Artificial Intelligence in Chest Radiography—A Comparative Review of Human and Veterinary Medicine
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Human Medicine: Chest Radiographs
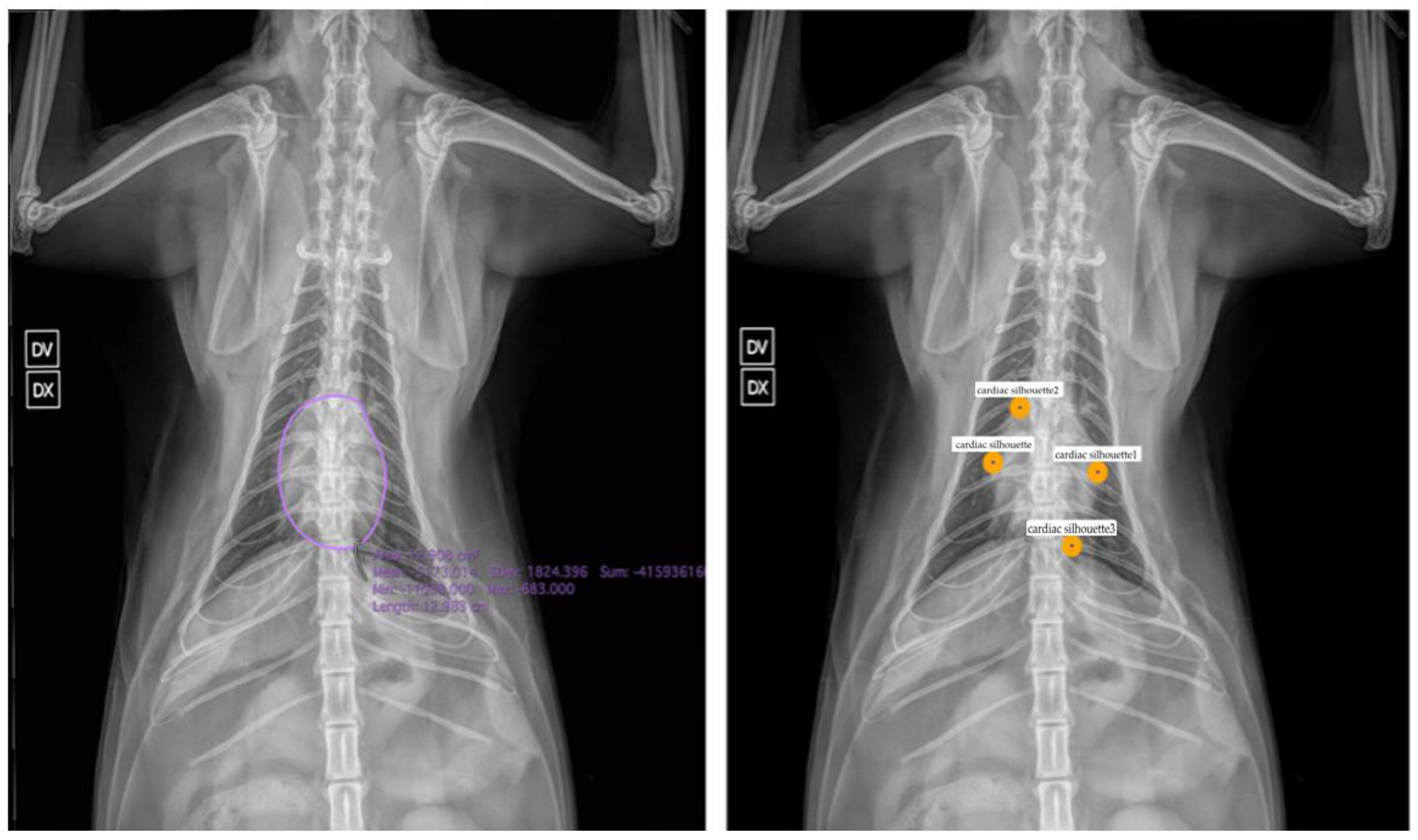
3. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Veterinary Medicine: Chest Radiographs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gottfredson, L.S. Mainstream science on intelligence: An editorial with 52 signatories, history and bibliography [Editorial]. Intelligence 1997, 24, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.J.; Stewart, C.L.; Freedman, B. Artificial intelligence in health care: Preparing for the fifth Industrial Revolution. Med. J. Aust. 2020, 213, 253–255.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, T.M. Machine Learning; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, K.P. Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Najjar, R. Redefining Radiology: A Review of Artificial Intelligence Integration in Medical Imaging. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.M.Z.; Prerepa, G.; Patil, V.; Shekhar, P.; Zahid Raza, S.; Karimi, H.; Paul, R.; Naik, N.; Modi, S.; Vigneswaran, G.; et al. Engineering and clinical use of artificial intelligence (AI) with machine learning and data science advancements: Radiology leading the way for future. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2021, 13, 17562872211044880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastav, S.; Chandrakar, R.; Gupta, S.; Babhulkar, V.; Agrawal, S.; Jaiswal, A.; Prasad, R.; Wanjari, M.B. ChatGPT in Radiology: The Advantages and Limitations of Artificial Intelligence for Medical Imaging Diagnosis. Cureus 2023, 15, e41435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Coelho, L. How Artificial Intelligence Is Shaping Medical Imaging Technology: A Survey of Innovations and Applications. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewert, B.; Sosna, J.; McNamara, A.; Raptopoulos, V.; Kruskal, J.B. Missed lesions at abdominal oncologic CT: Lessons learned from quality assurance. Radiogr. A Rev. Publ. Radiol. Soc. N. Am. Inc. 2008, 28, 623–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.J.; Kim, H.C.; Yang, D.M.; Kim, S.W.; Rhee, S.J.; Ahn, S.E. Diagnostic errors when interpreting abdominopelvic computed tomography: A pictorial review. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20160928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnan, A.J.; Ghobadi, E.H.; Hardy, P.; Krupinski, E.; Scali, E.P.; Stratchko, L.; Ulano, A.; Walker, E.; Wasnik, A.P.; Auffermann, W.F. Perceptual and Interpretive Error in Diagnostic Radiology-Causes and Potential Solutions. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, C.R.; Pfeiffer, D.U.; Mantis, P. Errors in radiographic interpretation made by veterinary students. J. Vet. Med. Educ. 2007, 34, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Fischetti, A.J.; Daverio, H. Veterinary radiologic error rate as determined by necropsy. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound Off. J. Am. Coll. Vet. Radiol. Int. Vet. Radiol. Assoc. 2023, 64, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Visser, L.C.; Wisner, E.R.; Cheng, H. Pilot study: Application of artificial intelligence for detecting left atrial enlargement on canine thoracic radiographs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound Off. J. Am. Coll. Vet. Radiol. Int. Vet. Radiol. Assoc. 2020, 61, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzke, M.; Stack, C.; Dourson, A.; Santana, R.M.B.; Wilson, D.; Ziemer, L.; Soin, A.; Lungren, M.P.; Fisher, P.; Parkinson, M. RapidRead: Global Deployment of State-of-the-Art Radiology AI for a Large Veterinary Teleradiology Practice. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.08165. [Google Scholar]
- Coghlan, S.; Quinn, T. Ethics of using artificial intelligence (AI) in veterinary medicine. AI Soc. 2024, 39, 2337–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond Geis, J.; Brady, A.P.; Wu, C.C.; Spencer, J.; Ranschaert, E.; Jaremko, J.L.; Langer, S.G.; Kitts, A.B.; Birch, J.; Shields, W.F.; et al. Ethics of artificial intelligence in radiology: Summary of the joint European and North American multisociety statement. Radiology 2019, 293, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, T.P.; Jacobs, S.; Senadeera, M.; Le, V.; Coghlan, S. The three ghosts of medical AI: Can the black-box present deliver? Artif. Intell. Med. 2022, 124, 102158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, K. The Atlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial Intelligence; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, E.J.; Park, S.; Jin, K.N.; Kim, J.I.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Goo, J.M.; Aum, J.; Yim, J.J.; Park, C.M.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning-based Automatic Detection Algorithm for Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis on Chest Radiographs. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2019, 69, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.G.; Park, S.; Hwang, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Jin, K.N.; Lim, K.Y.; Vu, T.H.; Sohn, J.H.; Hwang, S.; Goo, J.M.; et al. Development and Validation of Deep Learning-based Automatic Detection Algorithm for Malignant Pulmonary Nodules on Chest Radiographs. Radiology 2019, 290, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.J.; Park, S.; Jin, K.N.; Kim, J.I.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Goo, J.M.; Aum, J.; Yim, J.J.; Cohen, J.G.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning-Based Automated Detection Algorithm for Major Thoracic Diseases on Chest Radiographs. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e191095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.G.; Kim, M.; Park, J.; Hwang, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Hong, J.H.; Goo, J.M.; Park, C.M. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm detecting 10 common abnormalities on chest radiographs. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2003061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seah, J.C.Y.; Tang, C.H.M.; Buchlak, Q.D.; Holt, X.G.; Wardman, J.B.; Aimoldin, A.; Esmaili, N.; Ahmad, H.; Pham, H.; Lambert, J.F.; et al. Effect of a comprehensive deep-learning model on the accuracy of chest x-ray interpretation by radiologists: A retrospective, multireader multicase study. Lancet Digit. Health 2021, 3, e496–e506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Shan, H.; Feng, R. Editorial: Artificial intelligence applications for cancer diagnosis in radiology. Front. Radiol. 2025, 5, 1493783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juodelyte, D.; Lu, Y.; Jiménez-Sánchez, A.; Bottazzi, S.; Ferrante, E.; Cheplygina, V. Source Matters: Source Dataset Impact on Model Robustness in Medical Imaging. In Applications of Medical Artificial Intelligence. AMAI 2024; Wu, S., Shabestari, B., Xing, L., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 15384. [Google Scholar]
- Carloni, G.; Tsaftaris, S.A.; Colantonio, S. CROCODILE: Causality Aids RObustness via COntrastive DIsentangled LEarning. In Uncertainty for Safe Utilization of Machine Learning in Medical Imaging. UNSURE 2024; Sudre, C.H., Mehta, R., Ouyang, C., Qin, C., Rakic, M., Wells, W.M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 15167. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, X.; Liao, Z.; Xia, Y. GLANCE: Combating Label Noise Using Global and Local Noise Correction for Multi-label Chest X-Ray Classification. In Uncertainty for Safe Utilization of Machine Learning in Medical Imaging. UNSURE 2024; Sudre, C.H., Mehta, R., Ouyang, C., Qin, C., Rakic, M., Wells, W.M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 15167. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrosa, J.; Pereira, S.C.; Silva, J.; Mendonça, A.M.; Campilho, A. Anatomically-Guided Inpainting for Local Synthesis of Normal Chest Radiographs. In Deep Generative Models. DGM4MICCAI 2024; Mukhopadhyay, A., Oksuz, I., Engelhardt, S., Mehrof, D., Yuan, Y., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 15224. [Google Scholar]
- Brunswick, J.E.; Ilkhanipour, K.; Seaberg, D.C.; McGill, L. Radiographic interpretation in the emergency department. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 1996, 14, 346–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preston, C.A.; Marr, J.J., III; Amaraneni, K.K.; Suthar, B.S. Reduction of “callbacks” to the ED due to discrepancies in plain radiograph interpretation. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 1998, 16, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatt, M.E.; Spectre, G.; Paltiel, O.; Hiller, N.; Stalnikowicz, R. Chest radiographs in the emergency department: Is the radiologist really necessary? Postgrad. Med. J. 2003, 79, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, G.H.; Kang, D.; Kim, I.J.; Seo, J.; Andrews, J.R.; Park, C.M. Clinical Validation of a Deep Learning Algorithm for Detection of Pneumonia on Chest Radiographs in Emergency Department Patients with Acute Febrile Respiratory Illness. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, S.A.; Sanford, T.H.; Xu, S.; Turkbey, E.B.; Roth, H.; Xu, Z.; Yang, D.; Myronenko, A.; Anderson, V.; Amalou, A.; et al. Artificial intelligence for the detection of COVID-19 pneumonia on chest CT using multinational datasets. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, D.; Maino, C.; Gandola, D.; Franco, P.N.; Miron, R.; Barbu, V.; Bologna, M.; Corso, R.; Breaban, M.E. Artificial Intelligence Applied to Chest X-ray: A Reliable Tool to Assess the Differential Diagnosis of Lung Pneumonia in the Emergency Department. Diseases 2023, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obuchowicz, R.; Strzelecki, M.; Piórkowski, A. Clinical Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging and Image Processing-A Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.G.; Hwang, E.J.; Kim, J.; Park, N.; Lee, E.H.; Kim, H.J.; Nam, M.; Lee, J.H.; Park, C.M.; Goo, J.M. AI Improves Nodule Detection on Chest Radiographs in a Health Screening Population: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Radiology 2023, 307, e221894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Frias, E.; Kaviani, P.; Karout, L.; Fahimi, R.; Hosseini, S.; Putha, P.; Tadepalli, M.; Kiran, S.; Arora, C.; Robert, D.; et al. Early Detection of Heart Failure with Autonomous AI-Based Model Using Chest Radiographs: A Multicenter Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroz, D.; Anjos, A.; Berton, L. Using Backbone Foundation Model for Evaluating Fairness in Chest Radiography Without Demographic Data (FAIMI 2024, EPIMI 2024). In Ethics and Fairness in Medical Imaging.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 15198. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Y.; Hwang, T.; Lee, H. Prediction of radiographic abnormalities by the use of bag-of-features and convolutional neural networks. Vet. J. 2018, 237, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Fischetti, A.J.; Sreetharan, P.; Weltman, J.G.; Fox, P.R. Comparison of artificial intelligence to the veterinary radiologist’s diagnosis of canine cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound Off. J. Am. Coll. Vet. Radiol. Int. Vet. Radiol. Assoc. 2022, 63, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.R.; Solano, M.; Tsunemi, M.H. Accuracy of artificial intelligence software for the detection of confirmed pleural effusion in thoracic radiographs in dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound Off. J. Am. Coll. Vet. Radiol. Int. Vet. Radiol. Assoc. 2022, 63, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, M.; Bilbily, A.; Colak, E.; Dowdell, T.; Gray, B.; Perampaladas, K.; Barfett, J. Training and Validating a Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Computer-Aided Detection and Classification of Abnormalities on Frontal Chest Radiographs. Investig. Radiol. 2017, 52, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomerantz, L.K.; Solano, M.; Kalosa-Kenyon, E. Performance of a commercially available artificial intelligence software for the detection of confirmed pulmonary nodules and masses in canine thoracic radiography. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound Off. J. Am. Coll. Vet. Radiol. Int. Vet. Radiol. Assoc. 2023, 64, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederich, S.; Semik, M.; Lentschig, M.G.; Winter, F.; Scheld, H.H.; Roos, N.; Bongartz, G. Helical CT of pulmonary nodules in patients with extrathoracic malignancy: CT-surgical correlation. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1998, 172, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banzato, T.; Wodzinski, M.; Tauceri, F.; Donà, C.; Scavazza, F.; Müller, H.; Zotti, A. An AI-Based Algorithm for the Automatic Classification of Thoracic Radiographs in Cats. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 731936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumortier, L.; Guépin, F.; Delignette-Muller, M.L.; Boulocher, C.; Grenier, T. Deep learning in veterinary medicine, an approach based on CNN to detect pulmonary abnormalities from lateral thoracic radiographs in cats. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burti, S.; Longhin Osti, V.; Zotti, A.; Banzato, T. Use of deep learning to detect cardiomegaly on thoracic radiographs in dogs. Vet. J. 2020, 262, 105505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissady, E.; De La Comble, A.; Zhu, X.; Abbott, J.; Adrien-Maxence, H. Comparison of a Deep Learning Algorithm vs. Humans for Vertebral Heart Scale Measurements in Cats and Dogs Shows a High Degree of Agreement Among Readers. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 764570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, K.; Yu, D.; Xie, Q.; Liu, B.; Chen, D.; Xv, D.; Li, Z.; Liu, C. Computerized assisted evaluation system for canine cardiomegaly via key points detection with deep learning. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 193, 105399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnay, M.; Kováč, P. Bias, fatigue and other factors as potential source of errors in medical practice and forensic medicine. Rom. Soc. Leg. Med. 2024, 32, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Caruana, R.; Lou, Y.; Gehrke, J.; Koch, P.; Sturm, M.; Elhadad, N. Intelligible Models for HealthCare: Predicting Pneumonia Risk and Hospital 30-day Readmission. In Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD ‘15), Sydney, Australia, 10–13 August 2015; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Via, R.; Santacesaria, M.; Odone, F.; Pastore, V.P. Is In-Domain Data Beneficial in Transfer Learning for Landmarks Detection in X-Ray Images? In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, ISBI 2024, Athens, Greece, 27–30 May 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Via, R.; Odone, F.; Pastore, V.P. Self-Supervised Pre-Training with Diffusion Model for Few-Shot Landmark Detection in X-Ray Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, WACV 2025, Tucson, AZ, USA, 26 February–6 March 2025; pp. 3886–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Task | Species |
|---|---|---|
| Banzato et al., 2021 [46] | Detecting common radiographic findings | Dog/cat |
| Boissady et al., 2021 [49] | Automatically measuring VHS | Dog/cat |
| Burti et al., 2020 [48] | Classification of cardiomegaly based on VHS value | Dog |
| Fitzke et al., 2021 [15] | Detecting thoracic and extra-thoracic radiographic abnormalities | Dog/cat |
| Garza-Frias et al., 2024 [38] | Early detection of heart failure | Human |
| Hwang et al., 2019 [20] | Identification of tuberculosis, malignant nodules, and other anomalies | Human |
| Hwang et al., 2019 [22] | Use of commercial DL software in emergencies | Human |
| Ippolito et al., 2023 [35] | Distinguish different patterns of lung infections | Human |
| Kim et al., 2020 [33] | Deep learning algorithm for detection of pneumonia | Human |
| Kim et al., 2022 [41] | Presence/absence of cardiogenic pulmonary edema | Dog |
| Li et al., 2020 [14] | Detecting left atrial enlargement | Dog |
| Müller et al., 2022 [42] | Presence of pleural effusion | Dog |
| Nam et al., 2021 [23] | Detection of 10 common abnormalities in CXR scans | Human |
| Nam et al., 2023 [21] | Detection of lung nodules | Human |
| Obuchowicz et al., 2024 [36] | Real-time CXR | Human |
| Pomerantz et al., 2023 [44] | Attendance of pulmonary nodules and masses | Dog |
| Seah et al., 2021 [24] | Effect of a comprehensive deep learning model on the accuracy of CXR interpretation | Human |
| Yoon et al., 2018 [40] | Normal vs. abnormal cardiac silhouette and thoracic portions | Dog |
| Zhang et al., 2021 [50] | Identification of landmarks for calculating VHS | Dog |
| Banerjee et al., 2025 [25] | AI in cancer diagnosis in radiology | Human |
| Juodelyte et al., 2024 [26] | The importance of datasets | Human |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rubini, A.; Di Via, R.; Pastore, V.P.; Del Signore, F.; Rosto, M.; De Bonis, A.; Odone, F.; Vignoli, M. Artificial Intelligence in Chest Radiography—A Comparative Review of Human and Veterinary Medicine. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050404
Rubini A, Di Via R, Pastore VP, Del Signore F, Rosto M, De Bonis A, Odone F, Vignoli M. Artificial Intelligence in Chest Radiography—A Comparative Review of Human and Veterinary Medicine. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(5):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050404
Chicago/Turabian StyleRubini, Andrea, Roberto Di Via, Vito Paolo Pastore, Francesca Del Signore, Martina Rosto, Andrea De Bonis, Francesca Odone, and Massimo Vignoli. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence in Chest Radiography—A Comparative Review of Human and Veterinary Medicine" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 5: 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050404
APA StyleRubini, A., Di Via, R., Pastore, V. P., Del Signore, F., Rosto, M., De Bonis, A., Odone, F., & Vignoli, M. (2025). Artificial Intelligence in Chest Radiography—A Comparative Review of Human and Veterinary Medicine. Veterinary Sciences, 12(5), 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050404








