Antimicrobial Resistance and Genomic Characterization of an Escherichia coli Strain Harboring p0111 and an IncX1-Type Plasmid, Isolated from the Brain of an Ostrich
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Outbreak Description and Field Response
2.2. Specimen Collection and Viral Detection
2.3. Identification of the Bacterial Strain
2.4. 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.5. Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.6. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.7. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing (AST)
2.8. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
3. Results
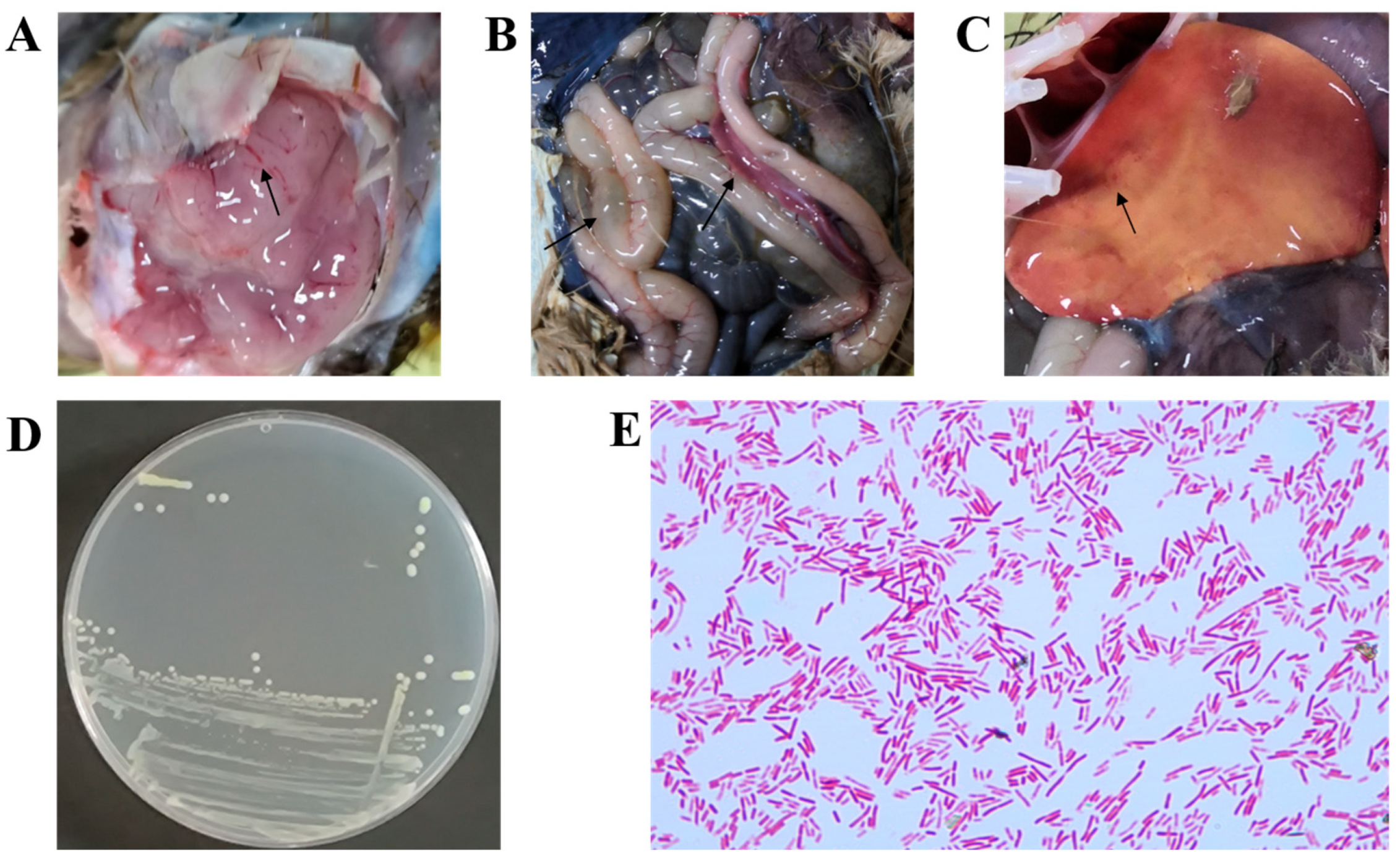
3.1. Tissue and Pathological Assessment with Bacterial Strain Identification
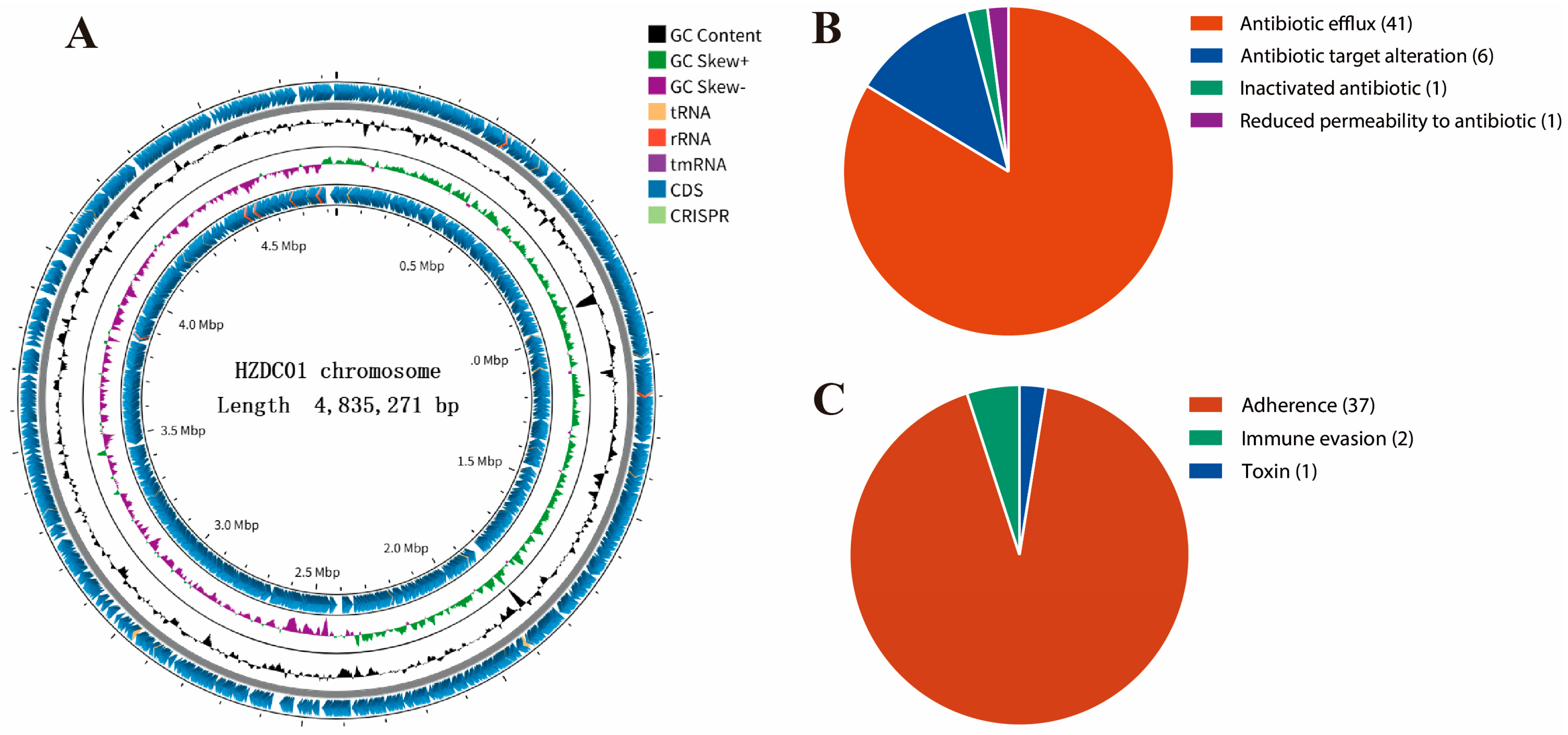
3.2. General Information About the Chromosomal Genome of the HZDC01 Strain
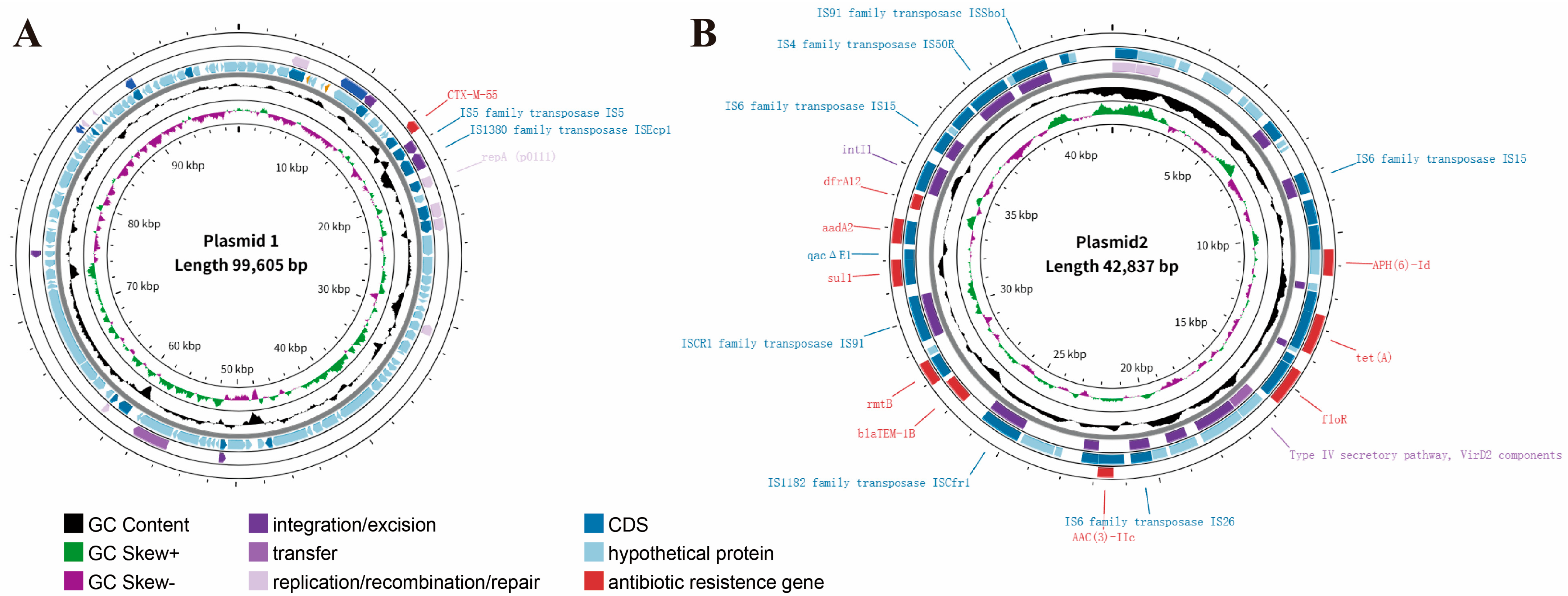
3.3. Detection of Resistance Genes
3.4. Virulence Factors of the HZDC01 Strain
3.5. HZDC01 Exhibits Multidrug Resistance
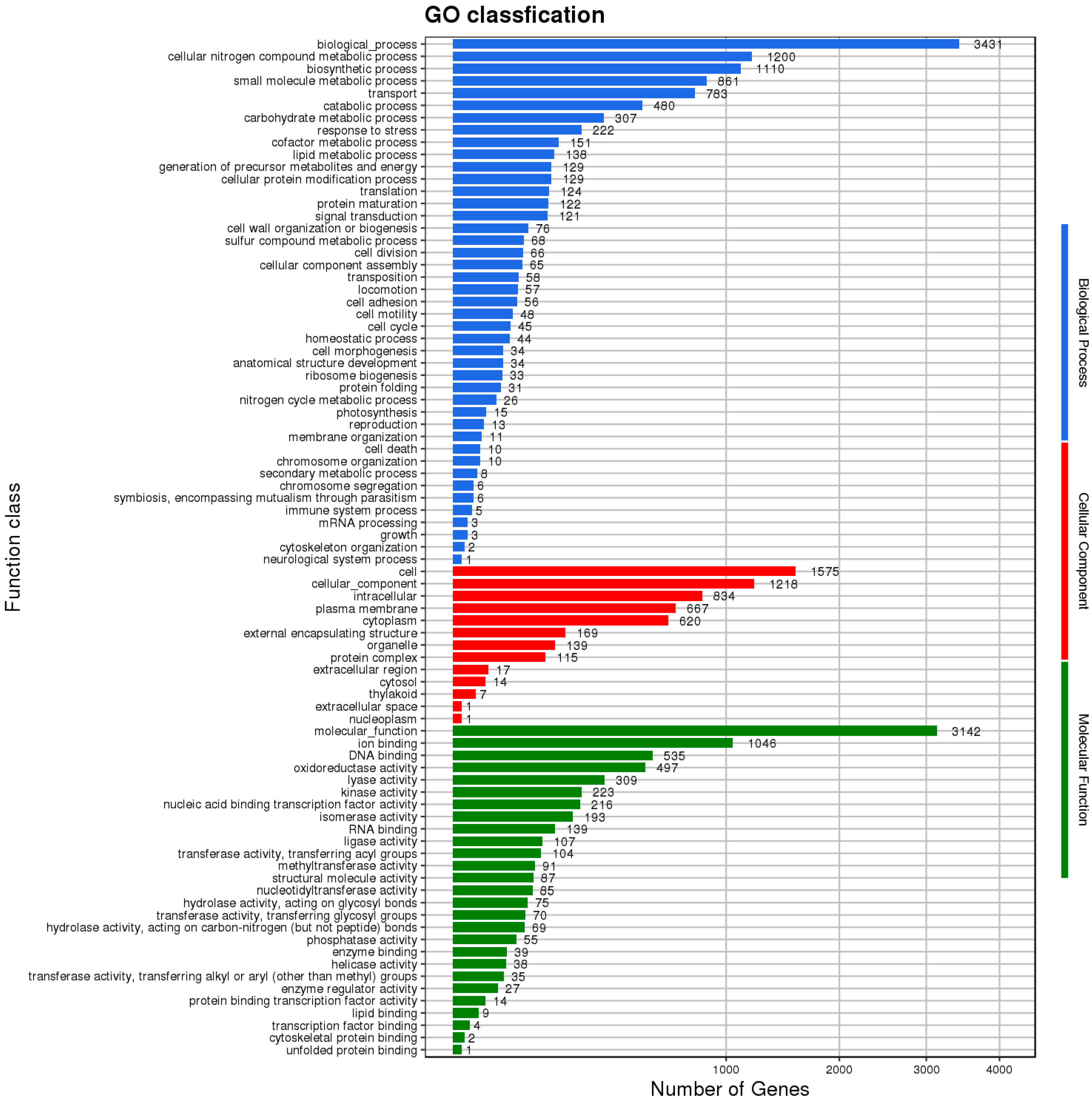
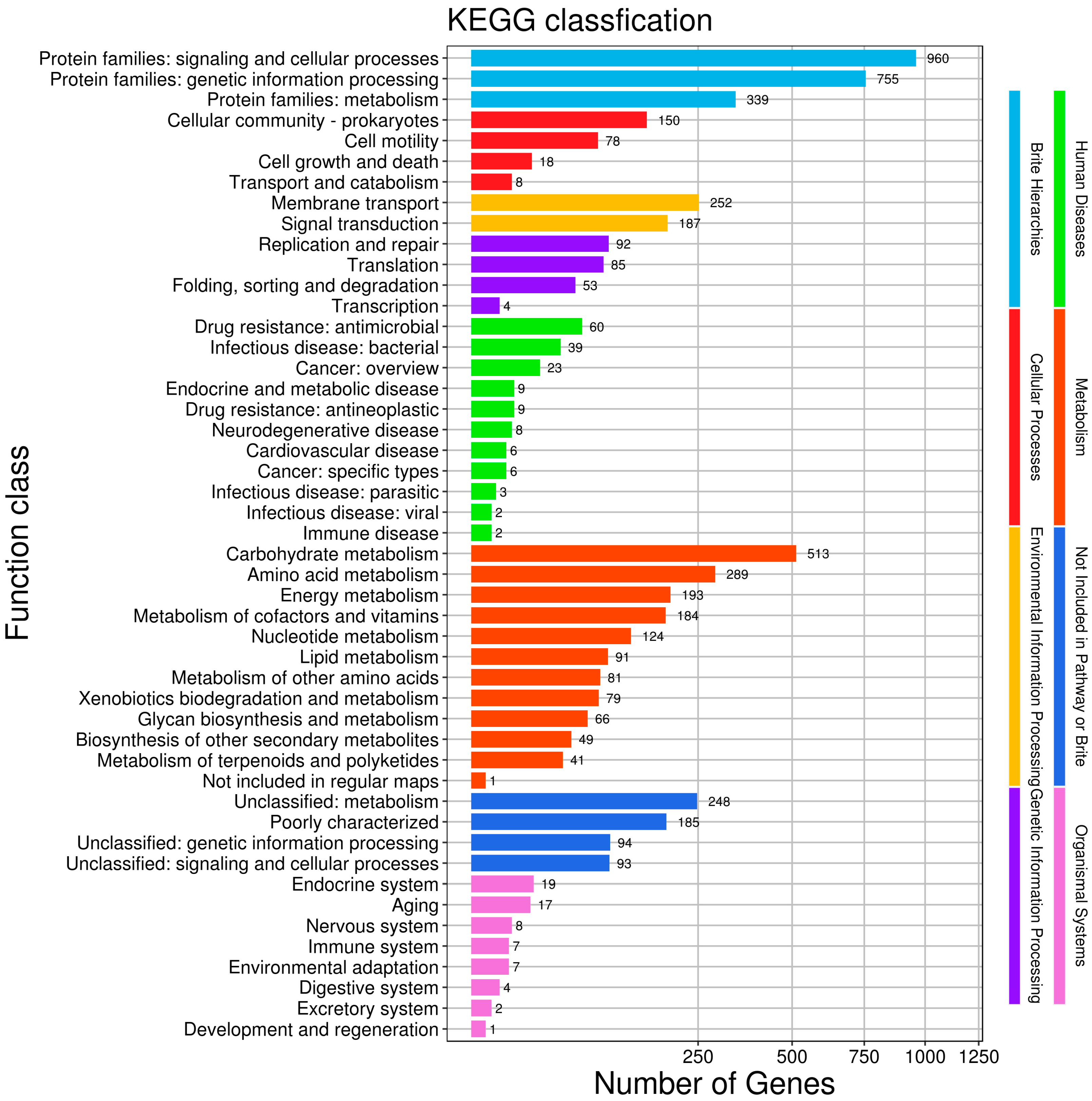
3.6. Functional Annotation of Protein-Coding Genes of HZDC01
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carneiro, C.; Araujo, C.; Goncalves, A.; Vinue, L.; Somalo, S.; Ruiz, E.; Uliyakina, I.; Rodrigues, J.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P.; et al. Detection of CTX-M-14 and TEM-52 extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in fecal Escherichia coli isolates of captive ostrich in Portugal. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guabiraba, R.; Schouler, C. Avian colibacillosis: Still many black holes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellata, M. Human and avian extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli: Infections, zoonotic risks, and antibiotic resistance trends. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 916–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keokilwe, L.; Olivier, A.; Burger, W.P.; Joubert, H.; Venter, E.H.; Morar-Leather, D. Bacterial enteritis in ostrich (Struthio camelus) chicks in the Western Cape Province, South Africa. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husna, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Badruzzaman, A.; Sikder, M.H.; Islam, M.R.; Rahman, M.T.; Alam, J.; Ashour, H.M. Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamases (ESBL): Challenges and Opportunities. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonca, J.; Guedes, C.; Silva, C.; Sa, S.; Oliveira, M.; Accioly, G.; Baylina, P.; Barata, P.; Pereira, C.; Fernandes, R. New CTX-M Group Conferring beta-Lactam Resistance: A Compendium of Phylogenetic Insights from Biochemical, Molecular, and Structural Biology. Biology 2022, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pana, Z.D.; Zaoutis, T. Treatment of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (ESBLs) infections: What have we learned until now? F1000Research 2018, 7, F1000 Faculty Rev-1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanheira, M.; Simner, P.J.; Bradford, P.A. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: An update on their characteristics, epidemiology and detection. JAC-Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 3, dlab92. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, H.; Bai, X.; Wang, D. Global spread characteristics of CTX-M-type extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: A genomic epidemiology analysis. Drug Resist. Update 2024, 73, 101036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, R.; Pirolo, M.; Goecke, N.B.; Toppi, V.; Good, L.; Guitian, J.; Guardabassi, L. Imported seafood is a reservoir of Enterobacteriaceae carrying CTX-M-encoding genes of high clinical relevance. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2025, 430, 111063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, E.; Rocha, E. Phage-plasmids promote recombination and emergence of phages and plasmids. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, H.A.; Haendiges, J.; Zormati, S.; Guermazi, S.; Gdoura, R.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Siala, M. Virulence and resistance genes profiles and clonal relationships of non-typhoidal food-borne Salmonella strains isolated in Tunisia by whole genome sequencing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 337, 108941. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Hao, X.; Lei, B.; Dong, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Yuan, W. Emergence and genomic analysis of a novel ostrich-origin GPV-related parvovirus in China. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.; Lindgreen, S.; Orlando, L. AdapterRemoval v2: Rapid adapter trimming, identification, and read merging. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Yuan, J.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. Erratum: SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. Gigascience 2015, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.S.; Peluso, P.; Sedlazeck, F.J.; Nattestad, M.; Concepcion, G.T.; Clum, A.; Dunn, C.; O’Malley, R.; Figueroa-Balderas, R.; Morales-Cruz, A.; et al. Phased diploid genome assembly with single-molecule real-time sequencing. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beghain, J.; Bridier-Nahmias, A.; Le Nagard, H.; Denamur, E.; Clermont, O. ClermonTyping: An easy-to-use and accurate in silico method for Escherichia genus strain phylotyping. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcock, B.P.; Huynh, W.; Chalil, R.; Smith, K.W.; Raphenya, A.R.; Wlodarski, M.A.; Edalatmand, A.; Petkau, A.; Syed, S.A.; Tsang, K.K.; et al. CARD 2023: Expanded curation, support for machine learning, and resistome prediction at the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D690–D699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Yao, Z.; Sun, L.; Shen, Y.; Jin, Q. VFDB: A reference database for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D325–D328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brettin, T.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Olsen, G.J.; Olson, R.; Overbeek, R.; Parrello, B.; Pusch, G.D.; et al. RASTtk: A modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.R.; Enns, E.; Marinier, E.; Mandal, A.; Herman, E.K.; Chen, C.Y.; Graham, M.; Van Domselaar, G.; Stothard, P. Proksee: In-depth characterization and visualization of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W484–W492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Gotz, S. Blast2GO: A comprehensive suite for functional analysis in plant genomics. Int. J. Plant Genom. 2008, 2008, 619832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Petty, N.K.; Beatson, S.A. Easyfig: A genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.; Chun, J. A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, Y.; Itoh, M.; Okuda, S.; Yoshizawa, A.C.; Kanehisa, M. KAAS: An automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W182–W185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M100; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2024.
- Salleh, M.Z.; Nik, Z.N.; Hajissa, K.; Ilias, M.I.; Deris, Z.Z. Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistant Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in Asia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, A.J.; Stillman, T.J.; Atkins, A.; Jamieson, S.J.; Bullough, P.A.; Green, J.; Artymiuk, P.J. E. coli hemolysin E (HlyE, ClyA, SheA): X-ray crystal structure of the toxin and observation of membrane pores by electron microscopy. Cell 2000, 100, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, X.H.; Arencibia, I.; Johansson, A.; Wai, S.N.; Oscarsson, J.; Kalfas, S.; Sundqvist, K.G.; Mizunoe, Y.; Sjostedt, A.; Uhlin, B.E. Cytocidal and apoptotic effects of the ClyA protein from Escherichia coli on primary and cultured monocytes and macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4363–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyborn, N.R.; Clark, A.; Roberts, R.E.; Jamieson, S.J.; Tzokov, S.; Bullough, P.A.; Stillman, T.J.; Artymiuk, P.J.; Galen, J.E.; Zhao, L.; et al. Properties of haemolysin E (HlyE) from a pathogenic Escherichia coli avian isolate and studies of HlyE export. Microbiology 2004, 150, 1495–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kim, K.S. Role of OmpA and IbeB in Escherichia coli K1 invasion of brain microvascular endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo. Pediatr. Res. 2002, 51, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.; Ienes, L.J.; Alvarez, N.S.; Logue, C.M. Whole-genome analysis of five Escherichia coli strains isolated from focal duodenal necrosis in laying hens reveals genetic similarities to the E. coli O25:H4 ST131 strain. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e211024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renzhammer, R.; Schwarz, L.; Cabal, R.A.; Ruppitsch, W.; Fuchs, A.; Simetzberger, E.; Ladinig, A.; Loncaric, I. Detection of mcr-1-1 Positive Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Isolates Associated with Post-Weaning Diarrhoea in an Organic Piglet-Producing Farm in Austria. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlMatar, M.; Albarri, O.; Makky, E.A.; Koksal, F. Efflux pump inhibitors: New updates. Pharmacol. Rep. 2021, 73, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwama, M.; Yamaguchi, A. Molecular mechanisms of AcrB-mediated multidrug export. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, L.P.; Woodward, M.J. The multiple antibiotic resistance (mar) locus and its significance. Res. Vet. Sci. 2002, 72, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Rah, S.Y.; Yeo, W.S.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, K.L.; Koh, Y.S.; Kang, S.O.; Roe, J.H. A reducing system of the superoxide sensor SoxR in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2614–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, S.A.; Boothe, D.M.; Suh, S.J. A novel alanine to serine substitution mutation in SoxS induces overexpression of efflux pumps and contributes to multidrug resistance in clinical Escherichia coli isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 2228–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. Global regulator SoxR is a negative regulator of efflux pump gene expression and affects antibiotic resistance and fitness in Acinetobacter baumannii. Medicine 2017, 96, e7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsolioutsou, A.; Pena-Llopis, S.; Demple, B. Constitutive soxR mutations contribute to multiple-antibiotic resistance in clinical Escherichia coli isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2746–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Singh, A.K.; Agrahari, A.K.; Pandey, A.K.; Gupta, M.K.; Chakravortty, D.; Tiwari, V.K.; Prakash, P. Galactose-Clicked Curcumin-Mediated Reversal of Meropenem Resistance among Klebsiella pneumoniae by Targeting Its Carbapenemases and the AcrAB-TolC Efflux System. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, R.; Shigemura, K.; Osawa, K.; Yang, Y.M.; Maeda, K.; Fang, S.B.; Sung, S.Y.; Onuma, K.; Uda, A.; Miyara, T.; et al. The Antimicrobial Resistance Characteristics of Imipenem-Non-Susceptible, Imipenemase-6-Producing Escherichia coli. Antibiotics 2021, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, M.A.; Talukder, A.; Piddock, L.J. Contribution of mutation at amino acid 45 of AcrR to acrB expression and ciprofloxacin resistance in clinical and veterinary Escherichia coli isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4390–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alekshun, M.N.; Levy, S.B. Regulation of chromosomally mediated multiple antibiotic resistance: The mar regulon. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 2067–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekshun, M.N.; Kim, Y.S.; Levy, S.B. Mutational analysis of MarR, the negative regulator of marRAB expression in Escherichia coli, suggests the presence of two regions required for DNA binding. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 35, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, C.; Hiasa, H.; Marians, K.J. DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV: Biochemical activities, physiological roles during chromosome replication, and drug sensitivities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1400, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivata, M.W.; Mbuchi, M.; Eyase, F.L.; Bulimo, W.D.; Kyanya, C.K.; Oundo, V.; Muriithi, S.W.; Andagalu, B.; Mbinda, W.M.; Soge, O.O.; et al. gyrA and parC mutations in fluoroquinolone-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates from Kenya. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.V.; Nguyen, T.V.; Nguyen, H. Le DV Mutations in the gyrA, parC, and mexR genes provide functional insights into the fluoroquinolone-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated in Vietnam. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.S.; Feng, Y.; Lv, X.Y.; Duan, J.H.; Chen, J.; Fang, L.X.; Xia, J.; Liao, X.P.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.H. Emergence of NDM-5- and MCR-1-Producing Escherichia coli Clones ST648 and ST156 from a Single Muscovy Duck (Cairina moschata). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6899–6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Chang, J.; Cao, L.; Luo, Q.; Xu, H.; Lyu, W.; Qian, M.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xia, X.; et al. Characterization of an NDM-5 carbapenemase-producing Escherichia coli ST156 isolate from a poultry farm in Zhejiang, China. Bmc Microbiol. 2019, 19, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yang, L.; Lu, L.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, P.; Song, H. Genomic features of an Escherichia coli ST156 strain harboring chromosome-located mcr-1 and plasmid-mediated bla(NDM-5). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 85, 104499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.H.; Feng, Y. Towards Understanding MCR-like Colistin Resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 794–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Zhu, H.; Liu, C.; Xie, H.; Li, C.; Cao, X.; Shen, H. Epidemiological and genomic characteristics of global mcr-positive Escherichia coli isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1105401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakthavatchalam, Y.D.; Veeraraghavan, B. Challenges, Issues and Warnings from CLSI and EUCAST Working Group on Polymyxin Susceptibility Testing. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, DL3–DL4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Song, C.; Duan, G.; Zhu, J.; Yang, H.; Xi, Y.; Fan, Q. Transposition of ISEcp1 modulates blaCTX-M-55-mediated Shigella flexneri resistance to cefalothin. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 42, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrouki, S.; Belhadj, O.; Chihi, H.; Mohamed, B.M.; Celenza, G.; Amicosante, G.; Perilli, M. Chromosomal blaCTX-M-(1)(5) associated with ISEcp1 in Proteus mirabilis and Morganella morganii isolated at the Military Hospital of Tunis, Tunisia. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 1286–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, L.; Wei, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; et al. Similarities of P1-Like Phage Plasmids and Their Role in the Dissemination of bla(CTX-M-55). Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e141022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.H.; Bentzon-Tilia, M.; Bentzon-Tilia, S.; Norman, A.; Rafty, L.; Sorensen, S.J. Design and synthesis of a quintessential self-transmissible IncX1 plasmid, pX1.0. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, W.; Xu, X.; Zhou, X.; Shi, C. Transmissible ST3-IncHI2 Plasmids Are Predominant Carriers of Diverse Complex IS26-Class 1 Integron Arrangements in Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Cheng, H.; Liang, Y.; Yu, S.; Yu, T.; Fang, J.; Zhu, C. Diverse Mobile Genetic Elements and Conjugal Transferability of Sulfonamide Resistance Genes (sul1, sul2, and sul3) in Escherichia coli Isolates from Penaeus vannamei and Pork from Large Markets in Zhejiang, China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lallement, C.; Pasternak, C.; Ploy, M.C.; Jove, T. The Role of ISCR1-Borne P(OUT) Promoters in the Expression of Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yang, X.; Li, R.; Wang, S.; Han, Z.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y. IS6 family insertion sequences promote optrA dissemination between plasmids varying in transfer abilities. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2024, 108, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allwright, D.M.; Wilson, M.; Vanrensburg, W.J. Botulism in ostriches (Struthio camelus). Avian Pathol. 1994, 23, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Wang, D.; Luan, Q.; Sun, J.; Gao, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, S.; Han, Y.; Qu, X.; Cui, Y.; et al. Whole Genome Characterization and Genetic Evolution Analysis of a New Ostrich Parvovirus. Viruses 2020, 12, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.H.; Wass, C.; Fu, Q.; Prasadarao, N.V.; Stins, M.; Kim, K.S. Escherichia coli invasion of brain microvascular endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo: Molecular cloning and characterization of invasion gene ibe10. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 4470–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Meng, X.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhong, H.; Xia, P.; Cui, L.; Zhu, G.; Wang, H. Transcriptome profiling of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli and the mouse microvascular endothelial cell line bEnd.3 during interaction. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9172. [Google Scholar]
- Witcomb, L.A.; Collins, J.W.; McCarthy, A.J.; Frankel, G.; Taylor, P.W. Bioluminescent imaging reveals novel patterns of colonization and invasion in systemic Escherichia coli K1 experimental infection in the neonatal rat. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 4528–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, G.; Beckloff, N.; Weinberg, A.; Kisich, K.O. The roles of antimicrobial peptides in innate host defense. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2377–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, S.; Cui, N.; Liu, S.; Langford, P.R.; Wang, C. The SapA Protein Is Involved in Resistance to Antimicrobial Peptide PR-39 and Virulence of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingzhi, L.; Haojie, G.; Dan, G.; Hongmei, M.; Yang, L.; Mengdie, J.; Chengkun, Z.; Xiaohui, Z. The role of two-component regulatory system in beta-lactam antibiotics resistance. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 215, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Jamal, S.B.; Hassan, S.S.; Carvalho, P.; Almeida, S.; Barh, D.; Ghosh, P.; Silva, A.; Castro, T.; Azevedo, V. Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems of Pathogenic Bacteria as Targets for Antimicrobial Therapy: An Overview. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensa, B.; Polizzi, N.F.; Molnar, K.S.; Natale, A.M.; Lemmin, T.; DeGrado, W.F. Allosteric mechanism of signal transduction in the two-component system histidine kinase PhoQ. eLife 2021, 10, e73336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Huang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, T.; Li, S.; Qi, K. Modulation of virulence genes by the two-component system PhoP-PhoQ in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 19, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Li, Q.; Xue, M.; Wang, Z.; Tu, J.; Song, X.; Shao, Y.; Han, X.; Xue, T.; Liu, H.; et al. The role of the phoP transcriptional regulator on biofilm formation of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Avian Pathol. 2019, 48, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meli, D.N.; Coimbra, R.S.; Erhart, D.G.; Loquet, G.; Bellac, C.L.; Tauber, M.G.; Neumann, U.; Leib, S.L. Doxycycline reduces mortality and injury to the brain and cochlea in experimental pneumococcal meningitis. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3890–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvao, P.A.; Lomar, A.V.; Francisco, W.; de Godoy, C.V.; Norrby, R. Cefoxitin penetration into cerebrospinal fluid in patients with purulent meningitis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1980, 17, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, S.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Pu, L.; Han, X.; Feng, Y. Genetic context diversity of plasmid-borne blaCTX-M-55 in Escherichia coli isolated from waterfowl. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 28, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Liao, Y.; Lu, J.; Pei, Z.; Yin, Y.; Ma, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Gong, Y.; et al. In vitro antibacterial efficacy of a novel chicken-derived Bacillus subtilis GX15 strain and its protective mechanisms in mice challenged by Salmonella enterica serovar typhymurium. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Shi, W.; Chen, L.; Kong, T.; Wang, B.; Chen, S.; Guo, X. CATH-2-derived antimicrobial peptide inhibits multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli infection in chickens. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1390934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Mis, S.K.; Chen, J. Ellagitannin content and anti-enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli activity of aqueous extracts derived from commercial pomegranate products. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Tan, Y.; Liao, Y.; Li, L.; Han, K.; Bai, H.; Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Gong, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Isolation, Characterization and Whole Genome Analysis of an Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Phage vB_EcoS_GN06. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Resistance Mechanism | AMR Genes Family | Antibiotic Resistance Genes |
|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic efflux | Major facilitator superfamily (MFS) antibiotic efflux pump | emrA, emrB, emrR, emrK, emrY, mdtH, mdtM, mdtN, mdtO, mdtP, mdtG, leuO, mdfA |
| Small multidrug resistance (SMR) antibiotic efflux pump | emrE | |
| Resistance–nodulation–cell division (RND) antibiotic efflux pump | acrA, acrB, acrD, acrE, acrF, acrS, mdtA, mdtB, mdtC, mdtE, mdtF, marA, cpxA, baeR, gadX, CRP, Ecol_marR_MULT, Ecol_acrR_MULT, | |
| ATP-binding cassette (ABC) antibiotic efflux pump | msbA, Yojl, | |
| Major facilitator superfamily (MFS) antibiotic efflux pump, resistance–nodulation–cell division (RND) antibiotic efflux pump | evgA, evgS, H-NS | |
| ATP-binding cassette (ABC) antibiotic efflux pump, major facilitator superfamily (MFS) antibiotic efflux pump, resistance–nodulation–cell division (RND) antibiotic efflux pump | tolC, Ecol_soxR_MULT, Ecol_soxS_MULT | |
| kdpDE | kdpE | |
| Reduced permeability to antibiotic | marA | |
| Antibiotic target alteration | Elfamycin-resistant EF-Tu | Ecol_EFTu_PLV |
| Fluoroquinolone-resistant gyrA | Ecol_gyrA_FLO | |
| Fluoroquinolone-resistant parC | Ecol_parC_FLO | |
| PMR phosphoethanolamine transferase | pmrF, ugd, eptA | |
| Undecaprenyl pyrophosphate-related proteins | bacA | |
| Inactivated antibiotic | EC beta-lactamase | EC-18 |
| Itemize | Plasmid 1 | Plasmid 2 | Plasmid 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size (bp) | 99,605 | 42,837 | 4018 |
| GC content (%) | 47.79 | 53.08 | 53.29 |
| ORFs | 109 | 51 | 4 |
| Replicon | p0111 | IncX1 | None |
| ARGs | blaCTX-M-55 | rmtB, sul1, APH(6)-Id, tet(A), AAC(3)-IIc, aadA2, blaTEM-1B, floR | None |
| VFs | none | none | None |
| Itemize | Virulence Factors | Related Genes |
|---|---|---|
| Adherence | CFA/I fimbriae | cfaB, cfaC, cfaD/cfaE |
| E. coli common pilus (ECP) | ecpA, ecpB, ecpC, ecpD, ecpE, ecpR | |
| E. coli laminin-binding fimbriae (ELF) | elfA, elfC, elfD, elfG | |
| EaeH | eaeH | |
| Hemorrhagic E. coli pilus (HCP) | hcpA, hcpB, hcpC | |
| Type I fimbriae | fimA, fimB, fimC, fimD, fimE, fimF, fimG, fimH, fimI | |
| Cah, AIDA-I type | cah | |
| Autotransporter | EhaB, AIDA-I type | ehaB |
| UpaG adhesin, trimeric AT | upaG/ehaG | |
| Invasion | Invasion of brain endothelial cells (Ibes) | ibeB, ibeC |
| Non-LEE encoded TTSS effectors | EspL1 | espL1 |
| EspL4 | espL4 | |
| EspR1 | espR1 | |
| EspX1 | espX1 | |
| EspX4 | espX4 | |
| EspX5 | espX5 | |
| Secretion system | ACE T6SS | aec16, ace17, aec18, aec19, aec22, aec23, aec24, aec25, aec26, aec27/clpV, aec28, aec29, aec30, aec31, aec32, aec7, aec8 |
| Toxin | Hemolysin/cytolysin A | hlyE/clyA |
| Classification of Antibiotics | Antibiotic Name | Inhibition Zone Diameter a (mm) | Antibiotic Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penicillins | Ampicillin | 10 | R |
| Amoxicillin | 8 | R | |
| Carbapenems | Meropenem | 14 | R |
| Imipenem | 30 | S | |
| Cephems | Cefoxintin | 19 | S |
| Ceftriaxone | 7 | R | |
| Ceftazidime | 10 | R | |
| Cefuroxime sodium | 7 | R | |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline | 7 | R |
| Doxycycline | 14 | I | |
| Quinolones and fluoroquinolones | Ciprofloxacin | 7 | R |
| Norfloxacin | 7 | R | |
| Ofloxacin | 7 | R | |
| Enrofloxacin | 8 | R | |
| Marbofloxacin b | 7 | / | |
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin | 7 | R |
| Tobramycin | 7 | R | |
| Amikacin | 7 | R | |
| Kanamycin b | 7 | / | |
| Chloramphenicols | Florfenicol b | 7 | / |
| Sulfonamides | Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim | 7 | R |
| Polymyxins a | Polymyxin B b | 15 | / |
| Macrolides a | Azithromycin b | 7 | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Tan, Y.; Yin, Y.; Pei, Z.; Li, C.; Bai, H.; Ma, C.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance and Genomic Characterization of an Escherichia coli Strain Harboring p0111 and an IncX1-Type Plasmid, Isolated from the Brain of an Ostrich. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090793
Hu J, Zhou J, Wang L, Chen Z, Tan Y, Yin Y, Pei Z, Li C, Bai H, Ma C, et al. Antimicrobial Resistance and Genomic Characterization of an Escherichia coli Strain Harboring p0111 and an IncX1-Type Plasmid, Isolated from the Brain of an Ostrich. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(9):793. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090793
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jing, Jiahe Zhou, Leping Wang, Zhongwei Chen, Yizhou Tan, Yangyan Yin, Zhe Pei, Changting Li, Huili Bai, Chunxia Ma, and et al. 2025. "Antimicrobial Resistance and Genomic Characterization of an Escherichia coli Strain Harboring p0111 and an IncX1-Type Plasmid, Isolated from the Brain of an Ostrich" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 9: 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090793
APA StyleHu, J., Zhou, J., Wang, L., Chen, Z., Tan, Y., Yin, Y., Pei, Z., Li, C., Bai, H., Ma, C., Teng, L., Feng, Y., Li, X., Wei, Y., & Peng, H. (2025). Antimicrobial Resistance and Genomic Characterization of an Escherichia coli Strain Harboring p0111 and an IncX1-Type Plasmid, Isolated from the Brain of an Ostrich. Veterinary Sciences, 12(9), 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090793





