.; Patriota, J.V.; Giorgi, R.R.; Patel, P.; Böhlken-Fascher, S.; Landt, O.; Niedrig, M.; et al. Rapid Molecular Detection of Zika Virus in Acute-Phase Urine Samples Using the Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay. PLoS Curr. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, Y.L.; Ismail, I.B.; Mustapa, N.I.B.; Lai, M.Y.; Tuan Soh, T.S.; Haji Hassan, A.; Peariasamy, K.M.; Lee, Y.L.; Abdul Kahar, M.K.B.; Chong, J.; et al. Development of a reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid and direct visual detection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehia, N.; Arafa, A.-S.; Abd El Wahed, A.; El-Sanousi, A.A.; Weidmann, M.; Shalaby, M.A. Development of reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification assay for avian influenza H5N1 HA gene detection. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 223, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Macdonald, J.; von Stetten, F. Review: A comprehensive summary of a decade development of the recombinase polymerase amplification. Analyst 2019, 144, 31–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Huang, H.; Zhu, P.; Yan, X.; Fan, J.; Jiang, J.; Xu, J. Recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick for equipment-free detection of Salmonella in shellfish. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonlapdecha, W.; Seetang-Nun, Y.; Wonglumsom, W.; Tuitemwong, K.; Erickson, L.E.; Hansen, R.R.; Tuitemwong, P. Antibody-conjugated ferromagnetic nanoparticles with lateral flow test strip assay for rapid detection of Campylobacter jejuni in poultry samples. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 286, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirawannaporn, S.; Limothai, U.; Tachaboon, S.; Dinhuzen, J.; Kiatamornrak, P.; Chaisuriyong, W.; Bhumitrakul, J.; Mayuramart, O.; Payungporn, S.; Srisawat, N. Rapid and sensitive point-of-care detection of Leptospira by RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a targeting lipL32. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daher, R.K.; Stewart, G.; Boissinot, M.; Bergeron, M.G. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification for Diagnostic Applications. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Meng, K.; Liu, J. Recombinase polymerase amplification-lateral flow dipstick (RPA-LFD) designed for rapid detection of canine distemper virus. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 86, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhu, Z.; Li, F.; Xie, X.; Ding, A. Rapid and sensitive detection of hepatitis B virus by lateral flow recombinase polymerase amplification assay. J. Virol. Methods 2021, 291, 114094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, D.S.; McNerney, R.; Teng Low, H.; Leader, B.T.; Pérez-Osorio, A.C.; Meyer, J.C.; O’Sullivan, D.M.; Brooks, D.G.; Piepenburg, O.; Forrest, M.S. Rapid Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Recombinase Polymerase Amplification. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euler, M.; Wang, Y.; Heidenreich, D.; Patel, P.; Strohmeier, O.; Hakenberg, S.; Niedrig, M.; Hufert, F.T.; Weidmann, M. Development of a Panel of Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assays for Detection of Biothreat Agents. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srivorakul, S.; Guntawang, T.; Sittisak, T.; Gordsueb, T.; Boonsri, K.; Khattiya, R.; Sthitmatee, N.; Pringproa, K. Development of Reverse Transcriptase Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Combined with Lateral Flow Dipstick for Rapid Detection of Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV): Pilot Study. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090845
Srivorakul S, Guntawang T, Sittisak T, Gordsueb T, Boonsri K, Khattiya R, Sthitmatee N, Pringproa K. Development of Reverse Transcriptase Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Combined with Lateral Flow Dipstick for Rapid Detection of Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV): Pilot Study. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(9):845. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090845
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrivorakul, Saralee, Thunyamas Guntawang, Tidaratt Sittisak, Thanchanok Gordsueb, Kittikorn Boonsri, Rutch Khattiya, Nattawooti Sthitmatee, and Kidsadagon Pringproa. 2025. "Development of Reverse Transcriptase Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Combined with Lateral Flow Dipstick for Rapid Detection of Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV): Pilot Study" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 9: 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090845
APA StyleSrivorakul, S., Guntawang, T., Sittisak, T., Gordsueb, T., Boonsri, K., Khattiya, R., Sthitmatee, N., & Pringproa, K. (2025). Development of Reverse Transcriptase Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Combined with Lateral Flow Dipstick for Rapid Detection of Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV): Pilot Study. Veterinary Sciences, 12(9), 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090845






