Abundance and Infestation of Mites on Bower’s White-Toothed Rat (Berylmys bowersi) in Southwest China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
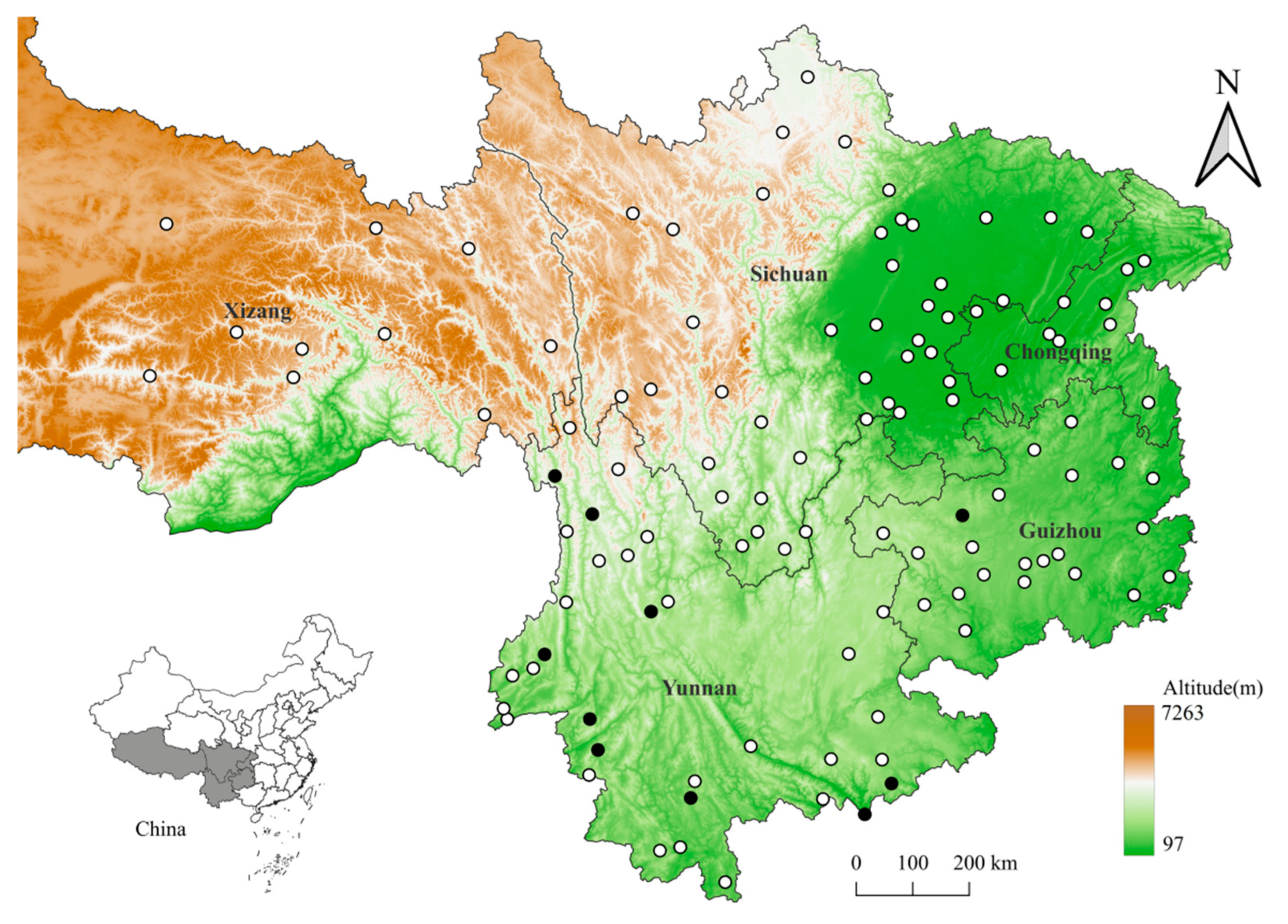
2.1. Collection and Identification of Mites and Their Rodent Hosts
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
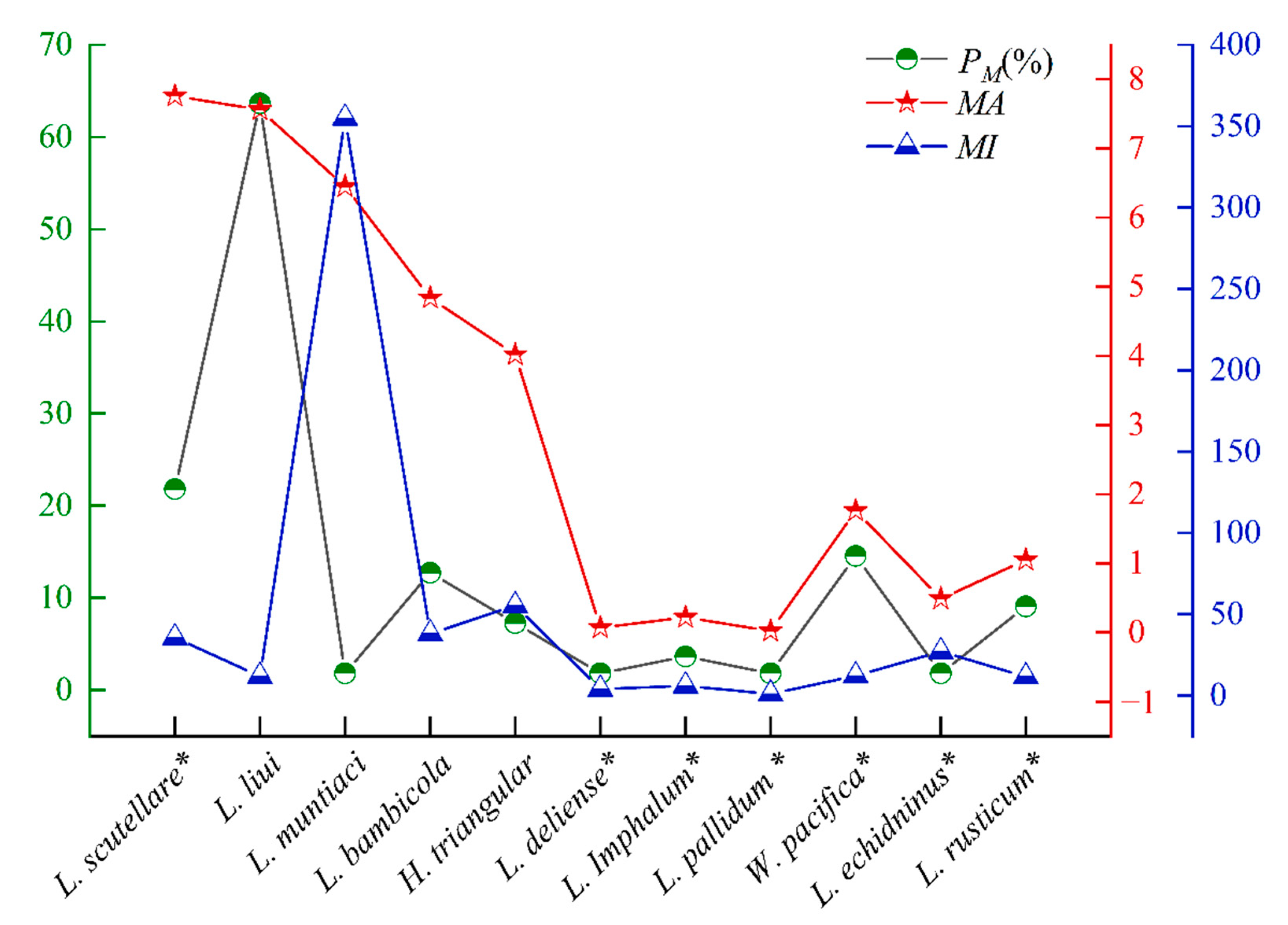
3.1. Species and Abundance of Mites on Berylmys bowersi
3.2. Variations in Mite Infestation on B. bowersi
3.3. Mutual Relationships of Mites on B. bowersi
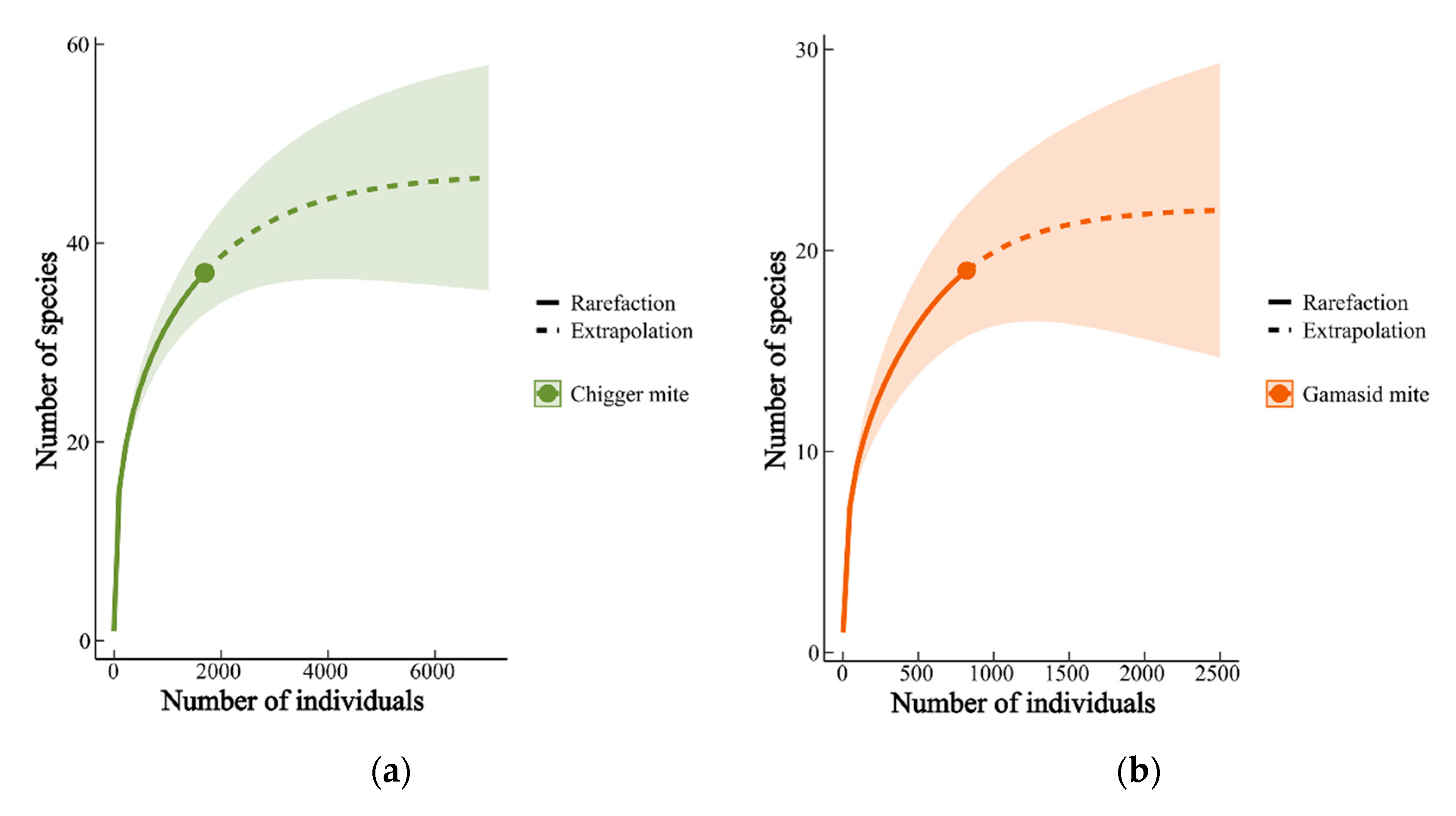
3.4. Estimation of the Number of Mite Species
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Acosta-Jamett, G.; Abello, R.; Jiang, J.; Richards, A.L.; Abarca, K.; Weitzel, T. Hosts and vectors of scrub typhus in Chile: Epidemiological study and molecular analyses of Orientia infection in rodents and rodent-associated mites. Parasites Vectors 2024, 17, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civen, R.; Ngo, V. Murine Typhus: An unrecognized suburban vectorborne disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, C.T.; Gao, J.; Chen, Z.Q.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.B.; Chen, Y.D.; Li, Z.C.; Chang, N.; Tao, Y.X.; et al. Spatiotemporal trends of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in China under climate variation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2312556121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.F. Plague: Recognition, treatment, and prevention. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 56, e01519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonovskaia, A.A.; Altshuler, E.P.; Balakirev, A.E.; Lopatina, Y.V. Explorational analysis of the abundance and prevalence of chigger and gamasid mites parasitic on small mammals in Vietnam. J. Med. Entomol. 2024, 61, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthee, S.; Stekolnikov, A.A.; Van Der Mescht, L.; Froeschke, G.; Morand, S. The diversity and distribution of chigger mites associated with rodents in the South African Savanna. Parasitology 2020, 147, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulraj, P.S.; Renu, G.; Ranganathan, K.; Veeramanoharan, R.; Kumar, A. Ectoparasites diversity on rodents and shrews at scrub typhus endemic Vellore district of Tamil Nadu, India. J. Arthropod. Borne Dis. 2022, 16, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axman, W.R.; Brummer, J.J. Chigger mite infestation. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2003, 93, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traub, R.; Hertig, M.; Lawrence, W.H.; Harriss, T.T. Potential vectors and reservoirs of hemorrhagic fever in Korea. Am. J. Hyg. 1954, 59, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.H.; Mendell, N.L. A scrub typhus vaccine presents a challenging unmet need. NPJ Vaccines 2023, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.J.; Tesh, R.B. The role of mites in the transmission and maintenance of hantaan virus (Hantavirus: Bunyaviridae). J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1693–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuyan, P.J.; Nath, A.J. Record of tropical rat mite, Ornithonyssus Bacoti (Acari: Mesostigmata: Macronyssidae) from domestic and peridomestic rodents (Rattus rattus) in Nilgiris, Tamil Nadu, India. J. Arthropod. Borne Dis. 2015, 10, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reeves, W.K.; Loftis, A.D.; Szumlas, D.E.; Abbassy, M.M.; Helmy, I.M.; Hanafi, H.A.; Dasch, G.A. Rickettsial pathogens in the tropical rat mite Ornithonyssus Bacoti (Acari: Macronyssidae) from egyptian rats (Rattus spp.). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2007, 41, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaraju, P.; Arumugam, B.; Mohan, I.; Paraman, M.; Ashokkumar, M.; Kasinathan, G.; Purushothaman, J. Evidence of natural infection of Orientia tsutsugamushi in vectors and animal hosts—Risk of scrub typhus transmission to humans in Puducherry, South India. Indian J. Public Health 2020, 64, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.W.; Zhang, T.C. A long-term retrospective analysis of the haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome epidemic from 2005 to 2021 in Jiangxi Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Xin, H.L.; Sun, J.L.; Lai, S.J.; Zeng, L.J.; Zheng, C.J.; Ray, S.E.; Weaver, N.D.; Wang, L.P.; Yu, J.X.; et al. Epidemiologic changes of scrub typhus in China, 1952–2016. J. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Kuang, L.; Hu, Y.X.; Shi, J.L.; Li, Q.; Tian, W. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of death from hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: A meta-analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1329683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M.; Kim, D.M. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: Literature review, epidemiology, clinical picture and pathogenesis. Infect. Chemother. 2022, 54, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondhiya, G.; Manjunathachar, H.V.; Singh, P.; Kumar, R. Unveiling the burden of scrub typhus in acute febrile illness cases across India: A systematic review & meta-analysis. Indian J. Med. Res. 2024, 159, 601–618. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, H.L.; Sun, J.L.; Yu, J.X.; Huang, J.L.; Chen, Q.L.; Wang, L.P.; Lai, S.J.; Clements, A.C.A.; Hu, W.B.; Li, Z.J. Spatiotemporal and demographic characteristics of scrub typhus in Southwest China, 2006-2017: An analysis of population-based surveillance data. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Kong, Y.C.; Yin, H.M.; Yang, Z.; Ren, T.L.; Zhang, Y.Z. A case of pulmonary tuberculosis patient complicated with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and scrub typhus in Yunnan, China: A case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, X.Y.; Song, Z.Z.; Wang, M.L.; Xi, J.X.; Liang, J.R.; Liang, Y.; Duan, R.; Tian, K.C.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Mechanism study on a plague outbreak driven by the construction of a large reservoir in Southwest China (surveillance from 2000–2015). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Zou, Y.; Fu, Z.F.; Plyusnin, A. Hantavirus infections in humans and animals, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musa, T.H.; Ahmad, T.; Wana, M.N.; Li, W.; Musa, H.H.; Sharun, K.; Tiwari, R.; Dhama, K.; Chaicumpa, W.; Campbell, M.C.; et al. The epidemiology, diagnosis and management of scrub typhus disease in China. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 3795–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musser, G.G.; Newcomb, C. Malaysian murids and the giant rat of Sumatra. Bull. AMNH 1983, 174, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Pimsai, U.; Pearch, M.J.; Satasook, C.; Bumrungsri, S.; Bates, P.J.J. Murine rodents (Rodentia: Murinae) of the Myanmar-Thai-Malaysian peninsula and Singapore: Taxonomy, distribution, ecology, conservation status, and illustrated identification keys. Bonn Zool. Bull. 2014, 63, 015–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.B.; Gui, B.Z.; Long, H.B.; Chen, Y.W.; Zhu, X.Q.; Wang, S.L.; Liu, G.H. Molecular detection and genotyping of Toxoplasma Gondii in edward’s long-tailed rats (Leopoldamys Edwardsi). Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.C. Preliminary survey on the biology of Rattus Bowersii Latouchei in Wuyi mountain area, Fujian. Wuyi Sci. J. 1986, 6, 215–219. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Takhampunya, R.; Longkunan, A.; Somchaimongkol, S.; Youngdech, N.; Chanarat, N.; Sakolvaree, J.; Tippayachai, B.; Promsathaporn, S.; Phanpheuch, B.; Poole-Smith, B.K.; et al. Borrelia miyamotoi a neglected tick-borne relapsing fever spirochete in Thailand. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordes, F.; Blasdell, K.; Morand, S. Transmission ecology of rodent-borne diseases: New Frontiers. Integr. Zool. 2015, 10, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, B.Z.; Zou, Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Li, F.; Jin, Y.C.; Liu, M.T.; Yi, J.N.; Zheng, W.B.; Liu, G.H. Novel genotypes and multilocus genotypes of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in two wild rat species in China: Potential for zoonotic transmission. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaisiri, K.; Cosson, J.F.; Morand, S. Infection of rodents by Orientia tsutsugamushi, the agent of scrub typhus in relation to land use in Thailand. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Zheng, W.B.; Zhang, N.Z.; Gui, B.Z.; Lv, Q.Y.; Yan, J.Q.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, G.H. Identification of Cryptosporidium viatorum XVa subtype family in two wild rat species in China. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugiere, D.; Fleury, M.C. Estimating primate densities using home range and line transect methods: A comparative test with the black colobus monkey Colobus satanas. Primates 2000, 41, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Fan, R.; Song, W.Y.; Peng, P.Y.; Zhao, Y.F.; Jin, D.C.; Guo, X.G. The distribution and host-association of the vector chigger species Leptotrombidium Imphalum in Southwest China. Insects 2024, 15, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.R.; Laake, J.L.; Crain, B.R.; Burnham, K.P. Guidelines for line transect sampling of biological populations. J. Wildl. Manag. 1979, 43, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Guo, X.G.; Jin, D.C.; Fan, R.; Zhao, C.F.; Zhang, Z.W.; Mao, K.Y.; Song, W.Y.; Dong, W.G.; Qian, T.J.; et al. Distribution and host selection of the chigger mite vector of scrub typhus, Leptotrombidium deliense, in Southwest China. Int. J. Acarol. 2021, 47, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.W.; Guo, X.G.; Jin, D.C.; Fan, R.; Zhao, C.F.; Zhang, Z.W.; Huang, X.B.; Mao, K.Y. Distribution and host selection of tropical rat mite, Ornithonyssus bacoti, in Yunnan Province of Southwest China. Animals 2021, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.J.; Chen, Y.X.; Wen, Y.X. Rodents of China, 1st ed.; Fudan University Press: Shanghai, China, 1995; pp. 1–286. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.; Xie, Y. A Guide to the Mammals of China, 1st ed.; Hunan Education Publishing House: Changsha, China, 2009; pp. 31–184. (in Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.W. Taxonomy and Distribution of Mammals in China, 1st ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2022; pp. 1–622. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.E.; Lacher, T.E.; Mittermeier, R.A. Handbook of the Mammals of the World: Vol. 7: Rodents II; Lynx Edicion: Barcelona, Spain, 2017; pp. 1–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, G.P.; Jiang, Z.J. Economic Insect Fauna of China Fasc. 40 Acari: Dermanyssoideae, 1st ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1993; pp. 1–389. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.P. Medical Acarology, 1st ed.; People’s Military Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 1–405. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.C. Trombiculid Mites of China: Studies on Vector and Pathogen of Tsutsugamushi Disease, 1st ed.; Guangdong Science and Technology Press: Guangzhou, China, 1997; pp. 1–570. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Stekolnikov, A.A. Leptotrombidium (Acari: Trombiculidae) of the World. Zootaxa 2013, 3728, 001–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Jiang, W.L.; Guo, X.G.; Fan, R.; Zhao, C.F.; Zhang, Z.W.; Mao, K.Y.; Xiang, R. Infestation and related ecology of chigger mites on the Asian house rat (Rattus tanezumi) in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Korean J. Parasitol. 2021, 59, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.Y.; Guo, X.G.; Jin, D.C.; Dong, W.G.; Qian, T.J.; Qin, F.; Yang, Z.H.; Fan, R. Landscapes with different biodiversity influence distribution of small mammals and their ectoparasitic chigger mites: A comparative study from Southwest China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.G.; Qian, T.J. Sex ratio and age structure of gamasid mites from small mammals in western Yunnan, China. Entomol. Sin. 2001, 8, 166–174. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.G.; Qian, T.J.; Meng, X.Y.; Dong, W.G.; Wu, D.; Shi, W.X. Preliminary analysis of chigger communities associated with house rats (Rattus flavipectus) from six counties in Yunnan, China. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2006, 11, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.Y.; Guo, X.G.; Ren, T.G.; Song, W.Y.; Dong, W.G.; Fan, R. Species diversity of ectoparasitic chigger mites (Acari: Prostigmata) on small mammals in Yunnan Province, China. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 3605–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, W.B.; Prat I Fornells, N. The introduction of entropy and information methods to ecology by ramon margalef. Entropy 2019, 21, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Abd Al-Hameed, K. Spearman’s correlation coefficient in statistical analysis. Int. J. Nonlinear Anal. 2022, 13, 3249–3255. [Google Scholar]
- de Winter, J.C.F.; Gosling, S.D.; Potter, J. Comparing the Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients across distributions and sample sizes: A tutorial using simulations and empirical data. Psychol. Methods 2016, 21, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Gotelli, N.J.; Hsieh, T.C.; Sander, E.L.; Ma, K.H.; Colwell, R.K.; Ellison, A.M. Rarefaction and extrapolation with hill numbers: A framework for sampling and estimation in species diversity studies. Ecol. Monogr. 2014, 84, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.C.; Ma, K.H.; Chao, A. iNEXT: An R package for rarefaction and extrapolation of species diversity (Hill Numbers). Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Guo, X.G.; Jin, D.C.; Song, W.Y.; Fan, R.; Zhao, C.F.; Zhang, Z.W.; Mao, K.Y.; Zou, Y.J.; Yang, Z.H. Relative abundance of a vector of scrub typhus, Leptotrombidium sialkotense, in southern Yunnan Province, China. Korean J. Parasitol. 2020, 58, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Meng, F.F.; Che, T.L.; Chen, J.J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Ji, Y.; Fan, Z.W.; Zhao, G.P.; Zhang, W.H.; Jiang, B.G.; et al. Mapping the distributions of blood-sucking mites and mite-borne agents in China: A modeling study. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2022, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Wang, X.W.; Wang, C.M.; He, H.X. A survey of ectoparasites from wild rodents and Anourosorex squamipes in Sichuan Province, Southwest China. J. Ecol. Nat. Environ. 2010, 2, 160–166. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.H.; Jiang, Z.K.; Wang, L.; Ding, L.Y.; Mao, C.Q.; Ma, B.Y. Accordance and identification of vector chigger mites of tsutsugamushi disease in China. Chin. J. Hyg. Insectic. Equip. 2013, 19, 286–292. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, H.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, J.; Gan, Y. The role of Leptotrombidium scutellare in the transmission of human diseases. Chin. Med. J. 1996, 109, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiang, R.; Ren, T.G.; Guo, X.G. Research history and progress of six vector chigger species of scrub typhus in China. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2022, 27, 1841–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Y. Tsutsugamushi disease in China. In Treatment of Human Parasitosis in Traditional Chinese Medicine; Mehlhorn, H., Wu, Z., Ye, B., Eds.; Parasitology Research Monographs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 6, pp. 255–268. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.C.; Zhou, H.F.; Lan, M.Y.; Tao, B.Z. Experimental study on the roles of gamasid mite in the transmission of epidemic haemorrhagic fever virus. Acta Acad. Med. Suzhou 1985, 1, 20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.L.; Guo, X.G.; Ding, F.; Lv, Y.; Yin, P.W.; Song, W.Y.; Zhao, C.F.; Zhang, Z.W.; Fan, R.; Peng, P.Y.; et al. Infestation of oriental house rat (Rattus tanezumi) with chigger mites varies along environmental gradients across five provincial regions of Southwest China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Guo, X.G.; Fan, R.; Song, W.Y.; Peng, P.Y.; Zhao, Y.F.; Jin, D.C. A Retrospective report on the infestation and distribution of chiggers on an endemic rodent species (Apodemus latronum) in Southwest China. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Hao, M.M.; Chen, S.; Ding, F.Y. The current and future risk of spread of Leptotrombidium deliense and Leptotrombidium scutellare in mainland China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniwal, R.; Renu, G.; Paulraj, P.S. Leptotrombidium deliense (Asian rodent chigger). Trends Parasitol. 2024, 40, 1199–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.W.; Deng, G.P. Economic Insect Fauna of China, Fasc. 17, Acarina: Gamasina, 1st ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1980; pp. 1–154. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Badyaev, A.V.; Hamstra, T.L.; Oh, K.P.; Acevedo Seaman, D.A. Sex-biased maternal effects reduce ectoparasite-induced mortality in a passerine bird. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14406–14411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, F.R.; Cruz, L.D.; Linhares, A.X. Effects of sex and locality on the abundance of lice on the wild rodent Oligoryzomys nigripes. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 1701–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawlena, H.; Abramsky, Z.; Krasnov, B.R. Age-biased parasitism and density-dependent distribution of fleas (Siphonaptera) on a desert rodent. Oecologia 2005, 146, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.L.; Guo, X.G.; Ren, T.G.; Zhang, L.; Fan, R.; Zhao, C.F.; Zhang, Z.W.; Mao, K.Y.; Huang, X.B.; Qian, T.J. Infestation and distribution of chigger mites on chevrieri’s field mouse (Apodemus chevrieri) in Southwest China. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2022, 17, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Taxonomic Taxa of Mites | Identified Species and Individuals of Mites (Figures in Brackets Are Corresponding Individuals) |
|---|---|
| Trombiculidae | A total of 1692 individuals in 37 species and 7 genera. |
| Leptotrombidium | L. scutellare (427) *; L. sinicum (35); L. eothenomydis (3); L. hiemalis (1); L. rusticum (58) *; L. wangi (7); L. densipunctatum (1); L. yongshengense (4); L. deliense (4) *; L. xiaguanense (35); L. imphalum (12) *; L. dianchi (4); L. jinmai (1); L. allosetum (2); L. pallidum (1) *; L. hsui (11); L. longchuanense (38); L. qiui (1); L. suense (51); L. baoshui (107); L. bambicola (266); L. muntiaci (355). |
| Trombiculindus | T. cuneatus (1); T. bambusoides (1); T. nujiange (2). |
| Neotrombicula | N. japonica (2); N. vulgaris (5). |
| Doloisia | D. manipurensis (2). |
| Ascoschoengastia | A. yunwui (1). |
| Herpetacarus | H. aristoclavus (3); H. fukienensis (7). |
| Walchia | W. pacifica (97) *; W. parapacifica (1); W. micropelta (11); W. kor (2); W. nanfangis (1); W. sheensis (132). |
| Laelapidae | A total of 814 individuals in 17 species and 6 genera. |
| Laelaps | L. echidninus (27) *; L. guizhouensis (2); L. paucisetosa (1); L. turkestanicus (14); L. traubi (2); L. liui (416); L. taingueni (1). |
| Haemolaelaps | H. triangular (221); H. traubi (3); H. petauristae (1); H. anomalis (1). |
| Dipolaelaps | D. jiangkouensis (55); D. anourosorecis (16). |
| Hypoaspis | H. pavlovskii (44); H. miles (1). |
| Androlaelaps | A. singularis (2). |
| Hirstionyssus | H. sunci (7). |
| Blattisocidae | A total of 4 individuals in 1 species and 1 genus. |
| Proctolaelaps | P. pygmaeus (4). |
| Aceosejidae | A total of 2 individuals in 1 species and 1 genus. |
| Lasioseius | L. medius (2). |
| Taxa of Mites | Community Indexes | Infestation Indexes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H′ | D | Mf | E | PM, % | MA | MI | |
| Chiggers | 2.28 | 0.85 | 4.84 | 0.63 | 52.73 | 30.76 | 58.34 |
| Gamasid mites | 1.48 | 0.66 | 2.68 | 0.50 | 78.18 | 14.91 | 19.07 |
| Total | 2.65 | 0.90 | 7.03 | 0.66 | 85.45 | 45.67 | 53.45 |
| Two Dominant and All Gamasid Mites | Number and Sex Ratio of Females | Number and Sex Ratio of Males | Adult | L | N1 | N2 | Immature | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Sex Ratio, % | No. | Sex Ratio, % | Cr, % | No. | No. | No. | Cr, % | |
| L. liui | 289 | 79.40 | 75 | 20.60 | 87.50 | 0 | 8 | 44 | 12.50 |
| H. triangular | 145 | 91.77 | 13 | 8.23 | 71.49 | 0 | 0 | 63 | 28.51 |
| All gamasid mites | 598 | 85.80 | 99 | 14.20 | 85.00 | 0 | 10 | 113 | 15.00 |
| Sexes and Ages of Gamasid Mites | Infected Host | PM, % | MA | MI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sexes | Female | 43 | 78.18 | 10.87 | 13.91 |
| Male | 19 | 34.55 | 1.80 | 5.21 | |
| Ages | Adult | 44 | 80.00 | 12.67 | 15.84 |
| Larva | 0 | / | 0.00 | / | |
| Protonymph | 2 | 3.64 | 0.18 | 5.00 | |
| Deutonymph | 16 | 29.09 | 2.05 | 7.06 | |
| Sexes and Ages of B. bowersi | No. of B. bowersi | Infestation Indexes of Chiggers | Infestation Indexes of Gamasid Mites | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM, % | MA | MI | PM, % | MA | MI | ||
| Females | 27 | 62.96 | 49.67 | 78.88 | 81.48 | 11.15 | 13.68 |
| Males | 28 | 42.86 | 12.54 | 29.25 | 82.14 | 18.54 | 22.57 |
| Total | 55 | 52.73 | 30.76 | 58.34 | 81.82 | 14.91 | 18.22 |
| Adults | 48 | 56.25 | 34.73 | 61.74 | 81.25 | 15.98 | 19.67 |
| Juveniles | 7 | 28.57 | 3.57 | 12.50 | 85.71 | 7.57 | 8.83 |
| Total | 55 | 52.73 | 30.76 | 58.34 | 81.82 | 14.91 | 18.22 |
| Mutual Relationship Between Two Groups of Mites | Gamasid Mites | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Infested Hosts (+) | No. of Uninfested Hosts (−) | |||
| Chiggers | No. of infested hosts (+) | 27 | 2 | 29 |
| No. of uninfested hosts (−) | 18 | 8 | 26 | |
| Total | 45 | 10 | 55 | |
| Association coefficient | V = 0.31 | |||
| Chi-square | χ2 = 5.25 | |||
| Significance | p = 0.00 < 0.001 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Guo, X.; Lv, Y.; Yin, P.; Song, W.; Peng, P.; Xiang, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, B. Abundance and Infestation of Mites on Bower’s White-Toothed Rat (Berylmys bowersi) in Southwest China. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050426
Liu C, Guo X, Lv Y, Yin P, Song W, Peng P, Xiang R, Chen Y, Li B. Abundance and Infestation of Mites on Bower’s White-Toothed Rat (Berylmys bowersi) in Southwest China. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(5):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050426
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chenxi, Xianguo Guo, Yan Lv, Pengwu Yin, Wenyu Song, Peiying Peng, Rong Xiang, Yanling Chen, and Bei Li. 2025. "Abundance and Infestation of Mites on Bower’s White-Toothed Rat (Berylmys bowersi) in Southwest China" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 5: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050426
APA StyleLiu, C., Guo, X., Lv, Y., Yin, P., Song, W., Peng, P., Xiang, R., Chen, Y., & Li, B. (2025). Abundance and Infestation of Mites on Bower’s White-Toothed Rat (Berylmys bowersi) in Southwest China. Veterinary Sciences, 12(5), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050426






