Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Salmon Oil on Canine Frozen–Thawed Semen
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Collection of Semen and Sperm Pre-Freezing Evaluation
2.3. Semen Freezing
2.4. Thawing and Post-Thaw Semen Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Motility (MOT), Viability (EN), and Hypo-Osmotic Swelling (HOST) Tests at Thawing
3.2. Motility (MOT) and Viability (EN) During the Thermoresistance (TRT) Test
3.3. Sperm Morphology During D0-D90-D180
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Curry, M.R. Cryopreservation of semen from domestic livestock. Rev. Reprod. 2000, 5, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polge, C.; Smith, A.U.; Parkes, A.S. Revival of spermatozoa after vitrification and dehydration at low temperature. Nature 1949, 164, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, G.F.; Morris, J.K.; Sikes, J.D.; Youngquist, R.S. Effect of storage temperature, cooling rates and two different semen extenders on canine spermatozoa motility. Theriogenology 1990, 34, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.D.S.; Tareq, K.M.A.; Hammano, K.I.; Tsujii, H. Effect of fatty acids on boar sperm motility, viability and acrosome reaction. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2007, 6, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocé, E.; Purdy, P.H.; Graham, J.K. Treating ram sperm with cholesterol-loaded cyclodextrins improves cryosurvival. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2010, 118, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, I.G. Lipids and calcium uptake of sperm in relation to cold shock and preservation: A review. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 1993, 5, 639–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucio, C.F.; Brito, M.M.; Angrimani, D.; Belaz, K.; Morais, D.; Zampieri, D.; Losano, J.; Assumpção, M.; Nichi, M.; Eberlin, M.N.; et al. Lipid composition of the canine sperm plasma membrane as markers of sperm motility. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2017, 52 (Suppl. S2), 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Very long-chain n-3 fatty acids and human health: Fact, fiction and the future. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2018, 77, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulliver, C.E.; Friend, M.A.; King, B.J.; Clayton, E.H. The role of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in reproduction of sheep and cattle. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2012, 131, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J. Timely topics in nutrition: Therapeutic use of fish oils in companion animals. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2011, 239, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendramini, T.H.A.; Marchi, P.H.; Olivindo, R.F.G.; Pedrinelli, V.; Amaral, A.R.; Miranda, M.S.; Príncipe, L.A.; Cesar, C.G.L.; Zafalon, R.V.A.; Perini, M.P.; et al. Exploring the efficacy and optimal dosages of omega-3 supplementation for companion animals. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2025, 11, 1–16, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinsko, S.P.; Varner, D.D.; Love, C.C.; Blanchard, T.L.; Day, B.C.; Wilson, M.E. Effect of feeding a DHA-enriched nutriceutical on the quality of fresh, cooled and frozen stallion semen. Theriogenology 2005, 63, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Ravina, C.; Aguirre-Lipperheide, M.; Pinto, F.; Martín-Lozano, D.; Fernández-Sánchez, M.; Blasco, V.; Santamaría-López, E.; Candenas, L. Effect of dietary supplementation with a highly pure and concentrated docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) supplement on human sperm function. Reprod. Biol. 2018, 18, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshvaght, A.; Towhidi, A.; Zare-shahneh, A.; Noruozi, M.; Zhandi, M.; Dadashpour Davachi, N.; Karimi, R. Dietary n-3 PUFAs improve fresh and post-thaw semen quality in Holstein bulls via alteration of sperm fatty acid composition. Theriogenology 2016, 85, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.C.; Milani, C.; Zucchini, P.; Quirino, C.R.; Romagnoli, S.; Cunha, I.C.N. Residual effect after salmon oil supplementation on semen quality and serum levels of testosterone in dogs. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2019, 54, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, R.; Sharafi, M.; Zare Shahneh, A.; Towhidi, A.; Kohram, H.; Zhandi, M.; Esmaeili, V.; Shahverdi, A. Effect of dietary fish oil supplementation on ram semen freeze ability and fertility using soybean lecithin– and egg yolk–based extenders. Theriogenology 2016, 86, 1583–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safari Asl, R.; Shariatmadari, F.; Sharafi, M.; Karimi Torshizi, M.A.; Shahverdi, A. Dietary fish oil supplemented with vitamin E improves quality indicators of rooster cold-stored semen through reducing lipid peroxidation. Cryobiology 2018, 84, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheradmand Garmsir, A.; Zareh Shahneh, A.; Ali Jalali, S.M.; Nouri, H.; Afshar, M. Effects of Dietary Thyme (Thymus vulgaris) and Fish Oil on Semen Quality of Miniature Caspian Horse. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2014, 34, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, C.; Lucas, M.; Julien, P.; Morin, R.; Gingras, S.; Dewailly, E. Fatty Acid Composition of Wild and Farmed Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) and Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Lipids 2005, 40, 529–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Examination and Processing of Human Semen, 5th ed.; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; p. 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oettlé, E.E. Sperm morphology and fertility in the dog. J. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. 1993, 47, 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- de reprodução Animal, C.B. Manual Para Exame Andrológico e Avaliação de Sêmen Animal, 3rd ed.; CBRA: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2013; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Rota, A.; Iguer-Ouada, M.; Verstegen, J.; Linde-Forsberg, C. Fertility after vaginal or uterine deposition of dog semen frozen in a tris extender with or without Equex STM paste. Theriogenology 1999, 51, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rota, A.; Milani, C.; Cabianca, G.; Martini, M. Comparison between glycerol and ethylene glycol for dog semen cryopreservation. Theriogenology 2006, 65, 1848–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, I.C.N.; Henning, H.; Urhausen, C.; Beyerbach, M.; Günzel-Apel, A.R. A commercial box for dog semen transport: What happens inside when the environmental temperature is increasing? Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 147, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomassen, R.; Farstad, W. Artificial insemination in canids: A useful tool in breeding and conservation. Theriogenology 2009, 71, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, S.J. A retrospective clinical study of endoscopic-assisted transcervical insemination in the bitch with frozen-thawed dog semen. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2017, 52 (Suppl. S2), 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagnoli, S.; Lopate, C. Transcervical artificial insemination in dogs and cats: Review of the technique and practical aspects. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2014, 49 (Suppl. S4), 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujoana, T.C.; Sehlabela, L.D.; Mabelebele, M.; Sebola, N.A. The potential significance of antioxidants in livestock reproduction: Sperm viability and cryopreservation. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2024, 267, 107512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasihormozi, S.; Shahverdi, A.; Kouhkan, A.; Cheraghi, J.; Akhlaghi, A.A.; Kheimeh, A. Relationship of leptin administration with production of reactive oxygen species, sperm DNA fragmentation, sperm parameters and hormone profile in the adult rat. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2013, 287, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, C.; Aurich, C. “Fine feathers make fine birds”—The mammalian sperm plasma membrane lipid composition and effects on assisted reproduction. Ani. Rep. Sci. 2022, 246, 106884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowhan, W.; Bogdanov, M.; Mileykovskaya, E. Functional roles of lipids in membranes. In Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 2–36. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Soto, J.C.; Landeras, J.; Gadea, J. Spermatozoa and seminal plasma fatty acids as predictors of cryopreservation success. Andrology 2013, 1, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer-Somi, S.; Colombo, M.; Luvoni, G.C. Canine Spermatozoa—Predictability of Cryotolerance. Animals 2022, 12, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahzadeh, S.; Riasi, A.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H.; Tavalaee, M.; Jafarpour, F. Effect of dietary omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids and herbal antioxidants on sperm quality and fatty acid profile in rams. Theriogenology 2025, 241, 117438, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymouri Zadeh, Z.; Shariatmadari, F.; Sharafi, M.; Karimi Torshizi, M.A. Amelioration effects of n-3, n-6 sources of fatty acids and rosemary leaves powder on the semen parameters, reproductive hormones, and fatty acid analysis of sperm in aged Ross broiler breeder roosters. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safari Asl, R.; Shariatmadari, F.; Sharafi, M.; Karimi Torshizi, M.A.; Shahverdi, A. Improvements in semen quality, sperm fatty acids, and reproductive performance in aged Ross breeder roosters fed a diet supplemented with a moderate ratio of n-3: n-6 fatty acids. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 4113–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.; Zamiri, M.J.; Akhlaghi, A.; Shahverdi, A.H.; Alizadeh, A.R.; Jaafarzadeh, M.R. Effect of dietary fish oil with or without vitamin E supplementation on fresh and cryopreserved ovine sperm. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2017, 57, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.L.; Bouéres, C.S.; Pignataro, T.A.; Gonçalves de Oliveira, F.J.; de Oliveira Viu, M.A.; de Oliveira, R.A. Quality of Fresh, Cooled, and Frozen Semen From Stallions Supplemented with Antioxidants and Fatty Acids. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2016, 46, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid-Lausigk, Y.; Aurich, C. Influences of a diet supplemented with linseed oil and antioxidants on quality of equine semen after cooling and cryopreservation during winter. Theriogenology 2014, 81, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.G.; de Moura, R.S.; Rocha, L.G.P.; Bottino, M.P.; Nichi, M.; Maculan, R.; Bertechini, A.G.; Souza, J.C. Dietary Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation Improves the Quality of Stallion Cryopreserved Semen. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2017, 54, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.C.; Milani, C.; Zucchini, P.; Quirino, C.R.; Romagnoli, S.; da Cunha, I.C.N. Salmon oil supplementation in dogs affects the blood flow of testicular arteries. Reprod. Dom. Anim. 2021, 56, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, H.P.; Kreysel, H.W. Polyunsaturated fatty acids in relation to sperm motility. Andrologia 1983, 15, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, W.E.; Lin, D.S.; Wolf, D.P.; Alexander, M. Uneven distribution of desmosterol and docosahexaenoic acid in the heads and tails of monkey sperm. J. Lipid Res. 1998, 39, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Li, H.; Lin, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, D.; Zeng, J.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Li, G. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) exhibits antioxidant activity via mitochondrial modulation. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, R.A.; Ogilvie, G.K.; Davenport, D.J.; Gross, K.L.; Walton, J.A.; Richardson, K.L.; Mallinckrodt, C.H.; Hand, M.S.; Fettman, M.J. Duration of effects of dietary fish oil supplementation on serum eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid concentrations in dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1998, 59, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckel, K.; Nielsen, L.H.; Fuhrmann, H.; Bachmann, L. Fatty acid patterns of dog erythrocyte membranes after feeding of a fish-oil based DHA-rich supplement with a base diet low in n-3 fatty acids versus a diet containing added n-3 fatty acids. Acta Vet. Scand. 2011, 53, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root Kustritz, M.V.; Olson, P.N.; Johnston, S.D.; Root, T.K. The effects of stains and investigators on assessment of morphology of canine spermatozoa. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 1998, 34, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaman, J.A.; Toth, T.L.; Furtado, J.; Campos, H.; Hauser, R.; Chavarro, J.E. Dietary fat and semen quality among men attending a fertility clinic. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John Morris, G.; Acton, E.; Murray, B.J.; Fonseca, F. Freezing injury: The special case of the sperm cell. Cryobiology 2012, 64, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenzi, A.; Picardo, M.; Gandini, L.; Dondero, F. Lipids of the sperm plasma membrane: From polyunsaturated fatty acids considered as markers of sperm function to possible scavenger therapy. Hum. Reprod. Update 1996, 2, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council. Nutrient Requirements of Dogs and Cats, 1st ed.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
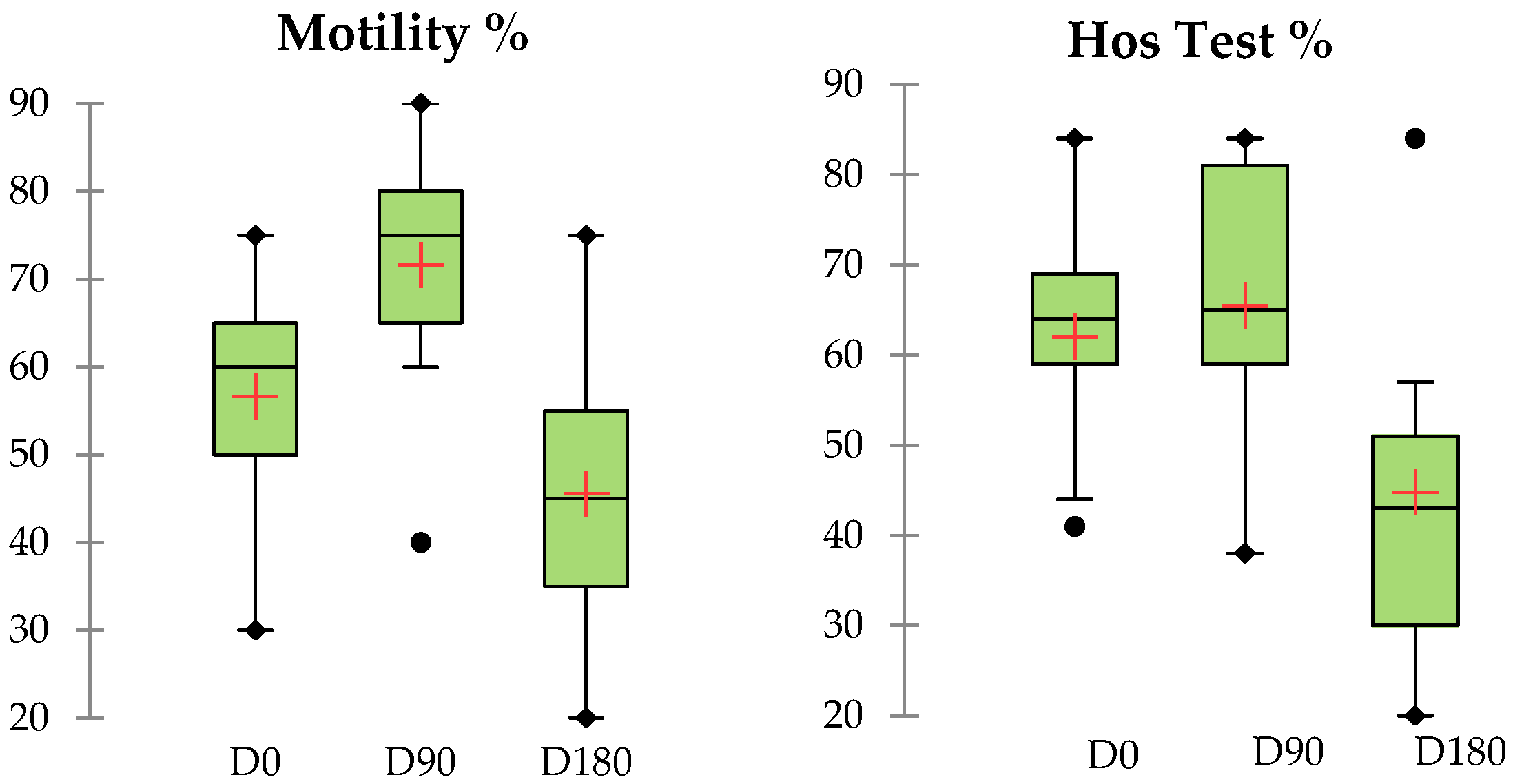
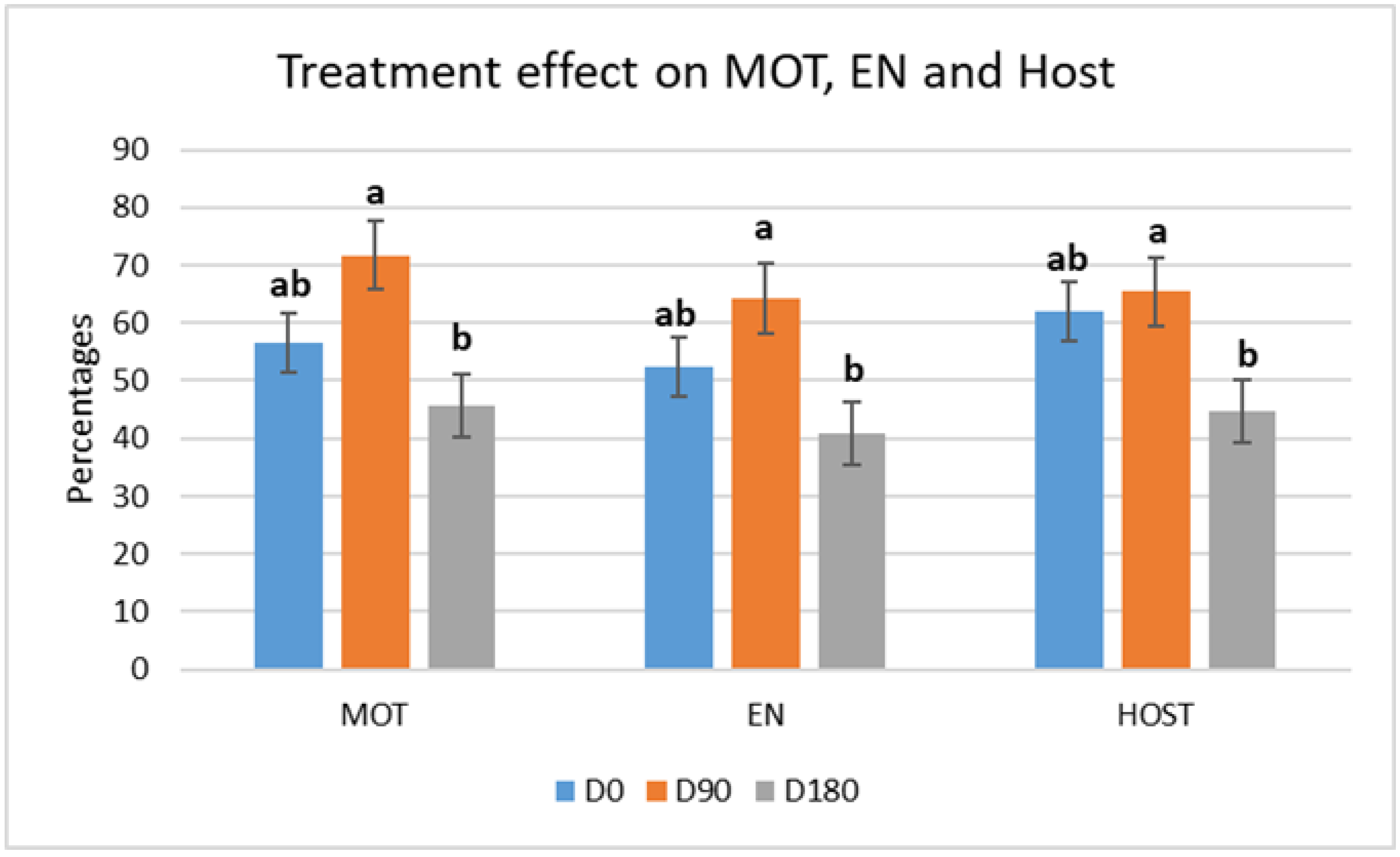
| MOT (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| T0h | T2h | T4h | |
| D0 | 56.7 ± 5.1 abα | 32.1 ± 6.3 β | 16.7 ± 5.9 bβ |
| D90 | 71.7 ± 5.1 aα | 46.7 ± 6 β | 37.8 ± 5.9 aβ |
| D180 | 45.6 ± 5.1 b | 38.9 ± 6 | 35.9 ± 5.9 ab |
| EN (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| T0h | T2h | T4h | |
| D0 | 52.3 ± 5.95 abα | 34.8 ± 5.3 β | 30.8 ± 6.4 β |
| D90 | 64.2 ± 5.95 aα | 38.3 ± 5.1 β | 32.7 ± 6.1 β |
| D180 | 40.8 ± 5.95 b | 36 ± 5.2 | 38.1 ± 6.1 |
| D0 | D90 | D180 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Spermatozoa (%) | 57.5 (45–65) b | 80 (75–86) a | 84 (83–87) a | 0.005 |
| Major Defects (%) | 6.5 (4.5–20) | 4 (2–7) | 6 (3–8) | 0.32 |
| Minor Defects (%) | 36 (26–40.5) a | 13 (11–19) b | 10 (9–11) b | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milani, C.; Santos, M.C.; Zucchini, P.; Contiero, B.; Romagnoli, S.; Quirino, C.R.; Cunha, I.C.N. Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Salmon Oil on Canine Frozen–Thawed Semen. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090797
Milani C, Santos MC, Zucchini P, Contiero B, Romagnoli S, Quirino CR, Cunha ICN. Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Salmon Oil on Canine Frozen–Thawed Semen. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(9):797. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090797
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilani, Chiara, Marcelo C. Santos, Paolo Zucchini, Barbara Contiero, Stefano Romagnoli, Celia R. Quirino, and Isabel C. N. Cunha. 2025. "Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Salmon Oil on Canine Frozen–Thawed Semen" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 9: 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090797
APA StyleMilani, C., Santos, M. C., Zucchini, P., Contiero, B., Romagnoli, S., Quirino, C. R., & Cunha, I. C. N. (2025). Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Salmon Oil on Canine Frozen–Thawed Semen. Veterinary Sciences, 12(9), 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090797







