Individual and Combined Effect of Zinc-L-Selenomethionine Complex with Mannan-Oligosaccharide on Growth Performance, Carcass Characteristics, Gut Development and Immune Response in Broilers
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Bird Husbandry
2.4. Parameters Studied
2.4.1. Growth Performance
2.4.2. Carcass Traits
2.4.3. Immune Status
2.4.4. Intestinal Morphology
2.4.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Carcass Characteristics
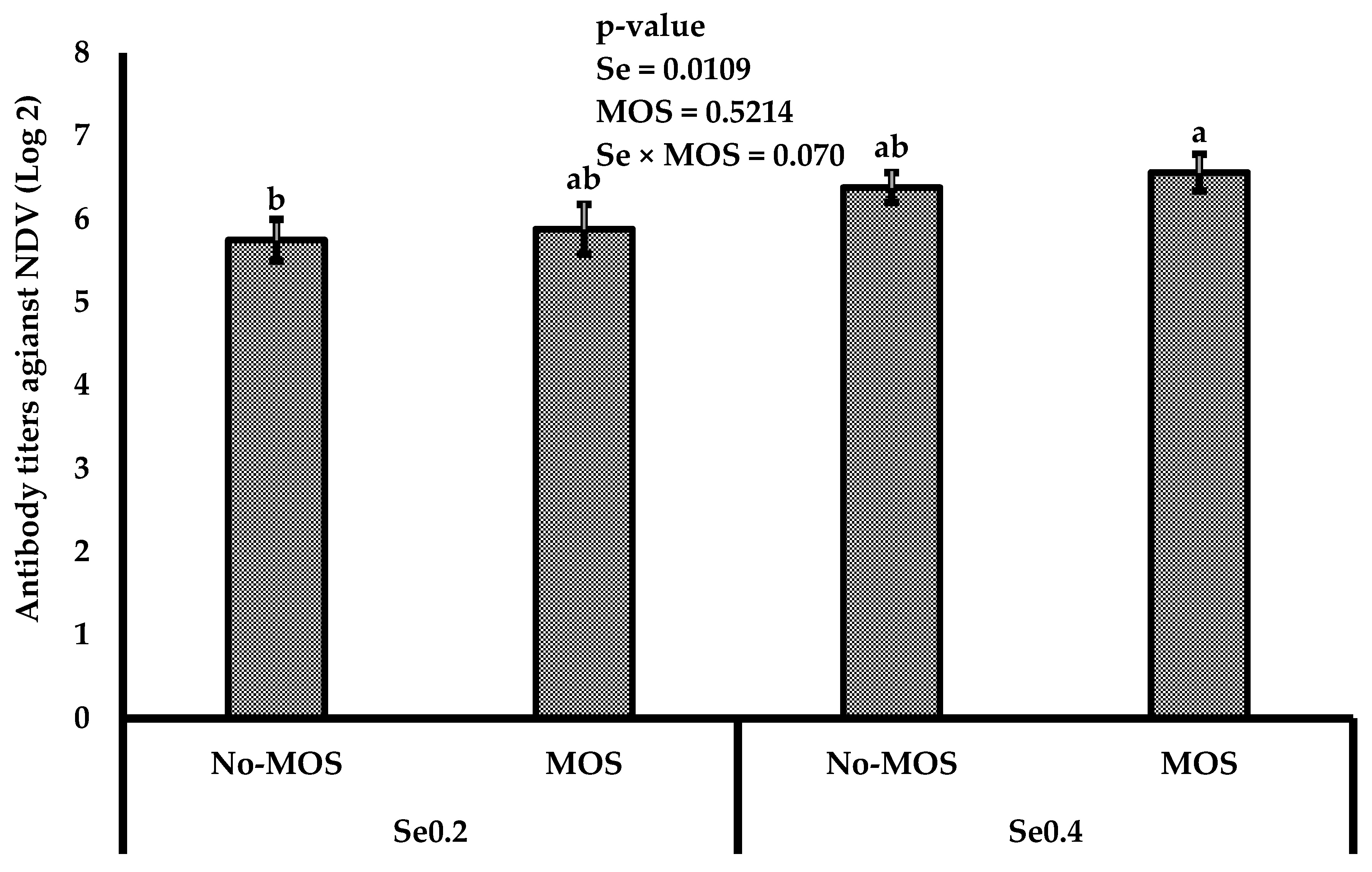
3.3. Immunity
3.4. Gut Morphology
4. Discussion
4.1. Growth Performance
4.2. Carcass Traits
4.3. Immunity
4.4. Gut Morphology
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patterson, J.A.; Burkholder, K.M. Application of prebiotics and probiotics in poultry production. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surai, P.; Karadas, F.; Pappas, A.; Sparks, N. Effect of organic selenium in quail diet on its accumulation in tissues and transfer to the progeny. Br. Poult. Sci. 2006, 47, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emborg, H.-D.; Ersbøll, A.K.; Heuer, O.E.; Wegener, H.C. Effects of termination of antimicrobial growth promoter use for broiler health and productivity. In Proceedings of the International Invitational Symposium Beyond Antimicrobial Growth Promoters in Food Animal Production, Foulum, Denmark, 6–7 November 2002; Volume 51, pp. 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Silbergeld, E.K.; Graham, J.; Price, L.B. Industrial food animal production, antimicrobial resistance, and human health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2008, 29, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume, M. Historic perspective: Prebiotics, probiotics, and other alternatives to antibiotics. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 2663–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogliani, C.; Goossens, H.; Greko, C. Restricting antimicrobial use in food animals: Lessons from Europe. Microbe 2011, 6, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froebel, L.K. Prebiotic and Probiotic Microbiology in Poultry. Master’s Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2020. Available online: https://oaktrust.library.tamu.edu/server/api/core/bitstreams/191aec3b-f3a6-4130-a1b8-eb95eebe78cd/content (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Muneeb, M.; Khan, E.U.; Ali, M.; Haque, M.N.U.; Khan, M.U.Z.; Ahmad, S. Comparative Effects of Antibiotic and Antimicrobial Peptide on Growth Performance, Gut Morphology, Intestinal Lesion Score, Ileal Microbial Counts, and Immune Status in Broilers Challenged with Necrotic Enteritis. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choct, M.; Naylor, A.; Reinke, N. Selenium supplementation affects broiler growth performance, meat yield and feather coverage. Br. Poult. Sci. 2004, 45, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Meng, F.; Wang, P.; Jiang, Y.; Yin, Q.; Chang, J.; Zuo, R.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, J. Effect of organic and inorganic selenium supplementation on growth performance, meat quality and antioxidant property of broilers. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 3031–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, J.R.; McKenzie, R.C.; Beckett, G.J. Selenium in the immune system. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1457S–1459S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surai, P.F.; Fisinin, V.I.; Karadas, F. Antioxidant systems in chick embryo development. Part 1. Vitamin E, carotenoids and selenium. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.M.; Arthur, J. Selenium, selenoproteins and human health: A review. Public Health Nutr. 2001, 4, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surai, P.F.; Kochish, I.I.; Fisinin, V.I.; Velichko, O.A. Selenium in poultry nutrition: From sodium selenite to organic selenium sources. J. Poult. Sci. 2018, 55, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalia, A.; Loh, T.; Sazili, A.; Jahromi, M.; Samsudin, A. Effects of vitamin E, inorganic selenium, bacterial organic selenium, and their combinations on immunity response in broiler chickens. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeson, S.; Summers, J.D. Nutrition of the Chicken, 4th ed.; Nottingham University Press: Nottingham, UK, 2001; pp. 1–591. [Google Scholar]
- Iji, P.A.; Saki, A.A.; Tivey, D.R. Intestinal structure and function of broiler chickens on diets supplemented with a mannan oligosaccharide. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 1186–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klis, F.M.; Boorsma, A.; De Groot, P.W. Cell wall construction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 2006, 23, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohail, M.; Hume, M.; Byrd, J.; Nisbet, D.; Ijaz, A.; Sohail, A.; Shabbir, M.; Rehman, H. Effect of supplementation of prebiotic mannan-oligosaccharides and probiotic mixture on growth performance of broilers subjected to chronic heat stress. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 2235–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, P.; Wenk, C.; Dawson, K.; Newman, K. The effects of dietary mannaoligosaccharides on cecal parameters and the concentrations of enteric bacteria in the ceca of salmonella-challenged broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2000, 79, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooge, D.M. Meta-analysis of broiler chicken pen trials evaluating dietary mannan oligosaccharide, 1993–2003. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2004, 3, 163–174. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz-Ahrens, K.E.; Ade, P.; Marten, B.; Weber, P.; Timm, W.; Aςil, Y.; Glüer, C.-C.; Schrezenmeir, J. Prebiotics, probiotics, and synbiotics affect mineral absorption, bone mineral content, and bone structure. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 838S–846S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demigné, C.; Jacobs, H.; Moundras, C.; Davicco, M.-J.; Horcajada, M.-N.; Bernalier, A.; Coxam, V. Comparison of native or reformulated chicory fructans, or non-purified chicory, on rat cecal fermentation and mineral metabolism. Eur. J. Nutr. 2008, 47, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, L.; Rodriguez, M.; Alzueta, C.; Rebolé, A.; Trevino, J. Effect of inulin on growth performance, intestinal tract sizes, mineral retention and tibial bone mineralisation in broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2009, 50, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, G.; Das, R.K.; Kaur Brar, S.; Rouissi, T.; Avalos Ramirez, A.; Chorfi, Y.; Godbout, S. Alternatives to antibiotics in poultry feed: Molecular perspectives. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 318–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, M.; Conjat, A.-S.; Briens, M.; Hachemi, M.A.; Geraert, P.-A. Bio-efficacy of organic selenium compounds in broiler chickens. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 20, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, S.L.; Sobolewska, S.; Rose, S.P.; Whiting, I.M.; Blanchard, A.; Ionescu, C.; Bravo, D.; Pirgozliev, V. Effect of feeding different sources of selenium on growth performance and antioxidant status of broilers. Br. Poult. Sci. 2020, 61, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajashree, K.; Muthukumar, T.; Karthikeyan, N. Comparative study of the effects of organic selenium on hen performance and productivity of broiler breeders. Br. Poult. Sci. 2014, 55, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumeh, E.A.; Mohebodini, H.; Toghyani, M.; Shabani, A.; Ashayerizadeh, A.; Jazi, V. Synergistic effects of fermented soybean meal and mannan-oligosaccharide on growth performance, digestive functions, and hepatic gene expression in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 6797–6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froebel, L.K.; Jalukar, S.; Lavergne, T.A.; Lee, J.T.; Duong, T. Administration of dietary prebiotics improves growth performance and reduces pathogen colonization in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 6668–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hafeez, H.M.; Saleh, E.S.E.; Tawfeek, S.S.; Youssef, I.M.I.; Abdel-Daim, A.S.A. Effects of probiotic, prebiotic, and synbiotic with and without feed restriction on performance, hematological indices and carcass characteristics of broiler chickens. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Farnell, Y.Z.; Peebles, E.D.; Kiess, A.S.; Wamsley, K.G.S.; Zhai, W. Effects of prebiotics, probiotics, and their combination on growth performance, small intestine morphology, and resident Lactobacillus of male broilers1. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ROSS. Broiler Management Handbook; Aviagen Company: Huntsville, AL, USA, 2025; Available online: https://aviagen.com/assets/Tech_Center/Ross_Broiler/Aviagen-ROSS-Broiler-Handbook-EN.pdf (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Aviagen. ROSS BROILER: Nutrition Specifications; Aviagen company: Huntsville, AL, USA, 2022; Volume 2025, Available online: https://aviagen.com/assets/Tech_Center/Ross_Broiler/Aviagen_RosaBroilerNutritionSupplement.pdf (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- AOAC. AOAC International, Official Methods of Analysis, 21st ed.; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Muneeb, M.; Khan, E.U.; Ali, M.; Suleman, M.; Shaheen, M.S.; Zafar, M.S.; Ahmad, S. Effects of replacing antibiotics with probiotics and antimicrobial peptides on performance, gut health, carcass traits, meat quality, and welfare in broilers infected with Eimeria and Clostridium perfringens. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2025, 57, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yameen, R.M.K.; Hussain, J.; Mahmud, A.; Saima. Effects of different light durations during incubation on hatching, subsequent growth, welfare, and meat quality traits among three broiler strains. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 3639–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojewola, G.; Abasiekong, S.; Nwachukwu, C. Methionine supplementation in the productive efficiency, carcass characteristics and economics of growing indigenous turkey. Niger. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 4, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-L.; Xing, G.-Z.; Wang, L.-S.; Li, S.-F.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Lin, L.; Luo, X.-G.; Liao, X.-D. Effects of selenium source and level on growth performance, antioxidative ability and meat quality of broilers. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wu, J.; Li, C. Effect of different selenium sources on production performance and biochemical parameters of broilers. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2014, 98, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, A. Effect of dietary mixture of Aspergillus probiotic and selenium nano-particles on growth, nutrient digestibilities, selected blood parameters and muscle fatty acid profile in broiler chickens. Anim. Sci. Pap. Rep. 2014, 32, 65–79. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhshalinejad, R.; Akbari Moghaddam Kakhki, R.; Zoidis, E. Effects of different dietary sources and levels of selenium supplements on growth performance, antioxidant status and immune parameters in Ross 308 broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2018, 59, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, R. Probiotics in man and animals. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1989, 66, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: Introducing the concept of prebiotics. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rycroft, C.E.; Jones, M.R.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. A comparative in vitro evaluation of the fermentation properties of prebiotic oligosaccharides. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 91, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, P.; Parsons, C.M.; Fahey, G.C. The effects of several oligosaccharides on growth performance, nutrient digestibilities, and cecal microbial populations in young chicks. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.L.; Yin, Y.L.; Wu, G.Y.; Zhang, Y.G.; Li, T.J.; Li, L.L.; Li, M.X.; Tang, Z.R.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; et al. Effect of dietary oligochitosan supplementation on ileal digestibility of nutrients and performance in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2005, 84, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, S.; Angeles, M.L.; Mojica, M.C.; Jalukar, S. Combination of an Enzymatically Hydrolyzed Yeast and Yeast Culture with a Direct-fed Microbial in the Feeds of Broiler Chickens. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 25, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Iji, P.; Choct, M. Dietary modulation of gut microflora in broiler chickens: A review of the role of six kinds of alternatives to in-feed antibiotics. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2009, 65, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.K.; Jalukar, S.; Brake, J. The effect of refined functional carbohydrates from enzymatically hydrolyzed yeast on the transmission of environmental Salmonella Senftenberg among broilers and proliferation in broiler housing. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, G.K.; Jalukar, S.; Brake, J. Effect of refined functional carbohydrates from enzymatically hydrolyzed yeast on the presence of Salmonella spp. in the ceca of broiler breeder females. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2684–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, W.A.; Ghareeb, K.; Abdel-Raheem, S.; Böhm, J. Effects of dietary inclusion of probiotic and synbiotic on growth performance, organ weights, and intestinal histomorphology of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudabos, A.; Al-Batshan, H.A.; Murshed, M. Effects of prebiotics and probiotics on the performance and bacterial colonization of broiler chickens. South Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 45, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahir, M.; Afsarian, O.; Ghasemi, S.; Tellez, G. Effects of Dietary Inclusion of Probiotic or Prebiotic on Growth Performance, Organ Weight, Blood Parameters and Antibody Titers Against Influenza and Newcastle in Broiler Chickens. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2014, 13, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruszynska-Oszmalek, E.; Kolodziejski, P.A.; Stadnicka, K.; Sassek, M.; Chalupka, D.; Kuston, B.; Nogowski, L.; Mackowiak, P.; Maiorano, G.; Jankowski, J.; et al. In ovo injection of prebiotics and synbiotics affects the digestive potency of the pancreas in growing chickens. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1909–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutful Kabir, S.M. The role of probiotics in the poultry industry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3531–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehimanesh, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Roostaei-Ali Mehr, M. Effect of dietary probiotic, prebiotic and synbiotic supplementation on performance, immune responses, intestinal morphology and bacterial populations in broilers. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 100, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whanger, P.D.; Butler, J.A. Effects of Various Dietary Levels of Selenium as Selenite or Selenomethionine on Tissue Selenium Levels and Glutathione Peroxidase Activity in Rats. J. Nutr. 1988, 118, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahan, D.C.; Kim, Y.Y. Effect of inorganic or organic selenium at two dietary levels on reproductive performance and tissue selenium concentrations in first-parity gilts and their progeny. J. Anim. Sci. 1996, 74, 2711–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.V.; Prakash, B.; Raju, M.V.; Panda, A.K.; Poonam, S.; Murthy, O.K. Effect of supplementing organic selenium on performance, carcass traits, oxidative parameters and immune responses in commercial broiler chickens. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 26, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.-F.; Huang, S.-C.; Cheng, S.-B.; Hsu, C.-C.; Huang, Y.-C. Glutathione and Selenium Supplementation Attenuates Liver Injury in Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Hepatocarcinogenic Mice by Enhancing Glutathione-Related Antioxidant Capacities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, K.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, T.; Huang, J. Potential Applications and Risks of Supranutritional Selenium Supplementation in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Critical Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, R.L.; Southern, L.L. Comparison of inorganic and organic selenium sources for broilers. Poult. Sci. 2005, 84, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelícia, K.; Mendes, A.A.; Saldanha, E.; Pizzolante, C.; Takahashi, S.; Moreira, J.; Garcia, R.; Quinteiro, R.R.; Paz, I.; Komiyama, C. Use of prebiotics and probiotics of bacterial and yeast origin for free-range broiler chickens. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2004, 6, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Rosales, S.; Angeles, M. Effects of an Enzymatically Hydrolyzed Yeast and Yeast Culture Combined with Flavomycin and Monensin on Finishing Broiler Chickens. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2011, 10, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Han, J.; Zhang, D.; Sun, H.; Zhang, F. Effects of prebiotic supplementation on growth performance, slaughter performance, growth of internal organs and small intestine and serum biochemical parameters of broilers. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2015, 43, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Shulukh, E.; Gibril, S.; Habib, A.; Abubakr, A.; Ibrahim, G.; Zeinelabdeen, W. Effect of Probiotics and Prebiotics on Carcass, Cut Yields and some Qualitative Traits of Broiler Chickens. Asian Acad. Res. J. Multidiscip. 2017, 4, 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, M.P.; Gershwin, M.E.; Keen, C.L.; Hurley, L. Nutrition and Immunology, pages 215–239 1988 Alan R. Liss, Inc. Nutr. Immunol. 1988, 11, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Pappas, A.; Zoidis, E. The role of selenium in chicken physiology: New insights. In Chickens: Physiology, Diseases and Farming Practices; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Lanari, M.C.; Schaefer, D.M. A review of dietary vitamin E supplementation for improvement of beef quality. J. Anim. Sci. 1995, 73, 3131–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Sodhi, S.; Kaur, R. Effects of dietary supplements of selenium, vitamin E or combinations of the two on antibody responses of broilers. Br. Poult. Sci. 2006, 47, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.J.; Wu, C.X.; Gong, L.M.; Song, T.; Wu, H.; Zhang, L.Y. Effects of nano-selenium on performance, meat quality, immune function, oxidation resistance, and tissue selenium content in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 2532–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani Moghaddam, A.K.; Mehraei Hamzekolaei, M.H.; Khajali, F.; Hassanpour, H. Role of Selenium from Different Sources in Prevention of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Syndrome in Broiler Chickens. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 180, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, H.J.; Yu, S.H.; Wu, S.G.; Yoon, I.; Quigley, J.; Gao, Y.P.; Qi, G.H. Effects of yeast culture in broiler diets on performance and immunomodulatory functions. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houshmand, M.; Azhar, K.; Idrus, Z.; Bejo, M.H.; Kamyab, A. Effects of nonantibiotic feed additives on performance, nutrient retention, gut pH, and intestinal morphology of broilers fed different levels of energy. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2011, 20, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinteiro-Filho, W.M.; Ribeiro, A.; Ferraz-de-Paula, V.; Pinheiro, M.L.; Sakai, M.; Sá, L.R.; Ferreira, A.J.; Palermo-Neto, J. Heat stress impairs performance parameters, induces intestinal injury, and decreases macrophage activity in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalia, A.M.; Loh, T.C.; Sazili, A.Q.; Samsudin, A.A. Influence of bacterial organic selenium on blood parameters, immune response, selenium retention and intestinal morphology of broiler chickens. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Li, P.; Yu, L.-H.; Li, L.; Li, K.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S.-H.; Long, M. Selenium-rich yeast attenuates ochratoxin A-induced small intestinal injury in broiler chickens by activating the Nrf2 pathway and inhibiting NF-KB activation. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 66, 103784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.W.; Lee, B.D.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, K.W.; An, G.H.; Song, K.B.; Lee, C.H. Effects of yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) cell components on growth performance, meat quality, and ileal mucosa development of broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2005, 84, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.K.; Croom, J.; Christensen, V.L.; Black, B.L.; Bird, A.R.; Daniel, L.R.; McBride, B.W.; Eisen, E.J. Jejunal glucose uptake and oxygen consumption in turkey poults selected for rapid growth. Poult. Sci. 1997, 76, 1738–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadipour, B.; Hassanpour, H.; Rafiei, F.; Khajali, F. Antioxidative, antihyperlipidemic, and growth-promoting effects of Kelussia odoratissima in meat-type chickens. Poult. Sci. J. 2015, 3, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, M.; Rodrigues, E.; Marques, R.; Gravena, R.; Guandolini, G.; Moraes, V. Performance and morphology of intestinal mucosa of broilers fed mannan-oligosaccharides and enzymes. Arq. Bras. De Med. Veterinária E Zootec. 2008, 60, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelicano, E.R.L.; Souza, P.D.; Souza, H.D.; Figueiredo, D.; Boiago, M.; Carvalho, S.; Bordon, V. Intestinal mucosa development in broiler chickens fed natural growth promoters. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2005, 7, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| A 2 × 2 Factorial Arrangement Under CRD | Organic Selenium (Zinc-L-Selenomethionine) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Se0.2 mg/kg | Se0.4 mg/kg | ||
| Manan-Oligosaccharide (MOS) | No MOS added (−) | Straight-run broilers 132 birds, 6 replicates 22 birds/replicate | Straight-run broilers 132 birds, 6 replicates 22 birds/replicate |
| MOS at 1.0 g/kg (+) | Straight-run broilers 132 birds, 6 replicates 22 birds/replicate | Straight-run broilers 132 birds, 6 replicates 22 birds/replicate | |
| Diet Composition | Starter (1–21 d) | Finisher (22–35 d) |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | % | % |
| Yellow corn | 58.1 | 61.1 |
| Canola Oil | 1.7 | 2.3 |
| Soybean meal | 36.5 | 33 |
| L-Lysine HCl | 0.45 | 0.4 |
| DL-Methionine | 0.23 | 0.21 |
| L-Threonine | 0.15 | 0.11 |
| Common salt | 0.47 | 0.48 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 0.7 | 0.5 |
| Limestone | 1.6 | 1.8 |
| Micro mineral premix 1* | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Vitamin premix 2 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
| Analyzed Nutrients (% otherwise noted) | ||
| Metabolizable Energy (Calculated, Kcal/kg) 3 | 3000 | 3100 |
| Crude protein | 23.00 | 21.5 |
| Ether extract | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Crude fiber | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Crude ash | 1.00 | 1.70 |
| Calcium | 0.96 | 0.87 |
| Available phosphorus | 0.48 | 0.43 |
| Dig-Lysine | 1.28 | 1.15 |
| Dig-Methionine | 0.51 | 1.47 |
| Dig-Threonine | 0.86 | 0.77 |
| Parameters | Treatments | SEM | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Se 0.2 mg/Kg | Se 0.4 mg/kg | |||||||
| Se0.2 | Se0.2 + MOS | Se0.4 | Se0.4 + MOS | Se | MOS | Se × MOS | ||
| FI, g/bird | ||||||||
| 1–21 d | 1123.03 a | 1088.92 b | 1111.49 a | 1058.74 c | 5.44 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| 22–35 d | 2187.26 b | 2027.57 d | 2224.10 a | 2140.80 c | 15.44 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| 1–35 d | 3310.28 b | 3116.49 d | 3335.59 a | 3199.54 c | 18.48 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| BWG, g/bird | ||||||||
| 1–21 d | 846.04 c | 900.04 a | 867.85 b | 895.94 a | 5.67 | 0.232 | <0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| 22–35 d | 1099.75 c | 1269.97 a | 1190.31 b | 1199.65 ab | 17.17 | 0.690 | 0.002 | 0.004 |
| 1–35 d | 1945.79 c | 2170.00 a | 2058.16 b | 2095.59 b | 20.13 | 0.430 | <0.0001 | 0.001 |
| FCR | ||||||||
| 1–21 d | 1.33 a | 1.21 c | 1.28 b | 1.18 c | 0.01 | 0.006 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| 22–35 d | 2.00 a | 1.60 c | 1.87 b | 1.79 b | 0.04 | 0.473 | <0.0001 | 0.001 |
| 1–35 d | 1.71 a | 1.44 d | 1.62 b | 1.53 c | 0.02 | 0.901 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Liv, % | ||||||||
| 1–35 d | 99.09 b | 99.85 a | 98.94 b | 97.39 ab | 0.11 | 0.1181 | 0.0039 | 0.0125 |
| Parameters | Treatments | SEM | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Se 0.2 mg/Kg | Se 0.4 mg/kg | |||||||
| Se0.2 | Se0.2 + MOS | Se0.4 | Se0.4 + MOS | Se | MOS | Se × MOS | ||
| CW, g | 1383.89 b | 1285.65 c | 1386.91 b | 1501.22 a | 14.29 | <0.0001 | 0.7417 | <0.0001 |
| CY, % | 65.75 bc | 64.77 c | 66.72 ab | 67.66 a | 0.29 | 0.0006 | 0.9621 | 0.0021 |
| Hrt W, g | 11.31 | 11.43 | 11.00 | 11.43 | 0.10 | 0.4466 | 0.1673 | 0.3807 |
| Liv W, g | 46.61 b | 45.98 b | 49.25 a | 49.87 a | 0.28 | <0.0001 | 1.0000 | <0.0001 |
| Giz W, g | 42.71 b | 43.84 b | 45.35 a | 46.23 a | 0.29 | <0.0001 | 0.0580 | <0.0001 |
| LQW, g | 284.24 a | 263.86 b | 274.08 ab | 290.31 a | 2.92 | 0.1464 | 0.7095 | 0.0063 |
| Br W, g | 529.61 b | 485.03 c | 544.96 b | 602.73 a | 7.51 | <0.0001 | 0.5989 | <0.0001 |
| Parameters | Treatments | SEM | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Se 0.2 mg/Kg | Se 0.4 mg/kg | |||||||
| Se0.2 | Se0.2 + MOS | Se0.4 | Se0.4 + MOS | Se | MOS | Se × MOS | ||
| Spleen (g) | 2.61 d | 2.72 c | 2.77 b | 2.85 a | 0.02 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Bursa (g) | 1.92 b | 2.17 a | 2.22 a | 2.28 a | 0.03 | 0.0002 | 0.0034 | <0.0001 |
| Parameters | Treatments | SEM | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Se 0.2 mg/Kg | Se 0.4 mg/kg | |||||||
| Se 0.2 | Se 0.2 + MOS | Se 0.4 | Se 0.4 + MOS | Se | MOS | Se × MOS | ||
| VH | 1525.36 | 1602.22 | 1608.00 | 1737.25 | 31.19 | 0.0734 | 0.0888 | 0.654 |
| CD | 278.82 | 298.33 | 275.50 | 304.50 | 5.91 | 0.9018 | 0.0458 | 0.2268 |
| VH/CD | 5.57 | 5.37 | 5.92 | 5.71 | 0.15 | 0.2764 | 0.5090 | 0.6423 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Talib, H.; Khan, E.U.; Muneeb, M.; Mateen, A.; Naveed, S.; Hussain, J.; Ahmad, S.; Soumeh, E.A.; Matar, A.M. Individual and Combined Effect of Zinc-L-Selenomethionine Complex with Mannan-Oligosaccharide on Growth Performance, Carcass Characteristics, Gut Development and Immune Response in Broilers. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080768
Talib H, Khan EU, Muneeb M, Mateen A, Naveed S, Hussain J, Ahmad S, Soumeh EA, Matar AM. Individual and Combined Effect of Zinc-L-Selenomethionine Complex with Mannan-Oligosaccharide on Growth Performance, Carcass Characteristics, Gut Development and Immune Response in Broilers. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(8):768. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080768
Chicago/Turabian StyleTalib, Hammad, Ehsaan Ullah Khan, Muhammad Muneeb, Abdul Mateen, Saima Naveed, Jibran Hussain, Sohail Ahmad, Elham Assadi Soumeh, and Abdulkareem M. Matar. 2025. "Individual and Combined Effect of Zinc-L-Selenomethionine Complex with Mannan-Oligosaccharide on Growth Performance, Carcass Characteristics, Gut Development and Immune Response in Broilers" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 8: 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080768
APA StyleTalib, H., Khan, E. U., Muneeb, M., Mateen, A., Naveed, S., Hussain, J., Ahmad, S., Soumeh, E. A., & Matar, A. M. (2025). Individual and Combined Effect of Zinc-L-Selenomethionine Complex with Mannan-Oligosaccharide on Growth Performance, Carcass Characteristics, Gut Development and Immune Response in Broilers. Veterinary Sciences, 12(8), 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080768










