Epidemiological Exploration of Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia intestinalis, Enterocytozoon bieneusi, and Blastocystis spp. in Yaks: Investigating Ecological and Zoonotic Dynamics in Lhasa, Xizang
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
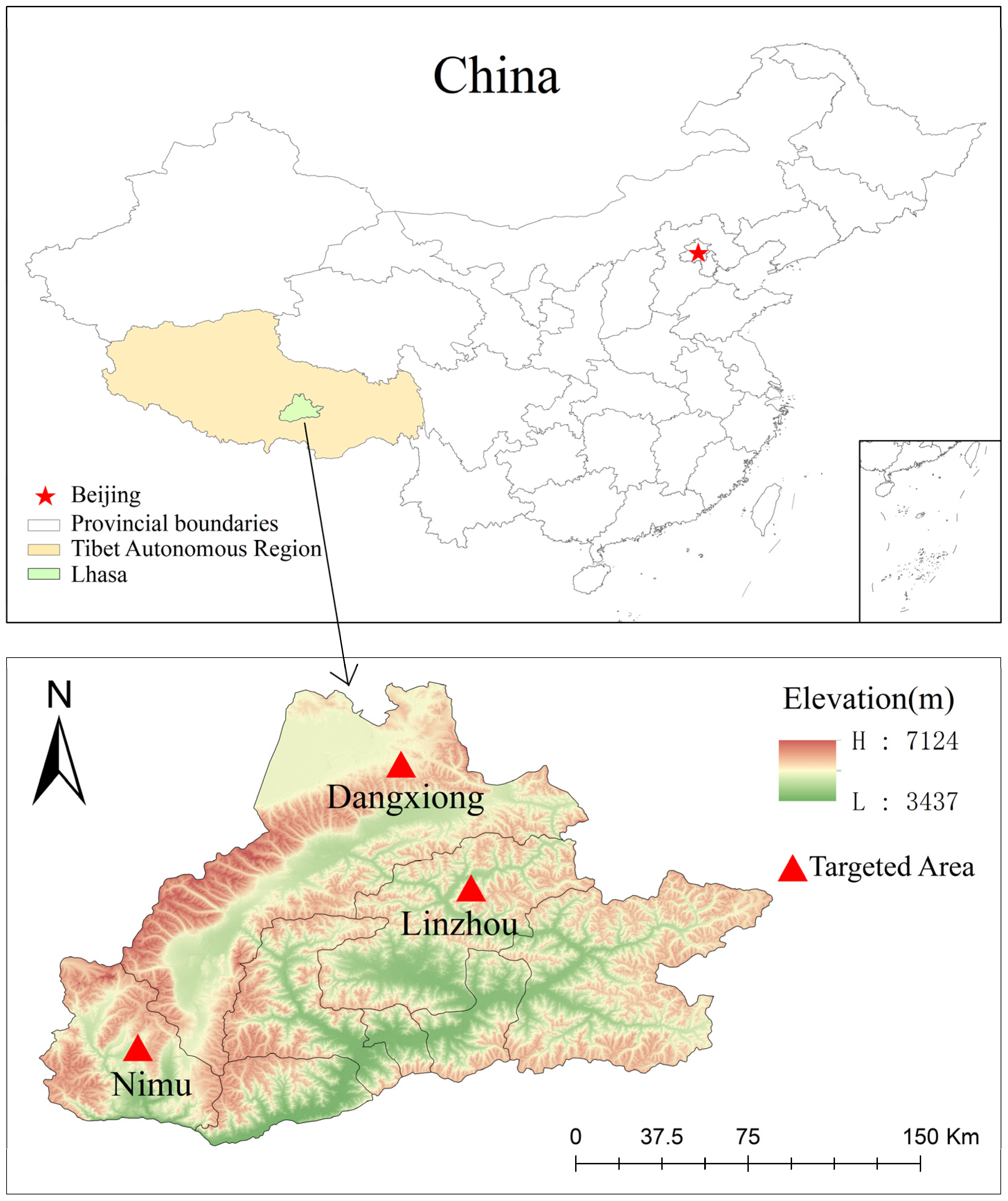
2.1. Collection of Fecal Samples
2.2. Ethical Statement
2.3. Total DNA Extraction
2.4. Gene Amplification and DNA Electrophoresis
2.5. Sequencing Procedure and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
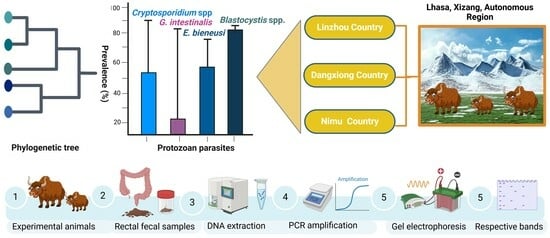
3. Results
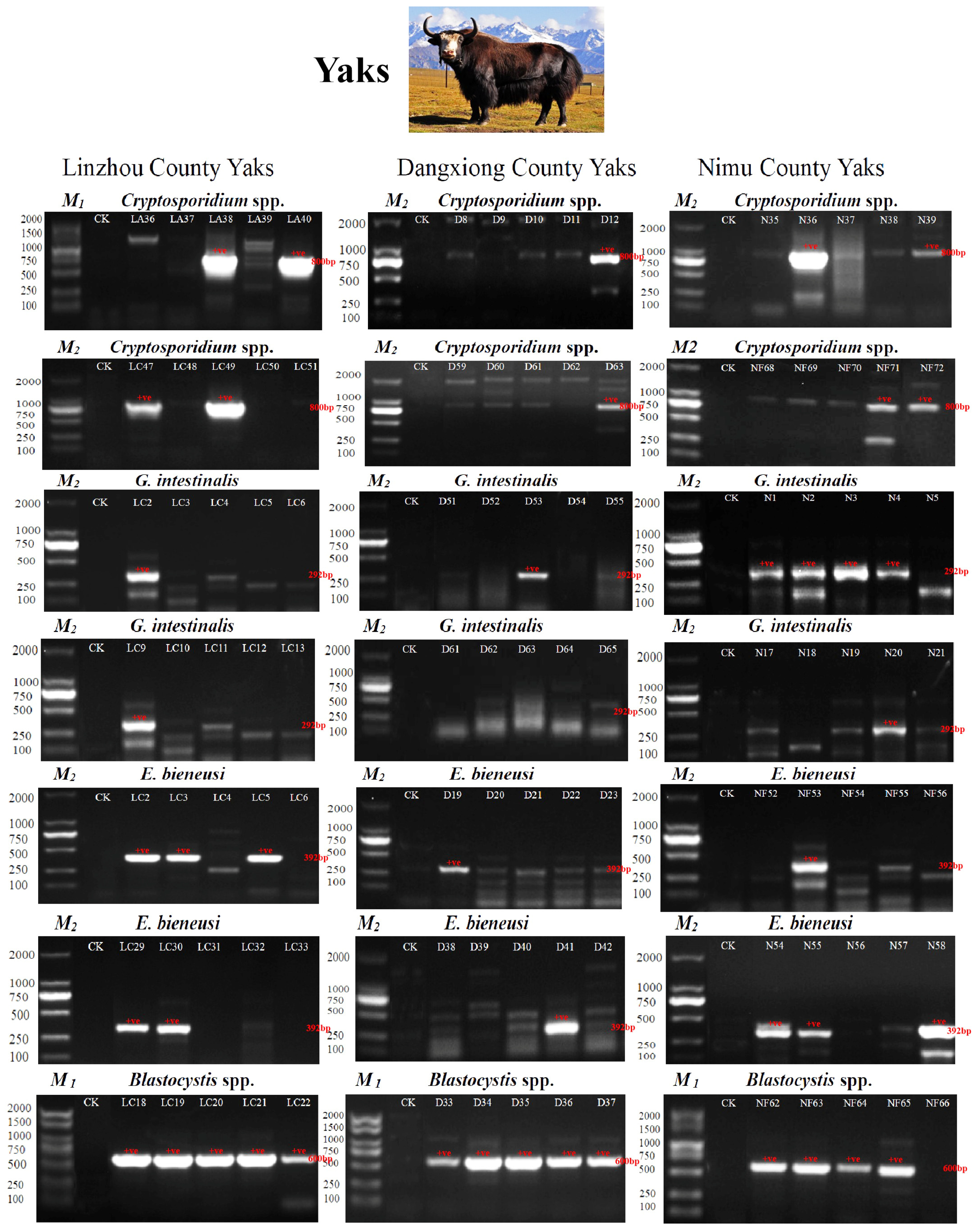
3.1. Infection Status of Yaks Against Four Types of Parasites
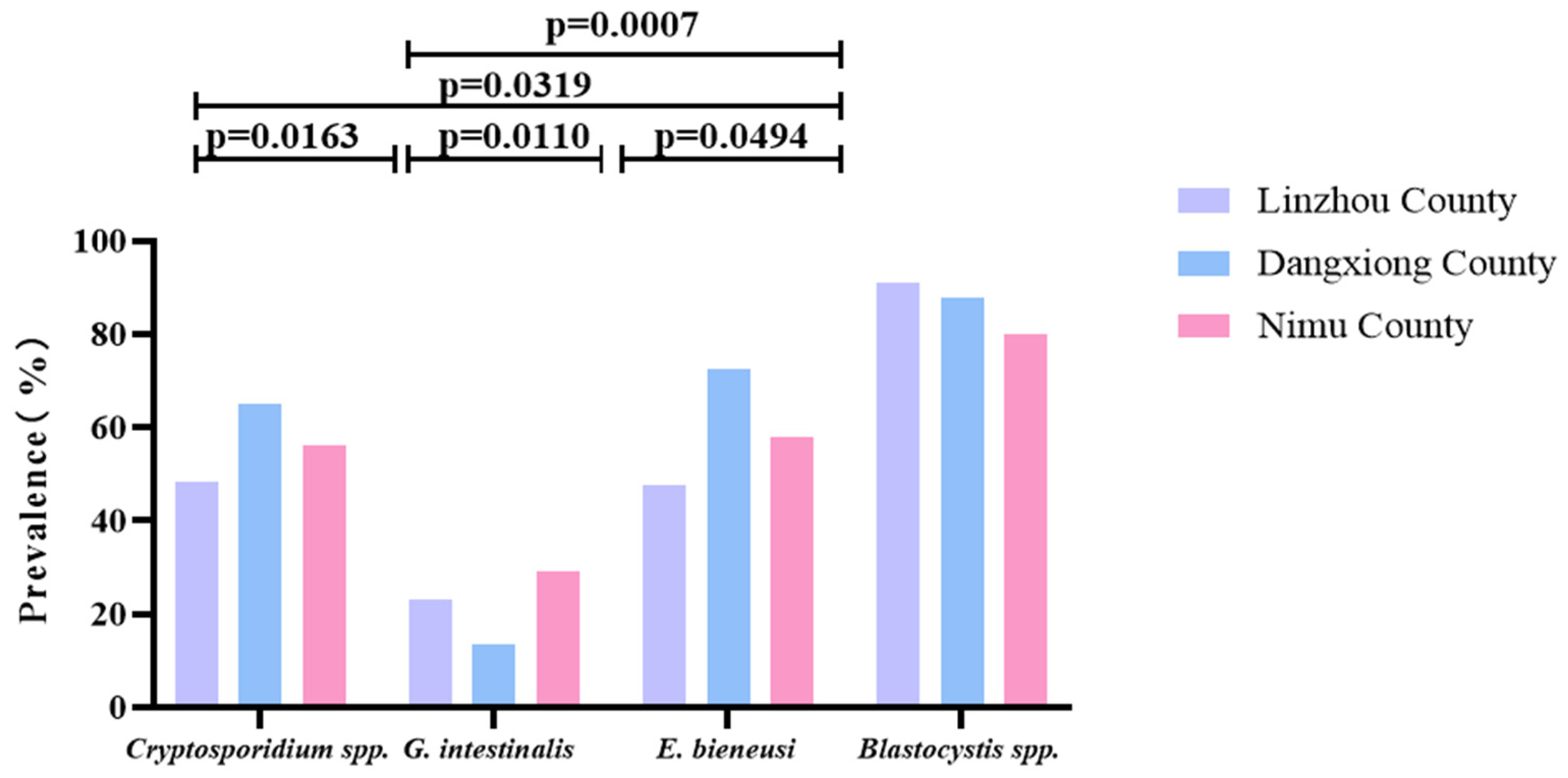
3.2. The Multiregional Difference in Prevalence Among Yaks
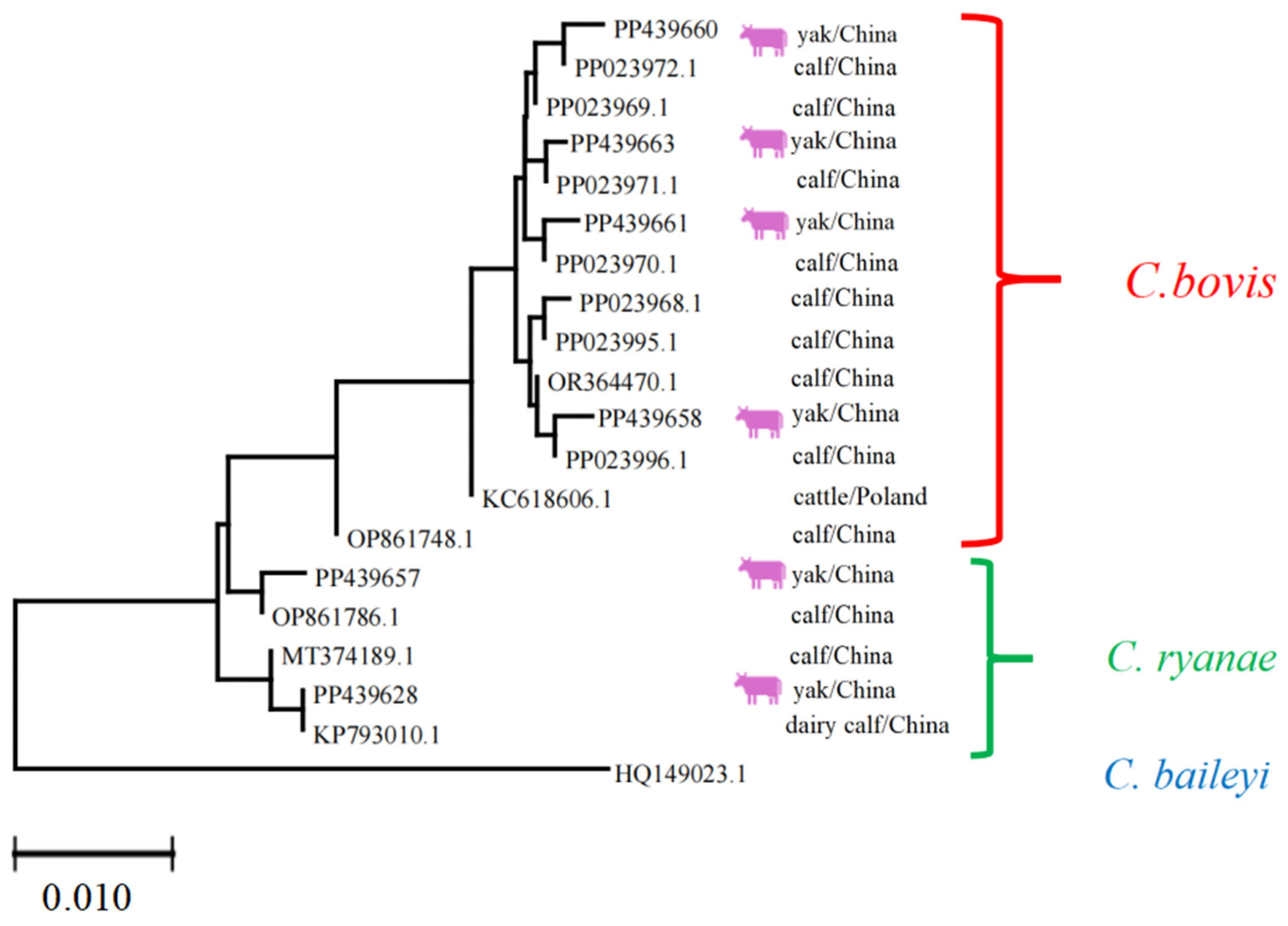
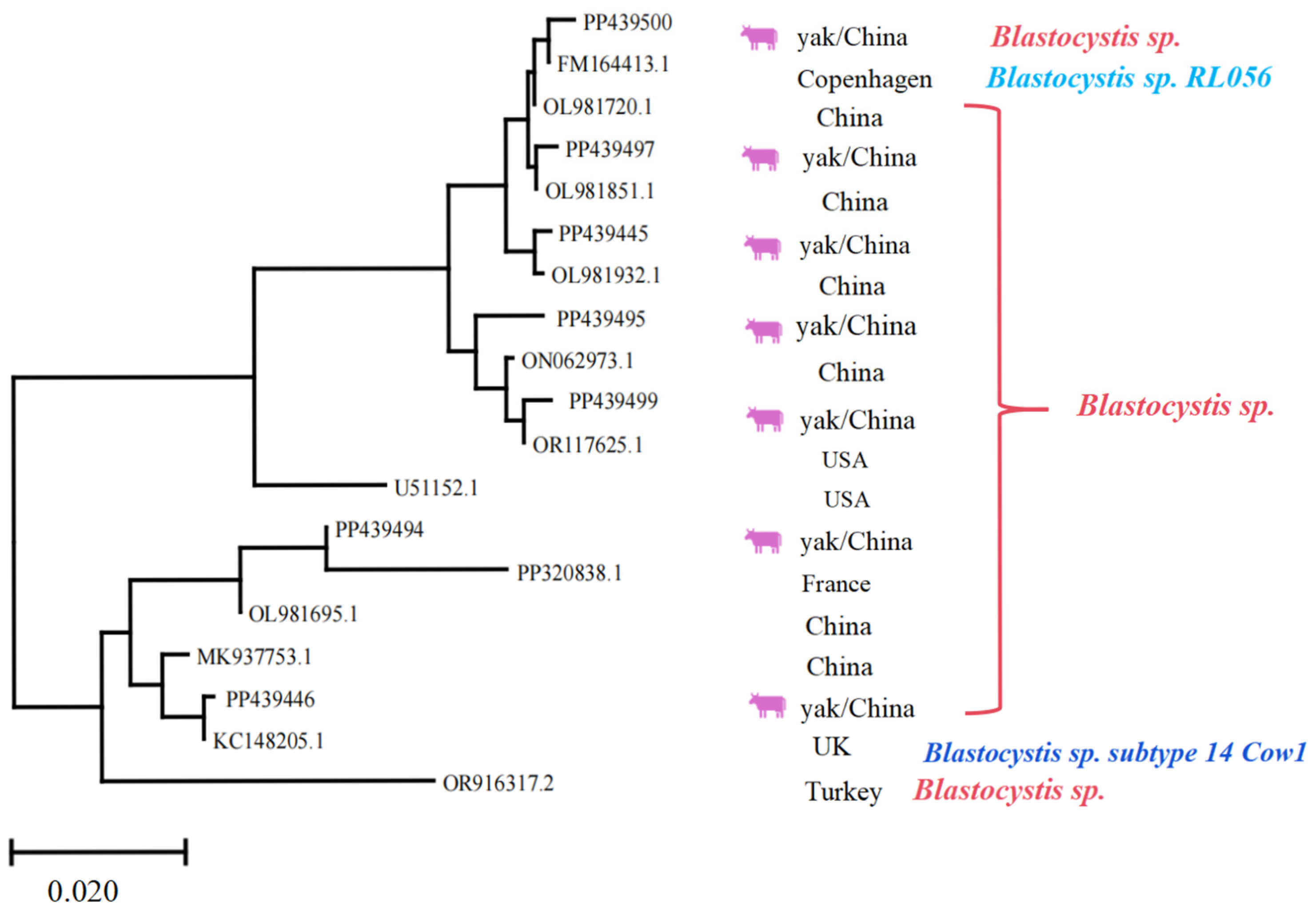
3.3. Multiple Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis of Different Gene Sequences
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaminsky, R.; Mäser, P. Global Impact of Parasitic Infections and the Importance of Parasite Control. Front. Parasitol. 2025, 4, 1546195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijjawi, N.; Zahedi, A.; Al-Falah, M.; Ryan, U. A Review of the Molecular Epidemiology of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) Region. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022, 98, 105212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.-Y.; Yin, M.-Y.; Song, G.-Y.; Tan, Q.-D.; Wang, J.-L.; Zhou, D.-H. Prevalence of Gastrointestinal Parasites in Free-Range Yaks (Bos grunniens) in Gansu Province, Northwest China. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cidan, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Ali, M.; Fouad, D.; Ataya, F.S.; Zhu, Y.; Basang, W.; Li, K. Comparative Analysis of Microbiota in Jiani Yaks with Different Rib Structures. Life 2024, 14, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Gao, J.; Shahzad, M.; Han, Z.; Nabi, F.; Liu, M.; Zhang, D.; Li, J. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Yaks (Bos grunniens) on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of China. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 205, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chai, Z.; Hu, D.; Ji, Q.; Xin, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, J. A Global Analysis of CNVs in Diverse Yak Populations Using Whole-Genome Resequencing. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Shrestha, L.; Bisht, N.; Wu, N.; Ismail, M.; Dorji, T.; Dangol, G.; Long, R. Ethnic and Cultural Diversity amongst Yak Herding Communities in the Asian Highlands. Sustainability 2020, 12, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Cidan, Y.; Sun, G.; Li, X.; Shahid, M.A.; Luosang, Z.; Suolang, Z.; Suo, L.; Basang, W. Comparative Analysis of Gut Fungal Composition and Structure of the Yaks under Different Feeding Models. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1193558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, G.; JianLin, H.; Ruijun, L. The Yak Second Edition, Published by the Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Bangkok, Thailand. 2003. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/AD347E/ad347e00.htm (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- Ali, M.; Xu, C.; Nawaz, S.; Ahmed, A.E.; Hina, Q.; Li, K. Anti-Cryptosporidial Drug-Discovery Challenges and Existing Therapeutic Avenues: A “One-Health” Concern. Life 2024, 14, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio, M.; Jovana, J.; Melina, M.; Arturo, S.S. Frequency of Giardia spp. and Cryptosporidium spp. in Domestic and Captive Wild Animals in the North of Veracruz, Mexico. Pak. Vet. J. 2023, 43, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, A.; Monis, P.; Gofton, A.W.; Oskam, C.L.; Ball, A.; Bath, A.; Bartkow, M.; Robertson, I.; Ryan, U. Cryptosporidium species and Subtypes in Animals Inhabiting Drinking Water Catchments in Three States across Australia. Water Res. 2018, 134, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehata, A.A.; El-Emam, M.M.A.; Gouda, H.; El-Said, B.M.; Salman, M.B.; Abd-Elfatah, E.B. Molecular Characterization of Cryptosporidium Infection and Analysis of Hematological and Biochemical Changes in Diarrheic Pre-Weaned Calves in Egypt. Pak. Vet. J. 2024, 44, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Xu, C.; Saleem, M.U.; Babar, W.; Idrees, A. Epidemiological Investigation of Cryptosporidium Infection in Yaks in Chamdo, China. Pak. Vet. J. 2024, 44, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayan, A.; Celik, B.A.; Celik, O.Y.; Akyildiz, G.; Kilinc, O.O.; Ayan, O.O. First Report of Zoonotic Cryptosporidium parvum Subtype IIaA15G2R1 in Dogs in Türkiye. Pak. Vet. J. 2024, 44, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L. Molecular Epidemiology of Cryptosporidiosis: An Update. Exp. Parasitol. 2010, 124, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Zoonotic Potential and Molecular Epidemiology of Giardia species and Giardiasis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 110–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydarian, M.; Manouchehri Naeini, K.; Kheiri, S.; Abdizadeh, R. Prevalence and Subtyping of Blastocystis sp. in Ruminants in Southwestern Iran. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Feng, Y.; Santin, M. Host Specificity of Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Public Health Implications. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmy, Y.A.; Hafez, H.M. Cryptosporidiosis: From Prevention to Treatment, a Narrative Review. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santin, M. Cryptosporidium and Giardia in Ruminants. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2020, 36, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Ji, Y.; Xu, C.; Hina, Q.; Javed, U.; Li, K. Food and Waterborne Cryptosporidiosis from a One Health Perspective: A Comprehensive Review. Animals 2024, 14, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Karanis, G.; Jian, Y.; Ma, L.; Karanis, P. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis in 1–2-Month-Old Highland Yaks in Qinghai Province, China. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Cai, J.; Cai, M.; Wu, W.; Li, C.; Lei, M.; Xu, H.; Feng, L.; Ma, J.; Feng, Y.; et al. Distribution of Cryptosporidium species in Tibetan Sheep and Yaks in Qinghai, China. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 215, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Li, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Li, A.; Mehmood, K.; Shahzad, M.; Gao, K.; Li, J. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. in Yaks (Bos grunniens) in Naqu, China. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 144, 104190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghipour, A.; Bahadory, S.; Abdoli, A. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Global Prevalence of Cattle Microsporidiosis with Focus on Enterocytozoon bieneusi: An Emerging Zoonotic Pathogen. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 200, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, P.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Zou, Y.; Chen, X.-Q. Prevalence and Genotypes/Subtypes of Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Blastocystis sp. in Different Breeds of Cattle in Jiangxi Province, Southeastern China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022, 98, 105216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cian, A.; El Safadi, D.; Osman, M.; Moriniere, R.; Gantois, N.; Benamrouz-Vanneste, S.; Delgado-Viscogliosi, P.; Guyot, K.; Li, L.L.; Monchy, S.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Blastocystis sp. in Various Animal Groups from Two French Zoos and Evaluation of Potential Zoonotic Risk. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauff-Adedotun, A.A.; Mohd Zain, S.N.; Farah Haziqah, M.T. Current Status of Blastocystis sp. in Animals from Southeast Asia: A Review. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 3559–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, N.; Nagoshi, M.; Takami, K.; Sawano, Y.; Yoshikawa, H. A Survey of Blastocystis sp. in Livestock, Pets, and Zoo Animals in Japan. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 106, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jung, B.; Lim, J.-S.; Seo, M.-G.; Lee, S.-H.; Choi, K.-H.; Hwang, M.-H.; Kim, T.-H.; Kwon, O.-D.; Kwak, D. Multilocus Genotyping of Giardia duodenalis from Pigs in Korea. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 78, 102154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-S.; Yuan, Y.-J.; Yin, Y.-L.; Hu, R.-S.; Song, J.-K.; Zhao, G.-H. Prevalence and Multilocus Genotyping of Giardia duodenalis in Pigs of Shaanxi Province, Northwestern China. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, Z.S.; Han, W.X.; Yang, B.; Chai, H.L.; Wang, M.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, W.H.; Ma, Y.M.; et al. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Giardia duodenalis in Dairy Cattle in Central Inner Mongolia, Northern China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, A.; Matsuda, Y.; Horikita, T.; Matsumoto, J. Subtype Analysis and Prevalence of Mixed Subtype Infection of Blastocystis in Farmed Pigs from Chiba Prefecture, Japan. Parasitol. Int. 2022, 87, 102490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, S.; Zou, Y.; Hong, Z.-W.; Wang, P.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Song, D.-P.; Chen, X.-Q. Prevalence and Subtype Distribution of Blastocystis sp. in Diarrheic Pigs in Southern China. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.-H.; Ren, W.-X.; Gao, M.; Bian, Q.-Q.; Hu, B.; Cong, M.-M.; Lin, Q.; Wang, R.-J.; Qi, M.; Qi, M.-Z.; et al. Genotyping Cryptosporidium andersoni in Cattle in Shaanxi Province, Northwestern China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelbee, A.J.; Frederick, L.M.; Heitman, T.L.; Olson, M.E. Prevalence and Genotyping of Giardia duodenalis from Beef Calves in Alberta, Canada. Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 112, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, I.M.; Fayer, R.; Yang, C.; Santin, M.; Matos, O.; Xiao, L. Molecular Characterization of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in Cattle Indicates That Only Some Isolates Have Zoonotic Potential. Parasitol. Res. 2004, 92, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scicluna, S.M.; Tawari, B.; Clark, C.G. DNA Barcoding of Blastocystis. Protist 2006, 157, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlan, P.D.; Stensvold, C.R.; Cotter, P.D. Development and Application of a Blastocystis Subtype-Specific PCR Assay Reveals That Mixed-Subtype Infections Are Common in a Healthy Human Population. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4071–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Ahmed, U.N.; Andersen, L.O.; Nielsen, H.V. Development and Evaluation of a Genus-Specific, Probe-Based, Internal-Process-Controlled Real-Time PCR Assay for Sensitive and Specific Detection of Blastocystis spp. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1847–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, J.J.; Stensvold, C.R. Molecular Testing for Clinical Diagnosis and Epidemiological Investigations of Intestinal Parasitic Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 371–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, P.; Borghesan, T.C.; Tavares, L.E.R.; Ferreira, V.L.; Teixeira, M.M.G.; Paiva, F. Hepatozoon Caimani Carini, 1909 (Adeleina: Hepatozoidae) in Wild Population of Caiman Yacare Daudin, 1801 (Crocodylia: Alligatoridae), Pantanal, Brazil. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, T.; Sonobe, T.; Hayashi, K. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification for Direct Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex, M. avium, and M. intracellulare in Sputum Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2616–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Zhao, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.S. Seasonal Changes in Weight and Body Composition of Yak Grazing on Alpine-Meadow Grassland in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of China. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 83, 1908–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Molecular Epidemiological Investigation of Cryptosporidium sp., Giardia duodenalis, Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Blastocystis sp. Infection in Free-Ranged Yaks and Tibetan Pigs on the Plateau. Pak. Vet. J. 2022, 42, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Chang, Y.; Yu, F.; Zhang, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, L. Prevalence and Molecular Characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis in Dairy Cattle in Gansu, Northwest China. Parasite 2020, 27, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Liu, S.S.; Chen, C.C.; Hsu, H.Y. Cryptosporidium parvum Infection and Management-Based Risk Factors of Dairy Calves in Taiwan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 83, 1838–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, X.; Jian, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Hu, Y.; Karanis, P. Detection of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in the Slaughterhouse, Sewage and River Waters of the Qinghai Tibetan Plateau Area (QTPA), China. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.-L.; Ni, H.-B.; Li, J.-H.; Jiang, J.; Wang, W.; Wei, X.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.-T. Prevalence of Cryptosporidium spp. in Yaks (Bos grunniens) in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 770612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.Y.P.; Chen, T.T.-W.; Tseng, Y.-C.; Chang, K.-C.; Yang, T.-H.; Peng, S. Detection and Genotyping of Giardia duodenalis from Cattle and Pigs in Hualien Country, Eastern Taiwan. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2021, 54, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buret, A.; DenHollander, N.; Wallis, P.M.; Befus, D.; Olson, M.E. Zoonotic Potential of Giardiasis in Domestic Ruminants. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 162, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L. Giardia Infection in Farm Animals. Parasitol. Today 1994, 10, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; Ma, L.; Karanis, G.; Christodoulou-Vafeiadou, E.; Karanis, P. Detection of Giardia duodenalis Assemblage E Infections at the Tibetan Plateau Area: Yaks Are Suitable Hosts. Acta Trop. 2017, 169, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cai, J.; Li, P.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Li, C.; Lei, M.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Enterocytozoon bieneusi Genotypes in Tibetan Sheep and Yaks. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.-X.; Zou, Y.; Li, T.-S.; Chen, H.; Wang, S.-S.; Cao, F.-Q.; Yang, J.-F.; Sun, X.-L.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Zou, F.-C. First Report of the Prevalence and Genetic Characterization of Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium spp. in Yunling Cattle in Yunnan Province, Southwestern China. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 158, 105025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, U.; Fayer, R.; Xiao, L. Cryptosporidium species in Humans and Animals: Current Understanding and Research Needs. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1667–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugo, R.L.E.; Birrell, G.W. Proteomics of Anopheles Vectors of Malaria. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 961–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodr, A.; Kay, E.; Gomez-Valero, L.; Ginevra, C.; Doublet, P.; Buchrieser, C.; Jarraud, S. Molecular Epidemiology, Phylogeny and Evolution of Legionella. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 43, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Fragment Length (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSU rRNA | CP-SSU-F1 | CCCATTTCCTTCGAAACAGGA | 55 | 830 | [36] |
| CP-SSU-R1 | TTCTAGAGCTAATACATGCG | ||||
| CP-SSU-F2 | AAGGAGTAAGGAACAACCTCCA | 58 | 800 | ||
| CP-SSU-R2 | GGAAGGGTTGTATTATTAGATAAAG | ||||
| SSU rRNA | GD-Gia2029-F1 | AAGTGTGGTGCAGACGGACTC | 55 | 497 | [37] |
| GD-Gia2150c-R1 | CTGCTGCCGTCCTTGGATGT | ||||
| GD-RH11-F1 | CATCCGGTCGATCCTGCC | 59 | 292 | ||
| GD-RH4-R2 | AGTCGAACCCTGA TTCTCCGCCAGG | ||||
| ITS | AL4037-F1 | GATGGTCATAGGGATG AAGAGCTT | 55 | 410 | [38] |
| AL4039-R1 | AATACAGGATCACTTGGATCCGT | ||||
| AL4038-F2 | AGGGATGAAGAGCTTCGGCTCTG | 55 | 392 | ||
| AL4040-R2 | AATATCCCTAATACAGGATCACT | ||||
| SSU rRNA | Bs-RD5-F | ATCTGGTTGATCCTGCCAGT | 59 | 600 | [39] |
| Bs-BhRDr-R | GAGCTTTTTAACTGCAACAACG |
| No. of Positive Samples (n) | Linzhou (161) | Dangxiong (66) | Nimu (150) | Total (377) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parasite Genus/Species | No. Tested/Prevalence% (95% CI Values) | |||
| Cryptosporidium spp. | 78/48.5 a (40.7–56.2) | 43/65.2 (53.6–76.7) | 84/56.0 (48.1–63.9) | 205/54.4 (49.4–59.4) |
| G. intestinalis | 37/22.9 (16.5–29.5) | 9/13.6 (5.4–21.9) | 44/29.3 (22.0–36.6) | 90/23.9 (19.6–28.2) |
| E. bieneusi | 77/47.8 (40.1–55.6) | 48/72.7 b (62.0–83.5) | 87/58.0 c (50.1–65.9) | 212/56.2 (51.2–61.2) |
| Blastocystis spp. | 146/90.7 d (86.2–95.2) | 58/87.9 e (80.0–95.8) | 120/80.0 (73.6–86.4) | 324/85.9 (82.4–89.5) |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + G. intestinalis | 20/12.4 (7.3–17.5) | 4/6.1 (0.0–11.8) | 22/14.7 (9.0–20.3) | 46/12.2 (8.9–15.5) |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + E. bieneusi | 39/24.2 (17.6–30.8) | 35/53.0 (36.5–69.5) | 51/34.0 (26.4–41.6) | 125/33.2 (24.9–41.5) |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + Blastocystis spp. | 76/47.2 (39.5–54.9) | 40/60.6 (48.8–72.4) | 71/47.3 (39.3–55.3) | 187/49.6 (44.6–54.7) |
| G. intestinalis + E. bieneusi | 25/15.5 (9.9–21.1) | 9/13.7 (5.4–21.9) | 21/14.0 (8.5–19.6) | 55/14.6 (11.0–18.2) |
| G. intestinalis + Blastocystis spp. | 35/21.7 (15.4–28.1) | 9/13.7 (5.4–21.9) | 44/29.3 (22.0–36.6) | 88/23.4 (19.1–27.6) |
| E. bieneusi + Blastocystis spp. | 70/43.5 (35.8–51.1) | 48/72.7 (62.0–83.5) | 66/44.0 (36.1–51.9) | 184/48.8 (41.6–56.0) |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + G. intestinalis + E. bieneusi | 13/8.1 (3.9–12.3) | 4/6.1 (0.0–11.8) | 14/9.3 (4.7–14.0) | 31/8.2 (5.5–11.0) |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + G. intestinalis Blastocystis spp. | 20/12.4 (7.3–17.5) | 4/6.1 (0.0–11.8) | 22/14.7 (9.0–20.3) | 46/12.2 (8.9–15.5) |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + E. bieneusi + Blastocystis spp. | 39/24.2 (17.6–30.8) | 34/51.5 (34.7–68.3) | 41/27.3 (20.2–34.5) | 114/30.2 (21.8–38.6) |
| G. intestinalis + E. bieneusi + Blastocystis spp. | 24/14.9 (9.4–20.4) | 9/13.7 (5.4–21.9) | 21/14.0 (8.5–19.6) | 54/14.3 (10.8–17.9) |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + G. intestinalis + E. bieneusi+ Blastocystis spp. | 13/8.1 (3.9–12.3) | 4/6.1 (0.0–11.8) | 14/9.3 (4.7–14.0) | 31/8.2 (5.5–11.0) |
| Linzhou County Yaks | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Captive Yaks | Grazing Yaks | |||||||
| Yaks’ Calves | Adults Yaks | 1–2 Years Old Yaks | ||||||
| Protozoan Parasites | No. Tested/ No. Positive | Prevalence (%) | No. Tested/ No. Positive | Prevalence (%) | No. Tested/ No. Positive | Prevalence (%) | No. Tested/ No. Positive | Prevalence (%) |
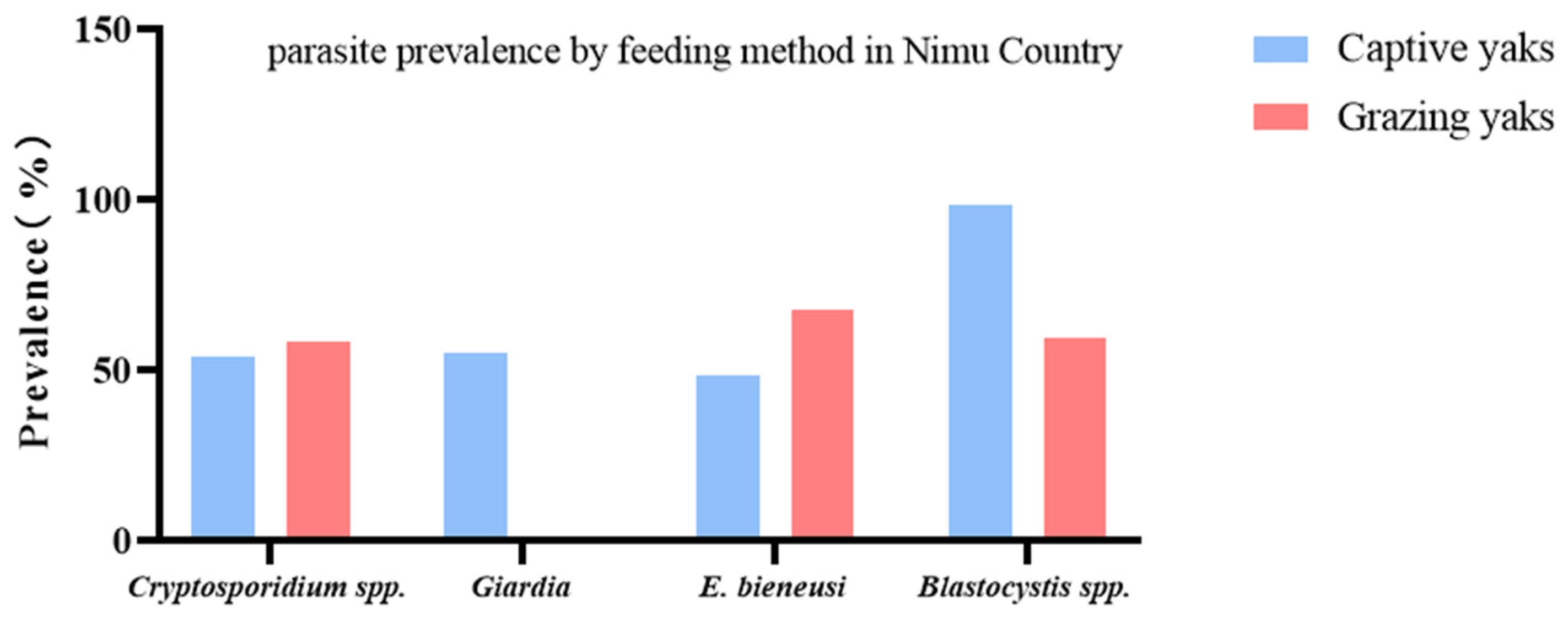
| Cryptosporidium spp. | 23/40 | 57.5 | 12/38 | 31.6 | 43/76 | 56.6 | 0 | 0.0 |
| G. intestinalis | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 36/76 | 47.4 | 1/7 | 14.3 |
| E. bieneusi | 9/40 | 22.5 | 10/38 | 26.3 | 51/76 | 67.1 | 7/7 | 100.0 |
| Blastocystis spp. | 38/40 | 95.0 | 33/38 | 86.8 | 75/76 | 98.7 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + G. intestinalis | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 20/76 a | 26.3 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + E. bieneusi | 8/40 | 20.0 | 2/38 | 5.3 | 29/76 | 38.2 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + Blastocystis spp. | 22/40 | 55.0 | 11/38 | 29.0 | 43/76 | 56.6 | 0 | 0.0 |
| G. intestinalis + E. bieneusi | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 24/76 b | 31.6 | 1/7 | 14.3 |
| G. intestinalis + Blastocystis spp. | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 35/76 b | 46.1 | 0 | 0.0 |
| E. bieneusi + Blastocystis spp. | 9/40 | 22.5 | 10/38 | 26.3 | 51/76 | 67.1 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + G. intestinalis + E. bieneusi | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 13/76 | 17.1 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + G. intestinalis + Blastocystis spp. | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 20/76 c | 26.3 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + E. bieneusi + Blastocystis spp. | 8/40 | 20.0 | 2/38 | 5.3 | 29/76 | 38.2 | 0 | 0.0 |
| G. intestinalis + E. bieneusi + Blastocystis spp. | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 24/76 d | 31.6 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + G. intestinalis + E. bieneusi + Blastocystis spp. | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 13/76 | 17.1 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Nimu County Yaks | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Captive Yaks | Grazing Yaks | |||
| Parasites | No. Positive/No. Tested | Prevalence (%) | No. Positive/No. Tested | Prevalence (%) |
| Cryptosporidium spp. | 42/78 | 53.9 | 42/72 | 58.3 |
| G. intestinalis | 43/78 | 55.1 | 1/72 | 1.4 |
| E. bieneusi | 38/78 | 48.7 | 49/72 | 68.1 |
| Blastocystis spp. | 77/78 | 98.7 | 43/72 | 59.7 |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + G. intestinalis | 21/78 | 26.9 | 1/72 | 1.4 |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + E. bieneusi | 22/78 | 28.2 | 29/72 | 40.3 |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + Blastocystis spp. | 42/78 | 53.9 | 29/72 | 40.3 |
| G. intestinalis + E. bieneusi | 20/78 | 25.6 | 1/72 | 1.4 |
| G. intestinalis + Blastocystis spp. | 43/78 | 55.1 | 1/72 | 1.4 |
| E. bieneusi + Blastocystis spp. | 38/78 | 48.7 | 28/72 | 38.9 |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + G. intestinalis + E. bieneusi | 13/78 | 16.7 | 1/72 | 1.4 |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + G. intestinalis + Blastocystis spp. | 21/78 | 26.9 | 1/72 | 1.4 |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + E. bieneusi + Blastocystis spp. | 22/78 | 28.2 | 19/72 | 26.4 |
| G. intestinalis + E. bieneusi +Blastocystis spp. | 20/78 | 25.6 | 1/72 | 1.4 |
| Cryptosporidium spp. + G. intestinalis + E. bieneusi + Blastocystis spp. | 13/78 | 16.7 | 1/72 | 1.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, Y.; Ali, M.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Kulyar, M.F.; Nawaz, S.; Mehmood, K.; Liu, M.; Li, K. Epidemiological Exploration of Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia intestinalis, Enterocytozoon bieneusi, and Blastocystis spp. in Yaks: Investigating Ecological and Zoonotic Dynamics in Lhasa, Xizang. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050504
Ji Y, Ali M, Xu C, Wang J, Kulyar MF, Nawaz S, Mehmood K, Liu M, Li K. Epidemiological Exploration of Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia intestinalis, Enterocytozoon bieneusi, and Blastocystis spp. in Yaks: Investigating Ecological and Zoonotic Dynamics in Lhasa, Xizang. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(5):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050504
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Yaru, Munwar Ali, Chang Xu, Jia Wang, Md. F. Kulyar, Shah Nawaz, Khalid Mehmood, Mingming Liu, and Kun Li. 2025. "Epidemiological Exploration of Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia intestinalis, Enterocytozoon bieneusi, and Blastocystis spp. in Yaks: Investigating Ecological and Zoonotic Dynamics in Lhasa, Xizang" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 5: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050504
APA StyleJi, Y., Ali, M., Xu, C., Wang, J., Kulyar, M. F., Nawaz, S., Mehmood, K., Liu, M., & Li, K. (2025). Epidemiological Exploration of Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia intestinalis, Enterocytozoon bieneusi, and Blastocystis spp. in Yaks: Investigating Ecological and Zoonotic Dynamics in Lhasa, Xizang. Veterinary Sciences, 12(5), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050504